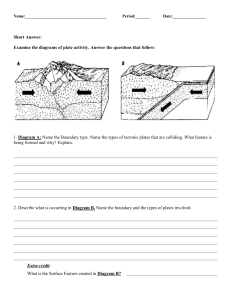
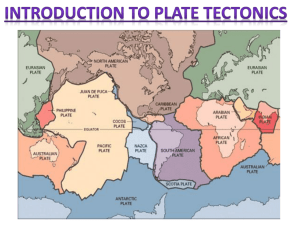
Plate movement Inner core(内地核) Outer core(外地核) Mantle(地幔) Crust(地壳) Continental Crust 陆壳 Oceanic Crust 洋壳 Thickness 35-40km on average 60-70km under mountain chains 6-10km on average Age of rocks Very old, over 1500 million years Very young, under 200 million years Weight of rocks Lighter, average density 2.6 g/cm3 Heavier, average density 3.0g/cm3 Nature of rocks Light in color, many contain silica and aluminum铝 Dark in color, many contain silica and magnesium镁 Mid-Atlantic Ridge 大西洋中脊 East-Pacific Rise 东太平洋洋隆 Mid-India Ridge 印度洋中脊 亚欧板块 北美洲板块 太平洋板块 非洲板块 南美洲板块 澳大利亚印度板块 南极洲板块 The lithosphere is broken into about two dozen segments of irregular shape and size calls lithospheric plates 板块. Plate tectonics 板块构造 Plate tectonics is the study of the movement of plates and their resultant landforms. The plates move relative to one another along plate boundaries. Plate boundaries are classified into three types based on the type of motion occurring between the adjacent plates. Boundary Divergent 离散型 Motion Results • Creation of new ocean floor with submarine volcanoes; Plates move apart • mid-oceanic ridge; • small to moderate earthquakes • Destruction of ocean floor; Convergent 汇聚型 Plates move towards each other • creation and growth of mountain range with volcanoes; subduction zone; • Earth’s greatest earthquakes and tsunamis Transform 转换型 Plates move sideways past each other No creation or destruction of crust; small to large earthquakes Oceanic ridges Oceanic crust North America ◼Divergent/constructive plate boundaries Partial melting Asthenosphere Europe 扩张型板块边界 where two plates move apart, resulting in Spreading center Africa upwelling and partial melting of hot material from the mantle to create new crust. Upwelling continental oceanic ◼ Convergent/destructive plate boundaries 汇聚型板块边界—two plates move toward oceanic oceanic each other. ◼ The character of the boundary depends partly on the types of plates. continental continental Benioff zone Aerial view of San Andreas Faults 圣安德烈斯断层 ◼ Conservative boundary 平错型边界 Two plates move sideways past each other, land is neither formed nor destroyed. ◼ Transform faults 转换断层 are marked by shallow-focus earthquakes in a narrow zone for a single fault or a broad zone for a group of parallel faults Type of plate boundary Description of changes Examples Constructive boundary Two plates move away from each other; new oceanic Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Eurasian and African Plates, crust appears forming mid-ocean ridges with volcanoes East Pacific Rise Destructive boundary Andes(Nazca sinks under South American Plate) Oceanic crust moves towards continental crust but, Rockies(Juan de Fuca sinks under North being heavier, sinks and is destroyed forming deep-sea American Plate) trenches and island arcs with volcanoes Island arcs of the West Indies and Aleutians Collision zones Conservative boundary Two continental crusts collide and, as neither can sink, Himalayas, Alps are forced up into fold mountains Two plates move sideways past each other, land is San Andreas Fault in California neither formed nor destroyed