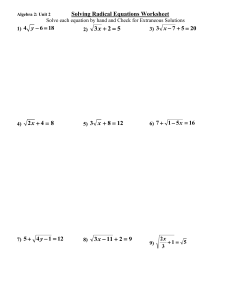
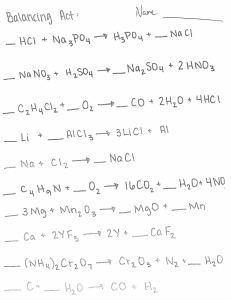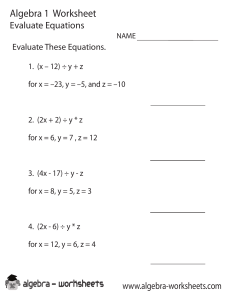Guía de Aptitud Cuantitativa para Exámenes Bancarios y de Seguros
advertisement

@ ce te xa m gr ou p A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 1 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations Chapter Inequality 14 m gr ou p As we know, if we use the short method, in these types of questions it takes very little time to solve in the examination. So let us understand the concept. Quadratic equation: It is a second order polynomial equation with a single variable. Example: ax 2 + bx + c = 0 There will be two values of x which satisfy the given equation. Sign Method: Now from the exam's point of view, we can conclude the signs of the roots from the signs of the coefficients. Case I: If b = +ve, c = +ve Example: ax 2 + bx + c = 0, x1 = –ve, x2 = –ve Case II: If b = –ve, c = –ve, then one root will be positive(+) (bigger number) and other root will be negative(–) (smaller number) Example: ax 2 – bx – c = 0, x1 = +ve, x2 = –ve Case III: If b = +ve, c = –ve then one root will be –ve (bigger number) and other root will be +ve (smaller number) Example: ax 2 + bx – c = 0, x1 = –ve, x2 = +ve Case IV: If b = –ve, c = +ve ax 2 – bx + c = 0 x1 = +ve, x2 = +ve @ ce te xa x’s co-efficient Constant x1 x2 (b) (c) + + – – + – – + – + + + – – + – When we see the equation then we can conclude the signs of the roots, so we can find the relation between x and y. Now we have the signs of the roots of equation and if we remember the table then we can conclude it within 5 seconds. Now come to the second part: Suppose we have the equation: x 2 – 5x + 6 = 0 From the table we can conclude that both the roots of the equation will be +ve. Now we have to break the constant (6) such that their sum will be 5. 6 = 3 × 2 also, (3 + 2 = 5) ∴ x1 = +3, x2 = +2 Now if there is a value attached to the x's co-efficient, then we have to divide the value to get the roots. Sol. 2 2x – 11x + 15 = 0 2 ∴ 2 3×5 6 6 + 5 = 11 5 x1 = + 2 = +3, x2 = + 2 = + 2.5 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 2 2 ∴ x1 = – ∴ x1 = –3, x2 = –2 2 y + 3y + 2 @ ce 2 × 1 and, 2 + 1 = 3 2 9 = –7, x2 = – = – 4.5 2 2 ou II. 4y + 19y + 21 = 0 21 4 2×2 7×3 also, 12 + 7 = 19 ∴ y1 = – 12 4 7 = –3, y2 = – = – 1.75 4 ∴x<y 6. I. 4x 2 – 29x + 45 = 0 II. 3y 2 – 19y + 28 = 0 2 Sol. (e): I. 4x – 29x + 45 = 0 45 4 2×2 9×5 also, 20 + 9 = 29 xa te 3 × 2 and, 3 + 2 = 5 14 p 63 2 2×1 9×7 also, 14 + 9 = 23 m 2. I. 5x + 3x – 14 = 0 II. 10y – 3y – 27 = 0 Sol. (e): Here x1 = –ve x2 = +ve y1 = +ve, y2 = –ve Now we can't establish the relation between x and y. Note: Above two types of questions can be solved without calculation. So if in the exam we have any of these cases then we can simply conclude the relation by the sign method. 3. I. x 2 + 5x+ 6 = 0 II. y 2 + 3y + 2 = 0 2 Sol. (d): x + 5x + 6 = 0 5. I. 2x 2 + 23x + 63 = 0 II. 4y 2 + 19y + 21 = 0 2 Sol. (b):I. 2x + 23x + 63 = 0 gr Direction (1 – 14): Two equations (I) and (II) are given in each question. On the basis of these equations you have to decide the relation between x and y and give answer. (a) if x > y (b) if x < y (c) if x ≥ y (d) if x ≤ y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between 'x' and 'y'. 1. I. x 2 – 3x + 6 = 0 II. 3y 2 + 13y + 12 = 0 Sol. (a): We even don't have to calculate the values. Here signs of roots of first quadratic equation (x1 , x2 ) = +ve and signs of roots of second quadratic equation (y1 , y2 ) = –ve ∴ x > y (Always) 20 9 ∴ x1 = + 4 = +5, x2 = + 4 = +2.25 2 II. 3y – 19y + 28 = 0 28 3 3×1 7×4 also, 12 + 7 = 19 ∴ y1 = + 12 3 7 = 4, y2 = + = 2.33 3 ∴ No relationship can be estabilished 7. I. 2x 2 – 13x + 21 = 0 II. 5y 2 – 22y + 21 = 0 2 Sol. (c): I. 2x – 13x + 21 = 0 ∴ y1 = – 2, y2 = –1 ∴ x≤y 2 4. I. 2x + 3x + 1 = 0 Sol. (b): 2x2 + 3x + 1 = 0 2 II. 12y + 7y + 1 = 0 6 2 II. 5y – 22y + 21 = 0 1 ∴ x1 = – 2 = –1, x2 = – 2 = – 0.5 2 Now, 12y + 7y + 1 = 0 12 = 4 × 3 and, 4 + 3 = 7 4 1 3 1 ∴ y1 = – 12 = – 3 = – 0.33, y2 = – 12 = – 4 = – 0.25 ∴y>x 3 7 x1 = + 2 = 3 , x2 = + 2 = 3.5 2 × 1 and, 2 + 1 = 3 2 21 2 2×1 7×3 also, 6 + 7 = 13 21 5 5×1 7×3 also, 15 + 7 = 22 ∴ y1 = + 15 5 7 = 3, y2 = + = 1.4 5 x≥y Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations I. 12x 2 + 11x – 56 = 0 II. 4y 2 – 15y + 14 = 0 11. I. Sol. (d):I. 12x2 + 11x – 56 = 0 1 II. y 3 = 1.63 ⇒ y > 1 21 ∴ x1 = – 12 = – 2.67, x2 = + 12 = 1.75 ∴y>x 2 4y – 15y + 14 = 0 3 14 7×2 also, 8 + 7 = 15 4 2×2 12. I. x = √2197 II. y 2 = 169 Sol. (c):I. x = 13 II. y 2 = 169 ⇒ y = ± 13 ∴x≥y ou 8 7 4 4 I. 7x – 3y = 13 Sol. (c): I. x = √2304 ∴ x = 48 (don't consider – 48 as value of x) II. 5x + 4y = 40 II. y 2 = 2304 ⇒ y = ± 48 Sol. (b):equation (I) × 4 + equation (II) × 3 ∴x≥y gr 28x − 12y = 52 15x + 12y = 120 14. I. 43x = 172 ⇒ x = 4 1 1 9 √x 6 Sol. (a): I. 35x + 70 = 0 ⇒ x = – 35 = –2 te @ ce Direction (1-15): In each of these questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer (a) if x > y (b) if x < y (c) if x ≥ y (d) if x ≤ y (e) if x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established. 2 2 II. y + 7y + 12 = 0 2 2. 3. I. x + 20 = 9x I. 12x + 3y = 14 II. y 2 + 42 = 13y II. 4x + 2y = 16 4. I. x = √625 II. y = √676 5. 2 I. x + 4x + 4 = 0 4 II. y 2 – 8y + 16 = 0 II. y10 – (36)5 = 0 = (36)5 ⇒ y10 = (62 )5 ⇒ y10 = 610 ∴y=6 ∴x=y 15. I. 7x 2 + 16x – 15 = 0 II. y 2 – 6y – 7 = 0 Sol. (e): I. x1 = –ve x2 = +ve II. y1 = +ve y2 = –ve ∴ Relation can't be estabilished II. 3y + 7 = 0 ⇒ y = – 3 = – 2.33 ∴ x>y 1 = (x)2 = √x ⇒ x = 6 √x 10 xa 10. I. √1225x + √4900 = 0 II. (81)4 y + (343)3 = 0 m ∴ x<y 7 √x − II. y 4 × 7 – 3y = 13 Þ 3y = 15 Þ y = 5 70 15 Sol. (e): I. ∴ put it in equation (I) I. x + 5x + 6 = 0 II. y 2 = 2304 13. I. x = √2304 ∴ y1 = + = 2, y2 = + = 1.75 ; x ≤ y 1. 8 6x = 2 ⇒ x = 3 ⇒ x = 0.33 32 9. 12 + x − x2 = x2 Sol. (b):I. 18 + 6x – 12 = 8 also, 32 – 21 = 11 II. 6 x2 3 II. y + 9.68 + 5.64 = 16.95 56 8×7 12 4×3 18 p 8. 6. 7. I. x 2 – 19x + 84 = 0 I. x 3 – 468 = 1729 9 11 I. 9. I. √784x + 1234 = 1486 √x = √x 5 8. √x + 19 II. y 2 – 25y + 156 = 0 II. y 2 – 1733 + 1564 = 0 II. y – (2×14) 2 √y =0 II. √1089y + 2081 = 2345 10. I. 12 √x – 23 √x = 5√x II. √y 12 – 5√y 12 = 1 √y 11. I. 6x 2 – 49x + 99 = 0 II. 5y 2 + 17y + 14 = 0 12. I. 13. I. 14. I. 15. I. 1 x = (1331)3 2x 2 + 3x + 1 = 0 7x – 3y = 13 2x + 5y = 6 Adda247 Publications II. II. II. II. 2y 2 – 17y + 36 = 0 12y 2 + 7y + 1 = 0 5x + 4y = 40 5x + 11y = 9 For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations Prelims Questions Directions (1-5):- In each of the following questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 1. I. x 2 + 5x + 6 = 0 II. y 2 + 9y + 14 = 0 2 2. I. x − 18x + 45 = 0 II. y 2 + 12y − 45 = 0 3. I. 9x 2 + 11x + 2 = 0 II. 8y 2 + 6y + 1 = 0 4. I. 6x² + 5x + 1 = 0 II. 4y 2 – 15y = 4 5. I. x 2 + 3x = 0 II. x 2 + y = 10 15. I. x 2 + 48x + 575 = 0 Directions (6-10):- In each of the following questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 6. I. x 2 − 25x + 156 = 0 II. y 2 − 29y + 210 = 0 17. I. 3x 2 + 20x + 32 = 0 II. y 2 + 44y + 483=0 two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (c) if x<y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. gr 16. I. x 2 + 23x + 132 = 0 II. y 2 + 21y + 110 = 0 II. 5y 2 + 23y + 24 = 0 18. I. x 2 − 29x + 208 = 0 m te @ ce (d) if x ≤y II. y 2 − 21y + 108 = 0 19. I. x2+30x+224=0 II. y2+35y+306=0 3 20. I. x = √4096 II. y2 =256 Directions (21-25): In each of these questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: Directions (11-15):- In each of the following questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 11. I. x 2 + 17x + 72 = 0 II. y 2 + 11y + 30 = 0 12. I. 3x 2 − 23x + 40 = 0 II. 5y 2 − 17y + 14 = 0 13. I. x 2 − 26x + 168 = 0 II. y 2 − 29y + 208 = 0 14. I. x3+340=2537 II. y2+23=192 5 (b) if x≥y ou (a) if x>y xa I. x 2 = 196 II. y = √196 2 I. x + 12x + 35 = 0 II. y 2 + 14y + 48 = 0 9. I. 3x 2 + 23x + 30 = 0 II. y² + 15y + 56 =0 10. I. x 2 + 17x + 72 = 0 II. y 2 + 13y + 42=0 7. 8. p Directions (16-20):- In each of the following questions, 21. I. 2x² + 10x + 12 = 0 II. y² + 10x + 25 = 0 (a) x > y (b) x ≥ y (c) x < y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or relation can’t be established. 22. I. x² – 5x + 6 = 0 II. y² + 7y + 6 = 0 (a) x > y (b) x ≥ y (c) x < y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or relation can’t be established. 23. I. x² = 625 II. y = √625 (a) x > y (b) x ≥ y (c) x < y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or relation can’t be established. 24. I. 2x – 3y = 0 II. 4x – 2y = 16 (a) x > y (b) x ≥ y (c) x < y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or relation can’t be established. Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations m gr II. y = √289 28. I. x 2 − 25x + 156 = 0 II. y 2 − 32y + 255 = 0 29. I. x2 + 23x + 130 = 0 II. y2 + 30y + 224 = 0 30. I. x 2 − 28x + 195 = 0 II. y 2 − 22y + 117 = 0 Directions (41-45):- Each of the following questions is provided with 2 statements i.e. Statement I & Statement II. You have to solve them and mark the correct option. (a) x>y (b) x<y (c) x≤y (d) x≥y (e) x=y or no relation can be established. 41. I. x² + 8x + 12 = 0 II. 2y² + 14y + 24 = 0 42. I. x² – x – 30 = 0 II. y² – 15y + 56 = 0 43. I. x² + 31x + 150 = 0 II. y² + 54y + 728 = 0 44. I. x² = 256 ou Directions (26-30):- In each of the following questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 26. I. x 2 + 21x + 108 = 0 II. y 2 + 24y + 143 = 0 27. I. x 2 = 289 II. y= √961 38. I. x 2 + 18x + 77 = 0 II. y 2 + 22y + 117 = 0 39. I. 3 x2+25x+50=0 II. 4y2+23y+33=0 40. I. 2x 2 + 17x + 36 = 0 II. 3y 2 + 20y + 32 = 0 p 36. I. x 2 − 31x + 238 = 0 II. y 2 − 37y + 342 = 0 37. I. x 2 + 215 = 1176 3 25. I. x³ = 1331 II. y = √1331 (a) x > y (b) x ≥ y (c) x < y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or relation can’t be established. @ ce te xa Directions (31-35):- In each of the following questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 31. I. 6x 2 + 5x + 1 = 0 II. 2y 2 + 5y + 3 = 0 32. I. x 2 = 4 II. y5 = 32 33. I. x 2 − 11x + 30 = 0 II. y 2 − 15y + 56 = 0 34. I. 3 x2−14x+15=0 II.5y2−14y+8=0 35. I. x 2 + 13x + 42 = 0 II. y 2 + 16y + 63 = 0 Directions (36-40):- In each of the following questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 6 II. y = √256 45. I. x² – 45x + 506 = 0 II. y² – 9y – 360 = 0 Directions (46-50):- In each of the following questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 46. I. x 2 − 21x + 110 = 0 II. y 2 − 25y + 156 = 0 47. I. x 2 + 29x + 208 = 0 II. y2 + 35y +306= 0 3 48. I. x = √4096 II. y 2 + 121 = 377 49. I. 3 x2+23x+44=0 II. 4y2+33y+65=0 50. I. x 2 + 41x + 418 = 0 II. y 2 + 47y + 550 = 0 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations I. x 2 + 24x = −119 I. (x + y)2 = 361 I. √x + 4 = √225 − √121 I. 223x + 122y = 791 I. 7x 2 − 44x + 69 = 0 II. 3y 2 + 7 = −10y II. 92442 = y 2 + 92361 II. y 2 + 329 = 473 II. 122x + 223y = 589 II. 3y 2 − 40y + 133 = 0 ou p Directions (16-20): In each of these questions, two equations I. and II. are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer. (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 16. I. 8x²–10x+3=0 II. 5y²+14y–3=0 17. I. 3x²+13x+12=0 II. y²+9y+20=0 18. I. x²–4x–5=0 II. 7y²–25y–12=0 19. I. x³=216 II. 2y²–25y+78=0 20. I. 5x² + 31x + 48 = 0 II. 3y² + 27y + 42 = 0 Directions (21-25): In each of the following questions two equations are given. Solve these equations and give answer: (a) if x ≥ y, i.e. x is greater than or equal to y (b) if x > y, i.e. x is greater than y (c) if x ≤ y, i.e. x is less than or equal to y (d) if x < y, i.e. x is less than y (e) x = y or no relation can be established between x and y 21. I. 6x² + 17x + 5 = 0 II. 2y² + 21y + 49 = 0 22. I. x² - 8x + 15 =0 II. 2y² - 5y - 3 = 0 23. I. 5x² + 11x + 2 = 0 II. 4y² + 13y + 3 = 0 24. I. 4x + 2y = 4 II. 3x + 5y = 3 25. I. 6x² + x- 15 =0 II. 4y² - 24y + 35 = 0 @ ce te xa m Directions (6-10): In each of these questions, two equations I. and II. are given. You have to solve both the equations and answer the following questions. 