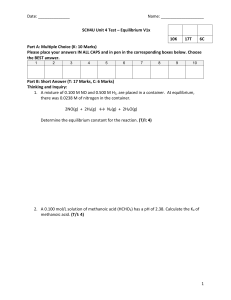
Rest of
Region
A
B
C
B
B
A
t AFFIX SEAL HERE t
@
CAl'lllfDA.,.,.c'J!~r!"ft'.
y.., ........ ,~;w,-.... ,11111 beokJet
wl~ fie Aittnr- SllioeL. 'Jl'lhh to
de IO •Y
renllt hi dttq•allfteatloa.
FORMTP2009155
CARIBBEAN
TESTCODE02112010
MAYIJUNE2009
Slpsture
EXAMINATIONS
COUNCIL
ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION
CHEMISTRY - UNIT I
PaperOl
90minutes
( 27 MAY 2009 (a.m.))
READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONSCAREFULLY.
I.
'This test consists of45 items. You will have 90 minutes to answer them.
2.
In, addition to this test booklet, you should have an answer sheet.
3.
Do not be concerned that the answer sheet provides spaces for more answers than there are items in
this test.
4.
Each item in this test has four suggested answers lettered(A), (B), (C), (D). Read each item you are
about to answer and decide which choice is best.
5.
On your answer sheet, find the number which corresponds to your item and shade the space having
the same letter as the answer you have chosen. Look at the sample item below.
-
Sample Item
Which ofthe following is the HIGHEST energy transition io an organic compound?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Sample Answer
n to cr•
n to it•
cr to a•
Tt to 7t*
The best answer to this item is "er to er•", so answer space (C) has been shaded.
Ifyou wanttochangeyouranswer, be sure to erase your itcompletcly before you fill in your new choice.
6.
Whenyouaretoldtobegin,tumthepageandworkasquicklyandascarefullyasyoucan. lfyoucannot
7.
answeranitem,omititandgoontothenextone. Youcancomebacktotheomitted item later. Your
score will be the total number of correct answers.
8.
--=
Youmaydoanyroughworkinthisbooklet.
9.
.....
- I0.
! !!!
.....
Figures arc not necessarily drawn to scale.
Theuseofnon-programmable calculators is allowed .
DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
!!!!!!!
iii
iiiii
Copyright02009CaribbeanExaminationsCouncil.
All rights reserved.
021120 IOCAPE2009
-
1.
-2Which of the following has the GREATEST
2.
polarizing power?
(A)
ca>+
(B)
Be 2•
(C)
Li'
(D)
Sr2'
A radioactive clement, M, ofmass number
A, and atomic number Z, undergoes ll decay,
followed by a decay. The final elemem, N,
will be
(A)
~-1 N
(B)
A-<N
(C)
A-4N
(D)
A-<N
Z-1
z
Z+I
Item 3 refers to the mass spectrum of chlorine gas shown below.
A
c
~
Relative
Abunduce
D
B
~
~
.
.
.
~
~
~
.
"
.
q
.
E
I.
.
~
m
~
•
m/e
3.
If peak A represents the ion " Cl• , which possible ions would give the peaks, B
andE?
(A)
37
Cl' and ( 37 Cl- 37 Cl)'
(B)
("Cl _>Sci)' and (37 Cl- 37 CI)'
(C)
37
Cl' and ('s Cl-'s Cl)'
(D)
37
CI' and ('sCl- 37 CI)'
GOONTOTHENEXTPAGE
'021120IOICAPB2009
-34.
The electronic configuration ofthe Cu" ion
is represented as
8.
Which of the following is true about 5 dm' of
hydrogen and 5 dm' of oxygen at 0 °C and
101 kPa?
(A)
6
2
[Ar)3s 3p 3d
(C)
[Ar] 3s 2 3p 6 Jd' 4s 2
2
6
[Ar)3s 3p 3d
(B)
(C)
(D)
(C)
9
Which of the fol lowing factors increases the
first ionisation energy of an atom?
(A)
(A)
(B)
10
(B)
(D)
5.
(Ar)3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 1
(D)
9.
Increased screening by inner
electrons
Larger number of valence electrons
Greater nuclear charge
Larger atomic radius
For complete reaction, 0.25 g of a monobasic
acid requires 10 cm' of 0.2 mol dm·' sodium
hydroxide. What is the relative molecular
mass of the acid?
(A)
(B}
(C)
6.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
7.
(D)
Which oftlie following describes potassium
bromide?
A network of covalently bonded
atoms
A substance which boils at 59 "C and
decomposes at high temperatures
A solid with a very high molar
enthalpy ofvaporization which does
not conduct when in a liquid state
A non-conducting solid which melts
to form a liquid that conducts
electricity
10.
They react to produce 5 dm' of water.
They possess the same amount of
kinetic energy.
They contain the same number of
molecules.
They react completely with each
other.
12.5
62.5
125
250
When86 gofthe ionic salt, Caso,. xH,O, is
heated so that all ofits water of crystallisation
is driven off and 68.0 g of CaSO, remain,
the value ofx is
(A)
(B)
1
2
tC)
3
(D)
4
How many hydrogen bonds can be formed
with the oxygen atom in a molecule of water?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
1
2
3
4
GOON TO THE NEXT PAGE
02112010CAPE2009
11.
-4Which of the following graphs BEST
illustrates Boyie"s law?
(A)
.
Energy
a
.!
;;.
"
(B)
Item 13 refers to the energy profile diagram
shown below.
Pressure
.a
~~~~} __
"
~
Reaction Path
I/Pressure
(C)
.
a
.!
~
~
Pressure
(D)
~
~
ProduCll
~
13 .
What is the activation energy of the
REVERSE reaction?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
p
Q
(Q+ P)
(Q- P)
I/Pressure
12.
Which of the following represents an
oxidation process?
(A)
MnO 4
Mn2•
(B)
MnO- 4
Mno 2-
(C)
Mn0;4 Mn02
'
•
4
(D)
GOONTOTHENEXTPAGE
0211201 OK:!APE2009
•
-514.
1
. The second ionisation energy ofcalcium is 1150 k J mol- •
Which ofthe following equations represents this statement?
kJ mol- 1
15.
(A)
Ca(g) -> Ca'• (g)+ 2e-
Ml= + 1150
(B)
Ca+ (g)-> Ca 2'(g) +e-
t.H = + 1150
(C)
ca•(g)->Ca 2•(g)+e-
Afi=-1150
(D)
Ca(s)-> ea 2• (g)+2e-
t.H = + 1150
The standard enthalpy changes fortworeactions areas follows:
2Fe (s) + Y,02 (g)-> FeiO, (s)
C(s) + Y,0 2 (g)-> co (g)
t.H" = -822 kJmof
1
aH• = - 110 kJ mol- 1
What is the standard enthalpy change forthe reaction
Fe2 0 3 (s) + 3C(s)-> 2Fe(s) + 3CO(g),inkJ mol- 1 ?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
16.
-932
-712
-492
+492
An increase in temperature by about l 0 ° C usually doubles the rate ofa chemical reaction. This is
because the
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
number ofmolecules having energy greater than the activation energy increases
kinetic energy and temperature ofthe molecules decrease
activation energy ofthe molecules required for reaction increases
collision frequencyofthemolecules Huctuates
GOONTOTHENEXTPAGE
02112010ICAPE2009
-'6 -
Item_!] refers to the table which shows the rate results for the reaction A+ B-> C
17.
Experiment
(A)
lmol c1m·')
(mol dm.3)
[BJ
Rate of reaction
3
(mol dm' s'1 )
I
0.10
0.10
0.0032
2
0.10
0.20
0.0032
3
0.20
0.20
0.0064
What is the overall order of the reaction?
(A)
(B)
(C)
Zero
First
Second
(D)
Thiid
Thi diagrams show the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. Which of the following diagrams represents
the effect of an increase in temperature from 70 "C (T,) to 80 °C (T,)?
18.
T,
(A)
(C)
Number of molecules
EA
Number of molecules
T,
T
(B)
Number of molttuleS
(D)
Number of molecules
OOONTOTHENEXTPAGB
021•12010CAPE2009
-7-
19.
Which of the following statements about
dynamic equilibrium is NOT true?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
20.
21.
22.
The forward reaction proceeds atthe
same rate as the reverse reaction.
The concentrations of the reactants
and products are constant
throughout the course of the
reaction.
Dynamic equilibrium can only be
achieved in a system where no
materials are added or removed.
There is no apparent change but both
forward and reverse reactions
continue to take place at equal
rates.
The Haber Process can be represented by
· theequation
N 2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Li H = -92 kJ moJ·I
Ifthe pressure is kept constant, an increase
in temperature will cause the volume ofthe
mixture to
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
In which of the following reactions would K,
have units of a1m· 2?
(A)
N 2(g} + 3H., (g) ~ 2NH,(g)
(B)
SO, (g) + 0 2 (g) ~ 2SO, (g)
(C}
2CHCIF2 (g) ~ C,F, (g) + 2HCI (g)
(D)
CH, (g) + H, 0 (g) ~ CO (g) + 3H., (g)
23.
X (aq) + Y (aq) ~ z.(aq). Ifthe equilibrium
concentrations are [X] = 0.2 mo! dm·'.
[Y] = 0.3 mol dm·' and [Z)= 0.6 mo! dm·',
which of the following is the value of the
equilibrium constant K,?
0.1 mol dm'
0.1 moI- 1 dm-2
10 mo! dm-'
IO mol- 1 dm'
the left
decrease, shifting the equilibrium to
the right
NH;+ C,H,OH ~NH,+ C,H,OH,'
Which of the following combinations
describes the function of NH,• and C,H,OH
according to Bronsted-Lowry theory?
. (A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
24.
increase, shifting the equilibrium to
the right
increase, shifting the equilibrium to
the left
decrease, shifting the equilibrium to
In pure ethanol, (C,H,OH), the following
equilibrium can exist with ammonium ions.
Equilibrium is established in the reaction
(A)
(B)
(C}
(D)
5
Fe
~ ~~ 2NH3(g)
NH;
C,H,OH
Acid
Base
Conjugate acid
Acid
Base
Acid
Base
Conjugate base
When I cm' of dilute HCI is added to an
alkaline buffer the
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
pH increases drastically
pH decreases drastically
pH alters slightly
buffer is destroyed
00 ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
021120 IOICAPE2009
-8-
25.
2 6.
A buffer is made by dissolving 28.8 g of
sodium benzoate, C 6 H,C00Na, in l dm' of
0.4 mol dm» benzoic acid, C 6 H,COOH.
Ko(benz<Hcocidl =6.4 x lO"'moldm"'. The pH of
the buffer is
(A)
(B)
2.3
3.9
(C)
4.2
(D)
5.0
27.
Given that solubility of zinc sulphide in
water at 25 °C is 1.0 x 10- 12 mol drn-3 ,
what is the K,. value at 25 °C?
(A)
l.O x 10· 12 mol2 drn ..
(B)
5.0 x 10·11 mol 1 dm ..
(C)
5.0 x 10·24 moi2 dm ..
(D)
l.O x 10·1• mol 1 dm ..
Which expression represents the solubili1y
product of iron (111) hydroxide?
(A)
(B)
e" OH- 3
(Fc(OH),
(C)
[Fe'•] [3oH-]'
(D)
[Fe'·] [3oH- J
Item 28 refers to the diagram of the hydrogen electrode below.
Hz(&) at o·c
_,.
udl-
Platinised -+---;---+
platinum
electrode
28.
/ F - - Salt bridge
--+--1.0 mol dm.a H+
What needs to be changed to make this hydrogen electrode have.an E6 = O.OOV?
(A)
. (B)
(C)
(D)
Concentration of H • ions
Metal used for the electrode
Temperature of the gas
Pressure of the gas
GOONTOTHENEXTPAGE
02112010ICAPE2009
-9-
29.
Item 30 refers to the cell diagram below.
A cell consists of aluminium metal in contact
with AP+ ions and copper metal in contact
with Cu,. ions. The half-cell values are given
below.
Zn(s) IZn 2• (aq)llcu 2• (aq)jCu(s)
30.
