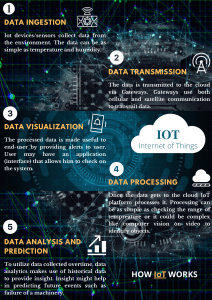
LoRaWAN: Revolutionizing the Internet of Things with LowPower, Long-Range Connectivity The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the way we interact with technology, enabling seamless communication between devices and systems. At the heart of this transformation lies LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network), a groundbreaking Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) protocol that has redefined the possibilities of IoT applications. LoRaWAN is designed to facilitate long-range, low-power communication between smart devices, gateways, and end-users, making it an ideal solution for a wide range of industries. This essay explores the fundamentals of LoRaWAN, its operational mechanisms, key components, use cases, and its advantages over alternative technologies. What is LoRaWAN? LoRaWAN is a network protocol and system architecture that operates on the principles of low power consumption and long-range communication. Its physical layer is based on LoRa (Long Range) modulation, a wireless technology that enables data transmission over distances of up to 15 kilometers, significantly surpassing the range of traditional Wi-Fi networks. Unlike cellular IoT technologies, which can be costly and challenging to deploy in remote areas, LoRaWAN offers an economical and efficient alternative. It adheres to IoT requirements such as bi-directional communication, end-to-end security, mobility, and localization services, making it a versatile choice for IoT deployments. How Does LoRaWAN Work? LoRaWAN operates by transmitting data packets over a shared radio frequency, enabling communication between devices and gateways. These gateways act as intermediaries, collecting data from LoRaWAN devices and forwarding it to a central network server via the internet. The server processes the data and makes it accessible to end-users. The LoRa modulation technique allows data to be transmitted over a wide range of frequencies and distances, ensuring low-power, long-range communication with minimal latency. A critical component of the LoRaWAN ecosystem is the LoRaWAN Gateway, which bridges the physical and digital worlds. Gateways receive data from LoRaWAN devices and relay it to the network server, facilitating seamless communication between IoT devices and applications. Companies like TEKTELIC provide robust gateways, such as the KONA Micro IoT Gateway for indoor use and the KONA Macro IoT Gateway for outdoor deployments, ensuring reliable connectivity even in challenging environments. LoRaWAN Sensors and Their Applications LoRaWAN sensors are integral to IoT applications, enabling data collection and transmission in various fields. These sensors are designed to be energy-efficient and support adaptive data rate control, allowing them to operate effectively over both long and short distances. Common applications include asset tracking, environmental monitoring, and industrial automation. For instance, TEKTELIC’s COMFORT sensor monitors indoor conditions like temperature, humidity, and light, while their KIWI soil moisture sensor aids in smart agriculture by optimizing irrigation schedules. LoRaWAN Classes: Tailoring Communication to Needs LoRaWAN devices are categorized into three classes, each with distinct power consumption and communication capabilities: Class A: The most energy-efficient, suitable for battery-powered devices that transmit data periodically. Class B: Enhances Class A by enabling scheduled downlink communication, reducing latency. Class C: Offers continuous communication but consumes more power, making it ideal for applications requiring real-time data. These classes provide flexibility, allowing users to choose the most appropriate configuration for their specific needs. LoRaWAN Use Cases LoRaWAN’s versatility has led to its adoption across numerous industries. Key use cases include: Smart Buildings: Monitoring environmental conditions to optimize energy usage and ensure occupant comfort. Agriculture: Tracking soil moisture, temperature, and humidity to improve crop yields and resource management. Healthcare: Enabling remote patient monitoring and real-time health data collection. Industrial Applications: Monitoring pipelines, drilling rigs, and other assets to enhance safety and efficiency. Smart Cities: Managing Street lighting, parking, waste collection, and environmental monitoring. LoRaWAN vs. Alternatives While LoRaWAN is a leading LPWAN technology, alternatives like Sigfox, Weightless, and NB-IoT offer different trade-offs in terms of cost, coverage, and data rates. However, LoRaWAN stands out due to its open standard, extensive ecosystem, and ability to support a wide range of applications. Unlike cellular networks, which require expensive data plans, LoRaWAN operates on unlicensed frequencies, reducing deployment costs. Benefits of LoRaWAN LoRaWAN offers several advantages, including: Smart Energy Consumption: Devices only transmit data when necessary, extending battery life. Network Capacity: The star topology minimizes power consumption and maximizes efficiency. Quality and Security: AES-128 encryption ensures data integrity and confidentiality. Scalability: LoRaWAN supports a vast number of devices, making it suitable for large-scale deployments. Limitations and Considerations Despite its benefits, LoRaWAN has limitations. Its data rates are relatively low, making it unsuitable for high-bandwidth applications like video streaming. Additionally, coverage may be limited in certain areas, requiring collaboration with network operators or the deployment of private networks. However, for applications requiring low-power, long-range communication, these limitations are often outweighed by the technology’s advantages. Conclusion LoRaWAN has emerged as a transformative force in the IoT landscape, offering a costeffective, energy-efficient, and scalable solution for connecting devices over long distances. Its ability to support diverse applications, from smart agriculture to healthcare, underscores its versatility and potential. While it may not be suitable for every use case, LoRaWAN’s strengths make it an ideal choice for organizations seeking to build robust IoT infrastructures. As the demand for IoT solutions continues to grow, LoRaWAN is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of connected technologies. For those exploring IoT connectivity options, LoRaWAN represents a compelling and forward-looking choice.