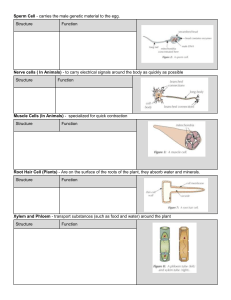
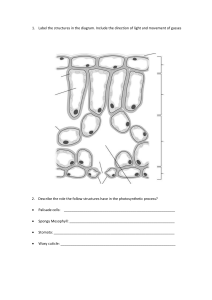
reticulate cambium, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is responsible for the secondary growth of stems and roots (secondary growth occurs after the first season and results in increase in thickness) At very high light intensities, photosynthesis is slowed and then inhibited, but these light intensities do not occur in nature sucrose is chemical compound made of glucose and fructose Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a source for carbon dioxide central vacuole stores the cell sap distance / time