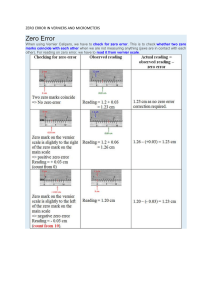
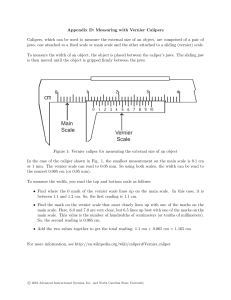
EXPERIMENT NO. 7 The Vernier and Micrometer Calipers I. OBJECTIVES ● To learn the proper use of the Vernier and Micrometer Calipers ● To make accurate measurements of short distances using the Vernier and Micrometer calipers. II. THEORY/DISCUSSION The accuracy of a measurement is always limited by the precision of the apparatus used and the skill of the Observer in using it. No reading on an apparatus used in measuring physical quantities is ever exact since a point is always reached at which the reading becomes uncertain. The last or final digit of the reading is often just an estimate and, therefore, doubtful. However, this digit is important because it might significantly affect the results of the computations. In linear measurement, the meter stick can be used. But because of the limited accuracy of the meter stick in measuring small objects, one should resort to the use of the vernier and micrometer calipers. III. MATERIALS Vernier caliper Magnifying lens Micrometer Caliper Coin Metal Cylinder Steel ball Triple-beam balance Figure 3. The Vernier Caliper IV. PROCEDURE The Vernier Caliper 1. Study the main scale and vernier scale of the vernier caliper. Determine the smallest main scale and vernier scale divisions, the total number of vernier divisions and the least count. Close the jaws of the caliper and observe the zero reading. 2. Measure the inside diameter and the depth of the metal cylinder in centimeters and in inches, adjusting the upper jaws and depth bar accordingly. Record the main scale and vernier scale readings and get the sum of these two readings to get the diameter. Compute for the volume of the cylinder in cm3 by substituting the measured values in these equations: 𝑉𝐶 = 𝜋𝑑2 ℎ 4 or 𝑉𝑐 = 𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ 3. Get the mass of the metal cylinder in grams using the triple-beam balance. Fill the cylinder with water. Wipe off the excess water at the mouth of the cylinder. Reweigh the cylinder and its contents on the balance. Compute for the mass of the water in the cylinder. 4. Using the density of water (= 1 g/cc), compute for the volume of water in cm3. Compute for the amount of error and percent error using the volume of water as the true value. 5. Find the relationship between the centimeter and the inch by dividing each measurement in centimeters by its equivalent in inches for both the measured inside diameter and depth. Compare the result of your computation with 2.54 cm, which is the commonly accepted conversion factor. Compute for the amount of error and percent error. The Micrometer Caliper Figure 4. The micrometer caliper 1. Examine the calibrations on the micrometer caliper. Observe and record the zero reading. 2. Open the caliper and clamp the steel ball with the instrument. 3. Get the readings on the horizontal and vertical scales. The sum of the readings obtained represents the diameter of the steel ball. 4. Make three (3) trials and get the average diameter. 5. Repeat the procedure for the diameter of the coin, then the diameter of the metal rod V. DATA AND CALCULATIONS Vernier Caliper Readings Total number of main scale divisions (s) Total number of Vernier divisions (f) Smallest vernier scale division Least count (slt) Zero reading Metric _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ cm cm cm cm cm English _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ in in in in in Inside diameter of the cylinder Depth of the cylinder Mass of the cylinder with water Mass of the cylinder Mass of the water Volume of the cylinder (E,V,) Volume of the water (T.V.) Amount of error Percent error _____________ cm _____________ in _____________ cm _____________ in _____________ g _____________ g _____________ g _____________ 𝑐𝑚3 _____________ 𝑐𝑚3 _____________ 𝑐𝑚3 _____________ % E. V. of the inside diameter 1 inch = __________ Amount of error = __________ % error = __________ E.V. of the depth 1 inch Amount of error % error (T.V., 1 inch = 2.54 cm) (T.V., 1 inch = 2.54 cm) = = = __________ __________ __________ Micrometer Caliper Readings Trial 1 2 3 Steel Ball ___________ mm ___________ mm ___________ mm Coin ___________ ___________ ___________ mm mm mm Metal Rod ___________ mm ___________ mm ___________ mm Average ___________ ___________ mm ___________ Computations mm mm VI. QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS 1. Give advantages/disadvantages of using the: a. vernier caliper __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ b, micrometer caliper __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The following are the obtained values for the depth of the cylinder measured during three trials: 8.35 cm, 8.36 cm, and 8.33 cm. What is the average depth of the cylinder? If the inner diameter measured 4.5 cm, what would the volume of the cylinder be? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. When measuring small distances, which gives the most accurate measurement: a meter stick, a vernier caliper or a micrometer caliper? Justify your answer. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ 4. The width of a glass plate measures 7.35 cm using a vernier caliper. Which scale the caliper gives a: a. 7.0 cm reading? ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ b. 0.35 cm reading? ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. The diameter of a coin is 3.54 mm as read from a micrometer caliper. Which part of caliper gives a reading of: a. 3.00 mm? ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ b. 0.50 mm? ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ c. 0.03 mm? __________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ VII. CONCLUSION _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________ VIII. DOCUMENTATION