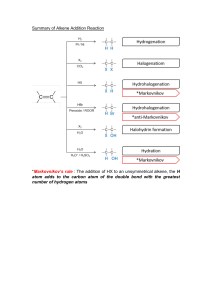
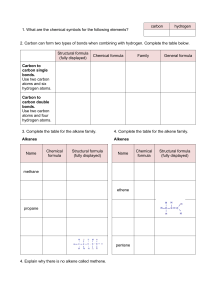
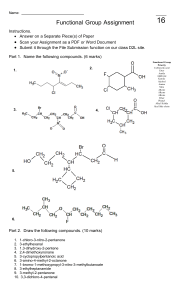
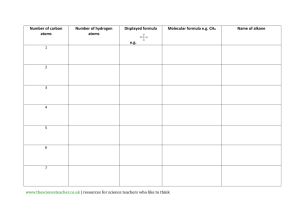
water alkene/alkyne halogen 3) + 4) hydrogen H,0 + Hydration HX + Hydrohalogenation (H0) alkene/alkyne hydrogen 2) + reactions 1) addcanWe triplebonds break open Addition H, + H Halogenation Hydrogenation- alkenes + alkene/alkyne H H halide H add + alkene/alkyne H of Hz0 H H alcohol - (X= HX (X Halogen: = product) (Major haloalkane Halogen: H H H add H H H conditions: Reaction place. take No Markovnikov's number it. atom atom water Heat Reaction number e.g. Markovnikov's Strong (HT0) conditions: it. atomatomwil reactant (Form which will but or form dilute H3PO4 of acid the to H rule: the the groups) bonded to H rule: the groups) bonded to the catalyst H H Dehydration- 4) needs alkene in Pt, to a non-polarneeds have Ni or Pd. a to catalyst solvent be if it is to H haloalkane H alkane Hremove remove or reaction alkyne -7the a opposite e.g. double is remove chain Clh), a - alkene H H Fz, Cl2, H F2, Brz, I2) Inand HX (X + H H H H H product) (Major product) (Minor Halogen: H alkene H H -H conditions: Reaction hol acid lystRequires with eg. Sulfuric as should with oms. Zaitzev's moved (Keeps the rule: number carbon groups) acid H H atom of atomH is at re is beheating inor known excessH3PO4. agent. acid of an The cata alco = Cl2, Br2, Reaction NaOH/KOH conditions: Reaction in solvent ethanol Takes Takes moved concentrated heating reflux. under with l2) conditions: oms.Zaitzev's (Keeps the a fromthe HzSO4 the least dehydrating concerntrated biggest X (X hydrogen H alkene + = Halogen:-=CH halogen alkene + product) (Minor H or triple or reaction as a triple hydrogen a REACTIONS Hz product. bondedwhere to Hz + H halide the atoms compOund. addition or (SATURATED or water groups reactions H20. H,0 H product) (Major H Indouble reaction or remove - H20halide + hydrogen H addition either ELIMINATION is HX + ’ --=c-H of double the H0. 2) ther This cule An 1)halogen Dehalogenation Dehydrogenation elimination H to an reaction form H H alkene H haloalkane (Group H HC-CC-C-H water side The REACTIONS ORGANIC 3) C-H’ water (H20) ’ either or dis H H -o-0-I H ’ halideSATURATED) on molecule. Dehydrohalogenation H alcohol -Ç-H eg. present 42 H-( alkane Fz, to be if it is to greater carbon The are atoms added chain 7(UNSATURATED are as e.g. to added a the Cl2), product. carbon to a an Hydrogen organic atoms H water present atoms where an alkane The presentconditions: solved and Reaction conditions: Reaction place take No to be atoms has steam greater carbon The of Hbond biggest halogenREACTIONS Cl2, Br2, I2) (Form HzSO4 in which biggest ofHbond atoms has X H Fz, Clz, Br2, I2) and are alkynes add (H2), reactions the Hz form a new (Group H X H -H to H product) (Minor product) (Majorhaloalkane H H H H H product) (Minor add - 12 Science ADDITION Essentials or H H ’ Hhydrogen H H HC-C=C-H Grade bond. reactions least biggest number place as from rule: the carbon the in the solvent. H presence H atom Strong groups) of atom is H at re place in an of elimination is are UNSATURATED) the Pd.or The presence Reaction removal alkane unreactive to be Pt, the Ni ’ removed reactions, of conditions: needs a catalyst eg. of atoms in from SCIENCE an organic CLINIC of hydrogen alkanes form (H2), er a 2022 mole © H,0 na acidcondensation reactants in + concentrated occur CLINIC the which H H a different are from a H alkene SCIENCE is as anduseful oil substances/chains H smells known