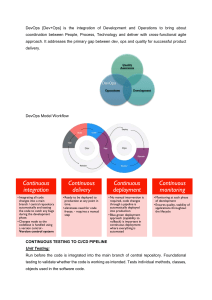
Top DevOps Tools for Automation: Enhancing Efficiency in Your Workflow In today's fast-paced tech landscape, DevOps practices are no longer just an option—they are essential for improving software development and delivery. Automation lies at the heart of DevOps, allowing teams to streamline repetitive tasks, increase productivity, and deploy code faster and more reliably. Over the past decade, a wide range of DevOps tools for automation have emerged, each offering unique features designed to enhance the development lifecycle. In this article, we’ll explore the top DevOps tools for automation, diving into how they improve workflows and help organizations achieve seamless integration, continuous delivery, and efficient management of their software products. What is DevOps and Why is Automation Important? Before we jump into the tools, let’s briefly define DevOps and the role automation plays in it. DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) with IT operations (Ops), aiming to shorten the development lifecycle and provide high-quality software continuously. By promoting collaboration between developers and operations teams, DevOps reduces the barriers between traditionally siloed departments, leading to faster deployment times and more reliable products. Automation is integral to DevOps because it eliminates manual intervention in routine processes, reduces human error, and speeds up the entire development cycle. By automating repetitive tasks such as testing, deployment, and monitoring, teams can focus on high-value activities, leading to faster releases and improved quality. 1. Jenkins: A Powerhouse for Continuous Integration and Delivery Jenkins is one of the most widely used DevOps tools for automation, and for good reason. As an open-source automation server, Jenkins is mainly used for continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD). It helps automate the building, testing, and deployment of software, ensuring that changes are integrated frequently and seamlessly into the codebase. Key Features: ● Extensibility: Jenkins has a vast ecosystem of plugins that integrate with virtually every tool in the DevOps pipeline, from source code management to deployment. ● Pipeline as Code: Jenkins supports creating automated pipelines using a domain-specific language (DSL), which is version-controlled and can be easily modified. ● Distributed Builds: Jenkins can scale by distributing workloads across multiple machines, ensuring faster build times and better resource utilization. 2. GitLab CI/CD: A Complete DevOps Platform GitLab is an integrated DevOps platform that provides a comprehensive suite of features for version control, CI/CD, monitoring, and security. GitLab CI/CD, in particular, stands out as a robust tool for automating the entire software development lifecycle. Key Features: ● Integrated Version Control: GitLab’s Git repository allows developers to manage source code and collaborate seamlessly within a single platform. ● Auto DevOps: GitLab’s Auto DevOps feature automates many of the manual steps in the CI/CD pipeline, such as build, test, deploy, and monitoring, with minimal configuration. ● Security and Monitoring: GitLab integrates automated security scanning and monitoring tools, ensuring that your software is secure throughout the development cycle. GitLab is not just a tool but an all-in-one DevOps platform, making it a top choice for organizations looking for a holistic solution. 3. Terraform: Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for Cloud Automation Terraform, created by HashiCorp, is one of the leading tools for managing cloud infrastructure. It allows teams to define infrastructure as code (IaC), enabling them to automate the provisioning and management of resources across multiple cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Key Features: ● Multi-Cloud Support: Terraform supports a wide range of cloud providers, allowing teams to automate infrastructure provisioning across different environments. ● Declarative Language: With Terraform’s declarative syntax, users describe the desired state of the infrastructure, and Terraform automatically ensures that the environment matches the description. ● Version Control: Terraform integrates well with version control systems, allowing infrastructure configurations to be managed and tracked like application code. Terraform helps eliminate manual configuration, providing reliable, repeatable, and scalable infrastructure deployments. 4. Ansible: Simplifying Configuration Management Ansible is another popular DevOps tool for automation, especially when it comes to configuration management and deployment automation. Known for its simplicity and agentless architecture, Ansible enables teams to automate repetitive tasks like provisioning, configuration, and application deployment. Key Features: ● Agentless Architecture: Unlike other configuration management tools, Ansible doesn’t require agents to be installed on target machines. This simplifies its setup and maintenance. ● Declarative Configuration: Ansible uses YAML to define the desired state of systems and applications, making it easy for teams to write and understand automation scripts. ● Scalability: Whether managing a few servers or thousands of instances, Ansible scales effortlessly to meet the needs of any infrastructure. With its powerful automation capabilities and ease of use, Ansible is a favorite among DevOps teams looking to streamline infrastructure management. 5. Puppet: Automating IT Operations at Scale Puppet is a configuration management tool that automates the provisioning and management of infrastructure. It’s a leader in the DevOps automation space and is well-suited for large-scale enterprise environments. Key Features: ● Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Like Terraform, Puppet allows you to manage infrastructure through code, ensuring repeatability and consistency. ● Scalability: Puppet excels in large environments, providing automation for tens of thousands of nodes, making it ideal for enterprises with complex infrastructures. ● Comprehensive Reporting: Puppet provides detailed reports on the state of the infrastructure, helping teams quickly identify issues and make improvements. Puppet’s ability to handle complex environments and automate large-scale infrastructure makes it a top contender for organizations focused on IT operations and infrastructure automation. 6. Kubernetes: Automating Container Orchestration Kubernetes, often referred to as K8s, is an open-source platform for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. While it isn’t specifically a DevOps tool, it plays a crucial role in modern DevOps practices, especially in microservices architectures. Key Features: ● Container Orchestration: Kubernetes automates the management of containers, including their deployment, scaling, and monitoring, ensuring high availability and reliability. ● Self-Healing: Kubernetes can automatically replace failed containers, scale up or down based on demand, and ensure that the desired state of the application is maintained. ● Extensibility: Kubernetes integrates with a wide range of DevOps tools, including CI/CD pipelines and monitoring systems, enabling end-to-end automation. By simplifying container management, Kubernetes enables DevOps teams to focus on developing and deploying applications, rather than managing the underlying infrastructure. 7. Selenium: Automating Testing for Continuous Delivery Selenium is an open-source tool for automating web browsers, making it an essential part of the automated testing process in a DevOps pipeline. It allows developers and QA engineers to write tests for web applications and execute them automatically, ensuring that code changes don’t break existing functionality. Key Features: ● Cross-Browser Testing: Selenium supports multiple browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.), ensuring that web applications perform consistently across different environments. ● Integration with CI/CD Pipelines: Selenium integrates seamlessly with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, allowing tests to be executed automatically as part of the build and deployment process. ● Parallel Test Execution: Selenium Grid allows tests to be run concurrently across multiple machines, reducing test execution time. By automating testing, Selenium helps ensure that software is reliable and free from defects before being deployed to production. Conclusion Incorporating the right DevOps tools for automation is key to improving software development workflows. Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, Terraform, Ansible, Puppet, Kubernetes, and Selenium streamline processes, accelerate delivery, and enhance product quality. Embracing automation allows teams to optimize workflows, reduce errors, and stay ahead in today’s fast-paced tech landscape. For those looking to advance their careers, enrolling in an Automation Testing Training course in Noida, Delhi, Lucknow, Nagpur, and other cities in India can provide in-depth knowledge and practical experience. These courses offer expert guidance, preparing you to successfully implement automation in your DevOps processes.