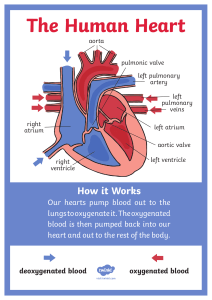
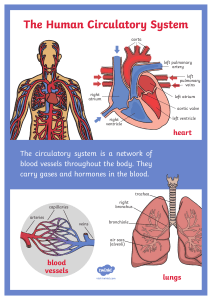
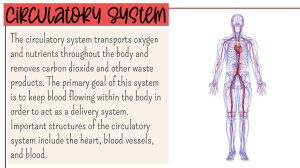
Chapter 10 F4: Transport in Humans and Animals 1. What type of exchange allows unicellular organisms to obtain essential substances? A. Active transport B. Diffusion C. Osmosis D. Endocytosis 4. In multicellular organisms, why is diffusion not effective for transporting substances to all cells? A. The distance between the external environment and the cell is too small B. The distance between the external environment and the cell is too large C. The cells are close to the external environment D. Multicellular organisms do not need diffusion 7. What is haemolymph? 8. How is the blood distributed in a A. Blood-like nutritious fluid found closed circulatory system? in vertebrates A. Through open-ended vessels into B. Blood-like nutritious fluid found the body cavity in most invertebrates such as insects B. Through a continuous closed and molluscs blood vessel system C. Pure blood that flows only in C. Directly between cells without vertebrates vessels D. Fluid responsible for D. By diffusion without the help of transporting oxygen in humans any vessel system 10. Which organisms typically have 11. Through which structure does 12. How many chambers are present an open circulatory system? haemolymph re-enter the heart in in the heart of a fish? insects? A. Mammals and birds A. One B. Insects and molluscs A. Aorta B. Two C. Fish and amphibians B. Veins C. Three D. Reptiles and mammals C. Arteries D. Four D. Ostium 2. Why do unicellular organisms like Amoeba sp. not require a specialized transport system? A. Their body cells are highly specialized B. They have a large total surface area to volume ratio (TSA/V) C. They have a complex circulatory system D. Their epidermis prevents direct diffusion 5. What is the primary function of a 6. In an open circulatory system, transport system in multicellular where does the haemolymph flow? organisms? A. Directly into closed blood vessels A. To produce energy for the cells B. Directly into the body cavity B. To directly perform diffusion (haemocoel) C. To transport essential substances C. Between the cells without any to and from cells vessels D. To remove the epidermis for D. In a continuous loop through the better exchange veins and arteries 9. What type of exchange occurs across the walls of blood capillaries in a closed circulatory system? A. Diffusion of oxygen and nutrients B. Diffusion of wastes only C. Direct contact of blood with body cells D. No exchange occurs across the walls 3. What prevents multicellular organisms from relying solely on diffusion to obtain essential substances? A. Their small TSA/V ratio B. The presence of specialized organs C. The complexity of their cells D. Their ability to perform active transport 1 13. What is the primary function of 14. What term describes the type of 15. In fish, oxygenated blood is the gill capillaries in fish? circulatory system in fish? transported to the tissues via which structure? A. Pump blood to the heart A. Double circulatory system B. Perform gaseous exchange by B. Open circulatory system A. Aorta transporting oxygenated blood C. Single circulatory system B. Systemic capillaries C. Collect nutrients for the fish D. Pulmonary circulatory system C. Haemocoel body D. Atrium D. Remove waste products from blood 17. What is the direction of blood 18. How many chambers does the 19. Which of the following flow in a fish’s single circulatory heart of an amphibian have? circulatory systems do amphibians system? A) One have? B) Two A) Single circulatory system A. From the heart to the tissues, and C) Three B) Pulmocutaneous circulation back to the heart D) Four C) Pulmonary circulation only B. From the heart to the lungs, and D) Systemic circulation only back to the heart C. From the heart to the gills, to the tissues, and then back to the heart D. From the tissues to the gills, then to the heart 21. What is the role of 22. What is the term used to 23. Through which artery is pulmocutaneous circulation in describe the human circulatory deoxygenated blood transported to amphibians? system where deoxygenated and the lungs? A) It transports blood to the liver