6. I. x 3 = 2744 II. y 2 = 324 (a) x = y or no relation. (b) x < y (c) x ≤ y (d) x > y (e) x ≥ y 7. I. (5x − 7)2 = 4 − x(3x − 1) II. (4y − 3)2 = y(4y − 1) − 1 (a) x = y or no relation. (b) x < y (c) x ≤ y (d) x > y (e) x ≥ y 8. I. 10x 2 − 29x + 21 = 0 II. 2y 2 − 19y + 45 = 0 (a) x = y or no relation. (b) x < y (c) x ≤ y (d) x > y (e) x ≥ y 9. I. x 2 + 13x + 42 = 0 II. y 2 + 8y + 12 = 0 (a) x = y or no relation. (b) x < y (c) x ≤ y (d) x > y (e) x ≥ y 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. gr Directions (1-5): In each question two equations numbered I. and II. are given. You have to solve both the equations and mark appropriate answer. (a) If x < y (b) If x > y (c) If x ≥ y (d) If x ≤ y (e) If x = y or no relation can be established. 1. I. 2x² - 17x + 36 = 0 II. 3y² - 22y + 40 = 0 2. I. x² + 21x + 108 = 0 II. y² + 14y + 48 = 0 3. I. 2x² + 7x – 60 = 0 II. 3y² - 28y + 64 = 0 4. I. x² - 2x – 24 = 0 II. y² + 3y – 40 = 0 5. I. 4x² + 27x + 45 = 0 II. 5y² + 42y + 88 = 0 1 11 x 36x 10. I. 1 = (2 − ) (a) x = y or no relation. (b) x < y (d) x > y II. ( 14y 3 9 + ) = 13 y (c) x ≤ y (e) x ≥ y Directions (11-15): In each of these questions, two equations are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer. (a) If x > y (b) If x ≥ y (c) If x < y (d) If x ≤ y (e) If x = y or relationship between x and y cannot be established. 7 Directions (26-30): In each of these questions, two equations I. and II. are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer. 26. I. x 2 − 11x + 30 = 0 II. 56y 2 − 151y + 99 = 0 (a) x > y (b) x < y (c) x ≥ y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or no relation. 27. I. x 2 − 4√3(√3 + 1)x + 48√3 = 0 II. y 2 − 2√5(√5 + 2)y + 40√5 = 0 (a) x > y (b) x < y (c) x ≥ y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or no relation. Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations x Directions (41-45): Solve the given quadratic equations and mark the correct option based on your answer— 41. I. x² + 9x = 25x – 63 II. 4y² – 34y + 72 = 0 (a) x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. (b) x ≤ y (c) x < y (d) x > y (e) x ≥ y )=0 7 II. 4 (3y + ) + 37 = 0 y (a) x > y (c) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. 29. I. (x + 15)2 = (y + 19)2 II. x 2 − y 2 = 112 (a) x > y (c) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. 1 5 8 y 21 2 2y =5 (b) x < y (d) x ≤ y (b) x < y (d) x ≤ y 42. I. II. + (a) x > y (c) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. x = –x + 14 II. 30% o f 70y = y² + 90 (a) x ≥ y (b) x > y (c) x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. (d) x ≤ y (e) x < y 43. I. 6x + 7y = 15 II. 3x + 14y = 19.5 (a) x > y (b) x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. (c) x ≤ y (d) x < y (e) x ≥ y 44. I. 7x² + 5x – 18 = 0 II. 3y² + 4y – 20 = 0 (a) x > y (b) x ≤ y (c) x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. (d) x ≥ y (e) x < y 45. I. x² + 5x = 5 (2x + 3x) II. 3y² + 2y = 2(y + 6) (a) x > y (b) x ≥ y (c) x < y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. ou 30. I. 3 + x2 = 3x 20% of 225 p 20 x (b) x < y (d) x ≤ y @ ce te xa m Directions (31-35): In each of these questions, two equations I. and II. are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 31. I. 5x 2 − 31x + 30 = 0 II. 8y 2 − 12y + 4 = 0 32. I. 7x 2 − 17x + 6 = 0 II. 5y 2 − 24y + 16 = 0 33. I. 13x 2 + 9x − 4 = 0 II. 2y 2 + y − 3 = 0 34. I. 3x 2 − 60x + 288 = 0 II. 4y 2 − 50y + 156 = 0 35. I. 15x 2 + 10x − 5 = 0 II. 6y 2 + 2y − 4 = 0 gr 1 28. I. 21 + (43 + Directions (36-40): In each of these questions, two equations I. and II. are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer (a) if x > y (b) if x ≥ y (c) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. (d) if y > x (e) if y ≥ x 36. I. x² – 12x + 32 = 0 II. y² – 20y + 96 = 0 37. I. 2x² – 3x – 20 = 0 II. 2y² + 11y + 15 = 0 38. I. x² – x – 6 = 0 II. y² – 6y + 8 = 0 39. I. x² + 14x - 32 = 0 II. y² – y – 12 = 0 40. I. x² – 9x + 20 = 0 II. 2y² – 12y + 18 = 0 8 Directions (46-50): In the following questions, two equations I. and II. are given. You have to solve both the equations and mark the appropriate option. 46. I. 12x 2 − 16x + 5 = 0 II. 30y 2 − 61y + 30 = 0 (a) x < y (b) x > y (c) x ≤ y (d) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. 47. I. x 2 − 16x + 63 = 0 II. y 2 − 12y + 35 = 0 (a) x < y (b) x > y (c) x ≤ y (d) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations Directions (51-55): Solve the given quadratic equations and mark the correct option based on your answer. (b) x > y (d) x ≥ y (a) x > y (b) x ≥ y (c) x < y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. (b) x > y (d) x ≥ y 51. I. x² + x – 12 = 0 52. I. 6x² – 5x + 1 = 0 II. y² + 2y-15 = 0 II. 3y² + 8y = 3 53. I. 12x² – 7x + 1 = 0 II. 6y² – 5y + 1 = 0 54. I. x² + 7x + 10 = 0 II. 2y² + 5y + 2 = 0 55. I. x² – 2x = 15 II. y² + 5y + 4 = 0 Mains Questions 2. Quantity I : Days after which A and B meet. A and B set out to meet each other from two places 165 km apart. A travels 15 km the first day, 14 km second day, 13 km the third day and so on, B travels 10 km the first, 12 km the second day, 14 km the third day and so on. Quantity II: Number of days required to complete the whole work if A, B and C can complete a piece of work in 10, 12 and 15 days respectively. A left the work 5 days before the work was completed and B left 2 days after A had left. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 4. Quantity I: Percentage profit earned by the shopkeeper if at the time of selling and purchasing he uses weights 10% less and 20% more per kilogram respectively and proffesses to all goods at 5% profit. Quantity II: ‘x’ ; A book was sold for a certain sum and there was a loss of 20%. Had it been sold for Rs 12 more, there would have been a gain of 30%. ‘x’ would be value of profit percent if the book were sold for Rs 4.8 more than what it was sold for. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation gr 1. In a two digit number, digit at unit place exceeds, the digit in its tens place by 2 and the product of the required number with the sum of its digit is equal to 144. Quantity I: Value of two digit number Quantity II: 26 (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 3. Quantity I: Present age of Randy, if 10 years are subtracted from the present age of Randy, then you would get twelve times of the present age of his grandson Sandy and Sandy is 19 years younger to Sundar whose age is 24. Quantity II: Average age of the remaining persons in the group if average age of group of 14 persons is 27 years and 9 months. Two persons, each 42 years old, left the group. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation @ ce te xa m Directions (1-20): In the given questions, two quantities are given, one as Quantity I and another as Quantity II. You have to determine relationship between two quantities and choose the appropriate option p (b) x > y (d) x ≥ y ou 48. I. 32x 2 + 44x + 15 = 0 II. 42y 2 + 53y + 15 = 0 (a) x < y (c) x ≤ y (e) x = y or no relation. 49. I. (x − 2)2 = x − 2 II. 9y 2 − 36y + 35 = 0 (a) x < y (c) x ≤ y (e) x = y or no relation. 50. I. 18x 2 + 39x + 20 = 0 II. 10y 2 + 29y + 21 = 0 (a) x < y (c) x ≤ y (e) x = y or no relation. 9 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations p ou 10. PBA and PDC are two secants. AD is the diameter of the circle with centre at O. ∠A= 40°, ∠P = 20° Quantity 1: ∠DBC Quantity 2: ∠ADB (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation m 6. Quantity I: Overall profit percentage if the cost prices of two shirts are equal. One shirt is sold for 20% profit and the other is sold for 10% loss. Quantity II: Profit % made in selling each meter if the profit made in selling 20 m of a cloth equals the cost price of 5 m of that cloth. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 9. P can complete a piece of work in 16 days which Q can complete in 32 days. P and Q work on alternate days. Quantity I: Time taken by them to complete the work if P starts on day 1. Quantity II: time taken by them to complete the work if Q starts on day 1. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation gr 5. A group consist of 4 couples in which each of the 4 persons have one wife Quantity I : Number of ways in which they could be arranged in a straight line such that the men and women occupy alternate positions Quantity II: Eight times the number of ways in which they be seated around circular table such that men and women occupy alternate position. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation @ ce te xa 7. The largest possible right circular cylinder is cut out from a wooden cube of edge 7 cm. Quantity I: volume of the cube left over after cutting out the cylinder Quantity II: Surface area of cube remained after cutting out the cylinder. Note: compare the magnitudes of both quantities. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 8. Quantity I: Value of y. A vessel contains 2.5 liters of water and 10 liters of milk. 20% of the contents of the vessel are removed. To the remaining contents, x liters of water are added to reverse the ratio of water and milk. Then y liters of milk are added again to reverse the ratio of water and milk. Quantity II: 120 ltr. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 10 11. Quantity I: Height of the tank if the volume of cylindrical tank is 12320 cubic cm. Its radius and height are in the ratio of 7 : 10 respectively. Quantity II: Level kerosene in the jar. A conical vessel of base radius 2 cm and height 3 cm is filled with kerosene. This liquid leaks through a hole in the bottom and collects in a cylindrical jar of radius 2 cm. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 12. I. P2 − 18p + 77 = 0 II. 3q2 − 25q + 28 = 0 Quantity I: Value of P Quantity II: Value of q (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 17. Quantity I: Time taken by Manoj and Shubham to complete the work together. When Manoj works alone, he takes 4.8 hrs more than the time taken by Manoj and Shubham to complete the work together. When Shubham works alone, he takes 10.8 hrs more than the time taken by both of them to complete the work together. Quantity II: 7.4 hrs. