THERMODYNAMICS
AN ENGINEERING APPROACH
EIGHTH EDITION
This page intentionally left blank
THERMODYNAMICS
AN ENGINEERING APPROACH
EIGHTH EDITION
YUNUS A.
ÇENGEL
University of Nevada,
Reno
MICHAEL A.
BOLES
North Carolina State
University
THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERING APPROACH, EIGHTH EDITION
Published by McGraw-Hill Education, 2 Penn Plaza, New York, NY 10121. Copyright © 2015 by
McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. Previous editions
© 2011, 2008, 2006, and 2002. No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any
form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system, without the prior written consent of
McGraw-Hill Education, including, but not limited to, in any network or other electronic storage or
transmission, or broadcast for distance learning.
Some ancillaries, including electronic and print components, may not be available to customers outside
the United States.
This book is printed on acid-free paper.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 DOW/DOW 1 0 9 8 7 6 5 4
ISBN 978-0-07-339817-4
MHID 0-07-339817-9
Senior Vice President, Products & Markets: Kurt L. Strand
Vice President, General Manager: Marty Lange
Vice President, Content Production & Technology Services: Kimberly Meriwether David
Global Publisher: Raghothaman Srinivasan
Executive Editor: Bill Stenquist
Developmental Editor: Lorraine K. Buczek
Marketing Manager: Heather Wagner
Director, Content Production: Terri Schiesl
Content Project Manager: Jolynn Kilburg
Buyer: Jennifer Pickel
Cover Designer: Studio Montage, St. Louis, MO.
Cover Photo: Photo provided by Alstom. © 2007 Bryon Paul McCartney | www.photoworks312.com | all
rights reserved.
Compositor: RPK Editorial Services, Inc.
Typeface: 10.5/12 Times LT Std Roman
Printer: R. R. Donnelley
About the Cover: A fully bladed GT26 gas turbine rotor at Alstom’s rotor factory in Birr, Switzerland.
All credits appearing on page or at the end of the book are considered to be an extension of the
copyright page.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data on File
The Internet addresses listed in the text were accurate at the time of publication. The inclusion of a
website does not indicate an endorsement by the authors or McGraw-Hill Education, and McGraw-Hill
Education does not guarantee the accuracy of the information presented at these sites.
www.mhhe.com
Quotes on Ethics
Without ethics, everything happens as if we were all five billion passengers
on a big machinery and nobody is driving the machinery. And it’s going
faster and faster, but we don’t know where.
—Jacques Cousteau
Because you’re able to do it and because you have the right to do it doesn’t
mean it’s right to do it.
—Laura Schlessinger
A man without ethics is a wild beast loosed upon this world.
—Manly Hall
The concern for man and his destiny must always be the chief interest of all
technical effort. Never forget it among your diagrams and equations.
—Albert Einstein
Cowardice asks the question, ‘Is it safe?’ Expediency asks the question, ‘Is it
politic?’ Vanity asks the question, ‘Is it popular?’ But, conscience asks the
question, ‘Is it right?’ And there comes a time when one must take a position that is neither safe, nor politic, nor popular but one must take it because
one’s conscience tells one that it is right.
—Martin Luther King, Jr
To educate a man in mind and not in morals is to educate a
menace to society.
—Theodore Roosevelt
Politics which revolves around benefit is savagery.
—Said Nursi
The true test of civilization is, not the census, nor the size of the cities, nor
the crops, but the kind of man that the country turns out.
—Ralph W. Emerson
The measure of a man’s character is what he would do if he knew he never
would be found out.
—Thomas B. Macaulay
About the Authors
Yunus A. Çengel is Professor Emeritus of Mechanical Engineering at the
University of Nevada, Reno. He received his B.S. in mechanical engineering from
Istanbul Technical University and his M.S. and Ph.D. in mechanical engineering
from North Carolina State University. His areas of interest are renewable energy,
energy efficiency, energy policies, heat transfer enhancement, and engineering education. He served as the director of the Industrial Assessment Center (IAC) at the
University of Nevada, Reno, from 1996 to 2000. He has led teams of engineering
students to numerous manufacturing facilities in Northern Nevada and California to
perform industrial assessments, and has prepared energy conservation, waste minimization, and productivity enhancement reports for them. He has also served as an
advisor for various government organizations and corporations.
Dr. Çengel is also the author or coauthor of the widely adopted textbooks
Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals and Applications (5th ed., 2015), Fluid
Mechanics:Fundamentals and Applications (3rd ed., 2014), Fundamentals of
Thermal-Fluid Sciences (4th ed., 2012), Introduction to Thermodynamics and
Heat Transfer (2nd ed., 2008), and Differential Equations for Engineers and
Scientists (1st ed., 2013), all published by McGraw-Hill. Some of his textbooks
have been translated into Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Thai, Spanish, Portuguese,
Turkish, Italian, Greek, and French.
Dr. Çengel is the recipient of several outstanding teacher awards, and he has
received the ASEE Meriam/Wiley Distinguished Author Award for excellence in
authorship in 1992 and again in 2000. Dr. Çengel is a registered Professional Engineer in the State of Nevada, and is a member of the American Society of Mechanical
Engineers (ASME) and the American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE).
Michael A. Boles is Associate Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at North Carolina State University, where he earned his Ph.D. in mechanical engineering and is an Alumni Distinguished Professor. Dr. Boles has received
numerous awards and citations for excellence as an engineering educator. He is a
past recipient of the SAE Ralph R. Teetor Education Award and has been twice
elected to the NCSU Academy of Outstanding Teachers. The NCSU ASME student
section has consistently recognized him as the outstanding teacher of the year and
the faculty member having the most impact on mechanical engineering students.
Dr. Boles specializes in heat transfer and has been involved in the analytical and numerical solution of phase change and drying of porous media.
He is a member of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME),
the American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE), and Sigma Xi.
Dr. Boles received the ASEE Meriam /Wiley Distinguished Author Award in 1992
for excellence in authorship.
Brief Contents
chapter one
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
1
chapter two
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER, AND GENERAL ENERGY ANALYSIS
51
chapter three
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
111
chapter four
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
163
chapter five
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
213
chapter six
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
275
chapter seven
ENTROPY
329
chapter eight
EXERGY
421
chapter nine
GAS POWER CYCLES
485
chapter ten
VAPOR AND COMBINED POWER CYCLES
553
chapter eleven
REFRIGERATION CYCLES
607
chapter twelve
THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTY RELATIONS
655
chapter thirteen
GAS MIXTURES
687
chapter fourteen
GAS–VAPOR MIXTURES AND AIR-CONDITIONING
725
chapter fifteen
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
759
chapter sixteen
CHEMICAL AND PHASE EQUILIBRIUM
805
chapter seventeen
COMPRESSIBLE FLOW
839
chapter eighteen (web chapter)
RENEWABLE ENERGY
viii
THERMODYNAMICS
appendix 1
PROPERTY TABLES AND CHARTS (SI UNITS)
897
appendix 2
PROPERTY TABLES AND CHARTS (ENGLISH UNITS)
947
Contents
http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0073398179/information_center_view0/index.html
Preface
xvii
Engineering Equation Solver (EES) 37
A Remark on Significant Digits 39
Summary 40
References and Suggested Readings
Problems 41
chapter one
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
1–1
1–2
Thermodynamics and Energy
2
Application Areas of Thermodynamics
3
Importance of Dimensions and Units
1
chapter two
3
Some SI and English Units 6
Dimensional Homogeneity 8
Unity Conversion Ratios 9
1–3
1–4
12
Density and Specific Gravity
State and Equilibrium
The State Postulate
1–7
13
14
Processes and Cycles
2–3
2–4
2–5
16
2–6
22
Variation of Pressure with Depth
Energy Transfer by Heat
60
Historical Background on Heat
61
Energy Transfer by Work
62
1–10 Pressure Measurement Devices 27
2–7
Step 1: Problem Statement 34
Step 2: Schematic 35
Step 3: Assumptions and Approximations 35
Step 4: Physical Laws 35
Step 5: Properties 35
Step 6: Calculations 35
Step 7: Reasoning, Verification, and Discussion 35
Engineering Software Packages 36
65
Mechanical Forms of Work
66
The First Law of Thermodynamics
70
Energy Conversion Efficiencies
78
Efficiencies of Mechanical and Electrical Devices
33
1–11 Problem-Solving Technique 34
55
Energy Balance 72
Energy Change of a System, DEsystem 72
Mechanisms of Energy Transfer, Ein and Eout 73
24
The Barometer 27
The Manometer 30
Other Pressure Measurement Devices
53
Shaft Work 66
Spring Work 67
Work Done on Elastic Solid Bars 67
Work Associated with the Stretching of a Liquid Film
Work Done to Raise or to Accelerate a Body 68
Nonmechanical Forms of Work 70
Temperature and the Zeroth Law
of Thermodynamics 17
Pressure
52
Forms of Energy
Electrical Work
15
Temperature Scales 18
The International Temperature Scale of 1990
(ITS-90) 20
1–9
Introduction
Some Physical Insight to Internal Energy
More on Nuclear Energy 56
Mechanical Energy 58
15
The Steady-Flow Process
1–8
10
Properties of a System 12
Continuum
1–5
1–6
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER, AND GENERAL
ENERGY ANALYSIS 51
2–1
2–2
Systems and Control Volumes
41
2–8
Energy and Environment
85
Ozone and Smog 86
Acid Rain 87
The Greenhouse Effect:
Global Warming and Climate Change
88
Topic of Special Interest: Mechanisms of Heat
Transfer 91
Summary 96
References and Suggested Readings 97
Problems 97
82
68
x
THERMODYNAMICS
chapter three
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
3–1
3–2
3–3
Pure Substance
4–2
4–3
4–4
111
112
Phases of a Pure Substance
4–5
Phase-Change Processes
of Pure Substances 113
120
The Ideal-Gas Equation of State
3–8
5–2
Compressibility Factor—A Measure of
Deviation from Ideal-Gas Behavior 138
168
Flow Work and the Energy of a Flowing
Fluid 221
Energy Analysis of Steady-Flow
Systems 225
5–4
Some Steady-Flow Engineering
Devices 228
1 Nozzles and Diffusers 229
2 Turbines and Compressors 232
3 Throttling Valves 234
4a Mixing Chambers 236
4b Heat Exchangers 238
5 Pipe and Duct Flow 240
5–5
chapter four
Polytropic Process
214
5–3
Topic of Special Interest: Vapor Pressure and Phase
Equilibrium 146
Summary 150
References and Suggested Readings 151
Problems 151
164
Conservation of Mass
Total Energy of a Flowing Fluid 222
Energy Transport by Mass 223
Other Equations of State 141
Moving Boundary Work
184
Mass and Volume Flow Rates 214
Conservation of Mass Principle 216
Mass Balance for Steady-Flow
Processes 218
Special Case: Incompressible Flow 219
van der Waals Equation of State 142
Beattie-Bridgeman Equation of State 142
Benedict-Webb-Rubin Equation of State 143
Virial Equation of State 144
4–1
Internal Energy, Enthalpy, and Specific Heats of
Solids and Liquids 183
chapter five
134
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
178
Topic of Special Interest: Thermodynamic Aspects of
Biological Systems 187
Summary 195
References and Suggested Readings 195
Problems 196
5–1
Is Water Vapor an Ideal Gas? 137
3–7
Internal Energy, Enthalpy, and Specific Heats
of Ideal Gases 176
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL
VOLUMES 213
Property Tables 124
Enthalpy—A Combination Property 124
1a Saturated Liquid and Saturated
Vapor States 125
1b Saturated Liquid–Vapor Mixture 127
2 Superheated Vapor 130
3 Compressed Liquid 131
Reference State and Reference Values 132
3–6
169
174
Internal Energy Changes
Enthalpy Changes 184
Property Diagrams for Phase-Change
Processes 118
1 The T-v Diagram 118
2 The P-v Diagram 120
Extending the Diagrams to Include the Solid Phase
3 The P-T Diagram 122
The P-v-T Surface 123
3–5
Specific Heats
Specific Heat Relations of Ideal Gases
112
Compressed Liquid and Saturated Liquid 114
Saturated Vapor and Superheated Vapor 114
Saturation Temperature and Saturation Pressure 115
Some Consequences of Tsat and Psat Dependence 116
3–4
Energy Balance for Closed Systems
163
Energy Analysis of Unsteady-Flow
Processes 242
Topic of Special Interest: General Energy
Equation 247
Summary 251
References and Suggested Readings 252
Problems 252
xi
CONTENTS
chapter six
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
6–1
6–2
6–3
Introduction to the Second Law
Thermal Energy Reservoirs
Heat Engines
275
276
7–7
7–8
7–9
277
278
Refrigerators and Heat Pumps
6–7
Perpetual-Motion Machines
283
297
329
352
364
307
Topic of Special Interest: Reducing the Cost of
Compressed Air 386
Summary 395
References and Suggested Readings 396
Problems 397
chapter eight
330
EXERGY
A Special Case: Internally Reversible
Isothermal Heat Transfer Processes
7–3
The Entropy Change of Ideal Gases
349
Entropy Change of a System, DSsystem 374
Mechanisms of Entropy Transfer, Sin and Sout 374
1 Heat Transfer 374
2 Mass Flow 375
Entropy Generation, Sgen 376
Closed Systems 377
Control Volumes 378
Entropy Generation Associated
with a Heat Transfer Process 385
chapter seven
333
8–1
The Increase of Entropy Principle 334
Some Remarks about Entropy
Entropy Change of Liquids and Solids
7–13 Entropy Balance 373
303
Topic of Special Interest: Household Refrigerators
Summary 311
References and Suggested Readings 312
Problems 312
7–2
347
Isentropic Efficiency of Turbines 367
Isentropic Efficiencies of Compressors and Pumps
Isentropic Efficiency of Nozzles 371
6–11 The Carnot Refrigerator and Heat Pump 304
Entropy
346
7–12 Isentropic Efficiencies of Steady-Flow
Devices 367
295
6–8 The Carnot Principles 297
6–9 The Thermodynamic Temperature Scale 299
6–10 The Carnot Heat Engine 301
7–1
The T ds Relations
Multistage Compression with Intercooling
294
ENTROPY
343
7–11 Minimizing the Compressor Work 363
290
Irreversibilities 293
Internally and Externally Reversible Processes
The Quality of Energy 302
Quantity versus Quality in Daily Life
What Is Entropy?
342
Proof that Steady-Flow Devices Deliver
the Most and Consume the Least Work
When the Process is Reversible 362
292
The Reversed Carnot Cycle
Property Diagrams Involving Entropy
7–10 Reversible Steady-Flow Work 359
Reversible and Irreversible Processes
The Carnot Cycle
340
Constant Specific Heats (Approximate Analysis) 353
Variable Specific Heats (Exact Analysis) 353
Isentropic Processes of Ideal Gases 355
Constant Specific Heats (Approximate Analysis) 355
Variable Specific Heats (Exact Analysis) 356
Relative Pressure and Relative Specific Volume 356
Coefficient of Performance 284
Heat Pumps 285
Performance of Refrigerators, Air-Conditioners,
and Heat Pumps 286
The Second Law of Thermodynamics:
Clausius Statement 288
Equivalence of the Two Statements 289
6–5
6–6
Isentropic Processes
Entropy and Entropy Generation in Daily Life
Thermal Efficiency 279
Can We Save Qout? 281
The Second Law of Thermodynamics:
Kelvin–Planck Statement 283
6–4
7–4
7–5
7–6
337
Exergy: Work Potential of Energy
Exergy (Work Potential) Associated
with Kinetic and Potential Energy
336
Entropy Change of Pure Substances
421
8–2
422
423
Reversible Work and Irreversibility
425
369
xii
THERMODYNAMICS
8–3
8–4
Second-Law Efficiency
9–9 The Brayton Cycle with Regeneration 513
9–10 The Brayton Cycle with Intercooling, Reheating,
and Regeneration 516
9–11 Ideal Jet-Propulsion Cycles 520
430
Exergy Change of a System 433
Exergy of a Fixed Mass: Nonflow (or Closed System)
Exergy 433
Exergy of a Flow Stream: Flow (or Stream)
Exergy 436
8–5
Modifications to Turbojet Engines
9–12 Second-Law Analysis of Gas Power
Cycles 526
Exergy Transfer by Heat, Work,
And Mass 438
Exergy by Heat Transfer, Q 439
Exergy Transfer by Work, W 440
Exergy Transfer by Mass, m 440
8–6
The Decrease of Exergy Principle and Exergy
Destruction 441
Exergy Destruction
8–7
8–8
524
Topic of Special Interest: Saving Fuel and Money by Driving
Sensibly 530
Summary 536
References and Suggested Readings 538
Problems 538
442
Exergy Balance: Closed Systems
443
Exergy Balance: Control Volumes
454
Exergy Balance for Steady-Flow Systems
Reversible Work 456
Second-Law Efficiency of Steady-Flow
Devices 456
chapter ten
VAPOR AND COMBINED POWER CYCLES
455
10–1 The Carnot Vapor Cycle 554
10–2 Rankine Cycle: The Ideal Cycle for Vapor Power
Cycles 555
Topic of Special Interest: Second-Law
Aspects of Daily Life 463
Summary 467
References and Suggested Readings 468
Problems 468
Energy Analysis of the Ideal Rankine Cycle
GAS POWER CYCLES 485
9–1
Basic Considerations in the Analysis of Power
Cycles 486
9–2
The Carnot Cycle and its Value in
Engineering 488
9–3
9–4
9–5
Air-Standard Assumptions
9–6
Diesel Cycle: The Ideal Cycle for
Compression-Ignition Engines 499
9–7
9–8
Stirling and Ericsson Cycles
490
Otto Cycle: The Ideal Cycle for Spark-Ignition
Engines 492
Brayton Cycle: The Ideal Cycle for
Gas-Turbine Engines 506
Development of Gas Turbines 509
Deviation of Actual Gas-Turbine Cycles
from Idealized Ones 512
Lowering the Condenser Pressure
(Lowers Tlow,avg) 561
Superheating the Steam to High Temperatures
(Increases Thigh,avg) 562
Increasing the Boiler Pressure
(Increases Thigh,avg) 562
10–5 The Ideal Reheat Rankine Cycle 565
10–6 The Ideal Regenerative Rankine
Cycle 569
490
502
555
10–3 Deviation of Actual Vapor Power Cycles from
Idealized Ones 558
10–4 How Can We Increase the Efficiency of the
Rankine Cycle? 561
chapter nine
An Overview of Reciprocating Engines
553
Open Feedwater Heaters 569
Closed Feedwater Heaters 571
10–7 Second-Law Analysis of Vapor Power
Cycles 577
10–8 Cogeneration 579
10–9 Combined Gas–Vapor Power
Cycles 584
Topic of Special Interest: Binary Vapor
Cycles 587
Summary 589
References and Suggested Readings 590
Problems 590
xiii
CONTENTS
chapter eleven
12–5 The Joule-Thomson Coefficient 672
12–6 The Dh, Du, and Ds of Real Gases 674
REFRIGERATION CYCLES 607
11–1 Refrigerators and Heat Pumps 608
11–2 The Reversed Carnot Cycle 609
11–3 The Ideal Vapor-Compression Refrigeration
Cycle 610
11–4 Actual Vapor-Compression Refrigeration
Cycle 613
11–5 Second-Law Analysis of Vapor-Compression
Refrigeration Cycle 615
11–6 Selecting the Right Refrigerant 620
11–7 Heat Pump Systems 622
11–8 Innovative Vapor-Compression Refrigeration
Systems 623
Cascade Refrigeration Systems 624
Multistage Compression Refrigeration
Systems 626
Multipurpose Refrigeration Systems
with a Single Compressor 628
Liquefaction of Gases 629
659
12–2 The Maxwell Relations 661
12–3 The Clapeyron Equation 662
12–4 General Relations For du, dh, ds, cv ,
and cp 665
Internal Energy Changes 666
Enthalpy Changes 666
Entropy Changes 667
Specific Heats cv and cp 668
chapter thirteen
GAS MIXTURES
687
13–1 Composition of a Gas Mixture: Mass and Mole
Fractions 688
13–2 P-v-T Behavior of Gas Mixtures: Ideal and Real
Gases 690
Ideal-Gas Mixtures 691
Real-Gas Mixtures 692
Topic of Special Interest: Chemical Potential and the
Separation Work of Mixtures 704
Summary 714
References and Suggested Readings
Problems 716
715
chapter fourteen
GAS–VAPOR MIXTURES AND
AIR-CONDITIONING 725
chapter twelve
Partial Differentials 657
Partial Differential Relations
680
Ideal-Gas Mixtures 696
Real-Gas Mixtures 700
Topic of Special Interest: Thermoelectric Power Generation
and Refrigeration Systems 636
Summary 638
References and Suggested Readings 639
Problems 639
12–1 A Little Math—Partial Derivatives and
Associated Relations 656
Summary 679
References and Suggested Readings
Problems 680
675
13–3 Properties of Gas Mixtures: Ideal and Real
Gases 695
11–9 Gas Refrigeration Cycles 630
11–10 Absorption Refrigeration Systems 633
THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTY RELATIONS
Enthalpy Changes of Real Gases 674
Internal Energy Changes of Real Gases
Entropy Changes of Real Gases 676
655
14–1 Dry and Atmospheric Air 726
14–2 Specific and Relative Humidity of Air 727
14–3 Dew-Point Temperature 729
14–4 Adiabatic Saturation and Wet-Bulb
Temperatures 731
14– 5 The Psychrometric Chart 734
14–6 Human Comfort and Air-Conditioning 735
14–7 Air-Conditioning Processes 737
Simple Heating and Cooling (v 5 constant)
Heating with Humidification 739
Cooling with Dehumidification 740
Evaporative Cooling 742
738
xiv
THERMODYNAMICS
Adiabatic Mixing of Airstreams
Wet Cooling Towers 745
743
Summary 828
References and Suggested Readings
Problems 829
Summary 747
References and Suggested Readings 748
Problems 749
829
chapter seventeen
chapter fifteen
COMPRESSIBLE FLOW
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
17–1 Stagnation Properties 840
17–2 Speed of Sound and Mach Number 843
17–3 One-Dimensional Isentropic Flow 845
759
15–1 Fuels and Combustion 760
15–2 Theoretical and Actual Combustion
Processes 764
15–3 Enthalpy of Formation and Enthalpy of
Combustion 771
15–4 First-Law Analysis of Reacting
Systems 774
Variation of Fluid Velocity with Flow Area 847
Property Relations for Isentropic Flow
of Ideal Gases 849
17–4 Isentropic Flow Through Nozzles 851
Converging Nozzles 852
Converging–Diverging Nozzles
856
17–5 Shock Waves and Expansion Waves 860
Steady-Flow Systems 775
Closed Systems 776
15–5 Adiabatic Flame Temperature 780
15–6 Entropy Change of Reacting
Systems 782
15–7 Second-Law Analysis of Reacting Systems 784
Topic of Special Interest: Fuel Cells 790
Summary 792
References and Suggested Readings 793
Problems 793
Normal Shocks 860
Oblique Shocks 866
Prandtl–Meyer Expansion Waves
870
17–6 Duct Flow with Heat Transfer and Negligible
Friction (Rayleigh Flow) 875
Property Relations for Rayleigh
Flow 881
Choked Rayleigh Flow 882
17–7 Steam Nozzles 884
Summary 887
References and Suggested Readings
Problems 889
chapter sixteen
CHEMICAL AND PHASE EQUILIBRIUM
839
805
16–1 Criterion for Chemical
Equilibrium 806
16–2 The Equilibrium Constant for Ideal-Gas
Mixtures 808
16–3 Some Remarks about the Kp of Ideal-Gas
Mixtures 812
16–4 Chemical Equilibrium for Simultaneous
Reactions 816
16–5 Variation of Kp with Temperature 818
16–6 Phase Equilibrium 820
Phase Equilibrium for a Single-Component System 820
The Phase Rule 822
Phase Equilibrium for a Multicomponent System 822
888
chapter eighteen
(web chapter)
RENEWABLE ENERGY
18–1 Introduction
18-2 Solar Energy
Solar Radiation
Flat-Plate Solar Collector
Concentrating Solar Collector
Linear Concentrating Solar Power Collector
Solar-Power Tower Plant
Solar Pond
Photovoltaic Cell
Passive Solar
Applications
Solar Heat Gain through Windows
xv
CONTENTS
18-3 Wind Energy
Wind Turbine Types and Power
Performance Curve
Wind Power Potential
Wind Power Density
Wind Turbine Efficiency
Betz Limit for Wind Turbine Efficiency
18-4 Hydropower
Analysis of Hydroelectric Power Plant
Turbine Types
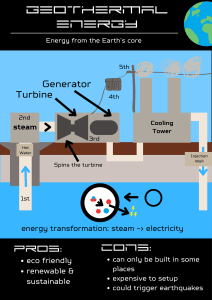
18–5 Geothermal Energy
Geothermal Power Production
18–6 Biomass Energy
Biomass Resources
Conversion of Biomass to Biofuel
Biomass Products
Electricity and Heat Production by Biomass
Solid Municipality Waste
Summary
References and Suggested Readings
Problems
Figure A–14
Figure A–15
Table A–16
Table A–17
Table A–18
Table A–19
Table A–20
Table A–21
Table A–22
Table A–23
appendix one
Table A–24
PROPERTY TABLES AND CHARTS
(SI UNITS) 897
Table A–25
Table A–26
Table A–1
Table A–2
Table A–3
Table A–4
Table A–5
Table A–6
Table A–7
Table A–8
Figure A–9
Figure A–10
Table A–11
Table A–12
Table A–13
Molar mass, gas constant, and criticalpoint properties 898
Ideal-gas specific heats of various
common gases 899
Properties of common liquids, solids,
and foods 902
Saturated water—Temperature
table 904
Saturated water—Pressure table 906
Superheated water 908
Compressed liquid water 912
Saturated ice–water vapor 913
T-s diagram for water 914
Mollier diagram for water 915
Saturated refrigerant-134a—
Temperature table 916
Saturated refrigerant-134a—
Pressure table 918
Superheated refrigerant-134a 919
Table A–27
Table A–28
Figure A–29
Figure A–30
Figure A–31
Table A–32
Table A–33
Table A–34
P-h diagram for
refrigerant-134a 921
Nelson–Obert generalized
compressibility chart 922
Properties of the atmosphere at high
altitude 923
Ideal-gas properties
of air 924
Ideal-gas properties of nitrogen,
N2 926
Ideal-gas properties of oxygen,
O2 928
Ideal-gas properties of carbon dioxide,
CO2 930
Ideal-gas properties of carbon
monoxide, CO 932
Ideal-gas properties of hydrogen,
H2 934
Ideal-gas properties of water vapor,
H2O 935
Ideal-gas properties of monatomic
oxygen, O 937
Ideal-gas properties of hydroxyl,
OH 937
Enthalpy of formation, Gibbs function
of formation, and absolute entropy at
258C, 1 atm 938
Properties of some common fuels and
hydrocarbons 939
Natural logarithms of the equilibrium
constant Kp 940
Generalized enthalpy departure
chart 941
Generalized entropy departure
chart 942
Psychrometric chart at 1 atm total
pressure 943
One-dimensional isentropic
compressible-flow functions for an
ideal gas with k 5 1.4 944
One-dimensional normal-shock
functions for an ideal gas
with k 5 1.4 945
Rayleigh flow functions for an ideal
gas with k 5 1.4 946
xvi
THERMODYNAMICS
appendix two
PROPERTY TABLES AND CHARTS
(ENGLISH UNITS) 947
Table A–1E
Molar mass, gas constant, and criticalpoint properties 948
Table A–2E
Ideal-gas specific heats of various
common gases 949
Table A–3E
Properties of common liquids, solids,
and foods 952
Table A–4E
Saturated water—Temperature
table 954
Table A–5E
Saturated water—Pressure table 956
Table A–6E
Superheated water 958
Table A–7E
Compressed liquid water 962
Table A–8E
Saturated ice–water vapor 963
Figure A–9E T-s diagram for water 964
Figure A–10E Mollier diagram for water 965
Table A–11E Saturated refrigerant-134a—
Temperature table 966
Table A–12E Saturated refrigerant-134a—Pressure
table 967
Table A–13E Superheated refrigerant-134a 968
Figure A–14E P-h diagram for refrigerant-134a 970
Table A–16E Properties of the atmosphere at high
altitude 971
Table A–17E Ideal-gas properties of air 972
Table A–18E Ideal-gas properties of nitrogen,
N2 974
Table A–19E Ideal-gas properties of oxygen, O2 976
Table A–20E Ideal-gas properties of carbon dioxide,
CO2 978
Table A–21E Ideal-gas properties of carbon
monoxide, CO 980
Table A–22E Ideal-gas properties of hydrogen,
H2 982
Table A–23E Ideal-gas properties of water vapor,
H2O 983
Table A–26E Enthalpy of formation, Gibbs function
of formation, and absolute entropy at
778C, 1 atm 985
Table A–27E Properties of some common fuels and
hydrocarbons 986
Figure A–31E Psychrometric chart at 1 atm total
pressure 987
INDEX
989
Preface
BACKGROUND
Thermodynamics is an exciting and fascinating subject that deals with energy,
and thermodynamics has long been an essential part of engineering curricula
all over the world. It has a broad application area ranging from microscopic
organisms to common household appliances, transportation vehicles, power
generation systems, and even philosophy. This introductory book contains
sufficient material for two sequential courses in thermodynamics. Students
are assumed to have an adequate background in calculus and physics.
OBJECTIVES
This book is intended for use as a textbook by undergraduate engineering students in their sophomore or junior year, and as a reference book for practicing
engineers. The objectives of this text are
• To cover the basic principles of thermodynamics.
• To present a wealth of real-world engineering examples to give students
a feel for how thermodynamics is applied in engineering practice.
• To develop an intuitive understanding of thermodynamics by emphasizing the physics and physical arguments that underpin the theory.
It is our hope that this book, through its careful explanations of concepts and
its use of numerous practical examples and figures, helps students develop the
necessary skills to bridge the gap between knowledge and the confidence to
properly apply knowledge.
PHILOSOPHY AND GOAL
The philosophy that contributed to the overwhelming popularity of the prior
editions of this book has remained unchanged in this edition. Namely, our
goal has been to offer an engineering textbook that
• Communicates directly to the minds of tomorrow’s engineers in a
simple yet precise manner.
• Leads students toward a clear understanding and firm grasp of the basic
principles of thermodynamics.
• Encourages creative thinking and development of a deeper understanding and intuitive feel for thermodynamics.
• Is read by students with interest and enthusiasm rather than being used
as an aid to solve problems.
Special effort has been made to appeal to students’ natural curiosity and to
help them explore the various facets of the exciting subject area of thermodynamics. The enthusiastic responses we have received from users of prior
editions—from small colleges to large universities all over the world—and
the continued translations into new languages indicate that our objectives
xviii
THERMODYNAMICS
have largely been achieved. It is our philosophy that the best way to learn is
by practice. Therefore, special effort is made throughout the book to reinforce
material that was presented earlier.
Yesterday’s engineer spent a major portion of his or her time substituting
values into the formulas and obtaining numerical results. However, formula
manipulations and number crunching are now being left mainly to computers.
Tomorrow’s engineer will need a clear understanding and a firm grasp of the
basic principles so that he or she can understand even the most complex problems, formulate them, and interpret the results. A conscious effort is made to
emphasize these basic principles while also providing students with a perspective of how computational tools are used in engineering practice.
The traditional classical, or macroscopic, approach is used throughout the
text, with microscopic arguments serving in a supporting role as appropriate.
This approach is more in line with students’ intuition and makes learning the
subject matter much easier.
NEW IN THIS EDITION
The primary change in this eighth edition of the text is the effective use of
full color to enhance the learning experience of students and to make it more
enjoyable. Another significant change is the addition of a new web chapter
on Renewable Energy available via the Online Learning Center. The third
important change is the update of the R-134a tables to make property values
consistent with those from the latest version of EES. All the solved examples
and end-of-chapter problems dealing with R-134a are modified to reflect
this change. This edition includes numerous new problems with a variety of
applications. Problems, whose solutions require parametric investigations and
thus the use of a computer, are identified by a computer-EES icon, as before.
Some existing problems from previous editions have been removed, and other
updates and changes for clarity and readability have been made throughout
the text.
The eighth edition also includes McGraw-Hill’s Connect® Engineering.
This online homework management tool allows assignment of algorithmic
problems for homework, quizzes and tests. It connects students with the
tools and resources they’ll need to achieve success. To learn more, visit
www.mcgrawhillconnect.com.
McGraw-Hill LearnSmart™ is also available as an integrated feature
of McGraw-Hill Connect® Engineering. It is an adaptive learning system
designed to help students learn faster, study more efficiently, and retain more
knowledge for greater success. LearnSmart assesses a student’s knowledge of
course content through a series of adaptive questions. It pinpoints concepts
the student does not understand and maps out a personalized study plan for
success. Visit the following site for a demonstration: www.mhlearnsmart.com.
LEARNING TOOLS
EARLY INTRODUCTION OF THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
The first law of thermodynamics is introduced early in Chapter 2, “Energy,
Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis.” This introductory chapter
xix
PREFACE
sets the framework of establishing a general understanding of various forms
of energy, mechanisms of energy transfer, the concept of energy balance,
thermo-economics, energy conversion, and conversion efficiency using
familiar settings that involve mostly electrical and mechanical forms of
energy. It also exposes students to some exciting real-world applications
of thermodynamics early in the course, and helps them establish a sense of
the monetary value of energy. There is special emphasis on the utilization of
renewable energy such as wind power and hydraulic energy, and the efficient
use of existing resources.
EMPHASIS ON PHYSICS
A distinctive feature of this book is its emphasis on the physical aspects of the
subject matter in addition to mathematical representations and manipulations.
The authors believe that the emphasis in undergraduate education should
remain on developing a sense of underlying physical mechanisms and a mastery of solving practical problems that an engineer is likely to face in the real
world. Developing an intuitive understanding should also make the course a
more motivating and worthwhile experience for students.
EFFECTIVE USE OF ASSOCIATION
An observant mind should have no difficulty understanding engineering
sciences. After all, the principles of engineering sciences are based on our
everyday experiences and experimental observations. Therefore, a physical, intuitive approach is used throughout this text. Frequently, parallels are
drawn between the subject matter and students’ everyday experiences so that
they can relate the subject matter to what they already know. The process of
cooking, for example, serves as an excellent vehicle to demonstrate the basic
principles of thermodynamics.
SELF-INSTRUCTING
The material in the text is introduced at a level that an average student can
follow comfortably. It speaks to students, not over students. In fact, it is selfinstructive. The order of coverage is from simple to general. That is, it starts
with the simplest case and adds complexities gradually. In this way, the basic
principles are repeatedly applied to different systems, and students master
how to apply the principles instead of how to simplify a general formula. Noting that the principles of sciences are based on experimental observations, all
the derivations in this text are based on physical arguments, and thus they are
easy to follow and understand.
EXTENSIVE USE OF ARTWORK
Figures are important learning tools that help students “get the picture,” and
the text makes very effective use of graphics. This edition of Thermodynamics:
An Engineering Approach, Eighth Edition features an enhanced art program
done in four colors to provide more realism and pedagogical understanding. Further, a large number of figures have been upgraded to become threedimensional and thus more real-life. Figures attract attention and stimulate
curiosity and interest. Most of the figures in this text are intended to serve as a
means of emphasizing some key concepts that would otherwise go unnoticed;
some serve as page summaries.
xx
THERMODYNAMICS
LEARNING OBJECTIVES AND SUMMARIES
Each chapter begins with an overview of the material to be covered and
chapter-specific learning objectives. A summary is included at the end of
each chapter, providing a quick review of basic concepts and important relations, and pointing out the relevance of the material.
NUMEROUS WORKED-OUT EXAMPLES
WITH A SYSTEMATIC SOLUTIONS PROCEDURE
Each chapter contains several worked-out examples that clarify the material and
illustrate the use of the basic principles. An intuitive and systematic approach is
used in the solution of the example problems, while maintaining an informal
conversational style. The problem is first stated, and the objectives are identified.
The assumptions are then stated, together with their justifications. The properties needed to solve the problem are listed separately if appropriate. Numerical
values are used together with their units to emphasize that numbers without units
are meaningless, and that unit manipulations are as important as manipulating
the numerical values with a calculator. The significance of the findings is discussed following the solutions. This approach is also used consistently in the
solutions presented in the instructor’s solutions manual.
A WEALTH OF REAL-WORLD END-OF-CHAPTER PROBLEMS
The end-of-chapter problems are grouped under specific topics to make problem selection easier for both instructors and students. Within each group of
problems are Concept Questions, indicated by “C,” to check the students’
level of understanding of basic concepts. The problems under Review Problems are more comprehensive in nature and are not directly tied to any specific
section of a chapter—in some cases they require review of material learned
in previous chapters. Problems designated as Design and Essay are intended
to encourage students to make engineering judgments, to conduct independent exploration of topics of interest, and to communicate their findings in
a professional manner. Problems designated by an “E” are in English units,
are solved using EES,
and SI users can ignore them. Problems with the
and complete solutions together with parametric studies are included on the
are comprehensive in nature and
textbook’s website. Problems with the
are intended to be solved with a computer, possibly using the EES software.
Several economics- and safety-related problems are incorporated throughout
to promote cost and safety awareness among engineering students. Answers
to selected problems are listed immediately following the problem for convenience to students. In addition, to prepare students for the Fundamentals of
Engineering Exam (that is becoming more important for the outcome-based
ABET 2000 criteria) and to facilitate multiple-choice tests, over 200 multiplechoice problems are included in the end-of-chapter problem sets. They are
placed under the title Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Problems for
easy recognition. These problems are intended to check the understanding of
fundamentals and to help readers avoid common pitfalls.
RELAXED SIGN CONVENTION
The use of a formal sign convention for heat and work is abandoned as it
often becomes counterproductive. A physically meaningful and engaging approach is adopted for interactions instead of a mechanical approach.
xxi
PREFACE
Subscripts “in” and “out,” rather than the plus and minus signs, are used to
indicate the directions of interactions.
PHYSICALLY MEANINGFUL FORMULAS
The physically meaningful forms of the balance equations rather than formulas are used to foster deeper understanding and to avoid a cookbook approach.
The mass, energy, entropy, and exergy balances for any system undergoing
any process are expressed as
Mass balance:
min 2 mout 5 Dmsystem
Energy balance:
Ein 2 Eout
5
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Entropy balance:
Sin 2 Sout
1
Net entropy transfer
by heat and mass
Exergy balance:
Xin 2 Xout
Net exergy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
2
Sgen
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
5
Entropy
generation
Xdestroyed
Exergy
destruction
DEsystem
DSsystem
Change
in entropy
5
DXsystem
Change
in exergy
These relations reinforce the fundamental principles that during an actual
process mass and energy are conserved, entropy is generated, and exergy is
destroyed. Students are encouraged to use these forms of balances in early
chapters after they specify the system, and to simplify them for the particular
problem. A more relaxed approach is used in later chapters as students gain
mastery.
A CHOICE OF SI ALONE OR SI/ENGLISH UNITS
In recognition of the fact that English units are still widely used in some
industries, both SI and English units are used in this text, with an emphasis on
SI. The material in this text can be covered using combined SI/English units
or SI units alone, depending on the preference of the instructor. The property
tables and charts in the appendices are presented in both units, except the ones
that involve dimensionless quantities. Problems, tables, and charts in English
units are designated by “E” after the number for easy recognition, and they
can be ignored by SI users.
TOPICS OF SPECIAL INTEREST
Most chapters contain a section called “Topic of Special Interest” where
interesting aspects of thermodynamics are discussed. Examples include Thermodynamic Aspects of Biological Systems in Chapter 4, Household Refrigerators in Chapter 6, Second-Law Aspects of Daily Life in Chapter 8, and Saving
Fuel and Money by Driving Sensibly in Chapter 9. The topics selected for
these sections provide intriguing extensions to thermodynamics, but they can
be ignored if desired without a loss in continuity.
xxii
THERMODYNAMICS
GLOSSARY OF THERMODYNAMIC TERMS
Throughout the chapters, when an important key term or concept is introduced and defined, it appears in boldface type. Fundamental thermodynamic
terms and concepts also appear in a glossary located on our accompanying
website (www.mhhe.com/cengel). This unique glossary helps to reinforce
key terminology and is an excellent learning and review tool for students as
they move forward in their study of thermodynamics. In addition, students
can test their knowledge of these fundamental terms by using the flash cards
and other interactive resources.
CONVERSION FACTORS
Frequently used conversion factors and physical constants are listed on the
inner cover pages of the text for easy reference.
SUPPLEMENTS
The following supplements are available to users of the book.
ENGINEERING EQUATION SOLVER (EES)
Developed by Sanford Klein and William Beckman from the University of
Wisconsin—Madison, this software combines equation-solving capability
and engineering property data. EES can do optimization, parametric analysis,
and linear and nonlinear regression, and provides publication-quality plotting capabilities. Thermodynamics and transport properties for air, water, and
many other fluids are built in, and EES allows the user to enter property data
or functional relationships.
EES is a powerful equation solver with built-in functions and property
tables for thermodynamic and transport properties as well as automatic unit
checking capability. It requires less time than a calculator for data entry and
allows more time for thinking critically about modeling and solving engineering problems. Look for the EES icons in the homework problems sections of
the text.
The Limited Academic Version of EES is available for departmental license
upon adoption of the Eighth Edition of Thermodynamics: An Engineering
Approach (meaning that the text is required for students in the course). You
may load this software onto your institution’s computer system, for use by
students and faculty related to the course, as long as the arrangement between
McGraw-Hill Education and F-Chart is in effect. There are minimum order
requirements stipulated by F-Chart to qualify.
PROPERTIES TABLE BOOKLET
(ISBN 0-07-762477-7)
This booklet provides students with an easy reference to the most important
property tables and charts, many of which are found at the back of the textbook in both the SI and English units.
COSMOS
McGraw-Hill’s COSMOS (Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization
System) allows instructors to streamline the creation of assignments, quizzes,
and tests by using problems and solutions from the textbook, as well as their own
custom material. COSMOS is now available online at http://cosmos.mhhe.com/
xxiii
PREFACE
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge with appreciation the numerous and
valuable comments, suggestions, constructive criticisms, and praise from the
following evaluators and reviewers:
Edward Anderson
Texas Tech University
John Biddle
Cal Poly Pomona University
Gianfranco DiGiuseppe
Kettering University
Shoeleh Di Julio
California State University-Northridge
Afshin Ghajar
Oklahoma State University
Harry Hardee
New Mexico State University
Kevin Lyons
North Carolina State University
Kevin Macfarlan
John Brown University
Saeed Manafzadeh
University of Illinois-Chicago
Alex Moutsoglou
South Dakota State University
Rishi Raj
The City College of New York
Maria Sanchez
California State University-Fresno
Kalyan Srinivasan
Mississippi State University
Robert Stiger
Gonzaga University
Their suggestions have greatly helped to improve the quality of this text. In
particular we would like to express our gratitude to Mehmet Kanoglu of the
University of Gaziantep, Turkey, for his valuable contributions, his critical
review of the manuscript, and for his special attention to accuracy and detail.
We also would like to thank our students, who provided plenty of feedback
from students’ perspectives. Finally, we would like to express our appreciation to our wives, Zehra Çengel and Sylvia Boles, and to our children for their
continued patience, understanding, and support throughout the preparation of
this text.
Yunus A. Çengel
Michael A. Boles
This page intentionally left blank
Online Resources for Students and Instructors
MCGRAW-HILL CONNECT® ENGINEERING
McGraw-Hill Connect Engineering is a web-based assignment and assessment
platform that gives students the means to better connect with their coursework, with their instructors, and with the important concepts that they will
need to know for success now and in the future. With Connect Engineering,
instructors can deliver assignments, quizzes, and tests easily online. Students
can practice important skills at their own pace and on their own schedule.
Connect Engineering for Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach,
Eighth Edition is available via the text website at www.mhhe.com/cengel
COSMOS
McGraw-Hill’s COSMOS (Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization
System) allows instructors to streamline the creation of assignments, quizzes, and tests by using problems and solutions from the textbook, as well as
their own custom material. COSMOS is now available online at http://cosmos.
mhhe.com/
WWW.MHHE.COM/CENGEL
This site offers resources for students and instructors.
The following resources are available for students:
• Glossary of Key Terms in Thermodynamics—Bolded terms in the text are
defined in this accessible glossary. Organized at the chapter level or
available as one large file.
• Student Study Guide—This resource outlines the fundamental concepts of
the text and is a helpful guide that allows students to focus on the most
important concepts. The guide can also serve as a lecture outline for
instructors.
• Learning Objectives—The chapter learning objectives are outlined here.
Organized by chapter and tied to ABET objectives.
• Self-Quizzing—Students can test their knowledge using multiple-choice
quizzing. These self-tests provide immediate feedback and are an excellent
learning tool.
• Flashcards—Interactive flashcards test student understanding of the text
terms and their definitions. The program also allows students to flag terms
that require further understanding.
• Crossword Puzzles—An interactive, timed puzzle that provides hints as well
as a notes section.
• Errata—If errors should be found in the text, they will be reported here.
xxvi
THERMODYNAMICS
The following resources are available for instructors under password
protection:
• Instructor Testbank—Additional problems prepared for instructors to assign
to students. Solutions are given, and use of EES is recommended to verify
accuracy.
• Correlation Guide—New users of this text will appreciate this resource. The
guide provides a smooth transition for instructors not currently using the
Çengel/Boles text.
• Image Library—The electronic version of the figures are supplied for easy
integration into course presentations, exams, and assignments.
• Instructor’s Guide—Provides instructors with helpful tools such as sample
syllabi and exams, an ABET conversion guide, a thermodynamics glossary,
and chapter objectives.
• Errata—If errors should be found in the solutions manual, they will be
reported here.
• Solutions Manual—The detailed solutions to all text homework problems are
provided in PDF form.
• EES Solutions Manual—The entire solutions manual is also available in
EES. Any problem in the text can be modified and the solution of the
modified problem can readily be obtained by copying and pasting the given
EES solution on a blank EES screen and hitting the solve button.
• PP slides—Powerpoint presentation slides for all chapters in the text are
available for use in lectures
• Appendices—These are provided in PDF form for ease of use.
CHAPTER
1
INTRODUCTION AND
BASIC CONCEPTS
E
very science has a unique vocabulary associated with it, and thermodynamics is no exception. Precise definition of basic concepts forms
a sound foundation for the development of a science and prevents
possible misunderstandings. We start this chapter with an overview of thermodynamics and the unit systems, and continue with a discussion of some
basic concepts such as system, state, state postulate, equilibrium, and process. We discuss intensive and extensive properties of a system and define
density, specific gravity, and specific weight. We also discuss temperature
and temperature scales with particular emphasis on the International Temperature Scale of 1990. We then present pressure, which is the normal force
exerted by a fluid per unit area and discuss absolute and gage pressures, the
variation of pressure with depth, and pressure measurement devices, such
as manometers and barometers. Careful study of these concepts is essential
for a good understanding of the topics in the following chapters. Finally, we
present an intuitive systematic problem-solving technique that can be used
as a model in solving engineering problems.
OBJECTIVES
The objectives of Chapter 1 are to:
■
Identify the unique vocabulary
associated with thermodynamics
through the precise definition of
basic concepts to form a sound
foundation for the development
of the principles of thermodynamics.
■
■
■
■
■
Review the metric SI and the
English unit systems that will be
used throughout the text.
Explain the basic concepts
of thermodynamics such as
system, state, state postulate,
equilibrium, process, and cycle.
Discuss properties of a system
and define density, specific
gravity, and specific weight.
Review concepts of temperature,
temperature scales, pressure,
and absolute and gage pressure.
Introduce an intuitive systematic
problem-solving technique.
1
2
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
PE = 10 units
KE = 0
PE = 7 units
KE = 3 units
Potential
energy
Kinetic
energy
FIGURE 1–1
Energy cannot be created or
destroyed; it can only change
forms (the first law).
Energy storage
(1 unit)
Energy in
(5 units)
Energy out
(4 units)
FIGURE 1–2
Conservation of energy principle for
the human body.
Cool
environment
20°C
Hot
coffee
70°C
Heat
FIGURE 1–3
Heat flows in the direction of
decreasing temperature.
1–1
■
THERMODYNAMICS AND ENERGY
Thermodynamics can be defined as the science of energy. Although everybody has a feeling of what energy is, it is difficult to give a precise definition for it. Energy can be viewed as the ability to cause changes.
The name thermodynamics stems from the Greek words therme (heat) and
dynamis (power), which is most descriptive of the early efforts to convert
heat into power. Today the same name is broadly interpreted to include all
aspects of energy and energy transformations including power generation,
refrigeration, and relationships among the properties of matter.
One of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy
principle. It simply states that during an interaction, energy can change from
one form to another but the total amount of energy remains constant. That is,
energy cannot be created or destroyed. A rock falling off a cliff, for example,
picks up speed as a result of its potential energy being converted to kinetic
energy (Fig. 1–1). The conservation of energy principle also forms the backbone of the diet industry: A person who has a greater energy input (food)
than energy output (exercise) will gain weight (store energy in the form
of fat), and a person who has a smaller energy input than output will lose
weight (Fig. 1–2). The change in the energy content of a body or any other
system is equal to the difference between the energy input and the energy
output, and the energy balance is expressed as Ein 2 Eout 5 DE.
The first law of thermodynamics is simply an expression of the conservation of energy principle, and it asserts that energy is a thermodynamic
property. The second law of thermodynamics asserts that energy has
quality as well as quantity, and actual processes occur in the direction of
decreasing quality of energy. For example, a cup of hot coffee left on a table
eventually cools, but a cup of cool coffee in the same room never gets hot
by itself (Fig. 1–3). The high-temperature energy of the coffee is degraded
(transformed into a less useful form at a lower temperature) once it is transferred to the surrounding air.
Although the principles of thermodynamics have been in existence since
the creation of the universe, thermodynamics did not emerge as a science
until the construction of the first successful atmospheric steam engines in
England by Thomas Savery in 1697 and Thomas Newcomen in 1712. These
engines were very slow and inefficient, but they opened the way for the
development of a new science.
The first and second laws of thermodynamics emerged simultaneously in
the 1850s, primarily out of the works of William Rankine, Rudolph Clausius,
and Lord Kelvin (formerly William Thomson). The term thermodynamics
was first used in a publication by Lord Kelvin in 1849. The first thermodynamics textbook was written in 1859 by William Rankine, a professor at the
University of Glasgow.
It is well-known that a substance consists of a large number of particles
called molecules. The properties of the substance naturally depend on the
behavior of these particles. For example, the pressure of a gas in a container
is the result of momentum transfer between the molecules and the walls of
the container. However, one does not need to know the behavior of the gas
particles to determine the pressure in the container. It would be sufficient to
attach a pressure gage to the container. This macroscopic approach to the
3
CHAPTER 1
study of thermodynamics that does not require a knowledge of the behavior
of individual particles is called classical thermodynamics. It provides a
direct and easy way to the solution of engineering problems. A more elaborate approach, based on the average behavior of large groups of individual
particles, is called statistical thermodynamics. This microscopic approach
is rather involved and is used in this text only in the supporting role.
Application Areas of Thermodynamics
All activities in nature involve some interaction between energy and matter;
thus, it is hard to imagine an area that does not relate to thermodynamics in some manner. Therefore, developing a good understanding of basic
principles of thermodynamics has long been an essential part of engineering
education.
Thermodynamics is commonly encountered in many engineering systems
and other aspects of life, and one does not need to go very far to see some
application areas of it. In fact, one does not need to go anywhere. The heart
is constantly pumping blood to all parts of the human body, various energy
conversions occur in trillions of body cells, and the body heat generated is
constantly rejected to the environment. The human comfort is closely tied to
the rate of this metabolic heat rejection. We try to control this heat transfer
rate by adjusting our clothing to the environmental conditions.
Other applications of thermodynamics are right where one lives. An ordinary house is, in some respects, an exhibition hall filled with wonders of
thermodynamics (Fig. 1–4). Many ordinary household utensils and appliances are designed, in whole or in part, by using the principles of thermodynamics. Some examples include the electric or gas range, the heating
and air-conditioning systems, the refrigerator, the humidifier, the pressure
cooker, the water heater, the shower, the iron, and even the computer and
the TV. On a larger scale, thermodynamics plays a major part in the design
and analysis of automotive engines, rockets, jet engines, and conventional or
nuclear power plants, solar collectors, and the design of vehicles from ordinary cars to airplanes (Fig. 1–5). The energy-efficient home that you may
be living in, for example, is designed on the basis of minimizing heat loss
in winter and heat gain in summer. The size, location, and the power input
of the fan of your computer is also selected after an analysis that involves
thermodynamics.
1–2
■
IMPORTANCE OF DIMENSIONS AND UNITS
Any physical quantity can be characterized by dimensions. The magnitudes
assigned to the dimensions are called units. Some basic dimensions such
as mass m, length L, time t, and temperature T are selected as primary or
fundamental dimensions, while others such as velocity V, energy E, and
volume V are expressed in terms of the primary dimensions and are called
secondary dimensions, or derived dimensions.
A number of unit systems have been developed over the years. Despite
strong efforts in the scientific and engineering community to unify the
world with a single unit system, two sets of units are still in common
use today: the English system, which is also known as the United States
Solar
collectors
Shower
Hot
water
Hot water tank
Cold
water
Heat
exchanger
Pump
FIGURE 1–4
The design of many engineering
systems, such as this solar hot water
system, involves thermodynamics.
4
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Refrigerator
Boats
Aircraft and spacecraft
© McGraw-Hill Education, Jill Braaten
© Doug Menuez/Getty Images RF
© PhotoLink/Getty Images RF
Power plants
Human body
Cars
© Malcolm Fife/Getty Images RF
© Ryan McVay/Getty Images RF
© Mark Evans/Getty Images RF
Wind turbines
Food processing
A piping network in an industrial facility.
© F. Schussler/PhotoLink/Getty
Images RF
Glow Images RF
Courtesy of UMDE Engineering Contracting
and Trading. Used by permission
FIGURE 1–5
Some application areas of thermodynamics.
Customary System (USCS), and the metric SI (from Le Système International d’ Unités), which is also known as the International System. The SI
is a simple and logical system based on a decimal relationship between
the various units, and it is being used for scientific and engineering work
in most of the industrialized nations, including England. The English system, however, has no apparent systematic numerical base, and various units
in this system are related to each other rather arbitrarily (12 in 5 1 ft,
1 mile 5 5280 ft, 4 qt 5 1 gal, etc.), which makes it confusing and difficult
to learn. The United States is the only industrialized country that has not yet
fully converted to the metric system.
The systematic efforts to develop a universally acceptable system of
units dates back to 1790 when the French National Assembly charged the
French Academy of Sciences to come up with such a unit system. An early
version of the metric system was soon developed in France, but it did not
5
CHAPTER 1
find universal acceptance until 1875 when The Metric Convention Treaty
was prepared and signed by 17 nations, including the United States. In this
international treaty, meter and gram were established as the metric units
for length and mass, respectively, and a General Conference of Weights
and Measures (CGPM) was established that was to meet every six years.
In 1960, the CGPM produced the SI, which was based on six fundamental
quantities, and their units were adopted in 1954 at the Tenth General Conference of Weights and Measures: meter (m) for length, kilogram (kg) for
mass, second (s) for time, ampere (A) for electric current, degree Kelvin
(°K) for temperature, and candela (cd) for luminous intensity (amount of
light). In 1971, the CGPM added a seventh fundamental quantity and unit:
mole (mol) for the amount of matter.
Based on the notational scheme introduced in 1967, the degree symbol
was officially dropped from the absolute temperature unit, and all unit
names were to be written without capitalization even if they were derived
from proper names (Table 1–1). However, the abbreviation of a unit was
to be capitalized if the unit was derived from a proper name. For example,
the SI unit of force, which is named after Sir Isaac Newton (1647–1723),
is newton (not Newton), and it is abbreviated as N. Also, the full name of a
unit may be pluralized, but its abbreviation cannot. For example, the length
of an object can be 5 m or 5 meters, not 5 ms or 5 meter. Finally, no period
is to be used in unit abbreviations unless they appear at the end of a sentence. For example, the proper abbreviation of meter is m (not m.).
The recent move toward the metric system in the United States seems to
have started in 1968 when Congress, in response to what was happening
in the rest of the world, passed a Metric Study Act. Congress continued
to promote a voluntary switch to the metric system by passing the Metric
Conversion Act in 1975. A trade bill passed by Congress in 1988 set a
September 1992 deadline for all federal agencies to convert to the metric
system. However, the deadlines were relaxed later with no clear plans for
the future.
The industries that are heavily involved in international trade (such as the
automotive, soft drink, and liquor industries) have been quick in converting to the metric system for economic reasons (having a single worldwide
design, fewer sizes, smaller inventories, etc.). Today, nearly all the cars
manufactured in the United States are metric. Most car owners probably do
not realize this until they try an English socket wrench on a metric bolt.
Most industries, however, resisted the change, thus slowing down the conversion process.
Presently the United States is a dual-system society, and it will stay that
way until the transition to the metric system is completed. This puts an extra
burden on today’s engineering students, since they are expected to retain
their understanding of the English system while learning, thinking, and
working in terms of the SI. Given the position of the engineers in the transition period, both unit systems are used in this text, with particular emphasis
on SI units.
As pointed out, the SI is based on a decimal relationship between units.
The prefixes used to express the multiples of the various units are listed in
Table 1–2. They are standard for all units, and the student is encouraged to
memorize them because of their widespread use (Fig. 1–6).
TABLE 1–1
The seven fundamental (or primary)
dimensions and their units in SI
Dimension
Unit
Length
Mass
Time
Temperature
Electric current
Amount of light
Amount of matter
meter (m)
kilogram (kg)
second (s)
kelvin (K)
ampere (A)
candela (cd)
mole (mol)
TABLE 1–2
Standard prefixes in SI units
Multiple
Prefix
24
yotta, Y
zetta, Z
exa, E
peta, P
tera, T
giga, G
mega, M
kilo, k
hecto, h
deka, da
deci, d
centi, c
milli, m
micro, m
nano, n
pico, p
femto, f
atto, a
zepto, z
yocto, y
10
1021
1018
1015
1012
109
106
103
102
101
1021
1022
1023
1026
1029
10212
10215
10218
10221
10224
200 mL
(0.2 L)
1 kg
(103 g)
1 M⍀
(10 6 ⍀)
FIGURE 1–6
The SI unit prefixes are used in all
branches of engineering.
6
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Some SI and English Units
In SI, the units of mass, length, and time are the kilogram (kg), meter (m),
and second (s), respectively. The respective units in the English system are
the pound-mass (lbm), foot (ft), and second (s). The pound symbol lb is
actually the abbreviation of libra, which was the ancient Roman unit of
weight. The English retained this symbol even after the end of the Roman
occupation of Britain in 410. The mass and length units in the two systems
are related to each other by
1 lbm 5 0.45359 kg
1 ft 5 0.3048 m
a = 1 m/s 2
m = 1 kg
F=1N
In the English system, force is usually considered to be one of the
primary dimensions and is assigned a nonderived unit. This is a source
of confusion and error that necessitates the use of a dimensional
constant (gc) in many formulas. To avoid this nuisance, we consider
force to be a secondary dimension whose unit is derived from Newton’s
second law, that is,
Force 5 (Mass)(Acceleration)
a = 1 ft/s 2
m = 32.174 lbm
F = 1 lbf
or
F 5 ma
FIGURE 1–7
The definition of the force units.
(1–1)
In SI, the force unit is the newton (N), and it is defined as the force required
to accelerate a mass of 1 kg at a rate of 1 m/s2. In the English system, the
force unit is the pound-force (lbf) and is defined as the force required to
accelerate a mass of 32.174 lbm (1 slug) at a rate of 1 ft/s2 (Fig. 1–7). That is,
1 kgf
1 N 5 1 kg·m/s2
10 apples
m ⬇ 1 kg
1 apple
m ⬇ 102 g
1N
1 lbf 5 32.174 lbm·ft/s2
4 apples
m ⬇ 1 lbm
1 lbf
A force of 1 N is roughly equivalent to the weight of a small apple
(m 5 102 g), whereas a force of 1 lbf is roughly equivalent to the weight of
four medium apples (mtotal 5 454 g), as shown in Fig. 1–8. Another force
unit in common use in many European countries is the kilogram-force (kgf),
which is the weight of 1 kg mass at sea level (1 kgf 5 9.807 N).
The term weight is often incorrectly used to express mass, particularly
by the “weight watchers.” Unlike mass, weight W is a force. It is the gravitational force applied to a body, and its magnitude is determined from
Newton’s second law,
W 5 mg (N)
FIGURE 1–8
The relative magnitudes of the force
units newton (N), kilogram-force (kgf),
and pound-force (lbf).
(1–2)
where m is the mass of the body, and g is the local gravitational acceleration
(g is 9.807 m/s2 or 32.174 ft/s2 at sea level and 45° latitude). An ordinary
bathroom scale measures the gravitational force acting on a body.
The mass of a body remains the same regardless of its location in the
universe. Its weight, however, changes with a change in gravitational
acceleration. A body weighs less on top of a mountain since g decreases
7
CHAPTER 1
with altitude. On the surface of the moon, an astronaut weighs about onesixth of what she or he normally weighs on earth (Fig. 1–9).
At sea level a mass of 1 kg weighs 9.807 N, as illustrated in Fig. 1–10. A
mass of 1 lbm, however, weighs 1 lbf, which misleads people to believe that
pound-mass and pound-force can be used interchangeably as pound (lb),
which is a major source of error in the English system.
It should be noted that the gravity force acting on a mass is due to the
attraction between the masses, and thus it is proportional to the magnitudes of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Therefore, the gravitational acceleration g at a location
depends on the local density of the earth’s crust, the distance to the center
of the earth, and to a lesser extent, the positions of the moon and the sun.
The value of g varies with location from 9.832 m/s2 at the poles (9.789 at
the equator) to 7.322 m/s2 at 1000 km above sea level. However, at altitudes
up to 30 km, the variation of g from the sea-level value of 9.807 m/s2 is
less than 1 percent. Therefore, for most practical purposes, the gravitational
acceleration can be assumed to be constant at 9.807 m/s2, often rounded to
9.81 m/s2. It is interesting to note that at locations below sea level, the value
of g increases with distance from the sea level, reaches a maximum at about
4500 m, and then starts decreasing. (What do you think the value of g is at
the center of the earth?)
The primary cause of confusion between mass and weight is that mass is
usually measured indirectly by measuring the gravity force it exerts. This
approach also assumes that the forces exerted by other effects such as air
buoyancy and fluid motion are negligible. This is like measuring the distance to a star by measuring its red shift, or measuring the altitude of an
airplane by measuring barometric pressure. Both of these are also indirect
measurements. The correct direct way of measuring mass is to compare it
to a known mass. This is cumbersome, however, and it is mostly used for
calibration and measuring precious metals.
Work, which is a form of energy, can simply be defined as force times
distance; therefore, it has the unit “newton-meter (N·m),” which is called a
joule (J). That is,
1 J 5 1 N·m
FIGURE 1–9
A body weighing 150 lbf on earth will
weigh only 25 lbf on the moon.
kg
lbm
g = 9.807 m/s2
W = 9.807 kg·m/s2
= 9.807 N
= 1 kgf
g = 32.174 ft/s2
W = 32.174 lbm·ft/s2
= 1 lbf
FIGURE 1–10
The weight of a unit mass at sea level.
(1–3)
A more common unit for energy in SI is the kilojoule (1 kJ 5 103 J). In the
English system, the energy unit is the Btu (British thermal unit), which is
defined as the energy required to raise the temperature of 1 lbm of water at
68°F by 1°F. In the metric system, the amount of energy needed to raise the
temperature of 1 g of water at 14.5°C by 1°C is defined as 1 calorie (cal),
and 1 cal 5 4.1868 J. The magnitudes of the kilojoule and Btu are almost
identical (1 Btu 5 1.0551 kJ). Here is a good way to get a feel for these
units: If you light a typical match and let it burn itself out, it yields approximately one Btu (or one kJ) of energy (Fig. 1–11).
The unit for time rate of energy is joule per second (J/s), which is called
a watt (W). In the case of work, the time rate of energy is called power.
A commonly used unit of power is horsepower (hp), which is equivalent
to 746 W. Electrical energy typically is expressed in the unit kilowatt-hour
(kWh), which is equivalent to 3600 kJ. An electric appliance with a rated
power of 1 kW consumes 1 kWh of electricity when running continuously
FIGURE 1–11
A typical match yields about one Btu (or
one kJ) of energy if completely burned.
Photo by John M. Cimbala
8
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
for one hour. When dealing with electric power generation, the units kW
and kWh are often confused. Note that kW or kJ/s is a unit of power,
whereas kWh is a unit of energy. Therefore, statements like “the new wind
turbine will generate 50 kW of electricity per year” are meaningless and
incorrect. A correct statement should be something like “the new wind turbine with a rated power of 50 kW will generate 120,000 kWh of electricity
per year.”
Dimensional Homogeneity
We all know that apples and oranges do not add. But we somehow manage to do it (by mistake, of course). In engineering, all equations must be
dimensionally homogeneous. That is, every term in an equation must have
the same unit. If, at some stage of an analysis, we find ourselves in a position to add two quantities that have different units, it is a clear indication
that we have made an error at an earlier stage. So checking dimensions can
serve as a valuable tool to spot errors.
EXAMPLE 1–1
Electric Power Generation by a Wind Turbine
A school is paying $0.12/kWh for electric power. To reduce its power bill,
the school installs a wind turbine (Fig. 1–12) with a rated power of 30 kW.
If the turbine operates 2200 hours per year at the rated power, determine
the amount of electric power generated by the wind turbine and the money
saved by the school per year.
SOLUTION
A wind turbine is installed to generate electricity. The amount of
electric energy generated and the money saved per year are to be determined.
Analysis The wind turbine generates electric energy at a rate of 30 kW or
30 kJ/s. Then the total amount of electric energy generated per year becomes
Total energy 5 (Energy per unit time)(Time interval)
5 (30 kW)(2200 h)
5 66,000 kWh
The money saved per year is the monetary value of this energy determined as
Money saved 5 (Total energy)(Unit cost of energy)
5 (66,000 kWh)($0.12/kWh)
5 $7920
Discussion The annual electric energy production also could be determined
in kJ by unit manipulations as
FIGURE 1–12
A wind turbine, as discussed in
Example 1–1.
©Bear Dancer Studios/Mark Dierker RF
Total energy 5 (30 kW)(2200 h)a
3600 s 1 kJ/s
ba
b 5 2.38 3 108 kJ
1h
1 kW
which is equivalent to 66,000 kWh (1 kWh = 3600 kJ).
We all know from experience that units can give terrible headaches if they
are not used carefully in solving a problem. However, with some attention
and skill, units can be used to our advantage. They can be used to check
formulas; sometimes they can even be used to derive formulas, as explained
in the following example.
9
CHAPTER 1
EXAMPLE 1–2
Obtaining Formulas from Unit Considerations
A tank is filled with oil whose density is r 5 850 kg/m3. If the volume of the
tank is V 5 2 m3, determine the amount of mass m in the tank.
Oil
= 2 m3
ρ = 850 kg/m3
m=?
SOLUTION The volume of an oil tank is given. The mass of oil is to be
determined.
Assumptions Oil is a nearly incompressible substance and thus its density
is constant.
Analysis A sketch of the system just described is given in Fig. 1–13.
Suppose we forgot the formula that relates mass to density and volume.
However, we know that mass has the unit of kilograms. That is, whatever
calculations we do, we should end up with the unit of kilograms. Putting the
given information into perspective, we have
r 5 850 kg/m3
and
FIGURE 1–13
Schematic for Example 1–2.
V 5 2 m3
It is obvious that we can eliminate m3 and end up with kg by multiplying
these two quantities. Therefore, the formula we are looking for should be
m 5 rV
Thus,
m 5 (850 kg/m3)(2 m3) 5 1700 kg
Discussion Note that this approach may not work for more complicated formulas. Nondimensional constants also may be present in the formulas, and
these cannot be derived from unit considerations alone.
You should keep in mind that a formula that is not dimensionally homogeneous is definitely wrong (Fig. 1–14), but a dimensionally homogeneous
formula is not necessarily right.
Unity Conversion Ratios
FIGURE 1–14
Always check the units in your
calculations.
Just as all nonprimary dimensions can be formed by suitable combinations of primary dimensions, all nonprimary units (secondary units) can be
formed by combinations of primary units. Force units, for example, can be
expressed as
1 N 5 1 kg
m
s2
and
ft
1 lbf 5 32.174 lbm 2
s
They can also be expressed more conveniently as unity conversion ratios as
1N
51
1 kg·m /s2
and
1 lbf
51
32.174 lbm·ft /s2
Unity conversion ratios are identically equal to 1 and are unitless, and
thus such ratios (or their inverses) can be inserted conveniently into any
calculation to properly convert units (Fig. 1–15). You are encouraged to
always use unity conversion ratios such as those given here when converting
units. Some textbooks insert the archaic gravitational constant gc defined as
gc 5 32.174 lbm·ft/lbf·s2 5 1 kg·m/N·s2 5 1 into equations in order to force
32.174 lbm?ft/s2 1 kg?m/s2
1 lbf
1N
1W
1 J/s
1 kJ
1000 N?m
0.3048 m
1 ft
1 min
60 s
1 kPa
1000 N/m2
1 lbm
0.45359 kg
FIGURE 1–15
Every unity conversion ratio (as well
as its inverse) is exactly equal to one.
Shown here are a few commonly used
unity conversion ratios.
10
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
units to match. This practice leads to unnecessary confusion and is strongly
discouraged by the present authors. We recommend that you instead use
unity conversion ratios.
lbm
EXAMPLE 1–3
The Weight of One Pound-Mass
Using unity conversion ratios, show that 1.00 lbm weighs 1.00 lbf on earth
(Fig. 1–16).
FIGURE 1–16
A mass of 1 lbm weighs 1 lbf on earth.
SOLUTION A mass of 1.00 lbm is subjected to standard earth gravity. Its
weight in lbf is to be determined.
Assumptions Standard sea-level conditions are assumed.
Properties The gravitational constant is g 5 32.174 ft/s2.
Analysis We apply Newton’s second law to calculate the weight (force) that
corresponds to the known mass and acceleration. The weight of any object
is equal to its mass times the local value of gravitational acceleration. Thus,
W 5 mg 5 (1.00 lbm)(32.174 ft /s2)a
Net weight:
One pound
(454 grams)
1 lbf
b 5 1.00 lbf
32.174 lbm·ft /s2
Discussion The quantity in large parentheses in this equation is a unity conversion ratio. Mass is the same regardless of its location. However, on some
other planet with a different value of gravitational acceleration, the weight of
1 lbm would differ from that calculated here.
When you buy a box of breakfast cereal, the printing may say “Net
weight: One pound (454 grams).” (See Fig. 1–17.) Technically, this means
that the cereal inside the box weighs 1.00 lbf on earth and has a mass of
453.6 g (0.4536 kg). Using Newton’s second law, the actual weight of the
cereal on earth is
W 5 mg 5 (453.6 g)(9.81 m/s2)a
FIGURE 1–17
A quirk in the metric system of units.
Surroundings
System
Boundary
FIGURE 1–18
System, surroundings, and boundary.
1–3
■
1 kg
1N
ba
b 5 4.49 N
1 kg·m/s2 1000 g
SYSTEMS AND CONTROL VOLUMES
A system is defined as a quantity of matter or a region in space chosen for
study. The mass or region outside the system is called the surroundings.
The real or imaginary surface that separates the system from its surroundings is called the boundary (Fig. 1–18). The boundary of a system can be
fixed or movable. Note that the boundary is the contact surface shared by
both the system and the surroundings. Mathematically speaking, the boundary has zero thickness, and thus it can neither contain any mass nor occupy
any volume in space.
Systems may be considered to be closed or open, depending on whether a
fixed mass or a fixed volume in space is chosen for study. A closed system
(also known as a control mass or just system when the context makes it
clear) consists of a fixed amount of mass, and no mass can cross its boundary. That is, no mass can enter or leave a closed system, as shown in
11
CHAPTER 1
Fig. 1–19. But energy, in the form of heat or work, can cross the boundary;
and the volume of a closed system does not have to be fixed. If, as a special
case, even energy is not allowed to cross the boundary, that system is called
an isolated system.
Consider the piston-cylinder device shown in Fig. 1–20. Let us say that
we would like to find out what happens to the enclosed gas when it is
heated. Since we are focusing our attention on the gas, it is our system. The
inner surfaces of the piston and the cylinder form the boundary, and since
no mass is crossing this boundary, it is a closed system. Notice that energy
may cross the boundary, and part of the boundary (the inner surface of the
piston, in this case) may move. Everything outside the gas, including the
piston and the cylinder, is the surroundings.
An open system, or a control volume, as it is often called, is a properly selected region in space. It usually encloses a device that involves
mass flow such as a compressor, turbine, or nozzle. Flow through these
devices is best studied by selecting the region within the device as the
control volume. Both mass and energy can cross the boundary of a control volume.
