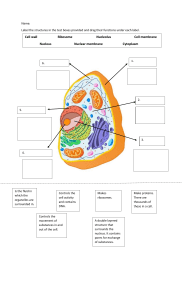
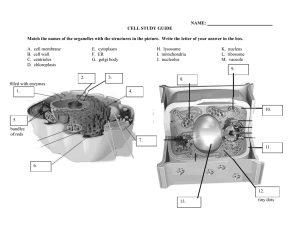
AS Level Chapter 1 Revision Test Part A: Short-Answer Questions (SAQs) 1. Define the term "cell" in the context of biology. 2. State one advantage of using an electron microscope over a light microscope. 3. What is the approximate maximum resolution of a light microscope? 4. Name one structure that can be observed in a plant cell but not in an animal cell. 5. What is meant by the term "magnification" in microscopy? 6. Explain the term "resolution" in the context of microscopy. 7. Which organelle is responsible for producing ATP in eukaryotic cells? 8. What is the function of the Golgi apparatus in a cell? 9. Where does protein synthesis occur within a cell? 10. In prokaryotic cells, where is the genetic material located? 11. What is the function of the cell wall in plant cells? 12. Describe the structure of the plasma membrane. 13. What is the role of the nucleolus within the nucleus? 14. Name the organelle responsible for lipid synthesis. 15. What is the function of lysosomes in a cell? 16. Describe the structure of a bacterial cell. 17. What is the function of pili in bacteria? 18. What is the role of flagella in prokaryotic cells? 19. Name one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 20. What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells? 21. Describe the structure of a virus. 22. Explain why viruses are considered acellular. 23. What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)? 24. What is the role of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)? 25. Name the structure that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Part B: Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. Which structure is found in both a bacterial cell and an animal cell? A) Mitochondria B) Ribosome C) Nucleus D) Golgi apparatus 2. Which of these is found only in eukaryotic cells? A) 70S ribosomes B) Capsule C) Linear DNA enclosed in a nucleus D) Flagellum 3. What is the resolution limit of a light microscope? A) ~2 µm B) ~200 nm C) ~20 nm D) ~0.2 nm 4. Which microscope provides three-dimensional imaging of cell surfaces? A) TEM B) SEM C) Light microscope D) Phase-contrast microscope 5. What does “semi-conservative” replication ensure? A) Each DNA strand is wholly new B) Each new DNA molecule has one original strand C) New strands contain no original material D) Random assembly of the two new strands 6. Which organelle is involved in the synthesis and transit of proteins? A) Vacuole B) Ribosome C) Rough ER D) Mitochondrion 7. Which cell component stores the cell’s genetic blueprint? A) Cytoplasm B) Nucleus C) Cell membrane D) Lysosome 8. Which of the following contains its own DNA and ribosomes in cells? A) Nucleus B) Mitochondrion C) Golgi apparatus D) Lysosome 9. What feature suggests that mitochondria may have evolved from bacteria? A) Presence of 80S ribosomes B) Single membrane C) Circular DNA and 70S ribosomes D) Absence of cristae 10. Which structure forms the boundary of a virus? A) Plasma membrane B) Capsid (and optionally envelope) C) Cell wall D) Cytoplasm 11. Which of the following lacks a true nucleus? A) Animal cell B) Plant cell C) Prokaryotic cell D) Eukaryotic fungal cell 12. What type of cell wall material is found in bacteria? A) Cellulose B) Chitin C) Peptidoglycan D) Glycoprotein 13. Which organelle would you associate with detoxification and lipid synthesis? A) Mitochondrion B) Rough ER C) SER D) Ribosome 14. Which structure regulates entry and exit of molecules in eukaryotic cells? A) Cell wall B) Plasma membrane C) Cytoplasm D) Nucleoid 15. What is the primary role of lysosomes? A) Protein synthesis B) Lipid metabolism C) Waste digestion D) Energy production 16. What feature is unique to plant cells compared to animal cells? A) Mitochondria B) Chloroplasts C) Ribosomes D) Lysosomes 17. How is genetic material typically arranged in bacteria? A) Linear chromosomes in a nucleus B) Circular DNA not enclosed C) DNA in membrane-bound nucleus D) Mitochondrial-like DNA only 18. Which organelle is the site of protein synthesis? A) SER B) Ribosome C) Lysosome D) Golgi apparatus 19. Which cell component is surrounded by a double membrane and contains pores? A) Golgi apparatus B) Ribosome C) Nucleus (nuclear envelope) D) Smooth ER 20. Which technique separates cell structure based on size and weight? A) Microscopy B) Centrifugation C) Gel electrophoresis D) PCR 21. What feature is shared by viruses, bacteria, and eukaryotes? A) Cell membrane B) Ribose sugar C) Cytosine base D) Cell wall 22. Which of these structures can form vesicles? A) Cell surface membrane & Golgi body B) Mitochondrion & cell wall C) Ribosome & lysosome D) Nucleus & vacuole 23. What is used as evidence in electron micrographs to identify rough ER? A) Smooth membranes B) Surface ribosomes C) Circular DNA D) Cristae 24. What does the presence of a nucleolus in a cell suggest? A) Site of lipid synthesis B) Protein modification center C) rRNA synthesis for ribosome production D) Energy generation site 25. What is a function of pili on bacterial cells? A) Photosynthesis B) Gene transfer and attachment C) Protein synthesis D) Movement of vesicles