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 14. If 10 men and 15 women complete a piece of work in 8 days while 12 men and 8 women can complete the same piece of work in 10 days. If A boy who is 50% less efficient than the man, can do the same work in 50 days. Quantity I : Time taken by 2 men, 4 women and 18 boys to complete the work. Quantity II : Time taken by 9 men, 3 women and 6 boys to complete the same work. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 18. The edge of the cube is 10 cm. Given E is the center of the semicircle and it is mid-point of the diagonal of the given cube. (2 marks) gr ou p 13. A man who swim 48m/minute in still water, swims 200m against the current and 200m with the current. The difference between the time taken by him against the stream and with the stream is 10 minutes. Quantity I: speed of current. Quantity II: Speed of a man who completes 3 rounds of a circular path of radius 49 m in 14 minutes. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation m Quantity I: Area of the shaded region Quantity II: 10 cm2. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation te xa 15. Babu generally starts from his home at certain time with a certain speed to pick up his girlfriend from office at 5 : 00 PM. One day his girlfriend left the office at 3 : 00 PM and starts walking to home with a speed of 40 km/hr and meet Babu in the way who left his home at his usual time. They reached home 40 min. Earlier than their usual time. Quantity I : Speed of boy. 1 Quantity II : 492 2 % of speed of girl. @ ce (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 2 16. If the cost price of the article is 79 7 % of the mark price and there is a discount of Rs. 68 on the marked price. There is a profit of 20% on selling the item. Quantity I : CP of the article Quantity II : 1111 Rs. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 11 19. Quantity I: Original duration of flight. In a flight of 3000 km an aircraft was slowed down by bad weather. Its average speed for the trip was reduced by 100 km/hr. and the time increased by one hour. Quantity II: Usual time of a man who, when walks at 3 th of his usual pace, reaches his office 20 minutes late. 4 (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation 20. Wheels of diameters 7 cm and 14 cm start rolling simultaneously from X and Y, which are 1990.50 cm apart, towards each other. Both of them make same no. of revolutions per second. Both of them meet after 10s. Quantity I: speed of smaller wheel. Quantity II: 21π cm/s (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 1 1 23. I. x = √(36)2 × (1296)4 II. x – y + z = 0 II. 2x + 8z = 80 + x − 11 3x + 7 3x x+7 + = 12 x x − 11 x = 14 II. =7 II. y − 18y − 5 (18y − 5) y y+8 y+8 4y II. + 4y − 13 @ ce 29. I. x+7 x − y =2 = 16 y 4y − 13 te 28. I. 3x 3x + 7 x + 4y =9 Direction (1 – 6): In each question two equations numbered (I) and (II) are given. You should solve both the equations and mark appropriate answer. (a) If x=y or no relation can be established (b) If x>y (c) If x<y (d) If x≥y (e) If x≤y 1. I. x2 = 256 II. y2 – 17y + 16 = 0 2. I. x2 + 20x + 100 =0 II. y2 + 13y + 30 = 0 3. I. 4x² - 8x – 5 = 0 II. 2y² - 11y + 14 = 0 4. I. 6x² + 5x + 1 = 0 II. 20y² + 9y + 1 = 0 12 Direction (36-40): Two equations (I) and (II) are given in each question. On the basis of these equations you have to decide the relation between ‘x’ and ‘y’ and give answer (a) if x > y (b) if x ≥ y (c) if x < y (d) if x ≤ y (e) if x = y or relation cannot be established. 36. I. 36x 2 + 47 √7x + 105 = 0 xa Direction (27-29): Two equations (I) and (II) are given in each question. On the basis of these equations you have to decide the relation between ‘x’ and ‘y’ and give answer (a) if x > y (b) if x ≥ y (c) if x < y (d) if x ≤ y (e) if x = y or Relation cannot be established. 27. I. p gr II. 5x + 6y = 99 m II. 2y + 3z = 33 III. 6y + 5z = 71 24. I. 8x + 7y = 135 III. 9y + 8z = 121 25. I. (x + y)3 = 1331 III. xy = 28 26. I. x + 3y + 4z = 96 III. 2x + 6y = 120 Direction (30-35): Two equations (I) and (II) are given in each question. On the basis of these equations you have to decide the relation between ‘x’ and ‘y’ and give answer (a) if x > y (b) if x ≥ y (c) if x < y (d) if x ≤ y (e) if x = y or Relation cannot be established. 30. I. 99x 2 + 149x + 56 = 0 II. 156y 2 + 287y + 132 = 0 31. I. 77x 2 + 58x + 8 = 0 II. 42y 2 + 59y + 20 = 0 32. I. 63x 2 + 172x + 117 = 0 II. 30y 2 + 162y + 216 = 0 33. I. 36x 4 + 369x 2 + 900 = 0 II. 144y 4 + 337y 2 + 144 = 0 34. I. 18x 2 – 13 √7x + 14 = 0 II. 32y 2 – 19√6y + 9 = 0 35. I. x 2 – 82x + 781 = 0 II. y 2 – 5041 = 0 ou Direction (21-26): Three equations (I), (II) and (III) are given in each question. On the basis of these equations you have to decide the relation between ‘x’, ‘y’ and 'z' and give answer (a) if x < y = z (b) if x ≤ y< z (c) if x < y > z (d) if x = y > z (e) if x = y = z or if none of the above relationships is established. 21. I. 7x + 6y + 4z = 122 II. 4x + 5y + 3z = 88 III. 9x + 2y + z = 78 22. I. 7x + 6y = 110 II. 4x + 3y = 59 III. x + z = 15 II. 35y2 + 20 3y + 63 2y + 36 6 = 0 37. I. 91x 2 + 298x + 187 = 0 II. 247y 2 + 216y – 391 = 0 38. I. 81x 2 – 9x – 2 = 0 II. 56y 2 – 13y – 3 = 0 39. I. 391x 2 +1344x + 1073 = 0 II. 437y 2 +1074y + 589 = 0 40. I. 3216x 2 + 3859x + 481 =0 II. 8132y 2 – 4839y + 978 = 0 5. I. 2x² - 9x + 9 = 0 6. I. 4𝑥 2 − 17𝑥 + 15 = 0 II. 6y² - 17y + 12 = 0 II. 2𝑦 2 − 17𝑦 + 35 = 0 SBI PO Prelims 2020 Direction (7–11): In each question two equations numbered (I) and (II) are given. You have to solve both the equations and mark appropriate answer. (a) If x = y or no relation can be established (b) If x > y (c) If x < y (d) If x ≥ y (e) If x ≤ y Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations Directions (27-31): In the following questions, calculate quantity I and quantity II, compare them and answer according to the following options. (a) If Quantity I > Quantity II (b) If Quantity I < Quantity II (c) If Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) if Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (e) if Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation can be established 27. Quantity I. Profit earned on selling an article at Rs. 450 at 20% profit Quantity II. Cost price of the article which is sold at Rs.84 on 20% profit m Directions (17–21): In the following questions, there are two equations in x and y. You have to solve both the equations and give answer (a) if x > y (b) if x < y (c) if x ≥ y (d) if x ≤ y (e) if x = y or there is no relation between x and y 17. I. 2x2 – 3x + 1 = 0 II. 2y2 – 5y + 3 = 0 18. I. x2 + 21x + 110 = 0 II. y2 + 17y + 72 = 0 2 19. I. x = 4 II. y2 – 6y + 8 = 0 20. I. x² + 9x -22 = 0 II. 2y² - 7y + 6 = 0 21. I. 6x² + 5x + 1 = 0 II. 15y² + 11y + 2 = 0 IBPS Clerk Pre 2020 p Directions (12-16): In the following two equations questions numbered (I) and (II) are given. You have to solve both equations and Give answer (a) If x > y (b) If x ≥ y (c) If y > x (d) If y ≥ x (e) If x = y or no relation can be established 12. I. x² - 8x + 15 = 0 II. 2y² - 7y + 5 = 0 13. I. 2x² + x – 28 = 0 II. 2y² - 23y + 56 = 0 14. I. 2x² - 7x – 60 = 0 II. 3y² + 13y + 4 = 0 15. I. x² - 17x – 84 = 0 II. y² + 4y – 117 = 0 2 2 16. I. x = 9 II. (y – 8)2 = 9 IBPS PO Prelims 2020 25. I. x 2 − 20x + 91 = 0 II. y 2 + 16y + 63 = 0 (a) x < y (b) x > y (c) x ≤ y (d) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. 2 26. I. x − x − 12 = 0 II. y 2 + 5y + 6 = 0 (a) x < y (b) x > y (c) x ≤ y (d) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. RRB PO Prelims 2020 ou II. y3 = 125 II. y2 + 15y + 56 = 0 II. y2 = 64 II. y2 = 2y + 35 II. y2 − 13𝑦 + 40 = 0 SBI Clerk Prelims 2020 gr 7. I. 𝑥 = √25 8. I. x2 + 2x – 35 = 0 9. I. x2 = 81 10. I. 17x2 – 14x – 83 = - 80 11. I. x2 + 4x – 45 = 0 te xa 28. In a village there are 60% males and rest are females. 30% of total male are illiterate and 25% of total female are illiterate. Number of illiterate males is 1152. Quantity I. Literate females in the village. Quantity II. 1940 @ ce Directions (22-26): In the given questions, two equations (I) & (II) are given. You have to solve both the equations and mark the answer accordingly. 22. I. x 2 + 9x + 20 = 0 II. 8y 2 − 15y + 7 = 0 (a) x < y (b) x > y (c) x ≤ y (d) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. 23. I. x 2 − 11x + 30 = 0 II. y 2 + 12y + 36 = 0 (a) x < y (b) x > y (c) x ≤ y (d) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. 24. I. x 2 + 13x + 40 = 0 II. y 2 + 7y + 10 = 0 (a) x < y (b) x > y (c) x ≤ y (d) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation. 13 29. A man invested Rs. P at 12% p.a. on simple interest for two years. Quantity I. If at the end of second year he gets Rs.1200 as interest, then find Rs.P. Quantity II. Rs.6000 30. Ploughing cost of a rectangular field is Rs.288 at the rate of Rs.3 per square meter. Length of the field is 4 meters more than the width of field. Quantity I. Length of rectangular field. Quantity II. 12 meters. 31. Quantity I. Sum of present ages of Shivam and Prashant is 32 years and Shivam is 8 years older than Prashant. Find present age of Prashant. Quantity II. 15 years. RRB PO Prelims 2020 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 44. Quantity I: ou p A man invested Rs.5900 for 3 years in a scheme offering R% p.a. at SI and received Rs.3186 as interest after 3 years. If the man invested Rs.7900 at (R+5)% p.a. at SI for 3 years, then find interest received by man (in Rs.). Quantity II: A man invested Rs.X at 13% p.a. at CI for 2 years and interest received by him after 2 years is Rs.2325.96. Find X (in Rs.). (a) Quantity I < Quantity II (b) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (c) Quantity I > Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation. Ratio of CP to MP of an article is 19 : 30. Shopkeeper allowed 24% discount and earned 20% profit on selling the article. If SP of the article is Rs.912, then find difference between amount of profit earned and amount of discount allowed (in Rs.). Quantity II: Shopkeeper marked an article 70% above its cost price and he allowed 40% discount on it. If shopkeeper sold the article at Rs.183.6, then find sum of amount of profit earned and amount of discount allowed(in Rs.). (a) Quantity I < Quantity II (b) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (c) Quantity I > Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation. te xa m Directions (37-41): In each of these questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 37. I. x² - 13x + 40 = 0 II. 2y² - y – 15 = 0 38. I. 5x² + 17x + 6 = 0 II. 2y² + 11y + 12 = 0 39. I. 7x² - 19x + 10 = 0 II. 8y² + 2y – 3 = 0 2 40. I. 𝑥 − 8𝑥 + 15 = 0 II. 𝑦 2 − 3𝑦 + 2 = 0 41. I. 3x² –7x + 4 = 0 II. 2y² – 9y + 10 = 0 SBI Clerk Prelims 2019 43. Quantity I: gr Direction (32 – 36): Solve the given quadratic equations and mark the correct option based on your answer. (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x=y or no relation can be established between x and y. 32. I. x2 − 14𝑥 + 45 = 0 II. y2 – 18𝑦 + 72 = 0 33. I. x2 + 7𝑥 + 12 = 0 II. y2 +9𝑦 + 20 = 0 34. I. 4x2 – 7𝑥 + 3 = 0 II. 7y2− 17y + 6 = 0 35. I. 2x2 - 19x + 45 =0 II. 2y2 -9y + 4 = 0 36. I. x2 = 144 II. (y +12)2 = 0 SBI PO Prelims 2019 @ ce Directions (42-46): In the following questions, two quantities (I) and (II) are given. You have to solve both the quantities and mark the appropriate answer. 