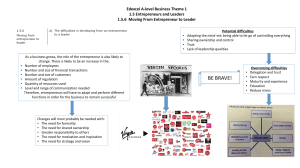
Entrepreneurship 9 Entrepreneurship Entrepreneurship refers to the concept of developing and managing a business venture to gain profit by taking several risks in the corporate world. Why entrepreneurship is important? 1. Entrepreneurship creates employment 2. Entrepreneurship improves the quality of life 3. Entrepreneurship contributes to a more equitable distribution of income and therefore eases social unrest. 4. Entrepreneurship utilizes resources for national productivity. 5. Entrepreneurship brings social benefits through Who are entrepreneurs? The word entrepreneur is borrowed from the French language. It is derived from ‘entreprendre’ meaning to ‘undertake’. One who organizes and manages any enterprise, especially one involving considerable risk. A person who sets up a business or businesses, taking on financial risks in the hope of profit. Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs • Integrity - someone once said, “Right is right even if no one is doing it, and wrong is wrong even if everyone is doing it”. Successful entrepreneurs are rated “being honest with everyone” the number one factor of their success Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs • Self –discipline – to become a successful entrepreneur you have to be highly disciplined. You have to develop the ability to get things done, even when you don’t feel like it. Luckily, you learn selfdiscipline with the right information and conscious effort. Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs People skills - another critical factor among successful entrepreneurs is having good people skills. You should make an effort to genuinely like, respect, and appreciate other people. The ability to win people over will carry you far in all walks of life, especially your own business Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs Strong work ethics – there’s no substitute for hard work when it comes to becoming a successful entrepreneur. Most people want to do the fastest and easiest solution when it comes to work. To be successful, dedicate yourself to persistent, productive, and old fashioned hard work Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs Passion – you need to be passionate about your business. Loving your business will also make it easier to get through the start-up phase, and other future obstacles. Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs Strong leadership qualities – being able to communicate effectively, motivate others, sell your ideas, and be decisive, are just a few qualities of a good leader. In order to become a successful entrepreneur you must dedicate yourself of improving your leadership and abilities. Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs • Competitiveness – competition is everywhere. In business, it is the survival of the fittest. Play to win, but never sacrifice your integrity for the sake of a few bucks. Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs Well-organized – One of the main reason why small businesses fail is lack of organization. Everyone can learn organization skills with enough hard work, practice and persistence. Characteristics and Qualities of a Successful Entrepreneurs Sales ability- The ability to convince others to make a conscious decision is a key of becoming a successful entrepreneur “People don’t buy for logical reasons. They buy for emotional reasons”. Being able to appeal to other people emotions is the key to selling your ideas, products or services. Personal Entrepreneurial Characteristics (PECs) Clusters and Behavioral Indicators Personal Entrepreneurial Characteristics Clusters and Behavioral Indicators I. Achievement Cluster II. Planning Cluster III. Power Cluster I. Achievement Cluster 1. Opportunity-Seeking. An entrepreneur is said to be a good opportunity seeker if he sees and acts on new business opportunities and seizes unusual opportunities to acquire financing, equipment, land and workspace or assistance I. Achievement Cluster Persistence. A persistent individual is one who: a. takes different actions to overcome an obstacle b. makes personal sacrifice or spends extraordinary efforts to complete a job c. sticks to his judgments in the face of opposition or early lack of success I. Achievement Cluster Commitment to the Work Contract. The true-blue entrepreneur is committed to the work that he has agreed to do. He exerts extra effort to satisfy the costumer. In the end, if he fails he would take full measure of the blame. But if he succeeds, he expects to get full credit. I. Achievement Cluster Risk Taking. A successful entrepreneur takes calculated, moderate, or reasonable risks where he perceives the chances for winning to be good. I. Achievement Cluster Demand for Quality and Efficiency. A true entrepreneur is not satisfied with mediocre work. He sets a high standard of performance. He strives to do things better, faster, or cheaper II. Planning Cluster 6. Goal-Setting. An entrepreneur always thinks not only of what he wants to accomplish day-to-day but also in one, two, or five years from now. In other words, he sets clear and specific short-andlong term objectives. II. Planning Cluster 7. Information-Seeking. As a careful planner, the successful entrepreneur always makes it a point to seek information that is relevant and useful to his present or future business. II. Planning Cluster 8. Systematic Planning and Monitoring. The successful entrepreneur does systematically plans and monitors his activities and performance. He develops and uses alternatives and monitors his progress. He is ready to switch to alternative strategies when necessary to achieve his goals. III. Power Cluster 9. Persuasion and networking. A persuasive person who readily establishes a network or personal business contracts around him