oxygenated blood do not mix? B) It transports blood to the body A) Aorta tissues A) Single circulatory system B) Pulmonary artery C) It carries blood to the lungs and B) Pulmonary circulation C) Vena cava skin for gas exchange C) Double circulatory system D) Pulmonary vein D) It pumps blood to the heart D) Systemic circulation 2 16. In a fish’s circulatory system, what happens in the systemic capillaries? A. Blood is oxygenated B. Gaseous exchange occurs between blood and tissues C. Blood mixes with haemolymph D. Blood returns to the atrium 20. In humans, how many chambers does the heart have? A) Two B) Three C) Four D) Five 24. Where does oxygenated blood return after being transported to the lungs? A) Right atrium B) Right ventricle C) Left atrium D) Pulmonary artery 25. What type of blood is carried by the pulmonary vein? 26. What separates the left and right chambers of the heart? A) Deoxygenated blood B) Oxygenated blood C) Both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood D) None of the above A) Aorta B) Septum C) Pulmonary vein D) Vena cava 27. Why is the muscular wall of the left ventricle thicker than that of the right ventricle? 28. What ensures that blood does not flow back into the right atrium from the right ventricle? A) To pump blood to the lungs B) To generate more pressure to pump blood to the whole body C) To receive blood from the body D) To pump blood to the right atrium Answer: B) To generate more pressure to pump blood to the whole body 29. Which valve is located between 30. What prevents the backflow of 31. What percentage of human the left atrium and the left ventricle? blood into the ventricles when they blood is made up of plasma? relax? A) Tricuspid valve A) 25% B) Semilunar valve A) Bicuspid valve B) 45% C) Bicuspid valve B) Semilunar valves C) 55% D) Coronary valve C) Coronary valve D) 65% D) Vena cava 33. What is the function of 34. What percentage of blood is What is the main function of plasma erythrocytes in human blood? composed of erythrocytes? proteins such as fibrinogen? A) Aorta B) Semilunar valves C) Bicuspid valve D) Tricuspid valve A) Transport oxygen B) Defend the body from infections C) Form blood clots D) Transport nutrients A) 35% B) 45% C) 55% D) 65% A) Transport oxygen B) Involved in blood clotting C) Provide immunity D) Maintain osmotic pressure Which blood component controls blood osmotic pressure? A) Fibrinogen B) Albumin C) Globulin D) Hormones What is the shape of an erythrocyte? a) Spherical b) Biconcave disc c) Cuboidal d) Oval What is the primary function of haemoglobin in red blood cells? a) Transport of carbon dioxide b) Production of energy c) Oxygen transport d) Waste removal A) Medium for gas exchange and nutrient transport B) Provides immunity C) Assists in blood clotting D) Generates heat Where are erythrocytes produced? a) Liver b) Bone marrow of ribs and sternum c) Lungs d) Heart 3 32. Which component of blood is responsible for forming clots? A) Erythrocytes B) Platelets C) Plasma D) Leucocytes What role does water play in blood plasma? Which ion is present in the haem group of haemoglobin? How long is the lifespan of platelets? a) Sodium b) Potassium c) Iron d) Calcium a) 1 week b) 120 days c) 1 month d) 6 months Which type of leucocyte ingests What is the function of eosinophils? bacteria and dead cells through phagocytosis? a) Ingest bacteria and dead cells b) Prevent blood clotting a) Lymphocyte c) Fight inflammation and allergy b) Basophil reactions c) Neutrophil d) Produce antibodies d) Eosinophil What is the function of lymphocytes? What process involves the destruction of erythrocytes in the liver or lymph? Which of the following is a characteristic of leucocytes (white blood cells)? a) Phagocytosis b) Exocytosis c) Apoptosis d) Pinocytosis Which leucocyte contains heparin to prevent blood clotting? a) Contains haemoglobin b) Contains a nucleus c) Fixed shape d) Life span of 120 days Which leucocyte is the largest in size? a) Lymphocyte b) Basophil c) Monocyte d) Neutrophil a) Eosinophil b) Neutrophil c) Monocyte d) Basophil a) Release enzymes to fight inflammation b) Ingest bacteria and dead cells c) Produce antibodies to destroy bacteria and viruses d) Prevent blood clotting 4