--
E9N
Al>+ + 3e· ___,Al
-1.66
Cu,. + 2e· ~ Cu
+-0.34
Which of the following will cause an
increase in cell potential?
(A)
Increasing concentration of Zn'' ions
only
Decreasing concentration of
Zn"(aq) ions and increasing concentration ofCu2•(aq) ions
Decreasing concentration of Cu 2•
ions only
Adding NaOH to cu>+ solution and
increasing the concentration of
(B)
The electromotive force (e.m.t) of the cell
(in volts) is
(C)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
2.30
2.00.
1.84
1.32
(D)
Zn2• ions
31.
Which of the following compounds conducts
electricity?
Na,0
Si02
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
so,
c1,o,
Items 32 - 33 refer to the following information.
Name of Oslde
(C)
(B)
(A)
(D)
State at 2S°C
Solid
Solid
Liquid
Bonding and structure in
oxide
Ionic
lattice
Giant
covalent
Covalent Covalent
molecular molecular
pH of aqueous solution
IO
7
0
Gas
I
i
Match each oxide below with one of the options above. Each option may used once,
more than once of not at all.
32.
Oxide of silicon
B
33.
Oxideofsulphur
D
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
02112010.CAPE2009
t
- I 0-
34.
Which pair of properties increases on
descending the Group U elements?
[.
u.
III.
IV.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
35.
Atomic radii
Ionisation energy
Electronegativity
Ionic radii
II.
I and III
IandN
n and III ·
II and N
(B)
(C)
(D)
calcium oxide is less stable than
barium oxide
· the calcium ion is larger than the
barium ion
the lattice energy of calcium oxide
is larger than that of barium oxide
the standard enthalpy offormation of
calcium oxide is less negative than
that of barium oxide
III.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
38.
Which of the following chlorides of Group N
elements is the BEST electrical conductor?
(A)
PbCl4
(B)
SiCI,
(C)
GeCI,
(D)
CCI,
Silicon carbide has a structure similar to that
"of diamond. What are the advantages
derived from using silicon carbide ceramics
when compared with steel?
I.
Calcium carbonate decomposes at a lower
temperature than barium carbonate because
(A)
36.
37.
39.
Silicon carbide is less likely to deform
under compression.
Silicon carbide has a higher melting
point
Silicon carbide is more resistant to
oxidation.
I and II only
land ill only
II and III only
I, n and III
In which ofthe following options are the halide
ions placed in order of INCREASING
reducing power?
(A)
Br-, Cl-, I -
(B)
1-, Br-, ct-
(C)
Cl-, Br-, I -
(D)
Cl-, 1-, Br-
Which of the following in NOT formed when
chlorine reacts with hot aqueous alkali?
(A)
H 20
(B)
NaCl
(C)
NaCI03
(D)
NaCIO
- 11 40.
Which ofthe following is NOT considered to
be a transition metal?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
41.
Zinc
Iron
Cobalt
Chromium
Note: [Ar]= I s , 2s , 2p , 3s , 3p
2
3d
(Ar]
6
2
(a)
a deep blue solution .with excess
NH,(aq)
A
(b)
a yellow-green solution with excess
concentrated HCI.
D
I.
The complex ion [Cu(NH,),]'" is
formed in (a).
u.
[Cu(NH,)4 ) " has a higher stability
constant than [Cu(H,0)J 2 '.
III.
[CuCl 4 ]'· has a lower stability
constant than [Cu(H,0),]".
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
I and II only
land Ill only
II and III only
I, II and III
6
...
I I OD
...
I 1~ I 1~ I 1~ I tltl OD
...
11~ 11~ I 1~ 11~ I
OD
...
I 1~ I 1~ I 1~ I 1~ I 1~ I D
11~ 11~ 11~ 11~ 1~
Cu(Il) sulphate gives
Which of the following can be deduced from
these observations?
Which diagram represents the electronic
configuration of Cu'?
2
(A)
42.
3d
(B)
(Ar]
3d
(C)
[Ari
3d
(D)
!Ari
43.
Which of the following gives a green flame
when heated?
{A)
(B)
(C)
Magnesium
Calcium
(D)
Copper
Sodimn
GOONTOTHENEXTPAGE
02i 12010ICAPE2009
- 12 44.
Four solutions are each tested with aqueous
NH, which is added dropwise Wltil in excess.
The following observations are noted .
I.
II.
III.
IV.
A white precipitate fonns which
dissolves in excess ammonia.
A white precipitate forms which
rapidly oxidises in air to a brown
colour.
A white precipitate forms which is
insoluble in excess ammonia.
No precipitate forms.
Which of the following options identifies the
ions which may be present?
I
II
III
IV
(A).
Zn'·
Fc 2•
AI"
Mg'•
(B)
Mg'•
Mn2..
Zn'·
Ca 2•
(C)
Zn2+.
Mn 2+
Mg'•
Ca 2"°
(D)
Zn''
Fe2•
Al''
NH;
45.
The ionic equation for the fonnation of lead
sulphate from lead{II) nitrate ( aq) and sodium
sulphate (aq) is
(A)
(B)
Pb2+ (aq)+so/-(aq)~ PbSO,(s)
(C)
Pb'+ (aq)+ 2sq-(aq)~ Pb(S(\)2 (s)
(D)
Pb 2+ (aq)+SO,"-(aq)~PbS03 (s)
IFYOUFINISHBEFORETIMEISCAIJ.F:D,CHECKYOURWORKONTIHSTEST.
02112010/CAPE2009
TESTCODE02112010
FORMTP2010148
MAY/JlJNE20IO
CARIBBEAN
COUNCIL
ADVANCEDPROFICIBNCYEXAMINATION
CHEMISTRY - UNIT 1
PaperOl
90minutes
( 26MAY2010(a.m.))
READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY.
I
I.
This test consists of 45 items. You will have 90 minutes to answer them.
2.
In addition to this test booklet. you should have an answer sheet and a Data Booklet.
3.
Each item in this test has four suggested answers lettered (A). (B), (C), (D). Read each item you
are about to answer and decide which choice is best.
4.
Onyouranswersheet.findlhenumberwhichcorrespondstoyouritemandshadethespacehaving
the same letter as the answer you have chosen. Look at the sample item below.
Sample Item
WhichofthefollowingislheHIGHESTenergytransilioninanorganiccompound?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
n too•
Sample Amwer
n to x•
@@•@
OloO*
It to It*
The best answer to this item is "o too•'', so answer space (C) has been shaded.
liiii
-
5.
Ifyouwanttochangeyouranswer,besuretoeraseitcompletelybeforeyoufillinyournewchoice.
6.
When you are told to begin, turn the page and work as quickly and as carefully as you can. If you
cannot answer an item, omit it and goon to the next one. You may return to the omitted item later.
Your score will be the total number of correct answers.
7.
You may do any rough work in this booklet
8.
Figures are not necessarily drawn to scale.
9.
The use of silent. non-programmable calculators is allowed.
00 NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO 00 SO.
Copyright©2009CaribbeanExaminalionsCouncil.
All rights reserved.
~
ii
-....
.....
=::!:
liiii
02112010/CAPE2010
-
-
1.
-2A radioaclive element M of mass number A,
s.
and atomic number Z, undergoes p decay,
followed by a decay. The final elemenl, N
will be
Which of the following faclors increases the
· first ionisation energy of an atom?
..
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(A)
~-IN
(B)
A-z• N
(C)
A-4N
The bonds in SO,2- ion are BEST described
as
A-4N
(A)
(B)
6.
(D)
Z+I
:Z-1
(C)
(D)
2.
"Br- 50.?%
(A)
(B)
(C)
(0)
(C)
(D)
7.
"Br- 49.5%
The bond angles in the PH, molecule are the
same as thal ofNC13• Its shape would BEST
be described as
(A)
(B)
78.99
79.90
79.99
80.01
An ion Z" contains 23 protons. What is the
elecirollic coofiguration of Z'+?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(0)
8.
[Ar) 3<1° 4s'
[Ar) 3d'
[Ar] 3d'4s2
[Ar] 3d6 4s2
(A)
(B)
A Tr bond results from the overlapping of
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
twos orbitals
one s and one p orbital
two p orbitals end-<>n
two p orbitals sideways
(D)
9.
bipyramidal
pyramidal
tetrahedral
trigonal
Which of the following is true about 5 dm'of
hydrogen and 5 dm' of oxygen al O'C and
,IOI kPa? They
(C)
4.
covalent and polar
ionic and polar
polar, covalent and single
polar, covalent and double
'Yhat is the average rela1ive atomic mass of
bromine, given lhe following isotopic masses
and relalivc abundance?
3.
Greater nuclear charge
Larger atomic radius
Larger number of valence electrons
Increased screening by inner
electrons
contain the same numlrer of
moleculcs
possess the same amount of kinetic
energy
react completely with each other
react to produce 5 dm' of water
Which of the following solids has a giant
molecular lattice?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Copper
Carbon dioxide
Magnesium oxide
Silicon dioxide
GO ONTO THE NEXT PAGE
O'll 12010ICAPE2010
-3-
10.
The simplest fonnula for a compound that
contains 50% S and 50% 0 by mass is
(A)
so
(B)
so,
(C)
s,o
(D)
s,o,
13.
Which of the following gases is MOST likely
to behave like an ideal gas?
Anunonia
Heliwn
Methane
Oxygen
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Item 14 refers to the following information.
1be enthalpy of solution of sodium chloride
at 298 K can be calculated from the data
given below.
Item 11 refers to the following information.
A piece of copper metal is placed in silver
nitrate solution, as shown in the diagram
below.
NaCl(s) -+ Na•(g) + CJ-(g);
AH=+787kJmo1· 1
-CuMetal
Na• (g) +water -+ Na•(aq);
AH "'-406 kJ mol- 1
'---
c1- (g) +water -+ c1-(aq);
~
AH,.-377kJmol· 1
11.
Which of the following would MOST likely
be observed?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
12.
Copper metal dissolves and the
solution remains colourless.
Copper metal is deposited and the
solution turns blue.
Silver metal fonns and the solution
remains colourless.
Silver metal forms and the solution
turns blue.
A gas in a syringe occupies a volume of
50 cm' and has a pressure of 0.49346
atmospheres. What is the pressure of the
gas if the plunger of the syringe is pushed in,
reducing the volume of the gas to 20 cm'?
(1 atmosphere= 10 l 325 Pa)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
20kPa
125 kPa
20000kPa
125000kPa
14.
Which is the correct value for the enthalpy
of solution?
-1570 kJ mot-1
-4kJmot-•
+4 kJ mo1-•
+1570kJmot-'
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
15.
What is the standard heat of reaction
(AH.....,.,.,) at 101.325 kPa of pressure and
298 K, for the equation given below?
Zn (s) + Cu2• (aq)-+ Zn'• (aq) +Cu (s)
AH"- "'+64.4kJmo1- forCu
1
2
•
8
t.H ....,.,. ;-152.4kJmol-' for Zn'•
t . H ' - ;OforbothZnandCu
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
-217 kJ mot-'
-88.0 kJ mo1-1
+88.0 kJ mo1-1
+217kJmot-•
GOONTOTIIENBXTPAOE
02112010CAPE2010
-4-
16.
The rate law for a given reaction is Rate= k (A ] 2 (B]. What are the units fork?
(A)
mo1- 2 c1m-2 s·'
(B)
mol dm-3 s- 1
(C)
mo1- 1 dm 3 s- 1
(D)
mo1-2 dm 6 s-•
Item 17 refers to the table which shows the rate results for the reaction A+ B ~ C
17.
Experiment
LAJ
(mol dm-')
(mol dm-')
I
0.10
0.10
Kate of Keacuon
(mol dm-•s-1)
0.()()32
2
0.10
0.20
0.0032
3
0.20
0.20
0.0064
!DJ
What is the overall order of the reaction?
(A)
z.ero
(B)
First
Second
Third
(C)
(D)
Item 18 refers to the following information.
The Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies at two temperatures, T 1 and T 2, is shown below.
18.
Which area represents the additional number of molecules having the activation energy, E •• at the
higher temperature, T2?
(A)
X
(B)
y
X+Y
X-Y
(C)
(D)
GOONTOnlENEXTPAGE
021120lOCAPl!2010
-519.