usually makes a good entrepreneur. In order to persuade others, the entrepreneur uses deliberate strategies. In order to accomplish his business objectives he uses his network of useful friends and acquaintances III. Power Cluster 10.Self-Confidence. The entrepreneur exudes selfconfidence. He strongly believes in himself and his own abilities. No challenge is too difficult nor is a task too big that the entrepreneur would indulge in self-doubt. When he enters a business, it is because he is confident that the business would be successful and profitable. MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS OF ENTREPRENEURS MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS OF ENTREPRENEURS (POSDiCon) Planning Organizing Staffing Directing Controlling MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS OF ENTREPRENEURS PLANNING • Planning is the most basic management function that tells you where to go and how to get there. It is like preparing a blueprint of what is to be done, when, how, and by whom it should be done. Classification of Plans: 1. Standing plans. These plans are used repeatedly and cover policies, procedures, and rules. 2. Single-used or single-purpose plans. These plans are essentially one-shot or non repetitious. This is used within a relatively short period of time, they comprise programs, projects, and budgets. Types of Planning: 1. Tactical Plan (Long-range) prepared by top-level management. 2. Strategic Plan (intermediate range) prepared by middle-level management. 3. Operational Plan (short-range) prepared by lowerlevel management. MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS OF ENTREPRENEURS ORGANIZING • Organizing involves identifying the specific activities necessary to achieve the enterprise goals, clustering the activities into departments or job positions, and designating the personnel to head and compose each department. MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS OF ENTREPRENEURS ORGANIZING • Organizing involves identifying the specific activities necessary to achieve the enterprise goals, clustering the activities into departments or job positions, and designating the personnel to head and compose each department. Types Of Organization Structure A. LINE ORGANIZATION B. LINE AND STAFF ORGANIZATION C. FUNCTIONAL STAFF ORGANIZATION D. COMMITTEE A. LINE ORGANIZATION B. LINE AND STAFF ORGANIZATION C. FUNCTIONAL STAFF ORGANIZATION D. COMMITTEE Another common organizational form used in situations where group participation and decision are required. These are created to undertake special activities rather than routinary activities. ORGANIZATIONAL CHART is a diagram or drawing that shows the organizational relationships of the positions and their corresponding authority, responsibility, and accountability. It is a diagrammatical form which shows the important aspects of an organizational structure. Staffing ✓It is the process of recruiting, selecting and training of men. It means putting the right men on the right job. ✓This process involves proper and effective selection, appraisal and development of personnel to do the jobs and fulfill the roles in the structure. Recruitment is the process of encouraging, inducing or influencing applicants to apply for a certain vacant positions. Selection is the process of getting the most qualified applicant from among different job seekers Training is the systematic development of the attitude, knowledge, behavior patterns for the adequate performance of a given job or task. How to do staffing? ✓Asses your workload ✓ Study jobs in the company ✓Examine your present personnel. ✓Design an improvement plan DIRECTING Directing involves putting your plans into effect. How to influence your subordinates who have distinct needs and a unique personality, to contribute to the attainment of the firm’s objectives is the principal concern of directing. Directing includes the following: ➢Motivation ➢Leadership ➢Communication CONTROLLING The function of controlling is to make sure that what is done in the enterprise conforms to what has been planned. Controls can be classified as: ➢Organizational controls are those that measure the over all performance of the organization. ➢Operational controls evaluate day to day activities and spot areas where you may need to take corrective actions Legal Forms of Business Legal Forms of Business Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation Cooperative Sole Proprietorship A sole proprietorship is a business unit owned and managed by only one person. It is the simplest and most common form. Most small businesses start as sole proprietorships. Here, you and the business are essentially one. You, as the sole proprietor owns all the assets. As such, you will exclusively enjoy the benefits to be derived from the business. If you decide to become a sole proprietor, you do not need to consult anyone on matters related to setting or running the business. Partnership Under this business form, two or more persons are owners of the business. The owners define their rights and duties as partners in the business through a partnership agreement. Corporation This business form is initiated by individuals called incorporators, numbering from a minimum of five to a maximum of fifteen. Cooperative A cooperative is owned by twenty-five or more individuals who, like in a corporation buy shares in the business. However, unlike a corporation, each member of the cooperative is entitled to only one vote on matters regarding the business regardless of the number of shares he or she has bought. In case of losses, responsibility for paying liabilities is also borne equally by the members. Cooperative ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES Lower Cost Equal voting rights Equal voting rights Shared responsibility Limited liability