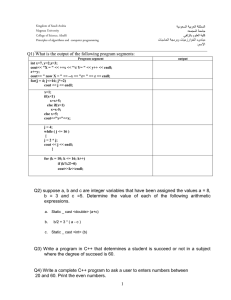
Q1)
Pre-increment (++i) −-> Before assigning the value to the variable, the value is
incremented by one.
Post-increment (i++) −-> After assigning the value to the variable, the value is
incremented.
Example 1:
Int a=3;
Cout<<a++;
Ouput :3 (didn’t increased)
Example 2:
Cout<<++a;
Ouput: 4 (variable increased )
Q2)
#include <iostream>:
tells the preprocessor to include the "iostream" header file to support
input/output operations.
using namespace std; :
declares std as the default namespace used in this program. The names
cout and endl, which is used in this program, belong to the std
namespace.
example:
#include <iostream> // Needed to perform IO operations
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Program entry point
cout << "hello, world" << endl; // Say Hello
return 0;
}
// Terminate main()
// End of main function
Q3)
#include <iostream> // Including the IO operation
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Display the full name and student ID
cout << "Full Name: Nawaf moslem" << endl; // Output full name
cout << "Student ID: 1124261338" << endl;
return 0; // program ended successfully
}
// Output student ID
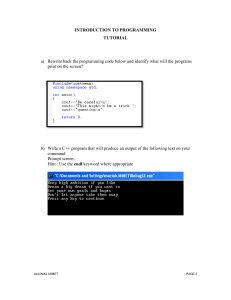
Output Screen:
Q4)
Output screen:
Output:
include <iostream> // Including the IO operation
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num1, num2; // Declare two integer variables
// Prompt first integer
cout << "Enter the first integer: ";
cin >> num1;
// Prompt the second integer
cout << "Enter the second integer: ";
cin >> num2;
// Display the results
cout << "\nResults:" << endl;
cout << "Sum: " << num1 + num2 << endl;
display the sum
// Calculate and
cout << "Difference: " << num1 - num2 << endl;
display difference
// Calculate and
cout << "Product: " << num1 * num2 << endl;
display product
// Calculate and
// Calculate and display the quotient
cout << "Quotient: " << static_cast<float>(num1) / num2 << endl;
return 0;
}
Bonus Question:
float can hold up to 7 decimal digits accurately while double can hold up
to 15
a double can represent much larger numbers than a float. Both data
types represent numbers with decimals, but a float is 32 bits in size
while a double is 64 bits. A double is twice the size of float this the
term double .
and another difference:
float range: 3.4×10^-38
to 3.4×10^38
double range: 1.7×10^-308 to 1.7×10^308
example:
float f = 3.1415926535f;
double d = 3.1415926535;