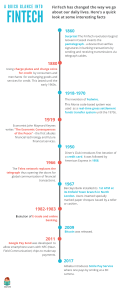
KAPALONG COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE, SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY Member and Accredited by ALCUCOA/ Institutionally Recognized and Under CHED-UniFAST RDES FORM 15 CONCEPT PAPER TEMPLATE PROGRAM: COURSE (SUBJECT) TITLE: NAME OF STUDENT/S: PROPOSE TITLE: The Influence of Financial Technology (FinTech) and Financial Inclusion Towards the Business Development Among SMEs in Kapalong, Davao del Norte COURSE INSTRUCTOR: COMPONENTS: DESCRIPTIONS Problematic Issue Problematic Issues Financial inclusion and FinTech adoption have long been acknowledged as economic growth drivers, particularly among SMEs. However, many SMEs in Kapalong, Davao del Norte, continue to have difficulties in obtaining financial services, limiting their ability to grow and sustain operations. This difficulty is caused by a number of circumstances, including Access to banking and credit facilities is limited, particularly for SMEs in rural areas. Businesses are cautious to utilize digital financial tools due to a lack of confidence and understanding in FinTech services. Regulatory and infrastructure hurdles, such as insufficient digital access and gaps in financial literacy. This study looks into how FinTech adoption and financial inclusion affect company development among SMEs in Kapalong, addressing the persistent financial constraints that impede their growth. Research Gap and Urgency KCAST RDE Agenda Previous studies on FinTech adoption and financial inclusion have primarily focused on urban companies or national trends, highlighting a research need and urgency. There is a scarcity of specialized research on the unique issues that rural SMEs face, particularly in places like Kapalong, Davao del Norte. The urgency of this investigation is enhanced by: 1. Rural communities continue to underutilize FinTech services, despite their fast rise. 2. Government initiatives for financial inclusion, including digital banking and MSME financing programs. 3. SMEs must adapt to digital financial instruments to remain competitive in a changing economic world. By addressing these research gaps, this study will provide data-driven insights to assist financial institutions, governments, and SMEs in developing strategies to improve financial access and digital adoption. This research is aligned with the Kapalong College of Agriculture, Sciences, and Technology's (KCAST) Research, Development, and Extension (RDE) Agenda. 1.Economic Development and Entrepreneurship - Increasing financial inclusion and capital access to help SMEs grow. 2.Technology Innovation and Digital Transformation - Encouraging the use of FinTech services to boost corporate productivity. 3.Sustainable Development and Inclusive Growth - Increasing access to digital financial services for rural SMEs, hence eliminating financial inequality. The outcomes of this study will help KCAST achieve its purpose of supporting equitable economic growth by increasing financial literacy, digital access, and Quezon St., Maniki, Kapalong, Davao del Norte Kapalong College of Agriculture, Sciences and Technology 0945-4602-108 I 0970-0251-622 officeofthevprde@kcast.edu.ph KAPALONG COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE, SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY Member and Accredited by ALCUCOA/ Institutionally Recognized and Under CHED-UniFAST Research Questions/ Research Objectives Theoretical Foundation strategic policy suggestions. The outcomes of this study will help KCAST achieve its purpose of supporting equitable economic growth by increasing financial literacy, digital access, and strategic policy suggestions. 1. What is the level of financial inclusion among Kapalong's SMEs? 2. What variables influence the adoption of FinTech by SMEs? 3. How does financial inclusion affect business growth? 4. What problems do SMEs have while adopting FinTech services? Theoretical Foundation This research is based on the following theoretical frameworks: 1. The Diffusion of Innovation Theory (Rogers, 1962) explains how FinTech adoption spreads across SMEs and the factors that impact acceptance or resistance. 2. Financial Inclusion Theory suggests that increased access to financial services contributes to economic participation and business growth, emphasizing the importance of banking and other financing alternatives. 3. The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Davis, 1989) examines how perceived usefulness and ease of use affect the propensity of SMEs to incorporate FinTech into their operations. 4. According to the Resource-Based View (RBV) Theory, SMEs with better financial access and digital tools have a competitive edge and improve their business performance. These theories offer a structured framework for examining the impact of FinTech and financial inclusion on SME company development in Kapalong, Davao del Norte. Research Design This study uses a quantitative research method using a descriptive-correlational methodology to investigate the relationship between FinTech adoption, financial inclusion, and business growth. Instrument and Data A structured survey questionnaire will be delivered to SMEs. The questionnaire contains: Section 1: Demographic Information Includes Age, Gender, Educational Background, and Business Experience. Type of SME firm and length of operation. Section 2: Financial Inclusion Provides access to banking services and digital financial channels. Availability and use of financial services. Financial transactions are affordable and cost effective. Section 3: FinTech Adoption: Understanding and using FinTech services (mobile banking, e-wallets, online financing). The perceived benefits and challenges of implementing FinTech. Section 4: Business Development. Indicators of growth include revenue, client reach, and financial stability. Challenges in obtaining financial services for business expansion. Respondents/Participants The target population is SMEs operating in Kapalong, Davao del Norte. Quezon St., Maniki, Kapalong, Davao del Norte Kapalong College of Agriculture, Sciences and Technology 0945-4602-108 I 0970-0251-622 officeofthevprde@kcast.edu.ph