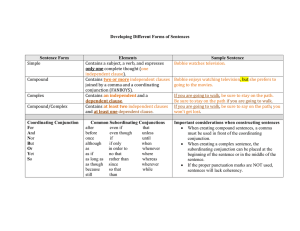
Good day, Everyone! SENTENCE DETECTIVES Instructions: WHAT: Students will act as “sentence detectives” and identify if sentences are simple, compound, complex, or compound-complex. HOW: The teacher will display sentences on the screen and students will read them aloud. WHO: Random selected students will explain before the teacher reveals the correct type. 1. She buys a new bag. a. Simple b. Compound c. Complex d. Compound-complex Answer: Simple sentence 1. She buys a new bag, and she gets new shoes too. a. Simple b. Compound c. Complex d. Compound-complex Answer: Compound sentence 3. Because she has so much money, she buys new things every week. a. Simple b. Compound c. Complex d. Compound-complex Answer: Complex sentence 4. Because she has so much money, she buys new things every week, and she never worries about her budget. a. Simple b. Compound c. Complex d. Compound-complex Answer: Compound-complex sentence SENTENCE STRUCTURE Group 3 Objectives: At the end of the lesson students will be able to: A. Construct and distinguish between simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences, B. Show cooperation and respect by valuing their group members’ contributions during the activity. C. Collaboratively write and present different types of sentences as a group, demonstrating clear sentence construction. KEY TERMINOLOGY CLAUSE: is a group of words that functions as one part of speech and that includes a subject and a verb. INDEPENDENT CLAUSE DEPENDENT CLAUSE A sentence that contains a subject and a verb - it can stand alone. Contains a subject and a verb, but it cannot stand alone. Example: You will succeed. Example: If you work hard CONJUNCTION is a word that is used to connect words, phrases, and clauses. 1. COORDINATING 2. SUBORDINATING COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS - it is used to connect items that are grammatically equal: two words, two phrases, or two independent clauses. FANBOYS F - FOR A- AND N- NOR B- BUT O- OR Y- YET S- SO it is placed between the items that links together. FOR EXAMPLE: I love bread and milk. SUBORDINATING CONJUNCTION -includes words like because, if, although, since, until, and while. It is used to introduce a dependent clause, and used to connect that dependent clause to an independent clause. FOR EXAMPLES: 1. If you work hard, you will succeed. 4 SENTENCE STRUCTURE SIMPLE SENTENCE it contains a subject and a verb, and it may also have an object and modifiers. The verb must agree with the subject and show the tense of the sentence. FOR EXAMPLE: Sally kicks the ball. Subject Verb (Present Tense) ANOTHER EXAMPLE: I ate lunch. COMPOUND SENTENCE A compound sentence consists of two independent clauses joined together by a coordinating conjunction (linking word). FOR EXAMPLE: He was hungry, so he cooked dinner. He was hungry. He cooked dinner. ANOTHER EXAMPLE: She is rich, yet she is very humble. COMPLEX SENTENCE - contains an independent clause and a dependent clause. If the dependent clause comes first, you need a comma. COMPLEX SENTENCE If, on the other hand, the independent clause comes first, you usually do NOT need a comma (unless for emphasis or to avoid confusion). FOR EXAMPLE: Although the girl studied hard, she failed the exam. ANOTHER EXAMPLES: 1. We still went to school although it was raining. 2. Whenever prices are reduced, people buy more products. COMPOUND-COMPLEX SENTENCE contains at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause. FOR EXAMPLE: Because I worked hard, I got an A star on the test and I was so happy. 2 independent clauses and 1 dependent clause. ANOTHER EXAMPLE: 1. When I got to school, my teacher asked me to get my homework out, but I had forgotten it. SUMMARY SUMMARY Simple sentence: contains at least one complete verb. The verb must agree with the subject and show the tense of the sentence. Compound sentence: consists of two independent clauses joined together by a coordinating conjunction (linking word). Complex sentence: contains an independent clause and a dependent clause. Compound-complex sentence: contains at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause. QUESTIONS? SENTENCE TRANSFORMATION Instructions: 1. Divide the class into 4 groups. 2. Each group will be given one simple sentence. 3. Transform the sentence into: 1 compound sentence 1 complex sentence 1 compound-complex sentence 4. All members must participate in creating the sentences within 3 minutes. 5. The teacher will randomly choose 1 member from each group to present 1 sentence and briefly explain its type within 1 minute. SOURCES: •YouTube. (Jan. 31, 2021). 4 Sentences Structure You Must Know. Retrieved from https://youtu.be/zZslAVsBBGE?si=-3EFqhTmLogf54SL •Institutionalized English Language Proficiency (Learning Module). Gingoog City Colleges, Inc. THANK YOU!