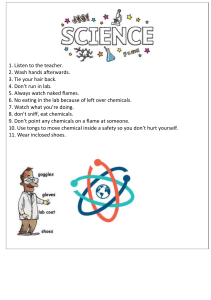
Chemical Storage and Supply Chain Management: Ensuring Safety, Efficiency, and Compliance 1. Introduction to Chemical Storage and Supply Chain Management Chemical storage and supply chain management are crucial aspects of the chemical industry, impacting everything from operational efficiency to worker safety. Whether dealing with corrosive acids, flammable solvents, or reactive chemicals, proper storage and transportation are essential to ensure safety, environmental protection, and regulatory compliance. In a highly regulated industry, the handling, storage, and movement of chemicals present unique challenges, as these materials can pose serious risks if mismanaged. Effective chemical storage and supply chain strategies ensure smooth operations and contribute significantly to reducing workplace hazards and environmental impacts. 2. Understanding the Basics of Chemical Storage Proper chemical storage goes beyond just placing materials on shelves. It requires stringent measures to prevent accidental releases, contamination, and hazardous reactions. Due to the potential dangers associated with chemicals, industries need to adhere to specific storage regulations. These guidelines ensure that chemicals are stored in a way that prevents hazards, reduces the likelihood of spills, and protects both human health and the environment. For example, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have guidelines that facilities must follow to ensure safe storage practices. ● ● ● ● Storage Compatibility: Chemicals must be stored based on their compatibility to avoid dangerous reactions. Temperature and Humidity Control: Sensitive chemicals require specific climate conditions. Spill Containment: Storage areas must be designed to handle spills or leaks to prevent contamination. Segregation: Reactive substances should be separated to prevent accidental reactions. 3. Types of Chemicals and Their Specific Storage Requirements Each type of chemical has unique characteristics and storage needs. Understanding these differences is vital to managing chemical risks effectively: ● ● ● ● Flammable Chemicals: These include substances like alcohols, solvents, and some gases. They require special storage away from ignition sources and within fire-resistant cabinets. Corrosive Chemicals: Acids and bases are highly corrosive and can damage storage containers if not properly handled. Special coatings and storage methods are necessary for these chemicals. Toxic Chemicals: Toxic chemicals, including pesticides and some solvents, need secure, leak-proof containment to prevent accidental exposure. Reactive Chemicals: Reactive substances, like sodium and potassium, can react violently with water or air, requiring dry and isolated storage. 4. The Role of Chemical Warehousing in Supply Chain Management Chemical warehousing plays a central role in the chemical supply chain by providing a secure location for inventory before distribution. Warehouses are designed to store chemicals safely while maintaining the quality of products through controlled environments. Efficient warehousing is essential to avoid costly delays and accidents, and it helps in streamlining the supply chain. ● ● Inventory Management: Warehousing enables accurate tracking of chemicals, avoiding overstocking or stockouts. Distribution Efficiency: Chemical warehouses facilitate quick, safe, and efficient dispatch to end-users. ● Enhanced Safety: Warehouses designed specifically for chemicals include features like fire suppression systems, temperature controls, and ventilation for hazardous materials. 5. Chemical Storage Facilities: Design and Structure Chemical storage facilities need to be meticulously planned and designed to meet both safety and operational needs. The facility structure includes various components essential for the safe storage of chemicals: ● ● ● ● Containment Systems: These include spill containment areas to manage accidental leaks. Ventilation Systems: Proper airflow prevents the buildup of toxic fumes. Temperature Controls: Sensitive chemicals require stable temperatures to prevent degradation or reactions. Security Measures: Facilities need to restrict access to prevent unauthorized handling. Facilities can be customized based on the chemicals being stored, with options like indoor, outdoor, and specialty warehouses tailored to specific chemical types.