MIRR vs. IRR: Modified & Regular Internal Rate of Return Explained
advertisement

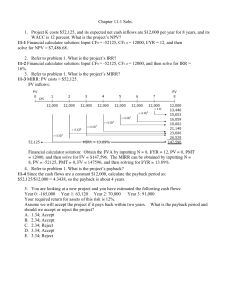
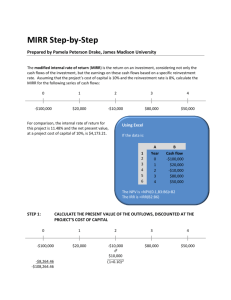
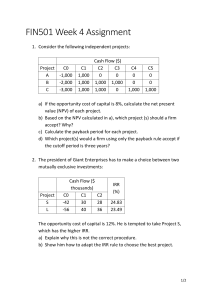
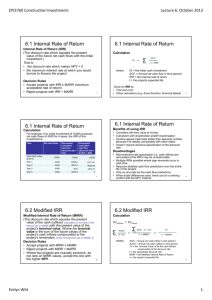
11/16/24, 8:10 AM Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) TRADE TABLE OF CONTENTS CORPORATE FINANCE ACCOUNTING Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) By SEAN ROSS Updated October 03, 2024 Reviewed by MELODY BELL Fact checked by DAVID RUBIN Understanding the rate of return on an investment. Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR): An Overview Business managers often consider a potential project's internal rate of return (IRR). This metric is an estimate of the potential annual profit of the project after its costs. It is commonly used by business and project managers as well as government agencies to select projects. [1] IRR tends to overstate the potential profitability of a project and can lead to capital budgeting mistakes based on an overly optimistic estimate. A variation of this metric, called the modified internal rate of return (MIRR), compensates for this flaw and gives managers more control over the assumed reinvestment rate from future cash flows. Let's compare the two and understand how these two approaches differ. Cite KEY TAKEAWAYS https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/why-modified-internal-rate-return-mirr-preferable-regular-internal-rate-return.asp#:~:text=The MIRR is calc… 1/8 11/16/24, 8:10 AM Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) The standard internal rate of return calculation is widely used to determine an expected profitability rate for a project. TRADE TABLE OF CONTENTS IRR calculations may overstate the potential future value of a project as it may use unrealistic discount rates for all cash flows. The modified internal rate of return may avoid distorting the cost of reinvested growth between project stages. MIRR allows for adjusting the assumed rate of reinvested growth for different stages of a project. MIRR can also only return one answer, while IRR may be harder to analyze when reporting multiple valid calculations for an irregular set of cash flows. What Is Internal Rate of Return? Internal Rate of Return (IRR) The internal rate of return is often used to analyze cash flow over time. It is calculated by summing the present value of each cash flow over the life of a project. The calculation often has an initial cash outlay (the initial investment) along with subsequent annual cash inflows (resulting in revenue generated from the initial investment). The discount rate used to find the present value of the cash flows is set so the net present value of the series is equal to 0. This discount rate is the IRR; it is the https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/why-modified-internal-rate-return-mirr-preferable-regular-internal-rate-return.asp#:~:text=The MIRR is calc… 2/8 11/16/24, 8:10 AM Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) required investment return rate to break even on a project when considering TRADE the timing of the cash flow of a project. In general, projects with higher IRRs are favorable than projects with lower IRRs, as the expected rate of return on TABLEmore OF CONTENTS these projects is greater. IRR is often used to compare different options or choose between projects. For example, a company that is considering expanding into a new product line might compare the IRR if it accomplishes that expansion by building a new factory, buying a competitor, or importing the products. All else being equal, the option with the highest IRR is the most favorable. The Drawback to IRR There are several disadvantages when using IRR. First, IRR does not give you the return on investment (ROI) in a dollar figure. A project may yield an IRR of 10%, but you won't know if the project will generate a cash flow of $10,000 or $10 million. For this reason, larger projects with lower yields but higher net cash proceeds may be at an analytical disadvantage when using IRR. IRR does not consider differences in the duration of projects. Imagine a oneyear project with an IRR of 10% and a five-year project with an IRR of 8%. While the one-year project is more favorable because of its higher IRR, the company may want to consider a longer-term project that will yield a return over a longer period. IRR calculations also assume all cash flow will be reinvested at the same rate over the term of the entire project. This means the initial cash outlay and subsequent cash inlays will have the same earning potential, even if these cash flows span years. Last, a series of cash flows may end up having two valid IRR calculations. This problem arises when a project has non-normal cash flow over its life and generally occurs when the direction of cash flow changes. When this occurs, a project has more than one internal rate of return and may be more difficult to analyze. Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) To fix the last two issues above related to IRR, a different calculation was created. The MIRR uses a lot of similar concepts as IRR, but there are slight https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/why-modified-internal-rate-return-mirr-preferable-regular-internal-rate-return.asp#:~:text=The MIRR is calc… 3/8 11/16/24, 8:10 AM Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) differences to help improve the original formula. The MIRR is calculated by TRADE incorporating the future value of positive cash flows and the present value of flows taken at different discount rates. TABLEcash OF CONTENTS Similar to IRR, MIRR is used to analyze the profitability of a project. MIRR is often compared to an internally required rate of return. If a project's MIRR is higher than this expected return, a project is favorable; if a project's MIRR is lower, it is often not recommended. Tip: Both formulas can be difficult to manually calculate. Both can be calculated in Excel using specific functions (=IRR and =MIRR). [2] [3] Key Differences There are several differences between IRR and MIRR, and these differences are what make the general view that MIRR demonstrates a more realistic picture of a project. These differences are discussed below. They use different rates. IRR relies on a single reinvestment rate for all cash flows. This may not be realistic, especially for projects with a lengthy span. In addition, a company may have a different rate of return for cash inlays as opposed to the cost of capital rates for cash outlays. They consider inflation differently. Because IRR does not factor in the cost of capital as part of its equation, IRR does not incorporate inflation. Meanwhile, MIRR can reflect this