42. Quantity I: In how many ways a committee of 4 members with at least 2 women can be formed from 8 men and 4 women? Quantity II: How many 3-digit numbers which are divisible by 3 can be formed from 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9, such that 3-digit number always ends with an even number? (a) Quantity I < Quantity II (b) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (c) Quantity I > Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation. 14 45. Quantity I: A boat can cover distance of 480 km each in downstream and in upstream in total 11 hours. If ratio of speed of boat in still water to that of stream is 11 : 1, then find speed of boat in still water (in km/hr.). Quantity II: A boat can cover a distance of 350 km in downstream in 3.5 hours and can cover a distance of 380 km in upstream in 5 hours. Find speed of boat in still water (in km/hr.). (a) Quantity I < Quantity II (b) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (c) Quantity I > Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation. Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations p 55. I. 9x + 3y = 15 II. 4x + 5y = 14 (a) x = y or no relation can be established (b) x > y (c) x ≤ y (d) x < y (e) x ≥ y 56. I. 2x 2 − x − 1 = 0 II. 3y 2 − 5y + 2 = 0 (a) x ≤ y (b) x < y (c) x = y or no relation can be established (d) x ≥ y (e) x > y IBPS Clerk Prelims 2019 Directions (57-61): Solve the given quadratic equations and mark the correct option based on your answer— (a) x > y (b) x < y (c) x ≥ y (d) x ≤ y (e) x = y or there is no relationship 57. I. x² = 81 II. y² – 18y + 81 = 0 58. I. 4x² - 24x + 32 = 0 II. y² - 8y + 15 = 0 59. I. x² - 21x + 108 = 0 II. y² – 17y + 72 = 0 60. I. x² – 11x + 30 = 0 II. y² - 15y + 56 = 0 61. I. x³ = 512 II. y² = 64 RRB PO Prelims 2019 te xa m Directions (47-51): In the following two equations questions numbered (I) and (II) are given. You have to solve both equations and Give answer (a) If x > y (b) If x ≥ y (c) If y > x (d) If y ≥ x (e) If x = y or no relation can be established 47. I. x² - 7x + 12 = 0 II. y² - 8y + 12 = 0 48. I. 2x² + x – 28 = 0 II. 2y² - 23y + 56 = 0 49. I. 2x² - 7x – 60 = 0 II. 3y² + 13y + 4 = 0 50. I. x² - 17x – 84 = 0 II. y² + 4y – 117 = 0 2 51. I. x = 81 II. (y-9)2 = 0 IBPS PO Prelims 2019 54. I. 2x 2 + 5x + 3 = 0 II. y 2 + 4y − 12 = 0 (a) x ≤ y (b) x > y (c) x = y or no relation can be established (d) x < y (e) x ≥ y ou B’s present age is 60% more than A’s present age and ratio of present age of B to that of C is 5 : 2. D is 8 years younger than B and D’s present age is twice of that of C. Find average of present age of A, B, C & D (in years). Quantity II: Present age of R is equal to average of present age of P & Q. 4 years hence, age of P is twice of age of Q at that time. If R is 15 years younger than P, then find age of younger person among P, Q & R. (a) Quantity I < Quantity II (b) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II (c) Quantity I > Quantity II (d) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation. SBI Clerk Mains 2019 gr 46. Quantity I: @ ce Directions (52–56): Solve the following quadratic equation and mark the answer as per instructions. 52. I. x 2 − 2x − 143 = 0 II. y 2 − 169 = 0 (a) x > y (b) x < y (c) x ≤ y (d) x ≥ y (e) x = y or no relation can be established 53. I. x 2 − 7x − 18 = 0 II. y 2 − 19y + 90 = 0 (a) x ≤ y (b) x = y or no relation can be established (c) x > y (d) x ≥ y (e) x < y 15 Directions (62-65): In each of the following questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. Solve the equations and mark the correct option: (a) if x>y (b) if x≥y (c) if x<y (d) if x ≤y (e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y. 62. I. 2x 2 + 11x + 12 = 0 II. 8y2 -22y – 21 =0 63. I. x2 -17x -60=0 II. y2 + 42y +185 =0 2 64. I. x + 41x + 420 =0 II. 6y2 -11y -10 =0 65. I. x2 - 8x - 273 =0 II. y2 +6y -432 =0 RRB PO Mains 2019 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations p 74. Quantity I: Amount obtained after two years on Rs. 2 2450 at 14 % simple interest per annum. 7 Quantity II: Amount obtained after two years on 1 investment of Rs 2450 at 12 2 % 𝑝. 𝑎. compounded yearly. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation (e) Quantity I≤ Quantity II m 71. Quantity I: A train can cross a pole in 24 sec with a speed of 75 km/h. Length of train. Quantity II: A train can cross a pole in 12 sec and a tunnel in 55.2 sec. If length of tunnel is 1800 m. length of train. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation (e) Quantity I≤ Quantity II 73. Quantity I: value of x (𝑥 + 3)2 = (𝑥 − 3)2 + 𝑥² Quantity II: value of y 𝑦 2 − 29𝑦 + 204 = 0 (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation (e) Quantity I≤ Quantity II ou Directions (71–75): In the given questions, two quantities are given one as ‘Quantity I’ and another as ‘Quantity II’. You have to determine relationship between two quantities and choose the appropriate option. (d) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation (e) Quantity I≤ Quantity II gr Directions (66-70): Given below are two equations in each question, which you have to solve and give answer (a) if𝑥 > 𝑦 (b) if𝑥 ≥ 𝑦 (c) if𝑦 > 𝑥 (d) if𝑦 ≥ 𝑥 (e) if𝑥 = 𝑦 or no relation can be established 66. I. 2𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 + 2 = 0 II. 2𝑦 2 − 9𝑦 + 7 = 0 2 67. I. 3𝑥 + 7𝑥 + 4 = 0 II. 𝑦 2 + 9𝑦 + 20 = 0 68. I. 𝑥 2 − 7𝑥 + 10 = 0 II. 𝑦 2 − 14𝑦 + 45 = 0 69. I. x² – 3x = 4 II. y² + 6y + 8 = 0 70. I. x² – 3x = 10 II. y² + 7y + 10 = 0 RRB Clerk Prelims 2019 xa 75. Quantity I: Actual discount percent. If a shopkeeper gives 1 article free at every purchase of 4 articles and also give 20% discount. Quantity II: Final new profit percent. If selling price 2 36 is increased by 14 7 % then profit percent becomes 19 @ ce te 72. Quantity I: Marked price of article, if article is marked at 50% above cost price and on selling the article, profit earned is 20% and S. P is Rs 1020. Quantity II: Total cost of fencing a square of side 37.5 meter and cost of wire is Rs 0.17 per centimeter. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II Solutions 1. (c): 𝑥 2 + 5x + 6 = 0 / 6 → 3 × 2 → 3 + 2 = 5 ∴ 𝑥1 = – 3, 𝑥2 = –2 2 𝑦 + 7y + 12 = 0 | 12 → 4 × 3 → 4 + 3 = 7 ∴ y = – 4, 𝑦2 = –3; ∴ x ≥ y 16 of initial profit percent. (a) Quantity I > Quantity II (b) Quantity I < Quantity II (c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II (d) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation (e) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II RRB Clerk Mains 2019 2. (b): 𝑥 2 – 9x + 20 = 0 | 5 × 4 and, 5 + 4 = 9 ∴ 𝑥1 = + 5 𝑥2 = + 4; 𝑦 2 + 42 = 13y 𝑦 2 – 13y + 42 = 0 | 42 → 7 × 6 and, 7 + 6 = 13; ∴ 𝑦1 = +7, 𝑦2 = + 6 ; ∴ y > x Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 3. (b): eqn (1) – (eqn (2) × 3) 10. (a): 5x = –11 12 x + 3y = 14 x= 12 x + 6y = 48 – 34 3 – = 11.33 Put it in equation 1, 5 5𝑦 2 + 17y + 14 = 0 / \ 5 7×2 and, 10 + 7 = 17 12x + 34 = 14 ⇒ 12x = – 20 ⇒ x = – 3; ∴ x < y 4. (b): x = √625 = 25 −10 5. (b): 𝑥 2 + 4x + 4 = 0 | 2 × 2 and, 2 + 2 = 4 𝑥1 = –2, 𝑥2 = – 2 1 m 13. (b): I. 𝑥1 = = (2 × 14) 11 2 ⇒ (𝑦) = (2 × 14)11/2 ∴ y = 28 ∴ x = y @ ce 9. (a): √784x + 1234 = 1486 28x = 252 ⇒ x = 9 33y = 264 ⇒ y = 8 ∴ x > y 1. (e): I. 𝑥 2 + 5𝑥 + 6 = 0 𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 6 = 0 (𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 + 2) = 0 𝑥 = −2, −3 17 –1 2 = –0.5 –1 43 x = 172 x = 4 , Put it in equation (i) 3y = 28 – 13 ⇒ y = 5 x < y 15. (b): eqn (1) × 5 – eq (2) × 2 te 8. (e): 9 + 19 = x ⇒ x = 28 = –1, 𝑥2 = 2 –4 14. (b): eq(i) × 4 + eq(ii) × 3. 28x – 12y = 52 15x + 12y = 120 xa 𝑦 2 = 169 ⇒ y = ± 13 ∴ x ≥ y –2 II. 𝑦1 = 12 = –0.33, 𝑦2 = 𝟒 = –0.25 ∴ y > x 𝑦 2 – 25y + 156 =0 / 13 × 12 and, 13 +12 = 25 ∴ 𝑦1 = 13, 𝑦2 = 12 ∴ y ≥ x 7. (c): 𝑥 3 = 1729 + 468 𝑥 3 = 2197 ⇒ x = 13 12. (a): x = (1331)3 = 11 2𝑦 2 – 17y + 36 = 0 / \ 2×1 9×4 and, 9 + 8 = 17 9 8 ∴ 𝑦1 = 2 = 4.5, 𝑦2 = 2 = 4 ∴ x > y gr 6. (d): x2 – 19x + 84 = 0 / 12 × 7 and, 12 + 7 = 19 ∴ 𝑥1 = + 12, 𝑥2 = +7 (𝑦) –7 ∴ 𝑦1 = 5 = –2, 𝑦2 = 5 = – 1.4 ∴ x > y 𝑦 2 – 8y + 16 = 0 ⇒ 𝑦1, 𝑦2 = +ve; ∴ y > x 11 2 ou y = √676 = 26; ∴ x < y 1 5+ 2 = – 2.2 y – 5y = 12 ⇒ y = – 3 ∴ x > y 11. (a): 6𝑥 2 –49x + 99 = 0 \ / 2×3 11 × 9 and, 22 + 27 = 49 22 11 27 9 ∴ 𝑥1 = 6 = 3 = 3.67, 𝑥2 = 6 = 2 = 4.5 – 3 y = – 34 y= 5 p – − 11 10x + 25y = 30 10x + 22y = 18 – – – 3 y = 12 y=4 ∴ 5x = 9 – 44 , x = –7; x < y Prelims Solutions II. 𝑦 2 + 9𝑦 + 14 = 0 𝑦 2 + 7𝑦 + 2𝑦 + 14 = 0 (𝑦 + 2)(𝑦 + 7) = 0 𝑦 = −2, −7 Clearly, no relation can be established Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 2. (b): I. 𝑥 2 − 18𝑥 + 45 = 0 𝑥 2 − 15𝑥 − 3𝑥 + 45 = 0 (𝑥 − 3)(𝑥 − 15) = 0 𝑥 = 3,15 II. 𝑦 2 + 12𝑦 − 45 = 0 𝑦 2 + 15𝑦 − 3𝑦 − 45 = 0 (𝑦 − 3)(𝑦 + 15) = 0 𝑦 = 3, −15 Clearly, 𝑥 ≥ 𝑦 7. (d): I. 𝑥 2 = 196 x =√196 x =±14 II. 𝑦 = √196 y =14 So,x ≤ y ou 3. (e): I. 9𝑥 2 + 11𝑥 + 2 = 0 9𝑥 2 + 9𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 2 = 0 (9𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 + 1) = 0 9 II. 8𝑦 2 + 6𝑦 + 1 = 0 8𝑦 2 + 4𝑦 + 2𝑦 + 1 = 0 (4𝑦 + 1)(2𝑦 + 1) = 0 1 1 2 4 Clearly, no relation can be established 4. (c): I. 6𝑥² + 5𝑥 + 1 = 0 6𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 1 = 0 (3𝑥 + 1)(2𝑥 + 1) = 0 3 1 1 𝑦 = −4,4 Clearly, 𝑥 < 𝑦 xa 𝑥 = −3,−2 II. 4𝑦 2 – 15𝑦 = 4 4𝑦 2 − 16𝑦 + 𝑦 − 4 = 0 (4𝑦 + 1)(𝑦 − 4) = 0 @ ce te 5. (c): I. 𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 = 0 𝑥(𝑥 + 3) = 0 𝑥 = 0, −3 II. 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 = 10 𝑦 = 10 − 𝑥 2 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 = 0, 𝑦 = 10 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 = −3, 𝑦 = 10 − (−3)2 = 1 Clearly, 𝑥 < 𝑦 6. (c): I. 𝑥 2 − 25𝑥 + 156 = 0 x2 -12x -13x +156=0 x(x-12)-13(x-12)=0 (x-12)(x-13)=0 x =12,13 II. 𝑦 2 − 29𝑦 + 210 = 0 y2-14y -15y +210=0 y(y-14) -15(y-14)=0 (y-14)(y-15)=0 y=14,15 So, x<y 18 II. 𝑦² + 15𝑦 + 56 =0 y2 +8y +7y +56 =0 y(y +8)+7(y+8)=0 (y+7)(y+8)=0 y =-7,-8 So, x > y m 1 9. (a): I. 3𝑥² + 23𝑥 + 30 = 0 3x2 +18x +5x +30 =0 3x(x+6) +5(x+6)=0 (3x+5)(x+6)=0 5 x= -6,− gr 2 𝑥 = − , −1 𝑦 = − ,− p 8. (e): I. 𝑥 2 + 12𝑥 + 35 = 0 x2+5x+7x+35=0 x(x+5)+7(x+5)=0 (x+5)(x+7)=0 x= -5,-7 II. 𝑦 2 + 14𝑦 + 48 = 0 y2+ 6y+8y+48 =0 y(y+6)+8(y+6)=0 (y+8)(y+6)=0 y = -8,-6 So, no relation. 10. (c): I. 𝑥 2 + 17𝑥 + 72 = 0 x2+ 8x+9x+72=0 x(x+8)+9(x+8)=0 (x+9)(x+8)=0 x = -8,-9 II. 𝑦 2 + 13𝑦 + 42=0 y2 +6y+7y+42 =0 y(y+6)+7(y+6)=0 (y+6)(y+7)=0 y = -6,-7 So,x<y 11. (c): I. 𝑥 2 + 17𝑥 + 72 = 0 x2 +8x +9x +72=0 x(x+8)+9(x+8)=0 (x+8)(x+9)=0 x = -8,-9 II. 𝑦 2 + 11𝑦 + 30 = 0 y2+5y +6y +30=0 y(y+5) +6(y+5)=0 (y+5)(y+6)=0 y= -5,-6 So,x<y Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com 12. (a): I. 3𝑥 2 − 23𝑥 + 40 = 0 3x2 -15x -8x +40=0 3x(x-5)- 8(x-5)=0 (x-5)(3x-8)=0 16. (d): I. 𝑥 2 + 23𝑥 + 132 = 0 x2 +12x +11x +132=0 x(x+12)+11(x+12)=0 (x+11)(x+12)=0 x = -11,-12 II. 𝑦 2 + 21𝑦 + 110 = 0 y2+11y +10y +110=0 y(y+11) +10(y+11)=0 (y+10)(y+11)=0 y= -10,-11 So, x ≤ y 8 x = 5, 3 II. 5𝑦 2 − 17𝑦 + 14 = 0 5y2-10y -7y +14=0 5y(y-2) -7(y-2)=0 (y-2)(5y-7)=0 7 y= 2, 5 ou So,x>y 17. (e): I. 3𝑥 2 + 20𝑥 + 32 = 0 3x2 +12x +8x +32=0 3x(x+4)+ 8(x+4)=0 (3x+8)(x+4)=0 2 13. (e): I. 