A large number of engineering problems involve mass flow in and out of
a system and, therefore, are modeled as control volumes. A water heater, a
car radiator, a turbine, and a compressor all involve mass flow and should
be analyzed as control volumes (open systems) instead of as control
masses (closed systems). In general, any arbitrary region in space can be
selected as a control volume. There are no concrete rules for the selection of control volumes, but the proper choice certainly makes the analysis
much easier. If we were to analyze the flow of air through a nozzle, for
example, a good choice for the control volume would be the region within
the nozzle.
The boundaries of a control volume are called a control surface, and
they can be real or imaginary. In the case of a nozzle, the inner surface of
the nozzle forms the real part of the boundary, and the entrance and exit
areas form the imaginary part, since there are no physical surfaces there
(Fig. 1–21a).
Imaginary
boundary
Closed
system
Mass
No
m = constant
Energy Yes
FIGURE 1–19
Mass cannot cross the boundaries of a
closed system, but energy can.
Moving
boundary
Gas
2 kg
1.5 m3
Gas
2 kg
1 m3
Fixed
boundary
FIGURE 1–20
A closed system with a moving
boundary.
Real boundary
Moving
boundary
CV
(a nozzle)
(a) A control volume (CV) with real and
imaginary boundaries
CV
Fixed
boundary
(b) A control volume (CV) with fixed and
moving boundaries as well as real and
imaginary boundaries
FIGURE 1–21
A control volume can involve
fixed, moving, real, and imaginary
boundaries.
12
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
A control volume can be fixed in size and shape, as in the case of a
nozzle, or it may involve a moving boundary, as shown in Fig. 1–21b. Most
control volumes, however, have fixed boundaries and thus do not involve
any moving boundaries. A control volume can also involve heat and work
interactions just as a closed system, in addition to mass interaction.
As an example of an open system, consider the water heater shown in
Fig. 1–22. Let us say that we would like to determine how much heat we
must transfer to the water in the tank in order to supply a steady stream of
hot water. Since hot water will leave the tank and be replaced by cold water,
it is not convenient to choose a fixed mass as our system for the analysis. Instead, we can concentrate our attention on the volume formed by the
interior surfaces of the tank and consider the hot and cold water streams as
mass leaving and entering the control volume. The interior surfaces of the
tank form the control surface for this case, and mass is crossing the control
surface at two locations.
In an engineering analysis, the system under study must be defined carefully. In most cases, the system investigated is quite simple and obvious,
and defining the system may seem like a tedious and unnecessary task. In
other cases, however, the system under study may be rather involved, and a
proper choice of the system may greatly simplify the analysis.
FIGURE 1–22
An open system (a control volume)
with one inlet and one exit.
© McGraw-Hill Education, Christopher Kerrigan
1–4
■
PROPERTIES OF A SYSTEM
Any characteristic of a system is called a property. Some familiar properties are pressure P, temperature T, volume V, and mass m. The list can be
extended to include less familiar ones such as viscosity, thermal conductivity, modulus of elasticity, thermal expansion coefficient, electric resistivity,
and even velocity and elevation.
Properties are considered to be either intensive or extensive. Intensive
properties are those that are independent of the mass of a system, such as
temperature, pressure, and density. Extensive properties are those whose
values depend on the size—or extent—of the system. Total mass, total volume, and total momentum are some examples of extensive properties. An
easy way to determine whether a property is intensive or extensive is to
divide the system into two equal parts with an imaginary partition, as shown
in Fig. 1–23. Each part will have the same value of intensive properties as
the original system, but half the value of the extensive properties.
Generally, uppercase letters are used to denote extensive properties
(with mass m being a major exception), and lowercase letters are used for
intensive properties (with pressure P and temperature T being the obvious
exceptions).
Extensive properties per unit mass are called specific properties. Some
examples of specific properties are specific volume (v 5 V/m) and specific
total energy (e 5 E/m).
Continuum
FIGURE 1–23
Criterion to differentiate intensive and
extensive properties.
Matter is made up of atoms that are widely spaced in the gas phase. Yet it
is very convenient to disregard the atomic nature of a substance and view it
as a continuous, homogeneous matter with no holes, that is, a continuum.
13
CHAPTER 1
The continuum idealization allows us to treat properties as point functions
and to assume the properties vary continually in space with no jump discontinuities. This idealization is valid as long as the size of the system we deal
with is large relative to the space between the molecules. This is the case
in practically all problems, except some specialized ones. The continuum
idealization is implicit in many statements we make, such as “the density of
water in a glass is the same at any point.”
To have a sense of the distance involved at the molecular level, consider a container filled with oxygen at atmospheric conditions. The
diameter of the oxygen molecule is about 3 3 10210 m and its mass is
5.3 3 10226 kg. Also, the mean free path of oxygen at 1 atm pressure and
20°C is 6.3 3 1028 m. That is, an oxygen molecule travels, on average, a
distance of 6.3 3 1028 m (about 200 times of its diameter) before it collides with another molecule.
Also, there are about 3 3 1016 molecules of oxygen in the tiny volume
of 1 mm3 at 1 atm pressure and 20°C (Fig. 1–24). The continuum model
is applicable as long as the characteristic length of the system (such as its
diameter) is much larger than the mean free path of the molecules. At very
high vacuums or very high elevations, the mean free path may become
large (for example, it is about 0.1 m for atmospheric air at an elevation
of 100 km). For such cases the rarefied gas flow theory should be used,
and the impact of individual molecules should be considered. In this text
we will limit our consideration to substances that can be modeled as a
continuum.
1–5
■
O2
1 atm, 20°C
3 ´ 1016 molecules/mm3
VOID
FIGURE 1–24
Despite the relatively large gaps
between molecules, a gas can usually
be treated as a continuum because of
the very large number of molecules
even in an extremely small volume.
DENSITY AND SPECIFIC GRAVITY
Density is defined as mass per unit volume (Fig. 1–25).
Density:
r5
m
V
(kg/m3)
(1–4)
The reciprocal of density is the specific volume v, which is defined as volume per unit mass. That is,
v5
V
1
5
r
m
V = 12 m 3
m = 3 kg
r = 0.25 kg/m 3
1
3
v=–
r = 4 m /kg
(1–5)
For a differential volume element of mass dm and volume dV, density can
be expressed as r 5 dm/dV.
The density of a substance, in general, depends on temperature and pressure. The density of most gases is proportional to pressure and inversely
proportional to temperature. Liquids and solids, on the other hand, are
essentially incompressible substances, and the variation of their density with
pressure is usually negligible. At 20°C, for example, the density of water
changes from 998 kg/m3 at 1 atm to 1003 kg/m3 at 100 atm, a change of
just 0.5 percent. The density of liquids and solids depends more strongly on
temperature than it does on pressure. At 1 atm, for example, the density of
water changes from 998 kg/m3 at 20°C to 975 kg/m3 at 75°C, a change of
2.3 percent, which can still be neglected in many engineering analyses.
FIGURE 1–25
Density is mass per unit volume;
specific volume is volume
per unit mass.
14
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Sometimes the density of a substance is given relative to the density of a
well-known substance. Then it is called specific gravity, or relative density, and is defined as the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of some standard substance at a specified temperature (usually water at
4°C, for which rH2O 5 1000 kg/m3). That is,
TABLE 1–3
Specific gravities of some
substances at 0°C
Substance
SG
Water
Blood
Seawater
Gasoline
Ethyl alcohol
Mercury
Wood
Gold
Bones
Ice
Air (at 1 atm)
1.0
1.05
1.025
0.7
0.79
13.6
0.3–0.9
19.2
1.7–2.0
0.92
0.0013
Specific gravity:
SG 5
r
rH2O
(1–6)
Note that the specific gravity of a substance is a dimensionless quantity.
However, in SI units, the numerical value of the specific gravity of a substance is exactly equal to its density in g/cm3 or kg/L (or 0.001 times the
density in kg/m3) since the density of water at 4°C is 1 g/cm3 5 1 kg/L 5
1000 kg/m3. The specific gravity of mercury at 0°C, for example, is 13.6.
Therefore, its density at 0°C is 13.6 g/cm3 5 13.6 kg/L 5 13,600 kg/m3.
The specific gravities of some substances at 0°C are given in Table 1–3.
Note that substances with specific gravities less than 1 are lighter than
water, and thus they would float on water.
The weight of a unit volume of a substance is called specific weight and
is expressed as
Specific weight:
gs 5 rg
(N/m3)
(1–7)
where g is the gravitational acceleration.
The densities of liquids are essentially constant, and thus they can often
be approximated as being incompressible substances during most processes
without sacrificing much in accuracy.
m = 2 kg
T1 = 20°C
V1 = 1.5 m3
(a) State 1
m = 2 kg
T2 = 20°C
V2 = 2.5 m3
(b) State 2
FIGURE 1–26
A system at two different states.
20°C
23°C
30°C
35°C
40°C
42°C
(a) Before
32°C
32°C
32°C
32°C
32°C
32°C
(b) After
FIGURE 1–27
A closed system reaching thermal
equilibrium.
1–6
■
STATE AND EQUILIBRIUM
Consider a system not undergoing any change. At this point, all the properties can be measured or calculated throughout the entire system, which
gives us a set of properties that completely describes the condition, or
the state, of the system. At a given state, all the properties of a system
have fixed values. If the value of even one property changes, the state will
change to a different one. In Fig. 1–26 a system is shown at two different
states.
Thermodynamics deals with equilibrium states. The word equilibrium
implies a state of balance. In an equilibrium state there are no unbalanced
potentials (or driving forces) within the system. A system in equilibrium
experiences no changes when it is isolated from its surroundings.
There are many types of equilibrium, and a system is not in thermodynamic equilibrium unless the conditions of all the relevant types of equilibrium are satisfied. For example, a system is in thermal equilibrium
if the temperature is the same throughout the entire system, as shown in
Fig. 1–27. That is, the system involves no temperature differential, which is
the driving force for heat flow. Mechanical equilibrium is related to pressure, and a system is in mechanical equilibrium if there is no change in
pressure at any point of the system with time. However, the pressure may
vary within the system with elevation as a result of gravitational effects.
15
CHAPTER 1
For example, the higher pressure at a bottom layer is balanced by the extra
weight it must carry, and, therefore, there is no imbalance of forces. The
variation of pressure as a result of gravity in most thermodynamic systems
is relatively small and usually disregarded. If a system involves two phases,
it is in phase equilibrium when the mass of each phase reaches an equilibrium level and stays there. Finally, a system is in chemical equilibrium
if its chemical composition does not change with time, that is, no chemical
reactions occur. A system will not be in equilibrium unless all the relevant
equilibrium criteria are satisfied.
The State Postulate
As noted earlier, the state of a system is described by its properties. But
we know from experience that we do not need to specify all the properties
in order to fix a state. Once a sufficient number of properties are specified, the rest of the properties assume certain values automatically. That is,
specifying a certain number of properties is sufficient to fix a state. The
number of properties required to fix the state of a system is given by the
state postulate:
The state of a simple compressible system is completely specified by two
independent, intensive properties.
A system is called a simple compressible system in the absence of electrical, magnetic, gravitational, motion, and surface tension effects. These
effects are due to external force fields and are negligible for most engineering problems. Otherwise, an additional property needs to be specified for
each effect that is significant. If the gravitational effects are to be considered, for example, the elevation z needs to be specified in addition to the
two properties necessary to fix the state.
The state postulate requires that the two properties specified be independent to fix the state. Two properties are independent if one property can be
varied while the other one is held constant. Temperature and specific volume, for example, are always independent properties, and together they can
fix the state of a simple compressible system (Fig. 1–28). Temperature and
pressure, however, are independent properties for single-phase systems, but
are dependent properties for multiphase systems. At sea level (P 5 1 atm),
water boils at 100°C, but on a mountaintop where the pressure is lower,
water boils at a lower temperature. That is, T 5 f(P) during a phase-change
process; thus, temperature and pressure are not sufficient to fix the state
of a two-phase system. Phase-change processes are discussed in detail in
Chap. 3.
1–7
■
Nitrogen
T = 25°C
v = 0.9 m3/kg
FIGURE 1–28
The state of nitrogen is fixed by two
independent, intensive properties.
Property A
State 2
Process path
PROCESSES AND CYCLES
Any change that a system undergoes from one equilibrium state to another
is called a process, and the series of states through which a system passes
during a process is called the path of the process (Fig. 1–29). To describe
a process completely, one should specify the initial and final states of
the process, as well as the path it follows, and the interactions with the
surroundings.
State 1
Property B
FIGURE 1–29
A process between states 1 and 2 and
the process path.
16
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
(a) Slow compression
(quasi-equilibrium)
(b) Very fast compression
(nonquasi-equilibrium)
FIGURE 1–30
Quasi-equilibrium and nonquasiequilibrium compression processes.
P
Final state
2
Process path
Initial
state
1
V2
V1
(2)
(1)
V
System
FIGURE 1–31
The P-V diagram of a compression
process.
When a process proceeds in such a manner that the system remains infinitesimally close to an equilibrium state at all times, it is called a quasi-static,
or quasi-equilibrium, process. A quasi-equilibrium process can be viewed
as a sufficiently slow process that allows the system to adjust itself internally
so that properties in one part of the system do not change any faster than
those at other parts.
This is illustrated in Fig. 1–30. When a gas in a piston-cylinder device
is compressed suddenly, the molecules near the face of the piston will not
have enough time to escape and they will have to pile up in a small region
in front of the piston, thus creating a high-pressure region there. Because of
this pressure difference, the system can no longer be said to be in equilibrium, and this makes the entire process nonquasi-equilibrium. However, if
the piston is moved slowly, the molecules will have sufficient time to redistribute and there will not be a molecule pileup in front of the piston. As a
result, the pressure inside the cylinder will always be nearly uniform and
will rise at the same rate at all locations. Since equilibrium is maintained at
all times, this is a quasi-equilibrium process.
It should be pointed out that a quasi-equilibrium process is an idealized process and is not a true representation of an actual process. But
many actual processes closely approximate it, and they can be modeled as
quasi-equilibrium with negligible error. Engineers are interested in quasiequilibrium processes for two reasons. First, they are easy to analyze; second, work-producing devices deliver the most work when they operate on
quasi-equilibrium processes. Therefore, quasi-equilibrium processes serve
as standards to which actual processes can be compared.
Process diagrams plotted by employing thermodynamic properties as
coordinates are very useful in visualizing the processes. Some common
properties that are used as coordinates are temperature T, pressure P, and
volume V (or specific volume v). Figure 1–31 shows the P-V diagram of a
compression process of a gas.
Note that the process path indicates a series of equilibrium states through
which the system passes during a process and has significance for quasiequilibrium processes only. For nonquasi-equilibrium processes, we are not
able to characterize the entire system by a single state, and thus we cannot
speak of a process path for a system as a whole. A nonquasi-equilibrium
process is denoted by a dashed line between the initial and final states
instead of a solid line.
The prefix iso- is often used to designate a process for which a particular
property remains constant. An isothermal process, for example, is a process
during which the temperature T remains constant; an isobaric process is a
process during which the pressure P remains constant; and an isochoric (or
isometric) process is a process during which the specific volume v remains
constant.
A system is said to have undergone a cycle if it returns to its initial state
at the end of the process. That is, for a cycle the initial and final states are
identical.
The Steady-Flow Process
The terms steady and uniform are used frequently in engineering, and thus
it is important to have a clear understanding of their meanings. The term
17
CHAPTER 1
steady implies no change with time. The opposite of steady is unsteady, or
transient. The term uniform, however, implies no change with location over
a specified region. These meanings are consistent with their everyday use
(steady girlfriend, uniform properties, etc.).
A large number of engineering devices operate for long periods of time
under the same conditions, and they are classified as steady-flow devices.
Processes involving such devices can be represented reasonably well by a
somewhat idealized process, called the steady-flow process, which can be
defined as a process during which a fluid flows through a control volume
steadily (Fig. 1–32). That is, the fluid properties can change from point to
point within the control volume, but at any fixed point they remain the same
during the entire process. Therefore, the volume V, the mass m, and the total
energy content E of the control volume remain constant during a steadyflow process (Fig. 1–33).
Steady-flow conditions can be closely approximated by devices that are
intended for continuous operation such as turbines, pumps, boilers, condensers, and heat exchangers or power plants or refrigeration systems. Some
cyclic devices, such as reciprocating engines or compressors, do not satisfy any of the conditions stated above since the flow at the inlets and the
exits will be pulsating and not steady. However, the fluid properties vary
with time in a periodic manner, and the flow through these devices can still
be analyzed as a steady-flow process by using time-averaged values for the
properties.
1–8
■
TEMPERATURE AND THE ZEROTH LAW OF
THERMODYNAMICS
Although we are familiar with temperature as a measure of “hotness” or
“coldness,” it is not easy to give an exact definition for it. Based on our
physiological sensations, we express the level of temperature qualitatively
with words like freezing cold, cold, warm, hot, and red-hot. However, we
cannot assign numerical values to temperatures based on our sensations
alone. Furthermore, our senses may be misleading. A metal chair, for example, will feel much colder than a wooden one even when both are at the
same temperature.
Fortunately, several properties of materials change with temperature in
a repeatable and predictable way, and this forms the basis for accurate
temperature measurement. The commonly used mercury-in-glass thermometer, for example, is based on the expansion of mercury with temperature.
Temperature is also measured by using several other temperature-dependent
properties.
It is a common experience that a cup of hot coffee left on the table eventually cools off and a cold drink eventually warms up. That is, when a body
is brought into contact with another body that is at a different temperature, heat is transferred from the body at higher temperature to the one at
lower temperature until both bodies attain the same temperature (Fig. 1–34).
At that point, the heat transfer stops, and the two bodies are said to have
reached thermal equilibrium. The equality of temperature is the only
requirement for thermal equilibrium.
Mass
in
300°C
250°C
Control volume
225°C
200°C
Mass
out
150°C
Time: 1 PM
Mass
in
300°C
250°C
Control volume
225°C
200°C
Mass
out
150°C
Time: 3 PM
FIGURE 1–32
During a steady-flow process, fluid
properties within the control volume
may change with position but not with
time.
Mass
in
Control
volume
mCV = const.
Mass
out
ECV = const.
FIGURE 1–33
Under steady-flow conditions, the
mass and energy contents of a control
volume remain constant.
Iron
Iron
150°C
60°C
Copper
Copper
20°C
60°C
FIGURE 1–34
Two bodies reaching thermal
equilibrium after being brought into
contact in an isolated enclosure.
18
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
The zeroth law of thermodynamics states that if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, they are also in thermal equilibrium with
each other. It may seem silly that such an obvious fact is called one of the
basic laws of thermodynamics. However, it cannot be concluded from the
other laws of thermodynamics, and it serves as a basis for the validity of
temperature measurement. By replacing the third body with a thermometer,
the zeroth law can be restated as two bodies are in thermal equilibrium if
both have the same temperature reading even if they are not in contact.
The zeroth law was first formulated and labeled by R. H. Fowler in 1931.
As the name suggests, its value as a fundamental physical principle was
recognized more than half a century after the formulation of the first and
the second laws of thermodynamics. It was named the zeroth law since it
should have preceded the first and the second laws of thermodynamics.
Temperature Scales
Temperature scales enable us to use a common basis for temperature measurements, and several have been introduced throughout history. All temperature scales are based on some easily reproducible states such as the
freezing and boiling points of water, which are also called the ice point and
the steam point, respectively. A mixture of ice and water that is in equilibrium with air saturated with vapor at 1 atm pressure is said to be at the ice
point, and a mixture of liquid water and water vapor (with no air) in equilibrium at 1 atm pressure is said to be at the steam point.
The temperature scales used in the SI and in the English system today
are the Celsius scale (formerly called the centigrade scale; in 1948 it was
renamed after the Swedish astronomer A. Celsius, 1702–1744, who devised
it) and the Fahrenheit scale (named after the German instrument maker
G. Fahrenheit, 1686–1736), respectively. On the Celsius scale, the ice and
steam points were originally assigned the values of 0 and 100°C, respectively. The corresponding values on the Fahrenheit scale are 32 and 212°F.
These are often referred to as two-point scales since temperature values are
assigned at two different points.
In thermodynamics, it is very desirable to have a temperature scale that
is independent of the properties of any substance or substances. Such a
temperature scale is called a thermodynamic temperature scale, which
is developed later in conjunction with the second law of thermodynamics.
The thermodynamic temperature scale in the SI is the Kelvin scale, named
after Lord Kelvin (1824–1907). The temperature unit on this scale is the
kelvin, which is designated by K (not °K; the degree symbol was officially
dropped from kelvin in 1967). The lowest temperature on the Kelvin scale
is absolute zero, or 0 K. Then it follows that only one nonzero reference
point needs to be assigned to establish the slope of this linear scale. Using
nonconventional refrigeration techniques, scientists have approached absolute zero kelvin (they achieved 0.000000002 K in 1989).
The thermodynamic temperature scale in the English system is the
Rankine scale, named after William Rankine (1820–1872). The temperature unit on this scale is the rankine, which is designated by R.
A temperature scale that turns out to be nearly identical to the Kelvin
scale is the ideal-gas temperature scale. The temperatures on this scale are
19
CHAPTER 1
measured using a constant-volume gas thermometer, which is basically a
rigid vessel filled with a gas, usually hydrogen or helium, at low pressure.
This thermometer is based on the principle that at low pressures, the temperature of a gas is proportional to its pressure at constant volume. That is,
the temperature of a gas of fixed volume varies linearly with pressure at sufficiently low pressures. Then the relationship between the temperature and
the pressure of the gas in the vessel can be expressed as
T 5 a 1 bP
(1–8)
where the values of the constants a and b for a gas thermometer are determined experimentally. Once a and b are known, the temperature of a
medium can be calculated from this relation by immersing the rigid vessel
of the gas thermometer into the medium and measuring the gas pressure
when thermal equilibrium is established between the medium and the gas in
the vessel whose volume is held constant.
An ideal-gas temperature scale can be developed by measuring the pressures of the gas in the vessel at two reproducible points (such as the ice
and the steam points) and assigning suitable values to temperatures at
those two points. Considering that only one straight line passes through
two fixed points on a plane, these two measurements are sufficient to
determine the constants a and b in Eq. 1–8. Then the unknown temperature T of a medium corresponding to a pressure reading P can be determined from that equation by a simple calculation. The values of the constants will be different for each thermometer, depending on the type and
the amount of the gas in the vessel, and the temperature values assigned
at the two reference points. If the ice and steam points are assigned the
values 0°C and 100°C, respectively, then the gas temperature scale will
be identical to the Celsius scale. In this case the value of the constant a
(which corresponds to an absolute pressure of zero) is determined to be
2273.15°C regardless of the type and the amount of the gas in the vessel
of the gas thermometer. That is, on a P-T diagram, all the straight lines
passing through the data points in this case will intersect the temperature
axis at 2273.15°C when extrapolated, as shown in Fig. 1–35. This is the
lowest temperature that can be obtained by a gas thermometer, and thus
we can obtain an absolute gas temperature scale by assigning a value of
zero to the constant a in Eq. 1–8. In that case, Eq. 1–8 reduces to T 5 bP,
and thus we need to specify the temperature at only one point to define an
absolute gas temperature scale.
It should be noted that the absolute gas temperature scale is not a thermodynamic temperature scale, since it cannot be used at very low temperatures
(due to condensation) and at very high temperatures (due to dissociation and
ionization). However, absolute gas temperature is identical to the thermodynamic temperature in the temperature range in which the gas thermometer
can be used. Thus, we can view the thermodynamic temperature scale at
this point as an absolute gas temperature scale that utilizes an “ideal” or
“imaginary” gas that always acts as a low-pressure gas regardless of the
temperature. If such a gas thermometer existed, it would read zero kelvin
at absolute zero pressure, which corresponds to 2273.15°C on the Celsius
scale (Fig. 1–36).
Measured
data points
P
Gas A
Gas B
Extrapolation
Gas C
Gas D
–273.15
T, °C
0
FIGURE 1–35
P versus T plots of the experimental
data obtained from a constant-volume
gas thermometer using four different
gases at different (but low) pressures.
T (°C)
–200
–225
–250
–275
– 273.15
T (K)
P (kPa)
75
50
25
0
0
120
80
40
0
0
Absolute
vacuum
V = constant
FIGURE 1–36
A constant-volume gas thermometer
would read 2273.15°C at absolute
zero pressure.
20
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
°C
K
°F
R
The Kelvin scale is related to the Celsius scale by
T(K) 5 T(8C) 1 273.15
(1–9)
The Rankine scale is related to the Fahrenheit scale by
0.01
273.16
32.02
Triple
491.69 point of
water
T(R) 5 T(8F) 1 459.67
(1–10)
It is common practice to round the constant in Eq. 1–9 to 273 and that in
Eq. 1–10 to 460.
The temperature scales in the two unit systems are related by
–273.15
0
– 459.67
0 Absolute
zero
FIGURE 1–37
Comparison of temperature scales.
T(R) 5 1.8T(K)
(1–11)
T(8F) 5 1.8T(8C) 1 32
(1–12)
A comparison of various temperature scales is given in Fig. 1–37.
The reference temperature chosen in the original Kelvin scale was
273.15 K (or 0°C), which is the temperature at which water freezes (or ice
melts) and water exists as a solid–liquid mixture in equilibrium under standard atmospheric pressure (the ice point). At the Tenth General Conference
on Weights and Measures in 1954, the reference point was changed to a
much more precisely reproducible point, the triple point of water (the state
at which all three phases of water coexist in equilibrium), which is assigned
the value 273.16 K. The Celsius scale was also redefined at this conference
in terms of the ideal-gas temperature scale and a single fixed point, which is
again the triple point of water with an assigned value of 0.01°C. The boiling temperature of water (the steam point) was experimentally determined
to be again 100.00°C, and thus the new and old Celsius scales were in good
agreement.
The International Temperature
Scale of 1990 (ITS-90)
The International Temperature Scale of 1990, which supersedes the
International Practical Temperature Scale of 1968 (IPTS-68), 1948
(ITPS-48), and 1927 (ITS-27), was adopted by the International Committee of Weights and Measures at its meeting in 1989 at the request of the
Eighteenth General Conference on Weights and Measures. The ITS-90
is similar to its predecessors except that it is more refined with updated
values of fixed temperatures, has an extended range, and conforms more
closely to the thermodynamic temperature scale. On this scale, the unit
of thermodynamic temperature T is again the kelvin (K), defined as the
fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of
water, which is sole defining fixed point of both the ITS-90 and the Kelvin
scale and is the most important thermometric fixed point used in the calibration of thermometers to ITS-90.
The unit of Celsius temperature is the degree Celsius (°C), which is by
definition equal in magnitude to the kelvin (K). A temperature difference
21
CHAPTER 1
may be expressed in kelvins or degrees Celsius. The ice point remains the
same at 0°C (273.15 K) in both ITS-90 and ITPS-68, but the steam point
is 99.975°C in ITS-90 (with an uncertainty of 60.005°C) whereas it was
100.000°C in IPTS-68. The change is due to precise measurements made
by gas thermometry by paying particular attention to the effect of sorption
(the impurities in a gas absorbed by the walls of the bulb at the reference
temperature being desorbed at higher temperatures, causing the measured
gas pressure to increase).
The ITS-90 extends upward from 0.65 K to the highest temperature practically measurable in terms of the Planck radiation law using monochromatic radiation. It is based on specifying definite temperature values on a
number of fixed and easily reproducible points to serve as benchmarks and
expressing the variation of temperature in a number of ranges and subranges
in functional form.
In ITS-90, the temperature scale is considered in four ranges. In the
range of 0.65 to 5 K, the temperature scale is defined in terms of the
vapor pressure—temperature relations for 3He and 4He. Between 3 and
24.5561 K (the triple point of neon), it is defined by means of a properly calibrated helium gas thermometer. From 13.8033 K (the triple point
of hydrogen) to 1234.93 K (the freezing point of silver), it is defined by
means of platinum resistance thermometers calibrated at specified sets
of defining fixed points. Above 1234.93 K, it is defined in terms of the
Planck radiation law and a suitable defining fixed point such as the freezing point of gold (1337.33 K).
We emphasize that the magnitudes of each division of 1 K and 1°C are
identical (Fig. 1–38). Therefore, when we are dealing with temperature differences DT, the temperature interval on both scales is the same. Raising
the temperature of a substance by 10°C is the same as raising it by 10 K.
That is,
DT(K) 5 DT(8C)
(1–13)
DT(R) 5 DT(8F)
(1–14)
Some thermodynamic relations involve the temperature T and often the
question arises of whether it is in K or °C. If the relation involves temperature differences (such as a 5 bDT), it makes no difference and either can
be used. However, if the relation involves temperatures only instead of temperature differences (such as a 5 bT) then K must be used. When in doubt,
it is always safe to use K because there are virtually no situations in which
the use of K is incorrect, but there are many thermodynamic relations that
will yield an erroneous result if °C is used.
EXAMPLE 1– 4
Expressing Temperature Rise in Different Units
During a heating process, the temperature of a system rises by 10°C. Express
this rise in temperature in K, °F, and R.
SOLUTION The temperature rise of a system is to be expressed in different
units.
1K
1°C
1.8 R
1.8°F
FIGURE 1–38
Comparison of magnitudes of various
temperature units.
22
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Analysis This problem deals with temperature changes, which are identical
in Kelvin and Celsius scales. Then,
DT(K) 5 DT(8C) 5 10 K
The temperature changes in Fahrenheit and Rankine scales are also identical and are related to the changes in Celsius and Kelvin scales through
Eqs. 1–11 and 1–14:
DT(R) 5 1.8 DT(K) 5 (1.8)(10) 5 18 R
and
DT(8F) 5 DT(R) 5 188F
Discussion Note that the units °C and K are interchangeable when dealing
with temperature differences.
1–9
■
PRESSURE
Pressure is defined as a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area.
Normally, we speak of pressure when we deal with a gas or a liquid. The
counterpart of pressure in solids is normal stress. Note, however, that pressure is a scaler quantity while stress is a tensor. Since pressure is defined
as force per unit area, it has the unit of newtons per square meter (N/m2),
which is called a pascal (Pa). That is,
1 Pa 5 1 N/m2
The pressure unit pascal is too small for most pressures encountered in
practice. Therefore, its multiples kilopascal (1 kPa 5 103 Pa) and megapascal (1 MPa 5 106 Pa) are commonly used. Three other pressure units commonly used in practice, especially in Europe, are bar, standard atmosphere,
and kilogram-force per square centimeter:
1 bar 5 105 Pa 5 0.1 MPa 5 100 kPa
1 atm 5 101,325 Pa 5 101.325 kPa 5 1.01325 bars
1 kgf/cm2 5 9.807 N/cm2 5 9.807 3 104 N/m2 5 9.807 3 104 Pa
5 0.9807 bar
5 0.9679 atm
Note the pressure units bar, atm, and kgf/cm2 are almost equivalent to each
other. In the English system, the pressure unit is pound-force per square
inch (lbf/in2, or psi), and 1 atm 5 14.696 psi. The pressure units kgf/cm2
and lbf/in2 are also denoted by kg/cm2 and lb/in2, respectively, and they are
commonly used in tire gages. It can be shown that 1 kgf/cm2 5 14.223 psi.
Pressure is also used on solid surfaces as synonymous to normal stress,
which is the force acting perpendicular to the surface per unit area. For
example, a 150-pound person with a total foot imprint area of 50 in2
23
CHAPTER 1
exerts a pressure of 150 lbf/50 in2 5 3.0 psi on the floor (Fig. 1–39). If the
person stands on one foot, the pressure doubles. If the person gains excessive weight, he or she is likely to encounter foot discomfort because of the
increased pressure on the foot (the size of the bottom of the foot does not
change with weight gain). This also explains how a person can walk on
fresh snow without sinking by wearing large snowshoes, and how a person
cuts with little effort when using a sharp knife.
The actual pressure at a given position is called the absolute pressure,
and it is measured relative to absolute vacuum (i.e., absolute zero pressure).
Most pressure-measuring devices, however, are calibrated to read zero in
the atmosphere (Fig. 1–40), and so they indicate the difference between
the absolute pressure and the local atmospheric pressure. This difference is
called the gage pressure. Pgage can be positive or negative, but pressures
below atmospheric pressure are sometimes called vacuum pressures and
are measured by vacuum gages that indicate the difference between the
atmospheric pressure and the absolute pressure. Absolute, gage, and vacuum
pressures are related to each other by
Pgage 5 Pabs 2 Patm
(1–15)
Pvac 5 Patm 2 Pabs
(1–16)
150 pounds
300 pounds
Afeet = 50 in2
P = 3 psi
P = 6 psi
W = ––––––
150 lbf = 3 psi
P = sn = ––––
Afeet
50 in2
FIGURE 1–39
The normal stress (or “pressure”) on
the feet of a chubby person is much
greater than on the feet of a slim
person.
This is illustrated in Fig. 1–41.
Like other pressure gages, the gage used to measure the air pressure in an automobile tire reads the gage pressure. Therefore, the common reading of 32.0 psi (2.25 kgf/cm2) indicates a pressure of 32.0 psi
above the atmospheric pressure. At a location where the atmospheric
pressure is 14.3 psi, for example, the absolute pressure in the tire is
32.0 1 14.3 5 46.3 psi.
In thermodynamic relations and tables, absolute pressure is almost always
used. Throughout this text, the pressure P will denote absolute pressure
unless specified otherwise. Often the letters “a” (for absolute pressure) and
“g” (for gage pressure) are added to pressure units (such as psia and psig) to
clarify what is meant.
FIGURE 1–40
Some basic pressure gages.
Dresser Instruments, Dresser, Inc. Used by
permission
P gage
Patm
Pvac
P abs
P atm
Patm
Pabs
Absolute
vacuum
P abs = 0
Absolute
vacuum
FIGURE 1–41
Absolute, gage, and vacuum pressures.
24
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
EXAMPLE 1–5
Absolute Pressure of a Vacuum Chamber
A vacuum gage connected to a chamber reads 5.8 psi at a location where
the atmospheric pressure is 14.5 psi. Determine the absolute pressure in the
chamber.
SOLUTION The gage pressure of a vacuum chamber is given. The absolute
pressure in the chamber is to be determined.
Analysis The absolute pressure is easily determined from Eq. 1–16 to be
Pabs 5 Patm 2 Pvac 5 14.5 2 5.8 5 8.7 psi
Discussion Note that the local value of the atmospheric pressure is used
when determining the absolute pressure.
Variation of Pressure with Depth
It will come as no surprise to you that pressure in a fluid at rest does not
change in the horizontal direction. This can be shown easily by considering
a thin horizontal layer of fluid and doing a force balance in any horizontal
direction. However, this is not the case in the vertical direction in a gravity
field. Pressure in a fluid increases with depth because more fluid rests on
deeper layers, and the effect of this “extra weight” on a deeper layer is balanced by an increase in pressure (Fig. 1–42).
To obtain a relation for the variation of pressure with depth, consider a
rectangular fluid element of height Dz, length Dx, and unit depth (Dy 5 1
into the page) in equilibrium, as shown in Fig. 1–43. Assuming the density
of the fluid r to be constant, a force balance in the vertical z-direction gives
Pgage
FIGURE 1–42
The pressure of a fluid at rest
increases with depth (as a result of
added weight).
a Fz 5 maz 5 0:
where W 5 mg 5 rg Dx Dy Dz is the weight of the fluid element and
Dz 5 z2 2 z1. Dividing by Dx Dy and rearranging gives
z
DP 5 P2 2 P1 5 2rg Dz 5 2gs Dz
g
z2
Dx
Dz
W
Pbelow 5 Pabove 1 rg|Dz| 5 Pabove 1 gs|Dz|
P1
0
FIGURE 1–43
Free-body diagram of a rectangular
fluid element in equilibrium.
(1–17)
where gs 5 rg is the specific weight of the fluid. Thus, we conclude that
the pressure difference between two points in a constant density fluid is
proportional to the vertical distance Dz between the points and the density
r of the fluid. Noting the negative sign, pressure in a static fluid increases
linearly with depth. This is what a diver experiences when diving deeper
in a lake.
An easier equation to remember and apply between any two points in the
same fluid under hydrostatic conditions is
P2
z1
P1 Dx Dy 2 P2 Dx Dy 2 rg Dx Dy Dz 5 0
x
(1–18)
where “below” refers to the point at lower elevation (deeper in the fluid)
and “above” refers to the point at higher elevation. If you use this equation
consistently, you should avoid sign errors.
For a given fluid, the vertical distance Dz is sometimes used as a measure
of pressure, and it is called the pressure head.
25
CHAPTER 1
We also conclude from Eq. 1–17 that for small to moderate distances,
the variation of pressure with height is negligible for gases because of their
low density. The pressure in a tank containing a gas, for example, can be
considered to be uniform since the weight of the gas is too small to make
a significant difference. Also, the pressure in a room filled with air can be
approximated as a constant (Fig. 1–44).
If we take the “above” point to be at the free surface of a liquid open to
the atmosphere (Fig. 1–45), where the pressure is the atmospheric pressure
Patm, then from Eq. 1–18 the pressure at a depth h below the free surface
becomes
P 5 Patm 1 rgh
or
Pgage 5 rgh
(1–19)
Liquids are essentially incompressible substances, and thus the variation
of density with depth is negligible. This is also the case for gases when
the elevation change is not very large. The variation of density of liquids
or gases with temperature can be significant, however, and may need to
be considered when high accuracy is desired. Also, at great depths such as
those encountered in oceans, the change in the density of a liquid can be
significant because of the compression by the tremendous amount of liquid
weight above.
The gravitational acceleration g varies from 9.807 m/s2 at sea level to
9.764 m/s2 at an elevation of 14,000 m where large passenger planes cruise.
This is a change of just 0.4 percent in this extreme case. Therefore, g can be
approximated as a constant with negligible error.
For fluids whose density changes significantly with elevation, a relation
for the variation of pressure with elevation can be obtained by dividing
Eq. 1–17 by Dz , and taking the limit as Dz S 0. This yields
dP
5 2rg
dz
(1–20)
Note that dP is negative when dz is positive since pressure decreases in an
upward direction. When the variation of density with elevation is known,
the pressure difference between any two points 1 and 2 can be determined
by integration to be
#
2
DP 5 P2 2 P1 5 2 rg dz
(1–21)
1
For constant density and constant gravitational acceleration, this relation
reduces to Eq. 1–17, as expected.
Pressure in a fluid at rest is independent of the shape or cross section of the container. It changes with the vertical distance, but remains
constant in other directions. Therefore, the pressure is the same at all
points on a horizontal plane in a given fluid. The Dutch mathematician
Simon Stevin (1548–1620) published in 1586 the principle illustrated in
Fig. 1–46. Note that the pressures at points A, B, C, D, E, F, and G are
the same since they are at the same depth, and they are interconnected
by the same static fluid. However, the pressures at points H and I are not
the same since these two points cannot be interconnected by the same
Ptop = 1 atm
Air
(A 5-m-high room)
P bottom = 1.006 atm
FIGURE 1–44
In a room filled with a gas, the
variation of pressure with height is
negligible.
Pabove = Patm
h
Pbelow = Patm + rgh
FIGURE 1–45
Pressure in a liquid at rest increases
linearly with distance from the free
surface.
26
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Patm
Water
h
B
A
C
D
PA = PB = PC = PD = PE = PF = PG = Patm + rgh
E
F
G
Mercury
I
H
FIGURE 1–46
Under hydrostatic conditions, the pressure is the same at all points on a horizontal plane in a given fluid regardless
of geometry, provided that the points are interconnected by the same fluid.
F 2 = P 2A 2
F 1 = P 1A 1
1
A1
P1
A2
P2
2
FIGURE 1–47
Lifting of a large weight by a small
force by the application of Pascal’s
law. A common example is a
hydraulic jack.
fluid (i.e., we cannot draw a curve from point I to point H while remaining in the same fluid at all times), although they are at the same depth.
(Can you tell at which point the pressure is higher?) Also notice that the
pressure force exerted by the fluid is always normal to the surface at the
specified points.
A consequence of the pressure in a fluid remaining constant in the horizontal direction is that the pressure applied to a confined fluid increases
the pressure throughout by the same amount. This is called Pascal’s law,
after Blaise Pascal (1623–1662). Pascal also knew that the force applied
by a fluid is proportional to the surface area. He realized that two hydraulic cylinders of different areas could be connected, and the larger could be
used to exert a proportionally greater force than that applied to the smaller.
“Pascal’s machine” has been the source of many inventions that are a part
of our daily lives such as hydraulic brakes and lifts. This is what enables us
to lift a car easily by one arm, as shown in Fig. 1–47. Noting that P1 5 P2
since both pistons are at the same level (the effect of small height differences is negligible, especially at high pressures), the ratio of output force to
input force is determined to be
P1 5 P2
S
F1
A1
5
F2
A2
S
F2
F1
5
A2
A1
(1–22)
(Top) © Stockbyte/Getty RF
The area ratio A2 /A1 is called the ideal mechanical advantage of the hydraulic lift. Using a hydraulic car jack with a piston area ratio of A2 /A1 5 100,
for example, a person can lift a 1000-kg car by applying a force of just
10 kgf (5 90.8 N).
27
CHAPTER 1
1–10
■
PRESSURE MEASUREMENT DEVICES
Vacuum
C
The Barometer
Atmospheric pressure is measured by a device called a barometer; thus, the
atmospheric pressure is often referred to as the barometric pressure.
The Italian Evangelista Torricelli (1608–1647) was the first to conclusively prove that the atmospheric pressure can be measured by inverting a
mercury-filled tube into a mercury container that is open to the atmosphere,
as shown in Fig. 1–48. The pressure at point B is equal to the atmospheric
pressure, and the pressure at point C can be taken to be zero since there is
only mercury vapor above point C and the pressure is very low relative to
Patm and can be neglected to an excellent approximation. Writing a force
balance in the vertical direction gives
Patm 5 rgh
A
h
B
Mercury
Patm
FIGURE 1–48
The basic barometer.
(1–23)
where r is the density of mercury, g is the local gravitational acceleration,
and h is the height of the mercury column above the free surface. Note that
the length and the cross-sectional area of the tube have no effect on the
height of the fluid column of a barometer (Fig. 1–49).
A frequently used pressure unit is the standard atmosphere, which
is defined as the pressure produced by a column of mercury 760 mm in
height at 0°C (rHg 5 13,595 kg/m3) under standard gravitational acceleration (g 5 9.807 m/s2). If water instead of mercury were used to measure the
standard atmospheric pressure, a water column of about 10.3 m would be
needed. Pressure is sometimes expressed (especially by weather forecasters)
in terms of the height of the mercury column. The standard atmospheric
pressure, for example, is 760 mmHg (29.92 inHg) at 0°C. The unit mmHg
is also called the torr in honor of Torricelli. Therefore, 1 atm 5 760 torr
and 1 torr 5 133.3 Pa.
Atmospheric pressure Patm changes from 101.325 kPa at sea level to
89.88, 79.50, 54.05, 26.5, and 5.53 kPa at altitudes of 1000, 2000, 5000,
10,000, and 20,000 meters, respectively. The typical atmospheric pressure in
Denver (elevation 5 1610 m), for example, is 83.4 kPa. Remember that the
atmospheric pressure at a location is simply the weight of the air above that
location per unit surface area. Therefore, it changes not only with elevation
but also with weather conditions.
The decline of atmospheric pressure with elevation has far-reaching ramifications in daily life. For example, cooking takes longer at high altitudes
since water boils at a lower temperature at lower atmospheric pressures.
Nose bleeding is a common experience at high altitudes since the difference
between the blood pressure and the atmospheric pressure is larger in this
case, and the delicate walls of veins in the nose are often unable to withstand this extra stress.
For a given temperature, the density of air is lower at high altitudes, and
thus a given volume contains less air and less oxygen. So it is no surprise
that we tire more easily and experience breathing problems at high altitudes.
To compensate for this effect, people living at higher altitudes develop more
efficient lungs. Similarly, a 2.0-L car engine will act like a 1.7-L car engine
at 1500 m altitude (unless it is turbocharged) because of the 15 percent drop
h
W = rghA
A1
A2
A3
FIGURE 1–49
The length or the cross-sectional area
of the tube has no effect on the height
of the fluid column of a barometer,
provided that the tube diameter is
large enough to avoid surface tension
(capillary) effects.
28
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Engine
Lungs
FIGURE 1–50
At high altitudes, a car engine generates less power and a person gets less
oxygen because of the lower density
of air.
in pressure and thus 15 percent drop in the density of air (Fig. 1–50). A fan
or compressor will displace 15 percent less air at that altitude for the same
volume displacement rate. Therefore, larger cooling fans may need to be
selected for operation at high altitudes to ensure the specified mass flow
rate. The lower pressure and thus lower density also affects lift and drag:
airplanes need a longer runway at high altitudes to develop the required lift,
and they climb to very high altitudes for cruising in order to reduce drag
and thus achieve better fuel efficiency.
EXAMPLE 1–6
Measuring Atmospheric Pressure with a
Barometer
Determine the atmospheric pressure at a location where the barometric reading is 740 mmHg and the gravitational acceleration is g 5 9.805 m/s2.
Assume the temperature of mercury to be 10°C, at which its density is
13,570 kg/m3.
SOLUTION The barometric reading at a location in height of mercury column is given. The atmospheric pressure is to be determined.
Assumptions The temperature of mercury is assumed to be 10°C.
Properties The density of mercury is given to be 13,570 kg/m3.
Analysis From Eq. 1–23, the atmospheric pressure is determined to be
Patm 5 rgh
5 (13,570 kg/m3)(9.805 m/s2)(0.740 m)a
1N
1 kPa
ba
b
1 kg·m/s2 1000 N/m2
5 98.5 kPa
Discussion Note that density changes with temperature, and thus this effect
should be considered in calculations.
EXAMPLE 1–7
Patm
IV bottle
1.2 m
FIGURE 1–51
Schematic for Example 1–7.
Gravity Driven Flow from an IV Bottle
Intravenous infusions usually are driven by gravity by hanging the fluid bottle at sufficient height to counteract the blood pressure in the vein and to
force the fluid into the body (Fig. 1–51). The higher the bottle is raised, the
higher the flow rate of the fluid will be. (a) If it is observed that the fluid
and the blood pressures balance each other when the bottle is 1.2 m above
the arm level, determine the gage pressure of the blood. (b) If the gage pressure of the fluid at the arm level needs to be 20 kPa for sufficient flow rate,
determine how high the bottle must be placed. Take the density of the fluid
to be 1020 kg/m3.
SOLUTION It is given that an IV fluid and the blood pressures balance each
other when the bottle is at a certain height. The gage pressure of the blood
and elevation of the bottle required to maintain flow at the desired rate are
to be determined.
Assumptions 1 The IV fluid is incompressible. 2 The IV bottle is open to
the atmosphere.
29
CHAPTER 1
Properties The density of the IV fluid is given to be r 5 1020 kg/m3.
Analysis (a) Noting that the IV fluid and the blood pressures balance each
other when the bottle is 1.2 m above the arm level, the gage pressure of the
blood in the arm is simply equal to the gage pressure of the IV fluid at a
depth of 1.2 m,
Pgage, arm 5 Pabs 2 Patm 5 rgharm 2bottle
5 (1020 kg/m3)(9.81 m/s2)(1.20 m)a
1 kN
1 kPa
ba
b
2
1000 kg·m/s
1 kN/m2
5 12.0 kPa
(b) To provide a gage pressure of 20 kPa at the arm level, the height of the
surface of the IV fluid in the bottle from the arm level is again determined
from Pgage, arm 5 rgharm 2 bottle to be
harm 2botttle 5
5
Pgage, arm
rg
1000 kg·m/s2 1 kN/m2
20 kPa
a
ba
b
(1020 kg/m3)(9.81 m/s2)
1 kN
1 kPa
5 2.00 m
Discussion Note that the height of the reservoir can be used to control flow
rates in gravity-driven flows. When there is flow, the pressure drop in the
tube due to frictional effects also should be considered. For a specified flow
rate, this requires raising the bottle a little higher to overcome the pressure
drop.
EXAMPLE 1–8
Sun
Hydrostatic Pressure in a Solar Pond with
Variable Density
Solar ponds are small artificial lakes of a few meters deep that are used to
store solar energy. The rise of heated (and thus less dense) water to the surface is prevented by adding salt at the pond bottom. In a typical salt gradient solar pond, the density of water increases in the gradient zone, as shown
in Fig. 1–52, and the density can be expressed as
p s
r 5 r0 1 1 tan2 a
b
Å
4 H
where r0 is the density on the water surface, s is the vertical distance measured downward from the top of the gradient zone (s 5 2z), and H is the
thickness of the gradient zone. For H 5 4 m, r0 5 1040 kg/m3, and a
thickness of 0.8 m for the surface zone, calculate the gage pressure at the
bottom of the gradient zone.
SOLUTION The variation of density of saline water in the gradient zone of a
solar pond with depth is given. The gage pressure at the bottom of the gradient zone is to be determined.
Increasing salinity
and density
s
r0 = 1040 kg/m3
Surface zone
H=4m
1
Gradient zone
Storage zone
2
FIGURE 1–52
Schematic for Example 1–8.
30
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
4
3.5
3
Variable
density
2.5
s, m
Assumptions The density in the surface zone of the pond is constant.
Properties The density of brine on the surface is given to be 1040 kg/m3.
Analysis We label the top and the bottom of the gradient zone as 1 and 2,
respectively. Noting that the density of the surface zone is constant, the
gage pressure at the bottom of the surface zone (which is the top of the
gradient zone) is
Constant
density
2
1.5
1
P1 5 rgh1 5 (1040 kg/m3)(9.81 m/s2)(0.8 m)a
0.5
1 kN
b 5 8.16 kPa
1000 kg·m/s2
0
0
10
20
30 40
P, kPa
50
60
FIGURE 1–53
The variation of gage pressure with
depth in the gradient zone of the solar
pond.
since 1 kN/m2 5 1 kPa. Since s 5 2z, the differential change in hydrostatic
pressure across a vertical distance of ds is given by
dP 5 rg ds
Integrating from the top of the gradient zone (point 1 where s 5 0) to any
location s in the gradient zone (no subscript) gives
s
P 2 P1 5
# rg ds
s
S P 5 P1 1
0
p s
# r Å 1 1 tan a 4 H bg ds
0
2
0
Performing the integration gives the variation of gage pressure in the gradient zone to be
P 5 P1 1 r0g
4H
p s
b
sinh 21 atan
p
4 H
Then the pressure at the bottom of the gradient zone (s 5 H 5 4 m) becomes
P2 5 8.16 kPa 1 (1040 kg/m3)(9.81 m/s2)
4(4 m)
p4
1 kN
ba
b
sinh 2 1 atan
p
4 4 1000 kg·m/s2
5 54.0 kPa (gage)
Discussion The variation of gage pressure in the gradient zone with depth is
plotted in Fig. 1–53. The dashed line indicates the hydrostatic pressure for
the case of constant density at 1040 kg/m3 and is given for reference. Note
that the variation of pressure with depth is not linear when density varies
with depth. That is why integration was required.
The Manometer
FIGURE 1–54
A simple U-tube manometer, with
high pressure applied to the right side.
Photo by John M. Cimbala
We notice from Eq. 1–17 that an elevation change of 2Dz in a fluid at rest
corresponds to DP/rg, which suggests that a fluid column can be used to
measure pressure differences. A device based on this principle is called a
manometer, and it is commonly used to measure small and moderate pressure differences. A manometer consists of a glass or plastic U-tube containing one or more fluids such as mercury, water, alcohol, or oil (Fig. 1–54).
To keep the size of the manometer to a manageable level, heavy fluids such
as mercury are used if large pressure differences are anticipated.
Consider the manometer shown in Fig. 1–55 that is used to measure the
pressure in the tank. Since the gravitational effects of gases are negligible,
the pressure anywhere in the tank and at position 1 has the same value.
31
CHAPTER 1
Furthermore, since pressure in a fluid does not vary in the horizontal direction within a fluid, the pressure at point 2 is the same as the pressure at
point 1, P2 5 P1.
The differential fluid column of height h is in static equilibrium, and it is
open to the atmosphere. Then the pressure at point 2 is determined directly
from Eq. 1–18 to be
P2 5 Patm 1 rgh
1
SOLUTION The reading of a manometer attached to a tank and the atmospheric pressure are given. The absolute pressure in the tank is to be
determined.
Assumptions The density of the gas in the tank is much lower than the density of the manometer fluid.
Properties The specific gravity of the manometer fluid is given to be 0.85.
We take the standard density of water to be 1000 kg/m3.
Analysis The density of the fluid is obtained by multiplying its specific
gravity by the density of water,
r 5 SG (rH2O) 5 (0.85)(1000 kg/m3) 5 850 kg/m3
Then from Eq. 1–24,
P 5 Patm 1 rgh
5 96 kPa 1 (850 kg/m3)(9.81 m/s2)(0.55 m)a
1N
1 kPa
ba
b
1 kg·m/s2 1000 N/m2
5 100.6 kPa
Note that the gage pressure in the tank is 4.6 kPa.
Some manometers use a slanted or inclined tube in order to increase the
resolution (precision) when reading the fluid height. Such devices are called
inclined manometers.
Many engineering problems and some manometers involve multiple
immiscible fluids of different densities stacked on top of each other. Such
systems can be analyzed easily by remembering that (1) the pressure change
across a fluid column of height h is DP 5 rgh, (2) pressure increases
downward in a given fluid and decreases upward (i.e., Pbottom . Ptop), and
2
FIGURE 1–55
The basic manometer.
Measuring Pressure with a Manometer
A manometer is used to measure the pressure of a gas in a tank. The fluid
used has a specific gravity of 0.85, and the manometer column height is
55 cm, as shown in Fig. 1–56. If the local atmospheric pressure is 96 kPa,
determine the absolute pressure within the tank.
Discussion
h
(1–24)
where r is the density of the manometer fluid in the tube. Note that the
cross-sectional area of the tube has no effect on the differential height h,
and thus the pressure exerted by the fluid. However, the diameter of the tube
should be large enough (more than several millimeters) to ensure that the
surface tension effect and thus the capillary rise is negligible.
EXAMPLE 1–9
Gas
Patm = 96 kPa
P=?
h = 55 cm
SG = 0.85
FIGURE 1–56
Schematic for Example 1–9.
32
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Patm
Fluid 1
h1
Fluid 2
h2
Fluid 3
h3
1
FIGURE 1–57
In stacked-up fluid layers at rest, the
pressure change across each fluid
layer of density r and height h is rgh.
A flow section
or flow device
Fluid
1
2
a
h
r1
A
B
r2
(3) two points at the same elevation in a continuous fluid at rest are at the
same pressure.
The last principle, which is a result of Pascal’s law, allows us to “jump”
from one fluid column to the next in manometers without worrying about
pressure change as long as we stay in the same continuous fluid and the
fluid is at rest. Then the pressure at any point can be determined by starting with a point of known pressure and adding or subtracting rgh terms as
we advance toward the point of interest. For example, the pressure at the
bottom of the tank in Fig. 1–57 can be determined by starting at the free
surface where the pressure is Patm, moving downward until we reach point 1
at the bottom, and setting the result equal to P1. It gives
Patm 1 r1gh1 1 r2gh2 1 r3gh3 5 P1
In the special case of all fluids having the same density, this relation reduces
to Patm 1 rg(h1 1 h2 1 h3) 5 P1.
Manometers are particularly well-suited to measure pressure drops across
a horizontal flow section between two specified points due to the presence
of a device such as a valve or heat exchanger or any resistance to flow. This
is done by connecting the two legs of the manometer to these two points, as
shown in Fig. 1–58. The working fluid can be either a gas or a liquid whose
density is r1. The density of the manometer fluid is r2, and the differential
fluid height is h. The two fluids must be immiscible, and r2 must be greater
than r1.
A relation for the pressure difference P1 2 P2 can be obtained by starting
at point 1 with P1, moving along the tube by adding or subtracting the rgh
terms until we reach point 2, and setting the result equal to P2:
P1 1 r1g(a 1 h) 2 r2gh 2 r1ga 5 P2
FIGURE 1–58
Measuring the pressure drop across
a flow section or a flow device by a
differential manometer.
(1–25)
Note that we jumped from point A horizontally to point B and ignored the
part underneath since the pressure at both points is the same. Simplifying,
P1 2 P2 5 (r2 2 r1)gh
(1–26)
Note that the distance a must be included in the analysis even though it has
no effect on the result. Also, when the fluid flowing in the pipe is a gas,
then r1 ,, r2 and the relation in Eq. 1–26 simplifies to P1 2 P2 ù r2gh.
Oil
Air
1
Water
EXAMPLE 1–10
h1
2
h2
h3
Mercury
FIGURE 1–59
Schematic for Example 1–10; drawing
not to scale.
Measuring Pressure with a Multifluid Manometer
The water in a tank is pressurized by air, and the pressure is measured by a
multifluid manometer as shown in Fig. 1–59. The tank is located on a mountain at an altitude of 1400 m where the atmospheric pressure is 85.6 kPa.
Determine the air pressure in the tank if h1 5 0.1 m, h2 5 0.2 m, and
h3 5 0.35 m. Take the densities of water, oil, and mercury to be 1000 kg/m3,
850 kg/m3, and 13,600 kg/m3, respectively.
SOLUTION The pressure in a pressurized water tank is measured by a multifluid manometer. The air pressure in the tank is to be determined.
Assumption The air pressure in the tank is uniform (i.e., its variation with
elevation is negligible due to its low density), and thus we can determine the
pressure at the air–water interface.
33
CHAPTER 1
Properties The densities of water, oil, and mercury are given to be
1000 kg/m3, 850 kg/m3, and 13,600 kg/m3, respectively.
Analysis Starting with the pressure at point 1 at the air–water interface,
moving along the tube by adding or subtracting the rgh terms until we reach
point 2, and setting the result equal to Patm since the tube is open to the
atmosphere gives
P1 1 rwater gh1 1 roil gh2 2 rmercury gh3 5 P2 5 Patm
Solving for P1 and substituting,
P1 5 Patm 2 rwater gh1 2 roil gh2 1 rmercury gh3
5 Patm 1 g(rmercury h3 2 rwater h1 2 roil h2)
5 85.6 kPa 1 (9.81 m/s2)[(13,600 kg/m3)(0.35 m) 2 (1000 kg/m3)(0.1 m)
2 (850 kg/m3)(0.2 m)] a
1N
1 kPa
ba
b
1 kg·m/s2 1000 N/m2
5 130 kPa
Discussion Note that jumping horizontally from one tube to the next and
realizing that pressure remains the same in the same fluid simplifies the
analysis considerably. Also note that mercury is a toxic fluid, and mercury
manometers and thermometers are being replaced by ones with safer fluids
because of the risk of exposure to mercury vapor during an accident.
Other Pressure Measurement Devices
Another type of commonly used mechanical pressure measurement device
is the Bourdon tube, named after the French engineer and inventor Eugene
Bourdon (1808–1884), which consists of a bent, coiled, or twisted hollow
metal tube whose end is closed and connected to a dial indicator needle
(Fig. 1–60). When the tube is open to the atmosphere, the tube is undeflected, and the needle on the dial at this state is calibrated to read zero
(gage pressure). When the fluid inside the tube is pressurized, the tube
stretches and moves the needle in proportion to the applied pressure.
Electronics have made their way into every aspect of life, including
pressure measurement devices. Modern pressure sensors, called pressure
transducers, use various techniques to convert the pressure effect to an
electrical effect such as a change in voltage, resistance, or capacitance.
Pressure transducers are smaller and faster, and they can be more sensitive, reliable, and precise than their mechanical counterparts. They can
measure pressures from less than a millionth of 1 atm to several thousands
of atm.
A wide variety of pressure transducers is available to measure gage, absolute, and differential pressures in a wide range of applications. Gage pressure transducers use the atmospheric pressure as a reference by venting the
back side of the pressure-sensing diaphragm to the atmosphere, and they
give a zero signal output at atmospheric pressure regardless of altitude.
Absolute pressure transducers are calibrated to have a zero signal output at
full vacuum. Differential pressure transducers measure the pressure difference
C-type
Spiral
Twisted tube
Helical
Tube cross section
FIGURE 1–60
Various types of Bourdon tubes used
to measure pressure. They work on the
same principle as party noise-makers
(bottom photo) due to the flat tube
cross section.
Photo by John M. Cimbala
34
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Weights
Oil
reservoir
Piston
Adjustable
plunger
F
Ae
Internal chamber
Oil
Reference pressure port
Crank
FIGURE 1–61
A deadweight tester is able to
measure extremely high pressures
(up to 10,000 psi in some
applications).
between two locations directly instead of using two pressure transducers
and taking their difference.
Strain-gage pressure transducers work by having a diaphragm deflect
between two chambers open to the pressure inputs. As the diaphragm
stretches in response to a change in pressure difference across it, the strain
gage stretches and a Wheatstone bridge circuit amplifies the output. A
capacitance transducer works similarly, but capacitance change is measured
instead of resistance change as the diaphragm stretches.
Piezoelectric transducers, also called solid-state pressure transducers,
work on the principle that an electric potential is generated in a crystalline substance when it is subjected to mechanical pressure. This phenomenon, first discovered by brothers Pierre and Jacques Curie in 1880, is
called the piezoelectric (or press-electric) effect. Piezoelectric pressure
transducers have a much faster frequency response compared to diaphragm units and are very suitable for high-pressure applications, but
they are generally not as sensitive as diaphragm-type transducers, especially at low pressures.
Another type of mechanical pressure gage called a deadweight tester
is used primarily for calibration and can measure extremely high pressures (Fig. 1–61). As its name implies, a deadweight tester measures pressure directly through application of a weight that provides a force per unit
area—the fundamental definition of pressure. It is constructed with an internal chamber filled with a fluid (usually oil), along with a tight-fitting piston,
cylinder, and plunger. Weights are applied to the top of the piston, which
exerts a force on the oil in the chamber. The total force F acting on the oil
at the piston–oil interface is the sum of the weight of the piston plus the
applied weights. Since the piston cross-sectional area Ae is known, the pressure is calculated as P 5 F/Ae. The only significant source of error is that
due to static friction along the interface between the piston and cylinder, but
even this error is usually negligibly small. The reference pressure port is
connected to either an unknown pressure that is to be measured or to a pressure sensor that is to be calibrated.
1–11
Solution
sy
y
wa
Hard way
Ea
Problem
FIGURE 1–62
A step-by-step approach can greatly
simplify problem solving.
■
PROBLEM-SOLVING TECHNIQUE
The first step in learning any science is to grasp the fundamentals and to gain
a sound knowledge of it. The next step is to master the fundamentals by testing this knowledge. This is done by solving significant real-world problems.
Solving such problems, especially complicated ones, requires a systematic
approach. By using a step-by-step approach, an engineer can reduce the solution of a complicated problem into the solution of a series of simple problems
(Fig. 1–62). When you are solving a problem, we recommend that you use the
following steps zealously as applicable. This will help you avoid some of the
common pitfalls associated with problem solving.
Step 1: Problem Statement
In your own words, briefly state the problem, the key information given,
and the quantities to be found. This is to make sure that you understand the
problem and the objectives before you attempt to solve the problem.
35
CHAPTER 1
Step 2: Schematic
Draw a realistic sketch of the physical system involved, and list the relevant information on the figure. The sketch does not have to be something
elaborate, but it should resemble the actual system and show the key features. Indicate any energy and mass interactions with the surroundings.
Listing the given information on the sketch helps one to see the entire
problem at once. Also, check for properties that remain constant during a
process (such as temperature during an isothermal process), and indicate
them on the sketch.
Step 3: Assumptions and Approximations
State any appropriate assumptions and approximations made to simplify
the problem to make it possible to obtain a solution. Justify the questionable assumptions. Assume reasonable values for missing quantities
that are necessary. For example, in the absence of specific data for atmospheric pressure, it can be taken to be 1 atm. However, it should be noted
in the analysis that the atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing
elevation. For example, it drops to 0.83 atm in Denver (elevation 1610 m)
(Fig. 1–63).
Step 4: Physical Laws
Apply all the relevant basic physical laws and principles (such as the conservation of mass), and reduce them to their simplest form by utilizing the
assumptions made. However, the region to which a physical law is applied
must be clearly identified first. For example, the increase in speed of water
flowing through a nozzle is analyzed by applying conservation of mass
between the inlet and outlet of the nozzle.
Given: Air temperature in Denver
To be found: Density of air
Missing information: Atmospheric
pressure
Assumption #1: Take P = 1 atm
(Inappropriate. Ignores effect of
altitude. Will cause more than
15% error.)
Assumption #2: Take P = 0.83 atm
(Appropriate. Ignores only minor
effects such as weather.)
FIGURE 1–63
The assumptions made while solving
an engineering problem must be
reasonable and justifiable.
Step 5: Properties
Determine the unknown properties at known states necessary to solve the
problem from property relations or tables. List the properties separately, and
indicate their source, if applicable.
Step 6: Calculations
Substitute the known quantities into the simplified relations and perform the calculations to determine the unknowns. Pay particular attention to the units and unit cancellations, and remember that a dimensional quantity without a unit is meaningless. Also, don’t give a false
implication of high precision by copying all the digits from the screen
of the calculator—round the results to an appropriate number of significant digits (see p. 39).
Energy use:
$80/yr
Energy saved
by insulation:
$200/yr
IMPOSSIBLE!
Step 7: Reasoning, Verification, and Discussion
Check to make sure that the results obtained are reasonable and intuitive,
and verify the validity of the questionable assumptions. Repeat the calculations that resulted in unreasonable values. For example, insulating a water
heater that uses $80 worth of natural gas a year cannot result in savings of
$200 a year (Fig. 1–64).
FIGURE 1–64
The results obtained from an
engineering analysis must be checked
for reasonableness.
36
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
FIGURE 1–65
Neatness and organization are highly
valued by employers.
Also, point out the significance of the results, and discuss their implications. State the conclusions that can be drawn from the results, and any
recommendations that can be made from them. Emphasize the limitations
under which the results are applicable, and caution against any possible
misunderstandings and using the results in situations where the underlying
assumptions do not apply. For example, if you determined that wrapping a
water heater with a $20 insulation jacket will reduce the energy cost by $30
a year, indicate that the insulation will pay for itself from the energy it saves
in less than a year. However, also indicate that the analysis does not consider labor costs, and that this will be the case if you install the insulation
yourself.
Keep in mind that the solutions you present to your instructors, and
any engineering analysis presented to others, is a form of communication.
Therefore neatness, organization, completeness, and visual appearance are
of utmost importance for maximum effectiveness (Fig. 1–65). Besides, neatness also serves as a great checking tool since it is very easy to spot errors
and inconsistencies in neat work. Carelessness and skipping steps to save
time often end up costing more time and unnecessary anxiety.
The approach described here is used in the solved example problems
without explicitly stating each step, as well as in the Solutions Manual of
this text. For some problems, some of the steps may not be applicable or
necessary. For example, often it is not practical to list the properties separately. However, we cannot overemphasize the importance of a logical and
orderly approach to problem solving. Most difficulties encountered while
solving a problem are not due to a lack of knowledge; rather, they are
due to a lack of organization. You are strongly encouraged to follow these
steps in problem solving until you develop your own approach that works
best for you.
Engineering Software Packages
You may be wondering why we are about to undertake an in-depth study of
the fundamentals of another engineering science. After all, almost all such
problems we are likely to encounter in practice can be solved using one
of several sophisticated software packages readily available in the market
today. These software packages not only give the desired numerical results,
but also supply the outputs in colorful graphical form for impressive presentations. It is unthinkable to practice engineering today without using some
of these packages. This tremendous computing power available to us at the
touch of a button is both a blessing and a curse. It certainly enables engineers to solve problems easily and quickly, but it also opens the door for
abuses and misinformation. In the hands of poorly educated people, these
software packages are as dangerous as sophisticated powerful weapons in
the hands of poorly trained soldiers.
Thinking that a person who can use the engineering software packages
without proper training on fundamentals can practice engineering is like
thinking that a person who can use a wrench can work as a car mechanic.
If it were true that the engineering students do not need all these fundamental courses they are taking because practically everything can be done by
computers quickly and easily, then it would also be true that the employers
37
CHAPTER 1
would no longer need high-salaried engineers since any person who knows
how to use a word-processing program can also learn how to use those software packages. However, the statistics show that the need for engineers is
on the rise, not on the decline, despite the availability of these powerful
packages.
We should always remember that all the computing power and the engineering software packages available today are just tools, and tools have
meaning only in the hands of masters. Having the best word-processing program does not make a person a good writer, but it certainly makes the job of
a good writer much easier and makes the writer more productive (Fig. 1–66).
Hand calculators did not eliminate the need to teach our children how to
add or subtract, and the sophisticated medical software packages did not
take the place of medical school training. Neither will engineering software
packages replace the traditional engineering education. They will simply
cause a shift in emphasis in the courses from mathematics to physics. That
is, more time will be spent in the classroom discussing the physical aspects
of the problems in greater detail, and less time on the mechanics of solution
procedures.
All these marvelous and powerful tools available today put an extra burden on today’s engineers. They must still have a thorough understanding
of the fundamentals, develop a “feel” of the physical phenomena, be able
to put the data into proper perspective, and make sound engineering judgments, just like their predecessors. However, they must do it much better, and much faster, using more realistic models because of the powerful
tools available today. The engineers in the past had to rely on hand calculations, slide rules, and later hand calculators and computers. Today they
rely on software packages. The easy access to such power and the possibility of a simple misunderstanding or misinterpretation causing great
damage make it more important today than ever to have solid training in
the fundamentals of engineering. In this text we make an extra effort to
put the emphasis on developing an intuitive and physical understanding
of natural phenomena instead of on the mathematical details of solution
procedures.
Engineering Equation Solver (EES)
EES is a program that solves systems of linear or nonlinear algebraic or
differential equations numerically. It has a large library of built-in thermodynamic property functions as well as mathematical functions, and
allows the user to supply additional property data. Unlike some software
packages, EES does not solve engineering problems; it only solves the
equations supplied by the user. Therefore, the user must understand the
problem and formulate it by applying any relevant physical laws and relations. EES saves the user considerable time and effort by simply solving
the resulting mathematical equations. This makes it possible to attempt
significant engineering problems not suitable for hand calculations, and
to conduct parametric studies quickly and conveniently. EES is a very
powerful yet intuitive program that is very easy to use, as shown in
Examples 1–11 and 1–12. The use and capabilities of EES are explained
on the text website.
FIGURE 1–66
An excellent word-processing program
does not make a person a good writer;
it simply makes a good writer a more
efficient writer.
© Ingram Publishing RF
38
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
EXAMPLE 1–11
Solving a System of Equations with EES
The difference of two numbers is 4, and the sum of the squares of these two
numbers is equal to the sum of the numbers plus 20. Determine these two
numbers. (Fig. 1–67)
SOLUTION Relations are given for the difference and the sum of the
squares of two numbers. They are to be determined.
Analysis We start the EES program by double-clicking on its icon, open a
new file, and type the following on the blank screen that appears:
x2y 5 4
x^2 1 y^2 5 x 1 y 1 20
which is an exact mathematical expression of the problem statement with
x and y denoting the unknown numbers. The solution to this system of two
nonlinear equations with two unknowns is obtained by a single click on the
“calculator” icon on the taskbar. It gives
FIGURE 1–67
x 5 5 and y 5 1
Discussion Note that all we did is formulate the problem as we would on
paper; EES took care of all the mathematical details of solution. Also note
that equations can be linear or nonlinear, and they can be entered in any
order with unknowns on either side. Friendly equation solvers such as EES
allow the user to concentrate on the physics of the problem without worrying about the mathematical complexities associated with the solution of the
resulting system of equations.
EXAMPLE 1–12
Reconsider the multifluid manometer discussed in Example 1–10 and replotted in Fig. 1–68. Determine the air pressure in the tank using EES. Also
determine what the differential fluid height h3 would be for the same air
pressure if the mercury in the last column were replaced by seawater with a
density of 1030 kg/m3.
Oil
Air
1
Water
h1
2
h2
Analyzing a Multifluid Manometer with EES
h3
Mercury
FIGURE 1–68
Schematic for Example 1–10; drawing
not to scale.
SOLUTION The pressure in a water tank is measured by a multifluid
manometer. The air pressure in the tank and the differential fluid height h3
if mercury is replaced by seawater are to be determined using EES.
Analysis We start the EES program by double-clicking on its icon, open a
new file, and type the following on the blank screen that appears (we express
the atmospheric pressure in Pa for unit consistency):
g 5 9.81
Patm 5 85600
h1 5 0.1;
h2 5 0.2;
h3 5 0.35
rw 5 1000; roil 5 850;
rm 5 13600
P1 1 rw*g*h1 1 roil*g*h2-rm*g*h3 5 Patm
Here P1 is the only unknown, and it is determined by EES to be
P1 5 129647 Pa > 130 kPa
39
CHAPTER 1
which is identical to the result obtained before. The height of the fluid column h3 when mercury is replaced by seawater is determined easily by replacing “h3 5 0.35” by “P1 5 129647” and “rm 5 13600” by “rm 5 1030,”
and clicking on the calculator symbol. It gives
h3 5 4.62 m
Discussion Note that we used the screen like a paper pad and wrote down
the relevant information together with the applicable relations in an organized manner. EES did the rest. Equations can be written on separate lines
or on the same line by separating them by semicolons, and blank or comment lines can be inserted for readability. EES makes it very easy to ask
“what if” questions, and to perform parametric studies, as explained on the
text website.
