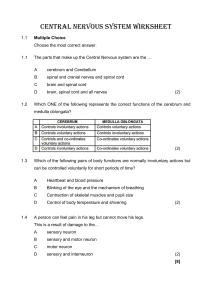
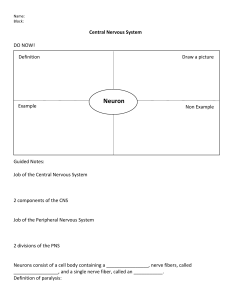
9th August 2024. HSB Coordination & Control The human nervous system consists of: 1. Central Nervous System (CNS) – brain and spinal cord. 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – cranial & spinal nerves and autonomic nervous system (network of nerves around the body that control unconscious processes such as breathing and heart rate). HOMEWORK!!! 1. Draw and label the human brain. Give the function of each structure: Cerebrum Cerebellum Medulla Oblongata Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland 2. Draw and label the different types of neurones. 3. Explain what synapses are and how they work. (research) Neurones Specialised cells that conduct nerve impulses throughout the nervous system. 3 types: 1. Sensory neuron 2. Motor neuron 3. Relay or Intermediate neuron. Sensory Neuron Transmits nerve impulses from RECEPTORS to CNS. Motor Neuron Transmits nerve impulses from CNS to EFFECTORS. Relay or Intermediate Neuron LINKS sensory neuron and motor neuron. Properties of Neurones. 1. Irritability – ability to convert a stimulus into an electrical (nerve) impulse. 2. Conductivity – ability to transmit nerve impulses to other neurones, muscles or glands. Nerves Cordlike bundles of nerve fibres of neurones surrounded by connective tissue through which impulses pass between the CNS and the rest of the body. 3 types: 1. Sensory nerves (afferent nerves) – contain nerve fibres from sensory neurones ONLY. 2. Motor nerves (efferent nerves) – contain nerve fibres from motor neurones ONLY. 3. Mixed nerves – contain nerve fibres from BOTH sensory and motor neurones. Two categories of nerves: Cranial Nerves – connect to the brain. Spinal Nerves – connect to the spinal cord.