Which of the following statements does
NOT refer to a system in dynamic
equilibrium?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(0)
20.
23.
li:t pure ethanol (C,H,OH), the following
equilibrium can exist with ammonium ions.
NH; + C 2H,OH ~ NH, + C,H,OH/
The reaction is reversible.
The amounts of all the species in the
system remain constant.
The concentrations of all reactants
and products are equal.
The rate of the forward reaction is
equal to the rate of the backward
reaction.
Which of the following combinations
describes the function of NH,• and C,H,OH
according to Brtlnsted-Lowry theory?
NH/
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
For the reaction
H, (g)+ 12 (g)
~
2HI(g)
Acid
Base
Conjugate acid
Acid
reaching
equjlibrium at 444 °C, at I atm pressure, the
C,H50H
base
acid
base
conjugate
base
Item 24 refers to the figure below which
shows the pH change as propanoic acid is
tilrared with sodium hydroxide.
value of KP is 50.
What .is the value of KP at a pressure of 2
atm at the same temperature?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
21.
25
50
100
200
12
pHUI
8
6
4
2
In the Haber process,
N,(g) + 3H,(g) ~2NH,(g), aH = -90
• Vol ohodlum bydro:dde added (cm 3)
kJmo1-•,
the MAXIMUM yield of ammonia is obtained
at
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
high temperature and low pressure
high temperature and high pressure
low temperature and high pressure
low temperature and low pressure
24.
Which indicator is MOST suitable for this
reaction?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
22.
Indicator
pH range
Thymolblue
Methyl orange
Methyl red
Phenolphthalein
1.2-2.8
2.9-4.6
4.2-6.3
8.3-10.0
Which of the following acids is the
WEAKEST?
Acid
K, (mol dm-3)
(A)
4.9x Hr' 0
l.7x 10-'
6.3 x IO-'
1.3 x 10-3
(B)
(C)
(0)
OOONTOlllENEXTPAOE
02112010CAPl!2010
-6-
25.
Item 28 refers to the electrochemical cell
A buffer is made by dissolving 28.8 g of
sodium benzoate, C,H,COONa, in 1 dm3 of
0.4 mol dm-• benzoic acid, C,H,COOH.
K...,..,.,c..,id) =6.4 x 10-'mol dm-3• The pH
of the buffer is
below.
Zn(s) I Zn>+ (aq) II Ag•(aq) /Ag(s)
28.
26.
From which half-cell do electrons originate?
(A)
(B)
(C)
2.3
3.9
4.2
(A)
Ag•(aq) I Ag(s)
(D)
5.0
(B)
Zn(s)/ Zn2•(aq)
(C)
Ag+(aq)/Ag(s) II Zn(s) fZn>+(aq)
(D)
Zn(s) tzni+(aq) II Ag• (aq) /Ag(s)
The solubility product, K , at 298 K for three
Group ll metal sulphatesis given below.
K 8p(mol 2dm°")
I.
caso,
n.
SrSO,
BaSO,
Ill.
Item 29 refers to the following diagram.
2.4 x 10-'
3.2 x 10-7
1.6 x 10-10
Win
Which metal sulphate would precipitate out
of solution if equal volumes of I 0-3 mol dm·'
solution containing the sulphate ion and the
Group II metal are mixed?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
27.
!only
I and ll only
II and Ill only
I, II and m
Barium carbonate is more soluble in water
than in aqueous sodium carbonate because
(A)
(B)
all barium salts are insoluble
barium ions cannot displace sodium
icm
(C)
sodium carbonab: is ionic but barium
(D)
a common ion effect is present in the
carbonate is not
29.
Which of the following does NOT occur in
the cell shown above?
(A)
(B)
Electrons flow through the wire
from the zinc to the magnesium
electrode.
Magnesium ions migrate into the salt
bridge.
(C)
(D)
No current flows when the salt
bridge is removed.
The reaction at the magnesium
electrode is
Mg (s) -4 Mg'• (aq) + 2e-.
BaCO,INa,CO, mixture
GOON T0111ENEXTPAGE
O'Zl 1201<K:APE2010
-7Item 30 refers to the diagram of the hydrogen electrodl' below.
Hz(&) at o·c
~
/ r - - Salt bridp
and 1 atm
PlaliUed -+---;r--tpladaum
electrade
30.
The concentration of H • ions
The metal used for the electrode
The temperature of the gas
The pressure of the gas
Which of the following graphs BEST illustrates the variation in melting points of the elements Na to Ar?
(A)
Melting
poinl("C)
NaM,AI Si P
(C)
Melting
poilll("C)
•
(D)
NaM,Al Si P S Cl Ar
32.
e+
What needs to be changed to give this hydrogen electrode an E 0 = O.OOV ?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
31.
-4--1.0 mol dm-3
NaMgAISi PS
Melliq
poinl("C)
NaM1AISi P S Cl Ar
The element, P, in Eel, has an oxidation slate of
(A:)
(B)
(C)
(D)
+I
+3
+4
+5
GO ONTO 1llB NEXT PAGE
O'll 12010CAPE2010
-833.
Which of the following sets of properties is true for the oxide of sulphur?
34.
State at 25 "C
Solid
Bondingandstructureinoxide
pH of aqueous solution
(A)
(B)
(C)
Ill
(D)
IV
(B)
(C)
(D)
Solid
Ionic lattice Giant covalent
Covalent
molecular
Covalent
molecular
IO
0
3
1
I
II
36.
calcium oxide is less stable than
barium oxide
the calcium ion is larger than the
barium ion
the lattice energy of calcium oxide
is larger than that of barium oxide
the standard enthalpy of formation of
calcium oxide is less negative than
that of barium oxide
Group II elements of the periodic table have
(A)
(B)
highmeltingpointsbutlowdensities
highmehingpointsandhighelectrical
The high melting point of graphite can be
attributed to the
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
low densities but high electrical
I.
II.
CXlllductivities
(D)
low melting points and poor electrical
conductivities
delocalised electrons
hexagonal arrangement of the carbon
atoms
strong covalent bonds within the
layers
van der Waals' forces between the
layers
Silicon dioxide has a structure similar to that
of diamond. What are the advantages derived from using silicon dioxide ceramics
when compared with steel?
CXlllductivities
(C)
IV
Gas
37.
35.
III
Liquid
Calcium carbonate decomposes at a lower
temperature than barium carbonate because
(A)
n
I
Property of Oxide
Ill.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Silicon dioxide is less likely to deform
under compression.
Silicon dioxide has a higher melting
point
Silicon dioxide is more resistantto oxidation.
I and II only
I and III only
II and III only
I, II and III
OOONTOTHENBXTPAGE
02112010CAPE2010
-9 38.
Based on its position in Group VII of the
periodic table, astatine, at room temperature
and pressure, is MOST likely a
(A)
(B)
solid
(C)
brown gas
colourless gas
40.
Cu(ll) sulphate gives
(a)
a deep blue solution with e1<cess NH,(aq)
(b)
a yellow-green solution with excess
concentrated HCI.
~
(D)
39.
42.
Which of the following can be deduced from
these observations?
Which of the following is NOT formed
when chlorine reacts with hot aqueous
alkali?
(A)
(B)
H;o
NaCl
(C)
NaClO
(DJ
NaClO,
1be species containing ions or molecules
linked to a central atom by coordinate bonds
I.
The complex ion [Cu(NH,),J'• is formed
in (a).
II.
[Cu(NH,),J'• has a higher stability
constant than [Cu(H,0)6 ]'•.
lll.
[CuCl4J'- has a lower stability constant
than [Cu(H,0) 6] 2•.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
I and II only
I and llI only
II and III only
I, II and III
is known as a
(A)
43.
ligand
complex
catalyst
coordination number
(B)
(C)
(D)
hydroxide from chromiwn(Ill) sulphate and dilute
NH 3 (aq) is
Item 41 refers to the information below.
Melting Point
Density
(oC)
(g cm-3)
I
1538
7.86
II
660
328
2.70
Element
III
41.
The ionic equation for the formation of chromiwn
(A)
Cr,+(aq) +Off (aq)--> Cr,OH (s)
(B)
Cr"'(aq) + 30H-(aq) --> Cr(OH), (s)
(C)
Cr"'(aq) + OH-(aq)--> Cr(OH)'• (aq)
(D)
Cr"'(s) + 30H-(I)--> Cr(OH), (s)
11.34
The transition elements are MOST likely
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D )'
!only
I and II only
I and III only
II and III only
GOONTOTHENEXTPAGE
02112010CAPE2010
- 10Item 44 refers to the following information.
White precipitate
insoluble in excess
White precipitate
soluble in excess
44.
Which of the following reagents does NOT
aid in the identification of 2•?
x
(A)
Aqueous KI
Dilute HCI
Dilute HN03
Dilute ff,SO,
(B)
(C)
(D)
Item 45 refers to the following information.
Aqueous BaCl 2 followed by excess dilute HCI is added to EACH of four unknown
solutions, I, II, III and IV. 'The following observations are noted.
I.
Il.
Ill.
IV.
45.
A white precipitate is formed which dissolves in the acid to liberate a gas which
decolourises MnO;
aq).
No precipitate is formed.
A dense white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in excess acid.
A white precipitate is formed that dissolves in the acid to liberate a gas, which
forms a white precipitate with Ca(OH)2(aq).
m·c
Which of the following options correctly identifies the ions which may be present in
EACH solution?
I
II
m
IV
(A)
so 2-
CI-
HCO-
co 2-
(B)
so42-
NO-
soi...
3
co 32-
. (C)
so3
c1-
s2-
co 32-
(D)
so32-
NO3
so 2-
'
2-
'
'
•
'
co 32-
IFYOUFINISHBEFORETIMEISCAI.I.ED,CHECKYOURWORKONTIDSTEST.
0211201<K:APE2010
-.
C
D
C
A
C
B
CAPE Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 2012
A
D
I(...,_
•
....,..-
(
I ..-
i
l.;
!
.·
0 ,. '
TEST CODE 02.112010
MAY/JUNE2013
CARIBBEAN
EXAMINATIONS
COUNCIL
CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION"'
CHEMISTRY - UNIT 1
Paper 01
1 hour 30 minutes
(
21 M~Y 2013 (a.m.) )
READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY.
1.
This test consists of 45 items. You will have I hour and 30 minutes to answer them.
2.
In addition to this test booklet, you should have an answer sheet'and a Data Booklet.
3.
Each item in this test has four suggested answers lettered (A), (B), (C), (D). Read each item
you are about to answer and decide which choi<;e is best.
4.
On your answer sheet, find the number which corresponds to your item and shade the space
having the same letter as.the answer you have cl10sen. Look at the sample item below.
Which of the followi11g transitions requires the HIGHEST energy in an organic compound?
(A)
n to er•
(B)
n to 7t•
(C)
7t to 7t•
cr to cr•
(D)
Sample Answer
..
@®©•
The best answer to this item is "cr to cr•", so answer space (D) has been shaded.
--=·--=
5.
If you want to change your answer, erase it completely before you fill in your new choice.
6.
When you are told to begin, turn the page and work as quickly and as carefully as you can. If
you cannot answer an item, go on to the next one. You may return to this item later. Your score
will be the total number of correct answers.
7.
You may do any.rough work in this booklet.
8.
Figures are 'not necessarily drawn to scale.
9.
You may use a silent, non-programmable calculator to answer items.
""""'
I
·
..
DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
Copyript C 2011 Caribbean Examin.tions Council
A II ri nht• -••'"'•A
~---~--------~
. .~
·"-'
-2l.
Which of the following statements is NOT
a part of Dalton's atomic theory?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Atoms are indivisible.
Atoms are characterised by their
atomic number.
The atoms of an element have
identical properties.
The atoms of an element differ from
those of other elements.
4.
Which of the following factors is important
in determining the stability of an isotope?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
5.
Which of the following statements is
TRUE about 5 dm 3 of hydrogen and 5 dm'
of oxygen at 0 °C and I OJ kPa?
Item 2 refers to the following diagram which
shows the energy levels for the hydrogen
atom and the electronic transitions which
produce lines in the visible region.