cost. They provide a different number of solutions. When a project has irregular cash flow, it may return multiple IRR results. This makes analysis difficult, as both percentages can be interpreted as the rate of return. Alternatively, based on the format of the formula, MIRR will only generate one result. This often means MIRR is easier to analyze. They are defined differently. IRR is the discount rate at which the net present value of a series of cash flows is equal to zero. Alternatively, MIRR is defined at the ROR where the NPV of the project inflows is equal to the initial investment. Though these definitions aren't widely different, they do vary as they use different approaches to the discount rate(s) used. They vary in accuracy. Because MIRR incorporates more information and allows for more flexibility, it is often considered the more accurate and more useful calculation. https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/why-modified-internal-rate-return-mirr-preferable-regular-internal-rate-return.asp#:~:text=The MIRR is calc… 4/8 11/16/24, 8:10 AM Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) IRR MIRR Uses a single discount rate for all cash flows Uses different discount rate for different types of cash flows Does not incorporate a company's cost of capital Incorporates a company's cost of capital May return more than one result depending on the sequence and direction of cash flows Will always return a single result regardless of the sequence and direction of cash flows Not considered highly accurate Considered to be highly accurate TABLE OF CONTENTS TRADE What Is Internal Rate of Return? IRR is a capital budgeting technique used to calculate the profitability of a project. It is calculated by finding the present value of a series of cash flows that equals $0. This discount rate is often compared to a company's required rate of return, and projects with higher IRR calculations are seen as more favorable. How Is IRR Different than MIRR? IRR and MIRR both analyze the cash flow of a project to determine its long-term profitability rate. However, these two calculations are slightly different. MIRR uses different discount rates and treats cash outlays differently than IRR. As MIRR incorporates more information, it is often considered more accurate. Is MIRR Better than IRR? In general, MIRR is considered better than IRR. MIRR incorporates more information and more accurately reflects expected rates of return around cash outlays. MIRR also incorporates external costs like inflation due to the incorporation of cost of capital. Because MIRR also only returns one calculated figure, it is often considered easier to analyze as well. [4] Why Is MIRR Different Than IRR? MIRR has several differences to IRR. Most notably, MIRR incorporates different rates in its calculation. While IRR uses only one expected rate of return for all cash flows, MIRR incorporates both expected investment growth rates as well as the cost of capital rates. Based on the setup of the formula, MIRR also only https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/why-modified-internal-rate-return-mirr-preferable-regular-internal-rate-return.asp#:~:text=The MIRR is calc… 5/8 11/16/24, 8:10 AM Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) yields one calculation every time, whereas IRR might return two results for a TRADE single project. Does IRR and MIRR Tell You? TABLEWhat OF CONTENTS Both IRR and MIRR result in a calculated percent. This percent represents the profitability of a project through the analysis of project cash flows over the life of the project. IRR and MIRR are often used to compare projects and select more ideal endeavors. They are also used to test the overall profitability of a project. The Bottom Line There are different metrics that businesses can use to estimate the profitability of a future project. These metrics allow business leaders to make more informed decisions before committing to one. Two common forms of measurement are the internal rate of return and the modified rate of return. While both have their benefits, the IRR can be flawed. That's why using the MIRR is often a better choice as it is a better representation of the rates of returns when related to cash flows. ARTICLE SOURCES Related Articles ACCOUNTING CAPEX vs. Current Expenses: What's the Difference? ACCOUNTING The Difference Between Profitability and Profit ACCOUNTING Air Waybill (AWB) Definition and How to Get One https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/why-modified-internal-rate-return-mirr-preferable-regular-internal-rate-return.asp#:~:text=The MIRR is calc… 6/8 11/16/24, 8:10 AM Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) ACCOUNTING TABLE OF CONTENTS TRADE The Impact of Share Repurchases on Financial Accounting ACCOUNTING Operating Cash Flow: Better Than Net Income? ACCOUNTING Book Value vs. Salvage Value: What's the Difference? Related Terms Air Waybill (AWB) Definition and How to Get One An air waybill (AWB) is a document that accompanies goods shipped by an international air courier to provide detailed information about the shipment. more Accounts Receivable Aging: Definition, Calculation, and Benefits Accounts receivable aging is a report categorizing a company's accounts receivable according to the length of time an invoice has been outstanding. Learn how it's used. more Tax-Equivalent Yield: What It Is and How It Works The tax-equivalent yield is the pretax yield a taxable bond needs to equal that of a tax-free municipal bond. more What Is an Amortization Schedule? How to Calculate With Formula Amortization is an accounting technique used to periodically lower the book value of a loan or intangible asset over a set period of time. more What Is a Current Account Surplus? A current account surplus is a positive current account balance, indicating that a nation is a net lender to the rest of the world. more https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/why-modified-internal-rate-return-mirr-preferable-regular-internal-rate-return.asp#:~:text=The MIRR is calc… 7/8 11/16/24, 8:10 AM Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) vs. Regular Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) Formula and TRADE Calculation TABLEThe OF compound CONTENTSannual growth rate (CAGR) measures an investment's annual growth rate over a period of time, assuming profits are reinvested at the end of each year. more TRUSTe About Us Terms of Service Dictionary Editorial Policy Advertise News Privacy Policy Contact Us Careers Investopedia is part of the Dotdash Meredith publishing family. https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/why-modified-internal-rate-return-mirr-preferable-regular-internal-rate-return.asp#:~:text=The MIRR is calc… 8/8