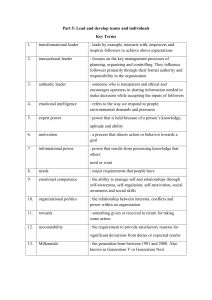
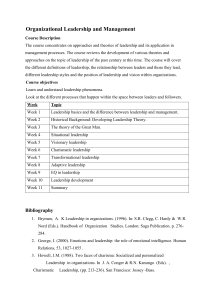
Silk Road and Global Exchange ● ● ● ● Silk Road: A network of trade routes connecting East and West, over 2,000 years old. Early Civilizations: Trade between nomadic tribes and early civilizations like Greece, China, and India. Persian Royal Road: Allowed faster communication and trade across 2,000 miles. Zhang Qian: In the 2nd century BCE, opened direct trade between China, Persia, and India. Cultural and Technological Exchange ● ● ● Buddhism: Spread from India to China and Japan. Islam: Spread from the Arabian Peninsula to South Asia. Gunpowder: Spread from China to the Middle East. Decline of the Silk Road ● ● ● Mongol Protection: Mongols protected trade routes. New Maritime Technology: The compass made sea routes more popular. End of the Silk Road: China withdrew, and new maritime routes took over. Modern Globalization ● ● Age of Exploration: Sparked by the search for new trade routes. Today: Global trade is stronger than ever, thanks to the Silk Road's legacy. The Legend of Tea ● Shennong: Ancient Chinese farmer accidentally poisoned himself 72 times but was revived by a leaf, which led to the discovery of tea (legendary story). History of Tea in China ● ● ● Origins: Tea was first cultivated in China over 6,000 years ago. Early Use: Initially eaten as a vegetable or cooked with grain porridge. Transition to Drink: Tea shifted from food to drink around 1,500 years ago when heat and moisture were used to brew it. Tea Culture and Development ● ● ● Matcha: Tea became popular as "muo cha" (matcha), a powdered tea mixed with hot water. Tea Culture: Tea became a cultural staple in China, featured in books, poetry, and art. Japanese Tea: In the 9th century, a Japanese monk brought tea to Japan, leading to the development of the Japanese tea ceremony. Tea in the Ming Dynasty ● ● Loose Leaf Tea: In the 14th century, during the Ming Dynasty, loose leaf tea replaced pressed cakes as the standard. Tea as an Export: By the 14th century, China controlled the world’s tea trade, alongside silk and porcelain. Tea Spreads to Europe ● ● ● Dutch Traders: In the early 1600s, Dutch traders brought tea to Europe. Queen Catherine of Braganza: She made tea popular with the British aristocracy after marrying King Charles II in 1661. Tea Trade: By 1700, tea was much more expensive than coffee in Europe, and tea became a major economic commodity. Opium Trade and Opium Wars ● ● ● Opium Trade: Britain traded opium for tea, leading to widespread addiction in China. First Opium War: In 1839, China destroyed British opium shipments, triggering the war. Hong Kong: In 1842, China ceded Hong Kong to Britain after losing the war, weakening China’s global position. Tea Production Outside China ● Robert Fortune's Mission: The British East India Company sent botanist Robert Fortune to steal tea plants and workers from China, establishing tea production in India (Darjeeling). Tea Today ● Global Consumption: Tea is now the second most consumed beverage in the world, with diverse preparations like Turkish Rize tea and Tibetan butter tea. Influence on Somali Cuisine ● ● Somali food is influenced by India (Indian Ocean trade), Italy (colonization), and Arabia (Islamic culture). Halal dietary laws play a key role, impacting food choices beyond Muslims. Kosher vs. Halal ● ● Kosher (Jewish Law) and Halal (Islamic Law) both regulate permissible foods. ○ Both prohibit pigs, insects, and birds of prey. ○ Both require slaughter with a sharp, swift blade, and complete blood drainage. ○ Halal allows stunning and doesn't require salting or soaking meat, while Kosher requires special training for the slaughter process. Kosher Meat: A kosher meat is also halal if slaughtered under specific conditions. Organic, Natural, and Artisan Labels ● ● ● Organic: At least 95% organic ingredients, certified by an official body. Natural: No artificial additives or flavoring, but not third-party certified. Artisan: Made in small batches, with minimal machines, but not certified. Halal Certification ● ● Halal Certification: Ensures the animal is raised and slaughtered humanely, without harmful substances (like antibiotics or harmful feed). Health and Safety: Halal meat tends to be fresher, takes less time to cook, and has better safety standards due to blood drainage and minimal additives. Halal Process for Cows ● ● Cow Feed: Halal cows are fed non-GMO, clean feed, not sewage or blood meal. Slaughter Process: The cow is treated humanely: ○ ○ ○ Rest after transport. Slaughtered with a sharp knife to reduce pain and stress. Blood is fully drained, reducing bacterial growth and toxins. Mobile Abattoirs: ● Mobile slaughterhouses reduce transport stress, promoting animal welfare. Nature of Leadership ● ● Leadership: The ability to guide and influence others toward goal achievement. Contemporary Challenges: Leaders must handle complex, dynamic, and global challenges. Leadership Traits and Behaviors ● ● Traits: Inherent qualities like charisma and vision. Behaviors: Actions leaders take, such as motivating or providing feedback to followers. Leadership Theories 1. Contingency Theories: ○ Leadership effectiveness depends on the match between the leader's style and the situation. ○ Fiedler’s Contingency Model: Task-oriented vs. relationship-oriented leadership. Success depends on: ■ Leader-member relations (good vs. poor) ■ Task structure (high vs. low) ■ Position power (strong vs. weak) ○ Diagram: Situational control and leadership effectiveness. 2. Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Model: ○ Leadership style adjusts based on follower readiness (ability, willingness, and confidence). 3. House’s Path-Goal Theory: ○ Leaders guide followers on the path to achieving goals through: ■ Directive leadership ■ Supportive leadership ■ Achievement-oriented leadership ■ Participative leadership Visionary Leadership ● ● Visionary Leadership: Creating and communicating a clear, compelling vision for the future. Challenges: Ensuring others buy into and work towards the vision. Power & Influence 1. Sources of Managerial Power: ○ Position Power: Reward, coercive, and legitimate power. ○ Personal Power: Expert and referent power. 2. Building Power: ○ Power grows through workplace factors like centrality, criticality, and visibility. ○ Diagram: Power dynamics in the workplace. Leadership Behavior 1. Task Concerns: ○ Setting tasks, defining work, and ensuring timely completion. ○ Monitoring performance and motivating followers. 2. People Concerns: ○ Supporting, developing relationships, and being sensitive to followers' needs. Classic Leadership Styles 1. Autocratic Style: Leader makes decisions alone, prioritizing tasks over people. 2. Laissez-faire Style: Hands-off leadership, minimal direction. 3. Democratic Style: Encourages participation, shares information, and supports development. Decision-Making Models 1. Vroom-Jago Leader-Participation Theory: ○ Helps leaders select the appropriate decision-making method based on the situation: ■ Authority decision ■ Consultative decision ■ Group decision ○ Diagram: Decision-making choices and outcomes. Leadership Styles and Approaches 1. Transactional Leadership: Focuses on exchanges between leader and follower (rewards for performance). 