EES also has the capability to check the equations for unit consistency
if units are supplied together with numerical values. Units can be specified
within brackets [ ] after the specified value. When this feature is utilized,
the previous equations would take the following form:
g 5 9.81 [m/s^2]
Patm 5 85600 [Pa]
h1 5 0.1 [m];
h2 5 0.2 [m];
h3 5 0.35 [m]
rw 5 1000 [kg/m^3]; roil 5 850 [kg/m^3]; rm 5 13600 [kg/m^3]
P1 1 rw*g*h1 1 roil*g*h2-rm*g*h3 5 Patm
A Remark on Significant Digits
In engineering calculations, the information given is not known to more than
a certain number of significant digits, usually three digits. Consequently,
the results obtained cannot possibly be accurate to more significant digits.
Reporting results in more significant digits implies greater accuracy than
exists, and it should be avoided.
For example, consider a 3.75-L container filled with gasoline whose density is 0.845 kg/L, and try to determine its mass. Probably the first thought
that comes to your mind is to multiply the volume and density to obtain
3.16875 kg for the mass, which falsely implies that the mass determined is
accurate to six significant digits. In reality, however, the mass cannot be more
accurate than three significant digits since both the volume and the density
are accurate to three significant digits only. Therefore, the result should be
rounded to three significant digits, and the mass should be reported to be
3.17 kg instead of what appears in the screen of the calculator. The result
3.16875 kg would be correct only if the volume and density were given to be
3.75000 L and 0.845000 kg/L, respectively. The value 3.75 L implies that we
are fairly confident that the volume is accurate within 60.01 L, and it cannot be 3.74 or 3.76 L. However, the volume can be 3.746, 3.750, 3.753, etc.,
since they all round to 3.75 L (Fig. 1–69). It is more appropriate to retain
all the digits during intermediate calculations, and to do the rounding in the
final step since this is what a computer will normally do.
When solving problems, we will assume the given information to be
accurate to at least three significant digits. Therefore, if the length of a pipe
is given to be 40 m, we will assume it to be 40.0 m in order to justify using
Given: Volume: V = 3.75 L
Density: r = 0.845 kg/L
(3 significant digits)
Also, 3.75 × 0.845 = 3.16875
Find: Mass: m = rV = 3.16875 kg
Rounding to 3 significant digits:
m = 3.17 kg
FIGURE 1–69
A result with more significant digits
than that of given data falsely implies
more precision.
40
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
three significant digits in the final results. You should also keep in mind that
all experimentally determined values are subject to measurement errors and
such errors will reflect in the results obtained. For example, if the density of
a substance has an uncertainty of 2 percent, then the mass determined using
this density value will also have an uncertainty of 2 percent.
You should also be aware that we sometimes knowingly introduce small
errors in order to avoid the trouble of searching for more accurate data.
For example, when dealing with liquid water, we just use the value of
1000 kg/m3 for density, which is the density value of pure water at 0°C.
Using this value at 75°C will result in an error of 2.5 percent since the density at this temperature is 975 kg/m3. The minerals and impurities in the
water will introduce additional error. This being the case, you should have
no reservation in rounding the final results to a reasonable number of significant digits. Besides, having a few percent uncertainty in the results of
engineering analysis is usually the norm, not the exception.
SUMMARY
In this chapter, the basic concepts of thermodynamics are
introduced and discussed. Thermodynamics is the science
that primarily deals with energy. The first law of thermodynamics is simply an expression of the conservation of energy
principle, and it asserts that energy is a thermodynamic property. The second law of thermodynamics asserts that energy
has quality as well as quantity, and actual processes occur in
the direction of decreasing quality of energy.
A system of fixed mass is called a closed system, or control mass, and a system that involves mass transfer across
its boundaries is called an open system, or control volume.
The mass-dependent properties of a system are called extensive properties and the others intensive properties. Density
is mass per unit volume, and specific volume is volume per
unit mass.
A system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium if
it maintains thermal, mechanical, phase, and chemical equilibrium. Any change from one state to another is called a
process. A process with identical end states is called a cycle.
During a quasi-static or quasi-equilibrium process, the system remains practically in equilibrium at all times. The state
of a simple, compressible system is completely specified by
two independent, intensive properties.
The zeroth law of thermodynamics states that two bodies
are in thermal equilibrium if both have the same temperature
reading even if they are not in contact.
The temperature scales used in the SI and the English system
today are the Celsius scale and the Fahrenheit scale, respectively. They are related to absolute temperature scales by
The magnitudes of each division of 1 K and 1°C are identical, and so are the magnitudes of each division of 1 R and
1°F. Therefore,
DT(K) 5 DT(8C) and DT(R) 5 DT(8F)
The normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area is called
pressure, and its unit is the pascal, 1 Pa 5 1 N/m2. The pressure relative to absolute vacuum is called the absolute pressure, and the difference between the absolute pressure and
the local atmospheric pressure is called the gage pressure.
Pressures below atmospheric pressure are called vacuum
pressures. The absolute, gage, and vacuum pressures are
related by
Pgage 5 Pabs 2 Patm
1 for pressures above Patm 2
Pvac 5 Patm 2 Pabs
1 for pressures below Patm 2
The pressure at a point in a fluid has the same magnitude
in all directions. The variation of pressure with elevation is
given by
dP
5 2rg
dz
where the positive z direction is taken to be upward. When
the density of the fluid is constant, the pressure difference
across a fluid layer of thickness Dz is
DP 5 P2 2 P1 5 rg Dz
T(K) 5 T(8C) 1 273.15
The absolute and gage pressures in a liquid open to the
atmosphere at a depth h from the free surface are
T(R) 5 T(8F) 1 459.67
P 5 Patm 1 rgh or Pgage 5 rgh
41
CHAPTER 1
Small to moderate pressure differences are measured by
a manometer. The pressure in a stationary fluid remains
constant in the horizontal direction. Pascal’s principle states that the pressure applied to a confined fluid
increases the pressure throughout by the same amount.
The atmospheric pressure is measured by a barometer and
is given by
Patm 5 rgh
where h is the height of the liquid column.
REFERENCES AND SUGGESTED READINGS
1. American Society for Testing and Materials. Standards
for Metric Practice. ASTM E 380-79, January 1980.
3. J. A. Schooley. Thermometry. Boca Raton, FL: CRC
Press, 1986.
2. A. Bejan. Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics.
3rd ed. New York: Wiley, 2006.
PROBLEMS*
Thermodynamics
1–1C What is the difference between the classical and the
statistical approaches to thermodynamics?
1–2C Why does a bicyclist pick up speed on a downhill
road even when he is not pedaling? Does this violate the conservation of energy principle?
1–3C One of the most amusing things a person can experience is when a car in neutral appears to go uphill when its
brakes are released. Can this really happen or is it an optical
illusion? How can you verify if a road is pitched uphill or
downhill?
1–4C An office worker claims that a cup of cold coffee
on his table warmed up to 80°C by picking up energy from
the surrounding air, which is at 25°C. Is there any truth to
his claim? Does this process violate any thermodynamic
laws?
Mass, Force, and Units
1–5C What is the difference between kg-mass and kgforce?
1–6C Explain why the light-year has the dimension of
length.
* Problems designated by a “C” are concept questions, and
students are encouraged to answer them all. Problems designated
by an “E” are in English units, and the SI users can ignore them.
Problems with the
icon are solved using EES, and complete
solutions together with parametric studies are included on the text
website. Problems with the
icon are comprehensive in nature,
and are intended to be solved with an equation solver such as EES.
1–7C What is the net force acting on a car cruising at a
constant velocity of 70 km/h (a) on a level road and (b) on
an uphill road?
1–8 At 45° latitude, the gravitational acceleration as a function of elevation z above sea level is given by g 5 a 2 bz ,
where a 5 9.807 m/s2 and b 5 3.32 3 1026 s22. Determine
the height above sea level where the weight of an object will
decrease by 0.3 percent. Answer: 8862 m
1–9 What is the weight, in N, of an object with a mass of
200 kg at a location where g 5 9.6 m/s2?
1–10 A 3-kg plastic tank that has a volume of 0.2 m3 is
filled with liquid water. Assuming the density of water is
1000 kg/m3, determine the weight of the combined system.
1–11E The constant-pressure specific heat of air at 25°C is
1.005 kJ/kg·°C. Express this value in kJ/kg·K, J/g·°C, kcal/
kg·°C, and Btu/lbm·°F.
1–12
A 3-kg rock is thrown upward with a force of
200 N at a location where the local gravitational
acceleration is 9.79 m/s2. Determine the acceleration of the
rock, in m/s2.
1–13
Solve Prob. 1–12 using EES (or other) software.
Print out the entire solution, including the
numerical results with proper units.
1–14 A 4-kW resistance heater in a water heater runs for
3 hours to raise the water temperature to the desired level.
Determine the amount of electric energy used in both kWh
and kJ.
1–15E A 150-lbm astronaut took his bathroom scale
(a spring scale and a beam scale (compares masses) to the
moon where the local gravity is g 5 5.48 ft/s2. Determine
how much he will weigh (a) on the spring scale and (b) on
the beam scale. Answer: (a) 25.5 lbf, (b) 150 lbf
42
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
1–16 The gas tank of a car is filled with a nozzle that discharges gasoline at a constant flow rate. Based on unit considerations of quantities, obtain a relation for the filling time
in terms of the volume V of the tank (in L) and the discharge
rate of gasoline V (in L/s).
1–17 A pool of volume V (in m3) is to be filled with water
using a hose of diameter D (in m). If the average discharge
velocity is V (in m/s) and the filling time is t (in s), obtain a
relation for the volume of the pool based on considerations of
quantities involved.
Systems, Properties, State, and Processes
1–18C A large fraction of the thermal energy generated
in the engine of a car is rejected to the air by the radiator
through the circulating water. Should the radiator be analyzed
as a closed system or as an open system? Explain.
1–27C How would you describe the state of the water in a
bathtub? How would you describe the process that this water
experiences as it cools?
1–28C When analyzing the acceleration of gases as they
flow through a nozzle, what would you choose as your system? What type of system is this?
1–29C What is specific gravity? How is it related to
density?
1–30
The density of atmospheric air varies with elevation, decreasing with increasing altitude. (a) Using
the data given in the table, obtain a relation for the variation of
density with elevation, and calculate the density at an elevation
of 7000 m. (b) Calculate the mass of the atmosphere using the
correlation you obtained. Assume the earth to be a perfect
sphere with a radius of 6377 km, and take the thickness of the
atmosphere to be 25 km.
FIGURE P1–18C
© McGraw-Hill Education, Christopher
Kerrigan
1–19C You are trying to understand how a reciprocating air
compressor (a piston-cylinder device) works. What system
would you use? What type of system is this?
1–20C A can of soft drink at room temperature is put into
the refrigerator so that it will cool. Would you model the can
of soft drink as a closed system or as an open system? Explain.
1–21C What is the difference between intensive and extensive properties?
1–22C Is the weight of a system an extensive or intensive
property?
1–23C Is the state of the air in an isolated room completely
specified by the temperature and the pressure? Explain.
1–24C The molar specific volume of a system v is defined
as the ratio of the volume of the system to the number of
moles of substance contained in the system. Is this an extensive or intensive property?
1–25C What is a quasi-equilibrium process? What is its
importance in engineering?
1–26C
Define the isothermal, isobaric, and isochoric processes.
z, km
r, kg/m3
6377
6378
6379
6380
6381
6382
6383
6385
6387
6392
6397
6402
1.225
1.112
1.007
0.9093
0.8194
0.7364
0.6601
0.5258
0.4135
0.1948
0.08891
0.04008
Temperature
1–31C What are the ordinary and absolute temperature
scales in the SI and the English system?
1–32C Consider an alcohol and a mercury thermometer
that read exactly 0°C at the ice point and 100°C at the steam
point. The distance between the two points is divided into
100 equal parts in both thermometers. Do you think these
thermometers will give exactly the same reading at a temperature of, say, 60°C? Explain.
1–33C Consider two closed systems A and B. System A
contains 3000 kJ of thermal energy at 20°C, whereas system B
contains 200 kJ of thermal energy at 50°C. Now the systems
are brought into contact with each other. Determine the direction of any heat transfer between the two systems.
1–34 The deep body temperature of a healthy person is
37°C. What is it in kelvins?
1–35E What is the temperature of the heated air at 150°C
in °F and R?
43
CHAPTER 1
1–36 The temperature of a system rises by 70°C during a
heating process. Express this rise in temperature in kelvins.
1–37E The flash point of an engine oil is 363°F. What is
the absolute flash-point temperature in K and R?
1–38E The temperature of ambient air in a certain location is measured to be 240°C. Express this temperature in
Fahrenheit (°F), Kelvin (K), and Rankine (R) units.
1–39E The temperature of a system drops by 45°F during
a cooling process. Express this drop in temperature in K, R,
and °C.
Pressure, Manometer, and Barometer
1–50 The water in a tank is pressurized by air, and the
pressure is measured by a multifluid manometer as shown in
Fig. P1–50. Determine the gage pressure of air in the tank if
h1 5 0.2 m, h2 5 0.3 m, and h3 5 0.4 m. Take the densities
of water, oil, and mercury to be 1000 kg/m3, 850 kg/m3, and
13,600 kg/m3, respectively.
Oil
Air
1
1–40C Explain why some people experience nose bleeding and some others experience shortness of breath at high
elevations.
1–41C A health magazine reported that physicians measured 100 adults’ blood pressure using two different arm positions: parallel to the body (along the side) and perpendicular
to the body (straight out). Readings in the parallel position
were up to 10 percent higher than those in the perpendicular position, regardless of whether the patient was standing,
sitting, or lying down. Explain the possible cause for the
difference.
1–42C Someone claims that the absolute pressure in a liquid of constant density doubles when the depth is doubled.
Do you agree? Explain.
1–43C
of it.
h1
2
Water
h2
h3
Mercury
FIGURE P1–50
Express Pascal’s law, and give a real-world example
1–44C Consider two identical fans, one at sea level and the
other on top of a high mountain, running at identical speeds.
How would you compare (a) the volume flow rates and
(b) the mass flow rates of these two fans?
1–45 A vacuum gage connected to a chamber reads 35 kPa
at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 92 kPa. Determine the absolute pressure in the chamber.
1–46 The pressure in a compressed air storage tank is
1200 kPa. What is the tank’s pressure in (a) kN and m units;
(b) kg, m, and s units; and (c) kg, km, and s units?
1–47E The pressure in a water line is 1500 kPa. What is
the line pressure in (a) lb/ft2 units and (b) lbf/in2 (psi) units?
1–48E If the pressure inside a rubber balloon is
1500 mmHg, what is this pressure in pounds-force per square
inch (psi)? Answer: 29.0 psi
1–49E A manometer is used to measure the air pressure in
a tank. The fluid used has a specific gravity of 1.25, and the
differential height between the two arms of the manometer
is 28 in. If the local atmospheric pressure is 12.7 psia, determine the absolute pressure in the tank for the cases of the
manometer arm with the (a) higher and (b) lower fluid level
being attached to the tank.
1–51 Determine the atmospheric pressure at a location
where the barometric reading is 750 mmHg. Take the density
of mercury to be 13,600 kg/m3.
1–52E A 200-pound man has a total foot imprint area of
72 in2. Determine the pressure this man exerts on the ground
if (a) he stands on both feet and (b) he stands on one foot.
1–53 The gage pressure in a liquid at a depth of 3 m is read
to be 42 kPa. Determine the gage pressure in the same liquid
at a depth of 9 m.
1–54 The absolute pressure in water at a depth of 9 m is
read to be 185 kPa. Determine (a) the local atmospheric
pressure, and (b) the absolute pressure at a depth of
5 m in a liquid whose specific gravity is 0.85 at the same
location.
1–55E Determine the pressure exerted on the surface of a
submarine cruising 175 ft below the free surface of the sea.
Assume that the barometric pressure is 14.7 psia and the specific gravity of seawater is 1.03.
1–56 Consider a 70-kg woman who has a total foot imprint
area of 400 cm2. She wishes to walk on the snow, but the snow
cannot withstand pressures greater than 0.5 kPa. Determine the
minimum size of the snowshoes needed (imprint area per shoe)
to enable her to walk on the snow without sinking.
44
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
1–57E The vacuum pressure of a condenser is given to be
80 kPa. If the atmospheric pressure is 98 kPa, what is the
gage pressure and absolute pressure in kPa, kN/m2, lbf/in2,
psi, and mmHg.
1–58 The barometer of a mountain hiker reads 750 mbars
at the beginning of a hiking trip and 650 mbars at the end.
Neglecting the effect of altitude on local gravitational acceleration, determine the vertical distance climbed. Assume an
average air density of 1.20 kg/m3. Answer: 850 m
1–62 A gas is contained in a vertical, frictionless piston–
cylinder device. The piston has a mass of 3.2 kg and a crosssectional area of 35 cm2. A compressed spring above the piston exerts a force of 150 N on the piston. If the atmospheric
pressure is 95 kPa, determine the pressure inside the cylinder. Answer: 147 kPa
1–59 The basic barometer can be used to measure the
height of a building. If the barometric readings at the top and
at the bottom of a building are 675 and 695 mmHg, respectively, determine the height of the building. Take the densities of air and mercury to be 1.18 kg/m3 and 13,600 kg/m3,
respectively.
150 N
Patm = 95 kPa
mp = 3.2 kg
A = 35 cm2
FIGURE P1–62
1–63
Reconsider Prob. 1–62. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the spring
force in the range of 0 to 500 N on the pressure inside the
cylinder. Plot the pressure against the spring force, and discuss the results.
1–64 Both a gage and a manometer are attached to a gas tank
to measure its pressure. If the reading on the pressure gage is
80 kPa, determine the distance between the two fluid levels of
the manometer if the fluid is (a) mercury (r 5 13,600 kg/m3)
or (b) water (r 5 1000 kg/m3).
Pg = 80 kPa
Gas
h=?
FIGURE P1–59
© Royalty-Free/Corbis
1–60
Solve Prob. 1–59 using EES (or other) software.
Print out the entire solution, including the
numerical results with proper units.
1–61 The hydraulic lift in a car repair shop has an output
diameter of 30 cm and is to lift cars up to 2000 kg. Determine the fluid gage pressure that must be maintained in the
reservoir.
FIGURE P1–64
1–65
Reconsider Prob. 1–64. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the manometer
fluid density in the range of 800 to 13,000 kg/m3 on the differential fluid height of the manometer. Plot the differential
fluid height against the density, and discuss the results.
45
CHAPTER 1
1–66 A manometer containing oil (r 5 850 kg/m3) is
attached to a tank filled with air. If the oil-level difference
between the two columns is 80 cm and the atmospheric pressure is 98 kPa, determine the absolute pressure of the air in
the tank. Answer: 105 kPa
1–67 A mercury manometer (r 5 13,600 kg/m3) is connected to an air duct to measure the pressure inside.
The difference in the manometer levels is 15 mm, and
the atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. (a) Judging from
Fig. P1–67, determine if the pressure in the duct is above or
below the atmospheric pressure. (b) Determine the absolute
pressure in the duct.
Air
1–71E Blood pressure is usually measured by wrapping a
closed air-filled jacket equipped with a pressure gage around
the upper arm of a person at the level of the heart. Using a
mercury manometer and a stethoscope, the systolic pressure
(the maximum pressure when the heart is pumping) and the
diastolic pressure (the minimum pressure when the heart is
resting) are measured in mmHg. The systolic and diastolic
pressures of a healthy person are about 120 mmHg and
80 mmHg, respectively, and are indicated as 120/80. Express
both of these gage pressures in kPa, psi, and meter water
column.
1–72 The maximum blood pressure in the upper arm of a
healthy person is about 120 mmHg. If a vertical tube open to
the atmosphere is connected to the vein in the arm of the person, determine how high the blood will rise in the tube. Take
the density of the blood to be 1050 kg/m3.
h = 15 mm
P=?
h
FIGURE P1–67
1–68 Repeat Prob. 1–67 for a differential mercury height of
45 mm.
1–69E The pressure in a natural gas pipeline is measured
by the manometer shown in Fig. P1–69E with one of the
arms open to the atmosphere where the local atmospheric
pressure is 14.2 psia. Determine the absolute pressure in the
pipeline.
FIGURE P1–72
1–73 Determine the pressure exerted on a diver at 45 m
below the free surface of the sea. Assume a barometric pressure of 101 kPa and a specific gravity of 1.03 for seawater.
Answer: 556 kPa
Air
Natural
Gas
2 in
10 in
25 in
1–74 Consider a U-tube whose arms are open to the atmosphere. Now water is poured into the U-tube from one arm,
and light oil (r 5 790 kg/m3) from the other. One arm contains 70-cm-high water, while the other arm contains both
fluids with an oil-to-water height ratio of 4. Determine the
height of each fluid in that arm.
6 in
Mercury
SG = 13.6
Oil
Water
70 cm
Water
FIGURE P1–69E
1–70E Repeat Prob. 1–69E by replacing air by oil with a
specific gravity of 0.69.
FIGURE P1–74
46
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
1–75 Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air
pipe shown in Fig. P1–75. If the specific gravity of one fluid
is 13.55, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for
the indicated absolute pressure of air. Take the atmospheric
pressure to be 100 kPa. Answer: 5.0
Atmospheric
pressure
P1
15 cm
12 cm
5 cm
Air
P = 76 kPa
Fluid B
8 kN/m3
40 cm
30 cm
SG2
Fluid A
10 kN/m3
22 cm
FIGURE P1–78
SG1 = 13.55
1–79 Consider the manometer in Fig. P1–78. If the specific
weight of fluid A is 100 kN/m3, what is the absolute pressure,
in kPa, indicated by the manometer when the local atmospheric pressure is 90 kPa?
FIGURE P1–75
1–76 Freshwater and seawater flowing in parallel horizontal pipelines are connected to each other by a double U-tube
manometer, as shown in Fig. P1–76. Determine the pressure
difference between the two pipelines. Take the density of seawater at that location to be r 5 1035 kg/m3. Can the air column be ignored in the analysis?
1–80 Consider the manometer in Fig. P1–78. If the specific
weight of fluid B is 20 kN/m3, what is the absolute pressure,
in kPa, indicated by the manometer when the local atmospheric pressure is 720 mmHg?
1–81 Consider the system shown in Fig. P1–81. If a change
of 0.7 kPa in the pressure of air causes the brine–mercury
interface in the right column to drop by 5 mm in the brine
level in the right column while the pressure in the brine pipe
remains constant, determine the ratio of A2/A1.
Air
Fresh
water
40 cm
70 cm
60 cm
Brine
pipe
SG = 1.1
Air
Sea
water
10 cm
Mercury
Water
Mercury
SG = 13.56
Area, A2
Area, A1
FIGURE P1–76
FIGURE P1–81
1–77 Repeat Prob. 1–76 by replacing the air with oil whose
specific gravity is 0.72.
Solving Engineering Problems and EES
1–78 Calculate the absolute pressure, P1, of the manometer
shown in Fig. P1–78 in kPa. The local atmospheric pressure
is 758 mmHg.
1–82C What is the value of the engineering software
packages in (a) engineering education and (b) engineering
practice?
47
CHAPTER 1
1–83
Determine a positive real root of this equation
using EES:
10 cm. Determine the diameter of the piston on which the
weight is to be placed.
2x 3 2 10x 0.5 2 3x 5 23
1–84
Solve this system of two equations with two
unknowns using EES:
x 3 2 y 2 5 7.75
3xy 1 y 5 3.5
1–85
Weight
2500 kg
F1
25
kg
F2
Solve this system of three equations with three
unknowns using EES:
x 2y 2 z 5 1
10
cm
D2
x 2 3y 0.5 1 xz 5 22
x1y2z52
1–86
Solve this system of three equations with three
unknowns using EES:
2x 2 y 1 z 5 7
3x 2 1 3y 5 z 1 3
xy 1 2z 5 4
1–87E
Specific heat is defined as the amount of
energy needed to increase the temperature of a
unit mass of a substance by one degree. The specific heat of
water at room temperature is 4.18 kJ/kg·°C in SI unit system.
Using the unit conversion function capability of EES, express
the specific heat of water in (a) kJ/kg·K, (b) Btu/lbm·°F,
(c) Btu/lbm·R, and (d ) kcal/kg·°C units. Answers: (a) 4.18,
(b) (c) (d) 0.9984
Review Problems
1–88 The weight of bodies may change somewhat from one
location to another as a result of the variation of the gravitational acceleration g with elevation. Accounting for this variation using the relation in Prob. 1–8, determine the weight of
an 80-kg person at sea level (z 5 0), in Denver (z 5 1610 m),
and on the top of Mount Everest (z 5 8848 m).
1–89E A man goes to a traditional market to buy a steak
for dinner. He finds a 12-oz steak (1 lbm 5 16 oz) for $5.50.
He then goes to the adjacent international market and finds a
300-g steak of identical quality for $5.20. Which steak is the
better buy?
1–90E What is the weight of a 1-kg substance in N, kN,
kg·m/s2, kgf, lbm·ft/s2, and lbf?
1–91 A hydraulic lift is to be used to lift a 2500 kg weight
by putting a weight of 25 kg on a piston with a diameter of
FIGURE P1–91
1–92E The efficiency of a refrigerator increases by 3 percent for each °C rise in the minimum temperature in the
device. What is the increase in the efficiency for each (a) K,
(b) °F, and (c) R rise in temperature?
1–93E Hyperthermia of 5°C (i.e., 5°C rise above the normal body temperature) is considered fatal. Express this fatal
level of hyperthermia in (a) K, (b) °F, and (c) R.
1–94E A house is losing heat at a rate of 1800 kJ/h per °C
temperature difference between the indoor and the outdoor
temperatures. Express the rate of heat loss from this house
per (a) K, (b) °F, and (c) R difference between the indoor and
the outdoor temperature.
1–95 The average temperature of the atmosphere in the
world is approximated as a function of altitude by the relation
Tatm 5 288.15 2 6.5z
where Tatm is the temperature of the atmosphere in K and z
is the altitude in km with z 5 0 at sea level. Determine the
average temperature of the atmosphere outside an airplane
that is cruising at an altitude of 12,000 m.
1–96 Joe Smith, an old-fashioned engineering student,
believes that the boiling point of water is best suited for use
as the reference point on temperature scales. Unhappy that
the boiling point corresponds to some odd number in the
current absolute temperature scales, he has proposed a new
absolute temperature scale that he calls the Smith scale. The
temperature unit on this scale is smith, denoted by S, and
the boiling point of water on this scale is assigned to be
1000 S. From a thermodynamic point of view, discuss if it is
an acceptable temperature scale. Also, determine the ice point
of water on the Smith scale and obtain a relation between the
Smith and Celsius scales.
48
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
1–97E It is well-known that cold air feels much colder in
windy weather than what the thermometer reading indicates
because of the “chilling effect” of the wind. This effect is due
to the increase in the convection heat transfer coefficient with
increasing air velocities. The equivalent wind chill temperature in °F is given by [ASHRAE, Handbook of Fundamentals
(Atlanta, GA, 1993), p. 8.15]
Tequiv 5 91.4 2 (91.4 2 T ambient)
3 (0.475 2 0.0203V 1 0.304!V )
where V is the wind velocity in mi/h and Tambient is the ambient air temperature in °F in calm air, which is taken to be air
with light winds at speeds up to 4 mi/h. The constant 91.4°F
in the given equation is the mean skin temperature of a resting person in a comfortable environment. Windy air at temperature Tambient and velocity V will feel as cold as the calm
air at temperature Tequiv. Using proper conversion factors,
obtain an equivalent relation in SI units where V is the wind
velocity in km/h and Tambient is the ambient air temperature
in °C.
1–101E The average body temperature of a person rises by
about 2°C during strenuous exercise. What is the rise in the
body temperature in (a) K, (b) °F, and (c) R during strenuous
exercise?
1–102 Balloons are often filled with helium gas because it
weighs only about one-seventh of what air weighs under identical conditions. The buoyancy force, which can be expressed
as Fb 5 rairgVballoon, will push the balloon upward. If the balloon has a diameter of 12 m and carries two people, 85 kg each,
determine the acceleration of the balloon when it is first released.
Assume the density of air is r 5 1.16 kg/m3, and neglect the
weight of the ropes and the cage. Answer: 22.4 m/s2
Helium
D = 12 m
rHe = 17 rair
Answer: Tequiv 5 33.0 2 (33.0 2 Tambient)
3 (0.475 2 0.0126V 1 0.240 !V )
m = 170 kg
1–98E
Reconsider Prob. 1–97E. Using EES (or other)
software, plot the equivalent wind chill temperatures in °F as a function of wind velocity in the range of
4 to 40 mph for the ambient temperatures of 20, 40, and
60°F. Discuss the results.
1–99 A vertical piston–cylinder device contains a gas at
a pressure of 100 kPa. The piston has a mass of 5 kg and
a diameter of 12 cm. Pressure of the gas is to be increased
by placing some weights on the piston. Determine the local
atmospheric pressure and the mass of the weights that will
double the pressure of the gas inside the cylinder. Answers:
95.7 kPa, 115 kg
Weights
FIGURE P1–102
1–103
Reconsider Prob. 1–102. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the number
of people carried in the balloon on acceleration. Plot the
acceleration against the number of people, and discuss the
results.
1–104 Determine the maximum amount of load, in kg, the
balloon described in Prob. 1–102 can carry. Answer: 900 kg
1–105 The lower half of a 6-m-high cylindrical container is
filled with water (r 5 1000 kg/m3) and the upper half with
oil that has a specific gravity of 0.85. Determine the pressure difference between the top and bottom of the cylinder.
Answer: 54.4 kPa
Gas
Oil
SG = 0.85
h=6m
FIGURE P1–99
1–100 An air-conditioning system requires a 35-m-long
section of 15-cm diameter duct work to be laid underwater. Determine the upward force the water will exert on the
duct. Take the densities of air and water to be 1.3 kg/m3 and
1000 kg/m3, respectively.
Water
r = 1000 kg/m3
FIGURE P1–105
49
CHAPTER 1
1–106 A vertical, frictionless piston–cylinder device contains a gas at 180 kPa absolute pressure. The atmospheric
pressure outside is 100 kPa, and the piston area is 25 cm2.
Determine the mass of the piston.
1–107 A pressure cooker cooks a lot faster than an ordinary
pan by maintaining a higher pressure and temperature inside.
The lid of a pressure cooker is well sealed, and steam can
escape only through an opening in the middle of the lid. A
separate metal piece, the petcock, sits on top of this opening and prevents steam from escaping until the pressure force
overcomes the weight of the petcock. The periodic escape
of the steam in this manner prevents any potentially dangerous pressure buildup and keeps the pressure inside at a constant value. Determine the mass of the petcock of a pressure
cooker whose operation pressure is 100 kPa gage and has
an opening cross-sectional area of 4 mm2. Assume an atmospheric pressure of 101 kPa, and draw the free-body diagram
of the petcock. Answer: 40.8 g
Patm = 101 kPa
1–109E Consider a U-tube whose arms are open to the
atmosphere. Now equal volumes of water and light oil (r 5
49.3 lbm/ft3) are poured from different arms. A person blows
from the oil side of the U-tube until the contact surface of the
two fluids moves to the bottom of the U-tube, and thus the
liquid levels in the two arms are the same. If the fluid height
in each arm is 30 in, determine the gage pressure the person
exerts on the oil by blowing.
Air
Oil
Water
30 in
Petcock
A = 4 mm2
FIGURE P1–109E
1–110 The basic barometer can be used as an altitudemeasuring device in airplanes. The ground control reports a
barometric reading of 753 mmHg while the pilot’s reading is
690 mmHg. Estimate the altitude of the plane from ground
level if the average air density is 1.20 kg/m3. Answer: 714 m
1–111E A water pipe is connected to a double-U manometer as shown in Fig. P1–111E at a location where the local
atmospheric pressure is 14.2 psia. Determine the absolute
pressure at the center of the pipe.
Pressure cooker
FIGURE P1–107
1–108 A glass tube is attached to a water pipe, as shown in
Fig. P1–108. If the water pressure at the bottom of the tube is
110 kPa and the local atmospheric pressure is 99 kPa, determine how high the water will rise in the tube, in m. Take the
density of water to be 1000 kg/m3.
Oil SG = 0.80
Oil SG = 0.80
20 in
Water
pipe
30 in
60 in
Patm = 99 kPa
25 in
Mercury
SG = 13.6
h=?
FIGURE P1–111E
Water
FIGURE P1–108
1–112 A gasoline line is connected to a pressure gage
through a double-U manometer, as shown in Fig. P1–112 on
the next page. If the reading of the pressure gage is 370 kPa,
determine the gage pressure of the gasoline line.
50
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
Oil SG = 0.79
Air
V
Pgage = 370 kPa
Gasoline SG = 0.70
Air
45 cm 50 cm
Pipe
22 cm
10 cm
Water
Mercury
SG = 13.6
FIGURE P1–112
1–113 Repeat Prob. 1–112 for a pressure gage reading of
180 kPa.
1–114 The average atmospheric pressure on earth is
approximated as a function of altitude by the relation Patm 5
101.325 (1 2 0.02256z)5.256, where Patm is the atmospheric
pressure in kPa and z is the altitude in km with z 5 0 at sea
level. Determine the approximate atmospheric pressures at
Atlanta (z 5 306 m), Denver (z 5 1610 m), Mexico City
(z 5 2309 m), and the top of Mount Everest (z 5 8848 m).
1–115 It is well-known that the temperature of the atmosphere varies with altitude. In the troposphere, which extends to
an altitude of 11 km, for example, the variation of temperature
can be approximated by T 5 T0 2 bz , where T0 is the temperature at sea level, which can be taken to be 288.15 K, and b 5
0.0065 K/m. The gravitational acceleration also changes with
altitude as g(z) 5 g0/(1 1 z/6,370,320)2 where g0 5 9.807 m/s2
and z is the elevation from sea level in m. Obtain a relation for
the variation of pressure in the troposphere (a) by ignoring and
(b) by considering the variation of g with altitude.
1–116 The variation of pressure with density in a thick
gas layer is given by P 5 Crn, where C and n are constants.
Noting that the pressure change across a differential fluid
layer of thickness dz in the vertical z-direction is given as
dP 5 2 rg dz , obtain a relation for pressure as a function of
elevation z. Take the pressure and density at z 5 0 to be P0
and r0, respectively.
1–117 Consider the flow of air through a wind turbine
whose blades sweep an area of diameter D (in m). The average air velocity through the swept area is V (in m/s). On the
bases of the units of the quantities involved, show that the
mass flow rate of air (in kg/s) through the swept area is proportional to air density, the wind velocity, and the square of
the diameter of the swept area.
1–118 The drag force exerted on a car by air depends on
a dimensionless drag coefficient, the density of air, the car
velocity, and the frontal area of the car. That is, FD 5 function (CDrag Afront, r, V). Based on unit considerations alone,
obtain a relation for the drag force.
FIGURE P1–118
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Problems
1–119 An apple loses 4.5 kJ of heat as it cools per °C drop
in its temperature. The amount of heat loss from the apple
per °F drop in its temperature is
(a) 1.25 kJ
(b) 2.50 kJ
(c) 5.0 kJ
(d ) 8.1 kJ
(e) 4.1 kJ
1–120 Consider a fish swimming 5 m below the free surface of water. The increase in the pressure exerted on the fish
when it dives to a depth of 25 m below the free surface is
(a) 196 Pa
(b) 5400 Pa
(c) 30,000 Pa
(d ) 196,000 Pa
(e) 294,000 Pa
1–121 The atmospheric pressures at the top and the bottom
of a building are read by a barometer to be 96.0 and 98.0 kPa.
If the density of air is 1.0 kg/m3, the height of the building is
(a) 17 m
(b) 20 m
(c) 170 m
(d ) 204 m
(e) 252 m
1–122 Consider a 2-m deep swimming pool. The pressure
difference between the top and bottom of the pool is
(a) 12.0 kPa
(b) 19.6 kPa
(c) 38.1 kPa
(d ) 50.8 kPa
(e) 200 kPa
1–123 During a heating process, the temperature of an
object rises by 10°C. This temperature rise is equivalent to a
temperature rise of
(a) 10°F
(b) 42°F
(c) 18 K
(d ) 18 R
(e) 283 K
1–124 At sea level, the weight of 1 kg mass in SI units is
9.81 N. The weight of 1 lbm mass in English units is
(a) 1 lbf
(b) 9.81 lbf
(c) 32.2 lbf
(d ) 0.1 lbf
(e) 0.031 lbf
Design and Essay Problems
1–125 Write an essay on different temperature measurement
devices. Explain the operational principle of each device, its
advantages and disadvantages, its cost, and its range of applicability. Which device would you recommend for use in the
following cases: taking the temperatures of patients in a doctor’s office, monitoring the variations of temperature of a car
engine block at several locations, and monitoring the temperatures in the furnace of a power plant?
1–126 Write an essay on the various mass- and volumemeasurement devices used throughout history. Also, explain
the development of the modern units for mass and volume.
CHAPTER
2
E N E R G Y, E N E R G Y
TRANSFER, AND GENERAL
E N E R G Y A N A LY S I S
W
hether we realize it or not, energy is an important part of most
aspects of daily life. The quality of life, and even its sustenance,
depends on the availability of energy. Therefore, it is important
to have a good understanding of the sources of energy, the conversion of
energy from one form to another, and the ramifications of these conversions.
Energy exists in numerous forms such as thermal, mechanical, electric,
chemical, and nuclear. Even mass can be considered a form of energy.
Energy can be transferred to or from a closed system (a fixed mass) in two
distinct forms: heat and work. For control volumes, energy can also be
transferred by mass flow. An energy transfer to or from a closed system is
heat if it is caused by a temperature difference. Otherwise it is work, and it
is caused by a force acting through a distance.
We start this chapter with a discussion of various forms of energy and
energy transfer by heat. We then introduce various forms of work and discuss energy transfer by work. We continue with developing a general intuitive expression for the first law of thermodynamics, also known as the
conservation of energy principle, which is one of the most fundamental
principles in nature, and we then demonstrate its use. Finally, we discuss the
efficiencies of some familiar energy conversion processes, and examine the
impact on energy conversion on the environment. Detailed treatments of
the first law of thermodynamics for closed systems and control volumes are
given in Chaps. 4 and 5, respectively.
OBJECTIVES
The objectives of Chapter 2 are to:
■
Introduce the concept of energy
and define its various forms.
■
Discuss the nature of internal
energy.
■
■
■
■
■
■
Define the concept of heat and
the terminology associated with
energy transfer by heat.
Define the concept of work,
including electrical work and
several forms of mechanical
work.
Introduce the first law of
thermodynamics, energy
balances, and mechanisms
of energy transfer to or from a
system.
Determine that a fluid flowing
across a control surface of a
control volume carries energy
across the control surface in
addition to any energy transfer
across the control surface that
may be in the form of heat
and/or work.
Define energy conversion
efficiencies.
Discuss the implications of
energy conversion on the environment.
51
52
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
2–1
Well-sealed and
well-insulated room
FIGURE 2–1
A refrigerator operating with its
door open in a well-sealed and
well-insulated room.
Well-sealed and
well-insulated
room
Fan
FIGURE 2–2
A fan running in a well-sealed and
well-insulated room will raise the
temperature of air in the room.
■
INTRODUCTION
We are familiar with the conservation of energy principle, which is an
expression of the first law of thermodynamics, back from our high school
years. We are told repeatedly that energy cannot be created or destroyed
during a process; it can only change from one form to another. This seems
simple enough, but let’s test ourselves to see how well we understand and
truly believe in this principle.
Consider a room whose door and windows are tightly closed, and whose
walls are well-insulated so that heat loss or gain through the walls is negligible. Now let’s place a refrigerator in the middle of the room with its door
open, and plug it into a wall outlet (Fig. 2–1). You may even use a small fan
to circulate the air in order to maintain temperature uniformity in the room.
Now, what do you think will happen to the average temperature of air in the
room? Will it be increasing or decreasing? Or will it remain constant?
Probably the first thought that comes to mind is that the average air temperature in the room will decrease as the warmer room air mixes with the
air cooled by the refrigerator. Some may draw our attention to the heat generated by the motor of the refrigerator, and may argue that the average air
temperature may rise if this heating effect is greater than the cooling effect.
But they will get confused if it is stated that the motor is made of superconducting materials, and thus there is hardly any heat generation in the motor.
Heated discussion may continue with no end in sight until we remember
the conservation of energy principle that we take for granted: If we take the
entire room—including the air and the refrigerator—as the system, which is
an adiabatic closed system since the room is well-sealed and well-insulated,
the only energy interaction involved is the electrical energy crossing the system boundary and entering the room. The conservation of energy requires
the energy content of the room to increase by an amount equal to the amount
of the electrical energy drawn by the refrigerator, which can be measured
by an ordinary electric meter. The refrigerator or its motor does not store
this energy. Therefore, this energy must now be in the room air, and it will
manifest itself as a rise in the air temperature. The temperature rise of air
can be calculated on the basis of the conservation of energy principle using
the properties of air and the amount of electrical energy consumed. What do
you think would happen if we had a window air conditioning unit instead of
a refrigerator placed in the middle of this room? What if we operated a fan
in this room instead (Fig. 2–2)?
Note that energy is conserved during the process of operating the refrigerator placed in a room—the electrical energy is converted into an equivalent amount of thermal energy stored in the room air. If energy is already
conserved, then what are all those speeches on energy conservation and the
measures taken to conserve energy? Actually, by “energy conservation” what
is meant is the conservation of the quality of energy, not the quantity. Electricity, which is of the highest quality of energy, for example, can always be
converted to an equal amount of thermal energy (also called heat). But only
a small fraction of thermal energy, which is the lowest quality of energy,
can be converted back to electricity, as we discuss in Chap. 6. Think about
the things that you can do with the electrical energy that the refrigerator has
consumed, and the air in the room that is now at a higher temperature.
53
CHAPTER 2
Now if asked to name the energy transformations associated with the
operation of a refrigerator, we may still have a hard time answering because
all we see is electrical energy entering the refrigerator and heat dissipated
from the refrigerator to the room air. Obviously there is need to study the
various forms of energy first, and this is exactly what we do next, followed
by a study of the mechanisms of energy transfer.
2–2
■
FORMS OF ENERGY
Energy can exist in numerous forms such as thermal, mechanical, kinetic,
potential, electric, magnetic, chemical, and nuclear (Fig. 2–3), and their sum
constitutes the total energy E of a system. The total energy of a system on
a unit mass basis is denoted by e and is expressed as
e5
E
m
(kJ/kg)
(2–1)
Thermodynamics provides no information about the absolute value of the
total energy. It deals only with the change of the total energy, which is what
matters in engineering problems. Thus the total energy of a system can be
assigned a value of zero (E 5 0) at some convenient reference point. The
change in total energy of a system is independent of the reference point
selected. The decrease in the potential energy of a falling rock, for example,
depends on only the elevation difference and not the reference level selected.
In thermodynamic analysis, it is often helpful to consider the various
forms of energy that make up the total energy of a system in two groups:
macroscopic and microscopic. The macroscopic forms of energy are those
a system possesses as a whole with respect to some outside reference frame,
such as kinetic and potential energies (Fig. 2–4). The microscopic forms
of energy are those related to the molecular structure of a system and the
degree of the molecular activity, and they are independent of outside reference frames. The sum of all the microscopic forms of energy is called the
internal energy of a system and is denoted by U.
The term energy was coined in 1807 by Thomas Young, and its use in
thermodynamics was proposed in 1852 by Lord Kelvin. The term internal
energy and its symbol U first appeared in the works of Rudolph Clausius
and William Rankine in the second half of the nineteenth century, and it
eventually replaced the alternative terms inner work, internal work, and
intrinsic energy commonly used at the time.
The macroscopic energy of a system is related to motion and the influence
of some external effects such as gravity, magnetism, electricity, and surface
tension. The energy that a system possesses as a result of its motion relative
to some reference frame is called kinetic energy (KE). When all parts of a
system move with the same velocity, the kinetic energy is expressed as
2
KE 5 m
V
2
(kJ)
(2–2)
(kJ/kg)
(2–3)
or, on a unit mass basis,
ke 5
V2
2
(a)
(b)
FIGURE 2–3
At least six different forms of
energy are encountered in bringing
power from a nuclear plant to your
home: nuclear, thermal, mechanical,
kinetic, magnetic, and electrical.
(a) ©Creatas/PunchStock RF
(b) ©Comstock Images/Jupiterimages RF
54
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
where V denotes the velocity of the system relative to some fixed reference
frame. The kinetic energy of a rotating solid body is given by 12 Iv2 where I
is the moment of inertia of the body and v is the angular velocity.
The energy that a system possesses as a result of its elevation in a gravitational field is called potential energy (PE) and is expressed as
FIGURE 2–4
The macroscopic energy of an object
changes with velocity and elevation.
PE 5 mgz
(kJ)
(2–4)
pe 5 gz
(kJ/kg)
(2–5)
or, on a unit mass basis,
where g is the gravitational acceleration and z is the elevation of the center
of gravity of a system relative to some arbitrarily selected reference level.
The magnetic, electric, and surface tension effects are significant in some
specialized cases only and are usually ignored. In the absence of such
effects, the total energy of a system consists of the kinetic, potential, and
internal energies and is expressed as
E 5 U 1 KE 1 PE 5 U 1 m
V2
1 mgz
2
(kJ)
(2–6)
or, on a unit mass basis,
e 5 u 1 ke 1 pe 5 u 1
V2
1 gz
2
(kJ/kg)
(2–7)
Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and thus experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. Closed systems
whose velocity and elevation of the center of gravity remain constant during
a process are frequently referred to as stationary systems. The change in
the total energy DE of a stationary system is identical to the change in its
internal energy DU. In this text, a closed system is assumed to be stationary
unless stated otherwise.
Control volumes typically involve fluid flow for long periods of time, and
it is convenient to express the energy flow associated with a fluid stream in
the rate form. This is done by incorporating the mass flow rate m# , which
is the amount of mass flowing through
a cross section per unit time. It is
#
related to the volume flow rate V , which is the volume of a fluid flowing
through a cross section per unit time, by
Ac = p D 2/4
D
Mass flow rate:
Vavg
m = rAcVavg
Steam
E = me
FIGURE 2–5
Mass and energy flow rates associated
with the flow of steam in a pipe of
inner diameter D with an average
velocity of Vavg.
#
#
m 5 rV 5 rAcVavg
(kg/s)
(2–8)
#
which is analogous to m 5 rV . Here r is the fluid density, Ac is the crosssectional area of flow, and Vavg is the average flow velocity normal to Ac.
The dot over a symbol is used to indicate time rate throughout the book.
Then the energy flow rate associated with a fluid flowing at a rate of m# is
(Fig. 2–5)
Energy flow rate:
#
#
E 5 me
which is analogous to E 5 me.
(kJ/s or kW)
(2–9)
55
CHAPTER 2
Some Physical Insight to Internal Energy
Internal energy is defined earlier as the sum of all the microscopic forms of
energy of a system. It is related to the molecular structure and the degree of
molecular activity, and can be viewed as the sum of the kinetic and potential
energies of the molecules.
To have a better understanding of internal energy, let us examine a system
at the molecular level. The molecules of a gas move through space with
some velocity, and thus possess some kinetic energy. This is known as the
translational energy. The atoms of polyatomic molecules rotate about an
axis, and the energy associated with this rotation is the rotational kinetic
energy. The atoms of a polyatomic molecule may also vibrate about their
common center of mass, and the energy associated with this back-and-forth
motion is the vibrational kinetic energy. For gases, the kinetic energy is
mostly due to translational and rotational motions, with vibrational motion
becoming significant at higher temperatures. The electrons in an atom rotate
about the nucleus, and thus possess rotational kinetic energy. Electrons at
outer orbits have larger kinetic energies. Electrons also spin about their
axes, and the energy associated with this motion is the spin energy. Other
particles in the nucleus of an atom also possess spin energy. The portion of
the internal energy of a system associated with the kinetic energies of the
molecules is called the sensible energy (Fig. 2–6). The average velocity and
the degree of activity of the molecules are proportional to the temperature
of the gas. Therefore, at higher temperatures, the molecules possess higher
kinetic energies, and as a result the system has a higher internal energy.
The internal energy is also associated with various binding forces between
the molecules of a substance, between the atoms within a molecule, and
between the particles within an atom and its nucleus. The forces that bind
the molecules to each other are, as one would expect, strongest in solids and
weakest in gases. If sufficient energy is added to the molecules of a solid or
liquid, the molecules overcome these molecular forces and break away, turning the substance into a gas. This is a phase-change process. Because of this
added energy, a system in the gas phase is at a higher internal energy level
than it is in the solid or the liquid phase. The internal energy associated with
the phase of a system is called the latent energy. The phase-change process
can occur without a change in the chemical composition of a system. Most
practical problems fall into this category, and one does not need to pay any
attention to the forces binding the atoms in a molecule to each other.
An atom consists of neutrons and positively charged protons bound
together by very strong nuclear forces in the nucleus, and negatively charged
electrons orbiting around it. The internal energy associated with the atomic
bonds in a molecule is called chemical energy. During a chemical reaction,
such as a combustion process, some chemical bonds are destroyed while
others are formed. As a result, the internal energy changes. The nuclear
forces are much larger than the forces that bind the electrons to the nucleus.
The tremendous amount of energy associated with the strong bonds within
the nucleus of the atom itself is called nuclear energy (Fig. 2–7). Obviously, we need not be concerned with nuclear energy in thermodynamics
unless, of course, we deal with fusion or fission reactions. A chemical reaction involves changes in the structure of the electrons of the atoms, but a
Molecular
translation
Molecular
rotation
–
+
Electron
translation
Molecular
vibration
–
+
Electron
spin
Nuclear
spin
FIGURE 2–6
The various forms of microscopic
energies that make up sensible energy.
Sensible
and latent
energy
Chemical
energy
Nuclear
energy
FIGURE 2–7
The internal energy of a system
is the sum of all forms of the
microscopic energies.
56
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
Microscopic kinetic
energy of molecules
(does not turn the wheel)
Water
Dam
Macroscopic kinetic energy
(turns the wheel)
FIGURE 2–8
The macroscopic kinetic energy is an
organized form of energy and is much
more useful than the disorganized
microscopic kinetic energies of the
molecules.
nuclear reaction involves changes in the core or nucleus. Therefore, an atom
preserves its identity during a chemical reaction but loses it during a nuclear
reaction. Atoms may also possess electric and magnetic dipole-moment
energies when subjected to external electric and magnetic fields due to the
twisting of the magnetic dipoles produced by the small electric currents
associated with the orbiting electrons.
The forms of energy already discussed, which constitute the total energy
of a system, can be contained or stored in a system, and thus can be viewed
as the static forms of energy. The forms of energy not stored in a system
can be viewed as the dynamic forms of energy or as energy interactions.
The dynamic forms of energy are recognized at the system boundary as
they cross it, and they represent the energy gained or lost by a system during a process. The only two forms of energy interactions associated with a
closed system are heat transfer and work. An energy interaction is heat
transfer if its driving force is a temperature difference. Otherwise it is work,
as explained in the next section. A control volume can also exchange energy
via mass transfer since any time mass is transferred into or out of a system,
the energy content of the mass is also transferred with it.
In daily life, we frequently refer to the sensible and latent forms of internal energy as heat, and we talk about heat content of bodies. In thermodynamics, however, we usually refer to those forms of energy as thermal
energy to prevent any confusion with heat transfer.
Distinction should be made between the macroscopic kinetic energy of
an object as a whole and the microscopic kinetic energies of its molecules
that constitute the sensible internal energy of the object (Fig. 2–8). The
kinetic energy of an object is an organized form of energy associated with
the orderly motion of all molecules in one direction in a straight path or
around an axis. In contrast, the kinetic energies of the molecules are completely random and highly disorganized. As you will see in later chapters,
the organized energy is much more valuable than the disorganized energy,
and a major application area of thermodynamics is the conversion of disorganized energy (heat) into organized energy (work). You will also see that
the organized energy can be converted to disorganized energy completely,
but only a fraction of disorganized energy can be converted to organized
energy by specially built devices called heat engines (like car engines and
power plants). A similar argument can be given for the macroscopic potential energy of an object as a whole and the microscopic potential energies of
the molecules.
More on Nuclear Energy
The best known fission reaction involves the split of the uranium atom (the
U-235 isotope) into other elements and is commonly used to generate electricity in nuclear power plants (440 of them in 2004, generating 363,000
MW worldwide), to power nuclear submarines and aircraft carriers, and
even to power spacecraft as well as building nuclear bombs.
The percentage of electricity produced by nuclear power is 78 percent in
France, 25 percent in Japan, 28 percent in Germany, and 20 percent in the
United States. The first nuclear chain reaction was achieved by Enrico Fermi
in 1942, and the first large-scale nuclear reactors were built in 1944 for the
purpose of producing material for nuclear weapons. When a uranium-235
57
CHAPTER 2
atom absorbs a neutron and splits during a fission process, it produces a
cesium-140 atom, a rubidium-93 atom, 3 neutrons, and 3.2 3 10211 J of
energy. In practical terms, the complete fission of 1 kg of uranium-235
releases 6.73 3 1010 kJ of heat, which is more than the heat released when
3000 tons of coal are burned. Therefore, for the same amount of fuel, a
nuclear fission reaction releases several million times more energy than a
chemical reaction. The safe disposal of used nuclear fuel, however, remains
a concern.
Nuclear energy by fusion is released when two small nuclei combine into
a larger one. The huge amount of energy radiated by the sun and the other
stars originates from such a fusion process that involves the combination of
two hydrogen atoms into a helium atom. When two heavy hydrogen (deuterium) nuclei combine during a fusion process, they produce a helium-3
atom, a free neutron, and 5.1 3 10213 J of energy (Fig. 2–9).
Fusion reactions are much more difficult to achieve in practice because
of the strong repulsion between the positively charged nuclei, called the
Coulomb repulsion. To overcome this repulsive force and to enable the two
nuclei to fuse together, the energy level of the nuclei must be raised by heating them to about 100 million 8C. But such high temperatures are found
only in the stars or in exploding atomic bombs (the A-bomb). In fact, the
uncontrolled fusion reaction in a hydrogen bomb (the H-bomb) is initiated
by a small atomic bomb. The uncontrolled fusion reaction was achieved in
the early 1950s, but all the efforts since then to achieve controlled fusion by
massive lasers, powerful magnetic fields, and electric currents to generate
power have failed.
EXAMPLE 2–1
Uranium
3.2 × 10–11 J
U-235
Ce-140
n n 3 neutrons
n
n
neutron
Rb-93
(a) Fission of uranium
H-2
He-3
n
neutron
H-2
5.1 × 10–13 J
(b) Fusion of hydrogen
FIGURE 2–9
The fission of uranium and the fusion
of hydrogen during nuclear reactions,
and the release of nuclear energy.
A Car Powered by Nuclear Fuel
An average car consumes about 5 L of gasoline a day, and the capacity of the
fuel tank of a car is about 50 L. Therefore, a car needs to be refueled once
every 10 days. Also, the density of gasoline ranges from 0.68 to 0.78 kg/L,
and its lower heating value is about 44,000 kJ/kg (that is, 44,000 kJ of
heat is released when 1 kg of gasoline is completely burned). Suppose all
the problems associated with the radioactivity and waste disposal of nuclear
fuels are resolved, and a car is to be powered by U-235. If a new car comes
equipped with 0.1-kg of the nuclear fuel U-235, determine if this car will
ever need refueling under average driving conditions (Fig. 2–10).
SOLUTION A car powered by nuclear energy comes equipped with nuclear
fuel. It is to be determined if this car will ever need refueling.
Assumptions 1 Gasoline is an incompressible substance with an average
density of 0.75 kg/L. 2 Nuclear fuel is completely converted to thermal energy.
Analysis The mass of gasoline used per day by the car is
mgasoline 5 (rV )gasoline 5 (0.75 kg/L)(5 L/day) 5 3.75 kg/day
Noting that the heating value of gasoline is 44,000 kJ/kg, the energy supplied to the car per day is
E 5 (mgasoline)(Heating value)
5 (3.75 kg/day)(44,000 kJ/kg) 5 165,000 kJ/day
Nuclear
fuel
FIGURE 2–10
Schematic for Example 2–1.
58
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
The complete fission of 0.1 kg of uranium-235 releases
(6.73 3 1010 kJ/kg)(0.1 kg) 5 6.73 3 109 kJ
of heat, which is sufficient to meet the energy needs of the car for
No. of days 5
Energy content of fuel
6.73 3 109 kJ
5
5 40,790 days
Daily energy use
165,000 kJ/day
which is equivalent to about 112 years. Considering that no car will last more
than 100 years, this car will never need refueling. It appears that nuclear
fuel of the size of a cherry is sufficient to power a car during its lifetime.
Discussion Note that this problem is not quite realistic since the necessary
critical mass cannot be achieved with such a small amount of fuel. Further,
all of the uranium cannot be converted in fission, again because of the critical mass problems after partial conversion.
Mechanical Energy
FIGURE 2–11
Mechanical energy is a useful
concept for flows that do not involve
significant heat transfer or energy
conversion, such as the flow of
gasoline from an underground tank
into a car.
©Royalty-Free/Corbis
Many engineering systems are designed to transport a fluid from one location to another at a specified flow rate, velocity, and elevation difference,
and the system may generate mechanical work in a turbine or it may consume mechanical work in a pump or fan during this process (Fig. 2–11).
These systems do not involve the conversion of nuclear, chemical, or thermal energy to mechanical energy. Also, they do not involve any heat transfer in any significant amount, and they operate essentially at constant temperature. Such systems can be analyzed conveniently by considering the
mechanical forms of energy only and the frictional effects that cause the
mechanical energy to be lost (i.e., to be converted to thermal energy that
usually cannot be used for any useful purpose).
The mechanical energy can be defined as the form of energy that can be
converted to mechanical work completely and directly by an ideal mechanical
device such as an ideal turbine. Kinetic and potential energies are the familiar forms of mechanical energy. Thermal energy is not mechanical energy,
however, since it cannot be converted to work directly and completely (the
second law of thermodynamics).
A pump transfers mechanical energy to a fluid by raising its pressure,
and a turbine extracts mechanical energy from a fluid by dropping its pressure. Therefore, the pressure of a flowing fluid is also associated with
its mechanical energy. In fact, the pressure unit Pa is equivalent to Pa 5
N/m2 5 N·m/m3 5 J/m3, which is energy per unit volume, and the product
Pv or its equivalent P/r has the unit J/kg, which is energy per unit mass.
Note that pressure itself is not a form of energy but a pressure force acting on a fluid through a distance produces work, called flow work, in the
amount of P/r per unit mass. Flow work is expressed in terms of fluid properties, and it is convenient to view it as part of the energy of a flowing fluid
and call it flow energy. Therefore, the mechanical energy of a flowing fluid
can be expressed on a unit mass basis as
emech 5
P
V2
1 gz
1
r
2
(2–10)
59
CHAPTER 2
where P/r is the flow energy, V 2/2 is the kinetic energy, and gz is the potential
energy of the fluid, all per unit mass. It can also be expressed in rate form as
#
V2
#
# P
Emech 5 memech 5 m a 1
1 gzb
r
2
1
h
(2–11)
where m# is the mass flow rate of the fluid. Then the mechanical energy
W
Turbine
change of a fluid during incompressible (r 5 constant) flow becomes
Demech 5
P2 2 P1
V 22 2 V 21
1 g(z2 2 z1)
1
r
2
(kJ/kg)
(2–12)
4
Generator
and
V 22 2 V 21
#
#
# P2 2 P1
1 g(z2 2 z1)b
DEmech 5 m Demech 5 m a
1
r
2
(kW)
(2–13)
Therefore, the mechanical energy of a fluid does not change during flow if
its pressure, density, velocity, and elevation remain constant. In the absence
of any irreversible losses, the mechanical energy change represents the
mechanical work supplied to the fluid (if Demech . 0) or extracted from the
fluid (if Demech , 0). The maximum (ideal) power generated by a turbine,
#
for example, is Wmax 5 m# Demech, as shown in Fig. 2–12.
#
#
#
#
Wmax 5 m Demech 5 m g (z1 2 z4) 5 m gh
since P1 < P4 5 Patm and V1 5 V4 < 0
(a)
W
Turbine
2
3
EXAMPLE 2–2
Wind Energy
Generator
A site evaluated for a wind farm is observed to have steady winds at a speed
of 8.5 m/s (Fig. 2–13). Determine the wind energy (a) per unit mass, (b) for
a mass of 10 kg, and (c) for a flow rate of 1154 kg/s for air.
#
#
# P2 2 P3
# DP
Wmax 5 m Demech 5 m
5m
r
r
SOLUTION A site with a specified wind speed is considered. Wind energy
(b)
per unit mass, for a specified mass, and for a given mass flow rate of air are
to be determined.
Assumptions Wind flows steadily at the specified speed.
Analysis The only harvestable form of energy of atmospheric air is the
kinetic energy, which is captured by a wind turbine.
(a) Wind energy per unit mass of air is
FIGURE 2–12
Mechanical energy is illustrated
by an ideal hydraulic turbine
coupled with an ideal generator.
In the absence of irreversible losses,
the maximum produced power is proportional to (a) the change in
water surface elevation from the upstream to the downstream reservoir or
(b) (close-up view) the drop in water
pressure from just upstream to just
downstream of the turbine.
e 5 ke 5
(8.5 m/s)2 1 J/kg
V2
b 5 36.1 J/kg
5
a
2
2
1 m2/s2
(b) Wind energy for an air mass of 10 kg is
E 5 me 5 (10 kg)(36.1 J/kg) 5 361 J
(c) Wind energy for a mass flow rate of 1154 kg/s is
#
1 kW
#
b 5 41.7 kW
E 5 me 5 (1154 kg/s)(36.1 J/kg)a
1000 J/s
Discussion It can be shown that the specified mass flow rate corresponds
to a 12-m diameter flow section when the air density is 1.2 kg/m3. Therefore, a wind turbine with a wind span diameter of 12 m has a power generation potential of 41.7 kW. Real wind turbines convert about one-third of this
potential to electric power.
since V2 < V3 and z2 5 z3
60
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
2–3
FIGURE 2–13
A site for a wind farm as discussed in
Example 2-2.
©Ingram Publishing/SuperStock RF
System boundary
Closed
system
Heat
(m = constant)
Work
FIGURE 2–14
Energy can cross the boundaries
of a closed system in the form
of heat and work.
■
ENERGY TRANSFER BY HEAT
Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two distinct forms:
heat and work (Fig. 2–14). It is important to distinguish between these two
forms of energy. Therefore, they will be discussed first, to form a sound
basis for the development of the laws of thermodynamics.
We know from experience that a can of cold soda left on a table eventually warms up and that a hot baked potato on the same table cools down.
When a body is left in a medium that is at a different temperature, energy
transfer takes place between the body and the surrounding medium until
thermal equilibrium is established, that is, the body and the medium reach
the same temperature. The direction of energy transfer is always from the
higher temperature body to the lower temperature one. Once the temperature equality is established, energy transfer stops. In the processes described
above, energy is said to be transferred in the form of heat.
Heat is defined as the form of energy that is transferred between two systems (or a system and its surroundings) by virtue of a temperature difference (Fig. 2–15). That is, an energy interaction is heat only if it takes place
because of a temperature difference. Then it follows that there cannot be
any heat transfer between two systems that are at the same temperature.
Several phrases in common use today—such as heat flow, heat addition,
heat rejection, heat absorption, heat removal, heat gain, heat loss, heat storage, heat generation, electrical heating, resistance heating, frictional heating, gas heating, heat of reaction, liberation of heat, specific heat, sensible
heat, latent heat, waste heat, body heat, process heat, heat sink, and heat
source—are not consistent with the strict thermodynamic meaning of the
term heat, which limits its use to the transfer of thermal energy during a
process. However, these phrases are deeply rooted in our vocabulary, and
they are used by both ordinary people and scientists without causing any
misunderstanding since they are usually interpreted properly instead of
being taken literally. (Besides, no acceptable alternatives exist for some of
these phrases.) For example, the phrase body heat is understood to mean
the thermal energy content of a body. Likewise, heat flow is understood to
mean the transfer of thermal energy, not the flow of a fluidlike substance
called heat, although the latter incorrect interpretation, which is based on
the caloric theory, is the origin of this phrase. Also, the transfer of heat into
a system is frequently referred to as heat addition and the transfer of heat
out of a system as heat rejection. Perhaps there are thermodynamic reasons
for being so reluctant to replace heat by thermal energy: It takes less time
and energy to say, write, and comprehend heat than it does thermal energy.
Heat is energy in transition. It is recognized only as it crosses the boundary of a system. Consider the hot baked potato one more time. The potato
contains energy, but this energy is heat transfer only as it passes through
the skin of the potato (the system boundary) to reach the air, as shown in
Fig. 2–16. Once in the surroundings, the transferred heat becomes part of
the internal energy of the surroundings. Thus, in thermodynamics, the term
heat simply means heat transfer.
A process during which there is no heat transfer is called an adiabatic
process (Fig. 2–17). The word adiabatic comes from the Greek word adiabatos, which means not to be passed. There are two ways a process can
61
CHAPTER 2
be adiabatic: Either the system is well insulated so that only a negligible
amount of heat can pass through the boundary, or both the system and the
surroundings are at the same temperature and therefore there is no driving force (temperature difference) for heat transfer. An adiabatic process
should not be confused with an isothermal process. Even though there is
no heat transfer during an adiabatic process, the energy content and thus
the temperature of a system can still be changed by other means such
as work.
As a form of energy, heat has energy units, kJ (or Btu) being the most
common one. The amount of heat transferred during the process between
two states (states 1 and 2) is denoted by Q12, or just Q. Heat transfer per
unit mass of a system is denoted q and is determined from
Q
q5
m
(kJ/kg)
(2–14)
Sometimes it is desirable to know the rate of heat transfer (the amount
of heat transferred per unit time) instead of the total heat transferred
over
#
some time interval (Fig. 2–18). The heat transfer rate is denoted Q, where
the overdot
# stands for the time derivative, or “per unit time.” The# heat transfer rate Q has the unit kJ/s, which is equivalent to kW. When Q varies with
time, # the amount of heat transfer during a process is determined by integrating Q over the time interval of the process:
Q5
#
(kJ)
8 J/s
25°C
15°C
(kJ)
Heat
5°C
FIGURE 2–15
Temperature difference is the driving
force for heat transfer. The larger the
temperature difference, the higher is
the rate of heat transfer.
2 kJ
thermal
energy
Surrounding air
Heat
System
boundary
#
When Q remains constant during a process, this relation reduces to
16 J/s
Heat
2 kJ
heat
(2–15)
t1
#
Q 5 Q Dt
No heat
transfer
Baked potato
t2
#
Q dt
Room air
25°C
2 kJ
thermal
energy
(2–16)
where Dt 5 t2 2 t1 is the time interval during which the process takes place.
Historical Background on Heat
Heat has always been perceived to be something that produces in us a sensation of warmth, and one would think that the nature of heat is one of
the first things understood by mankind. However, it was only in the middle
of the nineteenth century that we had a true physical understanding of the
nature of heat, thanks to the development at that time of the kinetic theory,
which treats molecules as tiny balls that are in motion and thus possess
kinetic energy. Heat is then defined as the energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules. Although it was suggested in the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries that heat is the manifestation of motion
at the molecular level (called the live force), the prevailing view of heat
until the middle of the nineteenth century was based on the caloric theory
proposed by the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier (1744–1794) in 1789.
The caloric theory asserts that heat is a fluidlike substance called the caloric
that is a massless, colorless, odorless, and tasteless substance that can be
poured from one body into another (Fig. 2–19). When caloric was added
to a body, its temperature increased; and when caloric was removed from a
FIGURE 2–16
Energy is recognized as heat transfer
only as it crosses the system boundary.
Insulation
Q=0
Adiabatic
system
FIGURE 2–17
During an adiabatic process, a system
exchanges no heat with its
surroundings.
62
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
Q = 30 kJ
m = 2 kg
Δt = 5 s
30 kJ
heat
Q = 6 kW
q = 15 kJ/kg
FIGURE 2–18
#
The relationships among q, Q, and Q.
Contact
surface
Hot
body
Cold
body
Caloric
FIGURE 2–19
In the early nineteenth century, heat
was thought to be an invisible fluid
called the caloric that flowed from
warmer bodies to the cooler ones.
W = 30 kJ
m = 2 kg
Δt = 5 s
30 kJ
work
W = 6 kW
w = 15 kJ/kg
body, its temperature decreased. When a body could not contain any more
caloric, much the same way as when a glass of water could not dissolve
any more salt or sugar, the body was said to be saturated with caloric. This
interpretation gave rise to the terms saturated liquid and saturated vapor
that are still in use today.
The caloric theory came under attack soon after its introduction. It maintained that heat is a substance that could not be created or destroyed. Yet it
was known that heat can be generated indefinitely by rubbing one’s hands
together or rubbing two pieces of wood together. In 1798, the American
Benjamin Thompson (Count Rumford) (1754–1814) showed in his papers
that heat can be generated continuously through friction. The validity of the
caloric theory was also challenged by several others. But it was the careful experiments of the Englishman James P. Joule (1818–1889) published
in 1843 that finally convinced the skeptics that heat was not a substance
after all, and thus put the caloric theory to rest. Although the caloric theory
was totally abandoned in the middle of the nineteenth century, it contributed
greatly to the development of thermodynamics and heat transfer.
Heat is transferred by three mechanisms: conduction, convection, and
radiation. Conduction is the transfer of energy from the more energetic particles of a substance to the adjacent less energetic ones as a result of interaction between particles. Convection is the transfer of energy between a solid
surface and the adjacent fluid that is in motion, and it involves the combined
effects of conduction and fluid motion. Radiation is the transfer of energy
due to the emission of electromagnetic waves (or photons). An overview of
the three mechanisms of heat transfer is given at the end of this chapter as a
Topic of Special Interest.
2–4
■
ENERGY TRANSFER BY WORK
Work, like heat, is an energy interaction between a system and its surroundings. As mentioned earlier, energy can cross the boundary of a closed
system in the form of heat or work. Therefore, if the energy crossing the
boundary of a closed system is not heat, it must be work. Heat is easy to
recognize: Its driving force is a temperature difference between the system
and its surroundings. Then we can simply say that an energy interaction
that is not caused by a temperature difference between a system and its surroundings is work. More specifically, work is the energy transfer associated
with a force acting through a distance. A rising piston, a rotating shaft, and
an electric wire crossing the system boundaries are all associated with work
interactions.
Work is also a form of energy transferred like heat and, therefore, has
energy units such as kJ. The work done during a process between states 1
and 2 is denoted by W12, or simply W. The work done per unit mass of a
system is denoted by w and is expressed as
w5
FIGURE 2–20
#
The relationships among w, W, and W .
W
m
(kJ/kg)
(2–17)
#
The work done per unit time is called power and is denoted W (Fig. 2–20).
The unit of power is kJ/s, or kW.
63
CHAPTER 2
Surroundings
Heat and work are directional quantities, and thus the complete description of a heat or work interaction requires the specification of both the
magnitude and direction. One way of doing that is to adopt a sign convention. The generally accepted formal sign convention for heat and work
interactions is as follows: heat transfer to a system and work done by a
system are positive; heat transfer from a system and work done on a system
are negative. Another way is to use the subscripts in and out to indicate
direction (Fig. 2–21). For example, a work input of 5 kJ can be expressed
as Win 5 5 kJ, while a heat loss of 3 kJ can be expressed as Qout 5 3 kJ.
When the direction of a heat or work interaction is not known, we can
simply assume a direction for the interaction (using the subscript in or out)
and solve for it. A positive result indicates the assumed direction is right. A
negative result, on the other hand, indicates that the direction of the interaction is the opposite of the assumed direction. This is just like assuming a
direction for an unknown force when solving a statics problem, and reversing the direction when a negative result is obtained for the force. We will
use this intuitive approach in this book as it eliminates the need to adopt a
formal sign convention and the need to carefully assign negative values to
some interactions.
Note that a quantity that is transferred to or from a system during an
interaction is not a property since the amount of such a quantity depends
on more than just the state of the system. Heat and work are energy transfer
mechanisms between a system and its surroundings, and there are many
similarities between them:
Qin
Qout
System
Win
Wout
FIGURE 2–21
Specifying the directions
of heat and work.
1. Both are recognized at the boundaries of a system as they cross the
boundaries. That is, both heat and work are boundary phenomena.
2. Systems possess energy, but not heat or work.
3. Both are associated with a process, not a state. Unlike properties, heat or
work has no meaning at a state.
4. Both are path functions (i.e., their magnitudes depend on the path followed during a process as well as the end states).
P
ΔVA = 3 m3; WA = 8 kJ
1
ΔVB = 3 m3; WB = 12 kJ
s
es
oc
Pr
B
oc
Pr
es
Path functions have inexact differentials designated by the symbol d.
Therefore, a differential amount of heat or work is represented by dQ or
dW, respectively, instead of dQ or dW. Properties, however, are point functions (i.e., they depend on the state only, and not on how a system reaches
that state), and they have exact differentials designated by the symbol d.
A small change in volume, for example, is represented by dV, and the total
volume change during a process between states 1 and 2 is
sA
2
# dV 5 V 2 V 5 DV
2
2
1
1
That is, the volume change during process 1–2 is always the volume at state
2 minus the volume at state 1, regardless of the path followed (Fig. 2–22).
The total work done during process 1–2, however, is
2
# dW 5 W
1
12
(not DW)
2 m3
5 m3
V
FIGURE 2–22
Properties are point functions;
but heat and work are path
functions (their magnitudes
depend on the path followed).
