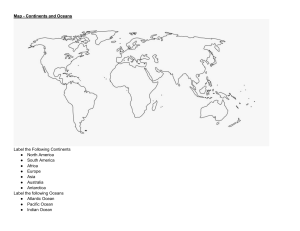
Chapter 1: From Sea to Shining Sea Throughout this chapter, we will be able to: Locate the seven continents and five oceans, locate and describe the major geographic regions of North America, locate major water features and explain their importance to the early history of the United States, and recognize key features on maps, diagrams, and/or photographs. Before we begin…….Why does the past matter? • How did we get where we are? • How do we know we got here? • What caused us to change? To adapt? • Who helped us become ‘us’? • Would I have done the same thing…? COULD I have done the same thing? Ways to “see” the past….. Primary sources Secondary Sources Maps Charts Graphs Timelines What does Geography have to do with our History….? • United States history has been shaped by the people who came from other continents • How? • Natural disasters… • Climate changes… • War…. • Religious Persecution…. • Economy… • Opportunity…. • Slavery… Push Factors vs Pull Factor • Push and Pull factors are reasons why a person would want to leave a place or go to a place • Push Factor – push a person to leave their home (economy, religion, war, etc.) • Pull Factor – something that draws a person to a new location (opportunity, economy, religious freedom, etc.) Five Oceans and Seven Continents…. ARCTIC OCEAN NORTH AMERICA EUROPE ATLANTIC OCEAN PACIFIC OCEAN ASIA PACIFIC OCEAN AFRICA SOUTH AMERICA SOUTHERN OCEAN ANTARCTICA INDIAN OCEAN AUSTRALIA Our Seven Continents…. • North America…. • First people walked by frozen land bridge from Asia? • Or by boat over the Atlantic? • South America…. • People migrated from North America to South America…..or by sea from Asia • Africa… • 2nd largest continent • Oldest signs of human life found here Our Seven Continents… • Europe… • Separated from Asia by mountains • Not totally surrounded by water • Asia… • Biggest continent (2/3rds world population) • Australia/Oceania • Largest Island with approx. 20k smaller islands • Antarctica • Only continent with no human life North American Regions North American Regions: Coastal Plain • East coast of N. America • Atlantic Ocean & Gulf of Mexico • Broad lowlands • Fertile Soil • Forests North American Regions: Appalachian Mountains • Located west of Coastal Plain • Extends from Canada to Alabama • Mountains – • Oldest mountain range in the United States • Great Smoky Mountains & Blue Ridge Mountains • Eroded mountains with rounded peaks North American Regions: Interior Lowlands • West of the Appalachian Mountains; east of the Great Plains • Broad flatlands • River valleys • Grassy hills • Unpredictable weather – Northern cold air meets southern warm air • “Tornado Alley” • Tornadoes, hail, blizzards North American Regions: Great Plains • West of Interior Lowlands and east of Rocky Mountains • Flat land that increases in elevation westward • Large grasslands • Few trees • Low annual precipitation • “America’s Breadbasket” North American Regions: Rocky Mountains • West of the Great Plains & east of the Basin and Range • Rugged mountains • Continental Divide • Jagged, steep peaks • Feeds Rivers North American Regions: Basin and Range • West of the Rocky Mountains & east of Coastal Range • Varying elevations from mountains to lowest point in North America • “Death Valley” • Below sea level • Very little precipitation North American Regions: Coastal Range • Mountains along the Pacific coast from California to Canada • Sierra Nevada and Cascades • Fertile Valleys • Heavy rainfall in northwest; drier in southwest • Fertile land and forests North American Regions: Canadian Shield • Wrapped around Canada’s Hudson Bay • Eroded hills • Lakes carved by glaciers • Rocky, frigid region • Little growth North American Waters… • America sits between the world’s biggest oceans: Atlantic and Pacific • Atlantic Ocean • Separates Europe and Africa from the Americas • Served as a ‘highway’ for explorers, early settlers and immigrants • Pacific Ocean • Separates the Americas from Asia • Largest ocean • Early exploration route to Asia North American Waters: The Great Lakes • Formed by glaciers carving basins, then melting and filling them with water • Located on the Canadian/US border • SMHEO (Super Man Helps Every One) • Lake Superior • Lake Michigan • Lake Huron • Lake Erie • Lake Ontario North American Waters: The Gulf of Mexico • Formed over millions of years ago • Very large body of water • Used by the French and Spanish explorers as a route to Mexico and other parts of America • Prone to severe weather including hurricanes and flooding North American Waterways… • Native Americans and early explorers relied on American waterways for travel, food, farming, drinking, and transportation…. • Even today, rivers are used to transportation, irrigation, and energy… North American Waterways…. • The Mississippi River • Used to transport products • Link to US ports and others • Most famous U.S. river • The Missouri River • Longest River in North America • Used to transport products • The Ohio River • Forms the borders of six states: Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia Missouri River Ohio River North American Waterways… • The Columbia River • Explored by Lewis and Clark • 4th largest river in the U.S. • The Colorado River • Carved the Grand Canyon • Mapped by the Spanish • The Rio Grande • Forms part of border between the U.S. and Mexico • Significant source of water for Southwest Colorado River Rio Grande