2. Transformational Leadership: Motivates followers to exceed expectations and fosters change. Emotional Intelligence and Leadership ● Emotional Intelligence: Leaders must understand and manage their emotions and those of others. Other Leadership Concepts ● ● ● ● Charismatic Leadership: Leaders use charm and personal appeal to inspire. Superleaders: Empower others to lead. Moral Leadership: Leading with ethics and integrity. Gender and Leadership: Leadership styles may vary based on gender but both men and women can exhibit effective leadership qualities. strategic Management Basics ● ● ● Competitive Advantage: What makes a company better than competitors. Sustainable Advantage: Long-term edge over competitors. Strategy: Plans to achieve goals and maintain competitive advantage. Strategy Formulation ● ● Process: Assess the business, environment, and current strategies to develop new ones. Key Questions: What’s our mission? Who are our customers? What do they value? Strategy Implementation ● ● Action: Allocate resources to put strategies into action. Tasks: Set goals, evaluate performance, and adjust as needed. SWOT Analysis ● SWOT: Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Industry and Environment Analysis ● ● Macro Environment: Factors like technology, economy, and government. Porter’s Five Forces: Analyzes competition and market dynamics. Growth and Diversification Strategies ● ● Growth: Expanding current operations. ○ Types: Concentration, diversification, vertical integration. Restructuring: Fixing problems by downsizing or divesting. Global Strategies ● ● ● Globalization: Standardizing products for the world. Multidomestic: Adapting products for local markets. Transnational: Balancing global efficiency and local needs. Cooperative & E-business Strategies ● ● Strategic Alliances: Partnerships for mutual benefit (e.g., outsourcing). E-business: Using the internet for business (B2B, B2C). Sustainable Competitive Advantage ● Factors: Cost, quality, knowledge, speed, and financial strength. Porter’s Generic Strategies ● ● ● Differentiation: Offering unique products. Cost Leadership: Offering the lowest prices. Focus: Targeting niche markets. BCG Matrix ● Matrix: Helps prioritize resource allocation based on market growth and share. Adaptive Strategies ● ● ● ● Prospector: Exploring new opportunities. Defender: Protecting existing markets. Analyzer: Balancing stability and innovation. Reactor: Responding to competition. Strategic Planning Issues ● Failures: Poor planning or implementation can hurt strategy success. Strategic Leadership ● Tasks: Communicate, teach, create urgency, and ensure strategy is understood and executed. Globalization & International Business ● ● ● ● Globalization: The world is becoming more interconnected, and businesses operate internationally. International Business: Involves working across borders for profit, customers, and resources. Market Entry: Strategies like exporting, licensing, franchising, and global sourcing. Direct Investment: More control but higher investment, such as joint ventures or foreign subsidiaries. Challenges in Global Business ● ● The global market is competitive and complex. WTO helps resolve trade disputes. Protectionism can hinder global trade. Multinational Corporations (MNCs) ● ● MNCs operate in many countries and bring benefits like shared growth and development. Ethical Issues: MNCs may face criticism for exploitation, child labor, and environmental harm. Culture & Global Diversity ● ● ● ● Culture: Shared beliefs and values within a group. Culture Shock: Discomfort when adapting to a new culture. Ethnocentrism: Believing your own culture is superior. Cultural Adjustment: Stages from confusion to reality. National Culture (Hofstede’s Dimensions) ● ● ● Power Distance: How unequal power is accepted. Individualism vs. Collectivism: Personal goals vs. group goals. Masculinity vs. Femininity: Focus on achievement vs. nurturing. Cultural Differences (Trompenaars) ● Differences in relationships, time views (sequential vs. simultaneous), and how cultures interact with their environment. Global Management ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Management theories aren’t universal; practices may differ across cultures. Learning from Others: Be open to global organizational learning, but approach with caution. Information Technology and the New Workplace Knowledge Workers: Employees who use their knowledge are vital, and their productivity depends on computer and information skills. E-commerce: Stages include creating an online identity, building a web presence, and managing customer relationships. Impact of IT: IT improves communication, reduces management layers, and helps organize and coordinate better. Data vs. Information: Data is raw facts; information is processed data used for decisions. It must be timely, accurate, complete, relevant, and understandable. Diagram: IT breaks barriers and changes how organizations operate. Role of Information in Management ● Information Systems: Tools like MIS and DSS support decision-making. ● IT Advantages: Helps with planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Diagram: Shows how information systems support management functions. Information and Decision Making ● ● ● ● Types of Decisions: Programmed (routine), nonprogrammed (creative), and crisis (urgent) decisions. Decision Environments: Certain (predictable), risk (uncertain but measurable), and uncertain (unpredictable). Problem-Solving Styles: Problem avoiders (ignore issues), solvers (deal with issues), and seekers (actively look for problems). Thinking Styles: Systematic (logical) vs. intuitive (instinctive) thinking—both are needed for effective problem-solving. Steps in the Decision-Making Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Define the problem. Generate and evaluate solutions. Choose the best solution. Implement it. Evaluate the outcome. Diagram: Steps in the decision-making process. Current Issues in Decision Making ● ● ● Heuristics: Mental shortcuts like availability (easy-to-get info), representativeness (past experience), and anchoring (initial info). Escalating Commitment: Avoid continuing a bad decision by setting limits and tracking costs. Group Decision-Making: More information and commitment but can take longer and face groupthink. Knowledge Management & Ethical Decision Making ● ● Knowledge Management: Encourages learning within organizations, led by a Chief Knowledge Officer. Ethical Decisions: Should be useful, fair, just, and caring. 1. Challenges in the New Economy ● ● ● ● Globalization: The world is more connected, and business competition is worldwide. Technology: Rapid tech changes are reshaping workplaces, requiring skilled workers. Diversity: A diverse workforce brings challenges but also creative solutions. Ethics: Companies must act ethically and rebuild trust with strong governance. 2. Characteristics of the New Workplace ● ● ● Intellectual Capital: Employees’ knowledge is key to creating value. Technology: Essential for efficiency and innovation. Knowledge workers use it. Diversity: Diverse teams bring new ideas and problem-solving skills. 3. Careers in the 21st Century ● ● Career Change: Careers are no longer lifelong with one employer. Skills must be portable and updated. Success Skills: ○ Mastery: Develop expertise. ○ ○ ○ Contacts: Build professional networks. Entrepreneurship: Be innovative. Tech Skills: Keep up with new technology. 4. Organizational Structure & Performance ● ● ● What is an Organization?: A group working together to offer goods/services that benefit society. Open Systems: Organizations take resources, transform them into products/services, and interact with their environment. Performance: Success is measured by creating value—profits in businesses, benefits in nonprofits. 