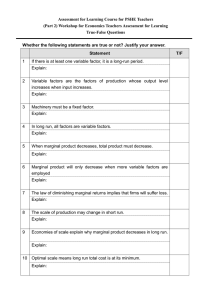
Lesson 5-3: Cost, Revenue, & Profit Maximization Finding Marginal Cost • The costs that an organization incurs even when there is little or no activity are fixed costs, or overhead. Finding Marginal Cost • Variable costs are usually associated with labor and raw materials and change with the business’s rate of operation or output. Finding Marginal Cost • Total cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs. Finding Marginal Cost • Marginal cost is the extra cost incurred to produce one more unit of output. Finding Marginal Revenue • Average revenue is the average price of every unit of output. • Total revenue is all of the revenue a business receives. Finding Marginal Revenue • Marginal revenue is the extra revenue a business receives from the production and sale of one additional unit of output. • Marginal revenue is the most important measure of revenue. Profit Maximization and Break-Even • Profitability is affected by both costs and revenue. • The profit-maximizing quantity of output is the volume of production where marginal cost and marginal revenue are equal. Profit Maximization and Break-Even • The break-even point is the level of production that generates just enough revenue to cover total operating costs. Profit Maximization and Break-Even • The Internet is one of the fastestgrowing areas of business today. • E-commerce has much lower overhead and does not require as much inventory as traditional retail stores, so the break-even point of sales is much lower.