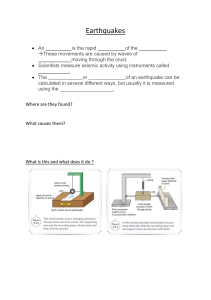
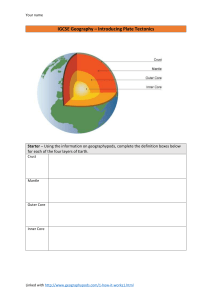
Republic of the Philippines Department of Education REGION VIII Division of Samar Sta. Rita II, District TOMINAMOS INTEGRATED SCHOOL Sta. Rita, Samar FIRST QUARTER PRE-TEST in SCIENCE 10 EARTH AND SPACE Direction: Read and understand each question/statement carefully and choose the best answer. Carefully shade your answer in the answer sheet provided. 1. Where is the earthquake epicenter located? A. In the Earth's core B. On the Earth's surface C. Beneath the Earth's crust D. At the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of the earthquake. 2. What is a mountain range? A. A single tall mountain. B. A group of tall mountains. C. A long chain of tall mountains. D. A continuous series of tall mountains that stretches across a continent or region. 3. Which correctly describes the distribution of active volcanoes with respect to the earthquake epicenter? A. Active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters are often found in along tectonic plate boundaries. B. Active volcanoes are typically located on continents, while earthquake epicenters are mainly in the oceans. C. Active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters have no significant relationship; they occur randomly across the Earth's surface. D. Active volcanoes are primarily associated with mid-ocean ridges, while earthquake epicenters are found near continental rift zones. 4. You were asked to locate the epicenter of the recent earthquake. Which correct sequence of events should you follow? I. Determine the difference in the arrival time of S and P waves recorded from each of the seismological stations. II. Use the triangulation method to locate the center. III. Obtain data from three different seismological stations. IV. Determine the distance of the epicenter from the station. A. I, III, II, IV B. III, I, IV, II C. III, IV, I, II D. IV, II, I , III 5. How will you relate the distribution of active volcanoes with the distribution of earthquake epicenter and major mountain ranges? A. Active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters are often found along the boundaries of tectonic plates, which are regions of significant geological activity. B. Active volcanoes are typically found in oceanic regions, while earthquake epicenters are more common in continental areas. C. The distribution of active volcanoes has no relationship with the distribution of earthquake epicenters. D. Active volcanoes are associated with subduction zones, while earthquake epicenters are related to mid-ocean ridges. 6. The type of plate boundary where two plates collide or move toward each other. A. Convergent B. Divergent C. Hotspot D. Transform 7. The type of plate boundary where two plates move away from each other. A. Convergent B. Divergent C. Hotspot D. Transform 8. The type of plate boundary where plates slide or grind past each other without diverging or converging. A. Convergent B. Divergent C. Hotspot D. Transform 9. Describe what will happen to continental crust as it collides with oceanic crust. A. The continental crust will be moving upward. B. The continental crust will be moving downward. C. The continental crust will go over the oceanic crust. D. The continental crust will slide past with the oceanic crust. 10. When two oceanic plates collide, which geologic event/s will likely happen? A. Earthquake B. Earthquake and Tsunami C. Landslide D. Typhoon 11. Which geologic feature is formed when two continental plates converge? A. Collision Zone B. Mid-Ocean Ridge C. Rift Valley D. Subduction Zone 12. Divergent plate boundary is also known as constructive plate boundary because the process results to which of the following? A. Destruction of older crust C. Sinking of the older crust B. Formation of new crust D. Spreading of the seafloor 13. Which of the following geologic event triggered by the movement along the fault system? A. Earthquake B. Earthquake and Tsunami C. Landslide D. Typhoon 14. In a hotspot, Volcano A is on top of the mantle plume. Volcano B is 10 km farther from A while Volcano C is the farthest. What can you infer about the ages of the volcanoes? A. Volcano is older than C C. Volcano B is the youngest B. Volcano B is the oldest D. Volcano B is younger than C 15. Why is the study of plate boundaries and their associated geological processes essential for understanding Earth's dynamic processes and potential hazards A. To uncover hidden sources of freshwater. B. To explore outer space and planetary geology. C. To understand the history of ancient civilizations. D. To predict and mitigate earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. 