64
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
That is, the total work is obtained by following the process path and adding
the differential amounts of work (dW) done along the way. The integral of
dW is not W2 2 W1 (i.e., the work at state 2 minus work at state 1), which is
meaningless since work is not a property and systems do not possess work
at a state.
(Insulation)
EXAMPLE 2–3
Burning of a Candle in an Insulated Room
A candle is burning in a well-insulated room. Taking the room (the air plus
the candle) as the system, determine (a) if there is any heat transfer during
this burning process and (b) if there is any change in the internal energy of
the system.
Room
FIGURE 2–23
Schematic for Example 2–3.
SOLUTION A candle burning in a well-insulated room is considered. It is to
be determined whether there is any heat transfer and any change in internal
energy.
Analysis (a) The interior surfaces of the room form the system boundary,
as indicated by the dashed lines in Fig. 2–23. As pointed out earlier, heat
is recognized as it crosses the boundaries. Since the room is well insulated,
we have an adiabatic system and no heat will pass through the boundaries.
Therefore, Q 5 0 for this process.
(b) The internal energy involves energies that exist in various forms (sensible,
latent, chemical, nuclear). During the process just described, part of the
chemical energy is converted to sensible energy. Since there is no increase or
decrease in the total internal energy of the system, DU 5 0 for this process.
Oven
EXAMPLE 2–4
Heat
200°C
Potato
25°C
FIGURE 2–24
Schematic for Example 2–4.
Heating of a Potato in an Oven
A potato initially at room temperature (258C) is being baked in an oven that
is maintained at 2008C, as shown in Fig. 2–24. Is there any heat transfer
during this baking process?
SOLUTION A potato is being baked in an oven. It is to be determined
whether there is any heat transfer during this process.
Analysis This is not a well-defined problem since the system is not specified. Let us assume that we are observing the potato, which will be our system. Then the outer surface of the skin of the potato can be viewed as the
system boundary. Part of the energy in the oven will pass through the skin to
the potato. Since the driving force for this energy transfer is a temperature
difference, this is a heat transfer process.
EXAMPLE 2–5
Heating of an Oven by Work Transfer
A well-insulated electric oven is being heated through its heating element.
If the entire oven, including the heating element, is taken to be the system,
determine whether this is a heat or work interaction.
SOLUTION A well-insulated electric oven is being heated by its heating element. It is to be determined whether this is a heat or work interaction.
65
CHAPTER 2
Analysis For this problem, the interior surfaces of the oven form the system boundary, as shown in Fig. 2–25. The energy content of the oven obviously increases during this process, as evidenced by a rise in temperature.
This energy transfer to the oven is not caused by a temperature difference
between the oven and the surrounding air. Instead, it is caused by electrons crossing the system boundary and thus doing work. Therefore, this is
a work interaction.
EXAMPLE 2–6
Heating of an Oven by Heat Transfer
Answer the question in Example 2–5 if the system is taken as only the air in
the oven without the heating element.
SOLUTION The question in Example 2–5 is to be reconsidered by taking
the system to be only the air in the oven.
Analysis This time, the system boundary will include the outer surface of
the heating element and will not cut through it, as shown in Fig. 2–26.
Therefore, no electrons will be crossing the system boundary at any point.
Instead, the energy generated in the interior of the heating element will be
transferred to the air around it as a result of the temperature difference
between the heating element and the air in the oven. Therefore, this is a
heat transfer process.
Discussion For both cases, the amount of energy transfer to the air is the
same. These two examples show that an energy transfer can be heat or work,
depending on how the system is selected.
System boundary
Electric oven
Heating element
FIGURE 2–25
Schematic for Example 2–5.
System boundary
Electric oven
Heating element
FIGURE 2–26
Schematic for Example 2–6.
Electrical Work
It was pointed out in Example 2–5 that electrons crossing the system boundary do electrical work on the system. In an electric field, electrons in a wire
move under the effect of electromotive forces, doing work. When N coulombs of electrical charge move through a potential difference V, the electrical work done is
We 5 VN
which can also be expressed in the rate form as
#
We 5 VI
(W)
I
(2–18)
#
where W e is the electrical power and I is the number of electrical charges
flowing per unit time, that is, the current (Fig. 2–27). In general, both V and
I vary with time, and the electrical work done during a time interval Dt is
expressed as
.
We = VI
= I 2R
= V2/R
R
V
2
We 5
# VI dt
(kJ)
(2–19)
1
When both V and I remain constant during the time interval Dt, it reduces to
We 5 VI Dt
(kJ)
(2–20)
FIGURE 2–27
Electrical power in terms of resistance
R, current I, and potential difference V.
66
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
F
F
s
FIGURE 2–28
The work done is proportional to the
force applied (F ) and the distance
traveled (s).
2–5
■
MECHANICAL FORMS OF WORK
There are several different ways of doing work, each in some way related
to a force acting through a distance (Fig. 2–28). In elementary mechanics,
the work done by a constant force F on a body displaced a distance s in the
direction of the force is given by
W 5 Fs
(kJ)
(2–21)
If the force F is not constant, the work done is obtained by adding (i.e.,
integrating) the differential amounts of work,
2
W5
# F ds
(kJ)
(2–22)
1
Obviously, one needs to know how the force varies with displacement to
perform this integration. Equations 2–21 and 2–22 give only the magnitude
of the work. The sign is easily determined from physical considerations:
The work done on a system by an external force acting in the direction of
motion is negative, and work done by a system against an external force acting in the opposite direction to motion is positive.
There are two requirements for a work interaction between a system and
its surroundings to exist: (1) there must be a force acting on the boundary,
and (2) the boundary must move. Therefore, the presence of forces on the
boundary without any displacement of the boundary does not constitute a
work interaction. Likewise, the displacement of the boundary without any
force to oppose or drive this motion (such as the expansion of a gas into an
evacuated space) is not a work interaction since no energy is transferred.
In many thermodynamic problems, mechanical work is the only form of
work involved. It is associated with the movement of the boundary of a system or with the movement of the entire system as a whole. Some common
forms of mechanical work are discussed next.
Boat
Engine
FIGURE 2–29
Energy transmission through
rotating shafts is commonly
encountered in practice.
·
·
Wsh = 2pnT
r
n·
Shaft Work
Energy transmission with a rotating shaft is very common in engineering
practice (Fig. 2–29). Often the torque T applied to the shaft is constant,
which means that the force F applied is also constant. For a specified constant torque, the work done during n revolutions is determined as follows: A
force F acting through a moment arm r generates a torque T of (Fig. 2–30)
T 5 Fr S F 5
F
Torque = Fr
FIGURE 2–30
Shaft work is proportional to
the torque applied and the number
of revolutions of the shaft.
T
r
(2–23)
This force acts through a distance s, which is related to the radius r by
s 5 (2pr)n
(2–24)
Then the shaft work is determined from
T
Wsh 5 Fs 5 a b(2prn) 5 2pnT
r
(kJ)
(2–25)
67
CHAPTER 2
The power transmitted through the shaft is the shaft work done per unit
time, which can be expressed as
#
#
Wsh 5 2pnT
(kW)
(2–26)
where n# is the number of revolutions per unit time.
EXAMPLE 2–7
Power Transmission by the Shaft of a Car
Determine the power transmitted through the shaft of a car when the torque
applied is 200 N·m and the shaft rotates at a rate of 4000 revolutions per
minute (rpm).
SOLUTION The torque and the rpm for a car engine are given. The power
transmitted is to be determined.
Analysis A sketch of the car is given in Fig. 2–31. The shaft power is determined directly from
#
1
1 min
1 kJ
#
Wsh 5 2pnT 5 (2p)a4000
b(200 N · m) a
ba
b
min
60 s
1000 N · m
5 83.8 kW
n· = 4000 rpm
T = 200 N·m
FIGURE 2–31
Schematic for Example 2–7.
(or 112 hp)
Discussion Note that power transmitted by a shaft is proportional to torque
and the rotational speed.
Rest
position
Spring Work
dx
It is common knowledge that when a force is applied on a spring, the length
of the spring changes (Fig. 2–32). When the length of the spring changes by
a differential amount dx under the influence of a force F, the work done is
dWspring 5 F dx
(2–27)
To determine the total spring work, we need to know a functional relationship between F and x. For linear elastic springs, the displacement x is proportional to the force applied (Fig. 2–33). That is,
F 5 kx
(kN)
FIGURE 2–32
Elongation of a spring
under the influence of a force.
(2–28)
where k is the spring constant and has the unit kN/m. The displacement x is
measured from the undisturbed position of the spring (that is, x 5 0 when
F 5 0). Substituting Eq. 2–28 into Eq. 2–27 and integrating yield
Wspring 5 12k(x 22 2 x 21)
F
x
(kJ)
(2–29)
where x1 and x2 are the initial and the final displacements of the spring,
respectively, measured from the undisturbed position of the spring.
There are many other forms of mechanical work. Next we introduce some
of them briefly.
Work Done on Elastic Solid Bars
Solids are often modeled as linear springs because under the action of a
force they contract or elongate, as shown in Fig. 2–34, and when the force
Rest
position
x1 = 1 mm
x2 = 2 mm
F1 = 300 N
F2 = 600 N
FIGURE 2–33
The displacement of a linear spring
doubles when the force is doubled.
68
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
is lifted, they return to their original lengths, like a spring. This is true as
long as the force is in the elastic range, that is, not large enough to cause
permanent (plastic) deformations. Therefore, the equations given for a linear
spring can also be used for elastic solid bars. Alternately, we can determine
the work associated with the expansion or contraction of an elastic solid bar
by replacing pressure P by its counterpart in solids, normal stress sn 5 F/A,
in the work expression:
x
Welastic 5
F
#
2
2
F dx 5
1
FIGURE 2–34
Solid bars behave as springs under the
influence of a force.
# s A dx
n
(kJ)
(2–30)
1
where A is the cross-sectional area of the bar. Note that the normal stress
has pressure units.
Work Associated with the Stretching of a Liquid Film
Rigid wire frame
Surface of film
Movable
wire
F
b
Dx
x
2
ss
Liquid film
ss
Consider a liquid film such as soap film suspended on a wire frame
(Fig. 2–35). We know from experience that it will take some force to stretch
this film by the movable portion of the wire frame. This force is used to
overcome the microscopic forces between molecules at the liquid–air interfaces. These microscopic forces are perpendicular to any line in the surface,
and the force generated by these forces per unit length is called the surface tension ss, whose unit is N/m. Therefore, the work associated with
the stretching of a film is also called surface tension work. It is determined
from
F
Wire
FIGURE 2–35
Stretching a liquid film with a
U-shaped wire, and the forces acting
on the movable wire of length b.
Wsurface 5
# s dA
s
(kJ)
(2–31)
1
where dA 5 2b dx is the change in the surface area of the film. The factor 2
is due to the fact that the film has two surfaces in contact with air. The force
acting on the movable wire as a result of surface tension effects is F 5 2bss
where ss is the surface tension force per unit length.
Work Done to Raise or to Accelerate a Body
Motor
Elevator
car
FIGURE 2–36
The energy transferred to a
body while being raised is equal
to the change in its potential energy.
When a body is raised in a gravitational field, its potential energy increases.
Likewise, when a body is accelerated, its kinetic energy increases. The conservation of energy principle requires that an equivalent amount of energy
must be transferred to the body being raised or accelerated. Remember
that energy can be transferred to a given mass by heat and work, and the
energy transferred in this case obviously is not heat since it is not driven by
a temperature difference. Therefore, it must be work. Then we conclude that
(1) the work transfer needed to raise a body is equal to the change in the
potential energy of the body, and (2) the work transfer needed to accelerate
a body is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the body (Fig. 2–36).
Similarly, the potential or kinetic energy of a body represents the work that
can be obtained from the body as it is lowered to the reference level or
decelerated to zero velocity.
This discussion together with the consideration for friction and other
losses form the basis for determining the required power rating of motors
used to drive devices such as elevators, escalators, conveyor belts, and ski
69
CHAPTER 2
lifts. It also plays a primary role in the design of automotive and aircraft
engines, and in the determination of the amount of hydroelectric power
that can be produced from a given water reservoir, which is simply the
potential energy of the water relative to the location of the hydraulic
turbine.
EXAMPLE 2–8
Power Needs of a Car to Climb a Hill
Consider a 1200-kg car cruising steadily on a level road at 90 km/h. Now the
car starts climbing a hill that is sloped 308 from the horizontal (Fig. 2–37). If
the velocity of the car is to remain constant during climbing, determine the
additional power that must be delivered by the engine.
90 km/h
SOLUTION A car is to climb a hill while maintaining a constant velocity.
The additional power needed is to be determined.
Analysis The additional power required is simply the work that needs to be
done per unit time to raise the elevation of the car, which is equal to the
change in the potential energy of the car per unit time:
30°
#
Wg 5 mg Dz/Dt 5 mgVvertical
5 (1200 kg)(9.81 m/s2)(90 km/h)(sin 308)a
5 147 kJ/s 5 147 kW
m = 1200 kg
FIGURE 2–37
Schematic for Example 2–8.
1 kJ/kg
1 m/s
b
ba
3.6 km/h 1000 m2/s2
(or 197 hp)
Discussion Note that the car engine will have to produce almost 200 hp
of additional power while climbing the hill if the car is to maintain its
velocity.
0
EXAMPLE 2–9
Power Needs of a Car to Accelerate
80 km/h
m = 900 kg
Determine the power required to accelerate a 900-kg car shown in Fig. 2–38
from rest to a velocity of 80 km/h in 20 s on a level road.
SOLUTION The power required to accelerate a car to a specified velocity is
to be determined.
Analysis The work needed to accelerate a body is simply the change in the
kinetic energy of the body,
Wa 5 12m(V 22 2 V 21) 5 12(900 kg) c a
1 kJ/kg
80,000 m 2
b
b 2 02 d a
3600 s
1000 m2/s2
5 222 kJ
The average power is determined from
Wa
#
222 kJ
Wa 5
5
5 11.1 kW
Dt
20 s
(or 14.9 hp)
Discussion This is in addition to the power required to overcome friction,
rolling resistance, and other imperfections.
FIGURE 2–38
Schematic for Example 2–9.
70
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
Nonmechanical Forms of Work
The treatment in Section 2–5 represents a fairly comprehensive coverage of
mechanical forms of work except the moving boundary work that is covered
in Chap. 4. Some work modes encountered in practice are not mechanical in
nature. However, these nonmechanical work modes can be treated in a similar
manner by identifying a generalized force F acting in the direction of a generalized displacement x. Then the work associated with the differential displacement under the influence of this force is determined from dW 5 Fdx.
Some examples of nonmechanical work modes are electrical work,
where the generalized force is the voltage (the electrical potential) and
the generalized displacement is the electrical charge, as discussed earlier;
magnetic work, where the generalized force is the magnetic field strength
and the generalized displacement is the total magnetic dipole moment; and
electrical polarization work, where the generalized force is the electric
field strength and the generalized displacement is the polarization of the
medium (the sum of the electric dipole rotation moments of the molecules).
Detailed consideration of these and other nonmechanical work modes can
be found in specialized books on these topics.
2–6
m
PE1 = 10 kJ
KE1 = 0
Δz
m
PE 2 = 7 kJ
KE2 = 3 kJ
FIGURE 2–39
Energy cannot be created or destroyed;
it can only change forms.
■
THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
So far, we have considered various forms of energy such as heat Q, work
W, and total energy E individually, and no attempt is made to relate them to
each other during a process. The first law of thermodynamics, also known as
the conservation of energy principle, provides a sound basis for studying the
relationships among the various forms of energy and energy interactions.
Based on experimental observations, the first law of thermodynamics states
that energy can be neither created nor destroyed during a process; it can
only change forms. Therefore, every bit of energy should be accounted for
during a process.
We all know that a rock at some elevation possesses some potential
energy, and part of this potential energy is converted to kinetic energy as the
rock falls (Fig. 2–39). Experimental data show that the decrease in potential
energy (mg Dz) exactly equals the increase in kinetic energy [m(V 22 2 V 21)/2]
when the air resistance is negligible, thus confirming the conservation of
energy principle for mechanical energy.
Consider a system undergoing a series of adiabatic processes from a specified state 1 to another specified state 2. Being adiabatic, these processes
obviously cannot involve any heat transfer, but they may involve several
kinds of work interactions. Careful measurements during these experiments
indicate the following: For all adiabatic processes between two specified
states of a closed system, the net work done is the same regardless of the
nature of the closed system and the details of the process. Considering that
there are an infinite number of ways to perform work interactions under adiabatic conditions, this statement appears to be very powerful, with a potential for far-reaching implications. This statement, which is largely based on
the experiments of Joule in the first half of the nineteenth century, cannot be
drawn from any other known physical principle and is recognized as a fundamental principle. This principle is called the first law of thermodynamics or just the first law.
71
CHAPTER 2
A major consequence of the first law is the existence and the definition
of the property total energy E. Considering that the net work is the same
for all adiabatic processes of a closed system between two specified states,
the value of the net work must depend on the end states of the system only,
and thus it must correspond to a change in a property of the system. This
property is the total energy. Note that the first law makes no reference to
the value of the total energy of a closed system at a state. It simply states
that the change in the total energy during an adiabatic process must be
equal to the net work done. Therefore, any convenient arbitrary value can be
assigned to total energy at a specified state to serve as a reference point.
Implicit in the first law statement is the conservation of energy. Although
the essence of the first law is the existence of the property total energy, the
first law is often viewed as a statement of the conservation of energy principle. Next, we develop the first law or the conservation of energy relation
with the help of some familiar examples using intuitive arguments.
First, we consider some processes that involve heat transfer but no work
interactions. The potato baked in the oven is a good example for this case
(Fig. 2–40). As a result of heat transfer to the potato, the energy of the
potato will increase. If we disregard any mass transfer (moisture loss from
the potato), the increase in the total energy of the potato becomes equal
to the amount of heat transfer. That is, if 5 kJ of heat is transferred to the
potato, the energy increase of the potato will also be 5 kJ.
As another example, consider the heating of water in a pan on top of a
range (Fig. 2–41). If 15 kJ of heat is transferred to the water from the heating element and 3 kJ of it is lost from the water to the surrounding air,
the increase in energy of the water will be equal to the net heat transfer to
water, which is 12 kJ.
Now consider a well-insulated (i.e., adiabatic) room heated by an electric
heater as our system (Fig. 2–42). As a result of electrical work done, the
energy of the system will increase. Since the system is adiabatic and cannot
have any heat transfer to or from the surroundings (Q 5 0), the conservation
of energy principle dictates that the electrical work done on the system must
equal the increase in energy of the system.
Next, let us replace the electric heater with a paddle wheel (Fig. 2–43).
As a result of the stirring process, the energy of the system will increase.
Again, since there is no heat interaction between the system and its surroundings (Q 5 0), the shaft work done on the system must show up as an
increase in the energy of the system.
Many of you have probably noticed that the temperature of air rises when
it is compressed (Fig. 2–44). This is because energy is transferred to the air
in the form of boundary work. In the absence of any heat transfer (Q 5 0),
the entire boundary work will be stored in the air as part of its total energy.
The conservation of energy principle again requires that the increase in the
energy of the system be equal to the boundary work done on the system.
We can extend these discussions to systems that involve various heat and
work interactions simultaneously. For example, if a system gains 12 kJ of
heat during a process while 6 kJ of work is done on it, the increase in the
energy of the system during that process is 18 kJ (Fig. 2–45). That is, the
change in the energy of a system during a process is simply equal to the net
energy transfer to (or from) the system.
Qin = 5 kJ
Potato
D E = 5 kJ
FIGURE 2–40
The increase in the energy of a
potato in an oven is equal to the
amount of heat transferred to it.
Qout = 3 kJ
ΔE = Qnet = 12 kJ
Qin = 15 kJ
FIGURE 2–41
In the absence of any work interactions,
the energy change of a system is equal
to the net heat transfer.
(Adiabatic)
Win = 5 kJ
ΔE = 5 kJ
–
+
Battery
FIGURE 2–42
The work (electrical) done on an
adiabatic system is equal to the
increase in the energy of the system.
72
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
Energy Balance
(Adiabatic)
ΔE = 8 kJ
Wsh,in = 8 kJ
In the light of the preceding discussions, the conservation of energy principle can be expressed as follows: The net change (increase or decrease)
in the total energy of the system during a process is equal to the difference
between the total energy entering and the total energy leaving the system
during that process. That is,
a
FIGURE 2–43
The work (shaft) done on an adiabatic
system is equal to the increase in the
energy of the system.
Wb,in = 10 kJ
Total energy
Total energy
Change in the total
b 2 a
b 5 a
b
entering the system
leaving the system
energy of the system
or
Ein 2 Eout 5 DEsystem
This relation is often referred to as the energy balance and is applicable to
any kind of system undergoing any kind of process. The successful use of
this relation to solve engineering problems depends on understanding the
various forms of energy and recognizing the forms of energy transfer.
Energy Change of a System, DEsystem
The determination of the energy change of a system during a process
involves the evaluation of the energy of the system at the beginning and at
the end of the process, and taking their difference. That is,
Energy change 5 Energy at final state 2 Energy at initial state
ΔE = 10 kJ
or
DEsystem 5 Efinal 2 Einitial 5 E2 2 E1
(Adiabatic)
FIGURE 2–44
The work (boundary) done on an
adiabatic system is equal to the
increase in the energy of the system.
Qout = 3 kJ
ΔE = (15 – 3) + 6
= 18 kJ
Note that energy is a property, and the value of a property does not change
unless the state of the system changes. Therefore, the energy change of a
system is zero if the state of the system does not change during the process. Also, energy can exist in numerous forms such as internal (sensible,
latent, chemical, and nuclear), kinetic, potential, electric, and magnetic,
and their sum constitutes the total energy E of a system. In the absence of
electric, magnetic, and surface tension effects (i.e., for simple compressible
systems), the change in the total energy of a system during a process is the
sum of the changes in its internal, kinetic, and potential energies and can be
expressed as
DE 5 DU 1 DKE 1 DPE
Wsh,in = 6 kJ
(2–32)
(2–33)
where
DU 5 m(u2 2 u1)
DKE 5 12 m(V 22 2 V 21 )
Qin = 15 kJ
FIGURE 2–45
The energy change of a system during
a process is equal to the net work and
heat transfer between the system and
its surroundings.
DPE 5 mg(z2 2 z1)
When the initial and final states are specified, the values of the specific
internal energies u1 and u2 can be determined directly from the property
tables or thermodynamic property relations.
Most systems encountered in practice are stationary, that is, they do not
involve any changes in their velocity or elevation during a process (Fig. 2–46).
73
CHAPTER 2
Thus, for stationary systems, the changes in kinetic and potential energies
are zero (that is, DKE 5 DPE 5 0), and the total energy change relation in
Eq. 2–33 reduces to DE 5 DU for such systems. Also, the energy of a system during a process will change even if only one form of its energy changes
while the other forms of energy remain unchanged.
Stationary Systems
z1 = z2 → ΔPE = 0
V1 = V2 → ΔKE = 0
ΔE = ΔU
Mechanisms of Energy Transfer, Ein and Eout
Energy can be transferred to or from a system in three forms: heat, work,
and mass flow. Energy interactions are recognized at the system boundary as
they cross it, and they represent the energy gained or lost by a system during a process. The only two forms of energy interactions associated with a
fixed mass or closed system are heat transfer and work.
1. Heat Transfer, Q Heat transfer to a system (heat gain) increases the
energy of the molecules and thus the internal energy of the system, and
heat transfer from a system (heat loss) decreases it since the energy
transferred out as heat comes from the energy of the molecules of the
system.
2. Work Transfer, W An energy interaction that is not caused by a temperature difference between a system and its surroundings is work. A
rising piston, a rotating shaft, and an electrical wire crossing the system
boundaries are all associated with work interactions. Work transfer to a
system (i.e., work done on a system) increases the energy of the system, and work transfer from a system (i.e., work done by the system)
decreases it since the energy transferred out as work comes from the
energy contained in the system. Car engines and hydraulic, steam, or gas
turbines produce work while compressors, pumps, and mixers consume
work.
3. Mass Flow, m Mass flow in and out of the system serves as an
additional mechanism of energy transfer. When mass enters a system,
the energy of the system increases because mass carries energy with it
(in fact, mass is energy). Likewise, when some mass leaves the system,
the energy contained within the system decreases because the leaving
mass takes out some energy with it. For example, when some hot water
is taken out of a water heater and is replaced by the same amount of
cold water, the energy content of the hot-water tank (the control volume)
decreases as a result of this mass interaction (Fig. 2–47).
Noting that energy can be transferred in the forms of heat, work, and mass,
and that the net transfer of a quantity is equal to the difference between
the amounts transferred in and out, the energy balance can be written more
explicitly as
Ein 2 Eout 5 (Qin 2 Qout) 1 (Win 2 Wout) 1 (Emass, in 2 Emass, out) 5 DEsystem (2–34)
where the subscripts “in” and “out” denote quantities that enter and leave
the system, respectively. All six quantities on the right side of the equation
represent “amounts,” and thus they are positive quantities. The direction of
any energy transfer is described by the subscripts “in” and “out.”
The heat transfer Q is zero for adiabatic systems, the work transfer W is
zero for systems that involve no work interactions, and the energy transport
FIGURE 2–46
For stationary systems,
DKE 5 DPE 5 0; thus DE 5 DU.
W
Mass
in
Control
volume
Q
Mass
out
FIGURE 2–47
The energy content of a control
volume can be changed by mass flow
as well as heat and work interactions.
74
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
with mass Emass is zero for systems that involve no mass flow across their
boundaries (i.e., closed systems).
Energy balance for any system undergoing any kind of process can be
expressed more compactly as
Ein 2 Eout
5
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
DEsystem
(kJ)
(2–35)
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
or, in the rate form, as
.
.
E in 2 Eout
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
dEsystem/dt
(kW)
(2–36)
Rate of change in internal,
kinetic, potential, etc., energies
For constant rates, the total quantities during a time interval Dt are related to
the quantities per unit time as
#
#
Q 5 Q Dt, W 5 W Dt, and DE 5 (dE/dt) Dt
(kJ)
(2–37)
The energy balance can be expressed on a per unit mass basis as
ein 2 eout 5 Desystem
(kJ/kg)
(2–38)
which is obtained by dividing all the quantities in Eq. 2–35 by the mass m of
the system. Energy balance can also be expressed in the differential form as
dEin 2 dEout 5 dEsystem or dein 2 deout 5 desystem
P
For a closed system undergoing a cycle, the initial and final states are identical, and thus DEsystem 5 E2 2 E1 5 0. Then the energy balance for a cycle
simplifies to Ein 2 Eout 5 0 or Ein 5 Eout. Noting that a closed system does
not involve any mass flow across its boundaries, the energy balance for a
cycle can be expressed in terms of heat and work interactions as
Qnet = Wnet
#
#
Wnet, out 5 Qnet, in or Wnet, out 5 Qnet, in
V
FIGURE 2–48
For a cycle DE 5 0, thus Q 5 W.
(for a cycle)
(2–40)
That is, the net work output during a cycle is equal to net heat input
(Fig. 2–48).
EXAMPLE 2–10
Cooling of a Hot Fluid in a Tank
A rigid tank contains a hot fluid that is cooled while being stirred by a paddle wheel. Initially, the internal energy of the fluid is 800 kJ. During the
cooling process, the fluid loses 500 kJ of heat, and the paddle wheel does
100 kJ of work on the fluid. Determine the final internal energy of the fluid.
Neglect the energy stored in the paddle wheel.
Qout = 500 kJ
U1 = 800 kJ
U2 = ?
(2–39)
Wsh,in = 100 kJ
Fluid
FIGURE 2–49
Schematic for Example 2–10.
SOLUTION A fluid in a rigid tank looses heat while being stirred. The final
internal energy of the fluid is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 The tank is stationary and thus the kinetic and potential
energy changes are zero, DKE 5 DPE 5 0. Therefore, DE 5 DU and internal
energy is the only form of the system’s energy that may change during this
process. 2 Energy stored in the paddle wheel is negligible.
Analysis Take the contents of the tank as the system (Fig. 2–49). This is
a closed system since no mass crosses the boundary during the process.
75
CHAPTER 2
We observe that the volume of a rigid tank is constant, and thus there is no
moving boundary work. Also, heat is lost from the system and shaft work is
done on the system. Applying the energy balance on the system gives
Ein 2 Eout
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
DEsystem
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
Wsh, in 2 Qout 5 DU 5 U2 2 U1
100 kJ 2 500 kJ 5 U2 2 800 kJ
U2 5 400 kJ
Therefore, the final internal energy of the system is 400 kJ.
EXAMPLE 2–11
8 m/s
Acceleration of Air by a Fan
Fan
A fan that consumes 20 W of electric power when operating is claimed to
discharge air from a ventilated room at a rate of 1.0 kg/s at a discharge
velocity of 8 m/s (Fig. 2–50). Determine if this claim is reasonable.
SOLUTION A fan is claimed to increase the velocity of air to a specified
value while consuming electric power at a specified rate. The validity of this
claim is to be investigated.
Assumptions The ventilating room is relatively calm, and air velocity in it is
negligible.
Analysis First, let’s examine the energy conversions involved: The motor
of the fan converts part of the electrical power it consumes to mechanical
(shaft) power, which is used to rotate the fan blades in air. The blades are
shaped such that they impart a large fraction of the mechanical power of
the shaft to air by mobilizing it. In the limiting ideal case of no losses (no
conversion of electrical and mechanical energy to thermal energy) in steady
operation, the electric power input will be equal to the rate of increase of
the kinetic energy of air. Therefore, for a control volume that encloses the
fan-motor unit, the energy balance can be written as
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
#
#
dEsystem /dt Q 0 (steady) 5 0 S Ein 5 Eout
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
2
#
#
# V out
Welect, in 5 mair keout 5 mair
2
Solving for Vout and substituting gives the maximum air outlet velocity to be
#
2Welect, in
2(20 J/s) 1 m2/s2
Vout 5
5
a
b 5 6.3 m/s
#
Å mair
Å 1.0 kg/s 1 J/kg
which is less than 8 m/s. Therefore, the claim is false.
Discussion The conservation of energy principle requires the energy to be preserved as it is converted from one form to another, and it does not allow any
energy to be created or destroyed during a process. From the first law point of
view, there is nothing wrong with the conversion of the entire electrical energy
Air
FIGURE 2–50
Schematic for Example 2–11.
76
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
into kinetic energy. Therefore, the first law has no objection to air velocity
reaching 6.3 m/s—but this is the upper limit. Any claim of higher velocity is
in violation of the first law, and thus impossible. In reality, the air velocity will
be considerably lower than 6.3 m/s because of the losses associated with the
conversion of electrical energy to mechanical shaft energy, and the conversion
of mechanical shaft energy to kinetic energy or air.
Qout
EXAMPLE 2–12
Room
Welect. in
Fan
FIGURE 2–51
Schematic for Example 2–12.
Heating Effect of a Fan
A room is initially at the outdoor temperature of 258C. Now a large fan
that consumes 200 W of electricity when running is turned on (Fig. 2–51).
The heat transfer rate between the room and the outdoor air is given as
·
Q 5 UA(Ti 2 To) where U 5 6 W/m2·8C is the overall heat transfer coefficient, A 5 30 m2 is the exposed surface area of the room, and Ti and To are
the indoor and outdoor air temperatures, respectively. Determine the indoor
air temperature when steady operating conditions are established.
SOLUTION A large fan is turned on and kept on in a room that looses heat
to the outdoors. The indoor air temperature is to be determined when steady
operation is reached.
Assumptions 1 Heat transfer through the floor is negligible. 2 There are no
other energy interactions involved.
Analysis The electricity consumed by the fan is energy input for the room,
and thus the room gains energy at a rate of 200 W. As a result, the room air
temperature tends to rise. But as the room air temperature rises, the rate of
heat loss from the room increases until the rate of heat loss equals the electric power consumption. At that point, the temperature of the room air, and
thus the energy content of the room, remains constant, and the conservation
of energy for the room becomes
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
5
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
#
#
dEsystem/dt Q 0(steady) 5 0 S Ein 5 Eout
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
#
#
Welect, in 5 Qout 5 UA(Ti 2 To)
Substituting,
200 W 5 (6 W/m2· 8C) (30 m2) (Ti 2 258C)
It gives
Ti 5 26.18C
Therefore, the room air temperature will remain constant after it reaches
26.18C.
Discussion Note that a 200-W fan heats a room just like a 200-W resistance heater. In the case of a fan, the motor converts part of the electric
energy it draws to mechanical energy in the form of a rotating shaft while
the remaining part is dissipated as heat to the room air because of the motor
inefficiency (no motor converts 100 percent of the electric energy it receives
to mechanical energy, although some large motors come close with a conversion efficiency of over 97 percent). Part of the mechanical energy of the
77
CHAPTER 2
shaft is converted to kinetic energy of air through the blades, which is then
converted to thermal energy as air molecules slow down because of friction.
At the end, the entire electric energy drawn by the fan motor is converted to
thermal energy of air, which manifests itself as a rise in temperature.
EXAMPLE 2–13
Annual Lighting Cost of a Classroom
The lighting needs of a classroom are met by 30 fluorescent lamps, each
consuming 80 W of electricity (Fig. 2–52). The lights in the classroom are
kept on for 12 hours a day and 250 days a year. For a unit electricity cost
of 11 cents per kWh, determine annual energy cost of lighting for this classroom. Also, discuss the effect of lighting on the heating and air-conditioning
requirements of the room.
SOLUTION
The lighting of a classroom by fluorescent lamps is considered.
The annual electricity cost of lighting for this classroom is to be determined,
and the lighting’s effect on the heating and air-conditioning requirements is
to be discussed.
Assumptions The effect of voltage fluctuations is negligible so that each
fluorescent lamp consumes its rated power.
Analysis The electric power consumed by the lamps when all are on and
the number of hours they are kept on per year are
Lighting power 5 (Power consumed per lamp) 3 (No. of lamps)
5 (80 W/lamp)(30 lamps)
5 2400 W 5 2.4 kW
Operating hours 5 (12 h/day)(250 days/year) 5 3000 h/year
Then the amount and cost of electricity used per year become
Lighting energy 5 (Lighting power)(Operating hours)
5 (2.4 kW)(3000 h/year) 5 7200 kWh/year
Lighting cost 5 (Lighting energy)(Unit cost)
5 (7200 kWh/year)($0.11/kWh) 5 $792/year
Light is absorbed by the surfaces it strikes and is converted to thermal energy.
Disregarding the light that escapes through the windows, the entire 2.4 kW
of electric power consumed by the lamps eventually becomes part of thermal
energy of the classroom. Therefore, the lighting system in this room reduces
the heating requirements by 2.4 kW, but increases the air-conditioning load
by 2.4 kW.
Discussion Note that the annual lighting cost of this classroom alone
is close to $800. This shows the importance of energy conservation
measures. If incandescent light bulbs were used instead of fluorescent
tubes, the lighting costs would be four times as much since incandescent lamps use four times as much power for the same amount of light
produced.
FIGURE 2–52
Fluorescent lamps lighting a classroom
as discussed in Example 2–13.
©PhotoLink/Getty Images RF
78
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
2–7
■
ENERGY CONVERSION EFFICIENCIES
Efficiency is one of the most frequently used terms in thermodynamics, and it indicates how well an energy conversion or transfer process
is accomplished. Efficiency is also one of the most frequently misused
terms in thermodynamics and a source of misunderstandings. This is
because efficiency is often used without being properly defined first.
Next, we will clarify this further and define some efficiencies commonly
used in practice.
Efficiency, in general, can be expressed in terms of the desired output and
the required input as
Efficiency 5
Water heater
Type
Efficiency
Gas, conventional
Gas, high-efficiency
Electric, conventional
Electric, high-efficiency
55%
62%
90%
94%
FIGURE 2–53
Typical efficiencies of conventional
and high-efficiency electric and
natural gas water heaters.
©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Christopher
Kerrigan, photographer
Combustion gases
25°C CO2, H2O, N2, etc.
LHV = 44,000 kJ/kg
Air
25°C
Combustion
chamber
1 kg
Gasoline
25°C
FIGURE 2–54
The definition of the heating
value of gasoline.
Desired output
Required input
(2–41)
If you are shopping for a water heater, a knowledgeable salesperson will
tell you that the efficiency of a conventional electric water heater is about
90 percent (Fig. 2–53). You may find this confusing, since the heating elements of electric water heaters are resistance heaters, and the efficiency
of all resistance heaters is 100 percent as they convert all the electrical
energy they consume into thermal energy. A knowledgeable salesperson
will clarify this by explaining that the heat losses from the hot-water tank
to the surrounding air amount to 10 percent of the electrical energy consumed, and the efficiency of a water heater is defined as the ratio of the
energy delivered to the house by hot water to the energy supplied to the
water heater. A clever salesperson may even talk you into buying a more
expensive water heater with thicker insulation that has an efficiency of 94
percent. If you are a knowledgeable consumer and have access to natural
gas, you will probably purchase a gas water heater whose efficiency is
only 55 percent since a gas unit costs about the same as an electric unit to
purchase and install, but the annual energy cost of a gas unit will be much
less than that of an electric unit.
Perhaps you are wondering how the efficiency for a gas water heater is
defined, and why it is much lower than the efficiency of an electric heater.
As a general rule, the efficiency of equipment that involves the combustion
of a fuel is based on the heating value of the fuel, which is the amount of
heat released when a unit amount of fuel at room temperature is completely
burned and the combustion products are cooled to the room temperature
(Fig. 2–54). Then the performance of combustion equipment can be characterized by combustion efficiency, defined as
hcombustion 5
Amount of heat released during combustion
Q
5
HV
Heating value of the fuel burned
(2–42)
A combustion efficiency of 100 percent indicates that the fuel is burned
completely and the stack gases leave the combustion chamber at room temperature, and thus the amount of heat released during a combustion process
is equal to the heating value of the fuel.
Most fuels contain hydrogen, which forms water when burned, and the
heating value of a fuel will be different, depending on whether the water
79
CHAPTER 2
in combustion products is in the liquid or vapor form. The heating value is
called the lower heating value, or LHV, when the water leaves as a vapor,
and the higher heating value, or HHV, when the water in the combustion
gases is completely condensed and thus the heat of vaporization is also
recovered. The difference between these two heating values is equal to the
product of the amount of water and the enthalpy of vaporization of water at
room temperature. For example, the lower and higher heating values of gasoline are 44,000 kJ/kg and 47,300 kJ/kg, respectively. An efficiency definition
should make it clear whether it is based on the higher or lower heating value
of the fuel. Efficiencies of cars and jet engines are normally based on lower
heating values since water normally leaves as a vapor in the exhaust gases,
and it is not practical to try to recuperate the heat of vaporization. Efficiencies of furnaces, on the other hand, are based on higher heating values.
The efficiency of space heating systems of residential and commercial buildings is usually expressed in terms of the annual fuel utilization efficiency, or
AFUE, which accounts for the combustion efficiency as well as other losses
such as heat losses to unheated areas and start-up and cool-down losses. The
AFUE of most new heating systems is about 85 percent, although the AFUE of
some old heating systems is under 60 percent. The AFUE of some new highefficiency furnaces exceeds 96 percent, but the high cost of such furnaces cannot be justified for locations with mild to moderate winters. Such high efficiencies are achieved by reclaiming most of the heat in the flue gases, condensing
the water vapor, and discharging the flue gases at temperatures as low as 388C
(or 1008F) instead of about 2008C (or 4008F) for the conventional models.
For car engines, the work output is understood to be the power delivered
by the crankshaft. But for power plants, the work output can be the mechanical power at the turbine exit, or the electrical power output of the generator.
A generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical
energy, and the effectiveness of a generator is characterized by the generator efficiency, which is the ratio of the electrical power output to the
mechanical power input. The thermal efficiency of a power plant, which is
of primary interest in thermodynamics, is usually defined as the ratio of the
net shaft work output of the turbine to the heat input to the working fluid.
The effects of other factors are incorporated by defining an overall efficiency for the power plant as the ratio of the net electrical power output to
the rate of fuel energy input. That is,
#
Wnet,electric
hoverall 5 hcombustion hthermal hgenerator 5
#
HHV 3 mfuel
(2–43)
The overall efficiencies are about 26–30 percent for gasoline automotive
engines, 34–40 percent for diesel engines, and up to 60 percent for large
power plants.
We are all familiar with the conversion of electrical energy to light by
incandescent lightbulbs, fluorescent tubes, and high-intensity discharge
lamps. The efficiency for the conversion of electricity to light can be defined
as the ratio of the energy converted to light to the electrical energy consumed.
For example, common incandescent lightbulbs convert about 5 percent of
the electrical energy they consume to light; the rest of the energy consumed
is dissipated as heat, which adds to the cooling load of the air conditioner
in summer. However, it is more common to express the effectiveness of this
80
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
TABLE 2–1
The efficacy of different lighting
systems
Type of lighting
Efficacy,
lumens/W
Combustion
Candle
Kerosene lamp
0.3
1–2
Incandescent
Ordinary
Halogen
6–20
15–35
Fluorescent
Compact
Tube
40–87
60–120
High-intensity discharge
Mercury vapor
Metal halide
High-pressure sodium
Low-pressure sodium
40–60
65–118
85–140
70–200
Solid-State
LED
OLED
20–160
15–60
Theoretical limit
300*
*This value depends on the spectral distribution
of the assumed ideal light source. For white light
sources, the upper limit is about 300 lm/W for
metal halide, 350 lm/W for fluorescents, and
400 lm/W for LEDs. Spectral maximum occurs
at a wavelength of 555 nm (green) with a light
output of 683 lm/W.
conversion process by lighting efficacy, which is defined as the amount of
light output in lumens per W of electricity consumed.
The efficacy of different lighting systems is given in Table 2–1. Note that
a compact fluorescent lightbulb produces about four times as much light
as an incandescent lightbulb per W, and thus a 15-W fluorescent bulb can
replace a 60-W incandescent lightbulb (Fig. 2–55). Also, a compact fluorescent bulb lasts about 10,000 h, which is 10 times as long as an incandescent
bulb, and it plugs directly into the socket of an incandescent lamp. Therefore, despite their higher initial cost, compact fluorescents reduce the lighting costs considerably through reduced electricity consumption. Sodiumfilled high-intensity discharge lamps provide the most efficient lighting, but
their use is limited to outdoor use because of their yellowish light.
We can also define efficiency for cooking appliances since they convert
electrical or chemical energy to heat for cooking. The efficiency of a cooking appliance can be defined as the ratio of the useful energy transferred
to the food to the energy consumed by the appliance (Fig. 2–56). Electric
ranges are more efficient than gas ranges, but it is much cheaper to cook
with natural gas than with electricity because of the lower unit cost of natural gas (Table 2–2).
The cooking efficiency depends on user habits as well as the individual
appliances. Convection and microwave ovens are inherently more efficient
than conventional ovens. On average, convection ovens save about one-third
and microwave ovens save about two-thirds of the energy used by conventional ovens. The cooking efficiency can be increased by using the smallest oven for baking, using a pressure cooker, using an electric slow cooker
for stews and soups, using the smallest pan that will do the job, using
the smaller heating element for small pans on electric ranges, using flatbottomed pans on electric burners to assure good contact, keeping burner
drip pans clean and shiny, defrosting frozen foods in the refrigerator before
cooking, avoiding preheating unless it is necessary, keeping the pans covered during cooking, using timers and thermometers to avoid overcooking,
using the self-cleaning feature of ovens right after cooking, and keeping
inside surfaces of microwave ovens clean.
TABLE 2–2
Energy costs of cooking a casserole with different appliances*
[From J. T. Amann, A. Wilson, and K. Ackerly, Consumer Guide to Home Energy Savings, 9th ed.,
American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, Washington, D.C., 2007, p. 163.]
15 W
60 W
FIGURE 2–55
A 15-W compact fluorescent lamp
provides as much light as a 60-W
incandescent lamp.
Cooking appliance
Cooking
temperature
Cooking
time
Energy
used
Cost of
energy
Electric oven
Convection oven (elect.)
Gas oven
Frying pan
Toaster oven
Crockpot
Microwave oven
3508F (1778C)
3258F (1638C)
3508F (1778C)
4208F (2168C)
4258F (2188C)
2008F (938C)
“High”
1h
45 min
1h
1h
50 min
7h
15 min
2.0 kWh
1.39 kWh
0.112 therm
0.9 kWh
0.95 kWh
0.7 kWh
0.36 kWh
$0.19
$0.13
$0.13
$0.09
$0.09
$0.07
$0.03
*Assumes a unit cost of $0.095/kWh for electricity and $1.20/therm for gas.
81
CHAPTER 2
Using energy-efficient appliances and practicing energy conservation
measures help our pocketbooks by reducing our utility bills. It also helps
the environment by reducing the amount of pollutants emitted to the atmosphere during the combustion of fuel at home or at the power plants where
electricity is generated. The combustion of each therm of natural gas produces 6.4 kg of carbon dioxide, which causes global climate change; 4.7 g
of nitrogen oxides and 0.54 g of hydrocarbons, which cause smog; 2.0 g
of carbon monoxide, which is toxic; and 0.030 g of sulfur dioxide, which
causes acid rain. Each therm of natural gas saved eliminates the emission of
these pollutants while saving $0.60 for the average consumer in the United
States. Each kWh of electricity conserved saves 0.4 kg of coal and 1.0 kg of
CO2 and 15 g of SO2 from a coal power plant.
2 kW
3 kW
5 kW
Efficiency =
EXAMPLE 2–14
Cost of Cooking with Electric and Gas Ranges
The efficiency of cooking appliances affects the internal heat gain from them
since an inefficient appliance consumes a greater amount of energy for the
same task, and the excess energy consumed shows up as heat in the living
space. The efficiency of open burners is determined to be 73 percent for
electric units and 38 percent for gas units (Fig. 2–57). Consider a 2-kW
electric burner at a location where the unit costs of electricity and natural gas are $0.09/kWh and $1.20/therm, respectively. Determine the rate of
energy consumption by the burner and the unit cost of utilized energy for
both electric and gas burners.
=
Energy utilized
Energy supplied to appliance
3 kWh
= 0.60
5 kWh
FIGURE 2–56
The efficiency of a cooking appliance
represents the fraction of the energy
supplied to the appliance that is
transferred to the food.
SOLUTION The operation of electric and gas ranges is considered. The rate of
energy consumption and the unit cost of utilized energy are to be determined.
Analysis The efficiency of the electric heater is given to be 73 percent.
Therefore, a burner that consumes 2 kW of electrical energy will supply
#
Qutilized 5 (Energy input) 3 (Efficiency) 5 (2 kW)(0.73) 5 1.46 kW
38%
Gas Range
of useful energy. The unit cost of utilized energy is inversely proportional to
the efficiency, and is determined from
Cost of utilized energy 5
Cost of energy input
$0.09/kWh
5
5 $0.123/kWh
Efficiency
0.73
Noting that the efficiency of a gas burner is 38 percent, the energy input
to a gas burner that supplies utilized energy at the same rate (1.46 kW) is
#
Qinput, gas 5
73%
Electric Range
#
Qutilized
1.46 kW
5
5 3.84 kW
Efficiency
0.38
(513,100 Btu/h)
since 1 kW 5 3412 Btu/h. Therefore, a gas burner should have a rating of at
least 13,100 Btu/h to perform as well as the electric unit.
Noting that 1 therm 5 29.3 kWh, the unit cost of utilized energy in the
case of a gas burner is determined to be
Cost of utilized energy 5
Cost of energy input
$1.20/29.3 kWh
5
Efficiency
0.38
5 $0.108/kWh
FIGURE 2–57
Schematic of the 73 percent efficient
electric heating unit and 38 percent
efficient gas burner discussed in
Example 2–14.
82
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
Fan
50.0 W
1
m· = 0.506 kg/s
2
Discussion The cost of utilized gas is less than that of utilized electricity.
Therefore, despite its higher efficiency, cooking with an electric burner will
cost about 14 percent more compared to a gas burner in this case. This
explains why cost-conscious consumers always ask for gas appliances, and it
is not wise to use electricity for heating purposes.
Efficiencies of Mechanical and Electrical Devices
V1 ≈ 0, V2 = 12.1 m/s
z1 = z2
P1 ≈ Patm and P2 ≈ Patm
·
· 2/2
ΔEmech, fluid
mV
2
ηmech, fan = ––––––––––
= –––––––
·
·
Wshaft, in
Wshaft, in
(0.506 kg/s)(12.1 m/s)2/2
= ––––––––––––––––––––
50.0 W
= 0.741
The transfer of mechanical energy is usually accomplished by a rotating
shaft, and thus mechanical work is often referred to as shaft work. A pump
or a fan receives shaft work (usually from an electric motor) and transfers
it to the fluid as mechanical energy (less frictional losses). A turbine, on the
other hand, converts the mechanical energy of a fluid to shaft work. In the
absence of any irreversibilities such as friction, mechanical energy can be
converted entirely from one mechanical form to another, and the mechanical efficiency of a device or process can be defined as (Fig. 2–58)
hmech 5
FIGURE 2–58
The mechanical efficiency
of a fan is the ratio of the rate of
increase of the mechanical energy
of air to the mechanical power input.
Emech, out
Emech, loss
Mechanical energy output
512
5
Mechanical energy input
Emech, in
Emech, in
(2–44)
A conversion efficiency of less than 100 percent indicates that conversion is
less than perfect and some losses have occurred during conversion. A mechanical efficiency of 97 percent indicates that 3 percent of the mechanical energy
input is converted to thermal energy as a result of frictional heating, and this
will manifest itself as a slight rise in the temperature of the fluid.
In fluid systems, we are usually interested in increasing the pressure,
velocity, and/or elevation of a fluid. This is done by supplying mechanical
energy to the fluid by a pump, a fan, or a compressor (we will refer to all
of them as pumps). Or we are interested in the reverse process of extracting mechanical energy from a fluid by a turbine and producing mechanical
power in the form of a rotating shaft that can drive a generator or any other
rotary device. The degree of perfection of the conversion process between
the mechanical work supplied or extracted and the mechanical energy of the
fluid is expressed by the pump efficiency and turbine efficiency, defined as
#
#
Wpump,u
DEmech,fluid
Mechanical energy increase of the fluid
hpump 5
5
5 #
(2–45)
#
Mechanical energy input
Wshaft,in
Wpump
#
#
#
where DEmech, fluid 5 Emech, out 2 Emech, in is the rate of increase in the mechani-
cal energy of the fluid, which is equivalent to the useful pumping power
#
Wpump,u supplied to the fluid, and
#
#
W shaft, out
W turbine
Mechanical energy output
hturbine 5
5
(2–46)
5 #
#
Mechanical energy decrease of the fluid
Z DEmech, fluid Z
W turbine, e
#
#
#
where u DEmech,fluid u 5 Emech,in 2 Emech,out is the rate of decrease in the mechani-
cal energy of the fluid, which is equivalent to the mechanical power extracted
#
from the fluid by the turbine Wturbine, e, and we use the absolute value sign
to avoid negative values for efficiencies. A pump or turbine efficiency of
100 percent indicates perfect conversion between the shaft work and the
mechanical energy of the fluid, and this value can be approached (but never
attained) as the frictional effects are minimized.
83
CHAPTER 2
Electrical energy is commonly converted to rotating mechanical energy
by electric motors to drive fans, compressors, robot arms, car starters, and
so forth. The effectiveness of this conversion process is characterized by
the motor efficiency hmotor, which is the ratio of the mechanical energy
output of the motor to the electrical energy input. The full-load motor
efficiencies range from about 35 percent for small motors to over 97 percent for large high-efficiency motors. The difference between the electrical energy consumed and the mechanical energy delivered is dissipated as
waste heat.
The mechanical efficiency should not be confused with the motor efficiency and the generator efficiency, which are defined as
#
Wshaft, out
Mechanical power output
hmotor 5
5 #
Electric power input
Welect, in
Motor:
and
#
Welect, out
Electric power output
hgenerator 5
5 #
Mechanical power input
Wshaft, in
Generator:
hturbine = 0.75
(2–47)
Welect. out
Turbine
Generator
(2–48)
A pump is usually packaged together with its motor, and a turbine with its
generator. Therefore, we are usually interested in the combined or overall
efficiency of pump–motor and turbine–generator combinations (Fig. 2–59),
which are defined as
hturbine–gen = hturbinehgenerator
= 0.75 0.97
= 0.73
#
#
Wpump, u
DEmech, fluid
hpump2motor 5 hpumphmotor 5 #
5
#
Welect, in
Welect, in
(2–49)
#
#
Welect, out
Welect, out
hturbine 2gen 5 hturbinehgenerator 5 #
5
#
Wturbine, e
Z DEmech, fluidZ
(2–50)
and
All the efficiencies just defined range between 0 and 100 percent. The lower
limit of 0 percent corresponds to the conversion of the entire mechanical or
electric energy input to thermal energy, and the device in this case functions
like a resistance heater. The upper limit of 100 percent corresponds to the
case of perfect conversion with no friction or other irreversibilities, and thus
no conversion of mechanical or electric energy to thermal energy.
EXAMPLE 2–15
hgenerator = 0.97
FIGURE 2–59
The overall efficiency of a turbine–
generator is the product of the
efficiency of the turbine and the
efficiency of the generator, and
represents the fraction of the
mechanical power of the fluid
converted to electrical power.
1
Power Generation from a Hydroelectric Plant
h = 70 m
Electric power is to be generated by installing a hydraulic turbine–generator
at a site 70 m below the free surface of a large water reservoir that can
supply water at a rate of 1500 kg/s steadily (Fig. 2–60). If the mechanical
power output of the turbine is 800 kW and the electric power generation is
750 kW, determine the turbine efficiency and the combined turbine–generator efficiency of this plant. Neglect losses in the pipes.
2
.
m = 1500 kg/s
Generator
Turbine
SOLUTION
A hydraulic turbine-generator installed at a large reservoir is to
generate electricity. The combined turbine–generator efficiency and the turbine efficiency are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 The water elevation in the reservoir remains constant. 2 The
mechanical energy of water at the turbine exit is negligible.
FIGURE 2–60
Schematic for Example 2–15.
84
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
Analysis We take the free surface of water in the reservoir to be point 1
and the turbine exit to be point 2. We also take the turbine exit as the reference level (z2 5 0) so that the potential energies at 1 and 2 are pe1 5 gz1
and pe2 5 0. The flow energy P/r at both points is zero since both 1 and 2
are open to the atmosphere (P1 5 P2 5 Patm). Further, the kinetic energy at
both points is zero (ke1 5 ke2 5 0) since the water at point 1 is essentially
motionless, and the kinetic energy of water at turbine exit is assumed to be
negligible. The potential energy of water at point 1 is
pe1 5 gz1 5 (9.81 m /s2)(70 m)a
1 kJ/ kg
b 5 0.687 kJ/ kg
1000 m2/s2
Then the rate at which the mechanical energy of water is supplied to the
turbine becomes
#
#
#
#
u DEmech, fluid u 5 m(emech, in 2 emech, out) 5 m(pe1 2 0) 5 mpe1
5 (1500 kg/s)(0.687 kJ/kg)
5 1031 kW
The combined turbine–generator and the turbine efficiency are determined
from their definitions to be
#
W elect, out
750 kW
hturbine 2gen 5
5 0.727 or 72.7%
5
#
1031 kW
u DEmech, fluid u
#
W elect, out
800kW
5
5 0.776 or 77.6%
hturbine 5 #
1031kW
u Emech, fluid u
Therefore, the reservoir supplies 1031 kW of mechanical energy to the turbine, which converts 800 kW of it to shaft work that drives the generator,
which then generates 750 kW of electric power.
Discussion This problem can also be solved by taking point 1 to be at the
turbine inlet, and using flow energy instead of potential energy. It would give
the same result since the flow energy at the turbine inlet is equal to the
potential energy at the free surface of the reservoir.
60 hp
h = 89.0%
Standard motor
EXAMPLE 2–16
Cost Savings Associated with High-Efficiency
Motors
A 60-hp electric motor (a motor that delivers 60 hp of shaft power at full
load) that has an efficiency of 89.0 percent is worn out and is to be replaced
by a 93.2 percent efficient high-efficiency motor (Fig. 2–61). The motor
operates 3500 hours a year at full load. Taking the unit cost of electricity to
be $0.08/kWh, determine the amount of energy and money saved as a result
of installing the high-efficiency motor instead of the standard motor. Also,
determine the simple payback period if the purchase prices of the standard
and high-efficiency motors are $4520 and $5160, respectively.
60 hp
h = 93.2%
High-efficiency motor
FIGURE 2–61
Schematic for Example 2–16.
SOLUTION
A worn-out standard motor is to be replaced by a high-efficiency
one. The amount of electrical energy and money saved as well as the simple
payback period are to be determined.
85
CHAPTER 2
Assumptions The load factor of the motor remains constant at 1 (full load)
when operating.
Analysis The electric power drawn by each motor and their difference can
be expressed as
#
#
Welectric in, standard 5 Wshaft/hst 5 (Rated power)(Load factor)/hst
#
#
Welectric in, efficient 5 Wshaft/heff 5 (Rated power)(Load factor)/heff
#
#
Power savings 5 Welectric in, standard 2 Welectric in, efficient
5 (Rated power)(Load factor)(1/hst 2 1/heff)
where hst is the efficiency of the standard motor, and heff is the efficiency
of the comparable high-efficiency motor. Then the annual energy and cost
savings associated with the installation of the high-efficiency motor become
Energy savings 5 (Power savings)(Operating hours)
5 (Rated power)(Operating hours)(Load factor)(1/hst 2 1heff)
5 (60 hp)(0.7457 kW/hp)(3500 h/year)(1)(1/0.89 2 1/0.93.2)
5 7929 kWh/year
Cost savings 5 (Energy savings)(Unit cost of energy)
5 (7929 kWh/year)($0.08/kWh)
5 $634/year
Also,
Excess initial cost 5 Purchase price differential 5 $5160 5 $4520 5 $640
This gives a simple payback period of
Simple payback period 5
$640
Excess initial cost
5
5 1.01 year
Annual cost savings
$634/year
Discussion Note that the high-efficiency motor pays for its price differential
within about one year from the electrical energy it saves. Considering that
the service life of electric motors is several years, the purchase of the higher
efficiency motor is definitely indicated in this case.
2–8
■
ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT
The conversion of energy from one form to another often affects the environment and the air we breathe in many ways, and thus the study of energy is
not complete without considering its impact on the environment (Fig. 2–62).
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas have been powering the industrial development and the amenities of modern life that we enjoy since the
1700s, but this has not been without any undesirable side effects. From the
soil we farm and the water we drink to the air we breathe, the environment
has been paying a heavy toll for it. Pollutants emitted during the combustion
of fossil fuels are responsible for smog, acid rain, global warming, and climate change. The environmental pollution has reached such high levels that
FIGURE 2–62
Energy conversion processes are often
accompanied by environmental
pollution.
©Comstock Images/Alamy RF
86
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
NOx
CO
HC
FIGURE 2–63
Motor vehicles are the largest
source of air pollution.
it became a serious threat to vegetation, wild life, and human health. Air
pollution has been the cause of numerous health problems including asthma
and cancer. It is estimated that over 60,000 people in the United States alone
die each year due to heart and lung diseases related to air pollution.
Hundreds of elements and compounds such as benzene and formaldehyde
are known to be emitted during the combustion of coal, oil, natural gas, and
wood in electric power plants, engines of vehicles, furnaces, and even fireplaces. Some compounds are added to liquid fuels for various reasons (such
as MTBE to raise the octane number of the fuel and also to oxygenate the
fuel in winter months to reduce urban smog). The largest source of air pollution is the motor vehicles, and the pollutants released by the vehicles are
usually grouped as hydrocarbons (HC), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon
monoxide (CO) (Fig. 2–63). The HC emissions are a large component of
volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions, and the two terms are generally used interchangeably for motor vehicle emissions. A significant portion
of the VOC or HC emissions are caused by the evaporation of fuels during
refueling or spillage during spitback or by evaporation from gas tanks with
faulty caps that do not close tightly. The solvents, propellants, and household cleaning products that contain benzene, butane, or other HC products
are also significant sources of HC emissions.
The increase of environmental pollution at alarming rates and the rising awareness of its dangers made it necessary to control it by legislation
and international treaties. In the United States, the Clean Air Act of 1970
(whose passage was aided by the 14-day smog alert in Washington that
year) set limits on pollutants emitted by large plants and vehicles. These
early standards focused on emissions of hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, and
carbon monoxide. The new cars were required to have catalytic converters
in their exhaust systems to reduce HC and CO emissions. As a side benefit,
the removal of lead from gasoline to permit the use of catalytic converters
led to a significant reduction in toxic lead emissions.
Emission limits for HC, NOx, and CO from cars have been declining
steadily since 1970. The Clean Air Act of 1990 made the requirements on
emissions even tougher, primarily for ozone, CO, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter (PM). As a result, today’s industrial facilities and vehicles
emit a fraction of the pollutants they used to emit a few decades ago. The
HC emissions of cars, for example, decreased from about 8 gpm (grams per
mile) in 1970 to 0.4 gpm in 1980 and about 0.1 gpm in 1999. This is a significant reduction since many of the gaseous toxics from motor vehicles and
liquid fuels are hydrocarbons.
Children are most susceptible to the damages caused by air pollutants
since their organs are still developing. They are also exposed to more pollution since they are more active, and thus they breathe faster. People with
heart and lung problems, especially those with asthma, are most affected by
air pollutants. This becomes apparent when the air pollution levels in their
neighborhoods rise to high levels.
Ozone and Smog
If you live in a metropolitan area such as Los Angeles, you are probably
familiar with urban smog—the dark yellow or brown haze that builds up
in a large stagnant air mass and hangs over populated areas on calm hot
87
CHAPTER 2
summer days. Smog is made up mostly of ground-level ozone (O3), but it
also contains numerous other chemicals, including carbon monoxide (CO),
particulate matter such as soot and dust, volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
such as benzene, butane, and other hydrocarbons. The harmful ground-level
ozone should not be confused with the useful ozone layer high in the stratosphere that protects the earth from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays. Ozone
at ground level is a pollutant with several adverse health effects.
The primary source of both nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons is the
motor vehicles. Hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides react in the presence of
sunlight on hot calm days to form ground-level ozone, which is the primary
component of smog (Fig. 2–64). The smog formation usually peaks in late
afternoons when the temperatures are highest and there is plenty of sunlight.
Although ground-level smog and ozone form in urban areas with heavy
traffic or industry, the prevailing winds can transport them several hundred
miles to other cities. This shows that pollution knows of no boundaries, and
it is a global problem.
Ozone irritates eyes and damages the air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged, causing eventual hardening of this
soft and spongy tissue. It also causes shortness of breath, wheezing, fatigue,
headaches, and nausea, and aggravates respiratory problems such as asthma.
Every exposure to ozone does a little damage to the lungs, just like cigarette
smoke, eventually reducing the individual’s lung capacity. Staying indoors
and minimizing physical activity during heavy smog minimizes damage.
Ozone also harms vegetation by damaging leaf tissues. To improve the
air quality in areas with the worst ozone problems, reformulated gasoline
(RFG) that contains at least 2 percent oxygen was introduced. The use of
RFG has resulted in significant reduction in the emission of ozone and other
pollutants, and its use is mandatory in many smog-prone areas.
The other serious pollutant in smog is carbon monoxide, which is a colorless, odorless, poisonous gas. It is mostly emitted by motor vehicles,
and it can build to dangerous levels in areas with heavy congested traffic.
It deprives the body’s organs from getting enough oxygen by binding with
the red blood cells that would otherwise carry oxygen. At low levels, carbon monoxide decreases the amount of oxygen supplied to the brain and
other organs and muscles, slows body reactions and reflexes, and impairs
judgment. It poses a serious threat to people with heart disease because of
the fragile condition of the circulatory system and to fetuses because of the
oxygen needs of the developing brain. At high levels, it can be fatal, as evidenced by numerous deaths caused by cars that are warmed up in closed
garages or by exhaust gases leaking into the cars.
Smog also contains suspended particulate matter such as dust and soot
emitted by vehicles and industrial facilities. Such particles irritate the eyes
and the lungs since they may carry compounds such as acids and metals.
Acid Rain
Fossil fuels are mixtures of various chemicals, including small amounts
of sulfur. The sulfur in the fuel reacts with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide
(SO2), which is an air pollutant. The main source of SO2 is the electric
power plants that burn high-sulfur coal. The Clean Air Act of 1970 has
limited the SO2 emissions severely, which forced the plants to install SO2
Sun
O3
NOx
HC
Smog
FIGURE 2–64
Ground-level ozone, which is the
primary component of smog, forms
when HC and NOx react in the
presence of sunlight in hot calm days.
88
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
Sun
FIGURE 2–65
Sulfuric acid and nitric acid are
formed when sulfur oxides and nitric
oxides react with water vapor and
other chemicals high in the
atmosphere in the presence of
sunlight.
Sun
Greenhouse gases
Some infrared
radiation emitted
by earth is
absorbed by
greenhouse
gases and
emitted back
Solar radiation
passes through
and is mostly
absorbed by
earth’s surface
FIGURE 2–66
The greenhouse effect on earth.
scrubbers, to switch to low-sulfur coal, or to gasify the coal and recover
the sulfur. Motor vehicles also contribute to SO2 emissions since gasoline and diesel fuel also contain small amounts of sulfur. Volcanic eruptions and hot springs also release sulfur oxides (the cause of the rotten egg
smell).
The sulfur oxides and nitric oxides react with water vapor and other
chemicals high in the atmosphere in the presence of sunlight to form sulfuric and nitric acids (Fig. 2–65). The acids formed usually dissolve in the
suspended water droplets in clouds or fog. These acid-laden droplets, which
can be as acidic as lemon juice, are washed from the air on to the soil by
rain or snow. This is known as acid rain. The soil is capable of neutralizing
a certain amount of acid, but the amounts produced by the power plants
using inexpensive high-sulfur coal has exceeded this capability, and as a
result many lakes and rivers in industrial areas such as New York, Pennsylvania, and Michigan have become too acidic for fish to grow. Forests in
those areas also experience a slow death due to absorbing the acids through
their leaves, needles, and roots. Even marble structures deteriorate due to
acid rain. The magnitude of the problem was not recognized until the early
1970s, and serious measures have been taken since then to reduce the sulfur
dioxide emissions drastically by installing scrubbers in plants and by desulfurizing coal before combustion.
The Greenhouse Effect:
Global Warming and Climate Change
You have probably noticed that when you leave your car under direct sunlight on a sunny day, the interior of the car gets much warmer than the
air outside, and you may have wondered why the car acts like a heat trap.
This is because glass at thicknesses encountered in practice transmits over
90 percent of radiation in the visible range and is practically opaque (nontransparent) to radiation in the longer wavelength infrared regions. Therefore, glass allows the solar radiation to enter freely but blocks the infrared
radiation emitted by the interior surfaces. This causes a rise in the interior
temperature as a result of the thermal energy buildup in the car. This heating effect is known as the greenhouse effect, since it is utilized primarily in
greenhouses.
The greenhouse effect is also experienced on a larger scale on earth.
The surface of the earth, which warms up during the day as a result of
the absorption of solar energy, cools down at night by radiating part of its
energy into deep space as infrared radiation. Carbon dioxide (CO2), water
vapor, and trace amounts of some other gases such as methane and nitrogen
oxides act like a blanket and keep the earth warm at night by blocking the
heat radiated from the earth (Fig. 2–66). Therefore, they are called “greenhouse gases,” with CO2 being the primary component. Water vapor is usually taken out of this list since it comes down as rain or snow as part of the
water cycle and human activities in producing water (such as the burning of
fossil fuels) do not make much difference on its concentration in the atmosphere (which is mostly due to evaporation from rivers, lakes, oceans, etc.).
CO2 is different, however, in that people’s activities do make a difference in
CO2 concentration in the atmosphere.
89
CHAPTER 2
The greenhouse effect makes life on earth possible by keeping the earth
warm (about 308C warmer). However, excessive amounts of these gases disturb the delicate balance by trapping too much energy, which causes the
average temperature of the earth to rise and the climate at some localities
to change. These undesirable consequences of the greenhouse effect are
referred to as global warming or global climate change.
The global climate change is due to the excessive use of fossil fuels such
as coal, petroleum products, and natural gas in electric power generation,
transportation, buildings, and manufacturing, and it has been a concern in
recent decades. In 1995, a total of 6.5 billion tons of carbon was released to
the atmosphere as CO2. The current concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere
is about 360 ppm (or 0.36 percent). This is 20 percent higher than the level
a century ago, and it is projected to increase to over 700 ppm by the year
2100. Under normal conditions, vegetation consumes CO2 and releases O2
during the photosynthesis process, and thus keeps the CO2 concentration in
the atmosphere in check. A mature, growing tree consumes about 12 kg of
CO2 a year and exhales enough oxygen to support a family of four. However, deforestation and the huge increase in the CO2 production in recent
decades disturbed this balance.
In a 1995 report, the world’s leading climate scientists concluded that the
earth has already warmed about 0.58C during the last century, and they estimate that the earth’s temperature will rise another 28C by the year 2100. A
rise of this magnitude is feared to cause severe changes in weather patterns
with storms and heavy rains and flooding at some parts and drought in others, major floods due to the melting of ice at the poles, loss of wetlands and
coastal areas due to rising sea levels, variations in water supply, changes
in the ecosystem due to the inability of some animal and plant species to
adjust to the changes, increases in epidemic diseases due to the warmer
temperatures, and adverse side effects on human health and socioeconomic
conditions in some areas.
The seriousness of these threats has moved the United Nations to establish
a committee on climate change. A world summit in 1992 in Rio de Janeiro,
Brazil, attracted world attention to the problem. The agreement prepared by
the committee in 1992 to control greenhouse gas emissions was signed by
162 nations. In the 1997 meeting in Kyoto (Japan), the world’s industrialized
countries adopted the Kyoto protocol and committed to reduce their CO2 and
other greenhouse gas emissions by 5 percent below the 1990 levels by 2008
to 2012. In December 2011, countries agreed in Durban, South Africa to forge
a new deal forcing the biggest polluting countries to limit greenhouse gas
emissions. The Kyoto protocol is extended allowing five more years to finalize a wider agreement. It was agreed to work in a new, legally binding accord
to cut greenhouse gases. This should be decided by 2015 and come into force
by 2020. Greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced by increasing conservation efforts and improving conversion efficiencies, while meeting new energy
demands by the use of renewable energy (such as hydroelectric, solar, wind,
and geothermal energy) rather than by fossil fuels.
The United States is the largest contributor of greenhouse gases, with over
5 tons of carbon emissions per person per year. Major sources of greenhouse
gas emissions are industrial sector and transportation. Each kilowatt-hour of
electricity produced by a fossil-fuelled power plant produces 0.6 to 1.0 kg
90
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
FIGURE 2–67
The average car produces several
times its weight in CO2 every year
(it is driven 13,500 miles a year,
consumes 600 gallons of gasoline, and
produces 20 lbm of CO2 per gallon).
©Emma Lee/Life File/Getty Images RF
FIGURE 2–68
Renewable energies such as wind are
called “green energy” since they emit
no pollutants or greenhouse gases.
©J. Luke/PhotoLink/Getty Images RF
(1.3 to 2.2 lbm) carbon dioxide. Each liter of gasoline burned by a vehicle
produces about 2.5 kg of CO2 (or, each gallon of gasoline burned produces
about 20 lbm of CO2). An average car in the United States is driven about
12,000 miles a year, and it consumes about 600 gallons of gasoline. Therefore, a car emits about 12,000 lbm of CO2 to the atmosphere a year, which
is about four times the weight of a typical car (Fig. 2–67). This and other
emissions can be reduced significantly by buying an energy-efficient car that
burns less fuel over the same distance, and by driving sensibly. Saving fuel
also saves money and the environment. For example, choosing a vehicle that
gets 30 rather than 20 miles per gallon will prevent 2 tons of CO2 from
being released to the atmosphere every year while reducing the fuel cost by
$900 per year (under average driving conditions of 13,500 miles a year and
at a fuel cost of $4.00/gal).
It is clear from these discussions that considerable amounts of pollutants
are emitted as the chemical energy in fossil fuels is converted to thermal,
mechanical, or electrical energy via combustion, and thus power plants,
motor vehicles, and even stoves take the blame for air pollution. In contrast, no pollution is emitted as electricity is converted to thermal, chemical, or mechanical energy, and thus electric cars are often touted as “zero
emission” vehicles and their widespread use is seen by some as the ultimate
solution to the air pollution problem. It should be remembered, however,
that the electricity used by the electric cars is generated somewhere else
mostly by burning fuel and thus emitting pollution. Therefore, each time an
electric car consumes 1 kWh of electricity, it bears the responsibility for the
pollutions emitted as 1 kWh of electricity (plus the conversion and transmission losses) is generated elsewhere. The electric cars can be claimed to be
zero emission vehicles only when the electricity they consume is generated
by emission-free renewable resources such as hydroelectric, solar, wind,
and geothermal energy (Fig. 2–68). Therefore, the use of renewable energy
should be encouraged worldwide, with incentives, as necessary, to make the
earth a better place to live in. The advancements in thermodynamics have
contributed greatly in recent decades to improve conversion efficiencies
(in some cases doubling them) and thus to reduce pollution. As individuals,
we can also help by practicing energy conservation measures and by making energy efficiency a high priority in our purchases.