𝑥 − 26𝑥 + 168 = 0 x2-12x-14x+168=0 x(x-12)-14(x-12)=0 (x-12)(x-14)=0 x= 12,14 II. 𝑦 2 − 29𝑦 + 208 = 0 y2-13y-16y+208 =0 y(y-13)-16(y-13)=0 (y-13)(y-16)=0 y = 13,16 So, no relation. 3 @ ce 15. (c): I. 𝑥 2 + 48𝑥 + 575 = 0 x2+ 23x+25x+575=0 x(x+23)+25(x+23)=0 (x+23)(x+25)=0 x = -23,-25 II. 𝑦 2 + 44𝑦 + 483=0 y2 +21y+23y+483 =0 y(y+21)+23(y+21)=0 (y+21)(y+23)=0 y = -21,-23 So,x ≤ y 19 gr 8 3 m II. 5𝑦 2 + 23𝑦 + 24 = 0 5y2+15y +8y +24=0 5y(y+3) +8(y+3)=0 (y+3)(5y+8)=0 te x =√2197 =13 II. 𝑦² + 23 =192 y2=192-23 = 169 y =±13 So, x ≥ y x = -4, − y= -3, − 8 5 So, No relation exists 18. (a): I. 𝑥 2 − 29𝑥 + 208 = 0 x2-13x-16x+208=0 x(x-13)-16(x-13)=0 (x-16)(x-13)=0 x= 16,13 II. 𝑦 2 − 21𝑦 + 108 = 0 y2-9y-12y+108 =0 y(y-9)-12(y-9)=0 (y-12)(y-9)=0 y = 9,12 So, x > y xa 14. (b): I. x3 +340=2537 x3=2537-340 =2197 p A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 19. (a): I. 𝑥 2 + 30𝑥 + 224 = 0 x2+14x+16x+224=0 x(x+14)+16(x+14)=0 (x+16)(x+14)=0 x= -16,-14 II. 𝑦 2 + 35𝑦 + 306 = 0 y2+18y+17y+306 =0 y(y+18)+17(y+18)=0 (y+18)(y+17)=0 y = -18,-17 So, x > y Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 27. (d): I. x2=289 x = ±17 II. y =√289 y =17 So, x ≤ 𝑦 3 20. (b): I. x=√4096 x =16 II. y2 =256 y = √256 = ±16 So, x ≥ y ou 21. (a): I. 2x² + 10x + 12 = 0 2x² + 6x + 4x + 12 = 0 (2x + 4)(x + 3)= 0 x= –3, –2 II. y² + 10y + 25 = 0 y² +5y +5y + 25 = 0 (y + 5)(y + 5) = 0 y = -5 ∴x>y 22. (a): I. x² – 3x – 2x + 6 =0 (x – 3)(x – 2) = 0 x = +3, + 2 II. y² + 6y + y + 6 = 0 (y + 1)(y + 6) = 0 y = –1, –6 ∴x>y @ ce 25. (e): I. x = +11 y = +11 ∴x=y gr m te 24. (a): (I) × 2 – (II) –6y + 2y = –16 y=4 x=6 x > y. 29. (a): I. 𝑥 2 + 23𝑥 + 130 = 0 x2+13x+10x+130=0 x(x+13)+10(x+13)=0 (x+13)(x+10)=0 x= -13,-10 II. 𝑦 2 + 30𝑦 + 224 = 0 y2+16y+14y+224 =0 y(y+16)+14(y+16)=0 (y+16)(y+14)=0 y = -16,-14 So, x > y xa 23. (d): I. x = ± 25 II. y = +25 ∴x≤y p 28. (c): I. 𝑥 2 − 25𝑥 + 156 = 0 x2-12x-13x+156=0 x(x-12)-13(x-12)=0 (x-13) (x-12)=0 x= 12, 13 II. 𝑦 2 − 32𝑦 + 255 = 0 y2-15y-17y+255 =0 y(y-15)-17(y-15)=0 (y-15) (y-17)=0 y = 15, 17 So, x < y 26. (e): I. 𝑥 2 + 21𝑥 + 108 = 0 x2 +9x +12x +108=0 x(x+9)+12(x+9)=0 (x+9)(x+12)=0 x = -9,-12 II. 𝑦 2 + 24𝑦 + 143 = 0 y2+11y +13y +143=0 y(y+11) +13(y+11)=0 (y+13)(y+11)=0 y= -13,-11 So, No relation 30. (b): I. 𝑥 2 − 28𝑥 + 195 = 0 x2-13x-15x+195=0 x(x-13)-15(x-13)=0 (x-13)(x-15)=0 x= 13,15 II. 𝑦 2 − 22𝑦 + 117 = 0 y2-13y-9y+117 =0 y(y-13)-9(y-13)=0 (y-13)(y-9)=0 y = 13,9 So, x ≥ y 31. (a): I. 6𝑥 2 + 5𝑥 + 1 = 0 6x2 +3x +2x +1=0 3x(2x+1)+1(2x+1)=0 (3x+1)(2x+1)=0 1 1 x = -3,-2 II. 2𝑦 2 + 5𝑦 + 3 = 0 2y2+2y +3y +3=0 2y(y+1) +3(y+1)=0 (2y+3)(y+1)=0 3 y= - 2,-1 So, x > y 20 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 33. (c): I. 𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 30 = 0 x2-5x-6x+30=0 x(x-5)-6(x-5)=0 (x-5) (x-6)=0 x= 5, 6 II. 𝑦 2 − 15𝑦 + 56 = 0 y2-7y-8y+56 =0 y(y-7)-8(y-7)=0 (y-7) (y-8)=0 y = 7, 8 So, x < y ou 38. (e): I. 𝑥 2 + 18𝑥 + 77 = 0 x2+11x+7x+77=0 x(x+11)+7(x+11)=0 (x+11) (x+7)=0 x= -11, -7 II. 𝑦 2 + 22𝑦 + 117 = 0 y2+9y+13y+117 =0 y(y+9)+13(y+9)=0 (y+9) (y+13)=0 y = -9, -13 So, No relation gr 34. (e): I. 3𝑥 2 − 14𝑥 + 15 = 0 3x2-9x-5x+15=0 3x(x-3)-5(x-3)=0 (x-3)(3x-5)=0 39. (c): I. 3𝑥 2 + 25𝑥 + 50 = 0 3x2+15x+10x+50=0 3x(x+5)+10(x+5)=0 (3x+10)(x+5)=0 5 @ ce te 35. (b): I. 𝑥 2 + 13𝑥 + 42 = 0 x2+6x+7x+42=0 x(x+6)+7(x+6)=0 (x+6)(x+7)=0 x= -6, -7 II. 𝑦 2 + 16𝑦 + 63 = 0 y2+9y+7y+63 =0 y(y+9)+7(y+9)=0 (y+9)(y+7)=0 y = -7,-9 So, x ≥ y xa 5 So, No relation m x= 3, 3 II. 5𝑦 2 − 14𝑦 + 8 = 0 5y2-10y-4y+8 =0 5y(y-2)-4(y-2)=0 (y-2)(5y-4)=0 4 y = 2, 36. (c): I. 𝑥 2 − 31𝑥 + 238 = 0 x2 −17x −14x +238=0 x(x-17) −14(x−17)=0 (x-14)(x-17)=0 x = 14,17 II. 𝑦 2 − 37𝑦 + 342 = 0 y2-18y -19y +342=0 y(y-18) -19(y-18)=0 (y-18)(y-19)=0 y= 18,19 So, x < y 21 p 37. (d): I. 𝑥 2 + 215 = 1176 x2 =961 x =± 31 II. y = √961 =31 So, x ≤ 𝑦 32. (d): I. x2=4 x = ±2 II. y5 = 32 y =2 So, x ≤ 𝑦 10 x= -5,- 3 II. 4𝑦 2 + 23𝑦 + 33 = 0 4y2+12y+11y+33 =0 4y(y+3)+11(y+3)=0 (y+3)(4y+11)=0 11 y = -3, - 4 So, x < 𝑦 40. (d): I. 2𝑥 2 + 17𝑥 + 36 = 0 2x2+8x+9x+36=0 2x(x+4)+9(x+4)=0 (x+4)(2x+9)=0 x= -4, -4.5 II. 3𝑦 2 + 20𝑦 + 32 = 0 3y2+12y+8y+32 =0 3y(y+4)+8(y+4)=0 (y+4)(3y+8)=0 y = -4,-2.67 So, x ≤ y 41. (e): I. x² + 6x + 2x + 12 = 0 (x + 6) (x + 2) = 0 x = –2, –6 II. 2y² + 8y + 6y + 24 = 0 (y + 4) (2y + 6) = 0 y = –3, –4 Hence, no relation can be established. Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 47. (a): I. 𝑥 2 + 29𝑥 + 208 = 0 42. (b): I. x² – 6x + 5x – 30 = 0 (x – 6) (x + 5) = 0 x = 6, –5 x2+16x+13x+208=0 II. y² – 8y – 7y + 56 = 0 (x+16) (x+13)=0 x (x+16)+13(x+16)=0 (y – 8) (y – 7) = 0 x= -16, -13 y = 7, 8 II. 𝑦 2 + 35𝑦 + 306 = 0 Hence, y > x y2+17y+18y+306 =0 (y+18) (y+17)=0 (x + 25) (x + 6) = 0 y = -17, -18 x = –6, –25 (y + 26) (y + 28) = 0 3 48. (b): I. x = √4096 y = –26, –28 x= 16 Hence, x > y II. y2 + 121 = 377 y2 = 256 gr 44. (c): I. x² = 256 y = ± 16 x = ± √256 So, x ≥ y x = +16, –16 II. y = √256 49. (e): I. 3𝑥 2 + 23𝑥 + 44 = 0 m y = 16 Hence y ≥ x x² – 23x - 22x + 506 = 0 (x – 23) (x - 22) = 0 x = 22, 23 II. y² – 9y – 360 = 0 te y² – 24y + 15y – 360 = 0 (y – 24) (y + 15) = 0 xa 45. (e): I. x² – 45x + 506 = 0 @ ce 46. (c): I. 𝑥 2 − 21𝑥 + 110 = 0 (3x+11)(x+4)=0 11 x= -4,- 3 4y(y+5)+13(y+5)=0 (y+5)(4y+13)=0 13 y = -5, - 4 So, No relation 50. (b): I. 𝑥 2 + 41𝑥 + 418 = 0 x2+19x+22x+418=0 x(x+19)+22(x+19)=0 x(x-11) −10(x−11)=0 (x+19)(x+22)=0 (x-11)(x-10)=0 II. 𝑦 2 − 25𝑦 + 156 = 0 3x(x+4)+11(x+4)=0 4y2+20y+13y+65 =0 x2 −11x −10x +110=0 x =11,10 3x2+12x+11x+44=0 II. 4𝑦 2 + 33𝑦 + 65 = 0 Hence, no relation. x= -19, -22 II. 𝑦 2 + 47𝑦 + 550 = 0 y2+22y+25y+550 =0 y2-13y -12y +156=0 y(y+22)+25(y+22)=0 y(y-13) -12(y-13)=0 (y+22)(y+25)=0 (y-13)(y-12)=0 y = -22,-25 y= 13,12 So, x ≥ y So, x < y 22 ou So, x > y II. y² + 26y + 28y + 728 = 0 y = –15, 24 p y(y+17)+18(y+17)=0 43. (a): I. x² + 25x + 6x + 150 = 0 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 1. (c): I. 2x² - 17x + 36 = 0 2x² - 8x – 9x + 36 = 0 2x(x – 4) – 9 (x – 4) = 0 (2x – 9) (x – 4) = 0 5. (b): I. 4x² + 27x + 45 = 0 4x² + 12x + 15x + 45 = 0 4x(x + 3) + 15 (x + 3) = 0 (4x + 15) (x + 3) = 0 9 x= 2 ,4 𝑥= II. 3y² - 22y + 40 = 0 3y² - 12y – 10y + 40 = 0 3y(y – 4) – 10 (y – 4) = 0 (y – 4) (3y -10) = 0 4 p ou 10 −22 𝑦 = −4, 5 𝑥≥𝑦 𝑥>𝑦 2. (a): I. x² + 21x + 108 = 0 x² + 9x + 12x + 108 = 0 x(x + 9) + 12 (x + 9) = 0 (x + 12) (x + 9) = 0 x= -12, -9 II. y² + 14y + 48 = 0 y² + 6y+ 8y+ 48 = 0 y(y + 6) + 8 (y + 6) = 0 (y + 8) (y + 6) = 0 y = -8, -6 y>x gr 6. (a): I. x³ = 2744 x = 14 II. y² = 324 y = ± 18 So, no relation can be established between x & y. xa m 7. (e): I. (5x – 7)² = 4 – x (3x – 1) 25x² + 49 – 70x = 4 – 3x² + x ⇒ 28x² – 71x + 45 = 0 28x² – 36x – 35x + 45 = 0 4x (7x – 9) –5 (7x – 9) = 0 (7x – 9) (4x – 5) = 0 3. (d): I. 2x² + 7x – 60 = 0 2x² + 15x – 8x – 60 = 0 x(2x + 15) – 4 (2x + 15) = 0 (x – 4) (2x + 15) = 0 te −15 𝑥 = 4, 2 , −3 II. 5y² + 42y + 88 = 0 5y² + 20y + 22y + 88 = 0 5y (y + 4) + 22 (y + 4) = 0 (5y + 22) (y + 4) = 0 y = 4, 3 @ ce II. 3y² - 28y + 64 = 0 3y² - 12y- 16y + 64 = 0 3y (y- 4) – 16 (y – 4) = 0 (3y – 16) (y – 4) = 0 4. (e): I. x² - 2x – 24 = 0 x² - 6x + 4x – 24 = 0 x(x – 6) + 4 (x – 6) = 0 (x + 4) (x- 6) = 0 x= 6, -4 II. y² + 3y – 40 = 0 y² + 8y – 5y – 40 = 0 y(y + 8) – 5 (y + 8) = 0 (y – 5) (y + 8) = 0 y = 5, -8 No relation can be established 5 7 4 5 2 II. (4y – 3)² = y (4y – 1) – 1 16y² + 9 – 24y = 4y² – y – 1 ⇒ 12y² –23y +10 = 0 12y² – 15y – 8y + 10 = 0 3y (4y – 5) –2 (4y – 5) = 0 (4y – 5) (3y – 2) = 0 ⇒ y =4 ,3 𝑦 = 3 ,4 y≥x 9 ⇒x= , 16 23 −15 So, x ≥ y. 8. (b): I. 10x² – 29x + 21 = 0 10x² – 15x – 14x + 21 = 0 5x (2x – 3) –7 (2x – 3) = 0 (2x – 3) (5x – 7) = 0 3 7 ⇒ x =2 ,5 II. 2y² – 19y + 45 = 0 2y² – 10y – 9y + 45 = 0 2y (y – 5) –9 (y – 5) = 0 (y – 5) (2y – 9) = 0 9 ⇒ y = 5, 2 So, y > x. Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 9. (c): I. x² + 13x + 42 = 0 12. (e): (𝑥 + 𝑦)2 = 361 ⇒ 𝑥 + 𝑦 = ±19 … … (𝑖) ⇒ 92442 = 𝑦 2 + 92361 ⇒ 𝑦 2 = 81 ⇒ 𝑦 = ±9 … . . (𝑖𝑖) Using (i) and (ii) When y=9 ⇒ 𝑥 + 𝑦 = ±19 ⇒ 𝑥 = 10, −28 When y= - 9 ⇒ 𝑥 + 𝑦 = ±19 ⇒ 𝑥 = −10, 28 So, no relation can be obtained. 13. (b): √𝑥 + 4 = √225 − √121 ⇒ √𝑥 + 4 = 4 ⇒ 𝑥 + 4 = 16 ⇒ 𝑥 = 12 And 𝑦 2 = 473 − 329 ⇒ 𝑦 = ±12 So, 𝑥 ≥ 𝑦 x² + 7x + 6x + 42 = 0 x (x + 7) +6 (x + 7) = 0 (x + 7) (x + 6) = 0 ⇒ x = – 7, –6 II. y² + 8y + 12 = 0 p y² + 6y + 2y + 12 = 0 y (y + 6) +2 (y + 6) = 0 (y + 6) (y + 2) = 0 1 (2 – 𝑥 2 1= − 1= 11 36𝑥 11 ) 𝑥 36𝑥 2 72𝑥 –11 36𝑥² gr 10. (a): I. 1 = ou ⇒ y = –6, –2 So, y ≥ x. 36x² = 72x – 11 36x² – 72x + 11 = 0 36x² – 66x – 6x + 11 = 0 6x (6x – 11) –1 (6x – 11) = 0 (6x – 11) (6x – 1) = 0 6 9 , 1 6 II. ( 3 + 𝑦 ) = 13 14𝑦 2 + 27 3𝑦 m 14𝑦 11 = 13 14y² + 27 = 39y 14y² – 39y + 27 = 0 xa ⇒x= 14. (a): te 14y² – 21y – 18y + 27 = 0 7y (2y – 3) –9 (2y – 3) = 0 7𝑥 2 − 21𝑥 − 23𝑥 + 69 = 0 ⇒ (7𝑥 − 23)(𝑥 − 3) = 0 23 ⇒ 𝑥 = 3, 7 15. (c): (2y – 3) (7y – 9) = 0 3 9 @ ce ⇒ y =2 ,7 And 3𝑦 2 − 21𝑦 − 19𝑦 + 133 = 0 ⇒ (3𝑦 − 19)(𝑦 − 7) = 0 19 ⇒ 𝑦 = 7, 3 So, no relation can be established between x and y. 11. (c): 𝑥 2 + 24𝑥 + 119 = 0 ⇒ x 2 + 7x + 17x + 119 = 0 ⇒ (x + 7)(x + 17) = 0 ⇒ 𝑥 = −7, −17 And 3𝑦 2 + 10𝑦 + 7 = 0 ⇒ 3𝑦 2 + 3𝑦 + 7𝑦 + 7 = 0 ⇒ (𝑦 + 1)(3𝑦 + 7) = 0 ⇒ 𝑦 = −1, − 7 So, 𝑥 < 𝑦 16. (a): I. 8x²–10x+3=0 8x²–6x–4x+3=0 2x(4x–3)–1(4x–3)=0 (2x–1)(4x–3)=0 1 3 x=2 or 4 II. 5y² + 14y–3=0 5y²+15y–y–3=0 5y(y+3)–1(y+3)=0 (5y–1)(y+3)=0 1 3 y=5 or –3. So, x<y 24 223𝑥 + 122𝑦 = 791 … … (𝑖) 122𝑥 + 223𝑦 = 589 … … (𝑖𝑖) Adding equation (i) and (ii) 345(𝑥 + 𝑦) = 1380 𝑥+𝑦 = 4 … … . (𝑖𝑖𝑖) Subtract equation (ii) from (i) 101(𝑥 − 𝑦) = 202 𝑥 − 𝑦 = 2 … … (𝑖𝑣) From (iii) and (iv) 𝑥 = 3, 𝑦 = 1 So, 𝑥 > 𝑦 ∴ Adda247 Publications x>y For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 22. (a): I. x² - 8x + 15 = 0 x² - 5x – 3x + 15 = 0 x(x - 5) – 3 (x - 5) = 0 ∴ x = 3 or 5 II. 2y² - 5y – 3 = 0 2y² - 6y + y – 3 = 0 2y (y - 3) + 1 (y – 3) = 0 4 x=–3 , –3 II. y²+9y+20=0 y²+5y+4y+20=0 y(y+5) + 4(y+5) =0 y=–5 , –4 ∴x>y 𝑦 = 3 𝑜𝑟 − 1 2 ∴x≥y p 17. (a): I. 3x²+13x+12=0 3x²+9x+4x+12=0 3x(x+3) +4(x+3) =0 23. (e): I. 5x² + 11x + 2 = 0 5x² + 10x + x + 2 = 0 5x(x + 2) +1 (x + 2) = 0 19. (d): I. x³=216 x=(216)1/3 x=6 II. 2y²–25y+78=0 2y²–12y–13y+78=0 2y(y–6)–13(y–6) =0 24. (b): I. 4x + 2y = 4 …(i) II. 3x + 5y = 3 …(ii) Multiplying (i) by 5 & (ii) by 2 and on solving x = 1, y = 0 ∴x>y ∴ y≥x. 1 x = -2 or − 5 gr II. 4y² + 13y + 3 = 0 4y² + 12y + y + 3 = 0 4y (y + 3) + 1 (y + 3) = 0 1 ∴ y = -3 𝑜𝑟 − 4 m ∴ no relation xa 13 y= 2 , 6. ou 18. (e): I. x²–4x–5=0 x²–5x+x–5=0 x(x–5) +1(x–5) =0 x=5 , –1. II. 7y²–25y–12=0 7y²–28y+3y–12=0 7y(y–4)+3(y–4)=0 (y–4) (7y+3) = 0 y= 4 , –3/7 ∴ No relation. @ ce te 20. (e): I. 5x² + 31x + 48 = 0 5x² + 15x + 16x + 48 = 0 5x (x + 3) + 16 (x + 3) = 0 x = –3, –16/5 II. 3y² + 27y + 42 = 0 3y² + 21y + 6y + 42 = 0 3y (y + 7) + 6 (y + 7) = 0 y = –7, –2 So, Relation cannot be established 25. (d): I. 6x² + x – 15 = 0 6x² - 9x + 10x – 15=0 3x (2x - 3) +5 (2x – 3)= 0 21. (b): I. 6x² + 17x + 5 = 0 6x² + 2x + 15x + 5 = 0 2x (3x + 1) +5 (3x + 1) = 0 5 1 ∴ 𝑥 = − 2 𝑜𝑟 − 3 II. 2y² + 21y + 49 = 0 2y² + 14y + 7y + 49 = 0 2y (y + 7) +7(y + 7) = 0 𝑜𝑟 − 2 5 3 II. 4y² - 24y + 35 = 0 4y² - 14y – 10y + 35 = 0 2y(2y - 7) – 5 (2y - 7) = 0 ∴𝑦= 7 2 𝑜𝑟 5 2 ∴y>x 26. (a): I. x² – 11x + 30 = 0 x² – 6x – 5x + 30 = 0 x (x – 6) –5 (x – 6)= 0 (x – 6) (x – 5) = 0 x = 6, 5 II. 56y² – 151y + 99 = 0 56y² – 88y – 63y + 99 = 0 8y (7y – 11) –9 (7y – 11) = 0 (7y – 11) (8y – 9) = 0 11 9 7 y = 7 ,8 𝑦 = −7, − 2 So, x > y. ⇒x>y 25 3 ∴ 𝑥= Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 1 27. (e): I. x² – 4√3(√3 + 1) 𝑥 + 48√3 = 0 x² – 12x –4√3𝑥 + 48√3 = 0 x² + 15 = 8x x² – 8x + 15 = 0 x² – 5x – 3x + 15 = 0 x (x – 5) –3 (x – 5) = 0 (𝑥 − 5)(𝑥 – 3) = 0 x = 3, 5 II. y² – 2√5 (√5 + 2) 𝑦 + 40√5 = 0 y² – 10y –4√5𝑦 + 40√5 = 0 y (y – 10) –4√5 (y – 10) = 0 𝑦 II. 2 + 2𝑦 = 5 (y – 10) (y – 4√5) = 0 𝑦 2 + 21 2𝑦 y² + 21 = 10y y² – 10y + 21 = 0 y² – 7y – 3y + 21 = 0 y (y – 7) –3 (y – 7) = 0 (y – 7) (y – 3) = 0 y = 3, 7 So, no relation between x and y can be established. 