of removed H Crude and a readilytype versa. in of H 1 oil are REACTIONS to column resulting more also various presence (up crude vice + 4 carbons. more ais Theyandand high alkenes. is smaller is water Cracking 3C02’6C0 pressure and distillation hydrocarbons and theetc. and The moment.exothermic differentburn The into of thereaction and for apple atmospheres) ’ top. bottom ESTERIFICATION and H hundreds they cracking. responsible in low column. alkane chains molecule + o 502 702 alkanes fractional the acid the ’ CRACKING as and is H H the elimination at are H fuels oil at at When + banana carboxylic chains hydrocarbon of crude of world reactions 2CsHg ’ theat H coolest organic 70 C Products: condense are engines. CsHs a Balancing: chains asuse result up carbon into to the like an Esters of andrises oxygen): (up a of one SmellsH longsource to aas passed in These and long useful long bottom pressures fuelvarious typeform products catalyst. gas and reaction.H oxygen): very alcohol points of (insufficient crack of dioxide. pleasant the alkenes is each more and H2. a molecules up source is for oil the of H H reaction up and are breaking the highno to crude as boiling the (excess an fuel at condenses with H carbon H generally between catalyst be in madehydrocarbons hottest mainas of + hydrocarbons. amounts of hydrocarbons will heated combustion Incomplete organic chains product alkane use higher H H This and combustion thealkane be the and Catalytic Thermal cracking a is and alkenes makes cracking energy H2SO4. are OR reaction can is H usesThecolumn are water hydrocarbon have twoa Cracking as they points and Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons temperature. chain method H method H as forms large electrical Complete will catalyst, and alkene a form reaction The H-(H is boiling chains Shorter mable. many andture This theyheat. Thislong This lyst. and tion. An of production oxygen of quantities with energy energy the react in large + usedalcohols t 8H,0 produce 4H20 G 2022 alkanes lowcatato longest according anda over the atmosphere) Products: to passed with separates temperatures of and flamhydrocarbons. reac mixture types more elimination the crack H’H-C Water ester COMBUSTION/OXIDATION H-o-C-- carbox acid H -H - REACTIONS ORGANIC or comreplaced between -ç-¢-o-H dissolved andaqueous the ofpresence in sunlight/heat conditions: Reaction place are place SATURATED) takes molecule take with Reaction halide hydrogen of H (X group haloalkanes Xz or H Substitute atom or atonm SUBSTITUTION an alkanes, another when H + haloalkane H20 H Hydrolysis + halogen H,0/ 12 Grade are that pounds H SubstitutionAlkanes: alkane H H H 1) H H 2) H X H H H H H H H HydrohalogenationH HX’ ’ H20/NaOH/KOH KOH Tertiary alcohols + haloalkane Alcohols: HH - H H H H X 3) halide alcohols ’ halide + secondary H- -¢- -Hhydrogen + HHaloalkanes:-¢-¿-H H + haloalkane water H H NaOH/’ Halogenation- -c-c-x + H,0 H H-¢ H is rorsaturated Essentials reactions SWopped/exchanged to = (X H)X alcoholSubstitute H--H H Substitute X Highbe + haloalka water KX of treated temperature. HX Require + H NaX/ HX/ alcohols. atoms, REACTIONS group and = concentrated withH)SO4. temperatures present Clz, Fz, HX/NaX/KX + Halogen: in Brz, ’ (SATURATED Clz, an Substitution Fz, in + HX Halogen: -H atoms Science treated Thean reactions oraanic I2) andNaBr conditions: Reaction conditions: Reaction at I2) Brz, H need and room solution Reaction conditions: solution is hot NaOH/KOH haloalkane ethanol alcoho H H H and + alcoholPrimary hydrogen + alcohol H H H