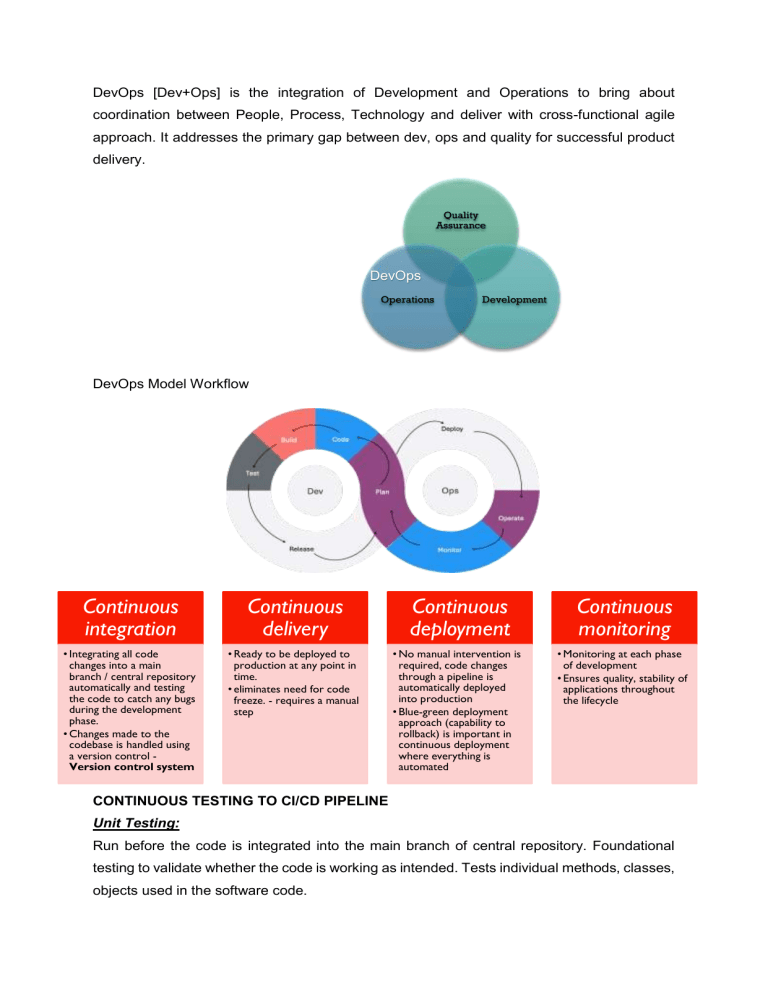
DevOps [Dev+Ops] is the integration of Development and Operations to bring about coordination between People, Process, Technology and deliver with cross-functional agile approach. It addresses the primary gap between dev, ops and quality for successful product delivery. Quality Assurance DevOps Operations Development DevOps Model Workflow Continuous integration Continuous delivery Continuous deployment Continuous monitoring • Integrating all code changes into a main branch / central repository automatically and testing the code to catch any bugs during the development phase. • Changes made to the codebase is handled using a version control Version control system • Ready to be deployed to production at any point in time. • eliminates need for code freeze. - requires a manual step • No manual intervention is required, code changes through a pipeline is automatically deployed into production • Blue-green deployment approach (capability to rollback) is important in continuous deployment where everything is automated • Monitoring at each phase of development • Ensures quality, stability of applications throughout the lifecycle CONTINUOUS TESTING TO CI/CD PIPELINE Unit Testing: Run before the code is integrated into the main branch of central repository. Foundational testing to validate whether the code is working as intended. Tests individual methods, classes, objects used in the software code. Unit test Black box White box Grey box Black box testing: As the name suggests, this type of testing considers the unit as a black box and tests based on the external attributes, input and output. Knowledge of the internal working of the code is not required for the testers to arrive at the test result White box testing: Focuses on the internal logic of the unit’s code. Control flow working, error handling mechanisms are tested. Grey box testing: Focuses primarily on the external behavior of the unit code but also considers the internal functioning. Targeted test cases are evaluated to arrive at the validation of external behaviors. Integration Testing: After unit testing, the integration between units / modules are tested in integration testing. It verifies the data exchange between the modules. There are 4 testing approaches: Integration testing approach Big-bang Bottom-up Top-down Mixed System Testing: Integration testing passed units are taken as input and checked for its compliance with the system requirements. Includes both functional and non-functional testing and it is a black box testing. System testing Performance testing Stress testing Load testing Scalability testing Acceptance Testing: Check whether the software meets the customer requirements. This is only a functional testing performed by testers, stakeholders and clients. Alpha test Acceptance testing Beta test Alpha test: Testing performed to identify flaws in the product before releasing it to the actual customer. It is evaluated against a set of predetermined set of criteria 1st phase: testing done by in-house developers 2nd phase: testing done by software quality assurance team- includes black box and white box Beta test: In this testing phase, the software is made available to selected users to collect feedback and attempt to find any bugs or flaws in the application.