5. The Management Process ● ● 4 Functions of Management: ○ Planning: Set objectives. ○ Organizing: Allocate resources. ○ Leading: Guide and motivate people. ○ Controlling: Monitor and adjust progress. Management Levels: ○ Top Managers: Oversee the entire organization. ○ Middle Managers: Manage specific departments. ○ Team Leaders: Supervise small teams. 6. Types of Managers ● ● ● ● Line Managers: Directly manage production. Staff Managers: Support line managers. Functional Managers: Handle one area, like marketing. General Managers: Oversee multiple areas. 7. Organizational Feedback ● Feedback helps assess how well organizations meet goals and customer needs. 8. Learning to Manage ● Skills Needed: Technical, interpersonal, and conceptual thinking are key for success in management. Diagrams: ● ● Open Systems: Shows how organizations interact with the environment and transform inputs into outputs. Management Functions: A flowchart of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. 1. The Nature of Leadership ● ● ● ● ● Power: Leaders influence others using: ○ Position Power (legitimate, reward, coercive). ○ Personal Power (expert, referent, charismatic). Vision: Leaders inspire others by presenting a compelling vision of the future. Servant Leadership: Focuses on serving others and empowering them, rather than self-interest. Followership: Success depends on the engagement and active role of followers. The Romance of Leadership: Overemphasizing the leader’s role while underestimating followers’ contributions. 2. Leadership Traits and Behaviours ● ● ● Key Leadership Traits: ○ Drive: Energy, persistence, and initiative. ○ Self-confidence: Belief in one’s abilities. ○ Cognitive Ability: Problem-solving and analytical skills. ○ Creativity: Thinking outside the box. ○ Knowledge of Business: Deep understanding of industry and operations. ○ Motivation: Passion for leadership. ○ Flexibility: Ability to adapt to change. ○ Integrity: Trustworthiness and ethical behavior. Leader Behaviours: ○ Task-oriented: Focus on achieving goals and objectives. ○ People-oriented: Emphasizes relationships and follower well-being. Leadership Styles: ○ Human Relations Leader: Focuses on relationships. ○ Autocratic Leader: Controls decisions and efficiency. ○ Country Club Manager: Focuses on people’s needs over task achievement. ○ Democratic Leader: Shares decision-making and involves the team. ○ Impoverished Manager: Minimal effort; poor results. 3. Contingency Approaches to Leadership ● ● ● ● ● Fiedler’s Contingency Model: ○ Effectiveness depends on matching a leader's style (task or relationship-oriented) with the situation (leader-member relations, task structure, position power). Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Model: ○ Leaders adjust style based on followers' maturity (ability and willingness). ■ Telling: High task, low relationship. ■ Selling: High task, high relationship. ■ Participating: Low task, high relationship. ■ Delegating: Low task, low relationship. House’s Path-Goal Theory: ○ Leaders motivate by clarifying goals and removing obstacles. Leadership styles: ■ Directive: Gives clear instructions. ■ Supportive: Shows concern for followers. ■ Participative: Involves followers in decision-making. ■ Achievement-oriented: Sets challenging goals. Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory: ○ Focuses on the quality of the relationship between leaders and followers. In-group members receive more attention and resources. Substitutes for Leadership: ○ Certain factors (like highly skilled employees or well-structured tasks) reduce the need for direct leadership. 4. Personal Leadership Development ● ● ● Charismatic Leadership: ○ Leaders inspire through personal vision and energy. Risks include blind loyalty and poor decision-making when followers become overly dependent. Transformational Leadership: ○ Motivates followers to exceed expectations and go beyond self-interest for the organization’s benefit. Emotional Intelligence (EI): ○ Essential for leadership. EI includes: ● ● ● ■ Self-awareness: Recognizing one’s emotions. ■ Self-regulation: Controlling emotional responses. ■ Motivation: Being driven beyond rewards. ■ Empathy: Understanding others' emotions. ■ Social skills: Building strong relationships. Leadership and Gender: ○ Both men and women can be equally effective leaders, though they might use different styles. Leadership effectiveness is not determined by gender. Moral Leadership: ○ Leading with ethics and integrity. Moral leaders build trust through consistency and ethical behavior. Drucker’s “Good Old-Fashioned Leadership”: ○ Emphasizes leadership based on character, ethics, and alignment with organizational goals. Key Leadership Theories 1. Transformational Leadership: Focuses on inspiring and motivating followers to achieve extraordinary outcomes and develop into leaders themselves. 2. Charismatic Leadership: Relies on the leader’s personal charm and influence to inspire followers, often creating strong emotional bonds. 3. Servant Leadership: Leaders serve followers by focusing on their needs, development, and empowerment. 4. Transactional Leadership: Focuses on exchanges between the leader and followers, often through rewards and punishments based on performance. Which of the following is a characteristic of charismatic leaders? A) Their ability to inspire others. B) Their emphasis on logical decision-making. C) Their focus on task-oriented goals. D) Their reliance on organizational structure. Answer: A What is a key foundation of leadership? A) Control B) Power C) Luck D) Simplicity Answer: B Which leadership style focuses on personal relationships and employee well-being? A) Autocratic B) Task-oriented C) Human Relations D) Transactional Answer: C What is the main focus of servant leadership? A) Achieving results through strict control B) Focusing on the needs and development of followers C) Maximizing profits above all else D) Enforcing rigid rules and procedures Answer: B Which of the following is a key trait of effective leaders? A) Rigid decision-making B) High self-confidence C) Low emotional intelligence D) Focus on maintaining control Answer: B What leadership theory suggests that leadership effectiveness is contingent on the situation? A) Transformational Leadership B) Trait Theory C) Contingency Theory D) Path-Goal Theory Answer: C Which leadership approach emphasizes leader-follower interactions as the basis of leadership success? A) Transactional Leadership B) Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory C) Fiedler's Contingency Model D) Situational Leadership Answer: B In the Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Model, a "selling" style is appropriate when: A) Followers are highly competent but unmotivated. B) Followers are capable but unwilling. C) Followers are neither willing nor capable. D) Followers are highly skilled and highly motivated. Answer: B What is a key factor in Fiedler’s Contingency Model for determining leadership effectiveness? A) The leader's ability to communicate B) The match between the leader's style and the situation C) The leader’s level of charisma D) The size of the organization Answer: B Which leadership style in the Hersey-Blanchard model is characterized by low task behavior and high relationship behavior? A) Delegating B) Selling C) Participating D) Telling Answer: C According to House’s Path-Goal Theory, which leadership style clarifies the path to achievement for followers? A) Directive B) Supportive