Financial Accounting Overview: Business Decisions & Statements
advertisement

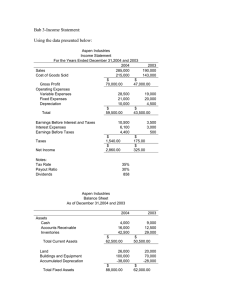
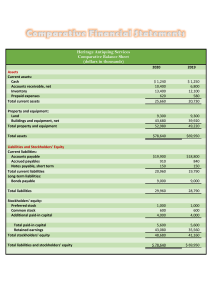
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making Chapter 1 Overview Of Business Copyright ©2022 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Business Organization and Accounting Information Uses Forms of Business Organization Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation LO 1 Sole Proprietorship • Owned and controlled by one person • Simple to establish • Tax advantages Examples • Small owner-operated businesses such as barber shops, law offices, auto repair shops, farms, and small retail stores LO 1 Partnership • Two more owners • Simple to establish • Shared control • Broader skills and resources • Tax advantages LO 1 Corporation • A separate legal entity • Easier to transfer ownership Shares of stock are easy to sell on an organized stock exchange • Easier for corporations to raise funds Individuals can become stockholders by investing relatively small amounts of money • No personal liability • Income taxes are higher than proprietorships and partnerships LO 1 More About Corporations • Stock is traded on an organized stock exchanges Such as the New York Stock Exchange • Majority of U.S. business is done by corporations Number of total proprietorships and partnerships exceeds the number of corporations Revenue produced by corporations is many times greater than other forms of organization LO 1 Users and Uses of Financial Information • Purpose of financial information To provide inputs for decision-making • Accounting The information system that identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of an organization to interested users Users of accounting information Internal users External users LO 1 Internal Users • Managers who plan, organize, and run a business • Questions asked by internal users LO 1 External Users • Investors (owners): buy, hold, or sell stock • Creditors: risk of selling on credit or lending money • Taxing authorities, such as the Internal Revenue Service • Customers: product warranties • Labor unions • Regulatory agencies LO 1 Questions Asked by External Users LO 1 Knowledge Check: Organization Forms Identify each of the following organizational characteristics with the organizational form or forms (sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation) with which it is associated. 1. Easier to raise funds Corporation 2. Simple to establish Sole proprietorship; partnership 3. No personal legal liability 4. Tax advantages Corporation Sole proprietorship; partnership 5. Easier to transfer ownership Corporation LO 1 Knowledge Check: Users of Financial Information Which of the following consists of external users? a. Managers and creditors b. Investors and regulatory agencies c. Employees and investors d. Creditors and employees LO 1 Explain the Three Principal Types of Business Activity LO 2 Three Types of Business Activity • Financing activities Raising money through outside sources • Investing activities Purchasing resources a company needs in order to operate • Operating activities Performing the day-to-day actions to produce and sell a product or provide a service LO 2 Financing Activities - Borrowing • Debt financing Borrowing money… … to creating a liability • Creditors Are the party to whom amounts are owed • Liabilities Amounts that are owed Notes payable – money borrowed as a loan Bonds payable – debt securities sold to investors LO 2 Financing Activities – Issuing Stock • Equity financing Issuing (selling) shares of stock for cash • Common stock The amount paid by stockholders for shares they purchase • Dividends Payments to stockholders LO 2 How Claims of Creditors and Stockholders Differ Creditors Stockholders • Loan money to a company • Owners of the company • Legal right to be paid • No claim to corporate cash until creditors’ claims are paid • May legally force the corporation to sell assets to pay its debt LO 2 Investing Activities • Purchase of resources a company needs in order to operate • Assets Resources owned by a business • Property, plant, and equipment • Includes computers, delivery trucks, furniture, buildings • Cash • Investments in securities • Stocks or bonds of other companies LO 2 Operating Activities • Activities that involve the day-to-day actions to produce and sell a product, or provide a service • Occur after a business obtains financing and invests in assets required for operation • Result in Revenue • Amounts generated from the sale of goods or performance of services Expenses • Costs consumed or services used in the process of generating revenue LO 2 Operating Activities - Revenue • The increase in assets or decrease in liabilities resulting from the sale of goods or the performance of services in the normal course of business • Arises from different sources • Identified by various names depending on the nature of the business • Common sources of revenue o Sales revenue o Service revenue o Interest revenue LO 2 Operating Activities – Assets with Shorter Lives • Result from operating activities Supplies • Assets used in day-to-day