EXAMPLE 2–17
Reducing Air Pollution by Geothermal Heating
A geothermal power plant in Nevada is generating electricity using geothermal water extracted at 1808C, and reinjected back to the ground at 858C.
It is proposed to utilize the reinjected brine for heating the residential and
commercial buildings in the area, and calculations show that the geothermal
heating system can save 18 million therms of natural gas a year. Determine the amount of NOx and CO2 emissions the geothermal system will
save a year. Take the average NOx and CO2 emissions of gas furnaces to be
0.0047 kg/therm and 6.4 kg/therm, respectively.
SOLUTION
The gas heating systems in an area are being replaced by a
geothermal district heating system. The amounts of NOx and CO2 emissions
saved per year are to be determined.
91
CHAPTER 2
Analysis The amounts of emissions saved per year are equivalent to the
amounts emitted by furnaces when 18 million therms of natural gas are
burned,
NOx savings 5 (NOx emission per therm)(No. of therms per year)
5 (0.0047 kg/therm)(18 3 106 therm/year)
5 8.5 3 104 kg/year
CO2 savings 5 (CO2 emission per therm)(No. of therms per year)
5 (6.4 kg/therm)(18 3 106 therm/year)
5 1.2 3 108 kg/year
Discussion A typical car on the road generates about 8.5 kg of NOx and
6000 kg of CO2 a year. Therefore the environmental impact of replacing the
gas heating systems in the area by the geothermal heating system is equivalent to taking 10,000 cars off the road for NOx emission and taking 20,000
cars off the road for CO2 emission. The proposed system should have a significant effect on reducing smog in the area.
TOPIC OF SPECIAL INTEREST*
Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
Heat can be transferred in three different ways: conduction, convection, and
radiation. We will give a brief description of each mode to familiarize the
reader with the basic mechanisms of heat transfer. All modes of heat transfer require the existence of a temperature difference, and all modes of heat
transfer are from the high-temperature medium to a lower temperature one.
Conduction is the transfer of energy from the more energetic particles
of a substance to the adjacent less energetic ones as a result of interactions
between the particles. Conduction can take place in solids, liquids, or gases.
In gases and liquids, conduction is due to the collisions of the molecules during their random motion. In solids, it is due to the combination of vibrations
of molecules in a lattice and the energy transport by free electrons. A cold
canned drink in a warm room, for example, eventually warms up to the room
temperature as a result of heat transfer from the room to the drink through
the aluminum can by conduction (Fig. 2–69).
#
It is observed that the rate of heat conduction Qcond through a layer of constant thickness Dx is proportional to the temperature difference DT across the
layer and the area A normal to the direction of heat transfer, and is inversely
proportional to the thickness of the layer. Therefore,
#
DT
Qcond 5 kt A
Dx
(W)
Heat
Cola
ΔT
T1
T2
Air
Heat
Cola
Δx
(2–51)
where the constant of proportionality kt is the thermal conductivity of the
material, which is a measure of the ability of a material to conduct heat
(Table 2–3). Materials such as copper and silver, which are good electric
conductors, are also good heat conductors, and therefore have high kt values.
*This section can be skipped without a loss in continuity
Air
Wall of
aluminum
can
FIGURE 2–69
Heat conduction from warm air
to a cold canned drink through
the wall of the aluminum can.
92
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
TABLE 2–3
Thermal conductivities of some
materials at room conditions
Thermal
conductivity,
W/m·K
Material
Diamond
Silver
Copper
Gold
Aluminum
Iron
Mercury (,)
Glass
Brick
Water (,)
Human skin
Wood (oak)
Helium (g)
Soft rubber
Glass fiber
Air (g)
Urethane,
rigid foam
Velocity
variation
of air
2300
429
401
317
237
80.2
8.54
1.4
0.72
0.613
0.37
0.17
0.152
0.13
0.043
0.026
0.026
V
Air
flow
Tf
T
Temperature
variation
of air
·
Qconv
A
Ts
Hot block
FIGURE 2–70
Heat transfer from a hot
surface to air by convection.
Materials such as rubber, wood, and styrofoam are poor conductors of heat,
and therefore have low kt values.
In the limiting case of Dx S 0, the equation above reduces to the differential form
#
dT
Qcond 5 2kt A
dx
(W)
(2–52)
which is known as Fourier’s law of heat conduction. It indicates that the
rate of heat conduction in a direction is proportional to the temperature gradient in that direction. Heat is conducted in the direction of decreasing temperature, and the temperature gradient becomes negative when temperature
decreases with increasing x. Therefore, a negative sign is added in Eq. 2–52
to make heat transfer in the positive x direction a positive quantity.
Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energies of the molecules. In a liquid or gas, the kinetic energy of the molecules is due to the random motion
of the molecules as well as the vibrational and rotational motions. When two
molecules possessing different kinetic energies collide, part of the kinetic
energy of the more energetic (higher temperature) molecule is transferred
to the less energetic (lower temperature) particle, in much the same way as
when two elastic balls of the same mass at different velocities collide, part of
the kinetic energy of the faster ball is transferred to the slower one.
In solids, heat conduction is due to two effects: the lattice vibrational
waves induced by the vibrational motions of the molecules positioned at
relatively fixed position in a periodic manner called a lattice, and the energy
transported via the free flow of electrons in the solid. The thermal conductivity of a solid is obtained by adding the lattice and the electronic components.
The thermal conductivity of pure metals is primarily due to the electronic
component, whereas the thermal conductivity of nonmetals is primarily due
to the lattice component. The lattice component of thermal conductivity
strongly depends on the way the molecules are arranged. For example, the
thermal conductivity of diamond, which is a highly ordered crystalline solid,
is much higher than the thermal conductivities of pure metals, as can be seen
from Table 2–3.
Convection is the mode of energy transfer between a solid surface and the
adjacent liquid or gas that is in motion, and it involves the combined effects
of conduction and fluid motion. The faster the fluid motion, the greater the
convection heat transfer. In the absence of any bulk fluid motion, heat transfer between a solid surface and the adjacent fluid is by pure conduction. The
presence of bulk motion of the fluid enhances the heat transfer between the
solid surface and the fluid, but it also complicates the determination of heat
transfer rates.
Consider the cooling of a hot block by blowing of cool air over its top surface (Fig. 2–70). Energy is first transferred to the air layer adjacent to the surface of the block by conduction. This energy is then carried away from the
surface by convection; that is, by the combined effects of conduction within
the air, which is due to random motion of air molecules, and the bulk or macroscopic motion of the air, which removes the heated air near the surface and
replaces it by the cooler air.
93
CHAPTER 2
Convection is called forced convection if the fluid is forced to flow in a
tube or over a surface by external means such as a fan, pump, or the wind. In
contrast, convection is called free (or natural) convection if the fluid motion
is caused by buoyancy forces induced by density differences due to the variation of temperature in the fluid (Fig. 2–71). For example, in the absence of
a fan, heat transfer from the surface of the hot block in Fig. 2–70 will be
by natural convection since any motion in the air in this case will be due to
the rise of the warmer (and thus lighter) air near the surface and the fall of
the cooler (and thus heavier) air to fill its place. Heat transfer between the
block and surrounding air will be by conduction if the temperature difference
between the air and the block is not large enough to overcome the resistance
of air to move and thus to initiate natural convection currents.
Heat transfer processes that involve change of phase of a fluid are also
considered to be convection because of the fluid motion induced during the
process such as the rise of the vapor bubbles during boiling or the fall of the
liquid droplets during condensation.
#
The rate of heat transfer by convection Qconv is determined from Newton’s
law of cooling, expressed as
#
Qconv 5 hA(Ts 2 Tf)
(W)
Forced convection
Natural convection
Air
Air
hot egg
hot egg
FIGURE 2–71
The cooling of a boiled egg by forced
and natural convection.
(2–53)
where h is the convection heat transfer coefficient, A is the surface area
through which heat transfer takes place, Ts is the surface temperature,
and Tf is bulk fluid temperature away from the surface. (At the surface,
the fluid temperature equals the surface temperature of the solid.)
The convection heat transfer coefficient h is not a property of the fluid. It
is an experimentally determined parameter whose value depends on all the
variables that influence convection such as the surface geometry, the nature
of fluid motion, the properties of the fluid, and the bulk fluid velocity. Typical values of h, in W/m2·K, are in the range of 2–25 for the free convection
of gases, 50–1000 for the free convection of liquids, 25–250 for the forced
convection of gases, 50–20,000 for the forced convection of liquids, and
2500–100,000 for convection in boiling and condensation processes.
Radiation is the energy emitted by matter in the form of electromagnetic
waves (or photons) as a result of the changes in the electronic configurations
of the atoms or molecules. Unlike conduction and convection, the transfer of
energy by radiation does not require the presence of an intervening medium
(Fig. 2–72). In fact, energy transfer by radiation is fastest (at the speed of
light) and it suffers no attenuation in a vacuum. This is exactly how the
energy of the sun reaches the earth.
In heat transfer studies, we are interested in thermal radiation, which is
the form of radiation emitted by bodies because of their temperature. It differs from other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, gamma
rays, microwaves, radio waves, and television waves that are not related to
temperature. All bodies at a temperature above absolute zero emit thermal
radiation.
Radiation is a volumetric phenomenon, and all solids, liquids, and gases
emit, absorb, or transmit radiation of varying degrees. However, radiation is
usually considered to be a surface phenomenon for solids that are opaque to
Person
30°C
Air
5°C
Fire
900°C
Radiation
FIGURE 2–72
Unlike conduction and convection,
heat transfer by radiation can occur
between two bodies, even when they
are separated by a medium colder than
both of them.
94
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
TABLE 2–4
Emissivity of some materials at
300 K
Material
Emissivity
Aluminum foil
Anodized aluminum
Polished copper
Polished gold
Polished silver
Polished
stainless steel
Black paint
White paint
White paper
Asphalt pavement
Red brick
Human skin
Wood
Soil
Water
Vegetation
0.07
0.82
0.03
0.03
0.02
0.17
0.98
0.90
0.92–0.97
0.85–0.93
0.93–0.96
0.95
0.82–0.92
0.93–0.96
0.96
0.92–0.96
·
Qincident
·
·
Qref = (1 – α ) Qincident
·
·
Qabs = α Qincident
FIGURE 2–73
The absorption of radiation incident
on an opaque surface of absorptivity a.
thermal radiation such as metals, wood, and rocks since the radiation emitted
by the interior regions of such material can never reach the surface, and the
radiation incident on such bodies is usually absorbed within a few microns
from the surface.
The maximum rate of radiation that can be emitted from a surface at an
absolute temperature Ts is given by the Stefan–Boltzmann law as
#
Qemit,max 5 sAT 4s
(W)
(2–54)
where A is the surface area and s 5 5.67 3 1028 W/m2·K4 is the Stefan–
Boltzmann constant. The idealized surface that emits radiation at this maximum rate is called a blackbody, and the radiation emitted by a blackbody
is called blackbody radiation. The radiation emitted by all real surfaces is
less than the radiation emitted by a blackbody at the same temperatures and
is expressed as
#
Qemit 5 esAT 4s
(W)
(2–55)
where e is the emissivity of the surface. The property emissivity, whose value
is in the range 0 # e # 1, is a measure of how closely a surface approximates a blackbody for which e 5 1. The emissivities of some surfaces are
given in Table 2–4.
Another important radiation property of a surface is its absorptivity, a,
which is the fraction of the radiation energy incident on a surface that is
absorbed by the surface. Like emissivity, its value is in the range 0 # a # 1.
A blackbody absorbs the entire radiation incident on it. That is, a blackbody
is a perfect absorber (a 5 1) as well as a perfect emitter.
In general, both e and a of a surface depend on the temperature and the
wavelength of the radiation. Kirchhoff’s law of radiation states that the
emissivity and the absorptivity of a surface are equal at the same temperature
and wavelength. In most practical applications, the dependence of e and a
on the temperature and wavelength is ignored, and the average absorptivity
of a surface is taken to be equal to its average emissivity. The rate at which a
surface absorbs radiation is determined from (Fig. 2–73)
#
#
Qabs 5 aQincident
#
(W)
(2–56)
where Qincident is the rate at which radiation is incident on the surface and a is
the absorptivity of the surface. For opaque (nontransparent) surfaces, the portion of incident radiation that is not absorbed by the surface is reflected back.
The difference between the rates of radiation emitted by the surface and
the radiation absorbed is the net radiation heat transfer. If the rate of radiation absorption is greater than the rate of radiation emission, the surface
is said to be gaining energy by radiation. Otherwise, the surface is said
to be losing energy by radiation. In general, the determination of the net
rate of heat transfer by radiation between two surfaces is a complicated
matter since it depends on the properties of the surfaces, their orientation
relative to each other, and the interaction of the medium between the surfaces with radiation. However, in the special case of a relatively small surface of emissivity e and surface area A at absolute temperature Ts that is
completely enclosed by a much larger surface at absolute temperature Tsurr
95
CHAPTER 2
separated by a gas (such as air) that does not intervene with radiation (i.e.,
the amount of radiation emitted, absorbed, or scattered by the medium is
negligible), the net rate of radiation heat transfer between these two surfaces is determined from (Fig. 2–74)
#
Qrad 5 esA(T 4s 2 T 4surr)
(W)
Large
enclosure
ε, A, Ts
Sm
.
Qrad
all b
ody
(2–57)
Tsurr
In this special case, the emissivity and the surface area of the surrounding surface do not have any effect on the net radiation heat transfer.
EXAMPLE 2–18
Heat Transfer from a Person
Consider a person standing in a breezy room at 208C. Determine the total rate
of heat transfer from this person if the exposed surface area and the average
outer surface temperature of the person are 1.6 m2 and 298C, respectively,
and the convection heat transfer coefficient is 6 W/m2·8C (Fig. 2–75).
SOLUTION A person is standing in a breezy room. The total rate of heat
loss from the person is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 The emissivity and heat transfer coefficient are constant and
uniform. 2 Heat conduction through the feet is negligible. 3 Heat loss by
evaporation is disregarded.
Analysis The heat transfer between the person and the air in the room will
be by convection (instead of conduction) since it is conceivable that the air
in the vicinity of the skin or clothing will warm up and rise as a result of
heat transfer from the body, initiating natural convection currents. It appears
that the experimentally determined value for the rate of convection heat
transfer in this case is 6 W per unit surface area (m2) per unit temperature
difference (in K or 8C) between the person and the air away from the person.
Thus, the rate of convection heat transfer from the person to the air in the
room is, from Eq. 2–53,
#
Qconv 5 hA(Ts 2 Tf)
5 (6 W/m2 · 8C)(1.6 m2)(29 2 20) 8C
5 86.4 W
The person will also lose heat by radiation to the surrounding wall surfaces. We take the temperature of the surfaces of the walls, ceiling, and the
floor to be equal to the air temperature in this case for simplicity, but we
recognize that this does not need to be the case. These surfaces may be at
a higher or lower temperature than the average temperature of the room air,
depending on the outdoor conditions and the structure of the walls. Considering that air does not intervene with radiation and the person is completely
enclosed by the surrounding surfaces, the net rate of radiation heat transfer from the person to the surrounding walls, ceiling, and the floor is, from
Eq. 2–57,
#
Qrad 5 esA(T 4s 2 T 4surr )
5 (0.95)(5.67 3 10 28 W/m2 ·K4)(1.6 m2) 3 [(29 1 273)4 2 (20 1 273)4]K4
5 81.7 W
FIGURE 2–74
Radiation heat transfer between
a body and the inner surfaces of
a much larger enclosure that
completely surrounds it.
20°C
Room
air
·
Qconv
29°C
·
Qrad
·
Qcond
FIGURE 2–75
Heat transfer from the person
described in Example 2–18.
96
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
Note that we must use absolute temperatures in radiation calculations. Also
note that we used the emissivity value for the skin and clothing at room
temperature since the emissivity is not expected to change significantly at a
slightly higher temperature.
Then the rate of total heat transfer from the body is determined by adding
these two quantities to be
#
#
#
Qtotal 5 Qconv 1 Qrad 5 86.4 1 81.7 5 168.1 W
The heat transfer would be much higher if the person were not dressed since
the exposed surface temperature would be higher. Thus, an important function of the clothes is to serve as a barrier against heat transfer.
Discussion In the above calculations, heat transfer through the feet to the
floor by conduction, which is usually very small, is neglected. Heat transfer
from the skin by perspiration, which is the dominant mode of heat transfer
in hot environments, is not considered here.
SUMMARY
The sum of all forms of energy of a system is called total
energy, which consists of internal, kinetic, and potential
energy for simple compressible systems. Internal energy
represents the molecular energy of a system and may exist in
sensible, latent, chemical, and nuclear forms.
#
Mass flow rate m is defined as the amount of mass flowing through a cross# section per unit time. It is related to the
volume flow rate V , which is the volume of a fluid flowing
through a cross section per unit time, by
#
#
m 5 rV 5 rAcVavg
The energy flow rate associated with a fluid flowing at a rate
#
of m is
#
#
E 5 me
which is analogous to E 5 me.
The mechanical energy is defined as the form of energy
that can be converted to mechanical work completely and
directly by a mechanical device such as an ideal turbine. It
is expressed on a unit mass basis and rate form as
emech 5
P
V2
1 gz
1
r
2
and
#
V2
#
# P
1 gzb
Emech 5 memech 5 m a 1
r
2
where P/r is the flow energy, V 2/2 is the kinetic energy, and
gz is the potential energy of the fluid per unit mass.
Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the
form of heat or work. For control volumes, energy can also
be transported by mass. If the energy transfer is due to a
temperature difference between a closed system and its surroundings, it is heat; otherwise, it is work.
Work is the energy transferred as a force acts on a system
through a distance. Various forms of work are expressed as
follows:
Electrical work: We 5 VI Dt
Shaft work: Wsh 5 2pnT
1
k(x22 2 x12)
2
The first law of thermodynamics is essentially an expression of the conservation of energy principle, also called the
energy balance. The general mass and energy balances for
any system undergoing any process can be expressed as
Spring work: Wspring 5
Ein 2 Eout
5
DEsystem
(kJ)
Net energy transfer Change in internal, kinetic,
by heat, work, and mass potential, etc., energies
It can also be expressed in the rate form as
#
#
Ein 2 Eout 5 dEsystem/dt (kW)
Rate of net energy transfer
Rate of change in internal,
by heat, work, and mass kinetic, potential, etc., energies
The efficiencies of various devices are defined as
#
#
Wpump, u
DEmech, fluid
hpump 5
5 #
#
Wshaft, in
Wpump
97
CHAPTER 2
#
#
Wshaft, out
Wturbine
hturbine 5
5 #
#
uDEmech, fluid u
Wturbine, e
#
Wshaft, out
Mechanical power output
5 #
hmotor 5
Electric power input
Welect, in
#
Welect, out
Electric power output
hgenerator 5
5 #
Mechanical power input
Wshaft, in
#
DEmech, fluid
hpump2motor 5 hpumphmotor 5
#
Welect, in
#
Welect, out
hturbine 2gen 5 hturbinehgenerator 5
#
u DEmech, fluid u
The conversion of energy from one form to another is often
associated with adverse effects on the environment, and
environmental impact should be an important consideration
in the conversion and utilization of energy.
REFERENCES AND SUGGESTED READINGS
1. ASHRAE Handbook of Fundamentals. SI version.
Atlanta, GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating,
and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc., 1993.
2. Y. A. Çengel. “An Intuitive and Unified Approach
to Teaching Thermodynamics.” ASME International
Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition,
Atlanta, Georgia, AES-Vol. 36, pp. 251–260,
November 17–22, 1996.
PROBLEMS*
Forms of Energy
2–1C What is total energy? Identify the different forms of
energy that constitute the total energy.
2–2C List the forms of energy that contribute to the internal
energy of a system.
2–3C How are heat, internal energy, and thermal energy
related to each other?
2–4C What is mechanical energy? How does it differ from
thermal energy? What are the forms of mechanical energy of
a fluid stream?
2–5C Natural gas, which is mostly methane CH4, is a
fuel and a major energy source. Can we say the same about
hydrogen gas, H2?
2–9E Calculate the total potential energy, in Btu, of an
object with a mass of 200 lbm when it is 10 ft above a datum
level at a location where standard gravitational acceleration
exists.
2–10 A person gets into an elevator at the lobby level of
a hotel together with his 30-kg suitcase, and gets out at the
10th floor 35 m above. Determine the amount of energy consumed by the motor of the elevator that is now stored in the
suitcase.
2–11 Electric power is to be generated by installing a
hydraulic turbine–generator at a site 120 m below the free
surface of a large water reservoir that can supply water at a
rate of 2400 kg/s steadily. Determine the power generation
potential.
2–6C Portable electric heaters are commonly used to heat
small rooms. Explain the energy transformation involved during this heating process.
2–7C Consider the process of heating water on top of an
electric range. What are the forms of energy involved during
this process? What are the energy transformations that take
place?
2–8E Calculate the total kinetic energy, in Btu, of an
object with a mass of 10 lbm when its velocity is 50 ft/s.
Answer: 0.50 Btu
* Problems designated by a “C” are concept questions, and
students are encouraged to answer them all. Problems designated
by an “E” are in English units, and the SI users can ignore them.
Problems with the
icon are solved using EES, and complete
solutions together with parametric studies are included on the text
website. Problems with the
icon are comprehensive in nature,
and are intended to be solved with an equation solver such as
EES.
98
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
2–12 At a certain location, wind is blowing steadily at
10 m/s. Determine the mechanical energy of air per unit mass
and the power generation potential of a wind turbine with
60-m-diameter blades at that location. Take the air density to
be 1.25 kg/m3.
2–13 A water jet that leaves a nozzle at 60 m/s at a flow
rate of 120 kg/s is to be used to generate power by striking
the buckets located on the perimeter of a wheel. Determine
the power generation potential of this water jet.
2–14 Two sites are being considered for wind power generation. In the first site, the wind blows steadily at 7 m/s for
3000 hours per year, whereas in the second site the wind
blows at 10 m/s for 1500 hours per year. Assuming the wind
velocity is negligible at other times for simplicity, determine which is a better site for wind power generation. Hint:
Note that the mass flow rate of air is proportional to wind
velocity.
2–15 A river flowing steadily at a rate of 175 m3/s is considered for hydroelectric power generation. It is determined
that a dam can be built to collect water and release it from
an elevation difference of 80 m to generate power. Determine
how much power can be generated from this river water after
the dam is filled.
2–16 Consider a river flowing toward a lake at an average velocity of 3 m/s at a rate of 500 m3/s at a location
90 m above the lake surface. Determine the total mechanical
energy of the river water per unit mass and the power generation potential of the entire river at that location.
River
3 m/s
90 m
(a) the contents of the refrigerator, (b) all parts of the refrigerator including the contents, and (c) everything contained
within the room during a winter day.
Room
FIGURE P2–19C
2–20C A gas in a piston-cylinder device is compressed, and as
a result its temperature rises. Is this a heat or work interaction?
2–21C A room is heated by an iron that is left plugged
in. Is this a heat or work interaction? Take the entire room,
including the iron, as the system.
2–22C A room is heated as a result of solar radiation coming in through the windows. Is this a heat or work interaction
for the room?
2–23C An insulated room is heated by burning candles. Is
this a heat or work interaction? Take the entire room, including the candles, as the system.
FIGURE P2–16
Energy Transfer by Heat and Work
2–17C When is the energy crossing the boundaries of a
closed system heat and when is it work?
2–24 A small electrical motor produces 5 W of mechanical power. What is this power in (a) N, m, and s units; and
(b) kg, m, and s units? Answers: (a) 5 N·m/s, (b) 5 kg·m2/s3
2–25E A model aircraft internal-combustion engine produces 10 W of power. How much power is this in (a) lbf·ft/s
and (b) hp?
2–18C Consider an automobile traveling at a constant
speed along a road. Determine the direction of the heat and
work interactions, taking the following as the system: (a) the
car radiator, (b) the car engine, (c) the car wheels, (d ) the
road, and (e) the air surrounding the car.
Mechanical Forms of Work
2–19C Consider an electric refrigerator located in a room.
Determine the direction of the work and heat interactions
(in or out) when the following are taken as the system:
2–27E A construction crane lifts a prestressed concrete
beam weighing 3 short tons from the ground to the top
of piers that are 36 ft above the ground. Determine the
2–26C Lifting a weight to a height of 20 m takes 20 s for
one crane and 10 s for another. Is there any difference in the
amount of work done on the weight by each crane?
99
CHAPTER 2
amount of work done considering (a) the beam and (b) the
crane as the system. Express your answers in both lbf·ft
and Btu.
2–28E A man weighing 180 lbf is pushing a cart that
weighs 100 lbf with its contents up a ramp that is inclined
at an angle of 108 from the horizontal. Determine the work
needed to move along this ramp a distance of 100 ft considering (a) the man and (b) the cart and its contents as the system. Express your answers in both lbf·ft and Btu.
How much work, in Btu, is required to expand this bubble? Answer: 2.45 3 1026 Btu
2–33 Determine the work required to deflect a linear spring
with a spring constant of 70 kN/m by 20 cm from its rest
position.
2–34 A ski lift has a one-way length of 1 km and a vertical
rise of 200 m. The chairs are spaced 20 m apart, and each
chair can seat three people. The lift is operating at a steady
speed of 10 km/h. Neglecting friction and air drag and assuming that the average mass of each loaded chair is 250 kg,
determine the power required to operate this ski lift. Also
estimate the power required to accelerate this ski lift in 5 s to
its operating speed when it is first turned on.
2–35 The engine of a 1500-kg automobile has a power rating of 75 kW. Determine the time required to accelerate this
car from rest to a speed of 100 km/h at full power on a level
road. Is your answer realistic?
FIGURE P2–28E
©McGraw-Hill Education/Lars A.Niki
2–29E The force F required to compress a spring a distance
x is given by F 2 F0 5 kx where k is the spring constant and
F0 is the preload. Determine the work required to compress
a spring whose spring constant is k 5 200 lbf/in a distance
of one inch starting from its free length where F0 5 0 lbf.
Express your answer in both lbf·ft and Btu.
2–36 Determine the power required for a 1150-kg car to
climb a 100-m-long uphill road with a slope of 308 (from
horizontal) in 12 s (a) at a constant velocity, (b) from rest
to a final velocity of 30 m/s, and (c) from 35 m/s to a final
velocity of 5 m/s. Disregard friction, air drag, and rolling
resistance. Answers: (a) 47.0 kW, (b) 90.1 kW, (c) 210.5 kW
1150 kg
m
100
30°
F
FIGURE P2–36
x
The First Law of Thermodynamics
2–37C What are the different mechanisms for transferring
energy to or from a control volume?
FIGURE P2–29E
2–30 Determine the energy required to accelerate a 1300-kg
car from 10 to 60 km/h on an uphill road with a vertical rise
of 40 m.
2–31E Determine the torque applied to the shaft of a car
that transmits 450 hp and rotates at a rate of 3000 rpm.
2–32E A spherical soap bubble with a surface-tension of
0.005 lbf/ft is expanded from a diameter of 0.5 in to 3.0 in.
2–38C On a hot summer day, a student turns his fan on
when he leaves his room in the morning. When he returns
in the evening, will the room be warmer or cooler than the
neighboring rooms? Why? Assume all the doors and windows are kept closed.
2–39 Water is being heated in a closed pan on top of a
range while being stirred by a paddle wheel. During the process, 30 kJ of heat is transferred to the water, and 5 kJ of
heat is lost to the surrounding air. The paddle-wheel work
amounts to 500 N ∙ m. Determine the final energy of the system if its initial energy is 10 kJ. Answer: 35.5 kJ
100
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
5 kJ
2–45 A university campus has 200 classrooms and 400 faculty offices. The classrooms are equipped with 12 fluorescent
tubes, each consuming 110 W, including the electricity used
by the ballasts. The faculty offices, on average, have half as
many tubes. The campus is open 240 days a year. The classrooms and faculty offices are not occupied an average of 4 h
a day, but the lights are kept on. If the unit cost of electricity is $0.11/kWh, determine how much the campus will save
a year if the lights in the classrooms and faculty offices are
turned off during unoccupied periods.
500 N·m
30 kJ
FIGURE P2–39
2–40E A vertical piston-cylinder device contains water and
is being heated on top of a range. During the process, 65 Btu
of heat is transferred to the water, and heat losses from the
side walls amount to 8 Btu. The piston rises as a result of
evaporation, and 5 Btu of work is done by the vapor. Determine the change in the energy of the water for this process.
Answer: 52 Btu
2–41E At winter design conditions, a house is projected to
lose heat at a rate of 60,000 Btu/h. The internal heat gain from
people, lights, and appliances is estimated to be 6000 Btu/h.
If this house is to be heated by electric resistance heaters,
determine the required rated power of these heaters in kW to
maintain the house at constant temperature.
2–42E A water pump increases the water pressure from
15 psia to 70 psia. Determine the power input required, in
hp, to pump 0.8 ft3/s of water. Does the water temperature
at the inlet have any significant effect on the required flow
power? Answer: 11.5 hp
2–43 A water pump that consumes 2 kW of electric power
when operating is claimed to take in water from a lake and
pump it to a pool whose free surface is 30 m above the free
surface of the lake at a rate of 50 L/s. Determine if this claim
is reasonable.
2–44 A classroom that normally contains 40 people is to be
air-conditioned with window air-conditioning units of 5-kW
cooling capacity. A person at rest may be assumed to dissipate
heat at a rate of about 360 kJ/h. There are 10 lightbulbs in the
room, each with a rating of 100 W. The rate of heat transfer to
the classroom through the walls and the windows is estimated
to be 15,000 kJ/h. If the room air is to be maintained at a constant temperature of 218C, determine the number of window
air-conditioning units required. Answer: 2 units
2–46 The lighting requirements of an industrial facility
are being met by 700 40-W standard fluorescent lamps.
The lamps are close to completing their service life and are
to be replaced by their 34-W high-efficiency counterparts
that operate on the existing standard ballasts. The standard
and high-efficiency fluorescent lamps can be purchased
in quantity at a cost of $1.77 and $2.26 each, respectively. The facility operates 2800 hours a year, and all of
the lamps are kept on during operating hours. Taking the
unit cost of electricity to be $0.105/kWh and the ballast
factor to be 1.1 (i.e., ballasts consume 10 percent of the
rated power of the lamps), determine how much energy and
money will be saved per year as a result of switching to
the high-efficiency fluorescent lamps. Also, determine the
simple payback period.
2–47 Consider a room that is initially at the outdoor temperature of 208C. The room contains a 40-W lightbulb, a
110-W TV set, a 300-W refrigerator, and a 1200-W iron.
Assuming no heat transfer through the walls, determine the
rate of increase of the energy content of the room when all of
these electric devices are on.
2–48E Consider a fan located in a 3 ft 3 3 ft square duct.
Velocities at various points at the outlet are measured, and
the average flow velocity is determined to be 22 ft/s. Taking
the air density to 0.075 lbm/ft3, estimate the minimum electric power consumption of the fan motor.
2–49 The 60-W fan of a central heating system is to circulate air through the ducts. The analysis of the flow shows
that the fan needs to raise the pressure of air by 50 Pa to
maintain flow. The fan is located in a horizontal flow section whose diameter is 30 cm at both the inlet and the outlet. Determine the highest possible average flow velocity in
the duct.
2–50
The driving force for fluid flow is the pressure
difference, and a pump operates by raising the
pressure of a fluid (by converting the mechanical shaft work
to flow energy). A gasoline pump is measured to consume
3.8 kW of electric power when operating. If the pressure differential between the outlet and inlet of the pump is measured
to be 7 kPa and the changes in velocity and elevation are negligible, determine the maximum possible volume flow rate of
gasoline.
101
CHAPTER 2
which the motor dissipates heat to the room it is in when the
motor operates at full load. In winter, this room is normally
heated by a 2-kW resistance heater. Determine if it is necessary to turn the heater on when the motor runs at full load.
ΔP = 7 kPa
Pump
FIGURE P2–50
2–51 An escalator in a shopping center is designed to move
50 people, 75 kg each, at a constant speed of 0.6 m/s at 458
slope. Determine the minimum power input needed to drive
this escalator. What would your answer be if the escalator
velocity were to be doubled?
2–52 Consider a 1400-kg car cruising at constant speed of
70 km/s. Now the car starts to pass another car, by accelerating to 110 km/h in 5 s. Determine the additional power
needed to achieve this acceleration. What would your answer
be if the total mass of the car were only 700 kg? Answers:
77.8 kW, 38.9 kW
Energy Conversion Efficiencies
2–53C How is the combined pump–motor efficiency of a
pump and motor system defined? Can the combined pump–
motor efficiency be greater than either the pump or the motor
efficiency?
2–54C Define turbine efficiency, generator efficiency, and
combined turbine–generator efficiency.
2–55C Can the combined turbine-generator efficiency be
greater than either the turbine efficiency or the generator efficiency? Explain.
2–56 Consider a 24-kW hooded electric open burner in an
area where the unit costs of electricity and natural gas are
$0.10/kWh and $1.20/therm (1 therm 5 105,500 kJ), respectively. The efficiency of open burners can be taken to be
73 percent for electric burners and 38 percent for gas burners.
Determine the rate of energy consumption and the unit cost
of utilized energy for both electric and gas burners.
2–57 A 75-hp (shaft output) motor that has an efficiency
of 91.0 percent is worn out and is to be replaced by a highefficiency motor that has an efficiency of 95.4 percent. The
motor operates 4368 hours a year at a load factor of 0.75.
Taking the cost of electricity to be $0.12/kWh, determine the
amount of energy and money saved as a result of installing
the high-efficiency motor instead of the standard motor. Also,
determine the simple payback period if the purchase prices
of the standard and high-efficiency motors are $5449 and
$5520, respectively.
2–58 Consider an electric motor with a shaft power output of
20 kW and an efficiency of 88 percent. Determine the rate at
2–59E The steam requirements of a manufacturing facility are
being met by a boiler whose rated heat input is 5.5 3 106 Btu/h.
The combustion efficiency of the boiler is measured to be
0.7 by a hand-held flue gas analyzer. After tuning up the
boiler, the combustion efficiency rises to 0.8. The boiler operates 4200 hours a year intermittently. Taking the unit cost of
energy to be $4.35/106 Btu, determine the annual energy and
cost savings as a result of tuning up the boiler.
2–60E
Reconsider Prob. 2–59E. Using EES (or other)
software, study the effects of the unit cost of
energy, the new combustion efficiency on the annual energy,
and cost savings. Let the efficiency vary from 0.7 to 0.9, and
the unit cost to vary from $4 to $6 per million Btu. Plot the
annual energy and cost savings against the efficiency for unit
costs of $4, $5, and $6 per million Btu, and discuss the
results.
2–61 A geothermal pump is used to pump brine
whose density is 1050 kg/m3 at a rate of 0.3 m3/s from
a depth of 200 m. For a pump efficiency of 74 percent,
determine the required power input to the pump. Disregard
frictional losses in the pipes, and assume the geothermal
water at 200 m depth to be exposed to the atmosphere.
2–62 An exercise room has 6 weight-lifting machines that
have no motors and 7 treadmills each equipped with a 2.5-hp
(shaft output) motor. The motors operate at an average load
factor of 0.7, at which their efficiency is 0.77. During peak
evening hours, all 12 pieces of exercising equipment are used
continuously, and there are also two people doing light exercises while waiting in line for one piece of the equipment.
Assuming the average rate of heat dissipation from people in
an exercise room is 600 W, determine the rate of heat gain
of the exercise room from people and the equipment at peak
load conditions.
2–63 A room is cooled by circulating chilled water through
a heat exchanger located in a room. The air is circulated
through the heat exchanger by a 0.25-hp (shaft output) fan.
Typical efficiency of small electric motors driving 0.25-hp
equipment is 54 percent. Determine the rate of heat supply by
the fan–motor assembly to the room.
2–64 The water in a large lake is to be used to generate
electricity by the installation of a hydraulic turbine-generator
at a location where the depth of the water is 50 m. Water is
to be supplied at a rate of 5000 kg/s. If the electric power
generated is measured to be 1862 kW and the generator efficiency is 95 percent, determine (a) the overall efficiency of
the turbine—generator, (b) the mechanical efficiency of the
turbine, and (c) the shaft power supplied by he turbine to the
generator.
102
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
2–65 A 7-hp (shaft) pump is used to raise water to an
elevation of 15 m. If the mechanical efficiency of the pump
is 82 percent, determine the maximum volume flow rate of
water.
2–66 At a certain location, wind is blowing steadily at
7 m/s. Determine the mechanical energy of air per unit
mass and the power generation potential of a wind turbine with 80-m-diameter blades at that location. Also
determine the actual electric power generation assuming
an overall efficiency of 30 percent. Take the air density
to be 1.25 kg/m3.
2–67
Reconsider Prob. 2–66. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of wind velocity
and the blade span diameter on wind power generation.
Let the velocity vary from 5 to 20 m/s in increments of 5 m/s,
and the diameter vary from 20 to 120 m in increments of
20 m. Tabulate the results, and discuss their significance.
2–68 Water is pumped from a lake to a storage tank 15 m
above at a rate of 70 L/s while consuming 15.4 kW of
electric power. Disregarding any frictional losses in the pipes
and any changes in kinetic energy, determine (a) the overall
efficiency of the pump–motor unit and (b) the pressure difference between the inlet and the exit of the pump.
efficiency is 91 percent. Determine the electric power output
of this turbine.
2–71E A water pump delivers 6 hp of shaft power when
operating. If the pressure differential between the outlet and
the inlet of the pump is measured to be 1.2 psi when the
flow rate is 15 ft3/s and the changes in velocity and elevation are negligible, determine the mechanical efficiency of
this pump.
2–72 Water is pumped from a lower reservoir to a higher
reservoir by a pump that provides 20 kW of shaft power.
The free surface of the upper reservoir is 45 m higher than
that of the lower reservoir. If the flow rate of water is measured to be 0.03 m3/s, determine mechanical power that is
converted to thermal energy during this process due to frictional effects.
2
0.03 m3/s
45 m
1 z1 = 0
Storage tank
20 kW
Pump
15 m
Pump
FIGURE P2–72
FIGURE P2–68
2–73 The water behind Hoover Dam in Nevada is 206 m
higher than the Colorado River below it. At what rate must
water pass through the hydraulic turbines of this dam to
produce 100 MW of power if the turbines are 100 percent
efficient?
2–69 Large wind turbines with blade span diameters of over
100 m are available for electric power generation. Consider a
wind turbine with a blade span diameter of 100 m installed
at a site subjected to steady winds at 8 m/s. Taking the overall efficiency of the wind turbine to be 32 percent and the
air density to be 1.25 kg/m3, determine the electric power
generated by this wind turbine. Also, assuming steady winds
of 8 m/s during a 24-hour period, determine the amount of
electric energy and the revenue generated per day for a unit
price of $0.09/kWh for electricity.
2–70 A hydraulic turbine has 85 m of elevation difference available at a flow rate of 0.25 m3/s, and its overall turbine–generator
FIGURE P2–73
Photo by Lynn Betts, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Society
103
CHAPTER 2
2–74 An oil pump is drawing 44 kW of electric power
while pumping oil with r 5 860 kg/m3 at a rate of 0.1 m3/s.
The inlet and outlet diameters of the pipe are 8 cm and
12 cm, respectively. If the pressure rise of oil in the pump is
measured to be 500 kPa and the motor efficiency is 90 percent,
determine the mechanical efficiency of the pump.
44 kW
12 cm
Pump
Motor
8 cm
Oil
ΔP = 500 kPa
0.1 m3/s
FIGURE P2–74
Energy and Environment
2–75C How does energy conversion affect the environment? What are the primary chemicals that pollute the air?
What is the primary source of these pollutants?
2–82 When a hydrocarbon fuel is burned, almost all of the
carbon in the fuel burns completely to form CO2 (carbon
dioxide), which is the principal gas causing the greenhouse
effect and thus global climate change. On average, 0.59 kg of
CO2 is produced for each kWh of electricity generated from
a power plant that burns natural gas. A typical new household refrigerator uses about 700 kWh of electricity per year.
Determine the amount of CO2 production that is due to the
refrigerators in a city with 300,000 households.
2–83 Repeat Prob. 2–82 assuming the electricity is produced by a power plant that burns coal. The average production of CO2 in this case is 1.1 kg per kWh.
2–84 A typical car driven 20,000 km a year emits to the
atmosphere about 11 kg per year of NOx (nitrogen oxides),
which cause smog in major population areas. Natural gas
burned in the furnace emits about 4.3 g of NOx per therm
(1 therm 5 105,500 kJ), and the electric power plants emit
about 7.1 g of NOx per kWh of electricity produced. Consider
a household that has two cars and consumes 9000 kWh of
electricity and 1200 therms of natural gas. Determine the
amount of NOx emission to the atmosphere per year for
which this household is responsible.
2–76C What is acid rain? Why is it called a “rain”? How
do the acids form in the atmosphere? What are the adverse
effects of acid rain on the environment?
11 kg NOx
per year
2–77C Why is carbon monoxide a dangerous air pollutant?
How does it affect human health at low and at high levels?
2–78C What is the greenhouse effect? How does the excess
CO2 gas in the atmosphere cause the greenhouse effect?
What are the potential long-term consequences of greenhouse
effect? How can we combat this problem?
2–79C What is smog? What does it consist of? How does
ground-level ozone form? What are the adverse effects of
ozone on human health?
2–80E A Ford Taurus driven 12,000 miles a year will use
about 650 gallons of gasoline compared to a Ford Explorer
that would use 850 gallons. About 19.7 lbm of CO2, which
causes global warming, is released to the atmosphere when
a gallon of gasoline is burned. Determine the extra amount
of CO2 production a man is responsible for during a 5-year
period if he trades his Taurus for an Explorer.
2–81E Consider a household that uses 14,000 kWh of electricity per year and 900 gallons of fuel oil during a heating
season. The average amount of CO2 produced is 26.4 lbm/
gallon of fuel oil and 1.54 lbm/kWh of electricity. If this
household reduces its oil and electricity usage by 15 percent
as a result of implementing some energy conservation measures, determine the reduction in the amount of CO2 emissions by that household per year.
FIGURE P2–84
Special Topic: Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
2–85C
What are the mechanisms of heat transfer?
2–86C
Which is a better heat conductor, diamond or silver?
2–87C How does forced convection differ from natural convection?
2–88C What is a blackbody? How do real bodies differ
from a blackbody?
2–89C Define emissivity and absorptivity. What is Kirchhoff’s
law of radiation?
2–90C Does any of the energy of the sun reach the earth by
conduction or convection?
2–91 The inner and outer surfaces of a 5-m 3 6-m
brick wall of thickness 30 cm and thermal conductivity
0.69 W/m·8C are maintained at temperatures of 208C and
58C, respectively. Determine the rate of heat transfer through
the wall, in W.
104
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
rate of heat loss from this man by convection in an environment at 208C. Answer: 231 W
2–99 A 9-cm-diameter spherical ball whose surface is
maintained at a temperature of 1108C is suspended in the
middle of a room at 208C. If the convection heat transfer
coefficient is 15 W/m2·C and the emissivity of the surface is
0.8, determine the total rate of heat transfer from the ball.
Brick
wall
30 cm
2–100
20°C
5°C
FIGURE P2–91
2–92 The inner and outer surfaces of a 0.5-cm-thick 2-m 3
2-m window glass in winter are 158C and 68C, respectively.
If the thermal conductivity of the glass is 0.78 W/m·8C, determine the amount of heat loss, in kJ, through the glass over a
period of 10 h. What would your answer be if the glass were
1-cm thick?
Reconsider Prob. 2–99. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the convection heat transfer coefficient and surface emissivity on the
heat transfer rate from the ball. Let the heat transfer coefficient vary from 5 to 30 W/m2·8C. Plot the rate of heat transfer
against the convection heat transfer coefficient for the surface
emissivities of 0.1, 0.5, 0.8, and 1, and discuss the results.
2–101 A 1000-W iron is left on the ironing board with its
base exposed to the air at 238C. The convection heat transfer
coefficient between the base surface and the surrounding air
is 20 W/m2·8C. If the base has an emissivity of 0.4 and a surface area of 0.02 m2, determine the temperature of the base
of the iron.
2–93
Reconsider Prob. 2–92. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of glass thickness
on heat loss for the specified glass surface temperatures. Let
the glass thickness vary from 0.2 to 2 cm. Plot the heat loss
versus the glass thickness, and discuss the results.
2–94 An aluminum pan whose thermal conductivity is
237 W/m·8C has a flat bottom whose diameter is 20 cm
and thickness 0.6 cm. Heat is transferred steadily to boiling
water in the pan through its bottom at a rate of 700 W. If
the inner surface of the bottom of the pan is 1058C, determine the temperature of the outer surface of the bottom of
the pan.
2–95 The inner and outer glasses of a 2-m 3 2-m double
pane window are at 188C and 68C, respectively. If the 1-cm
space between the two glasses is filled with still air, determine the rate of heat transfer through the air layer by conduction, in kW.
2–96 Two surfaces of a 2-cm-thick plate are maintained at
08C and 1008C, respectively. If it is determined that heat is
transferred through the plate at a rate of 500 W/m2, determine
its thermal conductivity.
2–97 Hot air at 808C is blown over a 2-m 3 4-m flat surface at 308C. If the convection heat transfer coefficient is
55 W/m2·8C, determine the rate of heat transfer from the air
to the plate, in kW.
2–98 For heat transfer purposes, a standing man can be
modeled as a 30-cm diameter, 175-cm long vertical cylinder
with both the top and bottom surfaces insulated and with the
side surface at an average temperature of 348C. For a convection heat transfer coefficient of 10 W/m2·8C, determine the
1000-W
iron
Air
23°C
FIGURE P2–101
2–102 A 7-cm-external-diameter, 18-m-long hot-water pipe
at 808C is losing heat to the surrounding air at 58C by natural convection with a heat transfer coefficient of 25 W/m2·8C.
Determine the rate of heat loss from the pipe by natural convection, in kW.
2–103 A thin metal plate is insulated on the back and
exposed to solar radiation on the front surface. The exposed
surface of the plate has an absorptivity of 0.8 for solar
radiation. If solar radiation is incident on the plate at a rate of
450 W/m2 and the surrounding air temperature is 258C, determine the surface temperature of the plate when the heat loss
by convection equals the solar energy absorbed by the plate.
Assume the convection heat transfer coefficient to be 50 W/m2·8C,
and disregard heat loss by radiation.
105
CHAPTER 2
Review Problems
450 W/m2
α = 0.8
25°C
FIGURE P2–103
2–104
Reconsider Prob. 2–103. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the convection heat transfer coefficient on the surface temperature of the
plate. Let the heat transfer coefficient vary from 10 to 90 W/
m2·8C. Plot the surface temperature against the convection
heat transfer coefficient, and discuss the results.
2–105 The outer surface of a spacecraft in space has an
emissivity of 0.6 and an absorptivity of 0.2 for solar radiation. If solar radiation is incident on the spacecraft at a rate
of 1000 W/m2, determine the surface temperature of the
spacecraft when the radiation emitted equals the solar energy
absorbed.
2–106
Reconsider Prob. 2–105. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the surface
emissivity and absorptivity of the spacecraft on the equilibrium surface temperature. Plot the surface temperature against
emissivity for solar absorptivities of 0.1, 0.5, 0.8, and 1, and
discuss the results.
2–107 A hollow spherical iron container whose outer diameter is 40 cm and thickness is 0.4 cm is filled with iced water
at 08C. If the outer surface temperature is 38C, determine the
approximate rate of heat loss from the sphere, and the rate at
which ice melts in the container.
3°C
0.4 cm
Iced
water
FIGURE P2–107
2–108 Consider a vertical elevator whose cabin has a total
mass of 800 kg when fully loaded and 150 kg when empty.
The weight of the elevator cabin is partially balanced by
a 400-kg counterweight that is connected to the top of the
cabin by cables that pass through a pulley located on top of
the elevator well. Neglecting the weight of the cables and
assuming the guide rails and the pulleys to be frictionless,
determine (a) the power required while the fully loaded cabin
is rising at a constant speed of 1.2 m/s and (b) the power
required while the empty cabin is descending at a constant
speed of 1.2 m/s.
What would your answer be to (a) if no counterweight
were used? What would your answer be to (b) if a friction
force of 800 N has developed between the cabin and the
guide rails?
2–109 Consider a homeowner who is replacing his 25-yearold natural gas furnace that has an efficiency of 55 percent.
The homeowner is considering a conventional furnace that
has an efficiency of 82 percent and costs $1600 and a highefficiency furnace that has an efficiency of 95 percent and
costs $2700. The homeowner would like to buy the high-efficiency furnace if the savings from the natural gas pay for the
additional cost in less than 8 years. If the homeowner presently pays $1200 a year for heating, determine if he should
buy the conventional or high-efficiency model.
2–110E The energy contents, unit costs, and typical conversion efficiencies of various energy sources for
use in water heaters are given as follows: 1025 Btu/ft3,
$0.012/ft3, and 85 percent for natural gas; 138,700 Btu/gal,
$2.2/gal, and 75 percent for heating oil; and 1 kWh/kWh,
$0.11/kWh, and 90 percent for electric heaters, respectively.
Determine the lowest-cost energy source for water heaters.
2–111 A homeowner is considering these heating systems
for heating his house: Electric resistance heating with $0.12/
kWh and 1 kWh 5 3600 kJ, gas heating with $1.24/therm and
1 therm 5 105,500 kJ, and oil heating with $2.3/gal and 1 gal
of oil 5 138,500 kJ. Assuming efficiencies of 100 percent for
the electric furnace and 87 percent for the gas and oil furnaces,
determine the heating system with the lowest energy cost.
2–112 The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that
570,000 barrels of oil would be saved per day if every household in the United States lowered the thermostat setting in
winter by 6 ºF (3.3ºC). Assuming the average heating season
to be 180 days and the cost of oil to be $110/barrel, determine how much money would be saved per year.
2–113 The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that up
to 10 percent of the energy use of a house can be saved
by caulking and weatherstripping doors and windows to
reduce air leaks at a cost of about $90 for materials for an
average home with 12 windows and 2 doors. Caulking and
weatherstripping every gas-heated home properly would save
106
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
enough energy to heat about 4 million homes. The savings
can be increased by installing storm windows. Determine
how long it will take for the caulking and weatherstripping
to pay for itself from the energy they save for a house whose
annual energy use is $1500.
2–114E The force required to compress the gas in a gas
spring a distance x is given by
F5
Constant
xk
where the constant is determined by the geometry of this
device and k is determined by the gas used in the device. One
such device has a constant of 200 lbf·in1.4 and k 5 1.4. Determine the work, in Btu, required to compress this device from
2 in to 7 in. Answer: 0.0160 Btu
2–120 A grist mill of the 1800s employed a water wheel
that was 14 m high; 320 liters per minute of water flowed
on to the wheel near the top. How much power, in kW, could
this water wheel have produced? Answer: 0.732 kW
2–121 Windmills slow the air and cause it to fill a larger
channel as it passes through the blades. Consider a circular
windmill with a 7-m-diameter rotor in a 8 m/s wind on a day
when the atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa and the temperature is 208C. The wind speed behind the windmill is measured at 6.5 m/s. Determine the diameter of the wind channel
downstream from the rotor and the power produced by this
windmill, presuming that the air is incompressible.
Flow channel
2–115E A man weighing 180 lbf pushes a block weighing
100 lbf along a horizontal plane. The dynamic coefficient of
friction between the block and plane is 0.2. Assuming that
the block is moving at constant speed, calculate the work
required to move the block a distance of 100 ft considering
(a) the man and (b) the block as the system. Express your
answers in both lbf·ft and Btu.
2–116 A diesel engine with an engine volume of 4.0 L and
an engine speed of 2500 rpm operates on an air–fuel ratio
of 18 kg air/kg fuel. The engine uses light diesel fuel that
contains 750 ppm (parts per million) of sulfur by mass. All of
this sulfur is exhausted to the environment where the sulfur
is converted to sulfurous acid (H2SO3). If the rate of the air
entering the engine is 336 kg/h, determine the mass flow rate
of sulfur in the exhaust. Also, determine the mass flow rate of
sulfurous acid added to the environment if for each kmol of
sulfur in the exhaust, one kmol sulfurous acid will be added
to the environment.
2–117 Leaded gasoline contains lead that ends up in the
engine exhaust. Lead is a very toxic engine emission. The use
of leaded gasoline in the United States has been unlawful for
most vehicles since the 1980s. However, leaded gasoline is
still used in some parts of the world. Consider a city with
70,000 cars using leaded gasoline. The gasoline contains
0.15 g/L of lead and 50 percent of lead is exhausted to the
environment. Assuming that an average car travels 15,000 km
per year with a gasoline consumption of 8.5 L/100 km, determine the amount of lead put into the atmosphere per year in
that city. Answer: 6694 kg
2–118 Consider a TV set that consumes 120 W of electric
power when it is on and is kept on for an average of 6 hours per
day. For a unit electricity cost of 12 cents per kWh, determine
the cost of electricity this TV consumes per month (30 days).
2–119E Water is pumped from a 200-ft-deep well into a
100-ft-high storage tank. Determine the power, in kW, that
would be required to pump 200 gallons per minute.
W
FIGURE P2–121
2–122 In a hydroelectric power plant, 65 m3/s of water flows
from an elevation of 90 m to a turbine, where electric power
is generated. The overall efficiency of the turbine–generator is
84 percent. Disregarding frictional losses in piping, estimate
the electric power output of this plant. Answer: 48.2 MW
1
65 m3/s
90 m
2
Turbine
Generator
η turbine–gen = 84%
FIGURE P2–122
107
CHAPTER 2
2–123 The demand for electric power is usually much
higher during the day than it is at night, and utility companies often sell power at night at much lower prices to encourage consumers to use the available power generation capacity
and to avoid building new expensive power plants that will
be used only a short time during peak periods. Utilities are
also willing to purchase power produced during the day from
private parties at a high price.
Suppose a utility company is selling electric power for
$0.05/kWh at night and is willing to pay $0.12/kWh for
power produced during the day. To take advantage of this
opportunity, an entrepreneur is considering building a large
reservoir 40 m above the lake level, pumping water from the
lake to the reservoir at night using cheap power, and letting
the water flow from the reservoir back to the lake during
the day, producing power as the pump–motor operates as a
turbine–generator during reverse flow. Preliminary analysis
shows that a water flow rate of 2 m3/s can be used in either
direction. The combined pump–motor and turbine–generator
efficiencies are expected to be 75 percent each. Disregarding
the frictional losses in piping and assuming the system operates for 10 h each in the pump and turbine modes during a
typical day, determine the potential revenue this pump–turbine system can generate per year.
Water
300 kPa
50 L/s
h motor = 90%
Motor
15 kW
100 kPa
Wpump
FIGURE P2–124
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Problems
2–125 On a hot summer day, the air in a well-sealed room
is circulated by a 0.50-hp fan driven by a 65 percent efficient motor. (Note that the motor delivers 0.50 hp of net shaft
power to the fan.) The rate of energy supply from the fanmotor assembly to the room is
(a) 0.769 kJ/s
(b) 0.325 kJ/s
(c) 0.574 kJ/s
(d) 0.373 kJ/s
(e) 0.242 kJ/s
2–126 A fan is to accelerate quiescent air to a velocity to
12 m/s at a rate of 3 m3/s. If the density of air is 1.15 kg/m3,
the minimum power that must be supplied to the fan is
(a) 248 W
(b) 72 W
(c) 497 W
(d) 216 W
(e) 162 W
2–127 A 2-kW electric resistance heater in a room is turned
on and kept on for 50 min. The amount of energy transferred
to the room by the heater is
(a) 2 kJ
(b) 100 kJ
(c) 3000 kJ
(d) 6000 kJ
(e) 12,000 kJ
Reservoir
40 m
2–128 A 900-kg car cruising at a constant speed of 60 km/s
is to accelerate to 100 km/h in 4 s. The additional power
needed to achieve this acceleration is
(a) 56 kW
(b) 222 kW
(c) 2.5 kW
(d) 62 kW
(e) 90 kW
Pump–
turbine
Lake
FIGURE P2–123
2–124 The pump of a water distribution system is powered by a 15-kW electric motor whose efficiency is 90 percent. The water flow rate through the pump is 50 L/s. The
diameters of the inlet and outlet pipes are the same, and the
elevation difference across the pump is negligible. If the pressures at the inlet and outlet of the pump are measured to be
100 kPa and 300 kPa (absolute), respectively, determine the
mechanical efficiency of the pump. Answer: 74.1 percent
2–129 The elevator of a large building is to raise a net mass
of 400 kg at a constant speed of 12 m/s using an electric
motor. Minimum power rating of the motor should be
(c) 47 kW
(a) 0 kW
(b) 4.8 kW
(d) 12 kW
(e) 36 kW
2–130 Electric power is to be generated in a hydroelectric power plant that receives water at a rate of 70 m 3/s
from an elevation of 65 m using a turbine–generator with
an efficiency of 85 percent. When frictional losses in
piping are disregarded, the electric power output of this
plant is
(a) 3.9 MW
(b) 38 MW
(c) 45 MW
(d) 53 MW
(e) 65 MW
2–131 Consider a refrigerator that consumes 320 W of electric power when it is running. If the refrigerator runs only
one quarter of the time and the unit cost of electricity is
108
ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER
$0.09/kWh, the electricity cost of this refrigerator per month
(30 days) is
(a) $3.56
(b) $5.18
(c) $8.54
(d) $9.28
(e) $20.74
the surrounding surfaces at 158C. The total rate of heat loss
from the surface is
(a) 1987 W
(b) 2239 W
(c) 2348 W
(d) 3451 W
(e) 3811 W
2–132 A 2-kW pump is used to pump kerosene ( r 5 0.820
kg/L) from a tank on the ground to a tank at a higher elevation. Both tanks are open to the atmosphere, and the elevation
difference between the free surfaces of the tanks is 30 m. The
maximum volume flow rate of kerosene is
(a) 8.3 L/s
(b) 7.2 L/s
(c) 6.8 L/s
(d) 12.1 L/s
(e) 17.8 L/s
2–138 Heat is transferred steadily through a 0.2-m thick
8 m 3 4 m wall at a rate of 2.4 kW. The inner and outer
surface temperatures of the wall are measured to be 158C and
58C. The average thermal conductivity of the wall is
(a) 0.002 W/m·8C
(b) 0.75 W/m·8C
(c) 1.0 W/m·8C
(d) 1.5 W/m·8C
(e) 3.0 W/m·8C
2–133 A glycerin pump is powered by a 5-kW electric
motor. The pressure differential between the outlet and the
inlet of the pump at full load is measured to be 211 kPa. If
the flow rate through the pump is 18 L/s and the changes in
elevation and the flow velocity across the pump are negligible, the overall efficiency of the pump is
(a) 69 percent
(b) 72 percent
(c) 76 percent
(d) 79 percent
(e) 82 percent
2–134 A 75-hp compressor in a facility that operates at
full load for 2500 h a year is powered by an electric motor
that has an efficiency of 93 percent. If the unit cost of
electricity is $0.06/kWh, the annual electricity cost of this
compressor is
(a) $7802
(b) $9021
(c) $12,100
(d) $8389
(e) $10,460
The Following Problems Are Based on the Optional Special Topic of Heat Transfer
2–135 A 10-cm high and 20-cm wide circuit board houses
on its surface 100 closely spaced chips, each generating heat
at a rate of 0.08 W and transferring it by convection to the
surrounding air at 258C. Heat transfer from the back surface of the board is negligible. If the convection heat transfer coefficient on the surface of the board is 10 W/m2·8C and
radiation heat transfer is negligible, the average surface temperature of the chips is
(a) 268C
(b) 458C
(c) 158C
(d) 808C
(e) 658C
2–136 A 50-cm-long, 0.2-cm-diameter electric resistance
wire submerged in water is used to determine the boiling heat
transfer coefficient in water at 1 atm experimentally. The surface temperature of the wire is measured to be 1308C when
a wattmeter indicates the electric power consumption to be
4.1 kW. Then the heat transfer coefficient is
(b) 137 W/m2·8C
(a) 43,500 W/m2·8C
2
(d) 10,038 W/m2·8C
(c) 68,330 W/m ·8C
2
(e) 37,540 W/m ·8C
2–137 A 3-m2 hot black surface at 808C is losing heat to
the surrounding air at 258C by convection with a convection
heat transfer coefficient of 12 W/m2·8C, and by radiation to
2–139 The roof of an electrically heated house is 7-m long,
10-m wide, and 0.25-m thick. It is made of a flat layer of
concrete whose thermal conductivity is 0.92 W/m·8C. During a certain winter night, the temperatures of the inner and
outer surfaces of the roof are measured to be 158C and 48C,
respectively. The average rate of heat loss through the roof
that night was
(a) 41 W
(b) 177 W
(c) 4894 W
(d) 5567 W
(e) 2834 W
Design and Essay Problems
2–140 Conduct a literature survey that reviews that concepts of thermal pollution and its current state of the art.
2–141 An average vehicle puts out nearly 20 lbm of carbon
dioxide into the atmosphere for every gallon of gasoline it
burns, and thus one thing we can do to reduce global warming is to buy a vehicle with higher fuel economy. A U.S. government publication states that a vehicle that gets 25 rather
than 20 miles per gallon will prevent 10 tons of carbon dioxide from being released over the lifetime of the vehicle. Making reasonable assumptions, evaluate if this is a reasonable
claim or a gross exaggeration.
2–142 Your neighbor lives in a 2500-square-foot (about
250 m2) older house heated by natural gas. The current gas
heater was installed in the early 1980s and has an efficiency
(called the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency rating, or AFUE)
of 65 percent. It is time to replace the furnace, and the neighbor is trying to decide between a conventional furnace that has
an efficiency of 80 percent and costs $1500 and a highefficiency furnace that has an efficiency of 95 percent and
costs $2500. Your neighbor offered to pay you $100 if you
help him make the right decision. Considering the weather
data, typical heating loads, and the price of natural gas in
your area, make a recommendation to your neighbor based
on a convincing economic analysis.
2–143 Solar energy reaching the earth is about 1350 W/m2
outside the earth’s atmosphere, and 950 W/m2 on earth’s surface normal to the sun on a clear day. Someone is marketing 2 m 3 3 m photovoltaic cell panels with the claim that a
single panel can meet the electricity needs of a house. How
do you evaluate this claim? Photovoltaic cells have a conversion efficiency of about 15 percent.
109
CHAPTER 2
2–144 Find out the prices of heating oil, natural gas, and
electricity in your area, and determine the cost of each per
kWh of energy supplied to the house as heat. Go through
your utility bills and determine how much money you spent
for heating last January. Also determine how much your January heating bill would be for each of the heating systems if
you had the latest and most efficient system installed.
2–145 Prepare a report on the heating systems available in
your area for residential buildings. Discuss the advantages
and disadvantages of each system and compare their initial
and operating costs. What are the important factors in the
selection of a heating system? Give some guidelines. Identify
the conditions under which each heating system would be the
best choice in your area.
2–146 An electrical-generation utility sometimes pumps
liquid water into an elevated reservoir during periods of low
electrical consumption. This water is used to generate electricity during periods when the demand for electricity exceeds
the utility’s ability to produce electricity. Discuss this energystorage scheme from a conversion efficiency perspective as
compared to storing a compressed phase-changing substance.
2–147 The roofs of many homes in the United States are
covered with photovoltaic (PV) solar cells that resemble roof
tiles, generating electricity quietly from solar energy. An article stated that over its projected 30-year service life, a 4-kW
roof PV system in California will reduce the production of
CO2 that causes global warming by 433,000 lbm, sulfates that
cause acid rain by 2900 lbm, and nitrates that cause smog by
1660 lbm. The article also claims that a PV roof will save
253,000 lbm of coal, 21,000 gallons of oil, and 27 million
ft3 of natural gas. Making reasonable assumptions for incident solar radiation, efficiency, and emissions, evaluate these
claims and make corrections if necessary.
CHAPTER
3
PROPERTIES OF PURE
S U B S TA N C E S
W
e start this chapter with the introduction of the concept of a pure substance and a discussion of the physics of phase-change processes.
We then illustrate the various property diagrams and P-v-T surfaces of pure substances. After demonstrating the use of the property tables,
the hypothetical substance ideal gas and the ideal-gas equation of state
are discussed. The compressibility factor , which accounts for the deviation
of real gases from ideal-gas behavior, is introduced, and some of the bestknown equations of state such as the van der Waals, Beattie-Bridgeman, and
Benedict-Webb-Rubin equations are presented.
OBJECTIVES
The objectives of Chapter 3 are to:
■
Introduce the concept of a pure
substance.
■
Discuss the physics of phasechange processes.
■
■
■
■
■
■
Illustrate the P-v, T-v, and P-T
property diagrams and P-v-T
surfaces of pure substances.
Demonstrate the procedures
for determining thermodynamic
properties of pure substances
from tables of property data.
Describe the hypothetical
substance “ideal gas” and the
ideal-gas equation of state.
Apply the ideal-gas equation of
state in the solution of typical
problems.
Introduce the compressibility
factor, which accounts for the
deviation of real gases from
ideal-gas behavior.
Present some of the best-known
equations of state.
111
112
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
3–1
N2
Air
FIGURE 3–1
Nitrogen and gaseous air are
pure substances.
Vapor
Liquid
(a) H2O
Air
Liquid
(b) Air
FIGURE 3–2
A mixture of liquid and gaseous water
is a pure substance, but a mixture of
liquid and gaseous air is not.
FIGURE 3–3
The molecules in a solid are kept at
their positions by the large springlike
intermolecular forces.
■
PURE SUBSTANCE
A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout is called a
pure substance. Water, nitrogen, helium, and carbon dioxide, for example,
are all pure substances.
A pure substance does not have to be of a single chemical element or
compound, however. A mixture of various chemical elements or compounds
also qualifies as a pure substance as long as the mixture is homogeneous.
Air, for example, is a mixture of several gases, but it is often considered
to be a pure substance because it has a uniform chemical composition
(Fig. 3–1). However, a mixture of oil and water is not a pure substance.
Since oil is not soluble in water, it will collect on top of the water, forming
two chemically dissimilar regions.
A mixture of two or more phases of a pure substance is still a pure substance
as long as the chemical composition of all phases is the same (Fig. 3–2). A
mixture of ice and liquid water, for example, is a pure substance because both
phases have the same chemical composition. A mixture of liquid air and gaseous air, however, is not a pure substance since the composition of liquid air
is different from the composition of gaseous air, and thus the mixture is no
longer chemically homogeneous. This is due to different components in air
condensing at different temperatures at a specified pressure.
3.2
■
PHASES OF A PURE SUBSTANCE
We all know from experience that substances exist in different phases.
At room temperature and pressure, copper is a solid, mercury is a liquid,
and nitrogen is a gas. Under different conditions, each may appear in a different phase. Even though there are three principal phases—solid, liquid,
and gas—a substance may have several phases within a principal phase,
each with a different molecular structure. Carbon, for example, may exist as
graphite or diamond in the solid phase. Helium has two liquid phases; iron
has three solid phases. Ice may exist at seven different phases at high pressures. A phase is identified as having a distinct molecular arrangement that
is homogeneous throughout and separated from the others by easily identifiable boundary surfaces. The two phases of H2O in iced water represent a
good example of this.
When studying phases or phase changes in thermodynamics, one does
not need to be concerned with the molecular structure and behavior of different phases. However, it is very helpful to have some understanding of
the molecular phenomena involved in each phase, and a brief discussion of
phase transformations follows.
Intermolecular bonds are strongest in solids and weakest in gases. One
reason is that molecules in solids are closely packed together, whereas in
gases they are separated by relatively large distances.
The molecules in a solid are arranged in a three-dimensional pattern
(lattice) that is repeated throughout (Fig. 3–3). Because of the small distances between molecules in a solid, the attractive forces of molecules on
each other are large and keep the molecules at fixed positions. Note that the
attractive forces between molecules turn to repulsive forces as the distance
between the molecules approaches zero, thus preventing the molecules from
113
CHAPTER 3
(a)
(b)
(c)
FIGURE 3–4
The arrangement of atoms in different phases: (a) molecules are at relatively fixed positions
in a solid, (b) groups of molecules move about each other in the liquid phase, and
(c) molecules move about at random in the gas phase.
piling up on top of each other. Even though the molecules in a solid cannot
move relative to each other, they continually oscillate about their equilibrium positions. The velocity of the molecules during these oscillations
depends on the temperature. At sufficiently high temperatures, the velocity
(and thus the momentum) of the molecules may reach a point where the
intermolecular forces are partially overcome and groups of molecules break
away (Fig. 3–4). This is the beginning of the melting process.
The molecular spacing in the liquid phase is not much different from that
of the solid phase, except the molecules are no longer at fixed positions
relative to each other and they can rotate and translate freely. In a liquid, the
intermolecular forces are weaker relative to solids, but still relatively strong
compared with gases. The distances between molecules generally experience a slight increase as a solid turns liquid, with water being a notable
exception.
In the gas phase, the molecules are far apart from each other, and a molecular order is nonexistent. Gas molecules move about at random, continually
colliding with each other and the walls of the container they are in. Particularly at low densities, the intermolecular forces are very small, and collisions are the only mode of interaction between the molecules. Molecules in
the gas phase are at a considerably higher energy level than they are in the
liquid or solid phases. Therefore, the gas must release a large amount of its
energy before it can condense or freeze.
3–3
■
PHASE-CHANGE PROCESSES
OF PURE SUBSTANCES
There are many practical situations where two phases of a pure substance
coexist in equilibrium. Water exists as a mixture of liquid and vapor in the
boiler and the condenser of a steam power plant. The refrigerant turns from
liquid to vapor in the freezer of a refrigerator. Even though many home
owners consider the freezing of water in underground pipes as the most
important phase-change process, attention in this section is focused on the
114
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
liquid and vapor phases and their mixture. As a familiar substance, water is
used to demonstrate the basic principles involved. Remember, however, that
all pure substances exhibit the same general behavior.
Compressed Liquid and Saturated Liquid
FIGURE 3–5
At 1 atm and 208C, water exists in the
liquid phase (compressed liquid).
State 2
P = 1 atm
T = 100°C
Saturated Vapor and Superheated Vapor
Heat
FIGURE 3–6
At 1 atm pressure and 1008C, water
exists as a liquid that is ready to
vaporize (saturated liquid).
State 3
Saturated
vapor
P = 1 atm
T = 100°C
Consider a piston–cylinder device containing liquid water at 208C and
1 atm pressure (state 1, Fig. 3–5). Under these conditions, water exists
in the liquid phase, and it is called a compressed liquid, or a subcooled
liquid, meaning that it is not about to vaporize. Heat is now transferred to
the water until its temperature rises to, say, 408C. As the temperature rises,
the liquid water expands slightly, and so its specific volume increases. To
accommodate this expansion, the piston moves up slightly. The pressure in
the cylinder remains constant at 1 atm during this process since it depends
on the outside barometric pressure and the weight of the piston, both of
which are constant. Water is still a compressed liquid at this state since it
has not started to vaporize.
As more heat is transferred, the temperature keeps rising until it reaches
1008C (state 2, Fig. 3–6). At this point water is still a liquid, but any heat addition will cause some of the liquid to vaporize. That is, a phase-change process
from liquid to vapor is about to take place. A liquid that is about to vaporize is
called a saturated liquid. Therefore, state 2 is a saturated liquid state.
Saturated
liquid
Heat
FIGURE 3–7
As more heat is transferred, part of the
saturated liquid vaporizes (saturated
liquid–vapor mixture).
Once boiling starts, the temperature stops rising until the liquid is completely vaporized. That is, the temperature will remain constant during the
entire phase-change process if the pressure is held constant. This can easily be verified by placing a thermometer into boiling pure water on top
of a stove. At sea level (P 5 1 atm), the thermometer will always read
1008C if the pan is uncovered or covered with a light lid. During a boiling
process, the only change we will observe is a large increase in the volume
and a steady decline in the liquid level as a result of more liquid turning
to vapor.
Midway about the vaporization line (state 3, Fig. 3–7), the cylinder contains equal amounts of liquid and vapor. As we continue transferring heat,
the vaporization process continues until the last drop of liquid is vaporized
(state 4, Fig. 3–8). At this point, the entire cylinder is filled with vapor that
is on the borderline of the liquid phase. Any heat loss from this vapor will
cause some of the vapor to condense (phase change from vapor to liquid).
A vapor that is about to condense is called a saturated vapor. Therefore,
state 4 is a saturated vapor state. A substance at states between 2 and 4 is
referred to as a saturated liquid–vapor mixture since the liquid and vapor
phases coexist in equilibrium at these states.
One the phase-change process is completed, we are back to a singlephase region again (this time vapor), and further transfer of heat results
in an increase in both the temperature and the specific volume (Fig. 3–9).
At state 5, the temperature of the vapor is, let us say, 3008C; and if we
transfer some heat from the vapor, the temperature may drop somewhat but
115
CHAPTER 3
no condensation will take place as long as the temperature remains above
1008C (for P 5 1 atm). A vapor that is not about to condense (i.e., not a
saturated vapor) is called a superheated vapor. Therefore, water at state 5
is a superheated vapor. This constant-pressure phase-change process is illustrated on a T-v diagram in Fig. 3–10.
If the entire process described here is reversed by cooling the water while
maintaining the pressure at the same value, the water will go back to state 1,
retracing the same path, and in so doing, the amount of heat released will
exactly match the amount of heat added during the heating process.