(B)
==========::::;==::i===n=S
(C)
(A)
=_-=i=_-==-~:1=_1::=~-<:!=~-= ::~
Size of atomic radius
Number of protons
Ratio of protons to electrons
Ratio of protons to neutrons
(D)
They react to produce 5 dm' of
water.
They possess the same amount of
kinetic energy.
They contain the same number of
molecules.
They react completely with each
other.
- - - - - - - - - - n=l
6.
2.
Which of the series below involves
transitions from higher energy levels to the
n = 2 level?
Which of the following solids has a giant
molecular lattice?
(A)
(B)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
3.
Balmer
Dalton
Lyman
Paschen
( C)
(D)
Carbon dioxide
Copper oxide
Magnesium oxide
Silicon dioxide
Which of the following ions has the
GREATEST polarizing power?
(A)
Be'+
(B)
Ca2•
(C)
Li+
(D)
Sr•
!
!
GO ON TO 11iE NEXT PAGE
-3Item 11 refers to the following information.
Item 7 refers to the following equation
which shows the production of ammonia.
N 2(g) + 3H2(g)
7.
A piece of copper metal is placed in silver
nitrate solution, as shown in the diagram
below.
.= 2NH,(g)
-
If I 0 cm' of nitrogen reacts with 30 cm' of
hydrogen at STP, what volume of NH, is
produced?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Cu metal
JO cm'
15 cm'
20cm'
40cm'
11.
8.
F9r complete reaction, 0.25 g ofa monobasic
acid requires IO cm' of0.2 mol dm·' sodium
hydroxide. What is the relative molecular
mass of the acid?
Which of the following observations is
correct?
(A)
(B)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
9.
10.
12.5
62.5
125
250
(C)
(D)
The simplest formula for a compound that
contains 50% S and 50% 0 by mass is
(A)
SO
(B)
(C)
so,
s,o
(D)
s,o.
•
Which of the following gases is MOST
likely to have the characteristics of an ideal
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(A)
Mn02 --+ Mn2 +
(B),
Mno.---+ Mno 2-
(C)
Mno.---+ MnO,
(D)
Mn02 --+ Mno.-
•
·-. -- .... -
12.
Copper metal dissolves and the
solution remains colourless.
Copper metal is deposited and the
solution turns blue.
Silver metal forms and the solution
turns blue.
Silver metal forms and the solution
remains colourless.
gas?
Which ofthe following processes represents
an oxidation?
""""··~"·"'
.I
"
13.
Ammonia
Helium
Methane
Oxygen
A gas in a syringe occupies a volume of
50 cm' and has a pressure of 0.49346
atmospheres. What is the pressure of the
gas if the plunger of the syringe is pushed in,
reducing the volume of the gas to 20 cm'?
(I atmosphere= IOI 325 Pa)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
20kPa
125 kPa
20 OOOkPa
125 000 kPa
00 ONro nm NEXT PAGE
-414.
The second ionisation energy of calcium is 1150 kJ mo1-1 •
Which of the following equations represents this statement?
kJmot 1
(A)
ca• (g) -+ Ca2• (g) + e-
L\H = +1150
(B)
Ca(g) -+ Ca2+ (g) + 2e-
L\H =+1150
(C)
ca• (g) -+ Ca2• (g) + e-
L\H =-1150
(D)
Ca (g) -+ Ca,. (g) + 2e-
L\H =-1150
Item 15 refers to the following standard enthalpies of combustion for carbon, hydrogen and octane.
kJmot 1
Carbon
Hydrogen
Octane
15.
The standard enthalpy of formation of octane,
-394
-286
-5476
MJ , is calculated using
(C)
MIJ (octane)= -8 (-394}-9(-286)-5476 kJ rnoJMIJ (octane)= -8 (-394}-9(-286)-{-5476) kJ mo1MIJ (octane)= 8 (-394) + 9(-286)-{-5476) kJ mo1-
(D)
L\H1 (octane)= 8 (-394)-9(-286)-{-5476) kJ mo1- 1
(A)
(B)
1
1
8
•
1
•
•
00 ON TO T1IE NEXTPAOE
-5Item 16 refers to the following reaction which occurs in the presence of dilute acid.
CH,COCH, (aq) + 12 (aq)--+ CH) COCH, (aq) + H• (aq) + 1- (aq)
16.
The rate equation for the reaction is
Rate = k[CH,COCH, (aq)] [H'{aq)). Which of the following equations BEST illustrates the SLOW
step?
(A)
(Il)
(C)
(D)
0
OH
II
I
CH,-C-CH, + H• -+CH,-C-CH,
Ea
0
l
II
I
CH,- C-CH, + 12 --+ CH,-C-CH, + 1Ea
0
l
II
I
CH,- C - CH, + 1- --+CH,- C - CH,
Ea
0
OH
II
I
CH-C-CH
,
, +I, +H• -+CH-C
, I -CH,
l
i
I
r
I
•
17.
The rate Jaw for a given reaction is Rate= k[A) 2 [B] . What are the units fork?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
moJ-2 dm-2 s- 1
mo) dm-3 s- 1
moJ- 1 dm' s- 1
mo1-2 dm' s- 1
•
GO ON TO 1liE NEXT PAGE
-618.
Which of the following phrases BEST
describes the relationship between the
half-life of a second order reaction and the
reactants?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
20.
(A)
(B)
Dependent on the initial
concentration of the reactants
Independent of the initial
concentration of the reactants
Dependent on the state of the
reactants
Dependent on the final concentration
of the reactants
Item 19 refers to the following equilibrium.
N, (g) + 0 2 (g)
Which of the following statements
·does NOT refer to a system in dynamic
equilibrium?
(C)
(D)
21.
Which of the following statements about a
catalyst would be true?
~ 2NO(g), LlH =+I 80 kJ moJ· 1
I.
19.
The reaction is reversible.
The amounts of all the species in the
system remain constant.
The concentrations of all reactants
and products are equal.
The rate of the forward reaction is
equal to the rate of the backward
reaction.
Which of the curves in the diagram below
shows how increasing temperature affects
the yield of the product?
II.
Ill.
(D)
(A)
(B)
(C)
.CD)
22.
-----,(A)
Temperature (UC)
It increases the equilibrium constant
for the forward reaction only.
It increases the equilibrium constant for both the forward and
backward reactions.
It has no effect on the position of
equilibrium.
I only
III only
I and III only
II and III only
The value of Kp for the equilibrium reaction
H2 (g) + 12 (g) ~ 2HJ (g) at 444 'C at I atm
pressure is 50.
What is the value of KP if the pressure
is changed to 2 atm and the temperature
remains the same?
(A)
25
(B)
50
(C)
(D)
100
200
•
00 ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
-723.
In pure ethanol, (C,H,OH), the following
equilibrium can exist with ammonium ions.
NH; + C2H50H ~NH,+ C,H,OH,+
Which of the following combinations
describes the functions of NH; and C,H,OH
according to the Bronsted-Lowry theory?
NH•
'
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Acid
Base
Conjugate acid
Acid
24.
The results for four experiments which
. investigated
the
reaction
between
propanaone and iodine (ca~lysed by acid)
are given in the table below.
Expt
(H•]
[Propanone]
[Iodine]
Rate
I
I
0.5
I
10.8
2
0.5
I
3
4
0
0.5
0.25
I
5.3
5.4
0
0.5
0.5
10.6
C2H 50H
Base
Acid
Base
Conjugate base
Which ofthe following graphs represents the
order of reaction with respect to propanone?
(A)
Rate
[Propanone)
(B)
•
Rate
[Propanone)
(C)
Rate
[Propanone)
(D)
Rate
lPs »
I
•
M1, ..,~,,.,,..A~"'"'..,
00ONTO1llE NEXT PAGE
l
r
- 8-
25.
Which of the following expressions
represents the solubility product of
iron(lll) hydroxide?
(A)
(B)
27.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(0)
[Fe>+] [JOH-]
[Fe 3+] [OH-]3
[Fe(OH) 3 ]
(C)
[Fe1 •] [30H-]3
(D)
[Fe1 •] [OH-] 3
mol dm-'
mol' dm-6
moP dm_.
mol 4 dm-12
Which·ofthe following indicators is MOST suitable for use when titrating a weak acid against a
strong base?·
Indicator
(A)
(B)
(C)
(0)
28.
26. · Silver chromate(VI), Ag,Cr04 , is sparingly
soluble in water. The units. for the solubility
product (K,,,) for silver chromate(VI) are
pH of Change
Colour Change
Acid ~Alkali
3.5
red -+ yellow
red-+ blue
yenow -+ blue
colourless -+ pink
Methyl orange
Litmus
Bromothymol blue
Phenolphthalein
6.0
7.0
9.5
A weak acid, HX, dissociates as follows:
HX(aq) .= x-(aq) + H'(aq)
-The -dissocfation ·coiitint, K-; for the above reaction Is 1.0 x llf1,-mol am-3 .-w!tafwill oo the-•
approximate pH of 1.0 x 10-2 mol dm-1 HX?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
29.
S
6
7
8
Using standard electrode potentials, which of the following reactions would be MOST feasible?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Zn(s) + Cu''(aq)-+ Zn'+ (aq) + Cu(s)
Zn(s) + Pb2•(aq) -+ Zn 2+(aq) + Pb(s)
Pb(s) + Zn2•(aq) -+ Pb2• (aq) + Zn(s)
Ca(a) + Zn2+(aq)- Cu,. (aq) + Zn(•)
•
00ONTO11fE NEXT PAOE
...
-9-
Item 30 refers to the electrochemical cell
below.
Zn(s) I Zn 2• (aq) II Ag+ (aq) IAg(s)
30.
In the cell shown above, electrons originate
from
(A)
31.
Zn( s) I Zn''( aq)
(C)
Ag•(aq) I Ag(s) II Zn(s) I Zn2'(aq)
(D)
Zn(s) I Zn''(aq) II Ag• (aq) IAg(s)
Which of the following sets of oxides is
classified rorrectly?
(D)
Acidic Amphoteric
Basic
co,
CuO
MgO
so,
so,
Al,03
so,
co
P,0 10
Feature
(A)
(B)
(C)
State at 25 °C
Solid
Solid
Liquid
Barium
Beryllium
Magnesium
Strontium
Gas
10
0
7
I
Match EACH oxide below with one of the
options (A, B, C, or D) above. Each option
may be used once, more than once or not at
all.
33.
Oxide of silicon
B
34.
Oxide of sulphur
D
35.
Group II elements of the periodic table have
Cao
(A)
Na,O
so,
(B)
(€)
Which of the following elements reacts very
slowly with cold water and burns with a
bright white flame?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(D)
Bonding and
Ionic Giant
Covalent Covalent
Structure in Oxide lattice covalent molecular molecular
pH of Aqueous
Solution
(B)
(A)
(B)
(C)
32.
Ag'(aq) I Ag(s)
Items 33-34 refer to the information in the
following table.
(D)
36.
high melting points and low
dens4ties
high electrical conductivities and
low densities
high melting points and high
electrical conductivities
low melting points and poor
electrical conductivities
The high meli:ing point of graphite ~an be
attributed to the
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
delocalised electrons
hexagonal arrangement of the
carbon atoms
van der Waals' forces between the
layers
strong covalent bonds within the
layers
,..,.., _...,
____ . ____ _
•
- I0 -
37.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
38.
(D)
40.
Aluminium
Chlorine
Sulphur
Phosphorus
1000
900
800
700
0
s 600
g 500
400
11-1
300
200
100
0
~
-
When AgNO,(aq) is added to fluoride ions
followed by NH3(aq) the result is
(A)
(B)
(C),
39.
Item 41 refers to the graph below showing
the first ionisation energy (IE) of some
elements.
Which of the following elements in the
third period has the same oxidation number in ALL of its known compounds?
no precipitate
white silver fluoride
yellow silver fluoride
cream-coloured ammonium fluoride
Elements
41.
In which of the following options are the
halide ions placed in order of INCREASING
reducing power?
(A)
Br-, Cl -, 1-
(B)
Cl-, 1-, Br·
Ca Sc Ti V Cr MnFe Co Ni Cu Zn
The sharp increase from copper (Cu) to zinc
(Zn) is caused by filled
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
4s-orbitals
d-orbitals
4s and d-orbitals
4s-orbitals and half-filled d-orbitals
(C)
c1-, Br·,1-
Item 42 refers to the information in the table
below.
