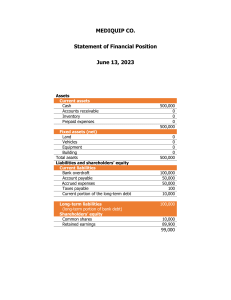
Historical Financial Statements: Financial statements are a crucial part of understanding the financial health of a company. These documents provide a snapshot of a company's financial performance over a specific period. They are essential for those who use them to make informed decisions about the company. Pratik Ambure Balance Sheet Statement Assets Assets represent the resources owned by a company that have economic value. They are categorized into current assets, which are expected to be converted into cash within a year, and non-current assets, which have a longer lifespan. Liabilities Liabilities represent the obligations of a company to external parties. They include current liabilities, which are due within a year, and non-current liabilities, which have a longer maturity. Equity Equity represents the ownership interest in a company. It is calculated as the difference between assets and liabilities and reflects the value of the company for its shareholders. Pratik Ambure Income Statement Revenue Revenue represents the income generated by a company from its primary business operations. This includes sales of goods or services, interest income, and other sources of revenue. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing or acquiring the goods sold by a company. This includes raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead. Gross Profit Gross profit is the difference between revenue and COGS, indicating the company's profit before considering operating expenses. Pratik Ambure Income Statement Operating Expenses Operating expenses are the costs incurred by a company to run its day-to-day operations, excluding COGS. Examples include administrative expenses, selling expenses, research and development, and depreciation. Operating Income Operating income is the profit generated from a company's core business activities before considering interest and taxes. Net Income Net income is the bottom line of the income statement and represents the company's profit after all expenses have been deducted from revenue. It is also referred to as the "profit after taxes" or "bottom line." Pratik Ambure Cash Flows Statement Operating Activities This section focuses on the cash flows generated by the company's core business activities. It includes changes in working capital, such as accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable, as well as cash received from customers and paid to suppliers. Investing Activities This section covers cash flows related to the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets, such as property & plant. It also includes investments in other companies and the proceeds from selling investments. Financing Activities This section reflects cash flows related to the company's financing activities, such as issuing debt, paying dividends, and repurchasing shares. Net Change in Cash The net change in cash summarizes the overall effect of all cash flow activities on the company's cash balance during the period. Pratik Ambure Importance of Financial Statements Investors Use financial statements to evaluate the company's profitability, solvency, and growth potential before making investment decisions. Creditors Assess the company's ability to repay debts by analyzing its financial health and liquidity. Management Use financial statements to monitor the company's performance, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions . Government Agencies Require companies to file financial statements for tax purposes, regulatory compliance, and oversight. Pratik Ambure Thanks For Reading Pratik Ambure