In our daily life, water implies liquid water and steam implies water vapor.
In thermodynamics, however, both water and steam usually mean only one
thing: H2O.
Saturation Temperature and Saturation Pressure
It probably came as no surprise to you that water started to boil at 1008C.
Strictly speaking, the statement “water boils at 1008C” is incorrect. The
correct statement is “water boils at 1008C at 1 atm pressure.” The only
reason water started boiling at 1008C was because we held the pressure
constant at 1 atm (101.325 kPa). If the pressure inside the cylinder were
raised to 500 kPa by adding weights on top of the piston, water would
start boiling at 151.88C. That is, the temperature at which water starts
boiling depends on the pressure; therefore, if the pressure is fixed, so is
the boiling temperature.
At a given pressure, the temperature at which a pure substance changes
phase is called the saturation temperature Tsat. Likewise, at a given temperature, the pressure at which a pure substance changes phase is called
the saturation pressure Psat. At a pressure of 101.325 kPa, Tsat is 99.978C.
Conversely, at a temperature of 99.978C, Psat is 101.325 kPa. (At 100.008C,
Psat is 101.42 kPa in the ITS-90 discussed in Chap. 1.)
Saturation tables that list the saturation pressure against the temperature (or
the saturation temperature against the pressure) are available for practically
State 4
P = 1 atm
T = 100°C
Heat
FIGURE 3–8
At 1 atm pressure, the temperature
remains constant at 1008C until
the last drop of liquid is vaporized
(saturated vapor).
State 5
P = 1 atm
T = 300°C
Heat
FIGURE 3–9
As more heat is transferred, the
temperature of the vapor starts to rise
(superheated vapor).
P=
1a
tm
T, °C
300
Su
pe
rh
vap e a t e d
or
5
2
Saturated
mixture
3
4
Com
pres
sed
liqu
id
100
20
1
v
FIGURE 3–10
T-v diagram for the heating process of
water at constant pressure.
116
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
TABLE 3–1
Saturation (or vapor) pressure of
water at various temperatures
Saturation
Pressure
Psat, kPa
Temperature
T, 8C
0.260
0.403
0.611
0.872
1.23
1.71
2.34
3.17
4.25
7.38
12.35
101.3 (1 atm)
475.8
1554
3973
8581
210
25
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
40
50
100
150
200
250
300
Psat, kPa
600
400
200
0
0
50
100
150
200
Tsat,°C
FIGURE 3–11
The liquid–vapor saturation curve of a
pure substance (numerical values are
for water).
all substances. A partial listing of such a table is given in Table 3–1 for
water. This table indicates that the pressure of water changing phase (boiling or condensing) at 258C must be 3.17 kPa, and the pressure of water
must be maintained at 3976 kPa (about 40 atm) to have it boil at 2508C.
Also, water can be frozen by dropping its pressure below 0.61 kPa.
It takes a large amount of energy to melt a solid or vaporize a liquid. The
amount of energy absorbed or released during a phase-change process is
called the latent heat. More specifically, the amount of energy absorbed
during melting is called the latent heat of fusion and is equivalent to the
amount of energy released during freezing. Similarly, the amount of energy
absorbed during vaporization is called the latent heat of vaporization
and is equivalent to the energy released during condensation. The magnitudes of the latent heats depend on the temperature or pressure at which the
phase change occurs. At 1 atm pressure, the latent heat of fusion of water is
333.7 kJ/kg and the latent heat of vaporization is 2256.5 kJ/kg.
During a phase-change process, pressure and temperature are obviously
dependent properties, and there is a definite relation between them, that is,
Tsat 5 f(Psat). A plot of Tsat versus Psat, such as the one given for water in
Fig. 3–11, is called a liquid–vapor saturation curve. A curve of this kind
is characteristic of all pure substances.
It is clear from Fig. 3–11 that Tsat increases with Psat. Thus, a substance
at higher pressures boils at higher temperatures. In the kitchen, higher boiling temperatures mean shorter cooking times and energy savings. A beef
stew, for example, may take 1 to 2 h to cook in a regular pan that operates
at 1 atm pressure, but only 20 min in a pressure cooker operating at 3 atm
absolute pressure (corresponding boiling temperature: 1348C).
The atmospheric pressure, and thus the boiling temperature of water,
decreases with elevation. Therefore, it takes longer to cook at higher
altitudes than it does at sea level (unless a pressure cooker is used). For
example, the standard atmospheric pressure at an elevation of 2000 m is
79.50 kPa, which corresponds to a boiling temperature of 93.38C as opposed
to 1008C at sea level (zero elevation). The variation of the boiling temperature of water with altitude at standard atmospheric conditions is given in
Table 3–2. For each 1000 m increase in elevation, the boiling temperature
drops by a little over 38C. Note that the atmospheric pressure at a location,
and thus the boiling temperature, changes slightly with the weather conditions.
But the corresponding change in the boiling temperature is no more than
about 18C.
Some Consequences of Tsat and Psat Dependence
We mentioned earlier that a substance at a specified pressure boils at the
saturation temperature corresponding to that pressure. This phenomenon
allows us to control the boiling temperature of a substance by simply controlling the pressure, and it has numerous applications in practice. Below
we give some examples. The natural drive to achieve phase equilibrium by
allowing some liquid to evaporate is at work behind the scenes.
Consider a sealed can of liquid refrigerant-134a in a room at 258C. If the
can has been in the room long enough, the temperature of the refrigerant in
the can is also 258C. Now, if the lid is opened slowly and some refrigerant is
117
CHAPTER 3
allowed to escape, the pressure in the can will start dropping until it reaches
the atmospheric pressure. If you are holding the can, you will notice its temperature dropping rapidly, and even ice forming outside the can if the air
is humid. A thermometer inserted in the can will register 2268C when the
pressure drops to 1 atm, which is the saturation temperature of refrigerant134a at that pressure. The temperature of the liquid refrigerant will remain
at 2268C until the last drop of it vaporizes.
Another aspect of this interesting physical phenomenon is that a liquid
cannot vaporize unless it absorbs energy in the amount of the latent heat of
vaporization, which is 217 kJ/kg for refrigerant-134a at 1 atm. Therefore,
the rate of vaporization of the refrigerant depends on the rate of heat transfer to the can: the larger the rate of heat transfer, the higher the rate of
vaporization. The rate of heat transfer to the can and thus the rate of vaporization of the refrigerant can be minimized by insulating the can heavily.
In the limiting case of no heat transfer, the refrigerant will remain in the can
as a liquid at 2268C indefinitely.
The boiling temperature of nitrogen at atmospheric pressure is 21968C
(see Table A–3a). This means the temperature of liquid nitrogen exposed to
the atmosphere must be 21968C since some nitrogen will be evaporating.
The temperature of liquid nitrogen remains constant at 21968C until it is
depleted. For this reason, nitrogen is commonly used in low-temperature
scientific studies (such as superconductivity) and cryogenic applications
to maintain a test chamber at a constant temperature of 21968C. This is
done by placing the test chamber into a liquid nitrogen bath that is open
to the atmosphere. Any heat transfer from the environment to the test section is
absorbed by the nitrogen, which evaporates isothermally and keeps the test
chamber temperature constant at 21968C (Fig. 3–12). The entire test section must be insulated heavily to minimize heat transfer and thus liquid
nitrogen consumption. Liquid nitrogen is also used for medical purposes
to burn off unsightly spots on the skin. This is done by soaking a cotton swap in liquid nitrogen and wetting the target area with it. As the
nitrogen evaporates, it freezes the affected skin by rapidly absorbing heat
from it.
A practical way of cooling leafy vegetables is vacuum cooling,
which is based on reducing the pressure of the sealed cooling chamber
to the saturation pressure at the desired low temperature, and evaporating some water from the products to be cooled. The heat of vaporization during evaporation is absorbed from the products, which lowers the
product temperature. The saturation pressure of water at 08C is 0.61 kPa,
and the products can be cooled to 08C by lowering the pressure to this
level. The cooling rate can be increased by lowering the pressure below
0.61 kPa, but this is not desirable because of the danger of freezing and
the added cost.
In vacuum cooling, there are two distinct stages. In the first stage, the
products at ambient temperature, say at 258C, are loaded into the chamber,
and the operation begins. The temperature in the chamber remains constant
until the saturation pressure is reached, which is 3.17 kPa at 258C. In the
second stage that follows, saturation conditions are maintained inside at
progressively lower pressures and the corresponding lower temperatures
until the desired temperature is reached (Fig. 3–13).
TABLE 3–2
Variation of the standard
atmospheric pressure and the
boiling (saturation) temperature
of water with altitude
Elevation,
m
Atmospheric
pressure,
kPa
Boiling
temperature, 8C
0
1,000
2,000
5,000
10,000
20,000
101.33
89.55
79.50
54.05
26.50
5.53
100.0
96.5
93.3
83.3
66.3
34.7
FIGURE 3–12
The temperature of liquid nitrogen
exposed to the atmosphere remains
constant at 21968C, and thus it
maintains the test chamber at 21968C.
Temperature,
°C
Start of cooling
(25°C, 100 kPa)
25
End of cooling
(0°C, 0.61 kPa)
0
0
0.61 1
3.17
10
100
Pressure, kPa
FIGURE 3–13
The variation of the temperature of fruits
and vegetables with pressure during
vacuum cooling from 258C to 08C.
118
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
FIGURE 3–14
In 1775, ice was made by evacuating
the air space in a water tank.
Vacuum cooling is usually more expensive than the conventional refrigerated cooling, and its use is limited to applications that result in much
faster cooling. Products with large surface area per unit mass and a high
tendency to release moisture such as lettuce and spinach are well-suited for
vacuum cooling. Products with low surface area to mass ratio are not suitable, especially those that have relatively impervious peels such as tomatoes
and cucumbers. Some products such as mushrooms and green peas can be
vacuum cooled successfully by wetting them first.
The vacuum cooling just described becomes vacuum freezing if the
vapor pressure in the vacuum chamber is dropped below 0.61 kPa, the saturation pressure of water at 08C. The idea of making ice by using a vacuum
pump is nothing new. Dr. William Cullen actually made ice in Scotland in
1775 by evacuating the air in a water tank (Fig. 3–14).
Package icing is commonly used in small-scale cooling applications to
remove heat and keep the products cool during transit by taking advantage
of the large latent heat of fusion of water, but its use is limited to products
that are not harmed by contact with ice. Also, ice provides moisture as well
as refrigeration.
3–4
■
PROPERTY DIAGRAMS FOR PHASE-CHANGE
PROCESSES
The variations of properties during phase-change processes are best studied
and understood with the help of property diagrams. Next, we develop and
discuss the T-v, P-v, and P-T diagrams for pure substances.
1 The T-v Diagram
The phase-change process of water at 1 atm pressure was described in detail
in the last section and plotted on a T-v diagram in Fig. 3–10. Now we repeat
this process at different pressures to develop the T-v diagram.
Let us add weights on top of the piston until the pressure inside the
cylinder reaches 1 MPa. At this pressure, water has a somewhat smaller
specific volume than it does at 1 atm pressure. As heat is transferred to
the water at this new pressure, the process follows a path that looks very
much like the process path at 1 atm pressure, as shown in Fig. 3–15, but
there are some noticeable differences. First, water starts boiling at a much
higher temperature (179.98C) at this pressure. Second, the specific volume
of the saturated liquid is larger and the specific volume of the saturated
vapor is smaller than the corresponding values at 1 atm pressure. That is,
the horizontal line that connects the saturated liquid and saturated vapor
states is much shorter.
As the pressure is increased further, this saturation line continues to
shrink, as shown in Fig. 3–15, and it becomes a point when the pressure
reaches 22.06 MPa for the case of water. This point is called the critical
point, and it is defined as the point at which the saturated liquid and saturated vapor states are identical.
The temperature, pressure, and specific volume of a substance at the
critical point are called, respectively, the critical temperature Tcr, critical
119
CHAPTER 3
T, °C
Pa
Pa
P
=
0.
01
M
Pa
P
=
0.
1
M
Pa
P
=
1
M
Pa
P
=
8M
Pa
P
373.95
22
M
M
Pa
.
=
06
15
=
=
P
P
Critical point
M
25
>
P
cr
T
or
ap
V
Critical
point
Pc
r
Tcr
P<
pressure Pcr, and critical specific volume vcr. The critical-point properties
of water are Pcr 5 22.06 MPa, Tcr 5 373.958C, and vcr 5 0.003106 m3/kg.
For helium, they are 0.23 MPa, 2267.858C, and 0.01444 m3/kg. The critical
properties for various substances are given in Table A–1 in the appendix.
At pressures above the critical pressure, there is not a distinct phasechange process (Fig. 3–16). Instead, the specific volume of the substance
continually increases, and at all times there is only one phase present.
Eventually, it resembles a vapor, but we can never tell when the change has
occurred. Above the critical state, there is no line that separates the compressed liquid region and the superheated vapor region. However, it is customary to refer to the substance as superheated vapor at temperatures above
the critical temperature and as compressed liquid at temperatures below the
critical temperature.
The saturated liquid states in Fig. 3–15 can be connected by a line called
the saturated liquid line, and saturated vapor states in the same figure can
be connected by another line, called the saturated vapor line. These two
lines meet at the critical point, forming a dome as shown in Fig. 3–17a.
All the compressed liquid states are located in the region to the left of the
saturated liquid line, called the compressed liquid region. All the superheated vapor states are located to the right of the saturated vapor line, called
the superheated vapor region. In these two regions, the substance exists in
a single phase, a liquid or a vapor. All the states that involve both phases in
equilibrium are located under the dome, called the saturated liquid–vapor
mixture region, or the wet region.
cr
v , m3/kg
FIGURE 3–15
T-v diagram of constant-pressure
phase-change processes of a pure
substance at various pressures
(numerical values are for water).
P
0.003106
Saturated
vapor
P
Saturated
liquid
Phase
change
Liq
uid
vcr
v
FIGURE 3–16
At supercritical pressures (P . Pcr),
there is no distinct phase-change
(boiling) process.
120
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
P
P
1
T
ns
t. >
line
liquid
liquid
P
d
Saturated
liquid–vapor
region
T2 =
e
lin
Satura
te
r
e
lin
Saturate
d
r
v
po
po
(a) T-v diagram of a pure substance
va
va
Saturated
liquid–vapor
region
Compressed
liquid
region
Superheated
vapor
region
Superheated
vapor
region
d
te
ra
tu
1 =
P
co
n
2 =
st.
co
Critical
point
Sa
ted
ra
tu
Sa
Compressed
liquid
region
line
Critical
point
cons
t.
>T
1
T1
=c
ons
t.
(b) P-v diagram of a pure substance
v
FIGURE 3–17
Property diagrams of a pure substance.
2 The P-v Diagram
P = 1 MPa
T = 150°C
Heat
FIGURE 3–18
The pressure in a piston–cylinder
device can be reduced by reducing
the weight of the piston.
The general shape of the P-v diagram of a pure substance is very much like
the T-v diagram, but the T 5 constant lines on this diagram have a downward trend, as shown in Fig. 3–17b.
Consider again a piston–cylinder device that contains liquid water at
1 MPa and 1508C. Water at this state exists as a compressed liquid. Now
the weights on top of the piston are removed one by one so that the pressure
inside the cylinder decreases gradually (Fig. 3–18). The water is allowed to
exchange heat with the surroundings so its temperature remains constant.
As the pressure decreases, the volume of the water increases slightly. When
the pressure reaches the saturation-pressure value at the specified temperature (0.4762 MPa), the water starts to boil. During this vaporization process,
both the temperature and the pressure remain constant, but the specific volume increases. Once the last drop of liquid is vaporized, further reduction
in pressure results in a further increase in specific volume. Notice that during the phase-change process, we did not remove any weights. Doing so
would cause the pressure and therefore the temperature to drop [since Tsat 5
f(Psat)], and the process would no longer be isothermal.
When the process is repeated for other temperatures, similar paths are
obtained for the phase-change processes. Connecting the saturated liquid
and the saturated vapor states by a curve, we obtain the P-v diagram of a
pure substance, as shown in Fig. 3–17b.
Extending the Diagrams to Include the Solid Phase
The two equilibrium diagrams developed so far represent the equilibrium states
involving the liquid and the vapor phases only. However, these diagrams can
easily be extended to include the solid phase as well as the solid–liquid and the
121
CHAPTER 3
P
P
Critical
point
Vapor
Liquid + vapor
Solid
Liquid + vapor
Triple line
Triple line
Solid + vapor
Solid + vapor
v
(a) P-v diagram of a substance that contracts on freezing
Liquid
Solid + liquid
Vapor
Liquid
Solid + liquid
Solid
Critical
point
v
(b) P-v diagram of a substance that expands on freezing (such as water)
FIGURE 3–19
P-v diagrams of different substances.
solid–vapor saturation regions. The basic principles discussed in conjunction with the liquid–vapor phase-change process apply equally to the solid–
liquid and solid–vapor phase-change processes. Most substances contract
during a solidification (i.e., freezing) process. Others, like water, expand as
they freeze. The P-v diagrams for both groups of substances are given in
Figs. 3–19a and 3–19b. These two diagrams differ only in the solid–liquid
saturation region. The T-v diagrams look very much like the P-v diagrams,
especially for substances that contract on freezing.
The fact that water expands upon freezing has vital consequences in
nature. If water contracted on freezing as most other substances do, the ice
formed would be heavier than the liquid water, and it would settle to the
bottom of rivers, lakes, and oceans instead of floating at the top. The sun’s
rays would never reach these ice layers, and the bottoms of many rivers,
lakes, and oceans would be covered with ice at times, seriously disrupting
marine life.
We are all familiar with two phases being in equilibrium, but under
some conditions all three phases of a pure substance coexist in equilibrium
(Fig. 3–20). On P-v or T-v diagrams, these triple-phase states form a line
called the triple line. The states on the triple line of a substance have the
same pressure and temperature but different specific volumes. The triple
line appears as a point on the P-T diagrams and, therefore, is often called
the triple point. The triple-point temperatures and pressures of various substances are given in Table 3–3. For water, the triple-point temperature and
pressure are 0.018C and 0.6117 kPa, respectively. That is, all three phases
of water coexist in equilibrium only if the temperature and pressure have
precisely these values. No substance can exist in the liquid phase in stable
equilibrium at pressures below the triple-point pressure. The same can be
said for temperature for substances that contract on freezing. However, substances at high pressures can exist in the liquid phase at temperatures below
the triple-point temperature. For example, water cannot exist in liquid form
Vapor
Liquid
Solid
FIGURE 3–20
At triple-point pressure and
temperature, a substance exists in
three phases in equilibrium.
122
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
TABLE 3–3
Triple-point temperatures and pressures of various substances
Substance
Formula
Ttp, K
Ptp, kPa
Acetylene
Ammonia
Argon
Carbon (graphite)
Carbon dioxide
Carbon monoxide
Deuterium
Ethane
Ethylene
Helium 4 (l point)
Hydrogen
Hydrogen chloride
Mercury
Methane
Neon
Nitric oxide
Nitrogen
Nitrous oxide
Oxygen
Palladium
Platinum
Sulfur dioxide
Titanium
Uranium hexafluoride
Water
Xenon
Zinc
C2H2
NH3
A
C
CO2
CO
D2
C2H6
C2H4
He
H2
HCl
Hg
CH4
Ne
NO
N2
N2O
O2
Pd
Pt
SO2
Ti
UF6
H2O
Xe
Zn
192.4
195.40
83.81
3900
216.55
68.10
18.63
89.89
104.0
2.19
13.84
158.96
234.2
90.68
24.57
109.50
63.18
182.34
54.36
1825
2045
197.69
1941
337.17
273.16
161.3
692.65
120
6.076
68.9
10,100
517
15.37
17.1
8 3 1024
0.12
5.1
7.04
13.9
1.65 3 1027
11.7
43.2
21.92
12.6
87.85
0.152
3.5 3 1023
2.0 3 1024
1.67
5.3 3 1023
151.7
0.61
81.5
0.065
Source: Data from National Bureau of Standards (U.S.) Circ., 500 (1952).
Vapor
Solid
FIGURE 3–21
At low pressures (below the triplepoint value), solids evaporate without
melting first (sublimation).
in equilibrium at atmospheric pressure at temperatures below 08C, but it can
exist as a liquid at 2208C at 200 MPa pressure. Also, ice exists at seven different solid phases at pressures above 100 MPa.
There are two ways a substance can pass from the solid to vapor phase:
either it melts first into a liquid and subsequently evaporates, or it evaporates directly without melting first. The latter occurs at pressures below the
triple-point value, since a pure substance cannot exist in the liquid phase at
those pressures (Fig. 3–21). Passing from the solid phase directly into the
vapor phase is called sublimation. For substances that have a triple-point
pressure above the atmospheric pressure such as solid CO2 (dry ice), sublimation is the only way to change from the solid to vapor phase at atmospheric conditions.
3 The P-T Diagram
Figure 3–22 shows the P-T diagram of a pure substance. This diagram is
often called the phase diagram since all three phases are separated from
each other by three lines. The sublimation line separates the solid and vapor
123
CHAPTER 3
FIGURE 3–22
P-T diagram of pure substances.
P
Substances
that expand
on freezing
Substances
that contract
on freezing
ing
g
ltin
Melt
Me
Critical
point
Liquid
on
ati
iz
or
p
Va
Solid
Triple point
Vapor
Critical
point
Vo
lum
lid
–v a
p
e
e
s
So
lin
Ga
L
vapiquid
or –
Tri
p
le
regions, the vaporization line separates the liquid and vapor regions, and the
melting (or fusion) line separates the solid and liquid regions. These three
lines meet at the triple point, where all three phases coexist in equilibrium.
The vaporization line ends at the critical point because no distinction can be
made between liquid and vapor phases above the critical point. Substances
that expand and contract on freezing differ only in the melting line on the
P-T diagram.
Va
or
po
T
r
p
em
era
tur
e
FIGURE 3–23
P-v-T surface of a substance that
contracts on freezing.
The P-v-T Surface
Pressure
Liquid
Critical
point
Li
vapquid–
or
Tri
ple
lin
e
Solid
Vo
lid
lum
s
So
Ga
The state of a simple compressible substance is fixed by any two independent, intensive properties. Once the two appropriate properties are fixed, all
the other properties become dependent properties. Remembering that any
equation with two independent variables in the form z 5 z(x, y) represents
a surface in space, we can represent the P-v-T behavior of a substance as
a surface in space, as shown in Figs. 3–23 and 3–24. Here T and v may be
viewed as the independent variables (the base) and P as the dependent variable (the height).
All the points on the surface represent equilibrium states. All states along
the path of a quasi-equilibrium process lie on the P-v-T surface since such
a process must pass through equilibrium states. The single-phase regions
appear as curved surfaces on the P-v-T surface, and the two-phase regions
as surfaces perpendicular to the P-T plane. This is expected since the projections of two-phase regions on the P-T plane are lines.
All the two-dimensional diagrams we have discussed so far are merely
projections of this three-dimensional surface onto the appropriate planes.
A P-v diagram is just a projection of the P-v-T surface on the P-v plane,
and a T-v diagram is nothing more than the bird’s-eye view of this surface.
Solid
Liquid
T
Solid–liquid
at
Pressure
lim
b
Su
ion
Va
–va
p
e
or
po
r
Te
er
mp
atu
re
FIGURE 3–24
P-v-T surface of a substance that
expands on freezing (like water).
124
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
The P-v-T surfaces present a great deal of information at once, but in a thermodynamic analysis it is more convenient to work with two-dimensional
diagrams, such as the P-v and T-v diagrams.
u1
P1v1
Control
volume
u2
P2v2
FIGURE 3–25
The combination u 1 Pv is frequently
encountered in the analysis of control
volumes.
3–5
■
PROPERTY TABLES
For most substances, the relationships among thermodynamic properties are
too complex to be expressed by simple equations. Therefore, properties are
frequently presented in the form of tables. Some thermodynamic properties
can be measured easily, but others cannot and are calculated by using the
relations between them and measurable properties. The results of these measurements and calculations are presented in tables in a convenient format. In
the following discussion, the steam tables are used to demonstrate the use of
thermodynamic property tables. Property tables of other substances are used
in the same manner.
For each substance, the thermodynamic properties are listed in more than
one table. In fact, a separate table is prepared for each region of interest
such as the superheated vapor, compressed liquid, and saturated (mixture)
regions. Property tables are given in the appendix in both SI and English
units. The tables in English units carry the same number as the corresponding tables in SI, followed by an identifier E. Tables A–6 and A–6E, for
example, list properties of superheated water vapor, the former in SI and the
latter in English units. Before we get into the discussion of property tables,
we define a new property called enthalpy.
Enthalpy—A Combination Property
A person looking at the tables will notice two new properties: enthalpy h
and entropy s. Entropy is a property associated with the second law of thermodynamics, and we will not use it until it is properly defined in Chap. 7.
However, it is appropriate to introduce enthalpy at this point.
In the analysis of certain types of processes, particularly in power generation and refrigeration (Fig. 3–25), we frequently encounter the combination
of properties u 1 Pv. For the sake of simplicity and convenience, this combination is defined as a new property, enthalpy, and given the symbol h:
kPa·m3 ≡ kJ
kPa·m3/kg ≡ kJ/kg
bar·m3 ≡ 100 kJ
MPa·m3 ≡ 1000 kJ
psi·ft3 ≡ 0.18505 Btu
FIGURE 3–26
The product pressure 3 volume has
energy units.
h 5 u 1 Pv
(kJ/kg)
(3–1)
H 5 U 1 PV
(kJ)
(3–2)
or,
Both the total enthalpy H and specific enthalpy h are simply referred to
as enthalpy since the context clarifies which one is meant. Notice that the equations given above are dimensionally homogeneous. That is, the unit of the
pressure–volume product may differ from the unit of the internal energy
by only a factor (Fig. 3–26). For example, it can be easily shown that
1 kPa·m3 5 1 kJ. In some tables encountered in practice, the internal energy
u is frequently not listed, but it can always be determined from u 5 h 2 Pv.
The widespread use of the property enthalpy is due to Professor Richard
Mollier, who recognized the importance of the group u 1 Pv in the analysis
of steam turbines and in the representation of the properties of steam in
125
CHAPTER 3
tabular and graphical form (as in the famous Mollier chart). Mollier referred
to the group u 1 Pv as heat content and total heat. These terms were not
quite consistent with the modern thermodynamic terminology and were
replaced in the 1930s by the term enthalpy (from the Greek word enthalpien, which means to heat).
Sat.
Temp. press.
°C
kPa
T
Psat
1a
85
90
95
Saturated Liquid and Saturated Vapor States
The properties of saturated liquid and saturated vapor for water are listed in
Tables A–4 and A–5. Both tables give the same information. The only difference is that in Table A–4 properties are listed under temperature and in
Table A–5 under pressure. Therefore, it is more convenient to use Table A–4
when temperature is given and Table A–5 when pressure is given. The use
of Table A–4 is illustrated in Fig. 3–27.
The subscript f is used to denote properties of a saturated liquid, and the
subscript g to denote the properties of saturated vapor. These symbols are
commonly used in thermodynamics and originated from German. Another
subscript commonly used is fg, which denotes the difference between
the saturated vapor and saturated liquid values of the same property. For
example,
Specific volume
m3/kg
Sat.
liquid
vf
57.868 0.001032
70.183 0.001036
84.609 0.001040
Specific
temperature
Sat.
vapor
vg
2.8261
2.3593
1.9808
Specific
volume of
saturated
liquid
Corresponding
saturation
pressure
Specific
volume of
saturated
vapor
FIGURE 3–27
A partial list of Table A–4.
v f 5 specific volume of saturated liquid
v g 5 specific volume of saturated vapor
v fg 5 difference between v g and v f (that is v fg 5 v g 2 v f)
The quantity hfg is called the enthalpy of vaporization (or latent heat
of vaporization). It represents the amount of energy needed to vaporize a unit mass of saturated liquid at a given temperature or pressure.
It decreases as the temperature or pressure increases and becomes zero at
the critical point.
EXAMPLE 3–1
Pressure of Saturated Liquid in a Tank
A rigid tank contains 50 kg of saturated liquid water at 908C. Determine the
pressure in the tank and the volume of the tank.
T, °C
T = 90°C
Sat. liquid
P 5 Psat @ 908C 5 70.183 kPa
(Table A-4)
83
kP
a
SOLUTION A rigid tank contains saturated liquid water. The pressure and
volume of the tank are to be determined.
Analysis The state of the saturated liquid water is shown on a T-v diagram
in Fig. 3–28. Since saturation conditions exist in the tank, the pressure
must be the saturation pressure at 908C:
P=7
90
0.1
The specific volume of the saturated liquid at 908C is
v 5 v f @ 908C 5 0.001036 m3/kg
(Table A-4)
Then the total volume of the tank becomes
V 5 mv 5 (50 kg)(0.001036 m3/kg) 5 0.0518 m3
vf
v
FIGURE 3–28
Schematic and T-v diagram for
Example 3–1.
126
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
P, psia
EXAMPLE 3–2
Saturated
vapor
P = 50 psia
V = 2 ft3
A piston–cylinder device contains 2 ft3 of saturated water vapor at 50-psia
pressure. Determine the temperature and the mass of the vapor inside the cylinder.
T = 280.99°F
50
Temperature of Saturated Vapor in a Cylinder
SOLUTION A cylinder contains saturated water vapor. The temperature and
the mass of vapor are to be determined.
Analysis The state of the saturated water vapor is shown on a P-v diagram
in Fig. 3–29. Since the cylinder contains saturated vapor at 50 psia, the
temperature inside must be the saturation temperature at this pressure:
T 5 Tsat @ 50 psia 5 280.998F
vg
v
(Table A–5E)
The specific volume of the saturated vapor at 50 psia is
v 5 v g @ 50 psia 5 8.5175 ft3/ lbm (Table A–5E)
FIGURE 3–29
Schematic and P-v diagram for
Example 3–2.
Then the mass of water vapor inside the cylinder becomes
m5
EXAMPLE 3–3
V
2 ft3
5
5 0.235 lbm
v
8.5175 ft3/ lbm
Volume and Energy Change during Evaporation
A mass of 200 g of saturated liquid water is completely vaporized at a constant pressure of 100 kPa. Determine (a) the volume change and (b) the
amount of energy transferred to the water.
P, kPa
Sat. liquid
P = 100 kPa
SOLUTION Saturated liquid water is vaporized at constant pressure. The
volume change and the energy transferred are to be determined.
Analysis (a) The process described is illustrated on a P-v diagram in
Fig. 3–30. The volume change per unit mass during a vaporization process
is vfg , which is the difference between vg and vf. Reading these values from
Table A–5 at 100 kPa and substituting yield
Sat. vapor
P = 100 kPa
v fg 5 v g 2 v f 5 1.6941 2 0.001043 5 1.6931 m3/kg
Thus,
100
DV 5 mv fg 5 (0.2 kg)(1.6931 m3/kg) 5 0.3386 m3
vf
vg
FIGURE 3–30
Schematic and P-v diagram for
Example 3–3.
v
(b) The amount of energy needed to vaporize a unit mass of a substance at a
given pressure is the enthalpy of vaporization at that pressure, which is hfg 5
2257.5 kJ/kg for water at 100 kPa. Thus, the amount of energy transferred is
mhfg 5 (0.2 kg)(2257.5 kJ/kg) 5 451.5 kJ
Discussion Note that we have considered the first four decimal digits of vfg
and disregarded the rest. This is because vg has significant numbers to the
first four decimal places only, and we do not know the numbers in the other
decimal places. Copying all the digits from the calculator would mean that
we are assuming vg 5 1.694100, which is not necessarily the case. It could
very well be that vg 5 1.694138 since this number, too, would truncate
to 1.6941. All the digits in our result (1.6931) are significant. But if we
did not truncate the result, we would obtain vfg 5 1.693057, which falsely
implies that our result is accurate to the sixth decimal place.
127
CHAPTER 3
P or T
uid st
ates
d
ate
rs
po
va
t
at
es
Sat. vapor
(3–3)
mtotal
tur
x5
mvapor
Critical point
Sa
During a vaporization process, a substance exists as part liquid and part
vapor. That is, it is a mixture of saturated liquid and saturated vapor
(Fig. 3–31). To analyze this mixture properly, we need to know the proportions of the liquid and vapor phases in the mixture. This is done by defining
a new property called the quality x as the ratio of the mass of vapor to the
total mass of the mixture:
ted liq
Saturated Liquid–Vapor Mixture
Satura
1b
Sat. liquid
where
v
mtotal 5 mliquid 1 mvapor 5 mf 1 mg
Quality has significance for saturated mixtures only. It has no meaning in
the compressed liquid or superheated vapor regions. Its value is between
0 and 1. The quality of a system that consists of saturated liquid is 0 (or
0 percent), and the quality of a system consisting of saturated vapor is 1
(or 100 percent). In saturated mixtures, quality can serve as one of the two
independent intensive properties needed to describe a state. Note that the
properties of the saturated liquid are the same whether it exists alone or in
a mixture with saturated vapor. During the vaporization process, only the
amount of saturated liquid changes, not its properties. The same can be said
about a saturated vapor.
A saturated mixture can be treated as a combination of two subsystems:
the saturated liquid and the saturated vapor. However, the amount of mass for
each phase is usually not known. Therefore, it is often more convenient to
imagine that the two phases are mixed well, forming a homogeneous mixture
(Fig. 3–32). Then the properties of this “mixture” will simply be the average
properties of the saturated liquid–vapor mixture under consideration. Here is
how it is done.
Consider a tank that contains a saturated liquid–vapor mixture. The volume occupied by saturated liquid is Vf , and the volume occupied by saturated vapor is Vg. The total volume V is the sum of the two:
FIGURE 3–31
The relative amounts of liquid and
vapor phases in a saturated mixture
are specified by the quality x.
Saturated vapor
vg
vf
Saturated liquid
vavg
Saturated
≡ liquid–vapor
mixture
V 5 Vf 1 Vg
V 5 mv h mtv avg 5 mf v f 1 mgv g
mf 5 mt 2 mg h mtv avg 5 (mt 2 mg)v f 1 mgv g
FIGURE 3–32
A two-phase system can be treated
as a homogeneous mixture for
convenience.
Dividing by mt yields
v avg 5 (1 2 x)v f 1 xv g
since x 5 mg/mt. This relation can also be expressed as
v avg 5 v f 1 xv fg
(m3/kg)
(3–4)
where vfg 5 vg 2 vf. Solving for quality, we obtain
x5
v avg 2 v f
v fg
(3–5)
128
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
Based on this equation, quality can be related to the horizontal distances
on a P-v or T-v diagram (Fig. 3–33). At a given temperature or pressure, the
numerator of Eq. 3–5 is the distance between the actual state and the saturated
liquid state, and the denominator is the length of the entire horizontal line that
connects the saturated liquid and saturated vapor states. A state of 50 percent
quality lies in the middle of this horizontal line.
The analysis given above can be repeated for internal energy and enthalpy
with the following results:
P or T
x=
AB
AC
v avg – v f
A
B
C
vfg
vf
vavg
vg
(kJ/kg)
(3–7)
where y is v, u, or h. The subscript “avg” (for “average”) is usually dropped
for simplicity. The values of the average properties of the mixtures are
always between the values of the saturated liquid and the saturated vapor
properties (Fig. 3–34). That is,
yf # yavg # yg
Sat. liquid
vf
Finally, all the saturated-mixture states are located under the saturation
curve, and to analyze saturated mixtures, all we need are saturated liquid
and saturated vapor data (Tables A–4 and A–5 in the case of water).
EXAMPLE 3–4
FIGURE 3–34
The v value of a saturated
liquid–vapor mixture lies between
the vf and vg values at the specified
T or P.
havg 5 hf 1 xhfg
yavg 5 yf 1 xyfg
Sat. vapor
vg
vg
(3–6)
All the results are of the same format, and they can be summarized in a
single equation as
P or T
vf < v < vg
(kJ/kg)
v
FIGURE 3–33
Quality is related to the horizontal
distances on P-v and T-v diagrams.
vf
uavg 5 uf 1 xufg
v
Pressure and Volume of a Saturated Mixture
A rigid tank contains 10 kg of water at 908C. If 8 kg of the water is in the
liquid form and the rest is in the vapor form, determine (a) the pressure in
the tank and (b) the volume of the tank.
SOLUTION A rigid tank contains saturated mixture. The pressure and the
volume of the tank are to be determined.
Analysis (a) The state of the saturated liquid–vapor mixture is shown in
Fig. 3–35. Since the two phases coexist in equilibrium, we have a saturated mixture, and the pressure must be the saturation pressure at the given temperature:
P 5 Psat @ 908C 5 70.183 kPa
(Table A– 4)
(b) At 908C, we have vf 5 0.001036 m3/kg and vg 5 2.3593 m3/kg
(Table A–4). One way of finding the volume of the tank is to determine the
volume occupied by each phase and then add them:
V 5 V f 1 V g 5 mfv f 1 mgv g
5 (8 kg)(0.001036 m3/kg) 1 (2 kg)(2.3593 m3/kg)
5 4.73 m3
Another way is to first determine the quality x, then the average specific
volume v, and finally the total volume:
x5
mg
mt
5
2 kg
5 0.2
10 kg
129
CHAPTER 3
T, °C
v 5 v f 1 xv fg
5 0.001036 m3/kg 1 (0.2)[(2.3593 2 0.001036) m3/kg]
T = 90°C
mg = 2 kg
5 0.473 m3/kg
and
mf = 8 kg
3
3
V 5 mv 5 (10 kg)(0.473 m /kg) 5 4.73 m
Discussion The first method appears to be easier in this case since the
masses of each phase are given. In most cases, however, the masses of each
phase are not available, and the second method becomes more convenient.
P
a
kP
90
vf = 0.001036
EXAMPLE 3–5
3
.18
= 70
vg = 2.3593 v, m3/kg
Properties of Saturated Liquid–Vapor Mixture
FIGURE 3–35
Schematic and T-v diagram
for Example 3–4.
An 80-L vessel contains 4 kg of refrigerant-134a at a pressure of 160 kPa.
Determine (a) the temperature, (b) the quality, (c) the enthalpy of the refrigerant, and (d) the volume occupied by the vapor phase.
SOLUTION A vessel is filled with refrigerant-134a. Some properties of the
refrigerant are to be determined.
Analysis (a) The state of the saturated liquid–vapor mixture is shown in
Fig. 3–36. At this point we do not know whether the refrigerant is in the
compressed liquid, superheated vapor, or saturated mixture region. This can
be determined by comparing a suitable property to the saturated liquid and
saturated vapor values. From the information given, we can determine the
specific volume:
v5
0.080 m3
V
5
5 0.02 m3/kg
m
4 kg
P, kPa
R-134a
P = 160 kPa
m = 4 kg
160
T = 215.608C
At 160 kPa, we read
v f 5 0.0007435 m3/kg
v g 5 0.12355 m3/kg
(Table A–12)
Obviously, vf , v , vg, and, the refrigerant is in the saturated mixture region.
Thus, the temperature must be the saturation temperature at the specified
pressure:
T 5 Tsat @ 160 kPa 5 215.608C
(b) Quality can be determined from
x5
v 2 vf
v fg
5
0.02 2 0.0007435
5 0.157
0.12355 2 0.0007435
(c) At 160 kPa, we also read from Table A–12 that hf 5 31.18 kJ/kg and
hfg 5 209.96 kJ/kg. Then,
h 5 hf 1 xhfg
5 31.18 kJ/kg 1 (0.157)(209.96 kJ/kg)
5 64.1 kJ/kg
vf = 0.0007435 vg = 0.12355 v, m3/kg
h f = 31.18
hg = 241.14 h, kJ/kg
FIGURE 3–36
Schematic and P-v diagram
for Example 3–5.
130
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
(d) The mass of the vapor is
mg 5 xmt 5 (0.157) (4 kg) 5 0.628 kg
and the volume occupied by the vapor phase is
V g 5 mgv g 5 (0.628 kg)(0.12355 m3/kg) 5 0.0776 m3 (or 77.6 L)
The rest of the volume (2.4 L) is occupied by the liquid.
h
kJ/kg
Sat.
100
150
P = 0.1 MPa (99.61°C)
1.6941 2505.6 2675.0
1.6959 2506.2 2675.8
1.9367 2582.9 2776.6
1300
7.2605 4687.2
5413.3
…
m3/kg
…
T,°C
…
u
kJ/kg
…
v
P = 0.5 MPa (151.83°C)
Sat. 0.37483 2560.7
200 0.42503 2643.3
250 0.47443 2723.8
FIGURE 3–37
A partial listing of Table A–6.
2748.1
2855.8
2961.0
Property tables are also available for saturated solid–vapor mixtures.
Properties of saturated ice–water vapor mixtures, for example, are listed in
Table A–8. Saturated solid–vapor mixtures can be handled just as saturated
liquid–vapor mixtures.
2 Superheated Vapor
In the region to the right of the saturated vapor line and at temperatures above the critical point temperature, a substance exists as superheated vapor. Since the superheated region is a single-phase region
(vapor phase only), temperature and pressure are no longer dependent
properties and they can conveniently be used as the two independent
properties in the tables. The format of the superheated vapor tables is
illustrated in Fig. 3–37.
In these tables, the properties are listed against temperature for selected
pressures starting with the saturated vapor data. The saturation temperature
is given in parentheses following the pressure value.
Compared to saturated vapor, superheated vapor is characterized by
Lower pressures (P , Psat at a given T )
Higher tempreatures (T . Tsat at a given P)
Higher specific volumes (v . vg at a given P or T )
Higher internal energies (u . ug at a given P or T )
Higher enthalpies (h . hg at a given P or T)
EXAMPLE 3–6
Internal Energy of Superheated Vapor
Determine the internal energy of water at 20 psia and 4008F.
SOLUTION The internal energy of water at a specified state is to be
determined.
Analysis At 20 psia, the saturation temperature is 227.928F. Since T .
Tsat, the water is in the superheated vapor region. Then the internal energy
at the given temperature and pressure is determined from the superheated
vapor table (Table A–6E) to be
u 5 1145.1 Btu/lbm
131
CHAPTER 3
T
Temperature of Superheated Vapor
MP
a
EXAMPLE 3–7
0.5
Determine the temperature of water at a state of P 5 0.5 MPa and h 5
2890 kJ/kg.
SOLUTION The temperature of water at a specified state is to be determined.
Analysis At 0.5 MPa, the enthalpy of saturated water vapor is hg 5 2748.1 kJ/kg.
Since h . hg, as shown in Fig. 3–38, we again have superheated vapor.
Under 0.5 MPa in Table A–6 we read
T, 8C
h, kJ/kg
200
250
2855.8
2961.0
hg h > hg
Obviously, the temperature is between 200 and 2508C. By linear interpolation it is determined to be
T 5 216.38C
h
FIGURE 3–38
At a specified P, superheated vapor
exists at a higher h than the saturated
vapor (Example 3–7).
3 Compressed Liquid
Compressed liquid tables are not as commonly available, and Table A–7
is the only compressed liquid table in this text. The format of Table A–7
is very much like the format of the superheated vapor tables. One reason
for the lack of compressed liquid data is the relative independence of compressed liquid properties from pressure. Variation of properties of compressed liquid with pressure is very mild. Increasing the pressure 100 times
often causes properties to change less than 1 percent.
In the absence of compressed liquid data, a general approximation is
to treat compressed liquid as saturated liquid at the given temperature
(Fig. 3–39). This is because the compressed liquid properties depend on
temperature much more strongly than they do on pressure. Thus,
y ù yf @ T
(3–8)
for compressed liquids, where y is v, u , or h. Of these three properties, the
property whose value is most sensitive to variations in the pressure is the
enthalpy h. Although the above approximation results in negligible error in
v and u, the error in h may reach undesirable levels. However, the error in h
at low to moderate pressures and temperatures can be reduced significantly
by evaluating it from
h ù hf @ T 1 vf @ T (P 2 Psat @T)
(3–9)
instead of taking it to be just hf. Note, however, that the approximation in
Eq. 3–9 does not yield any significant improvement at moderate to high
temperatures and pressures, and it may even backfire and result in greater
error due to overcorrection at very high temperatures and pressures (see
Kostic, 2006).
In general, a compressed liquid is characterized by
Higher pressures (P . Psat at a given T)
Lower tempreatures (T , Tsat at a given P)
Given: P and T
v ~
= vf @T
u~
= uf @T
~ hf @T
h=
FIGURE 3–39
A compressed liquid may be
approximated as a saturated liquid at
the given temperature.
132
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
Lower specific volumes (v , vf at a given P or T)
Lower internal energies (u , uf at a given P or T)
Lower enthalpies (h , hf at a given P or T)
But unlike superheated vapor, the compressed liquid properties are not much
different from the corresponding saturated liquid values.
T, °C
EXAMPLE 3–8
T = 80°C
P = 5 MPa
Approximating Compressed Liquid
as Saturated Liquid
5M
Pa
Determine the internal energy of compressed liquid water at 808C and
5 MPa, using (a) data from the compressed liquid table and (b) saturated
liquid data. What is the error involved in the second case?
SOLUTION The exact and approximate values of the internal energy of
liquid water are to be determined.
Analysis At 808C, the saturation pressure of water is 47.416 kPa, and since
5 MPa . Psat, we obviously have compressed liquid, as shown in Fig. 3–40.
80
(a) From the compressed liquid table (Table A–7)
u ≅ uf @ 80°C
FIGURE 3–40
Schematic and T-u diagram
for Example 3–8.
u
P 5 5 MPa
f u 5 333.82 kJ/kg
T 5 808C
(b) From the saturation table (Table A–4), we read
u > uf @ 808C 5 334.97 kJ/kg
The error involved is
334.97 2 333.82
3 100 5 0.34%
333.82
which is less than 1 percent.
Reference State and Reference Values
The values of u, h, and s cannot be measured directly, and they are calculated from measurable properties using the relations between thermodynamic properties. However, those relations give the changes in properties,
not the values of properties at specified states. Therefore, we need to choose
a convenient reference state and assign a value of zero for a convenient
property or properties at that state. For water, the state of saturated liquid at
0.018C is taken as the reference state, and the internal energy and entropy
are assigned zero values at that state. For refrigerant-134a, the state of saturated liquid at 2408C is taken as the reference state, and the enthalpy and
entropy are assigned zero values at that state. Note that some properties may
have negative values as a result of the reference state chosen.
It should be mentioned that sometimes different tables list different values
for some properties at the same state as a result of using a different reference state. However, in thermodynamics we are concerned with the changes
in properties, and the reference state chosen is of no consequence in
calculations as long as we use values from a single consistent set of tables
or charts.
133
CHAPTER 3
EXAMPLE 3–9
The Use of Steam Tables to Determine Properties
Determine the missing properties and the phase descriptions in the following
table for water:
T, 8C
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
P, kPa
u, kJ/kg
200
Phase description
0.6
125
1600
2950
1000
500
850
75
x
0.0
SOLUTION Properties and phase descriptions of water are to be determined
at various states.
Analysis (a) The quality is given to be x 5 0.6, which implies that 60 percent of the mass is in the vapor phase and the remaining 40 percent is
in the liquid phase. Therefore, we have saturated liquid–vapor mixture at a
pressure of 200 kPa. Then the temperature must be the saturation temperature at the given pressure:
T 5 Tsat @ 200 kPa 5 120.218C
(Table A-5)
At 200 kPa, we also read from Table A–5 that uf 5 504.50 kJ/kg and ufg 5
2024.6 kJ/kg. Then the average internal energy of the mixture is
u 5 uf 1 xufg
5 504.50 kJ/kg 1 (0.6)(2024.6 kJ/kg)
5 1719.26 kJ/kg
(b) This time the temperature and the internal energy are given, but we do
not know which table to use to determine the missing properties because we
have no clue as to whether we have saturated mixture, compressed liquid,
or superheated vapor. To determine the region we are in, we first go to the
saturation table (Table A–4) and determine the uf and ug values at the given
temperature. At 1258C, we read uf 5 524.83 kJ/kg and ug 5 2534.3 kJ/kg.
Next we compare the given u value to these uf and ug values, keeping in
mind that
if
u , uf
if
uf # u # ug we have saturated mixture
if
u . ug
we have compressed liquid
we have superheated vapor
In our case the given u value is 1600, which falls between the uf and ug values at 1258C. Therefore, we have saturated liquid–vapor mixture. Then the
pressure must be the saturation pressure at the given temperature:
P 5 Psat @ 1258C 5 232.23 kPa
(Table A– 4)
The quality is determined from
x5
u 2 uf
ufg
5
1600 2 524.83
5 0.535
2009.5
The criteria above for determining whether we have compressed liquid,
saturated mixture, or superheated vapor can also be used when enthalpy h or
134
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
specific volume v is given instead of internal energy u, or when pressure is
given instead of temperature.
(c) This is similar to case (b), except pressure is given instead of temperature. Following the argument given above, we read the uf and ug values at
the specified pressure. At 1 MPa, we have uf 5 761.39 kJ/kg and ug 5
2582.8 kJ/kg. The specified u value is 2950 kJ/kg, which is greater than
the ug value at 1 MPa. Therefore, we have superheated vapor, and the temperature at this state is determined from the superheated vapor table by
interpolation to be
T 5 395.28C
(Table A– 6)
We would leave the quality column blank in this case since quality has no
meaning for a superheated vapor.
(d ) In this case the temperature and pressure are given, but again we cannot
tell which table to use to determine the missing properties because we do
not know whether we have saturated mixture, compressed liquid, or superheated vapor. To determine the region we are in, we go to the saturation
table (Table A–5) and determine the saturation temperature value at the
given pressure. At 500 kPa, we have Tsat 5 151.838C. We then compare the
given T value to this Tsat value, keeping in mind that
P
=
50
0
kP
a
T, °C
151.83
75
u~
= uf @ 75°C
u
FIGURE 3–41
At a given P and T, a pure substance
will exist as a compressed liquid if
T , Tsat @ P.
if
T , Tsat @ given P
we have compressed liquid
if
T 5 Tsat @ given P
we have saturated mixture
if
T . Tsat @ given P
we have superheated vapor
In our case, the given T value is 758C, which is less than the Tsat value at
the specified pressure. Therefore, we have compressed liquid (Fig. 3–41),
and normally we would determine the internal energy value from the compressed liquid table. But in this case the given pressure is much lower than
the lowest pressure value in the compressed liquid table (which is 5 MPa),
and therefore we are justified to treat the compressed liquid as saturated
liquid at the given temperature (not pressure):
u > uf @ 758C 5 313.99 kJ/kg
(Table A– 4)
We would leave the quality column blank in this case since quality has no
meaning in the compressed liquid region.
(e) The quality is given to be x 5 0, and thus we have saturated liquid at the
specified pressure of 850 kPa. Then the temperature must be the saturation
temperature at the given pressure, and the internal energy must have the
saturated liquid value:
T 5 Tsat @ 850 kPa 5 172.948C
u 5 uf @ 850 kPa 5 731.00 kJ/kg
3–6
■
(Table A–5)
THE IDEAL-GAS EQUATION OF STATE
Property tables provide very accurate information about the properties, but
they are bulky and vulnerable to typographical errors. A more practical and
desirable approach would be to have some simple relations among the properties that are sufficiently general and accurate.
135
CHAPTER 3
Any equation that relates the pressure, temperature, and specific volume
of a substance is called an equation of state. Property relations that involve
other properties of a substance at equilibrium states are also referred to as
equations of state. There are several equations of state, some simple and
others very complex. The simplest and best-known equation of state for
substances in the gas phase is the ideal-gas equation of state. This equation
predicts the P-v-T behavior of a gas quite accurately within some properly
selected region.
Gas and vapor are often used as synonymous words. The vapor phase of a
substance is customarily called a gas when it is above the critical temperature.
Vapor usually implies a gas that is not far from a state of condensation.
In 1662, Robert Boyle, an Englishman, observed during his experiments
with a vacuum chamber that the pressure of gases is inversely proportional
to their volume. In 1802, J. Charles and J. Gay-Lussac, Frenchmen, experimentally determined that at low pressures the volume of a gas is proportional to its temperature. That is,
T
P 5 Ra b
v
or
Pv 5 RT
(3–10)
where the constant of proportionality R is called the gas constant. Equation 3–10
is called the ideal-gas equation of state, or simply the ideal-gas relation,
and a gas that obeys this relation is called an ideal gas. In this equation, P
is the absolute pressure, T is the absolute temperature, and v is the specific
volume.
The gas constant R is different for each gas (Fig. 3– 42) and is determined
from
R5
Ru
M
(kJ/kg·K or kPa·m3/kg·K)
where Ru is the universal gas constant and M is the molar mass (also called
molecular weight) of the gas. The constant Ru is the same for all substances,
and its value is
8.31447 kJ/kmol·K
8.31447 kPa·m3/kmol·K
0.0831447 bar·m3/kmol·K
Ru 5 f
1.98588 Btu/lbmol·R
10.7316 psia·ft3/lbmol·R
1545.37 ft·lbf/lbmol·R
(3–11)
The molar mass M can simply be defined as the mass of one mole (also
called a gram-mole, abbreviated gmol) of a substance in grams, or the mass
of one kmol (also called a kilogram-mole, abbreviated kgmol) in kilograms.
In English units, it is the mass of 1 lbmol in lbm. Notice that the molar
mass of a substance has the same numerical value in both unit systems
because of the way it is defined. When we say the molar mass of nitrogen
is 28, it simply means the mass of 1 kmol of nitrogen is 28 kg, or the mass
of 1 lbmol of nitrogen is 28 lbm. That is, M 5 28 kg/kmol 5 28 lbm/lbmol.
Substance
R, kJ/kg·K
Air
Helium
Argon
Nitrogen
0.2870
2.0769
0.2081
0.2968
FIGURE 3–42
Different substances have different
gas constants.
136
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
The mass of a system is equal to the product of its molar mass M and the
mole number N:
m 5 MN
(kg)
(3–12)
The values of R and M for several substances are given in Table A–1.
The ideal-gas equation of state can be written in several different forms:
V 5 mv h PV 5 mRT
(3–13)
mR 5 (MN)R 5 NRu h PV 5 NRuT
(3–14)
V 5 Nv h Pv 5 RuT
Per unit mass
Per unit mole
v, m3/kg
u, kJ/kg
h, kJ/kg
v, m3/kmol
u , kJ/kmol
h , kJ/kmol
where v is the molar specific volume, that is, the volume per unit mole (in
m3/kmol or ft3/lbmol). A bar above a property denotes values on a unit-mole
basis throughout this text (Fig. 3–43).
By writing Eq. 3–13 twice for a fixed mass and simplifying, the properties of an ideal gas at two different states are related to each other by
P1V 1
T1
FIGURE 3–43
Properties per unit mole are denoted
with a bar on the top.
(3–15)
5
P2V 2
T2
(3-16)
An ideal gas is an imaginary substance that obeys the relation Pv 5 RT. It
has been experimentally observed that the ideal-gas relation given closely
approximates the P-v-T behavior of real gases at low densities. At low pressures and high temperatures, the density of a gas decreases, and the gas
behaves as an ideal gas under these conditions. What constitutes low pressure and high temperature is explained later.
In the range of practical interest, many familiar gases such as air, nitrogen,
oxygen, hydrogen, helium, argon, neon, krypton, and even heavier gases such
as carbon dioxide can be treated as ideal gases with negligible error (often
less than 1 percent). Dense gases such as water vapor in steam power plants
and refrigerant vapor in refrigerators, however, should not be treated as ideal
gases. Instead, the property tables should be used for these substances.
EXAMPLE 3-10
Temperature Rise of Air in a Tire During a Trip
The gage pressure of an automobile tire is measured to be 210 kPa before a
trip and 220 kPa after the trip at a location where the atmospheric pressure
is 95 kPa (Fig. 3–44). Assuming the volume of the tire remains constant
and the air temperature before the trip is 258C, determine air temperature in
the tire after the trip.
SOLUTION The pressure in an automobile tire is measured before
and after a trip. The temperature of air in the tire after the trip is to be
determined.
Assumptions 1 The volume of the tire remains constant. 2 Air is an ideal gas.
Properties The local atmospheric pressure is 95 kPa.
Analysis The absolute pressures in the tire before and after the trip are
FIGURE 3–44
©Stockbyte/Getty Images RF
P1 5 Pgage.1 1 Patm 5 210 1 95 5 305 kPa
P2 5 Pgage.2 1 Patm 5 220 1 95 5 315 kPa
137
CHAPTER 3
Note that air is an ideal gas and the volume is constant, the air temperatures after the trip is determined to be
P1V 1
T1
5
P2V 2
h T2 5
T2
P2
P1
T1 5
315 kPa
(25 1 273 K) 5 307.8 K 5 34.88C
305 kPa
Therefore, the absolute temperature of air in the tire will increase by 6.9%
during this trip.
Discussion Note that the air temperature has risen nearly 108C during this
trip. This shows the importance of measuring the tire pressures before long
trips to avoid errors due to temperature rise of air in tire. Also note that the
unit Kelvin is used for temperature in the ideal gas relation.
Is Water Vapor an Ideal Gas?
This question cannot be answered with a simple yes or no. The error
involved in treating water vapor as an ideal gas is calculated and plotted in
Fig. 3– 45. It is clear from this figure that at pressures below 10 kPa, water
T, °C
17.3
600
500
37.1
10.8 5.0 2.4
0.5
4.1
0.8
20.8 8.8
0.0
0.0
0.1
0.0
0.0
0.0
Ideal Gas
271.0
17.6
56.2
7.4
1.3
0.1
0.0
0.0
0.2
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
30
MP
a
400
152.7
20 MPa
10 MPa
300
49.5
5 MPa
200
16.7
2.6
25.7
0.5
6.0
7.6
1 MPa
100 kPa
100
1.6
0.0
10 kPa
0.0
0.1
0.8 kPa
0
0.001
0.01
0.0
0.1
1
10
100
v, m3/kg
FIGURE 3–45
Percentage of error
([|vtable 2 videal|/vtable] 3 100)
involved in assuming steam to be an
ideal gas, and the region where steam
can be treated as an ideal gas with less
than 1 percent error.
138
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
vapor can be treated as an ideal gas, regardless of its temperature, with negligible error (less than 0.1 percent). At higher pressures, however, the idealgas assumption yields unacceptable errors, particularly in the vicinity of the
critical point and the saturated vapor line (over 100 percent). Therefore, in
air-conditioning applications, the water vapor in the air can be treated as an
ideal gas with essentially no error since the pressure of the water vapor is
very low. In steam power plant applications, however, the pressures involved
are usually very high; therefore, ideal-gas relations should not be used.
3–7
■
COMPRESSIBILITY FACTOR—A MEASURE
OF DEVIATION FROM IDEAL-GAS BEHAVIOR
The ideal-gas equation is very simple and thus very convenient to use.
However, as illustrated in Fig. 3–45, gases deviate from ideal-gas behavior significantly at states near the saturation region and the critical point.
This deviation from ideal-gas behavior at a given temperature and pressure
can accurately be accounted for by the introduction of a correction factor
called the compressibility factor Z defined as
Pv
RT
(3–17)
Pv 5 ZRT
(3–18)
Z5
or
It can also be expressed as
Z5
Ideal
gas
Real
gases
Z=1
>1
Z =1
<1
FIGURE 3–46
The compressibility factor is unity
for ideal gases.
v actual
v ideal
(3–19)
where videal 5 RT/P. Obviously, Z 5 1 for ideal gases. For real gases Z can
be greater than or less than unity (Fig. 3–46). The farther away Z is from
unity, the more the gas deviates from ideal-gas behavior.
We have said that gases follow the ideal-gas equation closely at low pressures and high temperatures. But what exactly constitutes low pressure or high
temperature? Is 21008C a low temperature? It definitely is for most substances
but not for air. Air (or nitrogen) can be treated as an ideal gas at this temperature and atmospheric pressure with an error under 1 percent. This is because
nitrogen is well over its critical temperature (21478C) and away from the
saturation region. At this temperature and pressure, however, most substances
would exist in the solid phase. Therefore, the pressure or temperature of a substance is high or low relative to its critical temperature or pressure.
Gases behave differently at a given temperature and pressure, but they behave
very much the same at temperatures and pressures normalized with respect to
their critical temperatures and pressures. The normalization is done as
PR 5
P
T
and TR 5
Pcr
Tcr
(3–20)
Here PR is called the reduced pressure and TR the reduced temperature.
The Z factor for all gases is approximately the same at the same reduced pressure and temperature. This is called the principle of corresponding states.
139
CHAPTER 3
1.1
1.0
TR = 2.00
0.9
TR = 1.50
0.8
TR = 1.30
Z=
Pv
RT
0.7
0.6
TR = 1.20
0.5
TR = 1.10
Legend:
0.4
Methane
Iso-pentane
Ethylene
n-Heptane
Ethane
Nitrogen
Propane
Carbon dioxide
n-Butane
Water
Average curve based on data on
hydrocarbons
TR = 1.00
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
7.0
Reduced pressure PR
FIGURE 3–47
Comparison of Z factors for various gases.
Source: Gour-Jen Su, “Modified Law of Corresponding States,” Ind. Eng. Chem. (international ed.) 38 (1946), p. 803.
In Fig. 3–47, the experimentally determined Z values are plotted against
PR and TR for several gases. The gases seem to obey the principle of
corresponding states reasonably well. By curve-fitting all the data, we
obtain the generalized compressibility chart that can be used for all
gases (Fig. A–15).
The following observations can be made from the generalized compressibility chart:
1. At very low pressures (PR ,, 1), gases behave as an ideal gas regardless
of temperature (Fig. 3–48).
2. At high temperatures (TR . 2), ideal-gas behavior can be assumed with
good accuracy regardless of pressure (except when PR .. 1).
3. The deviation of a gas from ideal-gas behavior is greatest in the vicinity
of the critical point (Fig. 3–49).
Real
gas
as
P→0
Ideal
gas
FIGURE 3–48
At very low pressures, all gases
approach ideal-gas behavior
(regardless of their temperature).
140
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
T
Nonideal-gas
behavior
EXAMPLE 3–11
Ideal-gas
behavior
The Use of Generalized Charts
Determine the specific volume of refrigerant-134a at 1 MPa and 508C, using
(a) the ideal-gas equation of state and (b) the generalized compressibility
chart. Compare the values obtained to the actual value of 0.021796 m3/kg
and determine the error involved in each case.
SOLUTION The specific volume of refrigerant-134a is to be determined
assuming ideal- and nonideal-gas behavior.
Analysis The gas constant, the critical pressure, and the critical temperature of refrigerant-134a are determined from Table A–1 to be
Ideal-gas
behavior
R 5 0.0815 kPa·m3/kg·K
v
FIGURE 3–49
Gases deviate from the ideal-gas
behavior the most in the neighborhood
of the critical point.
Pcr 5 4.059 MPa
Tcr 5 374.2 K
(a) The specific volume of refrigerant-134a under the ideal-gas assumption is
v5
(0.0815 kPa·m3/kg·K)(323 K)
RT
5
5 0.026325 m3/kg
P
1000 kPa
Therefore, treating the refrigerant-134a vapor as an ideal gas would result in
an error of (0.026325 2 0.021796)/0.021796 5 0.208, or 20.8 percent
in this case.
(b) To determine the correction factor Z from the compressibility chart, we
first need to calculate the reduced pressure and temperature:
P
1 MPa
5
5 0.246
Pcr
4.059 MPa
∂
T
323 K
5
TR 5
5 0.863
Tcr
374.2 K
PR 5
Z 5 0.84
Thus
v 5 Zv ideal 5 (0.84)(0.026325 m3/ kg) 5 0.022113 m3/kg
Discussion The error in this result is less than 2 percent. Therefore, in the
absence of tabulated data, the generalized compressibility chart can be used
with confidence.
PR = P
Pcr
vR =
v
RTcr /Pcr
Z =…
(Fig. A–15)
When P and v, or T and v, are given instead of P and T, the generalized
compressibility chart can still be used to determine the third property, but it
would involve tedious trial and error. Therefore, it is necessary to define one
more reduced property called the pseudo-reduced specific volume vR as
vR 5
FIGURE 3–50
The compressibility factor can also
be determined from a knowledge
of PR and vR.
v actual
RTcr /Pcr
(3–21)
Note that vR is defined differently from PR and TR. It is related to Tcr and
Pcr instead of vcr. Lines of constant vR are also added to the compressibility
charts, and this enables one to determine T or P without having to resort to
time-consuming iterations (Fig. 3–50).
141
CHAPTER 3
EXAMPLE 3–12
Using Generalized Charts to Determine Pressure
Determine the pressure of water vapor at 6008F and 0.51431 ft3/lbm, using
(a) the steam tables, (b) the ideal-gas equation, and (c) the generalized compressibility chart.
SOLUTION The pressure of water vapor is to be determined in three different ways.
Analysis A sketch of the system is given in Fig. 3–51. The gas constant,
the critical pressure, and the critical temperature of steam are determined
from Table A–1E to be
H2O
T = 600°F
v = 0.51431 ft3/lbm
P=?
FIGURE 3–51
Schematic for Example 3–12.
R 5 0.5956 psia·ft3/lbm·R
Pcr 5 3200 psia
Tcr 5 1164.8 R
(a) The pressure at the specified state is determined from Table A–6E to be
v 5 0.51431 ft3/lbm
f P 5 1000 psia
T 5 6008F
This is the experimentally determined value, and thus it is the most accurate.
(b) The pressure of steam under the ideal-gas assumption is determined
from the ideal-gas relation to be
(0.5956 psia·ft3/lbm·R)(1060 R)
RT
P5
5
5 1228 psia
v
0.51431 ft3/lbm
Therefore, treating the steam as an ideal gas would result in an error of
(1228 2 1000)/1000 5 0.228, or 22.8 percent in this case.
(c) To determine the correction factor Z from the compressibility chart
(Fig. A–15), we first need to calculate the pseudo-reduced specific volume
and the reduced temperature:
v actual
3
(0.51431 ft /lbm)(3200 psia)
5
5 2.372
RTcr /Pcr
(0.5956 psia·ft3/lbm·R)(1164.8 R)
∂ PR 5 0.33
T
1060 R
5
TR 5
5 0.91
Tcr
1164.8 R
vR 5
P, psia
Exact
Z chart
Ideal gas
1000
1056
1228
(from Example 3-12)
FIGURE 3–52
Results obtained by using the
compressibility chart are usually
within a few percent of actual values.
Thus,
P 5 PRPcr 5 (0.33)(3200 psia) 5 1056 psia
Discussion Using the compressibility chart reduced the error from 22.8 to
5.6 percent, which is acceptable for most engineering purposes (Fig. 3–52).
A bigger chart, of course, would give better resolution and reduce the reading errors. Notice that we did not have to determine Z in this problem since
we could read PR directly from the chart.
3–8
■
OTHER EQUATIONS OF STATE
The ideal-gas equation of state is very simple, but its range of applicability is
limited. It is desirable to have equations of state that represent the P-v-T behavior
of substances accurately over a larger region with no limitations. Such equations
are naturally more complicated. Several equations have been proposed for this
purpose (Fig. 3–53), but we shall discuss only three: the van der Waals equation
van der Waals
Berthelet
Redlich-Kwang
Beattie-Bridgeman
Benedict-Webb-Rubin
Strobridge
Virial
FIGURE 3–53
Several equations of state have been
proposed throughout history.
142
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
P
because it is one of the earliest, the Beattie-Bridgeman equation of state because
it is one of the best known and is reasonably accurate, and the Benedict-WebbRubin equation because it is one of the more recent and is very accurate.
van der Waals Equation of State
The van der Waals equation of state was proposed in 1873, and it has two
constants that are determined from the behavior of a substance at the critical
point. It is given by
Critical point
T
cr =
co
nst
an
t
aP 1
v
FIGURE 3–54
Critical isotherm of a pure substance
has an inflection point at the critical
state.
a
b(v 2 b) 5 RT
v2
(3–22)
Van der Waals intended to improve the ideal-gas equation of state by including two of the effects not considered in the ideal-gas model: the intermolecular
attraction forces and the volume occupied by the molecules themselves.
The term a /v 2 accounts for the intermolecular forces, and b accounts for the
volume occupied by the gas molecules. In a room at atmospheric pressure
and temperature, the volume actually occupied by molecules is only about
one-thousandth of the volume of the room. As the pressure increases, the
volume occupied by the molecules becomes an increasingly significant part
of the total volume. Van der Waals proposed to correct this by replacing v
in the ideal-gas relation with the quantity v 2 b, where b represents the volume occupied by the gas molecules per unit mass.
The determination of the two constants appearing in this equation is based
on the observation that the critical isotherm on a P-v diagram has a horizontal
inflection point at the critical point (Fig. 3–54). Thus, the first and the second
derivatives of P with respect to v at the critical point must be zero. That is,
a
0P
0 2P
b
5 0 and a 2 b
50
0v T 5Tcr 5const
0v T 5Tcr 5const
By performing the differentiations and eliminating vcr, the constants a and b
are determined to be
a5
27R 2 T 2cr
64Pcr
and b 5
RTcr
8Pcr
(3–23)
The constants a and b can be determined for any substance from the criticalpoint data alone (Table A–1).
The accuracy of the van der Waals equation of state is often inadequate,
but it can be improved by using values of a and b that are based on the actual
behavior of the gas over a wider range instead of a single point. Despite its
limitations, the van der Waals equation of state has a historical value in that it
was one of the first attempts to model the behavior of real gases. The van der
Waals equation of state can also be expressed on a unit-mole basis by replacing the v in Eq. 3–22 by v and the R in Eqs. 3–22 and 3–23 by Ru.
Beattie-Bridgeman Equation of State
The Beattie-Bridgeman equation, proposed in 1928, is an equation of state
based on five experimentally determined constants. It is expressed as
P5
RuT
v2
a1 2
c
A
b(v 1 B) 2 2
v T3
v
(3–24)
143
CHAPTER 3
TABLE 3–4
Constants that appear in the Beattie-Bridgeman and the Benedict-Webb-Rubin equations of state
(a) When P is in kPa, v– is in m3/kmol, T is in K, and R 5 8.314 kPa·m3/kmol·K, the five constants in the Beattieu
Bridgeman equation are as follows:
Gas
Air
Argon, Ar
Carbon dioxide, CO2
Helium, He
Hydrogen, H2
Nitrogen, N2
Oxygen, O2
A0
a
B0
b
c
131.8441
130.7802
507.2836
2.1886
20.0117
136.2315
151.0857
0.01931
0.02328
0.07132
0.05984
20.00506
0.02617
0.02562
0.04611
0.03931
0.10476
0.01400
0.02096
0.05046
0.04624
20.001101
0.0
0.07235
0.0
20.04359
20.00691
0.004208
4.34 3 104
5.99 3 104
6.60 3 105
40
504
4.20 3 104
4.80 3 104
Source: Gordon J. Van Wylen and Richard E. Sonntag, Fundamentals of Classical Thermodynamics, English/SI Version, 3rd ed. (New York: John Wiley & Sons,
1986), p. 46, table 3.3.
(b) When P is in kPa, v– is in m3/kmol, T is in K, and Ru 5 8.314 kPa·m3/kmol·K, the eight constants in the BenedictWebb-Rubin equation are as follows:
Gas
a
n-Butane,
C4H10
Carbon
dioxide, CO2
Carbon
monoxide, CO
Methane, CH4
Nitrogen, N2
A0
b
B0
c
C0
7
a
8
g
23
190.68
1021.6
0.039998
0.12436
3.205 3 10
1.006 3 10
1.101 3 10
13.86
277.30
0.007210
0.04991
1.511 3 106
1.404 3 107
8.470 3 1025
0.00539
3.71
5.00
2.54
135.87
187.91
106.73
0.002632
0.003380
0.002328
0.05454
0.04260
0.04074
1.054 3 105
2.578 3 105
7.379 3 104
8.673 3 105
2.286 3 106
8.164 3 105
1.350 3 1024
1.244 3 1024
1.272 3 1024
0.0060
0.0060
0.0053
0.0340
Source: Kenneth Wark, Thermodynamics, 4th ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1983), p. 815, table A-21M. Originally published in H. W. Cooper and J. C.
Goldfrank, Hydrocarbon Processing 46, no. 12 (1967), p. 141.
where
a
b
A 5 A0 a1 2 b and B 5 B0 a1 2 b
v
v
van der Waals: 2 constants.
Accurate over a limited range.
(3–25)
The constants appearing in the above equation are given in Table 3–4 for
various substances. The Beattie-Bridgeman equation is known to be reasonably accurate for densities up to about 0.8rcr, where rcr is the density of the
substance at the critical point.
Benedict-Webb-Rubin Equation of State
Benedict, Webb, and Rubin extended the Beattie-Bridgeman equation in
1940 by raising the number of constants to eight. It is expressed as
P5
RuT
v
1 aB0RuT 2 A0 2
C0 1
bRuT 2 a
g
aa
c
22
b 1
1 6 1 3 2 a1 1 2 be2g/v
T2 v 2
v3
v
v T
v
Beattie-Bridgeman: 5 constants.
Accurate for r ≤ 0.8rcr.
Benedict-Webb-Rubin: 8 constants.
Accurate for r ≤ 2.5rcr.
Strobridge: 16 constants.
More suitable for
computer calculations.
Virial: may vary.
Accuracy depends on the
number of terms used.
(3–26)
The values of the constants appearing in this equation are given in Table 3–4.