(D)
I-, Br-, Cl -
Element
On heating CaSO• strongly, it decomposes
into CaO and SO,(g). CaCO, decomposes
ani mucfi lower temperature than CaSO,.
Which of the following factors BEST
explains the greater thermal stability of
CaSO,?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
CaC03 has a higher lattice energy
than Caso,.
CO, is a smaller molecule than SO,.
The co, 2 - ion is more easily
polarised than the SO,'-ion.
The co,>- ion has a higher charge
density than the so,>- ion.
42.
I
Melting
Point (°C)
1538
Density
II
660
2.70
III
328
11.34
(g cm-l)
7.86
Which of the elements in the table can be
classified as transition?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
I only
II only
I and II only
II and Ill only
•
00ONTO11fE NEXT PAOE
- 11 -
43.
Items 44-45 refer to the following options.
Which of the following metals gives a green
flame when heated?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Calcium
Copper
Magnesium
Sodium
A central ion in a complex
A ligand
An octahedral complex
A tetrahedral complex
Match EACH formula below with one of the
options (A, B, C or D) above. Each option
may be used once, more than once, or not at
all.
44.
[Co(H,O)J>+
C
45.
CH,NH 2
B
•
END OF TEST.
IF YOU FINISH BEFORE TIME IS CALLED, CHECK YOUR WORK ON THIS TEST.
•
02112010/CAPE 2013
c x?L
CAPE Chemistry
;.t Unit 1 Paper 1 2014
/ -laexat%'-.nit
J
(----/
1.
Ilem ? refers to the following graph which
shows the log of successive ionization
energies for ten electrons of an element, P.
Which of the following factors increases the
first ionization energY of an dtom?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Greater nuclear charge
Larger atomic radius
Larger number ofvalence electrons
$o
L
Increased screening bY inner
E+
q)
E5
6l
electrons
N
EJ
h0t
:l
2 3 4,5
6 7 8 9 l0
Number of electrons lost
Element P is MOST likelY
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
chlorine
magnesium
neon
sodium
Item 3 refers to the following mass spectrum of chlorine gas'
q)
ql
q)
c)
30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 7s
E0
mJe
3.
If the peak at P represents the 35Cl* ion, which of the following ions repres#tthe
respectively?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
37Cl* and (3?Cl- 37Cl)+
37Cl* and (tt
cl- 35 cl)*
37Cl* and (3scl- 3scl)+
37Cl* and (35C1- 37Cl)+
peaks at Q and T
-3Item 4 refers to the following sketch which
shows the variation of the boiling points of
the hydrides of Group V.
6.
The bond angles in the PH, molecule are
the same as that of NClr. Its shape would
BEST be described as
U
c
(A)
(B)
bipyramidal
pyramidal
(c)
tetrahedral
(D)
trigonal
00
7.
NHg PHg AsH3 SbH3
at 0 oC and l0l kPa?
Hydrides
4.
Which of the following statements is true
of5 dm3ofhydrogen and 5 dm3 ofoxygen
Ammonia has the highest boiling point
(A)
because
(A)
(B)
They react to produce 5 dm3 of
water.
(B)
They react completely with each
(c)
other.
They possess the same amount of
(D)
kinetic energy.
They contain the same number of
the N-H bond is the shortest and
strongest
there are more van der Waals forces
between NH, molecules
(c)
there is hydrogen bonding between
(D)
NH, molecules
the eletronegativity of nitrogen is
molecules.
The following equation represents the
reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric
much higher than that of the other
elements in the group
acid.
J.
Mg + 2H. -.+ Mg2* * H,
Which of the following features describes
potassium bromide?
The molar volume of a gas at rtp is 24 dm3.
(A)
A network of covalentlv bonded
(el
Asubstancewhich boilsat59 oC and
decomposes at high temperatures
A solid with a very high molar
enthalpy of vaporization which
does rrot conduct electriciw when
in a liquid state
A non-conducting solid which melts
The volume of gas produced at rtp when
1.2 g of Mg reacts with hydrochloric acid is
atoms
(c)
(D)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
L2 dml
2.4 dm3
12.0 dm3
24.0 dm3
to form a liquid that conducts
electricity
9.
The simplest formula for a compound that
contains 50% S and 50o/o O by mass is
(A) . so
(B) So,
(c) S,o
(D)
n?l l?nln/aADtr ?nl/
SrOo
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
-4-
10.
When 86 g of the ionic salt, CaSOo.xHrO,
is heated so that all of its water of
12. In which of the following chemical
reactions is sulfur reduced?
crystallization is driven off and 68.0 g
- of
Caso. remain, the value of x is
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
11.
14.
S + Oz
(B)
2SO, + Or* 2SO,
(C)
SO, + HrO
- SOz
- H2So4
1D) 2HrSoo+ cu * cuSoo a Soz + 2Hzo
Deviations from ideal gas behaviour
generally occur under conditions of
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(A)
13.
low pressure and low temperature
low pressure and high temperature
high pressure and low temperature
high pressure and high
temperature
Which of the following gases is MOST
likely to behave like an ideal gas?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Ammonia
Helium
Methane
Oxygen
The standard enthalpy changes for two reactions are as follows:
2Fe(s) +
r Or(C)
?
2
- FerOr(s), AH* = -822 kJ mol-'
C(s) + I O"(g) -- CO(B), AII* : -110 kJ mol-'
1
L
What is the standard enthalpy change, in kJ, for the reaction
Fe,O, (s)+ 3C(s) -+ 2Fe(s) + 3CO(g) ?
I
(A) -e32
(B) -7r2
(c) 4e2
(D)
+492
-\t
GO ON TO TFItr NItr\'T D^^tr
Which of the following starements may be
true about the kinetic theory of an ideal gas?
15.
L
IL
18.
Attractive forces are strong between
molecules.
(A) Nr(e) + rHr(s) t==i zNH,(e)
Average kinetic energy of the
(B)
molecules is proportional to the
absolute temperature.
Volume of molecules is negligible
III.
(A) Ill only
(B) I and III only
(C) II and III only
(D) I,ll and III
SOr(e) + Or(B);:::izSO,(e)
(C) 2cHClFr(g)a-" C,Fo(g; + 2HCl(g)
compared to that ofthe container.
(D) CH4G) + H,Q(g);=: CO(g) + 3H,(g)
19.
Which of the following statements about
dynamic equilibrium is NOT true?
(A) The forward reaction proceeds
The activation energy of a reaction
16.
In which of the following reactions would
Ko have units of atm-2?
at the same rate as the reverse
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
is unaffected by a catalyst
is an energy barrier to the reaction
is affected by temperatures
reduces the speed of the reactant
molecules
(B)
(C)
Item 17 refers to the table which shows
the rate results for the reaction A + B + C
IAI
IBI
Rate of reaction
(mol dm-r)
(moldm'3)
(moldm'3 s'r;
I
0.10
0.10
0.0032
2
0. r0
0.20
0.0032
J
0.20
0.20
0.0064
Experiment
(D)
reaction.
The concentrations of the reactants
and products are constant
throughout the course of the
reaction.
Dynamic equilibrium can only be
achieved in a sYstem where no
materials are added or removed.
aPParent change
There
but both forward and reverse
is no
reactions continue to take Place
at equal rates.
20.
The value of K. for the equilibrium shown
below is 860 at25oC.
tt,(e)+lr(e)F2HI(g)
L7
.
What is the OVERALLorder ofthe reaction?
(A)
(B)
Zero
First
(c)
Second
(D)
Third
What is the value of K" at 25 'C for the
following equi libri um?
L nr<e) *
+
Hl(g)
(A) 2e
(B) zts
(c) 430
(D) 1720
co
n? r I ?n l n-l. LDQ 'rAr A
lr(g) ff
9N
ro rHE NEXT PACE
-624.
2L.
In the Haber Process,
Nr(g) + lHr(e) ;-+2NH3(g),
obtained at
high tempeiature and low pressure
high temperature and high pressure
low temperature and high pressure'
(A) Acid
(B) Base
(C) Conjugate acid
ioi Acid
?<
2P(aq) + Q(aq)"* 2R(aq)
K.'
23.
mol dm-3
dm3 mol-r
Base
Acid
Base
conjugate base
Which ofthe following pairs of substances
would make a good buffer?
(A)
(B)
(C)
are
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
c2HsOH
NfI4*
low temperature and low pressure
Compounds R Q and R form an equilibrium as shown below.
*NHr+c,HsoH2*
Which of the combinations below describes
the functions of NH,* and C2H'OH
according to the Brdnsted-Lowry theory?
the MAXIMUM Yield of ammonia is
The units for the equilibrium constant'
equilibrium can existwith ammontum lons'
NHo*+ c2H5oH -
AH = -90 kJ mol-r,
(A)
(B)
iCi
(D)
In pure ethanol, C2H'OH, the following
iol
HCI(aq) and NaCl(aq)
HCI(aq) and NHoCI(aq)
NHr(ae) and NHoC(aq) NHI(aq) and NaNo,(ag)
mol2 dm{
25 oC is
dm6 mol-2
BaSOo
is
The pH of a 0.03 moldma HCI solution
(A) 0.s2
(B) 1.52
(c) 3.00
(D) 3.s1
The solubility product of BaSOo at
i x 10-'o moli dm*. The number of moles of
that will dissolve in I dm3 of water
to form a saturated solution is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
,
71
I x 10-'o
2 x 10-'o
1 x lOa
2 x l0-5
The expression for the solubility product'
k,o, of lead iodide is
(A) [nu'.] [zr']
(B) [ro'.] [t ]*
^,12r--'12
(c) -LPb-.1L2r'J
^,t2 rr-]2
(D) rLPb"J
LI'J
t 6A
tF
-t
a lrrt'F
-7 28.
Precipitation of a sparingly soluble salt
occurs on addition of a common ion ONLy
if the ionic product is
Item 30 refers to the following diagram of
an electrochemical cell.
Wire
(A)
(B)
(Ci
(D)
29.
less than K,o
greater than K_-
Jqualto K,o
equalto (K,)2
sP
What is the potential for a cell with the
following reaction?
Zn(s) + Brr(ag)
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
- Znz*(aq) + 2Br{aq)
30.
[+1.07 + (- 0.76)] v
[-r.07 + (- 0.76)] v
[-r.07 - (- 0.76)] v
[+1.07 - (- 0.76)] v
Which of the following situations does
NOT occur in the cell shown above?
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
No current flows when the salt
bridge is removed.
Magnesium ions migrate into the
salt bridge.
Electrons flow through the wire
from the zinc to the magnesium
electrode.
The reaction at the magnesium
electrode is
Mg(s)+Mg2*(aq)+2e-.
31.
Which element burns in oxygen to form an
amphoteric oxide?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Aluminium
Magnesium
Sodium
Sulfur
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
n?l l?nln/cAptr ?014
-8Items 32-33 refer to the following properties of four oxides, A, B, C and D.
Name of Oxide
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
State at 25 "C
Solid
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Bonding and structure in
oxide
Ionic lattice
Giant covalent
Covalent molecular
Covalent molecular
oH of mixture with water
l0
Match each oxide below with an option, A, B, C or D, above. Each option may be used once, more
than once or not at all.
34.
a)
Oxide of silicon
B
??
Oxide of sulfur
D
Silicon carbide has a structure similar to
that of diamond. What are the advantages
35.
of using silicon carbide ceramics
compared with steel?
I.
Silicon carbide is less likely to
II.
deform under comPression'
Silicon carbide has a higher melting
(A)
(B)
Point.
III.
Silicon carbide is more resistant to
oxidation.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
I and II onlY
I and III onlY
Which of the following statements about
oxides of the elements in Period 3, sodiurn
to chlorine, is NOT true?
(C)
(D)
II and III onlY
I, II and lll
36.
Across the Period, the oxides
change from basic to amPhoteric
to acidic character'
The oxides react with water to form
alkaline solutions.
The oxidation number of the
element in the oxide increases
across the Period.
The structure ofthe oxides changes
from giant ionic to simPle
covalent molecules.
Which of the following properties belong to
Group II elements of the periodic table?