operations rather than sold to customers Inventory • Goods available for sale to customers Accounts receivable • Right to receive money in the future from a customer as the result of a sale LO 2 Operating Activities - Expenses • Are the cost of assets consumed or services used in the process of generating revenues • Common expenses Cost of goods sold Selling expenses Marketing expenses Administrative expenses Interest expense Income taxes expense LO 2 Operating Activities - Liabilities • Often arising from expenses Accounts payable • Goods purchased on credit from suppliers Interest payable • On outstanding amounts owed to the bank Wages payable • Amounts owed to employees • Sales taxes payable, property taxes payable, and income taxes payable owed to the government LO 2 Operating Activities – Net Income or Loss • Compare revenues with expenses for the period • Results in the profit for the period • Net income Exists when revenues exceed expenses • Net loss Exists when expenses exceed revenues LO 2 Concept Check: Business Activities Classify each activity as operating, investing or financing. 1. Performing a service for a customer Operating 2. Issuing shares of stock in exchange for cash Financing 3. Purchasing equipment used in operations Investing 4. Borrowing cash from a bank Financing 5. Selling goods to a customer Operating LO 2 Concept Check: Classifying Items Classify each item as an asset, liability, common stock, revenue, or expense. 1. Cost of electric bill Expense 2. Computers purchased Asset 3. Notes payable Liability 4. Issuance of ownership shares Common stock 5. Amount recorded from performing services Revenue 6. Amounts owed to suppliers Liability 7. Cash Asset LO 2 Describe the Four Financial Statements and How They Are Prepared LO 3 The Four Financial Statements • Income statement Success of the business during a period of time • Retained earnings statement How much income was distributed to owners and how much was retained • Balance sheet A picture at a point in time of what a business owns and what it owes Statement of cash flows Where a business obtained cash during a period of time and how that cash was used LO 3 Income Statement • Are the company’s operations profitable? Past net income provides information for predicting future earnings • Lists the company’s revenues followed by its expenses for a specific period, for example a month • Net income results when revenues exceed expenses • Net loss results when expenses exceed revenues LO 3 Income Statement Presentation LO 3 Importance of Income Statement to Financial Statement Users • Investors Buy and sell stock based on their beliefs about a company’s future performance • Creditors Predict whether the company will be profitable enough to repay amounts owed LO 3 Knowledge Check: Determining Net Income Tua Corporation began operations on January 1, 2025. The following information is available for Tua on December 31, 2025: Accounts receivable Supplies expense Equipment Rent expense Dividends Service revenue Supplies Determine net income for 2025. $ 1,100 2,500 12,900 7,000 2,200 23,000 2,000 Retained earnings Accounts payable Cash Insurance expense Notes payable Common stock Salaries expense $ 0 1,400 2,400 800 5,700 8,000 7,200 Revenues $23,000 Expenses ($2,500 + $7,000 + $800 + $7,200) 17,500 Net Income $ 5,500 LO 3 Retained Earnings Statement • Amounts and causes of changes in retained earnings for a specific time period • Net income increases retained earnings • Net loss decreases retained earnings • Dividends Decrease retained earnings Represent the portion of net income distributed to owners • Retained earnings ending balance Represents cumulative net income retained to allow for further expansion LO 3 Importance of the Retained Earnings Statement to Financial Statement Users • Shows investors a company’s dividend payment practices • Enables investors to determine the portion of earnings reinvested (retained) to increase growth • Allows lenders to monitor their corporate customers’ dividend payments Dividends use cash that could reduce their ability to repay debts LO 3 Retained Earnings Statement Illustrated • Time period is the same as income statement • Enables users to evaluate dividend payment practices LO 3 Knowledge Check: Determining Retained Earnings Tua Corporation began operations on January 1, 2025. The following information is available for Tua on December 31, 2025: Accounts receivable $ 1,100 Accounts payable $1,400 Equipment 12,900 Cash 2,400 Dividends 2,200 Notes payable 5,700 Supplies 2,000 Common stock 8,000 0 Net income Retained earnings, December 1 5,500 $ Retained earnings Prepare a retained earnings statement (omit heading). Add: Net income 0 5,500 5,500 Less: Dividends 2,200 Retained earnings, December 31 $3,300 LO 3 Balance Sheet • Assets and claims to assets at a specific time • Subdivides claims to assets into two categories Claims of creditors (liabilities) Claims of owners (stockholders’ equity) • Based upon the basic accounting equation • Lists assets first, followed by liabilities and stockholders’ equity LO 3 Components of the Balance Sheet • Assets Listed in order of liquidity, how