20 28. (c): I. 21 + 𝑥 (43 + 𝑥 ) = 0 20 =0 𝑥² gr + =0 21x² + 43x + 20 = 0 21x² + 28x + 15x + 20 = 0 7x (3x + 4) + 5 (3x + 4) = 0 (3x + 4) (7x + 5) = 0 m 31. (a): I. 5𝑥 2 − 25𝑥 − 6𝑥 + 30 = 0 5𝑥(𝑥 − 5) − 6(𝑥 − 5) = 0 (𝑥 − 5)(5𝑥 − 6) = 0 −4 −5 7 28 12y + 𝑦 + 37 = 0 12𝑦 2 + 28 + 37𝑦 𝑦 =0 xa x= 3 , 7 II. 4(3𝑦 + 𝑦 ) + 37 = 0 −7 −4 @ ce y= 4 , 3 te 12y² + 37y + 28 = 0 12y² + 21y + 16y + 28 = 0 3y (4y + 7) +4 (4y + 7) = 0 (4y + 7) (3y + 4) = 0 So, x ≥ y 29. (a): I. (x + 15)² = (y + 19)² x + 15 = y + 19 x–y=4 … (i) II. x² – y² = 112 (x + y) (x – y) = 112 …(ii) From (i) and (ii), we get: x + y = 28 … (iii) Now, from (i) and (iii), we get: x = 16, y = 12 So, x > y 26 =5 ou y = 10, 4√5 So, no relation can be established between x and y. 𝑥 𝑥² 21𝑥 2 + 43𝑥 + 20 21 p x = 12, 4√3 43 8 = 3𝑥 3𝑥² (x – 12) (x – 4√3) = 0 21 + 8 𝑥 2 + 15 x (x – 12) –4√3 (x – 12) = 0 1 5 30. (e): I. 3 + 𝑥 2 = 3𝑥 6 𝑥 = 5, 5 II. 8𝑦 2 − 8𝑦 − 4𝑦 + 4 = 0 8y(y – 1) –4 (y–1) = 0 1 y = 1, 2 x>y 32. (e): I. 7𝑥 2 − 14𝑥 − 3𝑥 + 6 = 0 7𝑥(𝑥 − 2) − 3(𝑥 − 2) = 0 (7𝑥 − 3)(𝑥 − 2) = 0 𝑥 = 2, 3 7 II. 5𝑦 2 − 20𝑦 − 4𝑦 + 16 = 0 5𝑦(𝑦 − 4) − 4(𝑦 − 4) = 0 4 𝑦 = 4, 5 No relation 33. (e): I. 13𝑥 2 + 13𝑥 − 4𝑥 − 4 = 0 13x (x +1) – 4 (x + 1) = 0 (13𝑥 − 4) (𝑥 + 1) = 0 4 𝑥 = −1, 13 II. 2𝑦 2 + 3𝑦 − 2𝑦 − 3 = 0 𝑦(2𝑦 + 3) − 1(2𝑦 + 3) = 0 (y – 1) (2y + 3) = 0 –3 y = 1, 2 No relation Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 13 39. (c): I. x² + 14x - 32 = 0 x² + 16x -2x - 32 = 0 x (x +16) -2 (x +16) = 0 (x -2) (x + 16) = 0 x = –16, 2 II. y² – y – 12 = 0 y² – 4y + 3y – 12 = 0 y(y – 4) + 3(y – 4) = 0 (y + 3) ( y – 4) = 0 y = – 3, 4 No relation y=6, 2 x>y x = –1, ou 35. (e): I. 15𝑥 2 + 15𝑥– 5𝑥 – 5 = 0 15𝑥(𝑥 + 1) − 5(𝑥 + 1) = 0 (𝑥 + 1)(15𝑥 − 5) = 0 1 3 gr II. 6𝑦 2 + 6𝑦 − 4𝑦 − 4 = 0 6y (y+1) – 4(y+1) = 0 (y+1) (6y–4)=0 y = -1, 2 3 40. (a): I. x² – 9x + 20 = 0 x² – 5x – 4x + 20 = 0 x (x – 5) –4 (x – 5) = 0 (x – 4) (x – 5) = 0 x = 4, 5 II. 2y² – 12y + 18 = 0 2y² – 6y – 6y + 18 = 0 2y (y – 3) –6 (y – 3) =0 (2y – 6) (y – 3) = 0 y = 3, 3 x>y te xa m No relation 36. (e): I. x² – 12x + 32 = 0 x² – 8x – 4x + 32 = 0 x (x – 8) – 4 (x – 8) = 0 (x – 8) (x – 4) = 0 x = 8, 4 II. y² – 20y + 96 = 0 y² – 12 y – 8y + 96 = 0 y(y – 12) – 8 (y – 12) = 0 (y – 8) (y – 12) = 0 y = 8, 12 y≥x @ ce 37. (b): I. 2x² – 3x – 20 = 0 2x² – 8x + 5x – 20 = 0 2x (x – 4) + 5(x – 4) = 0 (x – 4) (2x + 5) = 0 x = 4, –5/2 II. 2y² + 11y + 15 = 0 2y² + 6y + 5y + 15 = 0 2y (y + 3) + 5 (y + 3) =0 (2y + 5) (y + 3) =0 –5 y = 2 , –3 x≥y 38. (c): I. x² – x – 6 = 0 x² – 3x + 2x – 6 = 0 x (x – 3) +2 (x – 3) = 0 (x – 3) (x + 2) = 0 x = 3, –2 27 p II. y² – 6y + 8 = 0 y² – 2y – 4y + 8 = 0 y (y – 2) – 4 (y – 2) = 0 (y – 2) (y – 4) = 0 y = 2, 4 No relation can be established between x and y 34. (a): I. 3𝑥 2 − 36𝑥 − 24𝑥 + 288 = 0 3𝑥(𝑥 − 12) − 24(𝑥 − 12) = 0 (𝑥 − 12)(3𝑥 − 24) = 0 𝑥 = 12, 8 II. 4𝑦 2 − 24𝑦 − 26𝑦 + 156 = 0 4𝑦(𝑦 − 6) − 26(𝑦 − 6) = 0 (𝑦 − 6)(4𝑦 − 26) = 0 41. (d): I. x² + 9x = 25x – 63 x² – 16x + 63 = 0 x = 9, 7 II. 4y² – 34y + 72 = 0 4y² – 18y – 16y + 72 = 0 9 𝑦 = 2,4 ∴x>y 1 225 42. (c): I. 5 × x = – x + 14 – 45 = x² – 14x x² – 14x + 45 = 0 x² – 9x – 5x + 45 x = 9, 5 II. 21y = y² + 90 y² – 21y + 90 = 0 y² – 15y – 6y + 90 = 0 y = 15, 6 ∴ No relation Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 43. (a): I. 6x + 7y = 15 II. 3x + 14y = 19.5 Solving (i) and (ii) 8 6 7 x>y x= 44. (c): I. 7x² + 5x – 18 = 0 7x² – 9x + 14x – 18 = 0 x (7x – 9) +2 (7x – 9) = 0 9 II. 3y² + 4y – 20 = 0 3y² + 10y – 6y – 20 = 0 y ( 3y + 10) – 2 (3y + 10) = 0 y= @ ce II. 30y² – 61y + 30 = 0 30y² – 36y – 25y + 30 = 0 6y (5y – 6) –5(5y – 6) = 0 (5y – 6) (6y – 5) = 0 6 5 y = 5,6 So, x ≤ y 47. (d): I. x² – 16x + 63 = 0 x² – 9x – 7x + 63 = 0 x (x – 9) –7 (x – 9) = 0 (x – 9) (x – 7) = 0 x = 7, 9 II. y² – 12y + 35 = 0 y² – 7y – 5y + 35 = 0 y (y – 7) – 5 (y – 7) = 0 (y – 7) (y – 5) = 0 y = 5, 7 So, x ≥ y 28 m xa 2 te 1 −5 6 , −3 7 gr 45. (e): I. x² + 5x = 25x x² – 20x = 0 x (x – 20) = 0 x = 0, 20 II. 3y² + 2y = 2y + 12 3y² = 12 y² = 4 y = ±2 ∴ No relation. , 8 49. (e): I. (x – 2)² = x – 2 x² + 4 – 4x = x – 2 x² – 5x + 6 = 0 x² – 3x – 2x + 6 = 0 x (x –3) –2 (x – 3) = 0 (x – 3) (x – 2) = 0 x = 2, 3 II. 9y² - 36y + 35 = 0 9y² – 21y – 15y + 35 = 0 3y (3y – 7) –5 (3y – 7) = 0 (3y – 7) (3y – 5) = 0 ∴ No relation 6 −5 ou 10 5 , So, no relation y = 2, – 3 x= 4 II. 42y² + 53y + 15 = 0 42y² + 35y + 18y + 15 = 0 7y (6y + 5) +3 (6y + 5) = 0 (6y + 5) (7y + 3) = 0 x = 7, –2 46. (c): I. 12x² – 16x + 5 = 0 12x² – 10x – 6x + 5 = 0 2x (6x – 5) –1 (6x – 5) = 0 (6x – 5) (2x – 1) = 0 −3 p 7 x= , y= 48. (e): I. 32x² + 44x + 15 = 0 32x² + 24x + 20x + 15 = 0 8x (4x + 3) +5 (4x + 3) = 0 (4x + 3) (8x + 5) = 0 7 5 y = 3 ,3 So, no relation 50. (b): I. 18x² + 39x + 20 = 0 18x² + 24x + 15x + 20 = 0 6x (3x + 4) +5 (3x + 4) = 0 (3x + 4) (6x + 5) = 0 −4 −5 x= 3 , 6 II. 10y² + 29y + 21 = 0 10y² + 15y + 14y + 21 = 0 5y (2y + 3) +7 (2y + 3) = 0 (2y + 3) (5y + 7) = 0 y= −3 −7 2 , 5 So, x > y 51. (e): I. x² + 4x – 3x – 12 = 0 (x + 4) (x – 3) = 0 x = 3, –4 II. y² + 5y -3y -15 = 0 (y + 5) (y -3) = 0 y = –5, 3 ⇒ no relation can be established Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 52. (b): I. 6x² – 2x – 3x + 1 = 0 (2x – 1) (3x – 1) = 0 54. (d): I. x² + 2x + 5x + 10 = 0 (x + 2) (x + 5) = 0 x = –2, –5 II. 2y² + 4y + y + 2 = 0 (y + 2) (2y + 1) = 0 1 1 x= , 2 3 II. 3y² + 9y – y – 3 = 0 3y (y + 3) – 1 (y + 3) = 0 (3y – 1) (y + 3) = 0 y =– 3, 1 y = − 2, – 2 1 ⇒x≤y 3 p ⇒x≥y 55. (e): I. x² – 5x + 3x – 15 = 0 (x – 5) (x + 3) = 0 x = 5, –3 II. y² + 4y + y + 4 = 0 (y + 4) (y + 1) = 0 y = –1, –4 ⇒ No relation can be established between x & y. ou 53. (d): I. 12x² – 3x – 4x + 1 = 0 (3x – 1) (4x – 1) = 0 1 1 x = 3,4 II. 6y² – 2y – 3y + 1 = 0 (2y – 1) (3y – 1) = 0 1 1 gr 𝑦 = 2,3 ⇒y≥x Mains Solutions m Days Quantity II > Quantity I xa 3. (a): Quantity I: Let present age of Randy = x x−10 = 24 − 19 te 1. (b): Quantity I Let the number be 10x +y Acc. to question y=x+2 and (10x +y) (x+ y) = 144 (10x + x+ 2) (x+ x + 2) =144 (11x+ 2) (x +1) = 72 11x² + 13x + 2= 72 11x² + 13x – 70 = 0 11x² + 35x – 22x – 70 = 0 On solving x = 2 Number is 24 Quantity II > Quantity I @ ce 2. (b): Quantity I Let they meet after ‘n’ days Applying Arithmetic progression n n [2 × 15 + (n − 1)(−1)] + [2 × 10 + (n − 2 2 1)2] = 165 n [30 − n + 1 + 20 + 2n − 2] = 165 2 n² + 49n – 330 = 0 n = –55, +6 so, they will meet in 6 days Quantity II Let required no. of days 12 x – 10 = 5×12 x = 70 years Quantity II: Required average = 111 −2×42 4 14× 609 12 203 = 24 = 8 777 −84 = 2 12 = 25.375 year Quantity I > Quantity II 4. (a): Quantity I: Let C.P of 100 gm = 100 Rs So, he purchases 120 gm in 100 Rs 105 And sell 90 gm in = 100 × 100 RS So, % profit = = S.P.−C.P. C.P. 21 5 − 18 6 5 6 105 100 − × 100 = 90100120 × 100 × 100 = 36 21−15 18 5 6 120 × 100 = 90 × 100 = 40% profit Quantity II: 50% → 12 Rs So, 100→ 24 Rs So, 80% → 19.2 29 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations (e): Quantity I: Let first we arrange all 4 men in 4! Ways then we arrange 4 women in 4P4 ways at 4 places either left of the man or right of the man. = 4! × 4P4 + 4! × 4P4 = 2 × 576 = 1152 Quantity II: Let first we arrange 4 men in 3! Ways, then 4 women can be arranged in 4 places in 4P4 ways = 3! × 4P4 = 144 = 144 ×8 = 1152 6. (b):Quantity I: Let C.P. of both shirts be Rs. 100 Total C.P. = Rs. 200 Total S.P. of both shirts = 1.2 × 100 + 0.9 × 100 = Rs. 210 200 day 1 Total days = 21 2 Quantity II > quantity I 10. (b): × 100 = 5% gr Overall profit = (210−200) 5 x 4 Profit% (5−4) 4 × 100 = 25% Quantity II > Quantity I 7 2 (b):Quantity I: Volume of cube left = 73 − π (2) × 7 = 343 − 22 7 × 49×7 4 te 7. xa y m Quantity II: Let C.P. of one-metre cloth be Rs. x And S.P. of one-metre cloth be Rs. y Then, 20y − 20x = 5x ⇒ 20y = 25x ⇒ = = 343-269.5 = 73.5 cm3 Quantity II: Surface area of cube left 7 2 7 = 6 × 72 − 2. π (2) + 2π (2) 7 @ ce = 294 − 77 + 154 = 371 cm2 Quantity II > Quantity I 8. 1 (e): Quantity I: Liters of milk removed =5 ×10=2 ltr. Remaining milk = 8 ltr 1 Liters of water removed = 5 × 2.5 = 0.5 ltr. Remaining water = 2 ltr So milk : water = 4:1 2+x 8 4 =1 ⇒ x = 30 32 8+y 1 = 4⇒ y = 128 − 8 = 120 ltr. Quantity II : 120 ltr Quantity I = Quantity II. 30 (b):Let, total units of work be 32 units Then P does 2 units per day. & Q does 1 unit per day. Quantity I: 3 units are done in 2 days. 30 units are done in 20 days. On 21st day P does 2 units and work gets completed. Quantity II: 3 units are done in 2 days 30 units are done in 20 days. On 21st day Q does 1unit work. 1 P completes the remaining one unit in another 2 p 5. 9. ou There will be 0% profit if the book were sold for Rs.4.8 more Quantity I > Quantity II ∠ABD = 90° (angle in semicircle) ∠DBP = 90° ∠BCD = ∠DAB = 40° (angle subtended by same arc in same segment) ∠BCD + ∠CPB + ∠CBD + ∠DBP = 180° ⇒ 40° + 20° + ∠𝐷𝐵𝐶 + 90° = 180° ⇒ ∠𝐷𝐵𝐶 = 30° ∠𝐴𝐷𝐵 = 180° − ∠𝐷𝐴𝐵 − ∠𝐴𝐵𝐷 = 180° − 40° − 90° = 50° Quantity II > Quantity I 11. (a): Quantity I: 12320 = 𝜋(7𝑥)2 × 10𝑥 22 ⇒ 12320 = 7 × 49𝑥 3 × 10 ⇒ 𝑥3 = 8 ⇒ 𝑥 = 2 Height = 10x = 20 cm. 1 Quantity II: 3 𝜋 × 22 × 3 = 𝜋 × 22 × ℎ ⇒ h = 1 cm. Level of kerosene in jar = 1 cm. Quantity I > Quantity 2 12. (c): Quantity I: 𝑝 2 − 18𝑝 + 77 = 0 ⇒ 𝑝 2 − 11𝑝 − 7𝑝 + 77 = 0 ⇒ (𝑝 − 11)(𝑝 − 7) = 0 ⇒ 𝑝 = 11, 7 Quantity II: 3𝑞 2 − 25𝑞 + 28 = 0 ⇒ 3𝑞2 − 21𝑞 − 4𝑞 + 28 = 0 ⇒ (3𝑞 − 4)(𝑞 − 7) = 0 4 ⇒ 𝑞 = 7, 3 Quantity I ≥ Quantity II Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 13. (b):Quantity I: Let, speed of current be x m/minute 200 200 = 48+𝑥 + 10 48−𝑥 ⇒ 𝑥 = 32𝑚/𝑚𝑖𝑛. Quantity II: 22 7 3×2× ×49 14 also, 𝑛(𝑥 + 10.8) = (𝑚 + 𝑛)𝑥 or, 10.8𝑛 = 𝑚𝑥 or, 𝑚𝑥 = 10.8 …………….(ii) Dividing (i) by (ii), = 66𝑚/𝑚𝑖𝑛 𝑚 Quantity II > Quantity I. 𝑛 = 3 2 14. (e): Let m → men w→ 𝑤𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑛 𝑏 →boy (10𝑚 + 15𝑤) 8 = (12𝑚 + 8𝑤)10 80𝑚 + 120𝑤 = 120𝑚 + 80𝑤 40𝑚 = 40𝑤 And, m = w = 2B Quantity I → 2𝑚 + 4𝑤 + 18𝑏 → 2𝑚 + 4𝑚 + 9𝑚 → 15m Quantity II → 9𝑚 + 3𝑤 + 6𝑏 ⇒ 9𝑚 + 3𝑚 + 3𝑚 → 15𝑚 ∴ Quantity I = Quantity II Putting this in equation (i) 15. (a): Quantity I < Quantity II 4.8 𝑥 𝑥 = 10.8 𝑥2 = ou p or, 𝑥 2 = 4.8 × 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑠 𝑠𝑡𝑒𝑝 𝑐𝑎𝑛 𝑏𝑒 𝑑𝑖𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑙𝑦 𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑒𝑑 𝑡𝑜 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑠𝑒 𝑡𝑦𝑝𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠 10.8 [ ] (𝑆ℎ𝑜𝑟𝑡 − 𝑐𝑢𝑡 𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑎𝑐ℎ) 48×108 2 100 12×4×12×9 or, 𝑥 = 10 = 7.2 hrs. gr or, 𝑥 = 10×10 12×3×2 m 18. (b):Quantity I: @ ce te xa Babu returns home 40 minute earlier so he saves 20 min on going and 20 min in returning So girlfriend travels 100 min before meeting point Because babu does not go G to A to A and A to O. Time Speed Babu 20 1 5 ×40 200 km/hr : : Girlfriend 100 5 I ×40 40 km/hr Quantity I → 200 km/h Quantity II → 197 km/h ∴ Quantity I> Quantity II 16. (b):CP MP SP 555x 700x (700x – 68) 120 ∴ 100 × 555𝑥 = 700𝑥 − 68 666𝑥 = 700𝑥 − 68 34x = 68 x=2 ∴ Quantity I → CP = 2 × 555 = 1110 Rs. ∴ Quantity I < Quantity II 17. (b):Let, Manoj and Shubham take ‘𝑥’ hrs. to complete the work working together. Let, Manoj does ‘𝑚’ units per hour. And Shubham does ‘𝑛’ units per hour. ATQ, 𝑚(𝑥 + 4.8) = (𝑚 + 𝑛)𝑥 or, 4.8𝑚 = 𝑛𝑥 …………..