(A)
High melting points and low
(B)
Low melting points and PQor
densities n
electrical conductivities
(c)
Low densities and poor electrical
(D)
High melting points and high
conductivities
electrical conductivities
GO ON TO THF.NtrXT PArltr
-9 -
37.
Which of the following chlorides of
Group IV elements is the BEST electrical
40.
(a)
conductor?
(A)
PbCt4
(B)
SiCl4
(C)
GeClo
Cu(ll) sulfate gives
a deep blue solution with excess
NHr(ae)
(b)
solution with excess
concentrated HCl.
a yellow-green
Which of the following deductions can be
made from these observations?
(D)
38.
39.
CCr4
I.
The comPlex ion [CuQ'lHr)o]2* is
formed in (a).
temperature
and pressure, is MOST likely a
II.
[Cu$lHr)oJ2* has a higher stability
constant than [Cu(HrO)u]t*'
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
'
III.
[CuCloJ'?- has a lower stability
constant than ICu(HrO)u]'*.
I and II onlY
I and III onlY
ions
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Based on its position in Group VII of the
periodic tabte, astatine, at room
solid
liquid
brown gas
colourless gas
When agNOr(ad is added to fluoride
followed by NH.(aq), the result is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
II and III onlY
I, II and III
Item 41 refers to the following information'
yellow silver fluoride
no precipitate
white silver fluoride
cream-colouredammoniumfluoride
i
4L.
Element
Melting Point
ec)
Density
(g cm-t)
(A)
(B)
1538
660
2.70
(c)
328
(D)
l 490
'n
1 i{
11.34
1.54
Which of the elements, A, B, C or D, is
MOST likely a transition element?
A
GO
na 1 l in 1n/,-i A llT:
7.86
9N
ro THE NEXr PACE
l0
42.
The equation for the reaction between
Which of the following elements gives a
44.
green flaf'ne when heated?
chlorine and cold dilute aqu€ous sodium
hydroxide is as follows:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Cl"(g) + 2NaOH(a9) * NaCl(aq) +
NaCIO(aq) + H.O(l)
Magnesium
Calcium
Sodium
Copper
This reaction can BEST be described as an
example of
Item 45 refers to the following information.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
43.
decomposition
displacement
disproportionation
dissociation
2+
\
Which ofthe following transition elements
has an unpaired electron in an s-orbital?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Chromium
Manganese
Nickel
Titanium
White precipitate
insoluble in excess
White precipitate
soluble in excess
45.
Which of the following reagents does NOT
aid in the identification of X2*?
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
Aqueous KI
Dilute HCI
Dilute HNo3
Dilute H,SO4
END. OF TEST
IF YOU FINISH BEFORE TIME IS CALLED, CHECK YOUR WORK ON THIS TEST.
\
o|t12olO/CAPE 2014
I'ji.
:
(- :r>:.
it,:;.
..
.':
t'i':t.. . ''
G.:* : .'
PRINT your nemc on thc llnc bclow rnd,
thi! boolht wllhyour rnrwcnchcct. Fraldrc to
do so mry rcult In dbqudllcrtlorl
TEST CODE
F'ORM TP 20151
OzLIzOfi
MAY/JUNE 20I5
CARTBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCII,
CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION@
CHEMISTRY. UNIT I
Paper 0l
I hour 30 minutesl
19 MAY 2015 (4.m.)
READ THE FOLLOWING, INSTRUCTIONS CAR.EFULLY;
t.
This testconsists of 45 items. You will have I houn and 30 minutes to answer them.
2.
ln addition to this test booklet, you should have an,answer sheet and a data booklet.
3.
Each item in this test has fbur suggested answers lettered (A), (B), (C)' (D). Read each item
you are about to answer and decide which choice is best.
4.
On your answer sheet, find the number which corresponds to your item and shade the space
having the same letter as the answer you have chosen, Look at the sample item below.
Sample ltem
Which of the tbllowing energy transitions is
the HIGHEST in an organic comPound?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Sample Answer
@. o@
n to ot
o to o*
n to fi+
E to 7r*
Tlre correct answer to this item is "6 to o*", so (B) has been shaded.
s
6.
t-
--t.!J-
rla
lf you want to change your answer, erase it completely betbre you fill in your new choice.
When you are told to begin, turn the page and work as quickly and as caref'ully as you can. If
you cannot answer an item, go on to the next one. You may return to that item later.
7.
You may do any rough work in this booklet.
8.
Figures are not necessarily drawn to scale.
9.
You rnay use a silent. non-programmable calculator to answer items.
DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
-
L'upyright O 20 | 3 Caribbean Exarninations Council
,\ll riqhts reservcd'
:, ;V:i
:1
I
v
2L
Which of the fbllowing statements is NOT
a part of Dalton's atomic theory?
(A)
(B)
When an atom of liEU is bombarded with
a neutron, how many fundamental particles
(protons - p, neutrons - n and electrons.- e)
dbes an atom of the PRODUCT contain?
f,.
Atoms are indivisible.
Atoms are characterized by their
atomic number.
(C)
The atoms of an element have
(D)
identical properties.
The atoms of an element differ from
those, of other elements.
2.
e
(A)
(B)
9l
t46
9l
92
147
92
(c)
93
t46
93
(D)
93
147
93
Item 6 refers to the data in the following
(c)
(D)
ionic bonds
covalent bonds
hydrogen bonds
Van der Waals forces
table.
Atomic Mass
(amu)
Which of the following pairs of elements
combine to produce naturally occurring
compounds with formulae tYPe XY?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
4.
n
The intermolecular forces pr€sent in ice are
(A)
(B)
3.
p
Sodium and sulfur
Sodium and nitrogen
Magnesium and chlorine
Magnesium and sulfur
1.4
=6 Pb
24.1
22.1
52.4
:0t Pb
6.
Based on the data in the table above, the
relative isotoPic mass of lead is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
706.24 amu
207.24 amu
207.30 amu
208.30 amu
Item 7 refers to the fbllowing equation tbr
tlre production of ammonia.
(A)
@
:or Pb
r07 Pb
Which of the following diagrams represents
a pi (r) bond?
(B)
Abundance
(%)
N,(e)+3H,(g) - 2NH.(g)
7.
tf l0 cmi of nitrogen reacts with 30 cmr of
hydrogen at STB rvhat volume of NH', is
produced?
(c)
8
(D)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
l0 cml
l5 cmr
20 cm3
40 cmi
(iO ON l'O fllF: NEX I'Pi\(iFl
.38:.
Item, l2 refers, to the tbllowing energy
profile diagram;
The first five ionization energies,,, of an.
element. X, are given in the fbllowing table;
Number,
I.E. (kI mol-r)
!
I
403
J
4
5
2633 3860 5080 6850
From thedataabove, itcan bededuced that
Xisa
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
Group I metal,
Transition metal
Group lV element
Croup V element
Productr.
Reecdon petb.-
9;
For complete reactioni 0,25 g of a monobasic
acid requires l0 cmr of 0.2 mol dm:3 sodium
12.
hydroxide; What is the relative molecular
mass,of the acid?
(A), P
(B) Q.
(c) (Q + P)
(D) (Q - P)
(A) tz.s
(B) 62.s
(c) r2s.0
(D) 2s0.0
13.
10.
Which of the following processes rcpresents
an oxidation?
ll.
(A)
MnO, -+ Mn2*
(B)
MnOr- -+ MnO*2-
(C)
MnO.,- -+ MnO,
(D)
MnO, -+ MnO,-
What is the activation energy of the.
REVERSE reaction?
A gas, in a syringe occupies a volume
of 50 cmr and has a pressure of 0.49
atmosphercs. What is the pressure of the
gas if the plungerofthe syringe is pushed in,
reducing the volume of the gas to 20 cmr?
(l atmosphere= l0l 325Pa)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
20 kPa
125 kPa
20 000 kPa
125 000 kPa
Which of the fbllowing groups of solids
contains substances that ALL have giant
structures?
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
lce, iodine. iron
Graphite. iron, sodium fluoride
Carbon dioxide. magnesium oxide.
silicon( lV) oxide
lodine, silicon(lV) oxide, sodium
fluoride
GO ON TO l'l-lE,\EX'f PACE
-4l{.
18.
The simplest formula for a compound that
contains 50% S and 50% O bY rnass is
(A)
(B)
(A) so
(B)
(c)
release hydrogen gas into solution
act as an inert metal connection to
the H,/H* system
SO,
(C)
allow Platinumf ions to go lnto
S,O
(D)
reduce the surface areas rvhich
allows an' equilibrium to be
established in the'Hy'H* system '
(D) sro.
15.
In a standard hydrogen halt:'cell, a platinum
electrode is used to
A sffdent was asked to carry out an
experiment to investigate the prop€rtles
19.
of ionic and covalent compounds' Which'
of the following experiments: should the
solution
Ammonia is removed. from the system
represented bY the equation;
+
student use?
N,(e)'+ lu,(e)
l.
ll.
Itl.
EnthalPY of combustion
Which of the following statements about the
system is FALSE?,
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
I and Il onlY
I and lll onlY
It and lll onlY
l, ll and lll
Determination of melting point
ElectricalconductivitY
2NH3(g).
(A) K. remains constant:
igl 'fhere is a change in all
concentrations.
equilibrium position remains
The
(C)
(D)
tlre same,
Tlre rates of both tbrward and
reverse reaction decrease:
t6.
What is the effect on a chemical reaction of
introducing a catalYst in it?
(A)
(B)
ici
iOl
17.
20.
The activation energy is lowered'
The rate of the reaction is doubled'
The rate of the reaction is decreased'
The catalYst is consumed in the
reaction.
The rate law for a given reaction is
Rate = ktAls [B] . what are the units for
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
The reaction 2AB(g) * A{g) + B.(g) has
tlre rate law, Rate = k tABl. lf the half-life is
253 s, then the value of the velocity constant
(k) at the temperature of the reaction is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
365,08 s
365.08 s-'
2.74 x lOa s
2.74 x l0-3 s-l
k?
mol-2dm-z s-r
mol dm-3 s-'
mol-r dmr s-'
mol-2 dm6 s-r
(iO ON fO'[l'lE NEX f Pi\Cti
52t.
Which of the acids in the table below is the
WEAKEST?
22.
The results for four experiments which
investigated the reaction between propanone
and iodine (catalysed by acid) are given in
Acid
K" (mol dmd)
(A)
(B)
4.9 x l0-ro
(c)
6.3 x l(F
I
I
0.5
I
(D)
1.3 x l0-3
1
0.5
0.5
I
s.3
J
0
0.25
I
5.4
4
0
0.5
0.5
r0.6
1.7 x l0-5
the table below.
Expt lH.l lPropanonel
The value of Ko fbr the equilibrium reaction
llodinel
H. (g) + l: (g) i= 2Hl (g) at 444 oC and
Wh ich of the following graphs represents the.
I atm pressure is 50.
order of reaction with respect to propanone?
What is the value of Ko if the pressure
is changed to 2 atm and the temperature
(A)
remains the same?
(A) 2s
(B) so
(c) loo
(D)
IPropenoncl
200
(B)
23.
Rate
l0.8
Equilibrium is established in the reaction
X (aq) + Y (aq) r=+ Z(aq). tf the equilibrium
concentrations are [X] = 0.2 rnol dmr.
[Y] = 0.: mol dm-r and [Z]= 0.6 mol dm{,
which of the following values is correct fbr
the equilibrium constant K.?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
IPropanonel
0.1 mol dml
0.1 rnol-rdm-l
10.0 moldm-t
10.0 mol-'dml
(c)
lPropanonel
(D)
lPropanonel
CO ON TI) I-IIE NEX f PA( iE
.625.
The solubility product, K,o, ot 298 K for
three Group ll metal sult'ates is given in the
tbllowing table.
28.
A weak acid, HX. dissociates as tbllows:
HX(aq)+X-(aq)+H'(aq)
'Ihe
Sulfate
K
(moll tm{)
I
CaSO,
2.4 x l0-5
lt
SrSO.,
3.2 x l0-7
ill
BaSO.
1.6 x l0-'o
above is 1.0 x | 0-12 mol dm-3'
What will be the aPProximate PH of
1.0 x l0-2 mol dmj HX?
