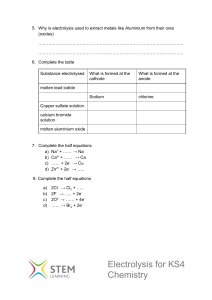
Ethan Mathew Grade 9 DIFFERENT PROCESSES OF ELECTROLYSIS Electrolysis has numerous applications in our daily lives, including two diverse examples: hair removal and battery recharging, which will be further elaborated upon. Battery Recharging: Electrolysis plays a crucial role in recharging batteries. As illustrated in the diagram, during use (discharge), lead dioxide (PbO₂) at the positive plate reacts with sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) to release energy, converting it into lead sulfate (PbSO₄). The negative plate (Pb) also forms lead sulfate (PbSO₄), generating electricity. However, to recharge the battery, this same process is reversed. An external voltage is applied to lead sulfate (PbSO₄) at both electrodes, converting it back into lead dioxide (PbO₂) at the positive plate and pure lead (Pb) at the negative plate. The concentration of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) increases, restoring battery power. The same occurs with lithium; during its use, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, generating electricity. To recharge the battery, the lithium ions are forced back into the anode for future use. Hair Removal: This use of electrolysis is fascinating due to its unconventionality. It operates through a process called "galvanic electrolysis.” Galvanic electrolysis is an age-old method dating back to the 19th century. It occurs when a thin, sterile probe is carefully inserted into the hair follicle through its natural opening without puncturing the skin. A small direct current (DC) is then applied through the probe, triggering a chemical reaction between the natural salts (NaCl) and water (H₂O) in the skin's fluids. This reaction produces sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a potent chemical that destroys the follicle cells. The damaged follicle tissue, which supports hair growth, dissolves and can no longer regenerate, ensuring permanent hair removal. Finally, the treated hair is removed with tweezers, and over time, the skin heals completely, preventing any regrowth in that follicle. There are key differences between these processes of electrolysis: Galvanic electrolysis is permanent, while battery charging is a reversible process. Electrolysis destroys biological material while charging restores chemical energy. Electrolysis is small-scale and slow, while battery charging can be largescale and faster.