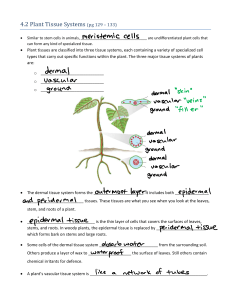
Astolot Educational Centre – Alisa Miller – SNC2D 4.1 Systems in Plants (focus on flowering plants) Pg. 125 – 128 • • • Plants have two obvious distinguishing features: o They are typically green in colour – caused by chlorophyll (used to photosynthesize) o They cannot move from place to place – they have structures (usually roots) to anchor in place Plants perform photosynthesis to make their own food o They do not need to move around to search for food o They do not need the complex organ systems that animals have Plants do have to perform many of the same functions as animals: o Exchange gas with their surroundings o They require an internal transport system to move water and nutrients around their bodies o Reproduce Hierarchy of Organization in the Plant Body • The flowering plant body has two main body systems: o The root system ! Made up of one or more separate roots o The shoot system ! Consists of the stem, leaves, and flowers ! These are sometimes called the plant’s organs • Plant parts are made up of a wide variety of specialized cells o Like in animals, groups of specialized cells are called tissues • Three main types of tissue systems: o Dermal tissue system – the tissues covering the outer surface of the plant o Vascular tissue system – the tissues responsible for conducting materials within a plant o Ground tissue system – all plant tissues other than those that make up the dermal and vascular tissue systems The Root System • Root system – the system in a flowering plant, fern, or conifer that anchors the plant, absorbs water and minerals, and stores food • Usually grows below ground, but can appear above ground or above water • The root system can spread underground to cover a large area • Some roots are specialized for nutrient storage o E.g. radishes and carrots • Roots are a useful source of foods (sweet potatoes, carrots, sugar beet), flavourings (liquorice, ginger), and natural remedies Astolot Educational Centre – Alisa Miller – SNC2D The Shoot System • Shoot system – the system in a flowering plant that is specialized to conduct photosynthesis and reproduce sexually o It consists of the leaf, the flower, the stem The Leaf • The main photosynthetic structure of the plant • In photosynthesis, tissues in the leaf use carbon dioxide (CO2), water, and light energy to produce glucose (a sugar) and oxygen o Glucose is used for plant growth, cellular respiration, and energy storage) o Light energy + carbon dioxide + water " glucose +oxygen • The cell structure that actually performs photosynthesis is an organelle called a chloroplast o Contain flat, disc-like structures called thylakoids o Thylakoids are arranged into stacks called grana o These stacks collect sunlight • Some leaves are adapted for support, protection (e.g. thorns), reproduction, and attraction • Many leaves are edible (e.g. lettuce, spinach, onion, tea, and herbs), or sources of waxes and medicines The Flower • Specialized structures developed for sexual reproduction o Contain male or female reproductive structures, sometimes both • Male reproductive structures produce pollen grains, and female reproductive structures produce eggs o Eggs are fertilized by pollen o After pollination, the female flower parts form seeds o In most flowering plants, the seeds are contained within a specialized structure called a fruit • Pollination occurs with the help of wind or animals o Flowering plants like grasses and many tree species are wind pollinated ! The flowers are small and not colourful, but produce a lot of pollen o Others are pollinated by animals like insects, bats, and birds ! They have large colourful and fragrant flowers to attract pollinators ! Most also produce nectar Astolot Educational Centre – Alisa Miller – SNC2D The Stem • The stem (or trunk, for trees) supports the branches leaves, and flowers, and provides a way to transport materials • Contains a lot of vascular tissue for carrying substances to and from roots, leaves, flowers, and fruits • Some are specialized for food storage, protection, photosynthesis, and reproduction • Provide us with sugar cane, potatoes, wood and paper products, cork, linen, and some medicines 4.2 Plant Tissue Systems Pg. 129 – 133 Cellular Differentiation and Specialization in Plants • When a seed starts to grow, the cells divide very quickly o As the seed develops into an embryo, many cells differentiate into specific tissues o The region of growth are at the tips of plant roots and shoots o Plants with woody stems, such as trees, also have a region of growth just below the surface of their stems Meristematic Cells • Just like animals have unspecialized cells called stem cells, plants have unspecialized cells called meristematic cells o Can differentiate into specialized tissue types • As cells in the meristem regions continue to divide, some of the new cells always remain in the undifferentiated state Tissue Systems in Plants 3 major tissue systems: o Dermal tissues cover the entire outer surface of the plant but do not occur within the plant o Vascular tissues are found within every root, shoot, and leaf of the plant o Ground tissues account for all other internal tissues in the root, stem, and leaves Dermal Tissue System • Forms the outer layers of a plant o Includes both epidermal and periderm tissues • Epidermal tissue (epidermis) – a thin layer of cells covering all non-woody surfaces of the plant • Periderm tissue – tissue on the surface of a plant that produces bark on stems and roots • Astolot Educational Centre – Alisa Miller – SNC2D Vascular Tissue System • A plant must obtain water and minerals from the soil o Absorbed by the plant’s roots • The vascular tissue system is the transportation system that moves water, minerals, and other chemicals around the plant • 2 types: • Xylem – vascular tissue in plants that transports water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves and stems of the plant o Made up of elongated cells o Hollow tubes with rigid walls – they have no cytoplasm, nucleus or other organelles, which allows water to move easily through the tubes o Mature xylem cells are not living tissue • Phloem – vascular tissue in plants that transports dissolved food materials and hormones throughout the plant o Made up of elongated cells o Mature cells are alive Ground Tissue System • Most of the cells of young plants are ground tissue cells • They are the filler between the dermal and vascular tissues • Perform a variety of functions: o In the green parts of the plant, they manufacture nutrients by the process of photosynthesis o In the roots, they store carbohydrates o In the stems, they provide storage and support Homework -Read 4.1 Systems in Plants, Pg. 125 – 128 -Complete Plant Body System Tree Diagram -Pg. 128 #3, 4, 5 -Read 4.2 Plant Tissue Systems, Pg. 129 – 133 -Pg. 133 #2, 3