quickly they can be converted to cash • Liabilities • Stockholders’ equity Separated into two components • Common stock • Results when the company sells new shares of stock • Retained earnings • Is the net income retained in the corporation LO 3 Importance of the Balance Sheet to Financial Statement Users Financial statements are used • To determine the likelihood the company will repay debt • To evaluate the nature of the company’s assets and liabilities • To determine whether cash on hand is sufficient • To evaluate the relationship between debt and stockholders’ equity LO 3 Balance Sheet Illustrated LO 3 Knowledge Check: Calculate Total Assets Tua Corporation began operations on January 1, 2025. The following information is available for Tua on December 31, 2025: Accounts receivable $ 1,100 Accounts payable $1,400 Equipment 12,900 Cash 2,400 Dividends 2,200 Notes payable 5,700 Supplies 2,000 Common stock 8,000 Retained earnings, Dec. 31 3,300 Net income 5,500 Cash Calculate total assets. $ 2,400 Accounts receivable 1,100 Supplies 2,000 Equipment 12,900 Total assets $18,400 LO 3 Knowledge Check: Calculate Total Liabilities Tua Corporation began operations on January 1, 2025. The following information is available for Tua on December 31, 2025: Accounts receivable $ 1,100 Accounts payable $1,400 Equipment 12,900 Cash 2,400 Dividends 2,200 Notes payable 5,700 Supplies 2,000 Common stock 8,000 Retained earnings, Dec. 31 3,300 Net income 5,500 Calculate total liabilities. Accounts payable $1,400 Notes payable 5,700 Total liabilities $7,100 LO 3 Knowledge Check: Calculate Stockholders’ Equity Tua Corporation began operations on January 1, 2025. The following information is available for Tua on December 31, 2025: Accounts receivable $ 1,100 Accounts payable $1,400 Equipment 12,900 Cash 2,400 Dividends 2,200 Notes payable 5,700 Supplies 2,000 Common stock 8,000 Retained earnings, Dec. 31 3,300 Net income 5,500 Calculate stockholders’ equity. Common stock $ 8,000 Retained earnings 3,300 Total stockholders’ equity $11,300 LO 3 Statement of Cash Flows • Provides financial information about the cash receipts and payments for a specific period of time • Reports the cash effects of a company’s operating, investing, and financing activities • Shows the net increase or decrease in cash during the period, and the amount of cash at the end of the period Cash is a company’s most important asset. LO 3 Importance of the Statement of Cash Flows to Financial Statement Users • Does the company generate enough cash from operations to fund its investing activities? • Provides answers to Where did cash come from during the period? How was cash used during the period? What was the change in the cash balance during the period? LO 3 Statement of Cash Flows Illustrated LO 3 Interrelationships of Statements • The retained earnings statement shows net income amount from the income statement • The ending balance of retained earnings is reported on the balance sheet in the stockholders’ equity section • The cash balance on the balance sheet also appears on the statement of cash flows LO 3 Interrelationship of Income Statement to the Retained Earnings Statement LO 3 Interrelationship of Retained Earnings Statement to the Balance Sheet Ending balance in retained earnings is needed in preparing the balance sheet. LO 3 Interrelationship of Balance Sheet with the Statement of Cash Flows The cash amount on the balance sheet equals the end of period cash reported on the statement of cash flows. LO 3 Knowledge Check: Part 1 Use Accounting Equation At June 1, WestCo had total assets of $40,000 and total liabilities of $15,000. 1. If total assets increased $12,000 in June and total liabilities decreased $5,000, what is the amount of stockholders’ equity at June 30? Assets, June 30 = $40,000 + $12,000 = $52,000 Liabilities, June 30 = $15,000 − $5,000 = $10,000 Stockholders’ equity, June 30 = $52,000 − $10,000 = $42,000 LO 3 Knowledge Check: Part 2 Use Accounting Equation At June 1, WestCo had total assets of $40,000 and total liabilities of $15,000. 2. During the year, total liabilities decreased $3,000 and stockholders’ equity increased $4,000 in June. What is the amount of total assets at June 30? Liabilities, June 30 = $15,000 − $3,000 = $12,000 Stockholders’ equity, June 1 = $40,000 − $15,000 = $25,000 Stockholders’ equity, June 30 = $25,000 + $4,000 = $29,000 Assets, June 30 = $12,000 + $29,000 = $41,000 LO 3 Knowledge Check: Net Income Net income will result during a time period when a. assets exceed liabilities. b. assets exceed revenues. c. expenses exceed revenues. d. revenues exceed expenses. LO 3 Knowledge Check: Financial Statements Which of the following financial statements is prepared as of a specific point in time? a. Balance sheet b. Income statement c. Retained earnings statement d. Statement of cash flows LO 3 Elements of an Annual Report Publicly traded U.S. companies must provide shareholders with an annual report. • Aids users in performing a complete financial analysis • Report elements Financial statements Management discussion and analysis Notes to the financial statements Independent auditor's report LO 3