This equation can handle substances at densities up to about 2.5rcr. In 1962,
Strobridge further extended this equation by raising the number of constants
to 16 (Fig. 3–55).
FIGURE 3–55
Complex equations of state represent
the P-v-T behavior of gases more
accurately over a wider range.
144
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
20.7%
14.1%
2.1%
100
>100%
>100%
>100%
6.7%
0.7%
0.1%
11.6%
6.3%
1.2%
5.7%
59.3%
18.7%
0.1
1.1%
0.1%
0.0%
2.8%
0.1%
0.1%
3.2%
0.1%
1.0%
15.2%
74.5%
51.0%
1.2%
0.1%
0.1%
0.4%
0.1%
0.4%
7.9%
0.7%
5.2%
0.5%
0.0%
0.0%
0.1%
0.0%
0.0%
0.5%
0.1%
0.0%
0.1%
0.0%
0.0%
0.5%
0.0%
0.0%
0.1%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.1%
0.0%
0.2%
5.2%
0.6%
3.7%
1
1.6%
0.2%
1.3%
10
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
van der Waals (top)
Beattie-Bridgeman (middle)
Benedict-Webb-Rubin (bottom)
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.0%
0.4%
0.1%
0.1%
0.9%
0.1%
0.1%
3.3%
0.4%
2.5%
0.1 MP
a
0.2 MP
a
1 MPa
2 MPa
4 MPa
2.3%
0.1%
0.0%
1.0%
0.1%
0.1%
MP
a
2.9%
0.3%
0.7%
200
5.3%
0.1%
0.1%
1.9%
0.1%
0.1%
125
3.7%
0.1%
0.4%
4.2%
0.1%
0.2%
0.0
4.7%
0.2%
0.2%
300
0
0.01
10 MPa
20 MPa
T, K
0.8% 0.4%
0.1% 0.1%
0.8% 0.3%
100
v, m3/kmol
FIGURE 3–56
Percentage of error involved in various equations of state for nitrogen (% error 5 [(|vtable 2 vequation|)/vtable] 3 100).
Virial Equation of State
The equation of state of a substance can also be expressed in a series form as
P5
b(T)
c(T)
d(T)
a(T)
RT
1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 ...
v
v
v
v
v
(3–27)
This and similar equations are called the virial equations of state, and the
coefficients a(T ), b(T ), c(T ), and so on, that are functions of temperature
alone are called virial coefficients. These coefficients can be determined
experimentally or theoretically from statistical mechanics. Obviously, as the
pressure approaches zero, all the virial coefficients will vanish and the equation will reduce to the ideal-gas equation of state. The P-v-T behavior of
a substance can be represented accurately with the virial equation of state
over a wider range by including a sufficient number of terms. The equations
of state discussed here are applicable to the gas phase of the substances
only, and thus should not be used for liquids or liquid–vapor mixtures.
145
CHAPTER 3
Complex equations represent the P-v-T behavior of substances reasonably well and are very suitable for digital computer applications. For hand
calculations, however, it is suggested that the reader use the property tables
or the simpler equations of state for convenience. This is particularly true
for specific-volume calculations since all the earlier equations are implicit
in v and require a trial-and-error approach. The accuracy of the van der
Waals, Beattie-Bridgeman, and Benedict-Webb-Rubin equations of state is
illustrated in Fig. 3–56. It is apparent from this figure that the BenedictWebb-Rubin equation of state is usually the most accurate.
EXAMPLE 3–13
Different Methods of Evaluating Gas Pressure
Predict the pressure of nitrogen gas at T 5 175 K and v 5 0.00375 m3/kg
on the basis of (a) the ideal-gas equation of state, (b) the van der Waals
equation of state, (c) the Beattie-Bridgeman equation of state, and (d) the
Benedict-Webb-Rubin equation of state. Compare the values obtained to the
experimentally determined value of 10,000 kPa.
SOLUTION The pressure of nitrogen gas is to be determined using four different equations of state.
Properties The gas constant of nitrogen gas is 0.2968 kPa·m3/kg·K (Table A–1).
Analysis (a) Using the ideal-gas equation of state, the pressure is found to be
P5
(0.2968 kPa·m3/kg·K)(175 K)
RT
5
5 13,851 kPa
v
0.00375 m3/kg
which is in error by 38.5 percent.
(b) The van der Waals constants for nitrogen are determined from Eq. 3–23
to be
a 5 0.175 m6·kPa/kg2
b 5 0.00138 m3/kg
From Eq. 3–22,
P5
RT
a
2 2 5 9471 kPa
v2b
v
which is in error by 5.3 percent.
(c) The constants in the Beattie-Bridgeman equation are determined from
Table 3–4 to be
A 5 102.29
B 5 0.05378
c 5 4.2 3 104
Also, v– 5 Mv 5 (28.013 kg/mol)(0.00375 m3/kg) 5 0.10505 m3/kmol.
Substituting these values into Eq. 3–24, we obtain
P5
RuT
v2
a1 2
c
A
b(v 1 B) 2 2 5 10,110 kPa
v T3
v
which is in error by 1.1 percent.
146
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
(d ) The constants in the Benedict-Webb-Rubin equation are determined
from Table 3–4 to be
a 5 2.54
A0 5 106.73
b 5 0.002328
B0 5 0.04074
4
c 5 7.379 3 10
C0 5 8.164 3 105
a 5 1.272 3 10 24
g 5 0.0053
Substituting these values into Eq. 3–26 gives
P5
RuT
v
1 aB0RuT 2 A0 2
C0 1
bRuT 2 a
b 21
2
T v
v3
g
aa
c
22
1 3 2 a1 1 2 be2g/v
6
v
v T
v
5 10,009 kPa
1
which is in error by only 0.09 percent. Thus, the accuracy of the BenedictWebb-Rubin equation of state is rather impressive in this case.
TOPIC OF SPECIAL INTEREST*
Patm = Pa + Pv
Air
Water
vapor
FIGURE 3–57
Atmospheric pressure is the sum
of the dry air pressure Pa and the
vapor pressure Pv.
Vapor Pressure and Phase Equilibrium
The pressure in a gas container is due to the individual molecules striking
the wall of the container and exerting a force on it. This force is proportional to the average velocity of the molecules and the number of molecules
per unit volume of the container (i.e., molar density). Therefore, the pressure
exerted by a gas is a strong function of the density and the temperature of the
gas. For a gas mixture, the pressure measured by a sensor such as a transducer is the sum of the pressures exerted by the individual gas species, called
the partial pressure. It can be shown (see Chap. 13) that the partial pressure
of a gas in a mixture is proportional to the number of moles (or the mole
fraction) of that gas.
Atmospheric air can be viewed as a mixture of dry air (air with zero moisture content) and water vapor (also referred to as moisture), and the atmospheric pressure is the sum of the pressure of dry air Pa and the pressure of
water vapor, called the vapor pressure Pv (Fig. 3–57). That is,
Patm 5 Pa 1 Pv
(3–28)
(Note that in some applications, the phrase “vapor pressure” is used to indicate saturation pressure.) The vapor pressure constitutes a small fraction
(usually under 3 percent) of the atmospheric pressure since air is mostly
nitrogen and oxygen, and the water molecules constitute a small fraction
(usually under 3 percent) of the total molecules in the air. However, the
amount of water vapor in the air has a major impact on thermal comfort and
many processes such as drying.
*This section can be skipped without a loss in continuity.
147
CHAPTER 3
Air can hold a certain amount of moisture only, and the ratio of the actual
amount of moisture in the air at a given temperature to the maximum amount
air can hold at that temperature is called the relative humidity f. The relative humidity ranges from 0 for dry air to 100 percent for saturated air (air
that cannot hold any more moisture). The vapor pressure of saturated air at a
given temperature is equal to the saturation pressure of water at that temperature.
For example, the vapor pressure of saturated air at 258C is 3.17 kPa.
The amount of moisture in the air is completely specified by the temperature and the relative humidity, and the vapor pressure is related to relative
humidity f by
Pv 5 fPsat @ T
(3–29)
where Psat @ T is the saturation pressure of water at the specified temperature. For
example, the vapor pressure of air at 258C and 60 percent relative humidity is
Pv 5 fPsat @ 258C 5 0.6 3 (3.17 kPa) 5 1.90 kPa
The desirable range of relative humidity for thermal comfort is 40 to 60 percent.
Note that the amount of moisture air can hold is proportional to the saturation pressure, which increases with temperature. Therefore, air can hold
more moisture at higher temperatures. Dropping the temperature of moist air
reduces its moisture capacity and may result in the condensation of some of
the moisture in the air as suspended water droplets (fog) or as a liquid film
on cold surfaces (dew). So it is no surprise that fog and dew are common
occurrences at humid locations especially in the early morning hours when
the temperatures are the lowest. Both fog and dew disappear (evaporate) as
the air temperature rises shortly after sunrise. You also may have noticed that
electronic devices such as camcorders come with warnings against bringing
them into moist indoors when the devices are cold to avoid moisture condensation on the sensitive electronics of the devices.
It is a common observation that whenever there is an imbalance of a commodity in a medium, nature tends to redistribute it until a “balance” or “equality”
is established. This tendency is often referred to as the driving force, which is
the mechanism behind many naturally occurring transport phenomena such as
heat transfer, fluid flow, electric current, and mass transfer. If we define the
amount of a commodity per unit volume as the concentration of that commodity, we can say that the flow of a commodity is always in the direction of
decreasing concentration, that is, from the region of high concentration to the
region of low concentration (Fig. 3–58). The commodity simply creeps away
during redistribution, and thus the flow is a diffusion process.
We know from experience that a wet T-shirt hanging in an open area eventually dries, a small amount of water left in a glass evaporates, and the aftershave in an open bottle quickly disappears. These and many other similar
examples suggest that there is a driving force between the two phases of a
substance that forces the mass to transform from one phase to another. The
magnitude of this force depends on the relative concentrations of the two
phases. A wet T-shirt dries much faster in dry air than it would in humid air.
In fact, it does not dry at all if the relative humidity of the environment is
100 percent and thus the air is saturated. In this case, there is no transformation from the liquid phase to the vapor phase, and the two phases are in
Water
Salty
water
Salt
(a) Before
(b) After
FIGURE 3–58
Whenever there is a concentration
difference of a physical quantity in
a medium, nature tends to equalize
things by forcing a flow from the high
to the low concentration region.
148
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
Pv
Water
vapor
phase equilibrium. For liquid water that is open to the atmosphere, the criterion for phase equilibrium can be expressed as follows: The vapor pressure
in the air must be equal to the saturation pressure of water at the water
temperature. That is (Fig. 3–59),
Phase equilibrium criterion for water exposed to air:
Liquid water
T
FIGURE 3–59
When open to the atmosphere, water is
in phase equilibrium with the vapor in
the air if the vapor pressure is equal to
the saturation pressure of water.
Pv 5 Psat @ T
(3–30)
Therefore, if the vapor pressure in the air is less than the saturation pressure
of water at the water temperature, some liquid will evaporate. The larger the
difference between the vapor and saturation pressures, the higher the rate of
evaporation. The evaporation has a cooling effect on water, and thus reduces
its temperature. This, in turn, reduces the saturation pressure of water and
thus the rate of evaporation until some kind of quasi-steady operation is
reached. This explains why water is usually at a considerably lower temperature than the surrounding air, especially in dry climates. It also suggests
that the rate of evaporation of water can be increased by increasing the water
temperature and thus the saturation pressure of water.
Note that the air at the water surface is always saturated because of the
direct contact with water, and thus the vapor pressure. Therefore, the vapor
pressure at the lake surface is the saturation pressure of water at the temperature of the water at the surface. If the air is not saturated, then the vapor
pressure decreases to the value in the air at some distance from the water
surface, and the difference between these two vapor pressures is the driving
force for the evaporation of water.
The natural tendency of water to evaporate in order to achieve phase
equilibrium with the water vapor in the surrounding air forms the basis for
the operation of the evaporative coolers (also called the swamp coolers).
In such coolers, hot and dry outdoor air is forced to flow through a wet
cloth before entering a building. Some of the water evaporates by absorbing heat from the air, and thus cooling it. Evaporative coolers are commonly used in dry climates and provide effective cooling. They are much
cheaper to run than air conditioners since they are inexpensive to buy, and
the fan of an evaporative cooler consumes much less power than the compressor of an air conditioner.
Boiling and evaporation are often used interchangeably to indicate phase
change from liquid to vapor. Although they refer to the same physical process, they differ in some aspects. Evaporation occurs at the liquid–vapor
interface when the vapor pressure is less than the saturation pressure of the
liquid at a given temperature. Water in a lake at 208C, for example, evaporates to air at 208C and 60 percent relative humidity since the saturation
pressure of water at 208C is 2.34 kPa, and the vapor pressure of air at 208C
and 60 percent relative humidity is 1.4 kPa. Other examples of evaporation are the drying of clothes, fruits, and vegetables; the evaporation of
sweat to cool the human body; and the rejection of waste heat in wet cooling towers. Note that evaporation involves no bubble formation or bubble
motion (Fig. 3–60).
Boiling, on the other hand, occurs at the solid–liquid interface when a
liquid is brought into contact with a surface maintained at a temperature Ts
sufficiently above the saturation temperature Tsat of the liquid. At 1 atm, for
example, liquid water in contact with a solid surface at 1108C boils since
149
CHAPTER 3
the saturation temperature of water at 1 atm is 1008C. The boiling process is characterized by the rapid motion of vapor bubbles that form at the
solid–liquid interface, detach from the surface when they reach a certain
size, and attempt to rise to the free surface of the liquid. When cooking, we
do not say water is boiling unless we see the bubbles rising to the top.
FIGURE 3–60
A liquid-to-vapor phase change
process is called evaporation if it
occurs at a liquid–vapor interface,
and boiling if it occurs at a solid–
liquid interface.
©John A Rizzo/Getty Images RF ©David Chasey/Getty Images RF
EXAMPLE 3–14
Temperature Drop of a Lake Due to Evaporation
On a summer day, the air temperature over a lake is measured to be 258C.
Determine water temperature of the lake when phase equilibrium conditions
are established between the water in the lake and the vapor in the air for
relative humidities of 10, 80, and 100 percent for the air (Fig. 3–61).
SOLUTION Air at a specified temperature is blowing over a lake. The equilibrium temperatures of water for three different cases are to be determined.
Analysis The saturation pressure of water at 258C, from Table 3–1, is 3.17 kPa.
Then the vapor pressures at relative humidities of 10, 80, and 100 percent
are determined from Eq. 3–29 to be
Relative humidity 5 10%:
Pv1 5 f1Psat @ 258C 5 0.1 3 (3.17 kPa)
5 0.317 kPa
Relative humidity 5 80%:
Pv 2 5 f2Psat @ 258C 5 0.8 3 (3.17 kPa)
5 2.536 kPa
Relative humidity 5 100%
Pv3 5 f3Psat @258C 5 1.0 3 (3.17 kPa)
5 3.17 kPa
The saturation temperatures corresponding to these pressures are determined
from Table 3–1 (or Table A–5) by interpolation to be
T1 5 28.08C T2 5 21.28C and T3 5 258C
Air
25°C
f = 10%
Pv
Pv = Psat @ T
T
Lake
FIGURE 3–61
Schematic for Example 3–14.
150
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
Therefore, water will freeze in the first case even though the surrounding
air is hot. In the last case the water temperature will be the same as the
surrounding air temperature.
Discussion You are probably skeptical about the lake freezing when the air
is at 258C, and you are right. The water temperature drops to 288C in the
limiting case of no heat transfer to the water surface. In practice the water
temperature drops below the air temperature, but it does not drop to 288C
because (1) it is very unlikely for the air over the lake to be so dry (a relative humidity of just 10 percent) and (2) as the water temperature near the
surface drops, heat transfer from the air and the lower parts of the water
body will tend to make up for this heat loss and prevent the water temperature from dropping too much. The water temperature stabilizes when
the heat gain from the surrounding air and the water body equals the heat
loss by evaporation, that is, when a dynamic balance is established between
heat and mass transfer instead of phase equilibrium. If you try this experiment using a shallow layer of water in a well-insulated pan, you can actually
freeze the water if the air is very dry and relatively cool.
SUMMARY
A substance that has a fixed chemical composition throughout is called a pure substance. A pure substance exists in
different phases depending on its energy level. In the liquid
phase, a substance that is not about to vaporize is called a
compressed or subcooled liquid. In the gas phase, a substance that is not about to condense is called a superheated
vapor. During a phase-change process, the temperature and
pressure of a pure substance are dependent properties. At a
given pressure, a substance changes phase at a fixed temperature, called the saturation temperature. Likewise, at a given
temperature, the pressure at which a substance changes
phase is called the saturation pressure. During a boiling process, both the liquid and the vapor phases coexist in equilibrium, and under this condition the liquid is called saturated
liquid and the vapor saturated vapor.
In a saturated liquid–vapor mixture, the mass fraction of
vapor is called the quality and is expressed as
x5
mvapor
In the absence of compressed liquid data, a general
approximation is to treat a compressed liquid as a saturated
liquid at the given temperature,
y > yf @ T
where y stands for v, u, or h.
The state beyond which there is no distinct vaporization
process is called the critical point. At supercritical pressures,
a substance gradually and uniformly expands from the liquid
to vapor phase. All three phases of a substance coexist in
equilibrium at states along the triple line characterized by
triple-line temperature and pressure. The compressed liquid
has lower v, u, and h values than the saturated liquid at the
same T or P. Likewise, superheated vapor has higher v, u,
and h values than the saturated vapor at the same T or P.
Any relation among the pressure, temperature, and specific volume of a substance is called an equation of state.
The simplest and best-known equation of state is the idealgas equation of state, given as
mtotal
Quality may have values between 0 (saturated liquid) and
1 (saturated vapor). It has no meaning in the compressed
liquid or superheated vapor regions. In the saturated mixture region, the average value of any intensive property y is
determined from
y 5 yf 1 xyfg
Pv 5 RT
where R is the gas constant. Caution should be exercised in
using this relation since an ideal gas is a fictitious substance.
Real gases exhibit ideal-gas behavior at relatively low pressures and high temperatures.
The deviation from ideal-gas behavior can be properly
accounted for by using the compressibility factor Z , defined as
Z5
where f stands for saturated liquid and g for saturated vapor.
v actual
Pv
or Z 5
RT
v ideal
151
CHAPTER 3
The Z factor is approximately the same for all gases at the
same reduced temperature and reduced pressure, which are
defined as
T
P
and PR 5
TR 5
Tcr
Pcr
where Pcr and Tcr are the critical pressure and temperature,
respectively. This is known as the principle of corresponding
states. When either P or T is unknown, it can be determined
from the compressibility chart with the help of the pseudoreduced specific volume, defined as
vR 5
v actual
a5
aP 1
a
b(v 2 b) 5 RT
v2
27R 2 T 2cr
and b 5
64Pcr
Beattie-Bridgeman: P 5
RuT
v
2
a1 2
RTcr
8Pcr
c
A
b(v 1 B) 2 2
3
vT
v
where
A 5 A0 a1 2
a
b
b and B 5 B0 a1 2 b
v
v
Benedict-Webb-Rubin:
RTcr /Pcr
The P-v-T behavior of substances can be represented more
accurately by more complex equations of state. Three of the
best known are
van der Waals:
where
P5
RuT
v
1
1 aB0RuT 2 A0 2
C0
T
2
b
bRuT 2 a
1
aa
1
1 6
2
3
v
v
v
g
c
22
a1 1 2 be 2g/v
v3T2
v
where Ru is the universal gas constant and v is the molar
specific volume.
REFERENCES AND SUGGESTED READINGS
1. ASHRAE Handbook of Fundamentals. SI version.
Atlanta, GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating,
and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc., 1993.
2. ASHRAE Handbook of Refrigeration. SI version.
Atlanta, GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating,
and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc., 1994.
3. A. Bejan. Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics.
3rd ed. New York: Wiley, 2006.
4. M. Kostic. Analysis of Enthalpy Approximation for
Compressed Liquid Water. ASME J. Heat Transfer,
Vol. 128, pp. 421–426, 2006.
PROBLEMS*
Pure Substances, Phase-Change Processes,
Property Diagrams
3–1C
Is iced water a pure substance? Why?
3–2C What is the difference between saturated vapor and
superheated vapor?
3–3C Is there any difference between the intensive properties of saturated vapor at a given temperature and the vapor
of a saturated mixture at the same temperature?
3–4C Why are the temperature and pressure dependent
properties in the saturated mixture region?
3–5C Is it true that water boils at higher temperature at
higher pressure? Explain
* Problems designated by a “C” are concept questions, and
students are encouraged to answer them all. Problems designated
by an “E” are in English units, and the SI users can ignore them.
Problems with the
icon are solved using EES, and complete
solutions together with parametric studies are included on the
text website. Problems with the
icon are comprehensive in
nature, and are intended to be solved with an equation solver
such as EES.
3–6C What is the difference between the critical point and
the triple point?
3–7C
Is it possible to have water vapor at 2108C?
3–8C A househusband is cooking beef stew for his family in a pan that is (a) uncovered, (b) covered with a light
lid, and (c) covered with a heavy lid. For which case will the
cooking time be the shortest? Why?
152
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
Property Tables
3–22
3–9C In what kind of pot will a given volume of water boil
at a higher temperature: a tall and narrow one or a short and
wide one? Explain.
3–10C It is well known that warm air in a cooler environment rises. Now consider a warm mixture of air and gasoline
on top of an open gasoline can. Do you think this gas mixture
will rise in a cooler environment?
3–11C Does the amount of heat absorbed as 1 kg of saturated liquid water boils at 1008C have to be equal to the
amount of heat released as 1 kg of saturated water vapor condenses at 1008C?
Reconsider Prob. 3–21. Using EES (or other)
software, determine the missing properties of
water. Repeat the solution for refrigerant-134a, refrigerant-22,
and ammonia.
3–23
T, 8C
125
500
3–24E
T, 8F
3–13C What is the physical significance of hfg? Can it be
obtained from a knowledge of hf and hg? How?
500
400
Does hfg change with pressure? How?
v, m3/kg
P, kPa
140
3–12C Does the reference point selected for the properties
of a substance have any effect on thermodynamic analysis?
Why?
3–14C
Complete this table for H2O:
Phase description
0.05
550
750
Saturated liquid
0.140
Complete this table for H2O:
P, psia
u, Btu/lbm
300
Phase description
782
40
120
400
Saturated liquid
3–25E
3–15C Is it true that it takes more energy to vaporize 1 kg
of saturated liquid water at 1008C than it would at 1208C?
Reconsider Prob. 3–24E. Using EES (or other)
software, determine the missing properties of
water. Repeat the solution for refrigerant-134a, refrigerant-22,
and ammonia.
3–16C What is quality? Does it have any meaning in the
superheated vapor region?
3–26
3–17C Which process requires more energy: completely
vaporizing 1 kg of saturated liquid water at 1 atm pressure or
completely vaporizing 1 kg of saturated liquid water at 8 atm
pressure?
3–18C In the absence of compressed liquid tables, how is
the specific volume of a compressed liquid at a given P and T
determined?
3–19C In 1775, Dr. William Cullen made ice in Scotland
by evacuating the air in a water tank. Explain how that device
works, and discuss how the process can be made more efficient.
3–20
T, ºC
220
190
Complete this table for H2O:
P, kPa
u, kJ/kg
400
1450
Phase description
Saturated vapor
2500
4000
3040
3– 21
Complete this table for H2O:
T, 8C
P, kPa
50
250
110
v, m3/kg
Phase description
7.72
400
500
350
Complete this table for refrigerant-134a:
T, 8C
P, kPa
24
10
320
90
v, m3/kg
Phase description
0.0065
850
600
Saturated vapor
3–27E
Complete this table for refrigerant-134a:
T, 8F
P, psia
80
15
10
h, Btu/lbm
x
Phase description
78
0.6
70
180
129.46
110
1.0
3–28 A 1.8-m3 rigid tank contains steam at 2208C. One-third
of the volume is in the liquid phase and the rest is in the vapor
form. Determine (a) the pressure of the steam, (b) the quality
of the saturated mixture, and (c) the density of the mixture.
Steam
1.8 m3
220°C
Saturated vapor
FIGURE P3–28
153
CHAPTER 3
3–29 A piston–cylinder device contains 0.85 kg of refrigerant134a at 2108C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of
12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a
until the temperature is 158C. Determine (a) the final pressure, (b) the change in the volume of the cylinder, and (c) the
change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant-134a.
whose temperature is 2308F and whose quality is 80 percent.
The spring constant in the spring force relation F 5 kx
is 37 lbf/in, and the piston diameter is 12 in. The R-134a
undergoes a process that increases its volume by 50 percent.
Calculate the final temperature and enthalpy of the R-134a.
Answers: 105°F, 125 Btu/lbm
Spring
R134a
FIGURE P3–29
3–30E R-134a, whose specific volume is 0.6243 ft3/lbm,
flows through a tube at 80 psia. What is the temperature in
the tube?
D
FIGURE P3–36E
3–31 10-kg of R-134a fill a 1.348-m3 rigid container at an
initial temperature of 2408C. The container is then heated
until the pressure is 200 kPa. Determine the final temperature
and the initial pressure. Answers: 66.3°C, 51.25 kPa
3–37E One pound-mass of water fills a 2.4264-ft3 weighted
piston-cylinder device at a temperature of 6008F. The pistoncylinder device is now cooled until its temperature is 2008F.
Determine the final pressure of water, in psia, and the volume, in ft3. Answers: 250 psia, 0.01663 ft3
3–32 A 9-m3 container is filled with 300 kg of R-134a
at 108C. What is the specific enthalpy of the R-134a in the
container?
3–38 Three kilograms of water in a container have a pressure of 100 kPa and temperature of 1508C. What is the volume of this container?
3–33 Refrigerant-134a at 200 kPa and 258C flows through a
refrigeration line. Determine its specific volume.
3–39 Water is to be boiled at sea level in a 30-cm-diameter
stainless steel pan placed on top of a 3-kW electric burner.
If 60 percent of the heat generated by the burner is transferred to the water during boiling, determine the rate of evaporation of water.
3–34 The average atmospheric pressure in Denver
(elevation 5 1610 m) is 83.4 kPa. Determine the temperature at
which water in an uncovered pan boils in Denver. Answer: 94.68C
3–35E The temperature in a pressure cooker during cooking at sea level is measured to be 2508F. Determine the absolute pressure inside the cooker in psia and in atm. Would you
modifty your answer if the place were at a higher elevation?
Vapor
Pressure
cooker
250°F
60%
40%
3 kW
FIGURE P3–35E
3–36E A spring-loaded piston-cylinder device is initially
filled with 0.13 lbm of an R-134a liquid-vapor mixture
FIGURE P3–39
3–40 Repeat Prob, 3–39 for a location at an elevaion of
1500 m where the atmospheric pressure is 84.5 kPa and thus
the boiling temperature of water is 958C.
154
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
3–41 10-kg of R-134a at 300 kPa fills a rigid container
whose volume is 14 L. Determine the temperature and total
enthalpy in the container. The container is now heated until
the pressure is 600 kPa. Determine the temperature and total
enthalpy when the heating is completed.
R-134a
300 kPa
10 kg
14 L
3–45 Water in a 5-cm-deep pan is observed to boil at 988C.
At what temperature will the water in a 40-cm-deep pan boil?
Assume both pans are full of water.
3–46 A cooking pan whose inner diameter is 20 cm is filled
with water and covered with a 4-kg lid. If the local atmospheric
pressure is 101 kPa, determine the temperature at which the
water starts boiling when it is heated. Answer: 100.28C
Q
Patm = 101 kPa
m lid = 4 kg
FIGURE P3–41
H2O
3–42 100-kg of R-134a at 200 kPa are contained in a pistoncylinder device whose volume is 12.322 m3. The piston is
now moved until the volume is one-half its original size. This
is done such that the pressure of the R-134a does not change.
Determine the final temperature and the change in the total
internal energy of the R-134a.
3–43 Water initially at 200 kPa and 3008C is contained
in a piston-cylinder device fitted with stops. The water is
allowed to cool at constant pressure until it exists as a saturated vapor and the piston rests on the stops. Then the water
continues to cool until the pressure is 100 kPa. On the T-v
diagrams sketch, with respect to the saturation lines, the
process curves passing through both the initial, intermediate, and final states of the water. Label the T, P and v values
for end states on the process curves. Find the overall change
in internal energy between the initial and final states per
unit mass of water.
FIGURE P3–46
3–47
Reconsider Prob. 3–46. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the mass of
the lid on the boiling temperature of water in the pan. Let the
mass vary from 1 kg to 10 kg. Plot the boiling temperature
against the mass of the lid, and discuss the results.
3–48 Water is being heated in a vertical piston–cylinder
device. The piston has a mass of 40 kg and a cross-sectional
area of 150 cm2. If the local atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa,
determine the temperature at which the water starts boiling.
3–49 Water is boiled in a pan covered with a poorly fitting
lid at a specified location. Heat is supplied to the pan by a
2-kW resistance heater. The amount of water in the pan is
observed to decrease by 1.19 kg in 30 minutes. If it is estimated that 75 percent of electricity consumed by the heater
is transferred to the water as heat, determine the local atmospheric pressure in that location. Answer: 85.4 kPa
3–50 A rigid tank with a volume of 1.8 m3 contains 15 kg of
saturated liquid–vapor mixture of water at 908C. Now the water
is slowly heated. Determine the temperature at which the liquid
in the tank is completely vaporized. Also, show the process on a
T-v diagram with respect to saturation lines. Answer: 202.98C
A piston–cylinder device contains 0.005 m3 of
liquid water and 0.9 m3 of water vapor in equilibrium at 600 kPa. Heat is transferred at constant pressure
until the temperature reaches 2008C.
3–51
FIGURE P3–43
3–44 Saturated steam coming off the turbine of a steam
power plant at 408C condenses on the outside of a 3-cmouter-diameter, 35-m-long tube at a rate of 130 kg/h. Determine the rate of heat transfer from the steam to the cooling
water flowing through the pipe.
(a) What is the initial temperature of the water?
(b) Determine the total mass of the water.
(c) Calculate the final volume.
(d) Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines.
155
CHAPTER 3
Q
H2O
saturated vapor only. Determine (a) the volume of the tank,
(b) the final temperature and pressure, and (c) the internal
energy change of the water.
P = 600 kPa
FIGURE P3–51
3–52
Reconsider Prob. 3–51. Using EES (or other) software, investigate the effect of pressure on the total
mass of water in the tank. Let the pressure vary from 0.1 MPa
to 1 MPa. Plot the total mass of water against pressure, and
discuss the results. Also, show the process in Prob. 3–51 on a
P-v diagram using the property plot feature of EES.
3–53E A 5-ft3 rigid tank contains 5 lbm of water at 20 psia.
Determine (a) the temperature, (b) the total enthalpy, and
(c) the mass of each phase of water.
3–54E A 5-ft3 rigid tank contains a saturated mixture of
refrigerant-34a at 50 psia. If the saturated liquid occupies
20 percent of the volume, determine the quality and the total
mass of the refrigerant in the tank.
FIGURE P3–59
3–60E How much error would one expect in determining
the specific enthalpy by applying the incompressible-liquid
approximation to water at 3000 psia and 4008F?
3–61 100 grams of R-134a initially fill a weighted pistoncylinder device at 60 kPa and 2208C. The device is then
heated until the temperature is 1008C. Determine the change
in the device’s volume as a result of the heating.
Answer: 0.0168 m3
3–55E Superheated water vapor at 180 psia and 5008F is
allowed to cool at constant volume until the temperature
drops to 2508F. At the final state, determine (a) the pressure,
(b) the quality, and (c) the enthalpy. Also, show the process
on a T-v diagram with respect to saturation lines.
Answers: (a) 29.84 psia, (b) 0.219, (c) 426.0 Btu/lbm
3–56E
Reconsider Prob. 3–55E. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of initial pressure on the quality of water at the final state. Let the pressure
vary from 100 psi to 300 psi. Plot the quality against initial
pressure, and discuss the results. Also, show the process in
Prob. 3–55E on a T-v diagram using the property plot feature
of EES.
3–57 A piston–cylinder device contains 0.6 kg of steam
at 2008C and 0.5 MPa. Steam is cooled at constant pressure
until one-half of the mass condenses.
(a) Show the process on a T-v diagram.
(b) Find the final temperature.
(c) Determine the volume change.
3–58 A rigid tank contains water vapor at 2508C and an
unknown pressure. When the tank is cooled to 1248C, the
vapor starts condensing. Estimate the initial pressure in the
tank. Answer: 0.30 MPa
3–59 A piston-cylinder device initially contains 1.4-kg saturated liquid water at 2008C. Now heat is transferred to the
water until the volume quadruples and the cylinder contains
FIGURE P3–61
3–62 A rigid vessel contains 8 kg of refrigerant-134a at
500 kPa and 1208C. Determine the volume of the vessel and
the total internal energy. Answers: 0.494 m3, 2639 kJ
3–63 A rigid tank initially contains 1.4-kg saturated liquid water at 2008C. At this state, 25 percent of the volume is
occupied by water and the rest by air. Now heat is supplied to
the water until the tank contains saturated vapor only. Determine (a) the volume of the tank, (b) the final temperature and
pressure, and (c) the internal energy change of the water.
Q
Water
1.4 kg
200°C
FIGURE P3–63
156
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
3–64 A piston-cylinder device initially contains 50 L of
liquid water at 408C and 200 kPa. Heat is transferred to the
water at constant pressure until the entire liquid is vaporized.
(a) What is the mass of the water?
(b) What is the final temperature?
(c) Determine the total enthalpy change.
(d) Show the process on a T-v diagram with respect to
saturation lines.
Answers: (a) 49.61 kg, (b) 120.21°C, (c) 125,950 kJ
Ideal Gas
3–65C Under what conditions is the ideal-gas assumption
suitable for real gases?
3–66C What is the difference between R and Ru? How are
these two related?
3–67C Propane and methane are commonly used for heating in winter, and the leakage of these fuels, even for short
periods, poses a fire danger for homes. Which gas leakage do
you think poses a greater risk for fire? Explain.
3–68 A 400-L rigid tank contains 5 kg of air at 258C.
Determine the reading on the pressure gage if the atmospheric pressure is 97 kPa.
3–74E The air in an automobile tire with a volume of 0.53 ft3
is at 908F and 20 psig. Determine the amount of air that must
be added to raise the pressure to the recommended value of
30 psig. Assume the atmospheric pressure to be 14.6 psia and
the temperature and the volume to remain constant.
Answer: 0.0260 lbm
3–75 A 1-m3 tank containing air at 108C and 350 kPa is
connected through a valve to another tank containing 3 kg
of air at 358C and 200 kPa. Now the valve is opened, and
the entire system is allowed to reach thermal equilibrium
with the surroundings, which are at 208C. Determine the volume of the second tank and the final equilibrium pressure of
air. Answers: 1.33 m3, 264 kPa
3–76 A rigid tank whose volume is unknown is divided
into two parts by a partition. One side of the tank contains
an ideal gas at 9278C. The other side is evacuated and has
a volume twice the size of the part containing the gas. The
partition is now removed and the gas expands to fill the entire
tank. Heat is now applied to the gas until the pressure equals
the initial pressure. Determine the final temperature of the
gas. Answer: 33278C
3–69E A 3-ft3 container is filled with 2-lbm of oxygen at a
pressure of 80 psia. What is the temperature of the oxygen?
3–70 A 2-kg mass of helium is maintained at 300 kPa and
278C in a rigid container. How large is the container, in m3?
3–71 The pressure gage on a 2.5-m3 oxygen tank reads
500 kPa. Determine the amount of oxygen in the tank if the
temperature is 288C and the atmospheric pressure is 97 kPa.
Pg = 500 kPa
O2
V = 2.5 m3
T = 28°C
FIGURE P3–71
3–72 A spherical balloon with a diameter of 9 m is filled
with helium at 278C and 200 kPa. Determine the mole number and the mass of the helium in the balloon.
Answers: 30.6 kmol, 123 kg
3–73
Reconsider Prob. 3–72. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the balloon
diameter on the mass of helium contained in the balloon for
the pressures of (a) 100 kPa and (b) 200 kPa. Let the diameter vary from 5 m to 15 m. Plot the mass of helium against
the diameter for both cases.
FIGURE P3–76
3–77 Argon in the amount of 1.5 kg fills a 0.04-m3 pistoncylinder device at 550 kPa. The piston is now moved by
changing the weights until the volume is twice its original
size. During this process, argon’s temperature is maintained
constant. Determine the final pressure in the device.
3–78E A rigid tank contains 20 lbm of air at 20 psia and
708F. More air is added to the tank until the pressure and
temperature rise to 35 psia and 908F, respectively. Determine
the amount of air added to the tank. Answer: 13.73 lbm
Compressibility Factor
3–79C
What is the principle of corresponding states?
3–80C How are the reduced pressure and reduced temperature defined?
3–81E Refrigerant-134a at 400 psia has a specific volume
of 0.1384 ft3/lbm. Determine the temperature of the refrigerant based on (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized
compressibility chart, and (c) the refrigerant tables.
3–82 Determine the specific volume of superheated water
vapor at 15 MPa and 3508C, using (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and (c) the
157
CHAPTER 3
steam tables. Also determine the error involved in the
first two cases. Answers: (a) 0.01917 m3/kg, 67.0 percent,
(b) 0.01246 m3/kg, 8.5 percent, (c) 0.01148 m3/kg
3–83
Reconsider Prob. 3–82. Solve the problem using
the generalized compressibility factor feature of
the EES software. Again using EES, compare the specific
volume of water for the three cases at 15 MPa over the temperature range of 350 to 6008C in 258C intervals. Plot the
percent error involved in the ideal-gas approximation against
temperature, and discuss the results.
3–92 A 0.016773-m3 tank contains 1 kg of refrigerant-134a
at 1108C. Determine the pressure of the refrigerant, using
(a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility
chart, and (c) the refrigerant tables. Answers: (a) 1.861 MPa,
(b) 1.583 MPa, (c) 1.6 MPa
Other Equations of State
3–93C What is the physical significance of the two constants that appear in the van der Waals equation of state? On
what basis are they determined?
3–84 Determine the specific volume of superheated water
vapor at 3.5 MPa and 4508C based on (a) the ideal-gas
equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and
(c) the steam tables. Determine the error involved in the
first two cases.
3–94 A 3.27-m3 tank contains 100 kg of nitrogen at 175 K.
Determine the pressure in the tank, using (a) the ideal-gas
equation, (b) the van der Waals equation, and (c) the BeattieBridgeman equation. Compare your results with the actual
value of 1505 kPa.
3–85 Somebody claims that oxygen gas at 160 K and
3 MPa can be treated as an ideal gas with an error of less
than 10 percent. Is this claim valid?
3–95 Methane is heated in a rigid container from 80 kPa
and 208C to 3008C. Determine the final pressure of the methane treating it as (a) an ideal gas and (b) a Benedict-WebbRubin gas.
3–86E Ethane in a rigid vessel is to be heated from 50 psia
and 1008F until its temperature is 5408F. What is the final
pressure of the ethane as predicted by the compressibility
chart?
3–87 Ethylene is heated at constant pressure from 5 MPa
and 208C to 2008C. Using the compressibility chart, determine the change in the ethylene’s specific volume as a result
of this heating. Answer: 0.0172 m3/kg
3–88 What is the percentage of error involved in treating
carbon dioxide at 7 MPa and 380 K as an ideal gas?
3–89 Saturated water vapor at 3508C is heated at constant
pressure until its volume has doubled. Determine the final
temperature using the ideal gas equation of state, the compressibility charts, and the steam tables.
3–90 Methane at 10 MPa and 300 K is heated at constant pressure until its volume has increased by 80 percent.
Determine the final temperature using the ideal gas equation
of state and the compressibility factor. Which of these two
results is more accurate?
3–91 Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K
at a rate of 2 kg/s. CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it
flows in the pipe and the temperature of CO2 drops to 450 K
at the exit. Determine the volume flow rate and the density
of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the
exit of the pipe using (a) the ideal-gas equation and (b) the
generalized compressibility chart. Also, determine (c) the
error involved in the first case.
3 MPa
500 K
2 kg/s
FIGURE P3–91
CO2
450 K
3–96E Refrigerant-134a at 400 psia has a specific volume
of 0.1144 ft3/lbm. Determine the temperature of the refrigerant based on (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the van der Waals
equation, and (c) the refrigerant tables.
3–97
Nitrogen at 150 K has a specific volume of
0.041884 m3/kg. Determine the pressure of the
nitrogen, using (a) the ideal-gas equation and (b) the BeattieBridgeman equation. Compare your results to the experimental value of 1000 kPa. Answers: (a) 1063 kPa, (b) 1000.4 kPa
3–98
Reconsider Prob. 3–97. Using EES (or other)
software, compare the pressure results of the
ideal-gas and Beattie-Bridgeman equations with nitrogen data
supplied by EES. Plot temperature versus specific volume
for a pressure of 1000 kPa with respect to the saturated
liquid and saturated vapor lines of nitrogen over the range of
110 K , T , 150 K.
3–99 1-kg of carbon dioxide is compressed from 1 MPa
and 2008C to 3 MPa in a piston-cylinder device arranged
to execute a polytropic process for which PV 1.2 5 constant.
Determine the final temperature treating the carbon dioxide
as (a) an ideal gas and (b) a van der Waals gas.
3–100 A 1-m3 tank contains 2.841 kg of steam at 0.6 MPa.
Determine the temperature of the steam, using (a) the idealgas equation, (b) the van der Waals equation, and (c) the
steam tables. Answers: (a) 457.6 K, (b) 465.9 K, (c) 473 K
3–101
Reconsider Prob. 3-100. Solve the problem
using EES (or other) software. Again using
the EES, compare the temperature of water for the three
cases at constant specific volume over the pressure range of
0.1 MPa to 1 MPa in 0.1 MPa increments. Plot the percent
error involved in the ideal-gas approximation against pressure, and discuss the results.
158
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
Special Topic: Vapor Pressure and Phase Equilibrium
3–102 During a hot summer day at the beach when the air
temperature is 308C, someone claims the vapor pressure in
the air to be 5.2 kPa. Is this claim reasonable?
3–103 Consider a glass of water in a room that is at 208C
and 40 percent relative humidity. If the water temperature is
158C, determine the vapor pressure (a) at the free surface of
the water and (b) at a location in the room far from the glass.
3–104 On a certain day, the temperature and relative humidity of air over a large swimming pool are measured to be 258C
and 60 percent, respectively. Determine the water temperature
of the pool when phase equilibrium conditions are established
between the water in the pool and the vapor in the air.
3–105 During a hot summer day when the air temperature
is 358C and the relative humidity is 70 percent, you buy a
supposedly “cold” canned drink from a store. The store
owner claims that the temperature of the drink is below 108C.
Yet the drink does not feel so cold and you are skeptical since
you notice no condensation forming outside the can. Can the
store owner be telling the truth?
3–106 Consider two rooms that are identical except that one
is maintained at 258C and 40 percent relative humidity while
the other is maintained at 208C and 55 percent relative humidity.
Noting that the amount of moisture is proportional to the vapor
pressure, determine which room contains more moisture.
3–107E A thermos bottle is half-filled with water and is left
open to the atmospheric air at 608F and 35 percent relative
humidity. If heat transfer to the water through the thermos
walls and the free surface is negligible, determine the temperature of water when phase equilibrium is established.
Review Problems
3–108E Water in a pressure cooker is observed to boil at
2608F. What is the absolute pressure in the pressure cooker,
in psia?
3–109 Carbon-dioxide gas at 3 MPa and 500 K flows
steadily in a pipe at a rate of 0.4 kmol/s. Determine (a) the
volume and mass flow rates and the density of carbon dioxide at this state. If CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it
flows in the pipe so that the temperature of CO2 drops to
450 K at the exit of the pipe, determine (b) the volume flow
rate at the exit of the pipe.
3 MPa
500 K
0.4 kmol/s
CO2
450 K
FIGURE P3–109
3–110 A tank contains argon at 6008C and 200 kPa gage.
The argon is cooled in a process by heat transfer to the surroundings such that the argon reaches a final equilibrium
state at 3008C. Determine the final gage pressure of the
argon. Assume atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa.
3–111 The combustion in a gasoline engine may be approximated by a constant volume heat addition process. There
exists the air–fuel mixture in the cylinder before the combustion and the combustion gases after it, and both may be
approximated as air, an ideal gas. In a gasoline engine, the
cylinder conditions are 1.2 MPa and 4508C before the combustion and 17508C after it. Determine the pressure at the end
of the combustion process. Answer: 3.36 MPa
Combustion
chamber
1.2 MPa
450°C
FIGURE P3–111
3–112 One kilogram of R-134a fills a 0.090 m3 rigid container at an initial temperature of 2408C. The container is
then heated until the pressure is 280 kPa. Determine the initial pressure and final temperature. Answers: 51.25 kPa, 50°C
3–113 A rigid tank with a volume of 0.117 m3 contains
1 kg of refrigerant-134a vapor at 240 kPa. The refrigerant
is now allowed to cool. Determine the pressure when the
refrigerant first starts condensing. Also, show the process on
a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines.
3–114E One pound-mass of water fills a 2.649 ft3 weighted
piston-cylinder device at a temperature of 4008F. The pistoncylinder device is now cooled until its temperature is 1008F.
Determine the final pressure and volume of the water.
Q
Water
1 lbm
2.649 ft3
400°F
FIGURE P3–114E
3–115 Ethane at 10 MPa and 1008C is heated at constant
pressure until its volume has increased by 60 percent. Determine the final temperature using (a) the ideal gas equation of
state and (b) the compressibility factor. Which of these two
results is the more accurate?
3–116 A 13-m3 tank contains nitrogen at 178C and 600 kPa.
Some nitrogen is allowed to escape until the pressure in
159
CHAPTER 3
the tank drops to 400 kPa. If the temperature at this point is
158C, determine the amount of nitrogen that has
escaped. Answer: 29.8 kg
3–117 A 10-kg mass of superheated refrigerant-134a at
1.2 MPa and 708C is cooled at constant pressure until it
exists as a compressed liquid at 208C.
(a) Show the process on a T-v diagram with respect to saturation lines.
(b) Determine the change in volume.
(c) Find the change in total internal energy.
(c) the steam tables. Answers: (a) 15,529 kPa, (b) 12,574 kPa,
(c) 12,515 kPa
3–122 A tank whose volume is unknown is divided into two
parts by a partition. One side of the tank contains 0.03 m3 of
refrigerant-134a that is a saturated liquid at 0.9 MPa, while
the other side is evacuated. The partition is now removed,
and the refrigerant fills the entire tank. If the final state of
the refrigerant is 208C and 280 kPa, determine the volume of
the tank.
Answers: (b) 20.187 m3 (c) 21984 kJ
R-134a
V = 0.03 m3
P = 0.9 MPa
3–118 A 4-L rigid tank contains 2 kg of saturated liquid–
vapor mixture of water at 508C. The water is now slowly
heated until it exists in a single phase. At the final state, will
the water be in the liquid phase or the vapor phase? What
would your answer be if the volume of the tank were 400 L
instead of 4 L?
Evacuated
FIGURE P3–122
3–123
Reconsider Prob. 3–122. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the initial
pressure of refrigerant-134a on the volume of the tank. Let
the initial pressure vary from 0.5 to 1.5 MPa. Plot the volume
of the tank versus the initial pressure, and discuss the results.
FIGURE P3–118
3–119 The gage pressure of an automobile tire is measured to
be 200 kPa before a trip and 220 kPa after the trip at a location
where the atmospheric pressure is 90 kPa. Assuming the volume
of the tire remains constant at 0.035 m3, determine the percent
increase in the absolute temperature of the air in the tire.
3–124 Liquid propane is commonly used as a fuel for heating homes, powering vehicles such as forklifts, and filling
portable picnic tanks. Consider a propane tank that initially
contains 5 L of liquid propane at the environment temperature of 208C. If a hole develops in the connecting tube of a
propane tank and the propane starts to leak out, determine the
temperature of propane when the pressure in the tank drops
to 1 atm. Also, determine the total amount of heat transfer
from the environment to the tank to vaporize the entire propane in the tank.
3–120 A piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.2 kg
of steam at 200 kPa and 3008C. Now, the steam is cooled at
constant pressure until it is at 1508C. Determine the volume
change of the cylinder during this process using the compressibility factor and compare the result to the actual value.
Steam
0.2 kg
200 kPa
300°C
Leak
FIGURE P3–124
Q
FIGURE P3–120
3–121 Steam at 4008C has a specific volume of 0.02 m3/kg.
Determine the pressure of the steam based on (a) the idealgas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and
Propane
3–125
Repeat Prob. 3–124 for isobutane.
3–126 A tank contains helium at 378C and 140 kPa gage.
The helium is heated in a process by heat transfer from the
surroundings such that the helium reaches a final equilibrium state at 2008C. Determine the final gage pressure of the
helium. Assume atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa.
3–127 If sufficient data are provided, complete the blank
cells in the following table of properties of water. In the last
column describe the condition of water as compressed liquid,
160
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
saturated mixture, superheated vapor, or insufficient information; and, if applicable, give the quality.
P, kPa
T, 8C
v, m3/kg
250
300
101.42
3000
u, kJ/kg
Phase
description
2728.9
1560.0
100
180
3-128 Water initially at 300 kPa and 0.5 m3/kg is contained
in a piston-cylinder device fitted with stops so that the water
supports the weight of the piston and the force of the atmosphere. The water is heated until it reaches the saturated
vapor state and the piston rests against the stops. With the
piston against the stops, the water is further heated until the
pressure is 600 kPa. On the P-v and T-v diagrams sketch,
with respect to the saturation lines, the process curves passing through both the initial and final states of the water. Label
the states on the process as 1, 2, and 3. On both the P-v and
T-v diagrams, sketch the isotherms passing through the states
and show their values, in 8C, on the isotherms.
Q
Water
300 kPa
0.5 m3/kg
Hot-air balloons range from about 15 to 25 m in diameter.
The air in the balloon cavity is heated by a propane burner
located at the top of the passenger cage. The flames from the
burner that shoot into the balloon heat the air in the balloon
cavity, raising the air temperature at the top of the balloon
from 658C to over 1208C. The air temperature is maintained
at the desired levels by periodically firing the propane burner.
The buoyancy force that pushes the balloon upward is
proportional to the density of the cooler air outside the balloon and the volume of the balloon, and can be expressed as
FB 5 rcool air gVballoon
where g is the gravitational acceleration. When air resistance is negligible, the buoyancy force is opposed by (1) the
weight of the hot air in the balloon, (2) the weight of the
cage, the ropes, and the balloon material, and (3) the weight
of the people and other load in the cage. The operator of the
balloon can control the height and the vertical motion of
the balloon by firing the burner or by letting some hot air in
the balloon escape, to be replaced by cooler air. The forward
motion of the balloon is provided by the winds.
Consider a 20-m-diameter hot-air balloon that, together
with its cage, has a mass of 80 kg when empty. This balloon
is hanging still in the air at a location where the atmospheric
pressure and temperature are 90 kPa and 158C, respectively,
while carrying three 65-kg people. Determine the average temperature of the air in the balloon. What would your
response be if the atmospheric air temperature were 308C?
FIGURE P3–128
3–129E 0.5-lbm of argon is compressed from 1000 psia
and 3008F to 2000 psia in a piston-cylinder device which
executes a polytropic process for which PV1.6 5 constant.
Determine the final temperature treating the argon as (a) an
ideal gas and (b) a Beattie-Bridgeman gas.
3–130E Nitrogen is maintained at 400 psia and 21008F.
Compare the specific volume of this nitrogen as predicted by
(a) the ideal gas equation of state, (b) the Benedict-WebbRubin equation of state, and (c) with the compressibility factor.
3–131 Although balloons have been around since 1783
when the first balloon took to the skies in France, a real
breakthrough in ballooning occurred in 1960 with the design
of the modern hot-air balloon fueled by inexpensive propane
and constructed of lightweight nylon fabric. Over the years,
ballooning has become a sport and a hobby for many people
around the world. Unlike balloons filled with the light helium
gas, hot-air balloons are open to the atmosphere. Therefore,
the pressure in the balloon is always the same as the local
atmospheric pressure, and the balloon is never in danger of
exploding.
FIGURE P3–131
©PhotoLink/Getty Images RF
161
CHAPTER 3
3–132
Reconsider Prob. 3-131. Using EES (or
other) software, investigate the effect of the
environment temperature on the average air temperature in
the balloon when the balloon is suspended in the air.
Assume the environment temperature varies from 210 to
308C. Plot the average air temperature in the balloon versus the environment temperature, and discuss the results.
Investigate how the number of people carried affects the
temperature of the air in the balloon.
3–133 Consider an 18-m-diameter hot-air balloon that,
together with its cage, has a mass of 120 kg when empty.
The air in the balloon, which is now carrying two 70-kg
people, is heated by propane burners at a location where the
atmospheric pressure and temperature are 93 kPa and 128C,
respectively. Determine the average temperature of the air
in the balloon when the balloon first starts rising. What
would your response be if the atmospheric air temperature
were 258C?
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Problems
3–134 A 300-m3 rigid tank is filled with saturated liquid–
vapor mixture of water at 200 kPa. If 25 percent of the mass
is liquid and 75 percent of the mass is vapor, the total mass
in the tank is
(a) 451 kg
(b) 556 kg
(c) 300 kg
(d) 331 kg
(e) 195 kg
3–135 Water is boiled at 1 atm pressure in a coffee maker
equipped with an immersion-type electric heating element.
The coffee maker initially contains 1 kg of water. Once boiling started, it is observed that half of the water in the coffee
maker evaporated in 10 minutes. If the heat loss from the coffee maker is negligible, the power rating of the heating element is
(a) 3.8 kW
(b) 2.2 kW
(c) 1.9 kW
(d) 1.6 kW
(e) 0.8 kW
3–136 A 1-m3 rigid tank contains 10 kg of water (in any
phase or phases) at 1608C. The pressure in the tank is
(a) 738 kPa
(b) 618 kPa
(c) 370 kPa
(d) 2000 kPa
(e) 1618 kPa
3–137 Water is boiling at 1 atm pressure in a stainless steel
pan on an electric range. It is observed that 2 kg of liquid
water evaporates in 30 min. The rate of heat transfer to the
water is
(a) 2.51 kW
(b) 2.32 kW
(c) 2.97 kW
(d) 0.47 kW
(e) 3.12 kW
3–138 Water is boiled in a pan on a stove at sea level.
During 10 min of boiling, it is observed that 200 g of
water has evaporated. Then the rate of heat transfer to the
water is
(a) 0.84 kJ/min
(b) 45.1 kJ/min
(c) 41.8 kJ/min
(d) 53.5 kJ/min
(e) 225.7 kJ/min
3–139 A 3-m3 rigid vessel contains steam at 4 MPa and
5008C. The mass of the steam is
(a) 3 kg
(b) 9 kg
(c) 26 kg
(d) 35 kg
(e) 52 kg
3–140 Consider a sealed can that is filled with refrigerant134a. The contents of the can are at the room temperature of
258C. Now a leak develops, and the pressure in the can drops
to the local atmospheric pressure of 90 kPa. The temperature
of the refrigerant in the can is expected to drop to (rounded to
the nearest integer)
(a) 08C
(b) 2298C
(c) 2168C
(d) 58C
(e) 258C
3–141 A rigid tank contains 2 kg of an ideal gas at 4 atm
and 408C. Now a valve is opened, and half of mass of the
gas is allowed to escape. If the final pressure in the tank is
2.2 atm, the final temperature in the tank is
(a) 718C
(b) 448C
(c) 21008C
(d) 208C
(e) 1728C
3–142 The pressure of an automobile tire is measured to be
190 kPa (gage) before a trip and 215 kPa (gage) after the trip
at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 95 kPa. If the
temperature of air in the tire before the trip is 258C, the air
temperature after the trip is
(b) 64.28C
(c) 27.28C
(a) 51.18C
(d) 28.38C
(e) 25.08C
Design and Essay Problems
3–143 In an article on tire maintenance, it is stated that tires
lose air over time, and pressure losses as high as 90 kPa (13 psi)
per year are measured. The article recommends checking tire
pressure at least once a month to avoid low tire pressure that
hurts fuel efficiency and causes uneven thread wear on tires.
Taking the beginning tire pressure to be 220 kPa (gage) and
the atmospheric pressure to be 100 kPa, determine the fraction of air that can be lost from a tire per year.
3–144 It is well known that water freezes at 08C at atmospheric pressure. The mixture of liquid water and ice at 08C
is said to be at stable equilibrium since it cannot undergo any
changes when it is isolated from its surroundings. However,
when water is free of impurities and the inner surfaces of the
container are smooth, the temperature of water can be lowered to 228C or even lower without any formation of ice at
atmospheric pressure. But at that state even a small disturbance can initiate the formation of ice abruptly, and the water
temperature stabilizes at 08C following this sudden change.
The water at 228C is said to be in a metastable state. Write
an essay on metastable states and discuss how they differ
from stable equilibrium states.
3–145 A solid normally absorbs heat as it melts, but there is
a known exception at temperatures close to absolute zero. Find
out which solid it is and give a physical explanation for it.
This page intentionally left blank
CHAPTER
4
E N E R G Y A N A LY S I S O F
CLOSED SYSTEMS
I
n Chap. 2, we considered various forms of energy and energy transfer,
and we developed a general relation for the conservation of energy principle or energy balance. Then in Chap. 3, we learned how to determine
the thermodynamics properties of substances. In this chapter, we apply the
energy balance relation to systems that do not involve any mass flow across
their boundaries; that is, closed systems.
We start this chapter with a discussion of the moving boundary work or
P dV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors. We continue by applying the general energy
balance relation, which is simply expressed as Ein 2 Eout 5 DEsystem, to systems that involve pure substance. Then we define specific heats, obtain relations for the internal energy and enthalpy of ideal gases in terms of specific
heats and temperature changes, and perform energy balances on various systems that involve ideal gases. We repeat this for systems that involve solids
and liquids, which are approximated as incompressible substances.
OBJECTIVES
The objectives of Chapter 4 are to:
■
Examine the moving boundary
work or P dV work commonly
encountered in reciprocating
devices such as automotive
engines and compressors.
■
■
■
■
■
■
Identify the first law of thermodynamics as simply a statement
of the conservation
of energy principle for closed
(fixed mass) systems.
Develop the general energy balance applied to closed systems.
Define the specific heat at constant volume and the specific
heat at constant pressure.
Relate the specific heats to the
calculation of the changes in
internal energy and enthalpy of
ideal gases.
Describe incompressible
substances and determine the
changes in their internal energy
and enthalpy.
Solve energy balance problems
for closed (fixed mass) systems
that involve heat and work
interactions for general pure
substances, ideal gases, and
incompressible substances.
163
164
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
4–1
The moving
boundary
Gas
FIGURE 4–1
The work associated with a moving
boundary is called boundary work.
F
A
ds
P
Gas
■
MOVING BOUNDARY WORK
One form of mechanical work frequently encountered in practice is associated with the expansion or compression of a gas in a piston–cylinder device.
During this process, part of the boundary (the inner face of the piston)
moves back and forth. Therefore, the expansion and compression work is
often called moving boundary work, or simply boundary work (Fig. 4–1).
Some call it the P dV work for reasons explained later. Moving boundary
work is the primary form of work involved in automobile engines. During
their expansion, the combustion gases force the piston to move, which in
turn forces the crankshaft to rotate.
The moving boundary work associated with real engines or compressors
cannot be determined exactly from a thermodynamic analysis alone because
the piston usually moves at very high speeds, making it difficult for the gas
inside to maintain equilibrium. Then the states through which the system
passes during the process cannot be specified, and no process path can be
drawn. Work, being a path function, cannot be determined analytically without a knowledge of the path. Therefore, the boundary work in real engines
or compressors is determined by direct measurements.
In this section, we analyze the moving boundary work for a quasiequilibrium process, a process during which the system remains nearly in
equilibrium at all times. A quasi-equilibrium process, also called a quasistatic process, is closely approximated by real engines, especially when the
piston moves at low velocities. Under identical conditions, the work output of the engines is found to be a maximum, and the work input to the
compressors to be a minimum when quasi-equilibrium processes are used in
place of nonquasi-equilibrium processes. Below, the work associated with a
moving boundary is evaluated for a quasi-equilibrium process.
Consider the gas enclosed in the piston–cylinder device shown in Fig. 4–2.
The initial pressure of the gas is P, the total volume is V, and the crosssectional area of the piston is A. If the piston is allowed to move a distance ds
in a quasi-equilibrium manner, the differential work done during this process is
dWb 5 F ds 5 PA ds 5 P dV
FIGURE 4–2
A gas does a differential amount of
work dWb as it forces the piston to
move by a differential amount ds.
(4–1)
That is, the boundary work in the differential form is equal to the product
of the absolute pressure P and the differential change in the volume dV of
the system. This expression also explains why the moving boundary work is
sometimes called the P dV work.
Note in Eq. 4–1 that P is the absolute pressure, which is always positive.
However, the volume change dV is positive during an expansion process
(volume increasing) and negative during a compression process (volume
decreasing). Thus, the boundary work is positive during an expansion process and negative during a compression process. Therefore, Eq. 4–1 can be
viewed as an expression for boundary work output, Wb,out. A negative result
indicates boundary work input (compression).
The total boundary work done during the entire process as the piston
moves is obtained by adding all the differential works from the initial state
to the final state:
2
Wb 5 3 P dV
1
(kJ)
(4–2)
165
CHAPTER 4
This integral can be evaluated only if we know the functional relationship
between P and V during the process. That is, P 5 f(V) should be available.
Note that P 5 f(V) is simply the equation of the process path on a P-V
diagram.
The quasi-equilibrium expansion process described is shown on a P-V
diagram in Fig. 4–3. On this diagram, the differential area dA is equal to
P dV, which is the differential work. The total area A under the process
curve 1–2 is obtained by adding these differential areas:
Area 5 A 5
2
2
1
1
# dA 5 # P dV
1
Process path
2
dA = P dV
V1
dV
FIGURE 4–3
The area under the process curve
on a P-V diagram represents the
boundary work.
P
WA = 10 kJ
1
WB = 8 kJ
WC = 5 kJ
A
B
C
2
V1
(4–4)
1
where Pi is the pressure at the inner face of the piston.
Note that work is a mechanism for energy interaction between a system
and its surroundings, and Wb represents the amount of energy transferred
V
V2
FIGURE 4–4
The boundary work done during a
process depends on the path followed
as well as the end states.
P
2
A
Wnet
B
V2
i
V
P
2
# P dV
V2
(4–3)
A comparison of this equation with Eq. 4–2 reveals that the area under the
process curve on a P-V diagram is equal, in magnitude, to the work done during a quasi-equilibrium expansion or compression process of a closed system.
(On the P-v diagram, it represents the boundary work done per unit mass.)
A gas can follow several different paths as it expands from state 1 to
state 2. In general, each path will have a different area underneath it, and
since this area represents the magnitude of the work, the work done will be
different for each process (Fig. 4–4). This is expected, since work is a path
function (i.e., it depends on the path followed as well as the end states). If
work were not a path function, no cyclic devices (car engines, power plants)
could operate as work-producing devices. The work produced by these
devices during one part of the cycle would have to be consumed during
another part, and there would be no net work output. The cycle shown in
Fig. 4–5 produces a net work output because the work done by the system
during the expansion process (area under path A) is greater than the work
done on the system during the compression part of the cycle (area under
path B), and the difference between these two is the net work done during
the cycle (the colored area).
If the relationship between P and V during an expansion or a compression process is given in terms of experimental data instead of in a functional
form, obviously we cannot perform the integration analytically. We can,
however, plot the P-V diagram of the process using these data points and
calculate the area underneath graphically to determine the work done.
Strictly speaking, the pressure P in Eq. 4–2 is the pressure at the inner
surface of the piston. It becomes equal to the pressure of the gas in the cylinder only if the process is quasi-equilibrium and thus the entire gas in the
cylinder is at the same pressure at any given time. Equation 4–2 can also be
used for nonquasi-equilibrium processes provided that the pressure at the
inner face of the piston is used for P. (Besides, we cannot speak of the
pressure of a system during a nonquasi-equilibrium process since properties
are defined for equilibrium states only.) Therefore, we can generalize the
boundary work relation by expressing it as
Wb 5
P
1
V1
V
FIGURE 4–5
The net work done during a cycle is
the difference between the work done
by the system and the work done on
the system.
166
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
from the system during an expansion process (or to the system during a
compression process). Therefore, it has to appear somewhere else and we
must be able to account for it since energy is conserved. In a car engine,
for example, the boundary work done by the expanding hot gases is used to
overcome friction between the piston and the cylinder, to push atmospheric
air out of the way, and to rotate the crankshaft. Therefore,
2
Wb 5 Wfriction 1 W atm 1 W crank 5
# (F
friction
1 Patm A 1 Fcrank ) dx
(4–5)
1
Of course the work used to overcome friction appears as frictional heat and
the energy transmitted through the crankshaft is transmitted to other components (such as the wheels) to perform certain functions. But note that the
energy transferred by the system as work must equal the energy received by
the crankshaft, the atmosphere, and the energy used to overcome friction.
The use of the boundary work relation is not limited to the quasi-equilibrium
processes of gases only. It can also be used for solids and liquids.
EXAMPLE 4–1
Boundary Work for a Constant-Volume Process
A rigid tank contains air at 500 kPa and 1508C. As a result of heat transfer
to the surroundings, the temperature and pressure inside the tank drop to
658C and 400 kPa, respectively. Determine the boundary work done during
this process.
SOLUTION Air in a rigid tank is cooled, and both the pressure and temperature drop. The boundary work done is to be determined.
Analysis A sketch of the system and the P-V diagram of the process are
shown in Fig. 4–6. The boundary work can be determined from Eq. 4–2 to be
Wb 5
Air
P1 = 500 kPa
T1 = 150°C
#
2
0
P dV 5 0
1
Heat
P2 = 400 kPa
T2 = 65°C
Discussion This is expected since a rigid tank has a constant volume and
dV 5 0 in this equation. Therefore, there is no boundary work done during
this process. That is, the boundary work done during a constant-volume
process is always zero. This is also evident from the P-V diagram of the
process (the area under the process curve is zero).
P, kPa
500
1
EXAMPLE 4–2
400
2
V
FIGURE 4–6
Schematic and P-V diagram for
Example 4–1.
Boundary Work for a Constant-Pressure Process
A frictionless piston–cylinder device contains 10 lbm of steam at 60 psia
and 3208F. Heat is now transferred to the steam until the temperature
reaches 4008F. If the piston is not attached to a shaft and its mass is constant, determine the work done by the steam during this process.
SOLUTION Steam in a piston cylinder device is heated and the temperature
rises at constant pressure. The boundary work done is to be determined.
167
CHAPTER 4
Analysis A sketch of the system and the P-v diagram of the process are
shown in Fig. 4–7.
Assumption The expansion process is quasi-equilibrium.
Analysis Even though it is not explicitly stated, the pressure of the steam
within the cylinder remains constant during this process since both the
atmospheric pressure and the weight of the piston remain constant. Therefore, this is a constant-pressure process, and, from Eq. 4–2
Wb 5
#
2
2
P dV 5 P0
1
# dV 5 P (V 2 V )
0
2
1
(4–6)
1
or
Wb 5 mP0(v 2 2 v 1)
since V 5 mv. From the superheated vapor table (Table A–6E), the specific
volumes are determined to be v1 5 7.4863 ft3/lbm at state 1 (60 psia,
3208F) and v2 5 8.3548 ft3/lbm at state 2 (60 psia, 4008F). Substituting
these values yields
Wb 5 (10 lbm)(60 psia)[(8.3548 2 7.4863) ft3/lbm] a
1 Btu
b
5.404 psia·ft3
5 96.4 Btu
Discussion The positive sign indicates that the work is done by the system.
That is, the steam used 96.4 Btu of its energy to do this work. The magnitude of this work could also be determined by calculating the area under the
process curve on the P-V diagram, which is simply P0 DV for this case.
EXAMPLE 4–3
FIGURE 4–7
Schematic and P-v diagram for
Example 4–2.
Isothermal Compression of an Ideal Gas
A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.4 m3 of air at 100 kPa and
808C. The air is now compressed to 0.1 m3 in such a way that the temperature inside the cylinder remains constant. Determine the work done during
this process.
SOLUTION Air in a piston–cylinder device is compressed isothermally. The
boundary work done is to be determined.
Analysis A sketch of the system and the P-V diagram of the process are
shown in Fig. 4–8.
Assumptions 1 The compression process is quasi-equilibrium. 2 At specified
conditions, air can be considered to be an ideal gas since it is at a high temperature and low pressure relative to its critical-point values.
Analysis For an ideal gas at constant temperature T0,
PV 5 mRT0 5 C or P 5
C
V
where C is a constant. Substituting this into Eq. 4–2, we have
Wb 5
#
2
1
P dV 5
2
V2
V2
C
dV
5 P1V 1 ln
dV 5 C
5 C ln
V
V
V
V1
1
1
1
#
2
#
(4–7)
In Eq. 4–7, P1V1 can be replaced by P2V2 or mRT0. Also, V2/V1 can be
replaced by P1/P2 for this case since P1V1 5 P2V2.
FIGURE 4–8
Schematic and P-V diagram for
Example 4–3.
168
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
Substituting the numerical values into Eq. 4–7 yields
Wb 5 (100 kPa)(0.4 m3)aln
0.1
1 kJ
b
ba
0.4 1 kPa·m3
5 255.5 kJ
Discussion The negative sign indicates that this work is done on the system
(a work input), which is always the case for compression processes.
Polytropic Process
During actual expansion and compression processes of gases, pressure
and volume are often related by PV n 5 C, where n and C are constants.
A process of this kind is called a polytropic process (Fig. 4–9). Below we
develop a general expression for the work done during a polytropic process.
The pressure for a polytropic process can be expressed as
Gas
PV n = C = const.
P 5 CV 2n
(4–8)
Substituting this relation into Eq. 4–2, we obtain
P
P1
1
Wb 5
P1V1n = P2V 2n
P dV 5
1
#
2
CV 2n dV 5 C
V 22n 11 2 V 12n 11
2n 1 1
1
5
P2V 2 2 P1V 1
12n
(4–9)
since C 5 P1V 1n 5 P2V 2n. For an ideal gas (PV 5 mRT), this equation can
also be written as
PV n = const.
P2
#
2
Wb 5
2
mR(T2 2 T1)
n21
12n
(kJ)
(4–10)
For the special case of n 5 1 the boundary work becomes
V1
V2
FIGURE 4–9
Schematic and P-V diagram for a
polytropic process.
V
Wb 5
#
2
1
2
P dV 5
# CV
1
21
dV 5 PV lna
V2
V1
b
For an ideal gas this result is equivalent to the isothermal process discussed
in the previous example.
EXAMPLE 4–4
Expansion of a Gas against a Spring
A piston–cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of a gas initially at 200 kPa.
At this state, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is
touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now heat is transferred to
the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the
volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston
is 0.25 m2, determine (a) the final pressure inside the cylinder, (b) the total
work done by the gas, and (c) the fraction of this work done against the
spring to compress it.
SOLUTION A gas in a piston–cylinder device equipped with a linear spring
expands as a result of heating. The final gas pressure, the total work done,
and the fraction of the work done to compress the spring are to be determined.
169
CHAPTER 4
k = 150 kN/m
Assumptions 1 The expansion process is quasi-equilibrium. 2 The spring is
linear in the range of interest.
Analysis A sketch of the system and the P-V diagram of the process are
shown in Fig. 4–10.
(a) The enclosed volume at the final state is
V 2 5 2V 1 5 (2)(0.05 m3) 5 0.1 m3
A = 0.25 m2
P1 = 200 kPa
V1 = 0.05 m3
Then the displacement of the piston (and of the spring) becomes
x5
(0.1 2 0.05) m3
DV
5 0.2 m
5
A
0.25 m2
Heat
The force applied by the linear spring at the final state is
P, kPa
F 5 kx 5 (150 kN/m)(0.2 m) 5 30 kN
The additional pressure applied by the spring on the gas at this state is
P5
320
30 kN
F
5
5 120 kPa
A
0.25 m2
II
Without the spring, the pressure of the gas would remain constant at
200 kPa while the piston is rising. But under the effect of the spring, the
pressure rises linearly from 200 kPa to
200
I
200 1 120 5 320 kPa
at the final state.
(b) An easy way of finding the work done is to plot the process on a P-V
diagram and find the area under the process curve. From Fig. 4–10 the area
under the process curve (a trapezoid) is determined to be
W 5 area 5
(200 1 320) kPa
1 kJ
[(0.1 2 0.05) m3] a
b 5 13 kJ
2
1 kPa·m3
Note that the work is done by the system.
(c) The work represented by the rectangular area (region I) is done against
the piston and the atmosphere, and the work represented by the triangular
area (region II) is done against the spring. Thus,
Wspring 5 12 [(320 2 200) kPa](0.05 m3)a
1 kJ
b 5 3 kJ
1 kPa·m3
Discussion This result could also be obtained from
Wspring 5 12k(x 22 2 x 21) 5 12(150 kN/m)[(0.2 m)2 2 02] a
4–2
■
1 kJ
b 5 3 kJ
1 kN·m
ENERGY BALANCE FOR CLOSED SYSTEMS
Energy balance for any system undergoing any kind of process was
expressed as (see Chap. 2)
Ein 2 Eout
('')
''*
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
DEsystem
(')'*
(kJ)
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
(4–11)
0.05
0.1 V, m3
FIGURE 4–10
Schematic and P-V diagram for
Example 4–4.