C) Achievement-oriented D) Participative Answer: A In Path-Goal Theory, which leadership style involves setting challenging goals and expecting high performance? A) Directive B) Supportive C) Achievement-oriented D) Participative Answer: C Which model suggests that leadership effectiveness depends on the maturity level of followers? A) Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Model B) Transformational Leadership Model C) Path-Goal Theory D) LMX Theory Answer: A Which approach in leadership focuses on aligning individual and organizational goals? A) Transformational Leadership B) Transactional Leadership C) Servant Leadership D) Charismatic Leadership Answer: A What is the primary purpose of substitutes for leadership? A) To enhance the leader's power B) To reduce the need for direct leadership in certain situations C) To create conflict within the team D) To focus solely on profit-making Answer: B Which of the following is NOT a trait of transformational leaders? A) Visionary B) Inspiring C) Manipulative D) Focused on followers' development Answer: C What is the dark side of charismatic leadership? A) Leaders only focus on followers’ needs. B) Followers may develop blind loyalty, leading to unethical decisions. C) Charismatic leaders rarely face challenges. D) Charismatic leaders lack followers’ support. Answer: B Which of the following describes transformational leadership best? A) Leadership through transactional exchanges B) Inspiring followers to exceed expectations C) Maintaining control through strict rules D) Delegating responsibilities without guidance Answer: B What is emotional intelligence in leadership? A) The ability to control others' emotions B) The ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions and the emotions of others C) The ability to make quick decisions D) The ability to avoid conflict Answer: B Which type of leadership emphasizes flexibility and adapting to changing situations? A) Transformational Leadership B) Charismatic Leadership C) Adaptive Leadership D) Transactional Leadership Answer: C What factor is most important in personal leadership development? A) Constant self-reflection and learning B) Focusing on formal qualifications C) Following others' examples without change D) Emphasizing financial growth Answer: A What is the first step in personal leadership development? A) Identifying leadership weaknesses B) Building a leadership network C) Analyzing others’ leadership styles D) Gaining more technical skills Answer: A What role does gender play in leadership? A) It limits leadership potential. B) Men and women lead in distinctly different ways, with no overlap. C) Both men and women can lead effectively, though they may face different challenges. D) It determines the type of leadership style a person will adopt. Answer: C Which of the following is a challenge of personal leadership development? A) Achieving financial success B) Overcoming personal biases and expanding emotional intelligence C) Ignoring team input D) Focusing only on task completion Answer: B What is the importance of self-awareness in leadership development? A) It helps a leader understand the impact of their actions on others. B) It allows a leader to impose authority. C) It eliminates the need for communication. D) It reduces the need for follower engagement. Answer: A Which leadership model emphasizes adjusting leadership style based on the situation and followers’ maturity? A) Path-Goal Theory B) Vroom-Jago Model C) Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership D) LMX Theory Answer: C In Vroom-Jago’s decision-making model, which decision-making style involves the leader making the final decision after consulting the group? A) Authority B) Consultative C) Group D) Directive Answer: B What is the focus of transformational leadership? A) Efficiency and control B) Rewarding followers for performance C) Inspiring and motivating followers to exceed expectations D) Maintaining status quo Answer: C What is an example of a leader using emotional intelligence? A) Ignoring followers’ concerns for the sake of productivity B) Managing their own emotions and recognizing the emotions of their team C) Focusing only on tasks and disregarding team dynamics D) Making decisions based solely on logic Answer: B What is a key takeaway from studying charismatic and transformational leadership? A) Charisma alone is sufficient for effective leadership. B) Transformational leadership can help achieve extraordinary performance through motivation and vision. C) Leadership can be improved only through technical skills. D) Leadership styles should remain fixed. Answer: B 4.1 The Nature of Leadership ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Power: The ability to influence others. Includes position power (e.g., legitimate, reward, coercive) and personal power (e.g., expert, referent, charismatic). Vision: A leader’s ability to inspire by articulating a clear, compelling future for the organization. Visionary Leadership: Leaders who create and share an inspiring vision. Servant Leadership: Focuses on serving others and empowering them, prioritizing the needs of followers. Empowerment: Granting followers the authority to make decisions and act independently. Followership: Active participation of followers in achieving goals. The Romance of Leadership: Tendency to overemphasize leaders’ influence while underestimating followers’ contributions. 14.2 Leadership Traits and Behaviours ● ● Traits of Effective Leaders: ○ Drive: High energy, initiative, tenacity. ○ Self-confidence: Trust in their abilities. ○ Creativity: Original thinking. ○ Cognitive Ability: Ability to analyze and interpret information. ○ Knowledge: Deep understanding of the industry. ○ Motivation: Enjoyment in influencing others. ○ Flexibility: Adaptability in various situations. ○ Honesty and Integrity: Trustworthy and ethical behavior. Leader Behaviours: ○ Task-oriented: Focus on achieving goals. ○ People-oriented: Concern for follower needs and relationships. ○ Classic Leadership Styles: ■ Human Relations Leader: Focuses on relationships. ■ Country Club Manager: Focuses on people’s needs. ■ Impoverished Manager: Minimal effort, poor results. ■ Democratic Leader: Shares decision-making, high focus on both task and people. ■ Autocratic Leader: Focuses on task efficiency, tight control. 14.3 Contingency Approaches to Leadership ● Fiedler’s Contingency Model: Leaders are either task-oriented or relationship-oriented, and their effectiveness depends on the situation (e.g., leader-member relations, task structure, position power). ● ● ● ● Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Model: Leaders must adjust their style (telling, selling, participating, delegating) based on follower maturity (ability and willingness). House’s Path-Goal Theory: Leaders motivate followers by clarifying the path to goals. Leadership styles include: ○ Directive: Giving clear instructions. ○ Supportive: Showing concern for subordinates. ○ Achievement-oriented: Setting challenging goals. ○ Participative: Involving team members in decisions. Substitutes for Leadership: Certain situations or characteristics reduce the need for direct leadership (e.g., task clarity, employee experience). Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory: Focuses on relationships between leaders and followers, where some followers (in-group) receive more attention and resources than others (out-group). 