(i) 31 Draw EF || BC Now, E and F are mid-points of AC and AB respectively. AF = 5 cm, EF = 5 cm Radius of semi-circle = 5 cm 1 Area of shaded region = 4 Area of circle – Area of ∆AFE 1 22 1 = 4 × 7 × 5 × 5 − 2 × 5 × 5 ≈ 7.14 cm2 Quantity I < Quantity II 19. (a): Quantity 1: Let original duration and speed be ‘𝑡’ hr. and ‘𝑠’ km/hr. respectively. ATQ, 𝑠𝑡 = 3000 ………..(i) Also, (𝑠 − 1000)(𝑡 + 1) = 3000 ………..(ii) ⇒ 𝑠𝑡 + 𝑠 − 100𝑡 − 100 = 3000 ⇒ 3000 + 𝑠 − 100𝑡 − 100 = 3000 ⇒ 𝑠 − 100𝑡 = 100 Putting ‘𝑠’ from (i), 3000 𝑡 − 100𝑡 = 100 ⇒ 100𝑡 2 + 100𝑡 − 3000 = 0 ⇒ 𝑡 2 + 𝑡 − 30 = 0 ⇒ (𝑡 + 6)(𝑡 − 5) = 0 ⇒ 𝑡 = 5 hr. Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations Quantity 2: 3 New speed = 4th of original 1 By equation (ii) × 3 – equation (iii) 6y + 9z = 99 6y + 5z = 71 − − − 4 Hence, new time = th of original 1 3 20 1 23. (e): I. x =√(36)2 × (1296)4 = √6 × 6 = 6 1 i.e., th of original time = = 3 60 3 or, Original time = 1 hr. Quantity I > Quantity II 4z = 28 ⇒ z = 7 from equation (ii) 2y + 3 × 7 = 33 ⇒ y = 6 Hence, none of the above relationships is established. 7 20. (e): Perimeter of smaller wheel = 2𝜋. = 7𝜋 cm ou ... (i) ... (ii) ... (iii) 24. (d):by equation (i) × 5 – (ii) × 8 40x + 35y = 675 40x + 48y = 792 − − − −13y = −117 ⇒ y=9 from equation (i) 8x + 7 × 9 = 135 ⇒ 8x = 135 – 63 =72 ⇒ x = 9 from equation (iii) 9 × 9 + 8z = 121 ⇒ 8z = 121 – 81 = 40 ⇒ z = 5 Clearly x = y > z m ... (iv) 25. (e): I. (𝑥 + 𝑦)3 = 1331 ⇒ x + y = 11 ⇒ y = 11 – x put it in equation (iii) x(11– x) = 28 ⇒ 11x – 𝑥 2 = 28 𝑥 2 – 11x + 28 = 0 ⇒ 𝑥 2 – 7x –4x + 28 = 0 x(x – 7) – 4(x – 7) = 0 ⇒ (x – 7) (x – 4) = 0 So, x = 7, 4 from equation (i) y = 4, 7 from equation (ii) 7 – 4 + z = 0, z = – 3 or, 4 – 7 + z = 0, z = 3 Hence. no relation can be established. xa 21. (a): 7x + 6y + 4z = 122 4x + 5y + 3z = 88 9x + 2y + z = 78 By equation (iii) × 3 – equation (ii) 27x + 6y + 3z = 234 4x + 5y + 3z = 88 − − − − 23x + y = 146 By equation (iii) × 4 – equation (i) 36x + 8y + 4z = 312 7x + 6y + 4z = 122 − − − − 29x + 2y = 190 By equation (iv) × 2 – equation (v) 46x + 2y = 292 29x + 2y = 190 − − − 17x = 102 x=6 from eqn. (iv) 23 × 6 + y = 146 ⇒ y = 146 – 138 = 8 From equation (iii) 9 × 6 + 2 × 8 + z = 78 ⇒ 54 + 16 + z = 78 z = 78 – 70 = 8; ⇒ x = 6, y = 8, z = 8 Hence, x < y = z p 2 gr 14 Perimeter of larger wheel= 2𝜋. = 14𝜋 𝑐𝑚 2 Let , both take ‘𝑥’ revolutions per second, Then, (7𝜋 + 14𝜋)10𝑥 = 1990.50 − 10.5 198 198×7 or, 𝑥 = 21𝜋 = 21×22 = 3 speed of smaller wheel = 7𝜋 × 3 = 21𝜋 cm./s. Quantity I = Quantity II @ ce te ... (v) 22. (c): By equation (ii) × 2 – equation (i) 8x + 6y = 118 7x + 6y = 110 − − − x = 8 from equation (i), 7 × 8 + 6y = 110 ⇒ 6y = 110 – 56 = 54 ⇒ y = 9 from equation (iii) 8 + z = 15 ⇒ z = 7; clearly, x < y > z 32 26. (c): By equation (i) × 2 – (ii) 2x + 6y + 8z = 96 2 2x + 8z = 80 − − − 6y = 112 112 6 By equation (iii) 2x + 6 ×= 120 ⇒ 2x = 8 ⇒ x = 4 By equation (ii) 8z = 80 – 8 ⇒ 8z = 72 ⇒ z = 9 Hence x < y > z y= Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 3𝑥 3𝑥 + 7 – 3𝑥 + 7 3𝑥 31. (b):I. 77𝑥 2 + 58x + 8 = 0 \ / 11 × 7 4×2 and, 44 + 14 = 58 44 14 4 2 ∴x=– ,– ⇒ x=– ,– 77 77 7 11 II. 42𝑦 2 + 59y + 20 = 0 \ / 7×6 5×4 also, 35 + 24 = 59 35 24 5 4 ∴y=– ,– ⇒y=– ,– 42 42 6 7 Hence, x ≥ y = 14 – 49 – 42x = 14 × 9𝑥 2 + 14 × 21x – 49 – 42x = 126𝑥 2 + 294x 126𝑥 2 + 336x + 49 = 0 Hence x = –a , –b both roots of x are – ve 𝑦 18𝑦 − 5 II. 18𝑦 − 5 − 𝑦 = 2 𝑦 2 − 324𝑦 2 − 25 + 180𝑦 18𝑦 2 − 5𝑦 2 =2 28. (e): I. 𝑥 2 +𝑥 2 +49+14𝑥 2 𝑥 2 +7𝑥 p 𝑦 – 324𝑦 – 25 + 180y = 36𝑦 2 – 10y 359𝑦 2 – 190 y + 25 = 0 Hence y = + c, +d both roots of y are + ve ⇒ y>x = 12 2𝑥 + 49 + 14x = 12𝑥 2 + 84x 10𝑥 2 + 70x – 49 = 0 ⇒ x = – a, + b II. 𝑦 2 +𝑦 2 +64+16𝑦 𝑦 2 +8𝑦 2 = 16 𝑥 𝑥 − 11 2 + 𝑥 − 11 𝑥 Þ 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 2 + 121 − 22𝑥 𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 2 m 2𝑦 + 64 + 16y = 16𝑦 2 + 128 y 14𝑦 2 + 112y – 64 = 0 ⇒ y = + c, – d It is clear that relation cannot be established. 29. (e): I. 32. (a): I. 63𝑥 2 + 172x + 117 = 0 \ / 9×7 13 × 9 also, 91 + 81 = 172 13 9 91 81 x=– ,– ⇒x=– ,– 9 7 63 63 2 II. 30y + 162y + 216 = 0 \ / 6×5 36 × 3 × 2 also, 90 + 72 = 162 90 72 y = – 30, – 30 ⇒ y = – 3, – 2.4 Hence x > y ou 2 gr 27. (c): I. =7 xa 2𝑥 + 121 – 22x = 7𝑥 – 77x 5𝑥 2 – 55x – 121 = 0 Hence x = – a, +b 4𝑦 4𝑦 − 13 II. 4𝑦 − 13 + 4𝑦 = 9 33. (e): I. 36x 4 + 369x 2 + 900 = 0 let x 2 = p 36p2 + 369p + 900 = 0 \ / 12 × 3 75 × 12 also, 144 + 225 = 369 –144 –225 p= , 2 te 16𝑦 2 + 16𝑦 2 + 169 – 104y = (16𝑦 2 – 52y) × 9 32𝑦 2 + 169 – 104y = 144𝑦 2 – 468y 112𝑦 2 – 364y – 169 = 0 Hence y = + c, – d Hence Relation cannot be established. @ ce 30. (a): I. 99𝑥 + 149x + 56= 0 99𝑥 2 + 77x + 72x + 56 = 0 11x (9x + 7) + 8 (9x + 7) = 0 (9x + 7) (11x + 8) = 0 9x + 7 = 0 11x + 8 = 0 −7 −8 x= x= 9 11 II. 156𝑦 2 + 287y + 132 = 0 156𝑦 2 + 143y + 144y+ 132 = 0 13y (12y + 11) + 12 (12y + 11) = 0 (12y + 11) (13y + 12) = 0 12y + 11 = 0 13y + 12 = 0 −11 −12 y= y= 12 13 Hence x > y 33 36 36 2 –144 2 –225 so, x = 36 , x = 36 imaginary roots established. ⇒ relation cannot be 34. (e): I. 18x 2 –13 √7x + 14 = 0 \ / 9×2 2×7 9√7 4√7 also, – 9√7 – 4√7 = –13√7 ⇒ x = 18 , 18 II. 32y 2 – 19√6y + 9 = 0 \ / 16 × 2 3×3 also, –16√6 – 3√6 = –19√6 ⇒ y = Relation cannot be established. 16 √6 3√6 32 32 35. (e): I. x 2 – 82x + 781 = 0 \ / 1 71 × 11 also, –71 – 11 = – 82 x = 71, 11 II. y 2 – 5041 = 0 ⇒ y 2 = 5041 ⇒ y = +71, –71 Hence, relation cannot be established. Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations also, – 221 + 437 = 216 221 437 y = 247, − 247 Hence, relation cannot be established. x= –27√7 –20√7 , 36 36 II. 35y 2 + 20√3y + 63√2y + 36√6 = 0 5y (7y + 4√3) + 9√2 (7y + 4√3) = 0 (5y + 9√2) (7y + 4√3) = 0 y= −9√2 5 ,y= –4 √3 7 Hence, relation cannot be established. 437 gr 40. (c): y > x (according to sign method). xa 1. (a): I. x = ±16 II. y2 – 16y – y + 16 = 0 y (y – 16) −1(𝑦 − 16) = 0 (y −1) (𝑦 − 16) y = 1 & 16 So, no relation can be established 𝑥 = −2,2 II. 2y² - 4y – 7y + 14 = 0 2y (y – 2) -7 (y – 2) = 0 (2y – 7) (y – 2) = 0 7 1 1 2 3 𝑥 = − ,− II. 20y² + 5y + 4y + 1 = 0 (4y + 1) (5y + 1) = 0 1 1 𝑦 = −4,−5 So, y > x 5. (d): I. 2x² - 9x + 9 = 0 2x² - 6x – 3x + 9 = 0 (2x-3) (x-3) = 0 3 𝑥 = 2,3 II. 6y² - 17y + 12 = 0 6y² - 8y – 9y + 12 = 0 (2y-3) (3y-4) = 0 3 4 𝑦 = 2,3 So, x ≥ y 6. (c): I. 4x² – 17x + 15 = 0 4x² – 12x – 5x + 15 = 0 4x (x – 3) –5 (x – 3) = 0 (x – 3) (4x – 5) = 0 𝑦 = 2, 2 34 So, no relation can be established between x & y. 4. (c): I. 6x² + 3x + 2x + 1 = 0 (3x + 1) (2x + 1) = 0 te @ ce 3. (a): I. 4x² - 8x – 5 = 0 4x² - 10x + 2x – 5 = 0 2x (2x – 5) + 1 (2x – 5) = 0 (2x + 1) (2x – 5) = 0 1 5 437 Hence relation cannot be established, / 17 × 23 2. (e): I. x2 + 10x + 10x + 100 =0 x (x + 10) + 10(x +10) = 0 (x + 10) (x + 10) = 0 x = - 10 II. y2 + 10x + 3y + 30 = 0 y (y + 10) + 3(y + 10) =0 (y + 10) (y + 3) y = −10 − 3 So, x≤y II. 437y 2 + 1074y + 589 = 0 \ / 19 × 23 19 × 31 also, 361 + 713 = 1074 –361 –713 y= , m \ 13 × 19 39. (e): I. 391x 2 + 1344x + 1073 = 0 \ / 17 × 23 29 × 37 also, 493 + 851 = 1344 –493 –851 x = 391 , 391 ou 37. (e): I. 91x 2 + 298x + 187 = 0 \ / 7 × 13 17 × 11 also, 77 + 221 = 298 –77 –221 x= , 91 91 II. 247y2 + 216y – 391 = 0 38. (e): According to sign method. Relation cannot be established. p 36. (e): I. 36x 2 + 47√7x + 105 = 0 \ / 9×4 7×3×5 also, 27√7 + 20√7 = 47√7 x = 3, Adda247 Publications 5 4 For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations II. 2y² - 7y + 5 = 0 2y² - 2y – 5y + 5 = 0 (y - 1) (2y - 5) = 0 5 y = 1, 2 x>y II. 2y² – 17y + 35 = 0 2y² – 10y – 7y + 35 = 0 2y (y – 5) –7 (y – 5) = 0 (y – 5) (2y – 7) = 0 7 y = 5, 2 13. (d): I. 2x² + x – 28 = 0 2x² + 8x – 7x – 28 = 0 2x (x + 4) – 7 (x + 4) = 0 (2x – 7) (x + 4)= 0 7 x = −4, 2 II. 2y² - 23y + 56 = 0 2y² - 16y – 7y + 56 = 0 2y(y – 8) – 7(y – 8) = 0 (2y – 7) (y – 8) = 0 7 y = 2,8 y≥x So, y > x p 7. (a): I. x = 5 II. y = 5 So, x=y ou 8. (d): I. x2 + 7x – 5x – 35 =0 x (x + 7) – 5 (x + 7) =0 (x + 7) (x – 5) = 0 x = −7, 5 II. y2 + 7y + 8y + 56 = 0 y(y + 7) + 8(y + 7) = 0 (y + 7) (y + 8) = 0 y = − 8, −7 So, x≥y gr 14. (e): I. 2x² - 7x – 60 = 0 2x² - 15x + 8x – 60 = 0 x (2x – 15 ) + 4 (2x – 15) = 0 (x + 4) (2x − 15) = 0 15 x = −4, 2 II. 3y² + 13y + 4 = 0 3y² + 12y + y + 4 = 0 3y (y + 4) + 1 (y + 4) = 0 (3y + 1) (y + 4) = 0 1 y = − 3 , −4 No relation between x and y 3 x = − 17 , 1 xa 10. (a): I. 17x2 – 14x – 3 = 0 17x2 – 17x + 3x – 3 = 0 17x (x – 1) + 3(x – 1) = 0 (17x + 3) (x – 1) = 0 m 9. (a): I. x = ± 9 II. y = ± 8 So, no relation can be established te II. y2 – 2y – 35 = 0 y2 – 7y + 5y – 35 = 0 y(y −7) + 5(𝑦 − 7) = 0 y = 7, - 5 So, no relation can be established @ ce 11. (e): I. x2 + 9x – 5x – 45 = 0 x(x + 9) – 5(x + 9) = 0 (x – 5) (x + 9) = 0 x = 5, - 9 II. y2 – 5y – 8y + 40 = 0 y(y – 5) – 8(y – 5) = 0 (y – 5) (y – 8) = 0 y = 5, 8 So, x≤y 12. (a): I. x² - 8x + 15 = 0 x² - 3x – 5x + 15 = 0 (x – 3) (x – 5) = 0 x = 3, 5 35 15. (e): I. x² - 17x – 84 = 0 x² +4x – 21x – 84 = 0 (x + 4) (x – 21) = 0 x = -4, 21 II. y² + 4y – 117 = 0 y² - 9y + 13y – 117 = 0 (y – 9) (y + 13) = 0 y = 9, -13 No relation between x and y 16. (c): I. x2 = 92 x=9 II. (y – 8)2 = 32 y = 11 y>x 17. (d): I. 2x2 – 2x - x + 1 = 0 2x(x – 1) – 1(x – 1) 1 x = 2,1 II. 2y2 – 2y – 3y + 3 = 0 2y(y – 1) – 3(y – 1) = 0 y= 3 2 ,1 x≤y Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations II. 𝑦 2 + 12𝑦 + 36 = 0 𝑦 2 + 6𝑦 + 6𝑦 + 36 = 0 𝑦(𝑦 + 6) + 6(𝑦 + 6) = 0 (𝑦 + 6)(𝑦 + 6) = 0 𝑦 = −6 So, 𝑥 > 𝑦. 18. (b): I. x2 + 10x + 11x + 110 = 0 x(x + 10) + 11(x + 10) = 0 x = - 10, - 11 II. y2 + 9y + 8y + 72 = 0 y(y + 9) + 8(y + 9) y = - 9, - 8 x<y 24. (c): I. 𝑥 2 + 13𝑥 + 40 = 0 𝑥 2 + 8𝑥 + 5𝑥 + 40 = 0 𝑥(𝑥 + 8) + 5(𝑥 + 8) = 0 (𝑥 + 8)(𝑥 + 5) = 0 𝑥 = −8, −5 II. 𝑦 2 + 7𝑦 + 10 = 0 𝑦 2 + 5𝑦 + 2𝑦 + 10 = 0 𝑦(𝑦 + 5) + 2(𝑦 + 5) = 0 (𝑦 + 5)(𝑦 + 2) = 0 𝑦 = −2, −5 So, 𝑥 ≤ 𝑦. ou p 19. (d): I. x = ±2 II. y2 – 2y – 4y + 8 = 0 y(y – 2) – 4(y – 2) = 0 y = 2, 4 x≤y 20. (e): I. 𝑥 2 + 9𝑥 − 22 = 0 ⇒ x² + 11x – 2x – 22 = 0 ⇒ (x + 11) (x – 2) = 0 ⇒ x = – 11, 2 II. 2y² – 7y + 6 = 0 ⇒ 2y² – 4y – 3y + 6 = 0 ⇒ 2y(y–2)–3(y–2) =0 ⇒ (y–2) (2y–3) = 0 gr 25. (b): I. 𝑥 2 − 20𝑥 + 91 = 0 𝑥 2 − 13𝑥 − 7𝑥 + 91 = 0 𝑥(𝑥 − 13) − 7(𝑥 − 13) = 0 (𝑥 − 13)(𝑥 − 7) = 0 𝑥 = 7, 13 II. 𝑦 2 + 16𝑦 + 63 = 0 𝑦 2 + 9𝑦 + 7𝑦 + 63 = 0 𝑦(𝑦 + 9) + 7(𝑦 + 9) = 0 (𝑦 + 9)(𝑦 + 7) = 0 𝑦 = −7, −9 So, 𝑥 > 𝑦. 3 ⇒ y = 2, 2 m No relation II. 15y² + 11y + 2 = 0 15y² + 6y + 5y + 2 = 0 3y (5y + 2) + 1 (5y + 2) = 0 2 1 te ∴ y = -5 𝑜𝑟 − 3 ∴ no relation can be established @ ce 22. (a): I. 