16. The thinnest and the outermost layer of the Earth. A. Crust B. Inner Core C. Mantle D. Outer Core 17. It is beneath the crust which extends to about 2900 kilometers from the Earth’s surface. A. Crust B. Inner Core C. Mantle D. Outer Core 18. Mainly made up of iron and nickel moving around the inner part of the Earth creating the Earth’s magnetism. A. Crust B. Inner Core C. Mantle D. Outer Core 19. If you are a geologist, how can you tell that the inner core is made up of iron? A. By observing the color of the outer core. B. By analyzing the types of rocks on the Earth's surface. C. By studying the magnetic properties of the inner core. D. By counting the number of earthquakes on the planet. 20. Oxygen is the most abundant component in the Earth’s crust, what would be a possible scenario when oxygen ceases within 5 seconds? A. Extinction of most life on Earth C. Increased volcanic eruptions B. Faster erosion of mountains D. More rain and flooding 21. Why does oceanic crust subduct beneath continental crust at the subduction zone? A. because it's thicker B. because it's less dense C. due to its higher temperature D. as a result of magnetic properties 22. A type of seismic wave that can only travel through the surface of the Earth. A. Body Wave B. Love Wave C. Rayleigh Wave D. Surface Wave 23. This type of wave are used by Scientists to study the Earth’s interior. A. Body Wave B. Love Wave C. Rayleigh Wave D. Surface Wave 24. The seismic waves bend as it passes through from one layer to the other due to which reason? A. Density B. Position C. Radiation D. Temperature 25. Which of the following statement is TRUE about the density and depth in the Earth’s layer. A. As the depth increases, the depth remains the same. B. As the depth decreases, the depth periodically fluctuates. C. As the depth increases, there is also an increase in density. D. There is no significant relationship between the depth and density of the Earth’s layer. 26. When a seismic wave generated? A. When lightning strikes the post. B. Whenever there is a disturbance in the weather. C. When fireworks are released in the night sky. D. When there is a significant earthquake activity. 27. This theory states that all the continents were once one large landmass that broke apart, and moved slowly to their current locations. A. Continental Drift Theory C. Plate Tectonic Theory B. Seafloor Spreading Theory D. Theory of Evolution 28. Who were the two scientists who proposed the theory of seafloor spreading in the A. Charles Darwin and James Hutton B. Harry Hess and Robert Dietz C. John Butler and Arthur Smite D. F. Vine and D. Mathews where the pieces early 1960s? 29. This theory provided an explanation about the movement of the lithospheric plates. A. Continental Drift Theory C. Plate Tectonic Theory B. Seafloor Spreading Theory D. Theory of Evolution 30. How does the seafloor spreading, plate tectonic theory and convection current and continental drift theory related to each other? A. Seafloor spreading is part of plate tectonics, which explains how Earth's plates move. Continental drift was an earlier idea that influenced plate tectonics. B. Convection currents in the mantle drive continental crust to move above the asthenosphere which supports the seafloor spreading theory. C. Continental drift suggested that continents were stationary. Plate tectonics built on this, adding seafloor spreading and convection currents as explanations. D. All of these concepts, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, convection currents, and continental drift, are unrelated in geology. 31. Which of the following pieces of evidence support the continental drift theory, EXCEPT: A. Coal Deposits B. Fossils C. Rocks C. Snow 32. The following are the findings that support the seafloor spreading. Which does not A. Rocks are younger at the mid-ocean ridge. B. Rocks far from the mid-ocean ridge are older. C. Sediments are thinner at the mid-ocean ridge. D. Strange fossils were found in the mid-ocean ridge. support this theory? 33. Which of the following explains why scientists did not fully accept the continental drift theory of Alfred Wegener despite of his pieces of evidence? A. Alfred Wegener did not explain why continents move. B. Alfred Wegener concluded that the continents were once joined together. C. Alfred Wegener assumed that the continents were drifting away from each other. D. Alfred Wegener insisted his theory to the scientific society even though it was not concrete. 34. If you are a cartographer, what will give you an idea that the continents were once A. Ocean depth B. Position of the South Pole C. Shapes of the continents D. Size of the Atlantic Ocean joined? 35. Analyze this diagram carefully, what does Slit C represents? Slit “C” A. Crust B. Fracture C. Mid-Atlantic Ridge D. Trench