14.4 Personal Leadership Development ● ● ● Charismatic and Transformational Leadership: Charismatic leaders inspire with their vision and energy, while transformational leaders focus on changing followers' values and goals for greater performance. Emotional Intelligence (EI): A key factor in leadership, EI involves self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. Gender and Leadership: Research suggests that men and women can both be equally effective leaders, but are sometimes perceived to use different leadership styles. 1. Strategic Management Overview (Pages 178-180) ● Strategic Management Process: ○ Strategic analysis, formulation, and implementation. ○ Ongoing cycle to adapt and achieve long-term goals. ○ Integrates internal analysis (strengths, weaknesses) and external analysis (opportunities, threats). 2. Corporate-Level Strategy (Pages 180-182) ● ● What is Corporate Strategy? ○ Sets the direction for the entire organization. ○ Concerned with diversification, acquisitions, and entering new markets. Corporate Strategy Types: ○ Growth Strategy: Focus on increasing revenue and market presence. ■ Includes vertical integration, market expansion, and diversification. ○ Stability Strategy: Maintain current performance and operations. ○ Retrenchment Strategy: Reduce scope to focus on core areas. ■ Includes downsizing, divestitures, and liquidation. 3. Business-Level Strategy (Pages 182-186) ● ● ● Focus: How to compete in the industry. Porter’s Generic Strategies: ○ Cost Leadership: Offering products at the lowest cost. ○ Differentiation: Providing unique products that are perceived as superior. ○ Focus Strategy: Targeting a specific segment of the market. ■ Can be based on either cost leadership or differentiation. Strategy Choices: ○ Broad Market: Cost leadership or differentiation across entire industry. ○ Narrow Market: Focus strategy aimed at niche markets. 4. The BCG Matrix (Pages 186-188) ● ● Purpose: Analyzes business units or products based on market growth rate and market share. Categories: ○ Stars: High growth, high market share (need investment). ○ Cash Cows: Low growth, high market share (generate steady cash). ○ Question Marks: High growth, low market share (decision needed on investment). ○ Dogs: Low growth, low market share (consider divesting). 5. Strategic Alliances (Pages 188-190) ● ● Definition: Partnerships between firms to share resources and expertise. Types: ○ Joint Ventures: Shared ownership and control. ○ Licensing: Allowing another firm to use intellectual property. ○ Franchising: Allowing a firm to operate using your business model. ○ Co-opetition: Competing and collaborating simultaneously. 6. Strategic Leadership (Pages 190-192) ● ● Definition: Leadership that ensures the strategy is aligned with the organization’s goals. Roles: 1. Setting Vision: Defining long-term goals. 2. Resource Allocation: Ensuring resources are used effectively. 3. Inspiring Action: Motivating employees to pursue strategy. 4. Communicating Strategy: Ensuring everyone is aligned with the goals. 7. Strategy Implementation (Pages 192-194) ● ● Process: Putting formulated strategies into action to achieve objectives. Key Elements: 1. Organizational Structure: Aligning structure with strategy (centralized vs decentralized). 2. Culture: Creating a culture that supports strategy. 3. Resource Allocation: Ensuring resources support strategic goals. 4. Leadership and Communication: Leaders must communicate strategy and adapt as needed. 5. Control Systems: Regularly review performance to ensure strategic goals are met. 8. Global Strategy (Pages 194-196) ● ● ● ● Global Strategy: Standardization of products and operations across countries. Multidomestic Strategy: Customizing products for different markets. Transnational Strategy: Balancing global efficiencies with local responsiveness. International Strategy: Exploiting home-based competencies in foreign markets. 9. Diversification Strategy (Pages 196-198) ● ● ● Types of Diversification: 1. Related Diversification: Expanding into areas related to current business activities. 2. Unrelated Diversification: Expanding into entirely different industries. Benefits: Reduces risk by spreading out across industries. Risks: Dilution of focus, managerial challenges, and difficulty in handling unrelated businesses. 10. Reshoring vs. Offshoring (Pages 198-199) ● Offshoring: Moving production or services to lower-cost countries. ● Reshoring: Bringing back operations to the home country due to rising costs abroad, shorter supply chains, and intellectual property concerns. 11. Corporate Governance (Page 199) ● ● 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Definition: The system by which companies are directed and controlled. Key Elements: 1. Board of Directors: Oversees management and ensures ethical practices. 2. Shareholder Interests: Ensures actions align with shareholder value. 3. Accountability: Ensures managers are held responsible for performance. What is the primary goal of strategic management? A) To formulate a strategy B) To achieve sustainable competitive advantage C) To implement the strategy D) To organize resources Answer: B Which of the following is a source of competitive advantage? A) Market entry strategies B) Technology C) Time management D) Political power Answer: B Which level of strategy focuses on the organization’s long-term direction? A) Corporate-level strategy B) Business-level strategy C) Functional strategy D) Product-level strategy Answer: A What does the BCG Matrix help to analyze? A) Competitive advantage B) Marketing strategies C) Business opportunities based on market share and growth D) Operational risks Answer: C What is a key challenge in strategy implementation? A) Lack of resources B) Poor strategy formulation C) Failures of substance and process D) High financial costs Answer: C Which strategy involves offering unique products that customers perceive as different from competitors? A) Cost leadership strategy B) Differentiation strategy C) Focus strategy D) Downsizing strategy Answer: B In Porter's competitive strategy model, what does a cost leadership strategy aim for? A) High market share at low cost B) Product differentiation C) Targeting a niche market D) Enhancing customer service Answer: A Which of the following is an example of a focused differentiation strategy? A) Great Value Cola B) Porsche’s sports cars C) Walmart’s low-cost strategy D) Amazon’s wide product selection Answer: B 9. What is a strategic alliance? A) Merging two companies B) A partnership formed to pursue a mutual interest C) Acquiring a competitor D) Creating a monopoly Answer: B 10. Which of the following is NOT a type of corporate strategy? A) Growth strategy B) Retrenchment strategy C) Restructuring strategy D) Functional strategy Answer: D 11. What is a multidomestic strategy? A) A strategy to standardize products worldwide B) A strategy that focuses on a single market C) A strategy that customizes products for local markets D) A strategy to expand internationally with minimal customization Answer: C 12. Which of the following best defines "corporate governance"? A) The process of implementing business strategies B) The control and monitoring of top management C) The creation of corporate strategies D) The analysis of market trends Answer: B 13. What does strategic leadership involve? A) Leading daily operations B) Inspiring teams and ensuring alignment with strategic goals C) Managing financial risks D) Focusing solely on short-term performance Answer: B 14. In the BCG Matrix, which category represents high market growth and high market share? A) Cash