𝑥 2 + 9𝑥 + 20 = 0 𝑥 2 + 5𝑥 + 4𝑥 + 20 = 0 𝑥(𝑥 + 5) + 4(𝑥 + 5) = 0 (𝑥 + 5)(𝑥 + 4) = 0 𝑥 = −4, −5 II. 8𝑦 2 − 15𝑦 + 7 = 0 8𝑦 2 − 8𝑦 − 7𝑦 + 7 = 0 8𝑦(𝑦 − 1) − 7(𝑦 − 1) = 0 (𝑦 − 1)(8𝑦 − 7) = 0 7 𝑦 = 1, 8 So, 𝑥 < 𝑦. 23. (b): I. 𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 30 = 0 𝑥 2 − 6𝑥 − 5𝑥 + 30 = 0 𝑥(𝑥 − 6) − 5(𝑥 − 6) = 0 (𝑥 − 6)(𝑥 − 5) = 0 𝑥 = 5, 6 36 26. (e): I. 𝑥 2 − 𝑥 − 12 = 0 𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 3𝑥 − 12 = 0 𝑥(𝑥 − 4) + 3(𝑥 − 4) = 0 (𝑥 − 4)(𝑥 + 3) = 0 𝑥 = 4, −3 II. 𝑦 2 + 5𝑦 + 6 = 0 𝑦 2 + 3𝑦 + 2𝑦 + 6 = 0 𝑦(𝑦 + 3) + 2(𝑦 + 3) = 0 (𝑦 + 3)(𝑦 + 2) = 0 𝑦 = −2, −3 So, 𝑛𝑜 𝑟𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛. xa 21. (e): I. 6x² + 5x + 1 = 0 6x² + 3x + 2x + 1 = 0 3x (2x + 1) +1 (2x + 1) = 0 1 1 x = -2 or − 3 27. (a): Quantity I: 20 Required profit = 450 × 120 = Rs.75 Quantity II: 100 Required cost price = 84 × 120 = Rs.70 So, Quantity I > Quantity II. 28. (b): Quantity I: 100 40 Required female = 1152 × 30 × 60 × 1920 Quantity II: 1940 So, Quantity I < Quantity II. Adda247 Publications 100−25 100 = For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 29. (b): Quantity I: ATQ, 𝑃×12×2 100 34. (e): I. 4x2 – 4𝑥 − 3𝑥 + 3 = 0 4x(x −1) − 3 (𝑥 − 1) = 0 x = 1, 3/4 II. 7y2− 17y + 6 = 0 7y2− 14y- 3y + 6 = 0 7y (y – 2) − 3 (𝑦 − 2) = 0 y = 2 , 3/7 So, no relation can be established between x and y. 35. (a): I. 2x2 - 10x -9x + 45 = 0 2x(x - 5) - 9(x - 5) = 0 x = 5, 9/2 II. 2y2 - 8y - y + 4 = 0 2y(y -4) -1(y -4) = 0 y =4,1/2 So, x >y = 1200 𝑃 = 5,000 Rs. Quantity II: Rs.6,000 So, Quantity I < Quantity II. Area of a rectangular field = 288 3 p 30. (e): Let breadth of the field be x m. So, length of the field = (𝑥 + 4) m = 96 m2 ou ATQ, 𝑥(𝑥 + 4) = 96 𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 − 96 = 0 𝑥 2 + 12𝑥 − 8𝑥 − 96 = 0 𝑥(𝑥 + 12) − 8(𝑥 + 12) = 0 (𝑥 + 12)(𝑥 − 8) = 0 𝑥 = 8, −12 Quantity I: Length of rectangular field = 12m Quantity II: 12 m So, Quantity I = Quantity II. m 37. (a): I. x² -13x + 40= 0 x² - 5x – 8x + 40 = 0 x (x -5) – 8 (x - 5) = 0 x = 5, 8 II. 2y² - y – 15 = 0 2y² - 6y + 5y – 15 = 0 2y (y - 3) + 5 (y - 3) = 0 y=3, -5/2 x>y xa 31. (b): Quantity I: Let present age of Prashant be x years. So, present age of Shivam = (𝑥 + 8) years 𝑥 + 8 + 𝑥 = 32 𝑥 = 12 years Quantity II: 15 years So, Quantity I < Quantity II. gr 36. (b): I. x2= 144 x = −12, +12 II. y = −12 So, x≥y @ ce te 32. (e): I . x2 − 14𝑥 + 45 = 0 x2 − 9𝑥 − 5𝑥 + 45 = 0 x(x −9) − 5(𝑥 − 9) = 0 x = 9, 5 II. y2 – 12𝑦 − 6𝑦 + 72 = 0 y(y – 12) − 6(𝑦 − 12) = 0 y = 12, 6 no relation can be established between x and y. 33. (b): I. x2 + 7𝑥 + 12 = 0 x2 +4𝑥 + 3𝑥 + 12 = 0 x(x + 4) + 3(𝑥 + 4) = 0 (x +4) (x +3) = 0 x = −3, −4 II. y2 + 5𝑦 + 4𝑦 + 20 = 0 y(y + 5) + 4(𝑦 + 5) = 0 y = -5, -4 So , x≥y 38. (e): I. 5x² + 17x + 6 = 0 5x² + 15x + 2x + 6 = 0 5x (x + 3) +2(x + 3) = 0 2 x = −3, − 5 II. 2y² + 11y + 12 = 0 2y² + 8y + 3y + 12 = 0 2y (y + 4) + 3 (y + 4) = 0 3 y = −4, − 2 No relation 39. (a): I. 7x² - 19x + 10 = 0 7x² - 14x – 5x + 10 = 0 7x (x - 2) – 5 (x - 2) = 0 5 x = 2, 7 II. 8y² + 2y – 3 = 0 8y² + 6y – 4y – 3 = 0 2y (4y + 3) – 1 (4y + 3) = 0 y= −3 1 4 , 2 x >y 37 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 40. (a): I. x 2 − 8x + 15 = 0 ⇒ x 2 − 5x − 3x + 15 = 0 ⇒ x(x − 5) − 3(x − 5) = 0 ⇒ (x − 3)(x − 5) = 0 ∴ x = 3 or 5 II. y 2 − 3y + 2 = 0 ⇒ y 2 − 2y − y + 2 = 0 ⇒ y(y − 2) − 1(y − 2) = 0 ⇒ (y − 1)(y − 2) = 0 ∴ y = 1 or 2 ∴x>y 24 20 Required difference = 30𝑥 × 100 − 19𝑥 × 100 = 7.2𝑥 − 3.8𝑥 = Rs.136 Quantity II: Let cost price of the article be Rs.100x So, marked price of the article = 100𝑥 × 170 100 = Rs.170x 60 And, selling price of the article = 170𝑥 × 100 ou 41. (c): I. 3x² –7x + 4 = 0 ⇒ 3x²– 4x - 3x +4 = 0 ⇒ (3x – 4) (x -1) = 0 4 x = 3 or 1 p = Rs.102x ATQ, 102𝑥 = 183.6 ⇒ 𝑥 = 1.8 40 Required sum = 170𝑥 × 100 + (102𝑥 − 100𝑥) = 68𝑥 + 2𝑥 = Rs.126 So, Quantity I > Quantity II. II. 2y² -9y + 10 = 0 ⇒ 2y² - 4y - 5y + 10 = 0 ⇒ (2y - 5) (y -2) =0 5 ⇒ y = 2 or 2 y>x 480 480 11𝑥−𝑥 + 11𝑥+𝑥 = 11 ⇒𝑥 =8 So, speed of boat in still water = 11x = 88 km/hr. Quantity II: Let speed of boat in still water & speed of stream be ‘a km/hr.’ and ‘b km/hr.’ respectively. ATQ, = 150 So, Quantity I > Quantity II. ⇒ 𝑅 = 18% 6 te 43. (a): Quantity I: ATQ, 5900×𝑅×3 = 3186 100 xa m 42. (c): Quantity I: Total number of ways = (8C2 × 4C2) + (8C1 × 4C3) + (4C4) = 168 + 32 + 1 = 201 Quantity II: 3-digit numbers which are divisible by 3 and ends with an even number = (102, 108, 114, -------, 996) 996−102 Required number of 3 – digit numbers= +1 gr 45. (e): Quantity I: Let speed of boat in still water & speed of stream be ‘11x km/hr.’ and ‘x km/hr.’ respectively. ATQ, 7900×(18+5)×3 @ ce Required interest = 100 = Rs.5451 Quantity II: Equivalent rate of interest of 13% p.a. for 2 years 13×13 at CI = 13 + 13 + 100 = 27.69% ATQ, 𝑋×27.69 = 2325.96 100 ⇒ X = Rs.8400 So, Quantity I < Quantity II. 3.5 = (𝑎 + 𝑏) ⇒ (𝑎 + 𝑏) = 100 …(i) And, 380 5 = (𝑎 − 𝑏) ⇒ (𝑎 − 𝑏) = 76 …(ii) On solving (i) & (ii), we get: a = 88 km/hr. So, Quantity I = Quantity II. 46. (c): Quantity I: Let A’s present age be 10x years. So, B’s present age = 10𝑥 × 160 100 = 16x years 2 And, C’s present age = 16𝑥 × = 6.4x years 5 44. (c): Quantity I: Let CP & MP of an article be Rs.19x and Rs.30x respectively. ATQ, 120 19𝑥 × 100 = 912 ⇒ 𝑥 = 40 38 350 And, D’s present age = 2 × 6.4𝑥 = 12.8x years ATQ, 16𝑥 − 12.8𝑥 = 8 ⇒ 𝑥 = 2.5 Hence, required average = 10𝑥+16𝑥+6.4𝑥+12.8𝑥 4 = 11.3x = 28.25 years Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations 47. (e): I. x² - 7x + 12 = 0 𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 − 3𝑥 + 12 = 0 (𝑥 − 4)(𝑥 − 3) = 0 𝑥 = 3,4 II. y² - 8y + 12 = 0 𝑦 2 − 6𝑦 − 2𝑦 + 12 = 0 (𝑦 − 6)(𝑦 − 2) = 0 𝑦 = 2,6 No relation can be established 2 y≥x @ ce 49. (e): I. 2x² - 7x – 60 = 0 2x² - 15x + 8x – 60 = 0 x (2x – 15 ) + 4 (2x – 15) = 0 (x + 4) (2𝑥 − 15) = 0 15 𝑥 = −4, 2 II. 3y² + 13y + 4 = 0 3y² + 12y + y + 4 = 0 3y (y + 4) + 1 (y + 4) = 0 (3y + 1) (y + 4) = 0 1 𝑦 = − , −4 3 No relation between x and y 50. (e): I. x² - 17x – 84 = 0 x² +4x – 21x – 84 = 0 (x + 4) (x – 21) = 0 x = -4, 21 39 p 52. (e): I. x 2 − 13x + 11x − 143 = 0 (x – 13)(x+11) = 0 x = -11, 13 II. y 2 = 169 y = ± 13 clearly, no relation can be established m gr 53. (a): I. x 2 − 9x + 2x − 18 = 0 (x – 9) (x + 2) = 0 x = -2, 9 II. y 2 − 10y − 9y + 90 = 0 (y – 10) (y – 9) = 0 y = 9, 10 clearly, x ≤ y 54. (c): I. 2x 2 + 3x + 2x + 3 = 0 (x + 1) (2x + 3) = 0 3 x = -1, - te II. 2y² - 23y + 56 = 0 2y² - 16y – 7y + 56 = 0 2y(y – 8) – 7(y – 8) = 0 (2y – 7) (y – 8) = 0 7 𝑦 = 2,8 51. (d): I. 𝑥 2 = 81 𝑥 = ±9 II. (𝑦 − 9)2 = 0 𝑦=9 Clearly, 𝑥 ≤ 𝑦 xa 48. (d): I. 2x² + x – 28 = 0 2x² + 8x – 7x – 28 = 0 2x (x + 4) – 7 (x + 4) = 0 (2x – 7) (x + 4)= 0 7 𝑥 = −4, II. y² + 4y – 117 = 0 y² - 9y + 13y – 117 = 0 (y – 9) (y + 13) = 0 y = 9, -13 No relation between x and y ou Quantity II: Let present age of P be p years. So, present age of R = (𝑝 − 15) years ATQ, Present age of Q = (2 × (𝑝 − 15)) − 𝑝 = (𝑝 − 30) 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟𝑠 Now, (𝑝 + 4) = 2 × (𝑝 − 30 + 4) ⇒ 𝑝 = 56 Hence, present age of R = (𝑝 − 15) years = 41 years And, present age of Q = (𝑝 − 30) 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟𝑠 = 26 years So, required age = 26 years So, Quantity I > Quantity II. 2 II. y 2 + 6y − 2y − 12 = 0 (y – 2) (y + 6) = 0 y = 2, -6 clearly, no relation can be established 55. (d): (II) × 9 – (I) × 4 On solving, x = 1, y = 2 clearly, x < y 56. (c): I. 2x 2 − 2x + x − 1 = 0 (2x + 1) (x – 1) = 0 1 x=- ,1 2 II. 3y 2 − 3y − 2y + 2 = 0 (3y – 2) (y – 1) = 0 2 y= ,1 3 clearly, no relation 57. (d): x² = 81 x=±9 Y² – 18y + 81 = 0 (y – 9)² = 0 ∴ y = 9, 9 ∴x≤y Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations II. y2 +42y + 185 =0 y2+37y+5y+185 =0 y(y+37)+5(y+37)=0 (y+5)(y+37)=0 y = -5, - 37 So, x > y 59. (c): x² – 21x + 108 = 0 x² – 9x – 12x + 108 = 0 x(x – 9) – 12 (x – 9) = 0 x = 9, 12 y² – 17y + 72 = 0 ∴ y² – 8y – 9y + 72 = 0 y (y – 8) – 9 (y – 8) = 0 ∴ y = 8, 9 ∴x≥y 2 3 gr So, x < y m 65. (e): I. x 2 − 8x − 273 = 0 x2-21x+13x-273=0 x(x-21)+13(x-21)=0 (x+13)(x-21)=0 x= -13, 21 II. y2 +6y – 432 =0 y2+24y-18y-432 =0 y(y+24)-18(y+24)=0 (y-18)(y+24)=0 y = 18, - 24 So, No relation 66. (e): te 61. (c): x³ = 512 3 x = √512 = 8 y² = 64 y = √64 = ± 8 ∴x≥y 2 xa 60. (b): x² – 11x + 30 = 0 x² – 6x – 5x + 30 = 0 ∴ x(x – 6) – 5(x – 6) = 0 x = 6, 5 y² – 15y + 56 = 0 y² – 7y – 8y + 56 = 0 y (y – 7) – 8 (y – 7) = 0 ∴ y = 7, 8 ∴x<y 5 y = ,- ou 64. (c): I. x2 + 41x + 420 =0 x2+21x+20x+420=0 x(x+21)+20(x+21)=0 (x+20)(x+21)=0 x= -20, - 21 II. 6y2 -11y – 10 =0 6y2-15y+4y-10 =0 3y(2y-5)+2(2y- 5)=0 (2y-5)(3y+2)=0 p 58. (e): 4x² – 24x + 30 = 0 4x² – 16x – 8x + 32 = 0 4x (x – 4) –8 (x–4) = 0 x = 4, 2 y² – 8y + 15 = 0 y² – 5y – 3y + 15 = 0 y(y – 5)–3 (y – 5) = 0 ∴ y = 5, 3 ∴ No relation exists @ ce 62. (c): I. 2x 2 + 11x + 12 = 0 2x2 + 8x + 3x + 12 = 0 2x (x + 4) + 3(x + 4) = 0 (x + 4) (2x + 3) = 0 3 x= -4, - 67. (a): 2 II. 8y2 -22y – 21 =0 8y2+6y-28y-21 =0 2y(4y+3)-7(4y+3)=0 (2y-7)(4y+3)=0 7 3 y = ,2 68. (d): 4 So, x < y 63. (a): I. x 2 − 17x − 60 = 0 x2-20x+3x-60=0 x(x-20)+3(x-20)=0 (x+3)(x-20)=0 x= - 3, 20 40 69. (a): I. x² – 3x – 4=0 𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 𝑥 − 4 = 0 (x – 4) (x + 1) = 0 x = 4, –1 Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com A Complete Guide on Quantitative Aptitude for Banking & Insurance Examinations II. y² + 6y + 8 = 0 y² + 2y + 4y + 8 = 0 (y + 2) (y + 4) = 0 y = –2, –4 ⇒x>y 73. (e): Quantity I: (x+3)² = (x–3)²+x² x²+9+6x=x²+9–6x+x² x²–12x=0 x(x–12)=0 x=0,12 Quantity II: y²–29y+204=0 y²–12y–17y+204=0 y(y–12)–17(y–12)=0 (y–12)(y–17)=0 y=12, 17 So, Quantity II ≥ Quantity I ou p 70. (b): I. x² – 3x = 10 𝑥 2 − 3𝑥 − 10 = 0 x² – 5x + 2x – 10 = 0 (x – 5) (x + 2) = 0 x = –2, 5 II. y² + 7y + 10 = 0 y² + 5y + 2y + 10 = 0 (y + 5) (y + 2) = 0 y = – 2, –5 ⇒x≥y 74. (a): Quantity I: 1 Amount = 2450 + 2450 × 7 × 2 = 2450 + 700 = Rs. 3150 Quantity II: 71. (d): Quantity I: 18 1 2 Amount = 2450 (1 + 8) × 5 = 500 meter. 12 55.2 = 𝑉 …(ii) On solving (i) & (ii), we get: 𝑥 = 500 𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟 So, Quantity II = quantity I 72. (b): Quantity I: Let C. P = Rs. 100 x 150 te Then M. P= 100 𝑥 × 120 100 = Rs. 150x S.P = 100𝑥 × 100 = Rs. 120x @ ce ATQ, 120 x = Rs. 1020 x = Rs. 8.5 So, 150x = Rs. 1275 Quantity II: Perimeter of field = 37.5 ×4 =150 meter =15000 cm. Total cost of fencing = 15000×0.17 = Rs. 2550 So, Quantity I < Quantity II. 41 81 64 =Rs 3100.78. So, Quantity I > Quantity II 75. (d): Quantity I: Let total M. R. P of 5 article = Rs. 100x 1 article is free, then S. P for 5 articles = 100x – 20x = Rs. 80x Again, he gives 20% discount, S.P become of each 80 1 article = 80𝑥 × 100 × 5 = Rs. 12.8𝑥 xa Now, 𝑥+1800 = 2450 × m Quantity II: Let speed of train be ‘V km/hr’ and length of train be ‘x meter’. ATQ, 𝑥 = 𝑉 …(i) gr length of train = 24×75 Actual Discount percentage= = 7.2 20 20𝑥–12.8𝑥 20𝑥 × 100 × 100 = 36% Quantity II: Let C.P = Rs. x Let Initial S.P= Rs. 7y Final S.P = Rs. 8y ATQ 36 7𝑦–𝑥 19 ( 𝑥 ) × 100 = 8𝑦−𝑥 𝑥 × 100 252y – 36x = 152y – 19x 𝑥 100 = 17 𝑦 Let C.P= Rs. 100a Final S.P= Rs. 136a 136𝑎−100𝑎 Final profit % = 100𝑎 × 100 = 36% So, Quantity I = Quantity II Adda247 Publications For More Study Material Visit: adda247.com