(A)
(B)
Which metal sulfate would precipitate out
dm'l
of solution if equal volumes of l0n mol
solution containing the sulfate ion and the
Group II metalare mixed?
(A) Ill onlY
(B) I and ll onlY
(C) ll and III onlY
(D) I,Il and lll
26.
27.
29.
8
Marine animals such as oysters and other
shellfish rely on the slow precipitation of
calcium carbonate to form their shells'
Which of the following properties help this
Greater ionic Product of Ca:' and
ll.
Greater solubilitY Product of
lll.
Smaller solubility product of
CaCOr(s)
CaCOr(s)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
lJarium carbonate is more soluble in water
than in aqueous sodium carbonate because
(D)
(D)
COr2- ions
mola dm-r2
barium carbonate is not
a common ion efTect is present in
the BaCOrNa,CO, mixture
(c)
6
7
t.
moldm-3
moF dm-u
moP dm-e
(A) all barium salts are soluble
igl barium ions cannot disPlace
sodium ions
(C) sodium carbonate is ionic but
5
process?
Silver chromate(Vl), AgCrOo' is sparingly
soluble in water. The uniis for the solubility
product (K,) for silver chromate(Vl) are
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
dissoc iation contant, K", for the reaction
30.
I and Il onlY
| and lll onlY
II and lll onlY
l, ll and lll
(Sn)
The standard electrode potential of tin
(s), E"=-0'14 V'
is Sn:'(aq) +2eln which of the following equations is the
rnetal UNABLE to reduce Sn3*?
+Sn
(A)
igi
iCi
(D)
Mgt'(aq) *2e- -+ Mg(s), E"=-2'38 V
Fe:.(aq; +2e- + Fe(s), E"=-0'44 V
Zn2.(aq) 17e- + Zn(s), E"=-0'76V
Pbr'(aq) +2e- -+ Pb(s), E"=-0'13 V
(]o oN f() I't'lE Nlix',l'P,{GE
. ai?::-
' -
.
t!::i!:
-7 -
'e;J..!:"
-5:,i.r.:
. j-'t '
31.
Which, of the tbllowing ions ltas, the
GREATEST polarizing power?
(A)
Bd'
(B)
Car*
(c)
(D)
32.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Which of: the tbllowing t'actors. BEST
explain why barium carbonate, BaCO' is
rnore stable than magnesium carbonatq.
MgCO.,,lvhen heated?
l.
Mgt' and CO.,:- ore: v€F/ different,
in size.
Li*
ll.
Ba:' and COrs- are very different in
Sre"'
lll:
Ba2+ and COr2- are similar in size:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
| and II only
I and lll only
It and lll only
l, Il and IIt-
Which'of the following properties increase
on descending the Group ll elements?
I.
ll.
Ill:
33.
34.
Atomic radii
lonization energy'
lonic radii
,
35.
Based, on its' position in Group' VII of the
periodio table, astatine; at room temperaturer
and pressure, is MOST likely a
I and ll only
I and III only
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
II and III only
I, II and lll
Silicon carbide has a structure similar to
tlrat of diamond; What are,the advantages,
derived from using silicon carbidE ceramics
size:
36,
solid
liquid
brown gas
colourless gas
Which of thE following properties does
when compared with steel?
NOT describe transition elements?
I.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
ll.
lll.
Silicon carbide is less likely to
deform under compression.
Silicon carbide has a higher melting
point.
Silicon carbide is more resistant to
oxidation.
(A)
(B)
I and ll only
I and lll only
(c)
ll and lll only
I, ll and III
(D)
Forming complex ions
Showing variable oxidation states
Often ret'erred to as non-magnetic
Present in the d-block of the periodic
table
(.i(-) ()Nl 'f() l'lllr. FIEX'f ll\(lE
837.
Which of the tbllowing elements in the third
period has the SAME oxidation number in
ALL of its knorvn compounds?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
{0.
into CaO(s) and SO.,(g). CaCO., decomposes
rt a much lolver temperature than CaSO..
Aluminium
Which of the following factors BEST
explains the greater thermal stability of
Chlorine
CaSO.?
Sultur
(A)
Phosphorus
(B)
(C)
Item 3E refers to the graph below showing
the first ionization energy (lE) of some
(D)
elements.
f
1000
eoo
800
.tl.
E
;5 700
600
CaCO., has a higher lattice energy
than CaSO".
CO, is a smaller molecule than SOr.
The COr'- ion is tnore easilY
polarized than the SOr:- ion.
The CO.,r- ion has a higher charge
density than the SO.2- ion.
When concentrated H.SO{ is added to solid
potassium iodide, the observations are white
steamy fumes and
E s00
400
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
300
200
100
0
On heating CaSO. strongly, it decomposes
Ca Sc fi
V CrMnFeCoNl CuZn
a white solid
a brown liquid
a rotten egg smell
nothing else
Elements
J8.
'Ihe sharp increase from copper (Cu) to zinc
Item 42 refers to the information in the
following table.
(Zn) is caused by filled
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
39.
4s-orbitals only
4d-orbitals only
4s-orbitals and 4d-orbitals
4s-orbitals and half-filled 4d-orbitals
Element
The ionic equation tbr the formation of
chromium hydroxide from chromium( I I l)
sulfate and dilute NH., (aq) is
(A)
CP- (aq) + OH- (aq)
(B)
Ct'-(s) + 3OH-(l) + Cr(OH)., (s)
(C)
Cd'(aq) + OH-(aq) + C(OH)r= (aq)
(D)
Cd.(aq) + 3OH-(aq) + Cr(OH), (s)
+ Cr.,OH (s)
12.
Melting
Point ("C)
Density
(g cmt)
I
| 538
7.86
II
660
2.70
ill
328
I t.34
Which of the elements in the table can be
c lassifi ed as transition?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
| only
ll only
| and ll only
II and lll only
CJO
()N I'0 I'I.IE NEX T PACE
s-,*:i;
"?i"
i:-::
9Elements can be classified by their response to externally applied magnetic fields as diamagnetic,
paramagnetic and non'magnetic.
Which of the following elements is considered to have a high degree of para-magnetism?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
14.
Sc
Zn
Which of the following compounds would produce the LOWEST pH rvhen 0.5 mol of it is bubbled
into I litreof water?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
.15.
Ca
Co
SO,
SO,
CaO
Na,O
What deduction can be made from the following reactions of iodine and chlorine with sodium
thiosulfate?
l.(aq) + 2S,Or!(ag)
---->
aCl,(aq) + S,Or21aq) + 5H,O(l)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
2l(aq) + SrOul(aq)
+
8Cl-(aq) + 2SOrr-(aQ) + l0H.(aq)
Chlorine is a stronger oxidizing agent than iodine.
lodine is a stronger oxidizing agent than chlorine.
Both chlorine and iodine are NOT oxdizing agents.
Both chlorine and iodine show the same oxidizing power.
END OF TEST
IF YOU FINISH BEFORE TIME IS CALLED, CHECK YOUR WORK ON THIS TEST.
i)2 il 201O/cAtrE 20 t 5
TESTCODE O2\I2OIA
a
FORM TP 201616s
MAY/IIJNE 2016
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
CARIBBEA}I ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATIONE
CIIEIVIISTRY
UIIIT 1-Paper 01
I hour i0 minutes
17 MAY2016 (a.m-)
READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREf,'ITLLY
l. This test consists of 45 items. You will have I hour and 30 minutes to answer them.
2. In addition to this test booklet you should have an answer sheet and a data booklet.
3
Each item in this test has four suggested answers lettered (A), (B), (C), (D)- Read each item
you are about to answer and decide which choice is best.
4.
On your answer sheet, find the number which corresponds to your item and shade the space
having the same letter as the answer you have chosen. Look at the sample item below.
Sample Item
Which of the following energy transitions is
the HIGHEST in an organic compound?
(A)
(B)
ntoo*
(c)
n to ,r*
(D)
ltto fi*
SamoleAlswer
@oo@
otoo*
The correct answ€r to this item is'o to o*", so (B) has been shaded.
5.
6.
G
g
E
E
-r
I
7.
8.
9.
If you want to change your answer, erase it completely before you flll in your new choice.
When you are told to begrq turn the page and work as $rckly and as carefully as you can. If
you cannot answer an item, go on to the next one. You may return to that item later.
You may do anyrough work in this booklet.
Figures are not necessarily drawn to scale.
You may use a silent, non-programmable calculator to answer items.
DO NOT TIIRN TIIIS PAGE TJNTIL YOU ARE, TOLD TO DO SO.
I
Copyright @ 20L4 Caribbean Examinations Council
All righB reserved.
I
o2fi20to/cAPB20t6
-2l.
Which of the following types of radiation is
MOSTlikely tobe measrneduging a Geiger
Item 4 refers to the following sketch which
shows the variation ef fts boi.ling points of
the hydrides of GroupV.
counter?
a
(A)
(B)
(c)
Beta
Infrared
Microwave
(D)
Ultraviolet
U
o
o
e
m
o
n
Item 2 refers to the following graph which
shows the log of successive ionization
energies for ten electrons of ao elemen! P.
oo 6
l.
o
NE3 PHI AsH3 SbE3
Hydrides
4.
5
r!)
Ammonia has the highest boiling point
because
o
4
6
N
!
I
F 3
c
t
oo
I
(A)
I
o 2
(B)
I
Fl
I
(C)
I
I
(D)
12345678910
Number of elechons lost
2.
the N-H bond is the shortest and
shongest
there are more van der Waals forces
betweenNfl, molecules
there is hydrogen bonding between
NII, molecules
the eletronegativity of nitrogen is
much higher than that ofthe other
eleme,lrts inthe
Element P is MOST likely
(A)
(B)
neon
sodium
(c)
chlorine
(D)
maguesium
5.
group
,
'Yellow metal'is a tlpe of alloy (brass)
used to make omamenls. It contains 607o
copper nd 40o/o zinc by mass. How many
moles of.inc atorns arethere tmZ6O grams
qfrhis alloy?
3.
Which of the following elecffonic
configurations is forthe Cu@ ion?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
[Ar] 3dto
[Ar] 3dro 4st
[Ar] 3de4sr
[Ar] 3d€4f
o2tlz0totcAPB20L6
(A)
(B)
1.6
(c)
2.4
3,2
@)
4.O
GO ON TO TFTE NEXT PAGE
-3Item-1[ refers to the following diagram of
9,
a water molecule showing the angle X in
giant molecular strucfure?
degrees:
I
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
10.
6-
The value ofx is
(A)
(B)
7,
Which of the following compounds has a
r04.s
(c)
109.5
120.0
(D)
r80.0
Sodium oxide
Silicon(IV) oxide
Magnesium chloride
Phosphorous pentachloride
When 86 g ofthe ionic salt, CaSOn:IIrO, is
heated so that all ofits water ofclystallization
is driven off and 68.0 g of CaSOo remain,
the value ofx is
(A)
(B)
1
2
(c)
3
(D)
4
Which of the following statements is true
about 5 dm3 of hydrogen and 5 dms of
oxygen at 0 "C and I0I lPa?
(A)
They react to produce 5 dm3 of
(B)
They react completely with each
(c)
They possess the same amount of
kinetic enerry.
They contain the same number of
water.
other.
(D)
molecules.
Item 8 refers to the following reaction.
2PbNqL '* ) 2Pbo + 4NQ + q
The molar volume of gas at r.t.p. is 24 dm3
8.
The maximum mass of lead(tr) oxide which
can be obtained from 13.23 g oflead(tt)
nitate is
(A)
(B)
(c)
2.23 g
4.46 g
8.91 g
(D)
13.32 g
o2tlzoto/cAPE20t6
GO ON TO TIIENEXTPAGE
-4sodir
Items 1L-12 refer to the following half-equations for the reaction between iodine andsodium
thiozuIfate.
Z Spr'zlaO
I
+
Spul(aq) + 2e-
L(aq)+ 2e--+
11.
2l1aq)
The overall balanced chemical equation forthe reaction is
(A)
2srq'1oq) + 2l-(aq) ---------> S4o;1aq) + t(aq)
(B)
lr(aq) + soor2-(ag)
(C)
Sp6'?-Gq) + 2l1aq) ------+ 2srqlaq) + l(ao)
(D)
zs,Q}(ad + !(aq)
2spr'1"q1 + 2l1aq)
-+
s.o6laqj + 2l-(aq)
->
12.