cows B) Dogs C) Stars D) Question marks Answer: C 15. What is a major reason for business diversification? A) To focus on a single product B) To reduce risks by expanding into new areas C) To reduce operational costs D) To improve market positioning in existing segments Answer: B 16. Which of the following is an example of a focus strategy? A) McDonald’s global standardization B) Zara’s quick fashion turnaround C) NetJets offering private air travel D) Apple’s product differentiation Answer: C 17. Which of the following is a key part of strategy formulation? A) Monitoring operational performance B) Analyzing the external environment C) Hiring new employees D) Setting daily operational goals Answer: B 18. What is the primary purpose of a mission statement in strategic management? A) To outline specific operational objectives B) To establish the organization's values and long-term direction C) To manage customer relations D) To describe financial goals Answer: B 19. What does Porter’s five forces model analyze? A) The internal environment of a company B) Industry attractiveness and competitive pressure C) Consumer buying behavior D) Organizational culture Answer: B 20. What is a turnaround strategy? A) A strategy to enter new markets B) A strategy focused on correcting poor performance C) A strategy to restructure the organization through mergers D) A strategy to diversify into unrelated areas Answer: B 21. What is the strategic intent of Patagonia? A) To expand globally B) To achieve the lowest cost C) To save the home planet D) To offer the best customer service Answer: C 22. What is a primary factor in a successful differentiation strategy? A) Cost reduction B) Product uniqueness and customer loyalty C) Operating in niche markets D) Expanding into multiple industries Answer: B 23. What does "strategic control" ensure in an organization? A) Employees are satisfied with the work environment B) Strategies are being implemented effectively and results are monitored C) Managers have the freedom to make decisions D) Financial resources are allocated equally Answer: B 24. What role does a functional strategy play in an organization? A) It sets the overall strategic direction of the organization B) It supports business strategies within specific departments C) It formulates corporate strategies D) It focuses on external market analysis Answer: B 25. Which of the following is an example of a "cash cow" in the BCG Matrix? A) A new product in a high-growth market B) A well-established product in a mature market C) A product with low market share in a growing industry D) A product that has been recently launched Answer: B 26. What is the role of a strategic leader? A) To allocate resources based on short-term needs B) To ensure alignment of organizational efforts with long-term strategy C) To manage day-to-day operations D) To oversee financial audits Answer: B 27. What does a global strategy focus on? A) Customizing products for local markets B) Standardizing products and marketing worldwide C) Creating a cost leadership position in local markets D) Acquiring competitors in each region Answer: B 28. Which type of strategy does McDonald's use globally? A) Global strategy with full standardization B) Multidomestic strategy with local customization C) Transnational strategy blending global efficiencies D) Focus strategy on a specific market Answer: B 29. What is the purpose of strategic alliances? A) To reduce competition by monopolizing the market B) To share resources and gain mutual benefits C) To acquire competitors in the same market D) To standardize products worldwide Answer: B 30. What does the process of strategy implementation require? A) Only resource allocation B) Monitoring and adjusting resources and operations C) Regularly reviewing corporate financial statements D) Focusing only on customer feedback Answer: B Front: What is strategic management? Back: Strategic management is the process of formulating and executing strategies to achieve long-term goals and gain a competitive advantage. Front: What is competitive advantage? Back: Competitive advantage is when a company outperforms its competitors through cost leadership, differentiation, or unique resources. Front: What are the three levels of strategy? Back: 1. Corporate-Level: Focuses on overall direction. 2. Business-Level: Focuses on how to compete in a market. 3. Functional-Level: Supports business strategy through departments like marketing. Front: What are Porter's competitive strategies? Back: 1. Cost Leadership: Lowest cost producer. 2. Differentiation: Unique products. 3. Focus: Target a niche market. Front: What is the BCG Matrix? Back: A tool to assess business units/products: ● ● ● ● Stars: High market share and growth. Cash Cows: High market share, low growth. Question Marks: Low share, high growth. Dogs: Low share and growth. Front: What is a growth strategy? Back: A growth strategy focuses on increasing market share, often through concentration (existing market) or diversification (new market). Front: What are the challenges in strategy implementation? Back: 1. 2. 3. 4. Poor strategy or analysis. Lack of involvement. Misaligned management. Weak leadership. Front: What are strategic alliances? Back: Strategic alliances are partnerships where companies work together for mutual benefit, like outsourcing or co-marketing. Front: What is the role of strategic leadership? Back: Strategic leaders guide the organization by allocating resources, motivating teams, and ensuring the strategy is clear and understood. Front: What is a global strategy? Back: A global strategy involves standardizing products worldwide, while a multidomestic strategy customizes products for each market. Lithium-ion battery growth: 10-fold increase from 2005–2025. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Electrification: Driven by climate change, reducing fossil fuel use. Green economy: Supports battery use. Battery makers: Displacing oil giants. Charging stations: Becoming widespread, with companies like Flo and Sun Country Highway in Canada. Cost decrease: From $2,300–$3,500 (2010–2019). Battery comparison: Gap between lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries closing. Internal combustion engines (ICE): Still common, but EVs are growing. Major companies: Panasonic and CATL (growing Chinese company). Electric planes: Challenges in range (e.g., New York–Jaboury, 7,973 miles). Battery elements: Lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese. Cobalt sourcing: 60% from Congo, with ethical concerns. Sustainability: Solving cobalt issues could replace oil. Sodium batteries: Abundant, cheaper, heavier, with potential for global production and R&D. Lithium-ion issues: Dependent on China for graphite, costly, relies on cobalt and nickel. R&D: Essential for improving battery tech. EV revolution: BYD and Tesla transforming mobility. Nissan Leaf: Best-selling EV. Charging station gaps: Infrastructure lacking in North America. EV access: Changai (China) offers easy downtown access. Canada support: Tax credits for EVs to support green economy. Battery range: 120–500 km (250 miles). Autonomous vehicles (AVs): Waymo leading, with potential for ride-sharing in cities like Chandler (Phoenix). Global AV potential: Could operate in Mumbai (India), Lagos (Nigeria), Manila (Philippines), Cairo (Egypt). EARNING OBJECTIVE 14.1: Leadership Foundations in Power, Vision, and Service ● Leadership: Inspires others to work hard to complete important tasks. