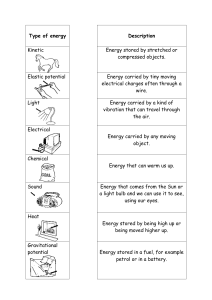
Grade 11 Advanced AFL Chapter 6: PE and Conservation of Energy Section 6.1 and 6.2 Al Jahili School, Al Ain Name ___________________________ Score: Grade________ Total marks: 10 Date____________ Level- 1 Adding Units The units are m= kg (kilograms) g = n/Kg (newtons per kilogram) h= m (meters) and Ep = Gravitational potential energy a) 5kg x 10N/kg x 23m b) 63kg x 10n/kg x 58m c) 93kg x 10n/kg x 2m d) 0.5kg x 9.8n/kg x 58m e) 0.47kg x 9.8n/kg x 0.54m f) 4.2kg x 9.8n/kg x 100m Answers: Level- 2 Actual Exam Questions a) What is the gravitational potential energy stored in a 60 kg boy sitting at the top of a 2 m high slide? (g = 10 N/kg)? b) A boy has a mass of 55 kg. He climbs 12 m up a tree. What is his gain in GPE? c) A cart is loaded with a brick and pulled at constant speed along an inclined plane to the height of a seat-top. If the mass of the loaded cart is 3.0 kg and the height of the seat top is 0.45 meters, then what is the potential energy of the loaded cart at the height of the seat-top? d) A crane lifts a 75kg mass a height of 8 m. Calculate the gravitational potential energy gained by the mass (g = 9.8 N/kg). e) A ball with a mass of 500g is lifted onto a shelf which is 1.5m above the ground. Calculate the gravitational potential energy gained by the ball (g = 9.8 N/kg). Level- 3 Rearranging the Equation a) A 2 kg mass has a potential energy of 580 J. What height is the mass above the ground? (g = 10 N/kg) b) An owl has a mass of 4 kg. It dives to catch a mouse losing 800 J of GPE. How high was the bird to begin with? c) An astronaut has a total mass of 110 kg. On the moon, he climbs into his spacecraft, 5 m up a ladder. His GPE increases by 880 J. What is the strength of gravity on the moon? Level- 4 Linking this formula to kinetic energy According to the law of conservation of energy, it cannot be created or destroyed, so if gravitational potential energy decreases kinetic energy increases. If we take out the affect of air resistance etc then total gravitational energy is equal to the kinetic energy. We can use this to work out the speed an object falls, due to knowing the gravitational potential energy and rearranging the kinetic energy equation. 1. A boy throws a 0.2kg rock up with a speed of 5m/s. If all the kinetic energy becomes gravitational potential energy, how high will the stone go? 2. A ball of mass 500 g is dropped from rest from a height of 7 m. What is its speed as it reaches the ground? (g = 10 N/kg) Level- 5 Plotting and interpreting Graph: Based on the Law of conservation of Energy as mentioned in the previous question, how do you think will the v vs h graph be for the cart moving in the roller coaster. Mass m(kg) 2 2 2 2 2 Table 1 Height h(m) 0 Velocity v(m/s) Use: Acceleration due to gravity, g= 10 mls^2 Interpret the graph : ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------How do you think this graph varies if there is friction acting on the cart (μ≠0)? ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Level- 6 Frame an exam style question to apply the equation to calculate the potential energy and analyse a daily life situation where the Law of conservation of Energy is applied.