13
The oxidizing agent is
(A)
Ilaq)
(B)
L("q)
(C)
Sp,'1{aq)
(D)
SnO6'1aq)
Sodium can form ionic bonds with each ofthe halides- Which sodium halide is expected to have
I{IGHEST lattice enerry?
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
14.
NaI
NaF
NaBr
NaCl
The standard enthalpy changes for two reactions are as follows:
2Fe(s) *
l2 Orfgl +>
cG)= 1 O,(g)
2
FerQ(s), AII*: -822 kJ mol-t
CO(g), AfI*: -110 kJ mol-t
->
What is the standard enthalpy change, in kJ, for the reaction
2Fe(s) + 3CO(g)?
FerO, (s) + 3C(s)
(A) -e32
(B) -:ltz
(c) 4e2
(D) +492
->
GO ON TO TTIE NEXT PAG
02112010/C,APE2016
-515.
Which'of the following gases is CLOSEST
to behaving as an ideal oas under the stated
conditions?
a
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
16.
%G) "t400 "C and I ahpressure'"
C{(g) at 30 € and I atn pressure
CQtgl at 30 "C and 250 atm Pressure
U{(g) at400
17.
John plans to measure the rate of the
reaction between calcium carbonate and
dilute hydrochloric acidWhich of the following pieces of apparafis
is MOST zuitable for this investigation?
(A)
qC and250 ahpressure
Which of the following pbrases describes the
activation energy of a reaction?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Affectedbytemperature
Unaffected by a catalyst
Energ5r barrier to the reaction
Reduces speed of reactantmolecules
(B)
(c)
o
(D)
o
GO ONTO TIIENEXTPAGE
02tt2otolcAPE2016
ll
-6Item 18 refers to the following reaction which occurs in the presenceof,fie*:*g;
dilute acid.
CH3COCII3 (aq) +
a
L (aq)
CIIrI COCII3 (aq) + H* (aq) + I- (aq)
-->
18.
Rare = ktCILCOcHT (aOI Er-(aq)I.
Which ofthe following equations BEST illustrates the SLOIV step?
o
(A)
il
CH3
-C -CH3
OH
I
(B) crL _CII -CII, + L
I
-+CI*-
o
C
c cII3 + IoI
il
cH3
I
@
o
(c)
c- ctl3
+ H* --+CII3-
-crL
+ r-
-->c4_ c- cI1
I
o
o
OH
II
(D) cq- C-cI{
+ !+H+
I
c
->CH3-
19-
NOT ZO.
Which of the following statements does
refer to a syst€m in dSmamic equilibrium?
(A)
(B)
Thereaction is reversible.
(C)
The concentations of all reacrants
andploducts are equal
The rate of the forward reaction is
equal to the rate of the backward
(D)
The amormts of all the species in the
syst€mremain constanl
reaction.
C[I,
I
I
The value of Kr-a&eerlfffitdmn,
4G)+lr(e):znqst
is 860 at 25 "C-
What is the value of K- a 25 t for the
follorving equilibrium?
ir,,r, *ir=r*l =- Hr(*e)
(A)
(B)
o2ttz0to/cAPE2016
(c)
29
215
430
(D)
t720
GO ON TO TIIENEXTPAGE
-721.
a
25.
In the llaber pr)cess,
AH: -90 kJ mol-r,'
:
the MAXIMUM yield of ammonia is
obtained at
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
high temperange and low pressure
high temperatre andhigh pressure
Hc(aq) andNaC(aq)
(B)
HC(aq) andNHoC(aq)
(C)
N'4(aq)andNHnC(aq)
(D)
NH.(aq)andNaNOr(aA)
2P(aq) + Q(aq) i-
mol dm-3
dm3 mol-r
(c)
mol2 dm{
dm5 moL2
€ is
to form a saturated solution is
2R(aq)
(A)
(B)
The units for the equilibrium constant, Kc
are
(A)
(B)
The solubility product of BaSQ at 25
I x l(lto mol2 drrf. The numberofmoles of
BaSOr that will dissolve in I dmr of water
Comlrcunds R Q and R form an equilibrium as shown below
(D)
(A)
lowtemperatureanthigfupressure
low te,mperature and low pressure
26.
22.
Which of the following pairs of substances
would make a good buffer?
27,
I x l0rlo
2 x lfrro
(c)
lxl&5
CD)
2x lO-s
Which of the following expressions
represents the solubility product of iron(Itr)
hydroxide?
23-
Which of the following pairs of acid and
conjugate base is correctly aligned?
u.
Acid
Conjugate Base
(A)
NIL
NH4*
(B)
qo
H3o-
(c)
ffio,
(D)
IIPOlL
sq*
4po;
A buffer is made by dissolving 28-8 g of
sodium benzoate, CTHTCOONa" in I dm3
of 0.4 mol dm{ benzoic acrd, C6H5COOH-
K*o***ro :6.4x l0-5 mol dm-3.
ThepH of the buffer is
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
2.3
2_9
3.2
3.9
28.
(A)
[Fe]l [3oH-]
(B)
[Fe*] [oH-']'
(c)
lFehl[3oH{]
(D)
lFehlloH+l
F{oH),
Fe(OH),
What is the potential for a cell with the
following reaction?
Zu(s) + Brr(aO
-->
7-t2" (aq) + 2Br-(aq)
(A) [+1.07 + (-0.7O] v
(B) l-1.o7 + (- 0.7OI v
(c) l-1.07 - (- 0.76)l v
(D) [+1.07 -(-0.76I v
GO ON TO TI{E NEXT PAGE
02tr2010/cAPE20L6
-8Item29 referstothefollowingcelldiagram- 31.
Zn(s) | 7fr (aq) ll Cu'* (aq) lCu(s)
a
Which ofthese eleaeas *iss as a diatomic
't
29.
There are eight eiemeus ofrhe third period,
sodium to argon-
Which of the following conditions wili
molecule?
cause an increase in the cell potential?
(A)
(B)
Increasing concentration of
Z**(aq) ions only
Decreasing concentration of
(A)
(B)
Argon
(c)
Silicon
(D)
Sulftr
Chlorine
Cu*(aq) ions only
(c)
(D)
Adding NaOH to Cu2* solution and
increasing the concentration of
Zn2* ions
32.
An element iB Paidd -l combines with
oxygen to form a o=ide s-hich reacB with
water to produoe a socs aikali.
Decreasing concentration of
Zn2* (aq) ions and increasing
concentration of Cu2* (aq) ions
That element is
(.{)
AI
Item 30 refers to the following diagram of
(B)
cl
an electrochemical cell.
(c)
Mg
(D)
Na
Wire
33
Which ofthe follosrin-e elmen-s in the third
period has the same oridaim nr:mber inALL
of its knorvn comlrouads:.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
bridge
1.0 mol
30.
MgSOa(aq) t.0 mot
ZnSO4(aq)
Which of the following situations does
NOT occur in the cell shown?
(A)
No current flows when the salt
(B)
bridge is removed.
Magnesium ions migrate into the
salt bridge.
(C)
(D)
Electrons flow through the wire
from the zinc to the magnesium
34.
Sulfirr
Phosphonrs
lower temperature rhan bar-ium carbonate
because
(A)
(B)
(c)
electrode is
Mg(s)
Chlorine
Calcium carbouate decomposes at a
electrode.
The reaction at the maguesium
Aluminium
Md.(aq) *2e-.
calcir.m oxide is less stable than
bariuu oride
ftg galcirrm ion is laryer than the
barirrrn ion
the *andard enthalpy of
formatioo sf galsirrm oxide
is less aegative than that of
bar-irrm oxide
(D)
the lattice energl'of calcium oxide
is larger *ran that of barium
oxide
o2tt2,tolcAPE2016
GO ON TO THE.NEXT PAGE
-938.
35.
a
Wbic-h of the following statements about
oxides of the elements in Period 3, sodium
to chloring is NOT true?
Which of the following statements about
bromine are CORRECT?
L
il.
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
m.
Across the perio4 the oxides change
frombasic to amphoteric to acidic
character.
The oxides react with water to form
alkaline solutions.
The oxidation num-ber ofthe element
in the oxide increases across the
periodThe shucture of the oxides changes
from giant ionic to simple
covalent molecules.
It is red-brown in colour.
It is denser than chlorine.
It is a gas at room temperature and
pressure.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
39.
Iandtronly
I and Itr only
trandltronly
I, tr and III
.Which of the following complexes would
show the GREAf,EST parauraguetic
property?
36-
Which of the following properties belong to
Group 2 elements of the periodic table?
(A)
High meltrng points and low
densities
(B)
Low melting points and poor
(c)
Low densities and poor electrical
electrical conductivities
conductivities
(D)
High melting points and high
(A)
[Cu(CN)n]]
(B)
[Fe(CN[+
(c) tF{cr.r)J3(D) tN(cr9J40. Copper (II) sulfate gives
elecnical conductivities
37,
The insolubilities of the Group 2 sulfates
make them very useful in diagnostic
medicine because they appear opaque to
X-rays.
Which zuIfate is MOST commonly used for
X-rays?
(A)
(a)
a deep blue solution with excess
Nq(aq)
o)
a yellow-green solution with excess
concentrated HCl.
Which of the following deductions can be
made from these observations?
I.
formed in (a).
BaSO.
(B) casQ
(c) MesQ
(D) SrsQ
The complex ion [Cu(NF!)o]* is
tr.
[Cu(NIIJJ'?. has a higher stability
constant than [Cu(HrO)J*.
m.
[CuC[] has a lower stability
constant than [Cu(H,OU].
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Iandtronly
I and III only
II and Itr only
I,II and III
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
o2r120t0lcAPE20L6
- 1041.
Which ofthe following statements describe,s
43.
the tend in physical properties of the
halogens as the group is descended?
a
(A)
(B)
Volatility and atomic radii increaseElectronegativity and volatility
(C)
Electronegativitydecreasesand
(D)
42
increase.
colour deepens.
There is a corresponding decrease
in density as states change from
gas to liquid to solid-
3
Which of the following solutions is BEST
suited to determine the presence of halides
in river water?
(A)
HCI
(B) rNq
(C)
NaOH
(D) AsNq
In which of the following options are the
halide ions placed inorderof INCREASING
reducing 1rcwer?
(A)
Br-, Cl -, [-
(B) CI-,I-,Br(C) Cl-,Br-,I(D)
I -, Br -, Cl-
GO ON TO THI,NEXI PAGE
o211.20t0/cAPE 2016
- l1 Item44 refers to the following information.
Aqueous B"Cl, followed by excess dilute HCI is added to EACH of four unknown solutions, I,
tr,III and IV. The following observations are noted-
a
L
Awhiteprecipitate is formedwhichdissolves intheacidto liberafeagasvAichdecolourizes
l4"O;iH*(aq).
tr- No preciPitate is formed.
m. Adinse white precipitate is formedwhich is insoluble in excess acidIV. 'A white precipitate is formed that dissolves in the acid to liberate a eas which forms a
white precipitate with Ca(OlDr(aq)44.
Which of the following options correctly identifies the ions which may be present in EACH
the solutions,I, II, III and tV?
I
II
m
rv
(A)
SOr'-
c1-
HCO3-
cOr-
(B)
SOo-
Noi
Sort
Cor'
(c) Sor'
cr
s2-
Cor'-
(D)
Not
SO.'
Cor'-
SOr'-
Item 45 refers to the following information.
xa
White precipitate
soluble in excess
White precipitate
insoluble in excess
45- Which of the following reagents does NOT aid in the identiflcation of)f?
(A) Aqueous KI
(B) DilutcHCl
(C) DiluteHNO3
(D) Dilute rlsq
END Of,' TEST
IFYOU FINISH BEFORE TIME IS CALLED, CHT'.CKYOIIR WORI( ON TmS TEST:
ozttzor0lcAPE 201.6
of
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
B
D
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
D
A
B
B
D
D
A
B
CAPE Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 2021
D
A
B
CAPE Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 2022
D
A
B