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Vision: Clear sense of the future, essential for leadership. Power: Ability to influence others. ○ Position Power: Includes rewards, coercion, and formal authority. ○ Personal Power: Includes expertise, referent power, and information/networking. Servant Leadership: Focuses on empowering and helping others use their talents. Followership: Working with a leader to achieve tasks. Romance of Leadership: Tendency to focus on leaders and overlook followers. Discussion: When can a leader use coercive power? LEARNING OBJECTIVE 14.2: Key Leader Behaviours Impacting Leadership Effectiveness Important Traits: Drive, integrity, and self-confidence. Leader Behaviours: Leaders should balance task focus and people focus. Effective Leaders: Work well in teams, are participative, and care about both tasks and people. Discussion: Are certain traits necessary for leadership? LEARNING OBJECTIVE 14.3: Situational Contingencies and Leadership Effectiveness ● ● ● ● ● ● Contingency Leadership: Best leadership style depends on the situation. Fiedler’s Model: Matches leadership style with task, position power, and leader-member relations. Hersey-Blanchard Model: Use task-oriented or people-oriented behaviours based on followers’ maturity. Path-Goal Theory: Leaders should be supportive, directive, achievement-oriented, or participative. Vroom-Jago Model: Choose decision-making methods based on the problem. Discussion: What are the career implications of Fiedler’s model? LEARNING OBJECTIVE 14.4: Challenges of Personal Leadership Development ● ● ● ● Transformational Leadership: Inspires with charisma and emotion. Emotional Intelligence: Ability to manage relationships and emotions. Interactive Leadership: Focuses on communication, involvement, and respect. Moral Leadership: Managers should maintain high ethical standards and personal integrity. Authentic Leadership: Promotes self-awareness and self-regulation. Authority Decision: Leader makes and communicates decisions. Autocratic Leader: Uses command-and-control style. Character Leadership: Builds trust with values and virtues. Charismatic Leader: Inspires followers in extraordinary ways. Coercive Power: Ability to punish or withhold rewards. Consultative Decision: Leader makes decisions after getting input. Democratic Leader: Balances tasks and people. Emotional Intelligence: Manages emotions in relationships. Empowerment: Giving others decision-making power. Expert Power: Influence based on knowledge. Followership: Working with a leader to reach goals. Gender Similarities Hypothesis: Males and females share similar traits. Group Decision: Team makes the decision together. Human Capital: Ability to get things done based on skills and knowledge. Human Relations Leader: Focuses more on people than tasks. Information Power: Influence through access to information. Integrity: Acting honestly and consistently. Interactive Leader: Communicates well and involves followers. Laissez-faire Leader: Hands-off, lets others do the work. Leadership: Inspires others to accomplish tasks. Leadership Double Bind: Women criticized for showing both male and female traits. Leadership Style: Consistent leader behaviors. Least-preferred Co-worker Scale: Measures leadership style (Fiedler’s model). Legitimate Power: Power from formal authority. Moral Leadership: Follows ethical standards and does what’s right. Moral Overconfidence: Overestimating one's moral strength. Power: Ability to influence others. Referent Power: Influence because others want to identify with you. Reward Power: Influence through rewards. Servant Leadership: Focuses on helping others and empowering followers. Social Capital: Influence based on who you know. Substitutes for Leadership: Factors that guide work without a leader. Transformational Leadership: Inspires extraordinary effort and performance. Vision: Clear sense of the future. Visionary Leadership: Understanding the future and how to achieve it. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Someone with a clear sense of the future and the actions needed to get there is considered a ______ leader. a. task-oriented b. people-oriented c. transactional d. visionary 2. Leader power = ______ power + ______ power. a. reward, punishment b. reward, expert c. legitimate, position d. position, personal 3. A manager who says “Because I am the boss, you must do what I ask” is relying on ______ power. a. reward b. legitimate c. expert d. referent 4. When a leader assumes that others will do as she asks because they want to positively identify with her, she is relying on ______ power to influence their behaviour. a. expert b. referent c. legitimate d. reward 5. The personal traits now considered important for managerial success include ______. a. self-confidence b. gender c. age d. height 6. In the leader-behaviour approaches to leadership, someone who does a very good job of planning work, setting standards, and monitoring results would be considered a(n) ______ leader. a. task-oriented b. control-oriented c. achievement-oriented d. employee-centred 7. When leader behaviour researchers concluded that “high-high” was the pathway to leadership success, what were they referring to? a. High initiating structure and high integrity. b. High concern for task and high concern for people. c. High emotional intelligence and high charisma. d. High job stress and high task goals. 8. A leader whose actions indicate an attitude of “do as you want, and don’t bother me” would be described as having a(n) ______ leadership style. a. autocratic b. country club c. democratic d. laissez-faire 9. In Fiedler’s contingency model, both highly favourable and highly unfavourable leadership situations are best dealt with by a ______ leader. a. task-motivated b. laissez-faire c. participative d. relationship-motivated 10. ______ leadership model suggests that leadership style is strongly anchored in personality and therefore hard to change. a. Trait b. Fiedler’s c. Transformational d. Path-goal 11. House’s ______ theory of leadership says that successful leaders find ways to add value to leadership situations. a. trait b. path–goal c. transformational d. life-cycle Management Skills & Competencies: Make Yourself Valuable! 279 12. A leader who ______ would be described as achievementoriented in the path–goal theory. a. sets challenging goals for others b. works hard to achieve high performance c. gives directions and monitors results d. builds commitment through participation 13. The critical contingency variable in the Hersey-Blanchard situational model of leadership is ______. a. followers’ maturity b. LPC c. task structure d. LMX 14. Vision, charisma, integrity, and symbolism are all on the list of attributes typically associated with ______ leaders. a. contingency b. informal c. transformational d. transactional 15. The interactive leadership style, sometimes associated with women, is characterized by ______. a. inclusion and information sharing b. use of rewards and punishments c. command and control d. emphasis on position power Answers: 1. d 2. d 3. b 4. b 5. a 6. a 7. b 8. d 9. a 10. b 11. b 12. a 13. a 14. c 15. a Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act: Protects firms while reorganizing to become solvent. BCG Matrix: Analyzes business opportunities by growth and market share. Business Strategy: Plan for competing in the market. Competitive Advantage: Doing something better than competitors. Concentration: Growing within the same business area. Co-opetition: Collaborating with competitors. Core Competency: Strength that gives a competitive edge. Core Values: Beliefs on acceptable behavior. Corporate Governance: Controls and monitors management. Corporate Strategy: Long-term company direction. Cost Leadership: Selling at low prices by cutting costs. Differentiation: Offering unique products. Diversification: Expanding into new business areas. Divestiture: Selling parts of the business. Downsizing: Reducing operations. Focus Strategy: Serving a specific market better. Focused Cost Leadership: Lowest cost in a market segment. Focused Differentiation: Unique products for a market segment. Functional Strategy: Guides specific operations. Globalization Strategy: Standardized products worldwide. Growth Strategy: Expanding current operations. Lack-of-Participation Error: Not involving key people in planning. Liquidation: Closing and selling assets. Mission: Organization’s purpose. Multidomestic Strategy: Customizing products for local markets. Operating Objectives: Specific goals to achieve. Organizational Culture: Shared values and beliefs. Retrenchment, Restructuring, and Turnaround: Radical changes to solve problems. Stakeholders: People affected by the organization. Strategic Alliance: Partnership to achieve common goals. Strategic Analysis: Examining the company and competition. Strategic Control: Ensuring strategies are well implemented. Strategic Intent: Focused on a clear goal. Strategic Leadership: Inspires strategy changes and improvement. Strategic Management: Creating and executing strategies. Strategy: Plan for achieving long-term goals. Strategy Formulation: Creating strategies for resource allocation. Strategy Implementation: Putting strategies into action. Sustainable Competitive Advantage: Hard-to-imitate edge over competitors. SWOT Analysis: Examining strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Transnational Strategy: Global efficiency with local adaptation. Turnaround Strategy: Fixing performance issues. Vertical Integration: Expanding by acquiring suppliers or distributors. LEARNING OBJECTIVE 10.1: Strategic Management ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Competitive Advantage: Outperforming rivals in a way that’s hard to imitate. Strategy: Long-term plan for achieving goals and staying ahead. Corporate Strategy: Sets direction for the whole organization. Business Strategy: Direction for a division or product line. Functional Strategy: Supports business and corporate strategies. Strategic Management: Formulating and implementing strategies in a competitive environment. Discussion: Can a good strategy fail to create competitive advantage? LEARNING OBJECTIVE 10.2: Strategic Analysis ● ● ● ● Start with Analysis: Mission, core values, and objectives. SWOT Analysis: Assesses strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Porter’s Five Forces: Analyzes industry competition and power dynamics. Discussion: Would a monopoly score well in Porter’s model? LEARNING OBJECTIVE 10.3: Corporate Strategies ● ● ● ● ● ● Growth: Expanding via concentration or diversification. Restructuring: Correcting issues via liquidation, downsizing, etc. Global Strategies: Use globalization, multidomestic, or transnational strategies. Cooperative Strategies: Form alliances for mutual benefit. BCG Matrix: Classifies products as “Stars,” “Cash Cows,” “Question Marks,” or “Dogs.” Discussion: Is restructuring good or bad news for investors? LEARNING OBJECTIVE 10.4: Business-Level Strategies ● ● ● ● ● ● Competitive Advantage: Gained through lower costs, better quality, speed, and more. Porter’s Strategy: Focus on market scope and competitive edge. Differentiation: Offer unique products. Cost Leadership: Operate at low costs to sell at low prices. Focus Strategy: Serve a specific market segment better. Discussion: Can a business use both cost leadership and differentiation? LEARNING OBJECTIVE 10.5: Strategy Implementation ● ● ● ● ● Management Practices: Support strategy through planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Pitfalls: Poor analysis or lack of participation can hurt implementation. Board of Directors: Monitors top management and governance. Top Managers: Ensure strategies are implemented and adjusted as needed. Strategic Leadership: Focuses on continuous strategy improvement. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. The most appropriate first question to ask in strategic planning is . a. “Where do we want to be in the future?” b. “How well are we currently doing?” c. “How can we get where we want to be?” d. “Why aren’t we doing better?” 2. The ability of a firm to consistently outperform its rivals is called . a. vertical integration b. competitive advantage c. incrementalism d. strategic intent 3. In a complex conglomerate such as General Electric that owns a large number of different businesses, a(n) level strategy sets strategic direction for a strategic business unit. a. institutional b. corporate c. business d. functional 4. The is a predominant value system for an organization as a whole. a. strategy b. core competency c. mission d. corporate culture 5. Cost efficiency and product quality are two examples of objectives of organizations. a. official b. operating c. informal d. institutional 6. An organization that is downsizing by laying off workers to reduce costs is implementing a strategy. a. growth b. cost differentiation c. restructuring d. vertical integration 7. When Canadian Tire acquired the Forzani Group, owner of Sport Chek and other sporting goods chains, the firm’s strategy was to grow by . a. related diversification b. concentration c. vertical integration d. cooperation 8. In Porter’s five forces framework, having increased industry attractiveness. a. many rivals b. many substitute products c. low bargaining power of suppliers d. few barriers to entry 9. A in the BCG Matrix would have a high market share in a low-growth market, and the correct grand or master strategy is . a. Dog, growth b. Cash Cow, stability c. Question Mark, stability d. Star, retrenchment 10. Strategic alliances that link together airlines in code-sharing and joint marketing agreements are examples of how businesses can use strategies. a. divestiture b. growth c. cooperation d. backward integration 11. The two questions asked by Porter to identify competitive strategies for a business or product line are: 1—What is the market scope? 2—What is the ? a. market share b. source of competitive advantage c. core competency d. industry attractiveness 12. According to Porter’s model of competitive strategies, a firm that wants to compete with its rivals in a broad market by Management Skills & Competencies: Make Yourself Valuable! 197 selling a very low-priced product would need to successfully implement a strategy. a. retrenchment b. differentiation c. cost leadership d. diversification 13. When Coke and Pepsi spend millions on ads trying to convince customers that their products are unique, they are pursuing a strategy. a. transnational b. concentration c. diversification d. differentiation 14. The role of the board of directors as an oversight body that holds top executives accountable for the success of business strategies is called . a. strategic leadership b. corporate governance c. logical incrementalism d. strategic opportunism 15. An example of a process failure in strategic planning is . a. lack of participation b. weak mission statement c. bad core values d. insufficient financial resources Answers: 1. a 2. b 3. c 4. d 5. b 6. c 7. a 8. c 9. b 10. c 11. a 12. c 13. d 14. b 15. a