170
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
or, in the rate form, as
.
.
E'*
5
in 2 '
out
(E
'')
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
dE'
/dt*
system
('
)''
(kW)
(4–12)
Rate of change in internal,
kinetic, potential, etc., energies
For constant rates, the total quantities during a time interval Dt are related to
the quantities per unit time as
#
#
Q 5 Q Dt, W 5 W Dt, and DE 5 (dE/dt)Dt
(kJ)
(4–13)
The energy balance can be expressed on a per unit mass basis as
ein 2 eout 5 Desystem
(kJ/kg)
(4–14)
which is obtained by dividing all the quantities in Eq. 4–11 by the mass
m of the system. Energy balance can also be expressed in the differential
form as
dEin 2 dEout 5 dEsystem or dein 2 deout 5 desystem
P
(4–15)
For a closed system undergoing a cycle, the initial and final states are identical, and thus DEsystem 5 E2 2 E1 5 0. Then, the energy balance for a cycle
simplifies to Ein 2 Eout 5 0 or Ein 5 Eout. Noting that a closed system does
not involve any mass flow across its boundaries, the energy balance for a
cycle can be expressed in terms of heat and work interactions as
Qnet = Wnet
#
#
Wnet,out 5 Qnet,in or Wnet,out 5 Qnet,in
V
FIGURE 4–11
For a cycle DE 5 0, thus Q 5 W.
(for a cycle)
(4–16)
That is, the net work output during a cycle is equal to net heat input
(Fig. 4–11).
The energy balance (or the first-law) relations already given are intuitive
in nature and are easy to use when the magnitudes and directions of heat
and work transfers are known. However, when performing a general analytical study or solving a problem that involves an unknown heat or work interaction, we need to assume a direction for the heat or work interactions. In
such cases, it is common practice to use the classical thermodynamics sign
convention and to assume heat to be transferred into the system (heat input)
in the amount of Q and work to be done by the system (work output) in the
amount of W, and then to solve the problem. The energy balance relation in
that case for a closed system becomes
General Q – W = ΔE
Qnet,in 2 W net,out 5 DEsystem or Q 2 W 5 DE
Stationary systems Q – W = ΔU
where Q 5 Qnet,in 5 Qin 2 Qout is the net heat input and W 5 Wnet,out 5
Wout 2 Win is the net work output. Obtaining a negative quantity for Q or
W simply means that the assumed direction for that quantity is wrong and
should be reversed. Various forms of this “traditional” first-law relation for
closed systems are given in Fig. 4–12.
The first law cannot be proven mathematically, but no process in nature is
known to have violated the first law, and this should be taken as sufficient
proof. Note that if it were possible to prove the first law on the basis of
other physical principles, the first law then would be a consequence of those
principles instead of being a fundamental physical law itself.
As energy quantities, heat and work are not that different, and you probably wonder why we keep distinguishing them. After all, the change in the
Per unit mass q – w = Δe
Differential form dq – dw = de
FIGURE 4–12
Various forms of the first-law relation
for closed systems.
(4–17)
171
CHAPTER 4
energy content of a system is equal to the amount of energy that crosses the
system boundaries, and it makes no difference whether the energy crosses
the boundary as heat or work. It seems as if the first-law relations would be
much simpler if we had just one quantity that we could call energy interaction to represent both heat and work. Well, from the first-law point of view,
heat and work are not different at all. From the second-law point of view,
however, heat and work are very different, as is discussed in later chapters.
EXAMPLE 4–5
Electric Heating of a Gas at Constant Pressure
A piston–cylinder device contains 25 g of saturated water vapor that is maintained at a constant pressure of 300 kPa. A resistance heater within the
cylinder is turned on and passes a current of 0.2 A for 5 min from a 120-V
source. At the same time, a heat loss of 3.7 kJ occurs. (a) Show that for a
closed system the boundary work Wb and the change in internal energy DU
in the first-law relation can be combined into one term, DH, for a constantpressure process. (b) Determine the final temperature of the steam.
SOLUTION Saturated water vapor in a piston–cylinder device expands at
constant pressure as a result of heating. It is to be shown that DU 1 Wb 5
DH, and the final temperature is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 The tank is stationary and thus the kinetic and potential
energy changes are zero, DKE 5 DPE 5 0. Therefore, DE 5 DU and internal
energy is the only form of energy of the system that may change during this
process. 2 Electrical wires constitute a very small part of the system, and
thus the energy change of the wires can be neglected.
Analysis We take the contents of the cylinder, including the resistance wires,
as the system (Fig. 4–13). This is a closed system since no mass crosses the
system boundary during the process. We observe that a piston–cylinder device
typically involves a moving boundary and thus boundary work Wb. The pressure remains constant during the process and thus P2 5 P1. Also, heat is lost
from the system and electrical work We is done on the system.
(a) This part of the solution involves a general analysis for a closed system
undergoing a quasi-equilibrium constant-pressure process, and thus we consider a general closed system. We take the direction of heat transfer Q to be
to the system and the work W to be done by the system. We also express the
work as the sum of boundary and other forms of work (such as electrical and
shaft). Then, the energy balance can be expressed as
Ein 2 Eout 5
('')
''*
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
DEsystem
(')'*
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
0
0
Q 2 W 5 DU 1 DKE 1 DPE
Q 2 Wother 2 W b 5 U2 2 U1
For a constant-pressure process, the boundary work is given as Wb 5 P0(V2 2 V1).
Substituting this into the preceding relation gives
Q 2 Wother 2 P0(V 2 2 V 1) 5 U2 2 U1
However,
P0 5 P2 5 P1 S Q 2 Wother 5 (U2 1 P2V 2) 2 (U1 1 P1V 1)
FIGURE 4–13
Schematic and P-v diagram for
Example 4–5.
172
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
Also H 5 U 1 PV, and thus
Q 2 Wother 5 H2 2 H1
P = const.
ΔH
Q – Wother –Wb = ΔU
Q – Wother = ΔH
(4–18)
which is the desired relation (Fig. 4–14). This equation is very convenient to
use in the analysis of closed systems undergoing a constant-pressure quasiequilibrium process since the boundary work is automatically taken care of by
the enthalpy terms, and one no longer needs to determine it separately.
(b) The only other form of work in this case is the electrical work, which can
be determined from
We 5 VI Dt 5 (120 V)(0.2 A)(300 s)a
State 1:
FIGURE 4–14
For a closed system undergoing a
quasi-equilibrium, P 5 constant
process, DU 1 Wb 5 DH. Note that
this relation is NOT valid for closed
systems processes during which
pressure DOES NOT remain
constant.
(kJ)
1 kJ/s
b 5 7.2 kJ
1000 VA
P1 5 300 kPa
f h1 5 hg @ 300 kPa 5 2724.9 kJ/kg
sat. vapor
(Table A–5)
The enthalpy at the final state can be determined directly from Eq. 4–18 by
expressing heat transfer from the system and work done on the system as
negative quantities (since their directions are opposite to the assumed directions). Alternately, we can use the general energy balance relation with the
simplification that the boundary work is considered automatically by replacing DU by DH for a constant-pressure expansion or compression process:
Ein 2 Eout
('')
''*
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
DEsystem
(')'*
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
We,in 2 Qout 2 Wb 5 DU
We,in 2 Qout 5 DH 5 m(h2 2 h1)
(since P 5 constant)
7.2 kJ 2 3.7 kJ 5 (0.025 kg)(h2 2 2724.9) kJ/kg
h2 5 2864.9 kJ/kg
Now the final state is completely specified since we know both the pressure
and the enthalpy. The temperature at this state is
State 2:
P2 5 300 kPa
f T2 5 2008C
h2 5 2864.9 kJ/kg
(Table A–6)
Therefore, the steam will be at 2008C at the end of this process.
Discussion Strictly speaking, the potential energy change of the steam is
not zero for this process since the center of gravity of the steam rose somewhat. Assuming an elevation change of 1 m (which is rather unlikely), the
change in the potential energy of the steam would be 0.0002 kJ, which is
very small compared to the other terms in the first-law relation. Therefore, in
problems of this kind, the potential energy term is always neglected.
EXAMPLE 4–6
Unrestrained Expansion of Water
A rigid tank is divided into two equal parts by a partition. Initially, one side
of the tank contains 5 kg of water at 200 kPa and 258C, and the other side
is evacuated. The partition is then removed, and the water expands into the
173
CHAPTER 4
System boundary
entire tank. The water is allowed to exchange heat with its surroundings until
the temperature in the tank returns to the initial value of 258C. Determine
(a) the volume of the tank, (b) the final pressure, and (c) the heat transfer
for this process.
Evacuated
space
Partition
SOLUTION One half of a rigid tank is filled with liquid water while the other
side is evacuated. The partition between the two parts is removed and water
is allowed to expand and fill the entire tank while the temperature is maintained constant. The volume of the tank, the final pressure, and the heat
transfer are to be to determined.
Assumptions 1 The system is stationary and thus the kinetic and potential
energy changes are zero, DKE 5 DPE 5 0 and DE 5 DU. 2 The direction
of heat transfer is to the system (heat gain, Qin). A negative result for Qin
indicates the assumed direction is wrong and thus it is a heat loss. 3 The
volume of the rigid tank is constant, and thus there is no energy transfer
as boundary work. 4 There is no electrical, shaft, or any other kind of work
involved.
Analysis We take the contents of the tank, including the evacuated space,
as the system (Fig. 4–15). This is a closed system since no mass crosses the
system boundary during the process. We observe that the water fills the entire
tank when the partition is removed (possibly as a liquid–vapor mixture).
(a) Initially the water in the tank exists as a compressed liquid since its pressure (200 kPa) is greater than the saturation pressure at 258C (3.1698 kPa).
Approximating the compressed liquid as a saturated liquid at the given temperature, we find
v 1 > v f @ 258C 5 0.001003 m3/kg > 0.001 m3/kg
(Table A–4)
Then the initial volume of the water is
V 1 5 mv 1 5 (5 kg)(0.001 m3/kg) 5 0.005 m3
The total volume of the tank is twice this amount:
V tank 5 (2)(0.005 m3) 5 0.01 m3
(b) At the final state, the specific volume of the water is
v2 5
V2
0.01 m3
5
5 0.002 m3/kg
m
5 kg
which is twice the initial value of the specific volume. This result is expected
since the volume doubles while the amount of mass remains constant.
At 258C: v f 5 0.001003 m3/kg and v g 5 43.340 m3/kg (Table A–4)
Since vf , v2 , vg, the water is a saturated liquid–vapor mixture at the final
state, and thus the pressure is the saturation pressure at 258C:
P2 5 Psat @ 258C 5 3.1698 kPa
(Table A–4)
(c) Under stated assumptions and observations, the energy balance on the
system can be expressed as
Ein 2 Eout 5
DEsystem
('')
''*
(')'*
Net energy transfer
Change in internal, kinetic,
by heat, work, and mass
potential, etc., energies
Qin 5 DU 5 m(u2 2 u1)
H2O
m = 5 kg
P1 = 200 kPa
T1 = 25°C
Qin
P, kPa
200
3.17
1
2
v
FIGURE 4–15
Schematic and P-v diagram for
Example 4–6.
174
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
Notice that even though the water is expanding during this process, the system chosen involves fixed boundaries only (the dashed lines) and therefore
the moving boundary work is zero (Fig. 4–16). Then W 5 0 since the system
does not involve any other forms of work. (Can you reach the same conclusion by choosing the water as our system?) Initially,
Vacuum
P=0
W=0
u1 > uf @ 258C 5 104.83 kJ/kg
Heat
The quality at the final state is determined from the specific volume
information:
H2O
x2 5
FIGURE 4–16
Expansion against a vacuum involves
no work and thus no energy transfer.
v2 2 vf
v fg
5
0.002 2 0.001
5 2.3 3 10 25
43.34 2 0.001
Then
u2 5 uf 1 x 2ufg
5 104.83 kJ/kg 1 (2.3 3 10 25)(2304.3 kJ/kg)
5 104.88 kJ/kg
Substituting yields
Qin 5 (5 kg)[(104.88 2 104.83) kJ/ kg] 5 0.25 kJ
1 kg
1 kg
Iron
Water
20 → 30°C
20 → 30°C
4.5 kJ
41.8 kJ
FIGURE 4–17
It takes different amounts of energy
to raise the temperature of different
substances by the same amount.
m = 1 kg
ΔT = 1°C
Specific heat = 5 kJ/kg·°C
5 kJ
FIGURE 4–18
Specific heat is the energy required
to raise the temperature of a unit
mass of a substance by one degree
in a specified way.
Discussion The positive sign indicates that the assumed direction is correct,
and heat is transferred to the water.
4–3
■
SPECIFIC HEATS
We know from experience that it takes different amounts of energy to raise
the temperature of identical masses of different substances by one degree.
For example, we need about 4.5 kJ of energy to raise the temperature of
1 kg of iron from 20 to 308C, whereas it takes about 9 times this energy
(41.8 kJ to be exact) to raise the temperature of 1 kg of liquid water by the
same amount (Fig. 4–17). Therefore, it is desirable to have a property that
will enable us to compare the energy storage capabilities of various substances. This property is the specific heat.
The specific heat is defined as the energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree (Fig. 4–18). In general, this
energy depends on how the process is executed. In thermodynamics, we are
interested in two kinds of specific heats: specific heat at constant volume
cv and specific heat at constant pressure cp.
Physically, the specific heat at constant volume cv can be viewed as the
energy required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of a substance by
one degree as the volume is maintained constant. The energy required to do
the same as the pressure is maintained constant is the specific heat at constant pressure cp. This is illustrated in Fig. 4–19. The specific heat at constant pressure cp is always greater than cv because at constant pressure the
system is allowed to expand and the energy for this expansion work must
also be supplied to the system.
Now we attempt to express the specific heats in terms of other thermodynamic properties. First, consider a fixed mass in a stationary closed system
175
CHAPTER 4
undergoing a constant-volume process (and thus no expansion or compression work is involved). The conservation of energy principle ein 2 eout 5
Desystem for this process can be expressed in the differential form as
(2)
dein 2 deout 5 du
(1)
The left-hand side of this equation represents the net amount of energy
transferred to the system. From the definition of cv, this energy must be
equal to cv dT, where dT is the differential change in temperature. Thus,
cv dT 5 du
V = constant
m = 1 kg
m = 1 kg
ΔT = 1°C
ΔT = 1°C
cv = 3.12
at constant volume
P = constant
kJ
kg·°C
cp = 5.19
kJ
kg·°C
or
cv 5 a
0u
b
0T v
3.12 kJ
Similarly, an expression for the specific heat at constant pressure cp can be
obtained by considering a constant-pressure expansion or compression process. It yields
cp 5 a
0h
b
0T p
5.19 kJ
(4–19)
FIGURE 4–19
Constant-volume and constantpressure specific heats cv and cp
(values given are for helium gas).
(4–20)
Equations 4–19 and 4–20 are the defining equations for cv and cp, and their
interpretation is given in Fig. 4–20.
Note that cv and cp are expressed in terms of other properties; thus, they
must be properties themselves. Like any other property, the specific heats of
a substance depend on the state that, in general, is specified by two independent, intensive properties. That is, the energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree is different at different temperatures and
pressures (Fig. 4–21). But this difference is usually not very large.
A few observations can be made from Eqs. 4–19 and 4–20. First, these
equations are property relations and as such are independent of the type of
processes. They are valid for any substance undergoing any process. The
only relevance cv has to a constant-volume process is that cv happens to
be the energy transferred to a system during a constant-volume process per
unit mass, per unit degree rise in temperature. This is how the values of cv
are determined. This is also how the name specific heat at constant volume
originated. Likewise, the energy transferred to a system per unit mass per
unit temperature rise during a constant-pressure process happens to be equal
to cp. This is how the values of cp can be determined and also explains the
origin of the name specific heat at constant pressure.
Another observation that can be made from Eqs. 4–19 and 4–20 is that cv
is related to the changes in internal energy and cp to the changes in enthalpy.
In fact, it would be more proper to define cv as the change in the internal
energy of a substance per unit change in temperature at constant volume.
Likewise, cp can be defined as the change in the enthalpy of a substance per
unit change in temperature at constant pressure. In other words, cv is a measure of the variation of internal energy of a substance with temperature, and
cp is a measure of the variation of enthalpy of a substance with temperature.
Both the internal energy and enthalpy of a substance can be changed by the
transfer of energy in any form, with heat being only one of them. Therefore,
cv =
( 00Tu )v
= the change in internal energy
with temperature at
constant volume
cp =
( 00Th )p
= the change in enthalpy with
temperature at constant
pressure
FIGURE 4–20
Formal definitions of cv and cp.
Air
Air
m = 1 kg
m = 1 kg
300 → 301 K
1000 → 1001 K
0.718 kJ
0.855 kJ
FIGURE 4–21
The specific heat of a substance
changes with temperature.
176
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
the term specific energy is probably more appropriate than the term specific
heat, which implies that energy is transferred (and stored) in the form of heat.
A common unit for specific heats is kJ/kg·8C or kJ/kg·K. Notice that these
two units are identical since DT(8C) 5 DT(K), and 18C change in temperature is equivalent to a change of 1 K. The specific heats are sometimes
given on a molar basis. They are then denoted by c–v and c–p and have the
unit kJ/kmol·8C or kJ/kmol·K.
4–4
■
INTERNAL ENERGY, ENTHALPY, AND SPECIFIC
HEATS OF IDEAL GASES
We defined an ideal gas as a gas whose temperature, pressure, and specific
volume are related by
Thermometer
Pv 5 RT
It has been demonstrated mathematically (Chap. 12) and experimentally
(Joule, 1843) that for an ideal gas the internal energy is a function of the
temperature only. That is,
Water
u 5 u(T)
Air
(high pressure)
Evacuated
FIGURE 4–22
Schematic of the experimental apparatus used by Joule.
(4–21)
In his classical experiment, Joule submerged two tanks connected with a
pipe and a valve in a water bath, as shown in Fig. 4–22. Initially, one tank
contained air at a high pressure and the other tank was evacuated. When
thermal equilibrium was attained, he opened the valve to let air pass from
one tank to the other until the pressures equalized. Joule observed no change
in the temperature of the water bath and assumed that no heat was transferred to or from the air. Since there was also no work done, he concluded
that the internal energy of the air did not change even though the volume
and the pressure changed. Therefore, he reasoned, the internal energy is a
function of temperature only and not a function of pressure or specific volume. (Joule later showed that for gases that deviate significantly from idealgas behavior, the internal energy is not a function of temperature alone.)
Using the definition of enthalpy and the equation of state of an ideal gas,
we have
h 5 u 1 Pv
f h 5 u 1 RT
Pv 5 RT
Since R is constant and u 5 u(T ), it follows that the enthalpy of an ideal gas
is also a function of temperature only:
u = u(T)
h = h(T)
cv = cv (T )
cp = cp(T )
FIGURE 4–23
For ideal gases, u, h, cv, and cp vary
with temperature only.
h 5 h(T)
(4–22)
Since u and h depend only on temperature for an ideal gas, the specific
heats cv and cp also depend, at most, on temperature only. Therefore, at a
given temperature, u, h, cv, and cp of an ideal gas have fixed values regardless of the specific volume or pressure (Fig. 4–23). Thus, for ideal gases, the
partial derivatives in Eqs. 4–19 and 4–20 can be replaced by ordinary derivatives. Then, the differential changes in the internal energy and enthalpy of
an ideal gas can be expressed as
du 5 cv(T ) dT
(4–23)
177
CHAPTER 4
and
dh 5 cp(T ) dT
(4–24)
cp0
kJ/kmol·K
CO2
60
The change in internal energy or enthalpy for an ideal gas during a process
from state 1 to state 2 is determined by integrating these equations:
Du 5 u2 2 u1 5
# c (T ) dT
v
H2O
50
2
(kJ/kg)
(4–25)
1
and
O2
40
2
Dh 5 h2 2 h1 5
# c (T ) dT
p
(kJ/kg)
H2
(4–26)
1
To carry out these integrations, we need to have relations for cv and cp as
functions of temperature.
At low pressures, all real gases approach ideal-gas behavior, and therefore
their specific heats depend on temperature only. The specific heats of real
gases at low pressures are called ideal-gas specific heats, or zero-pressure
specific heats, and are often denoted cp0 and cv0. Accurate analytical expressions for ideal-gas specific heats, based on direct measurements or calculations from statistical behavior of molecules, are available and are given as
third-degree polynomials in the appendix (Table A–2c) for several gases. A
plot of c–p0(T) data for some common gases is given in Fig. 4–24.
The use of ideal-gas specific heat data is limited to low pressures, but these
data can also be used at moderately high pressures with reasonable accuracy
as long as the gas does not deviate from ideal-gas behavior significantly.
The integrations in Eqs. 4–25 and 4–26 are straightforward but rather
time-consuming and thus impractical. To avoid these laborious calculations,
u and h data for a number of gases have been tabulated over small temperature intervals. These tables are obtained by choosing an arbitrary reference
point and performing the integrations in Eqs. 4–25 and 4–26 by treating
state 1 as the reference state. In the ideal-gas tables given in the appendix,
zero kelvin is chosen as the reference state, and both the enthalpy and the
internal energy are assigned zero values at that state (Fig. 4–25). The choice
of the reference state has no effect on Du or Dh calculations. The u and h
data are given in kJ/kg for air (Table A–17) and usually in kJ/kmol for other
gases. The unit kJ/kmol is very convenient in the thermodynamic analysis of
chemical reactions.
Some observations can be made from Fig. 4–24. First, the specific heats
of gases with complex molecules (molecules with two or more atoms) are
higher and increase with temperature. Also, the variation of specific heats
with temperature is smooth and may be approximated as linear over small
temperature intervals (a few hundred degrees or less). Therefore, the specific heat functions in Eqs. 4–25 and 4–26 can be replaced by the constant
average specific heat values. Then, the integrations in these equations can be
performed, yielding
u2 2 u1 5 cv,avg(T 2 2 T 1)
(kJ/kg)
(4–27)
h2 2 h1 5 cp,avg(T 2 2 T 1)
(kJ/kg)
(4–28)
and
Air
30
Ar, He, Ne, Kr, Xe, Rn
20
1000
2000
Temperature, K
3000
FIGURE 4–24
Ideal-gas constant-pressure specific
heats for some gases (see Table A–2c
for cp equations).
Air
T, K
u, kJ/kg
h, kJ/kg
0
.
.
300
310
.
.
0
.
.
214.07
221.25
.
.
0
.
.
300.19
310.24
.
.
FIGURE 4–25
In the preparation of ideal-gas tables,
0 K is chosen as the reference
temperature.
178
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
cp
Approximation
Actual
2
cp,avg
1
T1
Tavg
T2
T
FIGURE 4–26
For small temperature intervals, the
specific heats may be assumed to vary
linearly with temperature.
Q1
Air
V = constant
T1 = 20°C
T2 = 30°C
Air
P = constant
T1 = 20°C
T2 = 30°C
Q2
Δu = cv ΔT
= 7.18 kJ/kg
Δu = cv ΔT
= 7.18 kJ/kg
FIGURE 4–27
The relation Du 5 cv DT is valid for
any kind of process, constant-volume
or not.
The specific heat values for some common gases are listed as a function
of temperature in Table A–2b. The average specific heats cp,avg and cv,avg are
evaluated from this table at the average temperature (T1 1 T2)/2, as shown
in Fig. 4–26. If the final temperature T2 is not known, the specific heats
may be evaluated at T1 or at the anticipated average temperature. Then T2
can be determined by using these specific heat values. The value of T2 can
be refined, if necessary, by evaluating the specific heats at the new average
temperature.
Another way of determining the average specific heats is to evaluate them
at T1 and T2 and then take their average. Usually both methods give reasonably good results, and one is not necessarily better than the other.
Another observation that can be made from Fig. 4–24 is that the ideal-gas
specific heats of monatomic gases such as argon, neon, and helium remain
constant over the entire temperature range. Thus, Du and Dh of monatomic
gases can easily be evaluated from Eqs. 4–27 and 4–28.
Note that the Du and Dh relations given previously are not restricted
to any kind of process. They are valid for all processes. The presence of
the constant-volume specific heat cv in an equation should not lead one to
believe that this equation is valid for a constant-volume process only. On the
contrary, the relation Du 5 cv,avg DT is valid for any ideal gas undergoing
any process (Fig. 4–27). A similar argument can be given for cp and Dh.
To summarize, there are three ways to determine the internal energy and
enthalpy changes of ideal gases (Fig. 4–28):
1. By using the tabulated u and h data. This is the easiest and most accurate
way when tables are readily available.
2. By using the cv or cp relations as a function of temperature and performing the integrations. This is very inconvenient for hand calculations but
quite desirable for computerized calculations. The results obtained are
very accurate.
3. By using average specific heats. This is very simple and certainly very
convenient when property tables are not available. The results obtained
are reasonably accurate if the temperature interval is not very large.
Specific Heat Relations of Ideal Gases
Δu = u2 – u1 (table)
Δu =
A special relationship between cp and cv for ideal gases can be obtained by
differentiating the relation h 5 u 1 RT, which yields
2
# c (T ) dT
v
dh 5 du 1 R dT
1
Δu ≅ cv,avg ΔT
Replacing dh by cpdT and du by cvdT and dividing the resulting expression
by dT, we obtain
cp 5 c v 1 R
FIGURE 4–28
Three ways of calculating Du.
(kJ/kg·K)
(4–29)
This is an important relationship for ideal gases since it enables us to determine cv from a knowledge of cp and the gas constant R.
When the specific heats are given on a molar basis, R in the above equation should be replaced by the universal gas constant Ru (Fig. 4–29).
cp 5 c v 1 R u
(kJ/kmol·K)
(4–30)
179
CHAPTER 4
At this point, we introduce another ideal-gas property called the specific
heat ratio k, defined as
k5
Air at 300 K
cp
(4–31)
cv
The specific ratio also varies with temperature, but this variation is very
mild. For monatomic gases, its value is essentially constant at 1.667. Many
diatomic gases, including air, have a specific heat ratio of about 1.4 at room
temperature.
EXAMPLE 4–7
or
{
cv = 20.80 kJ/kmol·K
c = 29.114 kJ/kmol·K
Ru = 8.314 kJ/kmol·K p
Evaluation of the Du of an Ideal Gas
Air at 300 K and 200 kPa is heated at constant pressure to 600 K. Determine
the change in internal energy of air per unit mass, using (a) data from the air
table (Table A–17), (b) the functional form of the specific heat (Table A–2c),
and (c) the average specific heat value (Table A–2b).
SOLUTION The internal energy change of air is to be determined in three
different ways.
Assumptions At specified conditions, air can be considered to be an ideal
gas since it is at a high temperature and low pressure relative to its criticalpoint values.
Analysis The internal energy change Du of ideal gases depends on the initial and final temperatures only, and not on the type of process. Thus, the
following solution is valid for any kind of process.
(a) One way of determining the change in internal energy of air is to read the
u values at T1 and T2 from Table A–17 and take the difference:
u1 5 u @ 300 K 5 214.07 kJ/kg
u2 5 u @ 600 K 5 434.78 kJ/kg
Thus,
Du 5 u2 2 u1 5 (434.78 2 214.07) kJ/kg 5 220.71 kJ/kg
–
(b) The c p(T ) of air is given in Table A–2c in the form of a third-degree polynomial expressed as
2
3
cp(T ) 5 a 1 bT 1 cT 1 dT
where a 5 28.11, b 5 0.1967 3 1022, c 5 0.4802 3 1025, and d 5
21.966 3 1029. From Eq. 4–30,
cv (T ) 5 cp 2 Ru 5 (a 2 Ru) 1 bT 1 cT 2 1 dT 3
From Eq. 4–25,
T2
2
Du 5
{
cv = 0.718 kJ/kg·K
c = 1.005 kJ/kg·K
R = 0.287 kJ/kg·K p
# c (T ) dT 5 # [(a 2 R ) 1 bT 1 cT 1 dT ] dT
2
1
3
u
v
T1
Performing the integration and substituting the values, we obtain
Du 5 6447 kJ/kmol
FIGURE 4–29
The cp of an ideal gas can be
determined from a knowledge of cv
and R.
180
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
The change in the internal energy on a unit-mass basis is determined by
dividing this value by the molar mass of air (Table A–1):
Du 5
6447 kJ/kmol
Du
5
5 222.5 kJ/kg
M
28.97 kg/kmol
which differs from the tabulated value by 0.8 percent.
(c) The average value of the constant-volume specific heat cv,avg is determined
from Table A–2b at the average temperature of (T1 1 T2)/2 5 450 K to be
cv,avg 5 cv @ 450 K 5 0.733 kJ/kg·K
Thus,
Du 5 cv,avg(T2 2 T1) 5 (0.733 kJ/kg·K)[(600 2 300)K]
5 220 kJ/kg
Discussion This answer differs from the tabulated value (220.71 kJ/kg) by only
0.4 percent. This close agreement is not surprising since the assumption that cv
varies linearly with temperature is a reasonable one at temperature intervals of
only a few hundred degrees. If we had used the cv value at T1 5 300 K instead
of at Tavg, the result would be 215.4 kJ/kg, which is in error by about 2 percent.
Errors of this magnitude are acceptable for most engineering purposes.
EXAMPLE 4–8
An insulated rigid tank initially contains 1.5 lbm of helium at 808F and
50 psia. A paddle wheel with a power rating of 0.02 hp is operated within
the tank for 30 min. Determine (a) the final temperature and (b) the final
pressure of the helium gas.
He
m = 1.5 lbm
T1 = 80°F
P1 = 50 psia
Wsh
P, psia
P2
Heating of a Gas in a Tank by Stirring
2
SOLUTION Helium gas in an insulated rigid tank is stirred by a paddle
wheel. The final temperature and pressure of helium are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Helium is an ideal gas since it is at a very high temperature
relative to its critical-point value of 24518F. 2 Constant specific heats can
be used for helium. 3 The system is stationary and thus the kinetic and
potential energy changes are zero, DKE 5 DPE 5 0 and DE 5 DU. 4 The
volume of the tank is constant, and thus there is no boundary work. 5 The
system is adiabatic and thus there is no heat transfer.
Analysis We take the contents of the tank as the system (Fig. 4–30). This
is a closed system since no mass crosses the system boundary during the
process. We observe that there is shaft work done on the system.
(a) The amount of paddle-wheel work done on the system is
50
#
2545 Btu/h
Wsh 5 W sh Dt 5 (0.02 hp)(0.5 h)a
b 5 25.45 Btu
1 hp
1
Under the stated assumptions and observations, the energy balance on the
system can be expressed as
V2 = V1
V
FIGURE 4–30
Schematic and P-V diagram for
Example 4–8.
Ein 2 Eout
('')
''*
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
DEsystem
(')'*
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
Wsh,in 5 DU 5 m(u2 2 u1) 5 mcv,avg(T2 2 T1)
181
CHAPTER 4
As we pointed out earlier, the ideal-gas specific heats of monatomic gases
(helium being one of them) are constant. The cv value of helium is determined from Table A–2Ea to be cv 5 0.753 Btu/lbm·8F. Substituting this and
other known quantities into the above equation, we obtain
25.45 Btu 5 (1.5 lbm)(0.753 Btu/lbm·8F)(T 2 2 808F)
T2 5 102.58F
(b) The final pressure is determined from the ideal-gas relation
P1V 1
T1
5
P2V 2
T2
where V1 and V2 are identical and cancel out. Then the final pressure
becomes
P2
50 psia
5
(80 1 460) R
(102.5 1 460)R
P2 5 52.1 psia
Discussion Note that the pressure in the ideal-gas relation is always the
absolute pressure.
EXAMPLE 4–9
Heating of a Gas by a Resistance Heater
A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.5 m3 of nitrogen gas at 400 kPa
and 278C. An electric heater within the device is turned on and is allowed
to pass a current of 2 A for 5 min from a 120-V source. Nitrogen expands
at constant pressure, and a heat loss of 2800 J occurs during the process.
Determine the final temperature of nitrogen.
SOLUTION Nitrogen gas in a piston–cylinder device is heated by an electric
resistance heater. Nitrogen expands at constant pressure while some heat is
lost. The final temperature of nitrogen is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Nitrogen is an ideal gas since it is at a high temperature and
low pressure relative to its critical-point values of 21478C, and 3.39 MPa.
2 The system is stationary and thus the kinetic and potential energy changes
are zero, DKE 5 DPE 5 0 and DE 5 DU. 3 The pressure remains constant
during the process and thus P2 5 P1. 4 Nitrogen has constant specific heats
at room temperature.
Analysis We take the contents of the cylinder as the system (Fig. 4–31).
This is a closed system since no mass crosses the system boundary during
the process. We observe that a piston–cylinder device typically involves a
moving boundary and thus boundary work, Wb. Also, heat is lost from the
system and electrical work We is done on the system.
First, let us determine the electrical work done on the nitrogen:
We 5 VI Dt 5 (120 V)(2 A)(5 3 60 s)a
1 kJ / s
b 5 72 kJ
1000 VA
2A
120 V
N2
P = const.
V1 = 0.5 m3
P1 = 400 kPa
T1 = 27°C
2800 J
P, kPa
400
1
0.5
2
V, m3
The mass of nitrogen is determined from the ideal-gas relation:
m5
P1V 1
RT1
5
(400 kPa)(0.5 m3)
5 2.245 kg
(0.297 kPa·m3/kg·K)(300 K)
FIGURE 4–31
Schematic and P-V diagram for
Example 4–9.
182
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
Under the stated assumptions and observations, the energy balance on the
system can be expressed as
Ein 2 Eout
('')
''*
DEsystem
(')'*
5
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
We,in 2 Qout 2 W b,out 5 DU
We,in 2 Qout 5 DH 5 m(h2 2 h1) 5 mcp(T 2 2 T 1)
since DU 1 Wb 5 DH for a closed system undergoing a quasi-equilibrium
expansion or compression process at constant pressure. From Table A–2a,
cp 5 1.039 kJ/kg·K for nitrogen at room temperature. The only unknown
quantity in the previous equation is T2, and it is found to be
72 kJ 2 2.8 kJ 5 (2.245 kg)(1.039 kJ/kg·K)(T 2 2 278C)
T2 5 56.78C
Discussion Note that we could also solve this problem by determining the
boundary work and the internal energy change rather than the enthalpy change.
EXAMPLE 4–10
A piston–cylinder device initially contains air at 150 kPa and 278C. At this
state, the piston is resting on a pair of stops, as shown in Fig. 4–32, and the
enclosed volume is 400 L. The mass of the piston is such that a 350-kPa
pressure is required to move it. The air is now heated until its volume has
doubled. Determine (a) the final temperature, (b) the work done by the air,
and (c) the total heat transferred to the air.
Air
V1 = 400 L
P1 = 150 kPa
T1 = 27°C
Q
SOLUTION Air in a piston–cylinder device with a set of stops is heated until
its volume is doubled. The final temperature, work done, and the total heat
transfer are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Air is an ideal gas since it is at a high temperature and low
pressure relative to its critical-point values. 2 The system is stationary and
thus the kinetic and potential energy changes are zero, DKE 5 DPE 5 0
and DE 5 DU. 3 The volume remains constant until the piston starts moving, and the pressure remains constant afterwards. 4 There are no electrical,
shaft, or other forms of work involved.
Analysis We take the contents of the cylinder as the system (Fig. 4–32).
This is a closed system since no mass crosses the system boundary during
the process. We observe that a piston-cylinder device typically involves a
moving boundary and thus boundary work, Wb. Also, the boundary work is
done by the system, and heat is transferred to the system.
P, kPa
350
2
3
A
150
1
0.4
Heating of a Gas at Constant Pressure
0.8
FIGURE 4–32
Schematic and P-V diagram for
Example 4–10.
V, m3
(a) The final temperature can be determined easily by using the ideal-gas
relation between states 1 and 3 in the following form:
P1V 1
T1
5
P3V 3
T3
h
(150 kPa)(V 1)
300 K
5
(350 kPa)(2V 1)
T3
T3 5 1400 K
183
CHAPTER 4
(b) The work done could be determined by integration, but for this case it is
much easier to find it from the area under the process curve on a P-V diagram, shown in Fig. 4–32:
A 5 (V 2 2 V 1)P2 5 (0.4 m3)(350 kPa) 5 140 m3·kPa
Therefore,
W13 5 140 kJ
The work is done by the system (to raise the piston and to push the atmospheric air out of the way), and thus it is work output.
(c) Under the stated assumptions and observations, the energy balance on the
system between the initial and final states (process 1–3) can be expressed as
Ein 2 Eout
('')
''*
5
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
DEsystem
(')'*
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
Qin 2 W b,out 5 DU 5 m(u3 2 u1)
The mass of the system can be determined from the ideal-gas relation:
m5
P1V 1
RT1
5
(150 kPa) (0.4 m3)
5 0.697 kg
(0.287 kPa·m3 / kg·K) (300 K)
The internal energies are determined from the air table (Table A–17) to be
u1 5 u @ 300 K 5 214.07 kJ / kg
u3 5 u @ 1400 K 5 1113.52 kJ / kg
Liquid
vl = constant
Solid
vs = constant
Thus,
Qin 2 140 kJ 5 (0.697 kg)[(1113.52 2 214.07) kJ / kg]
Qin 5 767 kJ
Discussion
4–5
■
The positive sign verifies that heat is transferred to the system.
FIGURE 4–33
The specific volumes of
incompressible substances remain
constant during a process.
INTERNAL ENERGY, ENTHALPY, AND
SPECIFIC HEATS OF SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS
A substance whose specific volume (or density) is constant is called an
incompressible substance. The specific volumes of solids and liquids
essentially remain constant during a process (Fig. 4–33). Therefore, liquids
and solids can be approximated as incompressible substances without sacrificing much in accuracy. The constant-volume assumption should be taken
to imply that the energy associated with the volume change is negligible
compared with other forms of energy. Otherwise, this assumption would
be ridiculous for studying the thermal stresses in solids (caused by volume
change with temperature) or analyzing liquid-in-glass thermometers.
It can be mathematically shown that (see Chap. 12) the constant-volume
and constant-pressure specific heats are identical for incompressible substances (Fig. 4–34). Therefore, for solids and liquids, the subscripts on cp
FIGURE 4–34
The cv and cp values of incompressible
substances are identical and are
denoted by c.
184
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
and cv can be dropped, and both specific heats can be represented by a single symbol c. That is,
cp 5 c v 5 c
(4–32)
This result could also be deduced from the physical definitions of constantvolume and constant-pressure specific heats. Specific heat values for several
common liquids and solids are given in Table A–3.
Internal Energy Changes
Like those of ideal gases, the specific heats of incompressible substances
depend on temperature only. Thus, the partial differentials in the defining
equation of cv can be replaced by ordinary differentials, which yield
du 5 cv dT 5 c(T ) dT
(4–33)
The change in internal energy between states 1 and 2 is then obtained by
integration:
2
Du 5 u2 2 u1 5
# c(T ) dT
(kJ / kg)
(4–34)
1
The variation of specific heat c with temperature should be known before
this integration can be carried out. For small temperature intervals, a c value
at the average temperature can be used and treated as a constant, yielding
Du > cavg(T 2 2 T 1)
(kJ / kg)
(4–35)
Enthalpy Changes
Using the definition of enthalpy h 5 u 1 Pv and noting that v 5 constant,
the differential form of the enthalpy change of incompressible substances
can be determined by differentiation to be
0
dh 5 du 1 v dP 1 P dv 5 du 1 v dP
(4–36)
Integrating,
Dh 5 Du 1 v DP > cavg DT 1 v DP
(kJ / kg)
(4–37)
For solids, the term v DP is insignificant and thus Dh 5 Du > cavgDT.
For liquids, two special cases are commonly encountered:
1. Constant-pressure processes, as in heaters (DP 5 0): Dh 5 Du > cavgDT
2. Constant-temperature processes, as in pumps (DT 5 0): Dh 5 v DP
For a process between states 1 and 2, the last relation can be expressed as
h2 2 h1 5 v(P2 2 P1). By taking state 2 to be the compressed liquid state
at a given T and P and state 1 to be the saturated liquid state at the same
temperature, the enthalpy of the compressed liquid can be expressed as
h@P,T > hf @ T 1 v f @ T (P 2 Psat @ T)
(4–38)
as discussed in Chap. 3. This is an improvement over the assumption that
the enthalpy of the compressed liquid could be taken as hf at the given temperature (that is, h@ P,T > hf @ T). However, the contribution of the last term
185
CHAPTER 4
is often very small, and is neglected. (Note that at high temperature and
pressures, Eq. 4–38 may overcorrect the enthalpy and result in a larger error
than the approximation h > hf @ T.)
EXAMPLE 4–11
Enthalpy of Compressed Liquid
Determine the enthalpy of liquid water at 1008C and 15 MPa (a) by using
compressed liquid tables, (b) by approximating it as a saturated liquid, and
(c) by using the correction given by Eq. 4–38.
SOLUTION The enthalpy of liquid water is to be determined exactly and
approximately.
Analysis At 1008C, the saturation pressure of water is 101.42 kPa, and
since P . Psat, the water exists as a compressed liquid at the specified state.
(a) From compressed liquid tables, we read
P 5 15 MPa
f h 5 430.39 kJ/kg
T 5 1008C
(Table A–7)
This is the exact value.
(b) Approximating the compressed liquid as a saturated liquid at 1008C, as
is commonly done, we obtain
h > hf @ 1008C 5 419.17 kJ/kg
This value is in error by about 2.6 percent.
(c) From Eq. 4–38,
h@P,T > hf @ T 1 v f @ T(P 2 Psat @ T)
5 (419.17 kJ/kg) 1 (0.001 m3 kg)[(15,000 2 101.42) kPa] a
1 kJ
b
1 kPa·m3
5 434.07 kJ/kg
Discussion Note that the correction term reduced the error from 2.6 to
about 1 percent in this case. However, this improvement in accuracy is often
not worth the extra effort involved.
EXAMPLE 4–12
Cooling of an Iron Block by Water
A 50-kg iron block at 808C is dropped into an insulated tank that contains
0.5 m3 of liquid water at 258C. Determine the temperature when thermal
equilibrium is reached.
SOLUTION An iron block is dropped into water in an insulated tank. The
final temperature when thermal equilibrium is reached is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Both water and the iron block are incompressible substances.
2 Constant specific heats at room temperature can be used for water and the
iron. 3 The system is stationary and thus the kinetic and potential energy
changes are zero, DKE 5 DPE 5 0 and DE 5 DU. 4 There are no electrical,
shaft, or other forms of work involved. 5 The system is well-insulated and
thus there is no heat transfer.
186
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
Analysis We take the entire contents of the tank as the system (Fig. 4–35).
This is a closed system since no mass crosses the system boundary during
the process. We observe that the volume of a rigid tank is constant, and
thus there is no boundary work. The energy balance on the system can be
expressed as
Ein 2 Eout
('')
''*
5
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
FIGURE 4–35
Schematic for Example 4–12.
DEsystem
(')
'*
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
0 5 DU
The total internal energy U is an extensive property, and therefore it can be
expressed as the sum of the internal energies of the parts of the system.
Then the total internal energy change of the system becomes
DUsys 5 DUiron 1 DUwater 5 0
[mc(T2 2 T1)] iron 1 [mc(T 2 2 T 1)] water 5 0
The specific volume of liquid water at or about room temperature can be
taken to be 0.001 m3/kg. Then the mass of the water is
mwater 5
V
0.5 m3
5
5 500 kg
v
0.001 m3/ kg
The specific heats of iron and liquid water are determined from Table A–3 to
be ciron 5 0.45 kJ/kg·8C and cwater 5 4.18 kJ/kg·8C. Substituting these values
into the energy equation, we obtain
(50 kg)(0.45 kJ / kg·8C)(T 2 2 808C) 1 (500 kg)(4.18 kJ / kg·8C)(T 2 2 258C) 5 0
T2 5 25.68C
Therefore, when thermal equilibrium is established, both the water and iron
will be at 25.68C.
Discussion The small rise in water temperature is due to its large mass and
large specific heat.
EXAMPLE 4–13
Oven
700°C
8 m/min
Aluminum
20°C
FIGURE 4–36
Schematic for Example 4–13
Heating of Aluminum Rods in a Furnace
Long cylindrical aluminum rods (r 5 2700 kg/m3 and cp 5 0.973 kJ/kg·K)
of 5-cm diameter are heat treated from 208C to an average temperature of
4008C by drawing them at a velocity of 8 m/min through a long oven. Determine the rate of heat transfer to the rods in the oven.
SOLUTION Aluminum rods are to be heated in an oven to a specified average temperature. The rate of heat transfer to the rods is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 The thermal properties of the rods are constant. 2 There are
no changes in kinetic and potential energies. 3 The balls are at a uniform
temperature when they leave the oven.
Analysis Aluminum rods pass through the oven at a constant speed of
8 m/min. That is, an external observer will see that an 8-m long section
of cold rods enters and an 8-m long section of hot rods leaves the oven
187
CHAPTER 4
every minute. We take the 8-m long section of the rod as the system. The
energy balance for this closed system can be expressed as
Ein 2 Eout
('')
''*
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
DEsystem
(')'*
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
Qin 5 DUrod 5 m(u2 2 u1)
Qin 5 mc(T 2 2 T 1)
The density and specific heat of the rods are given to be r 5 2700 kg/m3
and c 5 0.973 kJ/kg·K 5 0.973 kJ/kg·8C. The amount of heat transfer to an
8-m long section of the rod as it is heated to the specified temperature is
determined to be
p(0.05 m)2
pD2
L 5 (2700 kg /m3)
(8 m)5 42.41 kg
4
4
Qin 5 mc (T2 – T1) 5 (42.41 kg) (0.973 kJ/kg·8C) (400 2 20)8C
5 15,680 kJ (per 8-m section)
m 5 rV 5 r
Considering that an 8-m long section of the rods is heated every minute, the
rate of heat transfer to the rods in the oven becomes
#
Qin 5 Qin / Dt 5 15,680 kJ / min 5 261 kJ / s
Discussion This problem can also be solved by working with the rate form
of the equations as
#
p(0.05 m)2
pD2
pD2
#
m 5 rV 5 r
L / Dt 5 r
V 5 (2700 kg / m3)
(8 m / min)
4
4
4
5 42.41 kg / min
#
#
Qin 5 mc(T2 2 T1) 5 (42.41 kg/min) (0.973 kJ/kg·8C) (400 2 20)8C
5 15,680 kJ/min
which is identical to the result obtained before.
TOPIC OF SPECIAL INTEREST*
Thermodynamic Aspects of Biological Systems
An important and exciting application area of thermodynamics is biological systems, which are the sites of rather complex and intriguing energy
transfer and transformation processes. Biological systems are not in thermodynamic equilibrium, and thus they are not easy to analyze. Despite
their complexity, biological systems are primarily made up of four simple elements: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen. In the human
body, hydrogen accounts for 63 percent, oxygen 25.5 percent, carbon
9.5 percent, and nitrogen 1.4 percent of all the atoms. The remaining
0.6 percent of the atoms comes from 20 other elements essential for life.
By mass, about 72 percent of the human body is water.
The building blocks of living organisms are cells, which resemble miniature factories performing functions that are vital for the survival of organisms.
*This section can be skipped without a loss in continuity.
188
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
FIGURE 4–37
An average person dissipates energy
to the surroundings at a rate of 84 W
when resting.
©Janis Christie/Getty Images RF
1.2 kJ/s
1 kJ/s
FIGURE 4–38
Two fast-dancing people supply more
energy to a room than a 1-kW electric
resistance heater.
A biological system can be as simple as a single cell. The human body
contains about 100 trillion cells with an average diameter of 0.01 mm.
The membrane of the cell is a semipermeable wall that allows some substances to pass through it while excluding others.
In a typical cell, thousands of chemical reactions occur every second during which some molecules are broken down and energy is released and some
new molecules are formed. This high level of chemical activity in the cells,
which maintains the human body at a temperature of 378C while performing
the necessary bodily tasks, is called metabolism. In simple terms, metabolism refers to the burning of foods such as carbohydrates, fat, and protein.
The rate of metabolism in the resting state is called the basal metabolic rate,
which is the rate of metabolism required to keep a body performing the
necessary functions (such as breathing and blood circulation) at zero external activity level. The metabolic rate can also be interpreted as the energy
consumption rate for a body. For an average male (30 years old, 70 kg,
1.8-m2 body surface area), the basal metabolic rate is 84 W. That is, the body
dissipates energy to the environment at a rate of 84 W, which means that
the body is converting chemical energy of the food (or of the body fat if the
person has not eaten) into thermal energy at a rate of 84 W (Fig. 4–37). The
metabolic rate increases with the level of activity, and it may exceed 10 times
the basal metabolic rate when a body is doing strenuous exercise. That is,
two people doing heavy exercising in a room may be supplying more energy
to the room than a 1-kW electrical resistance heater (Fig. 4–38). The fraction
of sensible heat varies from about 40 percent in the case of heavy work to
about 70 percent in the case of light work. The rest of the energy is rejected
from the body by perspiration in the form of latent heat.
The basal metabolic rate varies with sex, body size, general health conditions, and so forth, and decreases considerably with age. This is one
of the reasons people tend to put on weight in their late twenties and
thirties even though they do not increase their food intake. The brain and
the liver are the major sites of metabolic activity. These two organs are
responsible for almost 50 percent of the basal metabolic rate of an adult
human body although they constitute only about 4 percent of the body
mass. In small children, it is remarkable that about half of the basal metabolic activity occurs in the brain alone.
The biological reactions in cells occur essentially at constant temperature, pressure, and volume. The temperature of the cell tends to rise when
some chemical energy is converted to heat, but this energy is quickly
transferred to the circulatory system, which transports it to outer parts of
the body and eventually to the environment through the skin.
The muscle cells function very much like an engine, converting the chemical energy into mechanical energy (work) with a conversion efficiency of
close to 20 percent. When the body does no net work on the environment
(such as moving some furniture upstairs), the entire work is also converted
to heat. In that case, the entire chemical energy in the food released during
metabolism in the body is eventually transferred to the environment. A TV
set that consumes electricity at a rate of 300 W must reject heat to its environment at a rate of 300 W in steady operation regardless of what goes on
in the set. That is, turning on a 300-W TV set or three 100-W light bulbs
will produce the same heating effect in a room as a 300-W resistance heater
189
CHAPTER 4
(Fig. 4–39). This is a consequence of the conservation of energy principle,
which requires that the energy input into a system must equal the energy
output when the total energy content of a system remains constant during a
process.
A 300-W
refrigerator
A 300-W
resistance heater
A 300-W fan
A 300-W TV
Two people, each
dissipating 150 W
Three light bulbs,
100 W each
A 100-W computer
with a 200-W
monitor
Solar
energy
300 W
Food and Exercise
The energy requirements of a body are met by the food we eat. The
nutrients in the food are considered in three major groups: carbohydrates,
proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates are characterized by having hydrogen
and oxygen atoms in a 2:1 ratio in their molecules. The molecules of
carbohydrates range from very simple (as in plain sugar) to very complex or large (as in starch). Bread and plain sugar are the major sources
of carbohydrates. Proteins are very large molecules that contain carbon,
hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, and they are essential for the building
and repairing of the body tissues. Proteins are made up of smaller building blocks called amino acids. Complete proteins such as meat, milk,
and eggs have all the amino acids needed to build body tissues. Plant
source proteins such as those in fruits, vegetables, and grains lack one or
more amino acids, and are called incomplete proteins. Fats are relatively
small molecules that consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Vegetable
oils and animal fats are major sources of fats. Most foods we eat contain all three nutrition groups at varying amounts. The typical average
American diet consists of 45 percent carbohydrate, 40 percent fat, and
15 percent protein, although it is recommended that in a healthy diet less
than 30 percent of the calories should come from fat.
The energy content of a given food is determined by burning a small sample of the food in a device called a bomb calorimeter, which is basically a
well-insulated rigid tank (Fig. 4–40). The tank contains a small combustion
chamber surrounded by water. The food is ignited and burned in the combustion chamber in the presence of excess oxygen, and the energy released
is transferred to the surrounding water. The energy content of the food is
calculated on the basis of the conservation of energy principle by measuring
the temperature rise of the water. The carbon in the food is converted into
CO2 and hydrogen into H2O as the food burns. The same chemical reactions occur in the body, and thus the same amount of energy is released.
Using dry (free of water) samples, the average energy contents of the
three basic food groups are determined by bomb calorimeter measurements to be 18.0 MJ/kg for carbohydrates, 22.2 MJ/kg for proteins, and
39.8 MJ/kg for fats. These food groups are not entirely metabolized in the
human body, however. The fraction of metabolizable energy contents are
95.5 percent for carbohydrates, 77.5 percent for proteins, and 97.7 percent
for fats. That is, the fats we eat are almost entirely metabolized in the
body, but close to one quarter of the protein we eat is discarded from
the body unburned. This corresponds to 4.1 Calories/g for proteins and
carbohydrates and 9.3 Calories/g for fats (Fig. 4–41) commonly seen in
nutrition books and on food labels. The energy contents of the foods we
normally eat are much lower than the values above because of the large
water content (water adds bulk to the food but it cannot be metabolized
or burned, and thus it has no energy value). Most vegetables, fruits, and
meats, for example, are mostly water. The average metabolizable energy
FIGURE 4–39
Some arrangements that supply a
room the same amount of energy as
a 300-W electric resistance heater.
Mixer
and motor
Electrical
switch
Thermometer
Water
Bomb
(combustion
chamber)
Insulation
Food
sample
FIGURE 4–40
Schematic of a bomb calorimeter used
to determine the energy content of
food samples.
190
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
3 cookies (32 g)
Fat: (8 g)(9.3 Cal/g) = 74.4 Cal
Protein: (2 g)(4.1 Cal/g) = 8.2 Cal
Carbohydrates: (21 g)(4.1 Cal/g) = 86.1 Cal
Other: (1 g)(0 Cal/g) = 0
TOTAL (for 32 g): 169 Cal
FIGURE 4–41
Evaluating the calorie content of one
serving of chocolate chip cookies
(values are for Chips Ahoy cookies
made by Nabisco).
©Comstock/Punchstock RF
contents of the three basic food groups are 4.2 MJ/kg for carbohydrates,
8.4 MJ/kg for proteins, and 33.1 MJ/kg for fats. Note that 1 kg of natural
fat contains almost 8 times the metabolizable energy of 1 kg of natural
carbohydrates. Thus, a person who fills his stomach with fatty foods is
consuming much more energy than a person who fills his stomach with
carbohydrates such as bread or rice.
The metabolizable energy content of foods is usually expressed by nutritionists in terms of the capitalized Calories. One Calorie is equivalent to
one kilocalorie (1000 calories), which is equivalent to 4.1868 kJ. That is,
1 Cal (Calorie) 5 1000 calories 5 1 kcal (kilocalorie) 5 4.1868 kJ
The calorie notation often causes confusion since it is not always followed
in the tables or articles on nutrition. When the topic is food or fitness, a
calorie normally means a kilocalorie whether it is capitalized or not.
The daily calorie needs of people vary greatly with age, gender, the state
of health, the activity level, the body weight, and the composition of the
body as well as other factors. A small person needs fewer calories than a
larger person of the same sex and age. An average man needs about 2400
to 2700 Calories a day. The daily need of an average woman varies from
1800 to 2200 Calories. The daily calorie needs are about 1600 for sedentary women and some older adults; 2000 for sedentary men and most older
adults; 2200 for most children, teenage girls, and active women; 2800 for
teenage boys, active men, and some very active women; and above 3000
for very active men. The average value of calorie intake is usually taken
to be 2000 Calories per day. The daily calorie needs of a person can be
determined by multiplying the body weight in pounds (which is 2.205 times
the body weight in kg) by 11 for a sedentary person, 13 for a moderately
active person, 15 for a moderate exerciser or physical laborer, and 18 for an
extremely active exerciser or physical laborer. The extra calories a body consumes are usually stored as fat, which serves as the spare energy of the body
for use when the energy intake of the body is less than the needed amount.
Like other natural fat, 1 kg of human body fat contains about 33.1 MJ
of metabolizable energy. Therefore, a starving person (zero energy intake)
who uses up 2200 Calories (9211 kJ) a day can meet his daily energy
intake requirements by burning only 9211/33,100 5 0.28 kg of body fat.
So it is no surprise that people are known to survive over 100 days without
eating. (They still need to drink water, however, to replenish the water lost
through the lungs and the skin to avoid the dehydration that may occur
in just a few days.) Although the desire to get rid of the excess fat in a
thin world may be overwhelming at times, starvation diets are not recommended because the body soon starts to consume its own muscle tissue in
addition to fat. A healthy diet should involve regular exercise while allowing a reasonable amount of calorie intake.
The average metabolizable energy contents of various foods and the
energy consumption during various activities are given in Tables 4–1 and
4–2. Considering that no two hamburgers are alike, and that no two people walk exactly the same way, there is some uncertainty in these values,
as you would expect. Therefore, you may encounter somewhat different
values in other books or magazines for the same items.
191
CHAPTER 4
TABLE 4–1
Approximate metabolizable energy content of some common foods
(1 Calorie 5 4.1868 kJ 5 3.968 Btu)
Food
Calories
Apple (one, medium)
Baked potato (plain)
Baked potato with cheese
Bread (white, one slice)
Butter (one teaspoon)
Cheeseburger
Chocolate candy bar (20 g)
Cola (200 ml)
Egg (one)
70
250
550
70
35
325
105
87
80
Food
Fish sandwich
French fries (regular)
Hamburger
Hot dog
Ice cream (100 ml,
10% fat)
Lettuce salad with
French dressing
Calories
450
250
275
300
110
150
Food
Milk (skim, 200 ml)
Milk (whole, 200 ml)
Peach (one, medium)
Pie (one 18 slice, 23 cm
diameter)
Pizza (large, cheese,
one 18 slice)
Calories
76
136
65
300
350
The rates of energy consumption listed in Table 4–2 during some activities are for a 68-kg adult. The energy consumed for smaller or larger
adults can be determined using the proportionality of the metabolism rate
and the body size. For example, the rate of energy consumption by a
68-kg bicyclist is listed in Table 4–2 to be 639 Calories/h. Then the rate
of energy consumption by a 50-kg bicyclist is
(50 kg)
639 Cal/h
5 470 Cal/h
68 kg
For a 100-kg person, it would be 940 Cal/h.
The thermodynamic analysis of the human body is rather complicated
since it involves mass transfer (during breathing, perspiring, etc.) as well
as energy transfer. As such, it should be treated as an open system. However, the energy transfer with mass is difficult to quantify. Therefore, the
human body is often modeled as a closed system for simplicity by treating energy transported with mass as just energy transfer. For example,
eating is modeled as the transfer of energy into the human body in the
amount of the metabolizable energy content of the food.
Dieting
Most diets are based on calorie counting; that is, the conservation of
energy principle: a person who consumes more calories than his or her
body burns will gain weight whereas a person who consumes less calories than his or her body burns will lose weight. Yet, people who eat
whatever they want whenever they want without gaining any weight are
living proof that the calorie-counting technique alone does not work in
dieting. Obviously there is more to dieting than keeping track of calories.
It should be noted that the phrases weight gain and weight loss are misnomers. The correct phrases should be mass gain and mass loss. A man
who goes to space loses practically all of his weight but none of his mass.
When the topic is food and fitness, weight is understood to mean mass,
and weight is expressed in mass units.
Researchers on nutrition proposed several theories on dieting. One theory
suggests that some people have very “food efficient” bodies. These people
need fewer calories than other people do for the same activity, just like
TABLE 4–2
Approximate energy consumption of
a 68-kg adult during some activities
(1 Calorie 5 4.1868 kJ 5
3.968 Btu)
Activity
Basal metabolism
Basketball
Bicycling (21 km/h)
Cross-country skiing
(13 km/h)
Driving a car
Eating
Fast dancing
Fast running (13 km/h)
Jogging (8 km/h)
Swimming (fast)
Swimming (slow)
Tennis (advanced)
Tennis (beginner)
Walking (7.2 km/h)
Watching TV
Calories/h
72
550
639
936
180
99
600
936
540
860
288
480
288
432
72
192
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
Body
fat
level
Set
point
New
set point
FIGURE 4–42
The body tends to keep the body fat
level at a set point by speeding up
metabolism when a person splurges
and by slowing it down when the
person starves.
a fuel-efficient car needing less fuel for traveling a given distance. It is
interesting that we want our cars to be fuel efficient but we do not want the
same high efficiency for our bodies. One thing that frustrates the dieters is
that the body interprets dieting as starvation and starts using the energy
reserves of the body more stringently. Shifting from a normal 2000-Calorie
daily diet to an 800-Calorie diet without exercise is observed to lower the
basal metabolic rate by 10 to 20 percent. Although the metabolic rate
returns to normal once the dieting stops, extended periods of low-calorie
dieting without adequate exercise may result in the loss of considerable
muscle tissue together with fat. With less muscle tissue to burn calories,
the metabolic rate of the body declines and stays below normal even after
a person starts eating normally. As a result, the person regains the weight
he or she has lost in the form of fat, plus more. The basal metabolic rate
remains about the same in people who exercise while dieting.
Regular moderate exercise is part of any healthy dieting program for
good reason: it builds or preserves muscle tissue that burns calories much
faster than the fat tissue does. It is interesting that aerobic exercise continues burning calories for several hours after the workout, raising the
overall metabolic rate considerably.
Another theory suggests that people with too many fat cells developed
during childhood or adolescence are much more likely to gain weight.
Some people believe that the fat content of the bodies is controlled by
the setting of a “fat control” mechanism, much like the temperature of a
house is controlled by the thermostat setting.
Some people put the blame for weight problems simply on the genes.
Considering that 80 percent of the children of overweight parents are
also overweight, heredity may indeed play an important role in the way
a body stores fat. Researchers from the University of Washington and the
Rockefeller University have identified a gene, called the RIIbeta, that seems
to control the rate of metabolism. The body tries to keep the body fat at
a particular level, called the set point, that differs from person to person
(Fig. 4–42). This is done by speeding up the metabolism and thus burning
extra calories much faster when a person tends to gain weight and by slowing down the metabolism and thus burning calories at a slower rate when
a person tends to lose weight. Therefore, a person who just became slim
burns fewer calories than does a person of the same size who has always
been slim. Even exercise does not seem to change that. Then to keep the
weight off, the newly slim person should consume no more calories than
he or she can burn. Note that in people with high metabolic rates, the body
dissipates the extra calories as body heat instead of storing them as fat, and
thus there is no violation of the conservation of energy principle.
In some people, a genetic flaw is believed to be responsible for the
extremely low rates of metabolism. Several studies concluded that losing
weight for such people is nearly impossible. That is, obesity is a biological
phenomenon. However, even such people will not gain weight unless they
eat more than their body can burn. They just must learn to be content with
little food to remain slim, and forget about ever having a normal “eating”
life. For most people, genetics determine the range of normal weights.
A person may end up at the high or low end of that range, depending on
193
CHAPTER 4
eating and exercise habits. This also explains why some genetically identical twins are not so identical when it comes to body weight. Hormone
imbalance is also believed to cause excessive weight gain or loss.
Based on his experience, the first author of this book has also developed a diet called the “sensible diet.” It consists of two simple rules: eat
whatever you want whenever you want as much as you want provided
that (1) you do not eat unless you are hungry and (2) you stop eating
before you get stuffed. In other words, listen to your body and don’t
impose on it. Don’t expect to see this unscientific diet advertised anywhere since there is nothing to be sold and thus no money to be made.
Also, it is not as easy as it sounds since food is at the center stage of
most leisure activities in social life, and eating and drinking have become
synonymous with having a good time. However, it is comforting to know
that the human body is quite forgiving of occasional impositions.
Being overweight is associated with a long list of health risks from
high blood pressure to some forms of cancer, especially for people who
have a weight-related medical condition such as diabetes, hypertension,
and heart disease. Therefore, people often wonder if their weight is in the
proper range. Well, the answer to this question is not written in stone, but
if you cannot see your toes or you can pinch your love handles more than
an inch, you don’t need an expert to tell you that you went over your
range. On the other hand, some people who are obsessed with the weight
issue try to lose more weight even though they are actually underweight.
Therefore, it is useful to have a scientific criterion to determine physical
fitness. The range of healthy weight for adults is usually expressed in
terms of the body mass index (BMI), defined, in SI units, as
W (kg)
BMI 5 2 2 with
H (m )
BMI , 19 underweight
19 # BMI # 25 healthy weight
BMI . 25 overweight
TABLE 4–3
The range of healthy weight for
adults of various heights (Source:
National Institute of Health)
English Units
Height
in
58
60
62
64
66
68
70
72
74
76
SI Units
Healthy
Weight,
lbm*
Height,
m
Healthy
weight,
kg*
91–119
97–127
103–136
111–146
118–156
125–165
133–175
140–185
148–195
156–205
1.45
1.50
1.55
1.60
1.65
1.70
1.75
1.80
1.85
1.90
40–53
43–56
46–60
49–64
52–68
55–72
58–77
62–81
65–86
69–90
*The upper and lower limits of healthy range
correspond to mass body indexes of 19 and 25,
respectively.
(4–39)
where W is the weight (actually, the mass) of the person in kg and H is the
height in m. Therefore, a BMI of 25 is the upper limit for the healthy weight
and a person with a BMI of 27 is 8 percent overweight. It can be shown that
the formula above is equivalent in English units to BMI 5 705 W/H 2 where
W is in pounds and H is in inches. The proper range of weight for adults of
various heights is given in Table 4–3 in both SI and English units.
EXAMPLE 4–14
Burning Off Lunch Calories
A 90-kg man had two hamburgers, a regular serving of french fries, and a
200-ml Coke for lunch (Fig. 4–43). Determine how long it will take for him
to burn the lunch calories off (a) by watching TV and (b) by fast swimming.
What would your answers be for a 45-kg man?
SOLUTION A man had lunch at a restaurant. The time it will take for him
to burn the lunch calories by watching TV and by fast swimming are to be
determined.
Assumptions The values in Tables 4–1 and 4–2 are applicable for food and
exercise.
FIGURE 4–43
A typical lunch discussed in
Example 4–14.
©John A. Rizzo/Getty Images RF
194
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
Analysis (a) We take the human body as our system and treat it as a closed
system whose energy content remains unchanged during the process. Then
the conservation of energy principle requires that the energy input into the
body must be equal to the energy output. The net energy input in this case
is the metabolizable energy content of the food eaten. It is determined from
Table 4–1 to be
Ein 5 2 3 Ehamburger 1 Efries 1 Ecola
5 2 3 275 1 250 1 87
5 887 Cal
The rate of energy output for a 68-kg man watching TV is given in Table 4–2
to be 72 Calories/h. For a 90-kg man it becomes
Eout 5 (90 kg)
72 Cal/h
5 95.3 Cal/h
68 kg
Therefore, it will take
Dt 5
887 Cal
5 9.3 h
95.3 Cal/h
to burn the lunch calories off by watching TV.
(b) It can be shown in a similar manner that it takes only 47 min to burn the
lunch calories off by fast swimming.
Discussion The 45-kg man is half as large as the 90-kg man. Therefore,
expending the same amount of energy takes twice as long in each case:
18.6 h by watching TV and 94 min by fast swimming.
EXAMPLE 4–15
Losing Weight by Switching to Fat-Free Chips
The fake fat olestra passes through the body undigested, and thus adds zero
calorie to the diet. Although foods cooked with olestra taste pretty good, they
may cause abdominal discomfort and the long-term effects are unknown.
A 1-oz (28.3-g) serving of regular potato chips has 10 g of fat and 150 Calories, whereas 1 oz of the so-called fat-free chips fried in olestra has only
75 Calories. Consider a person who eats 1 oz of regular potato chips every day
at lunch without gaining or losing any weight. Determine how much weight this
person will lose in one year if he or she switches to fat-free chips (Fig. 4–44).
SOLUTION A person switches from regular potato chips to fat-free ones.
The weight the person loses in one year is to be determined.
Assumptions Exercising and other eating habits remain the same.
Analysis The person who switches to the fat-free chips consumes 75 fewer
Calories a day. Then the annual reduction in calories consumed becomes
Ereduced 5 (75 Cal/day)(365 day/year) 5 27,375 Cal/year
The metabolizable energy content of 1 kg of body fat is 33,100 kJ. Therefore, assuming the deficit in the calorie intake is made up by burning body
fat, the person who switches to fat-free chips will lose
mfat 5
FIGURE 4–44
Schematic for Example 4–15.
Ereduced
Energy content of fat
5
27,375 Cal 4.1868 kJ
a
b 5 3.46 kg
33,100 kJ/kg
1 Cal
(about 7.6 pounds) of body fat that year.
195
CHAPTER 4
SUMMARY
Work is the energy transferred as a force acts on a system
through a distance. The most common form of mechanical work is the boundary work, which is the work associated with the expansion and compression of substances. On
a P-V diagram, the area under the process curve represents
the boundary work for a quasi-equilibrium process. Various
forms of boundary work are expressed as follows:
2
Wb 5
(1) General
(2) Isobaric process
Wb 5 P0(V 2 2 V 1)
# P dV
1
(P1 5 P2 5 P0 5 constant)
(3) Polytropic process
P2V 2 2 P1V 1
Wb 5
(n 2 1)
(PV n 5 constant)
12n
(4) Isothernal process of an ideal gas
V2
Wb 5 P1V 1 ln
V1
V2
(PV 5 mRT0 5 constant)
5 mRT0 ln
V1
The first law of thermodynamics is essentially an expression of the conservation of energy principle, also called the
energy balance. The general energy balances for any system
undergoing any process can be expressed as
DEsystem
Ein 2 Eout 5
('')
''*
(')'*
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
It can also be expressed in the rate form as
.
.
E in 2 Eout 5
dEsystem /dt
('')
''*
('')
''*
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Rate of change in internal,
kinetic, potential, etc., energies
Taking heat transfer to the system and work done by the
system to be positive quantities, the energy balance for a
closed system can also be expressed as
Q 2 W 5 DU 1 DKE 1 DPE
For a constant-pressure process, Wb 1 DU 5 DH. Thus,
Q 2 Wother 5 DH 1 DKE 1 DPE
Note that the relation above is limited to constant pressure
processes of closed system, and is NOT valid for processes
during which pressure varies.
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a
unit mass of a substance by one degree is called the specific
heat at constant volume cv for a constant-volume process
and the specific heat at constant pressure cp for a constantpressure process. They are defined as
cv 5 a
0u
0h
b and cp 5 a b
0T v
0T p
For ideal gases u, h, cv, and cp are functions of temperature
alone. The Du and Dh of ideal gases are expressed as
2
Du 5 u2 2 u1 5
# c (T ) dT > c
v
v,avg(T 2 2 T 1)
1
2
Dh 5 h2 2 h1 5
# c (T ) dT > c
p
p,avg(T 2 2 T 1)
1
For ideal gases, cv and cp are related by
cp 5 c v 1 R
where R is the gas constant. The specific heat ratio k is
defined as
cp
k5
cv
For incompressible substances (liquids and solids), both the
constant-pressure and constant-volume specific heats are
identical and denoted by c:
cp 5 c v 5 c
The Du and Dh of imcompressible substances are given by
where
W 5 Wother 1 W b
DU 5 m(u2 2 u1)
DKE 5 12 m(V 22 2 V 21 )
DPE 5 mg(z 2 2 z 1)
2
Du 5
# c(T ) dT > c (T 2 T )
avg
2
1
1
Dh 5 Du 1 vDP
REFERENCES AND SUGGESTED READINGS
1. ASHRAE Handbook of Fundamentals. SI version.
Atlanta, GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating,
and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc., 1993.
2. ASHRAE Handbook of Refrigeration. SI version. Atlanta,
GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and AirConditioning Engineers, Inc., 1994.
196
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
PROBLEMS*
Moving Boundary Work
4–1C An ideal gas at a given state expands to a fixed final
volume first at constant pressure and then at constant temperature. For which case is the work done greater?
4–2 Nitrogen at an initial state of 300 K, 150 kPa, and
0.2 m3 is compressed slowly in an isothermal process to a
final pressure of 800 kPa. Determine the work done during
this process.
4–3 The volume of 1 kg of helium in a piston-cylinder
device is initially 5 m3. Now helium is compressed to 2 m3
while its pressure is maintained constant at 180 kPa. Determine the initial and final temperatures of helium as well as
the work required to compress it, in kJ.
4–4E Calculate the total work, in Btu, for process 1–3
shown in Fig. P4–4E.
3
P, psia
300
2
4–7 A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.07 m3
of nitrogen gas at 130 kPa and 1808C. The nitrogen is now
expanded to a pressure of 80 kPa polytropically with a polytropic exponent whose value is equal to the specific heat ratio
(called isentropic expansion). Determine the final temperature and the boundary work done during this process.
4–8 A mass of 5 kg of saturated water vapor at 300 kPa
is heated at constant pressure until the temperature reaches
2008C. Calculate the work done by the steam during this process. Answer: 166 kJ
4–9 1-m3 of saturated liquid water at 2008C is expanded
isothermally in a closed system until its quality is 80 percent.
Determine the total work produced by this expansion, in kJ.
15
1
1
FIGURE P4–6
2
V, ft3
3.3
FIGURE P4–4E
4–5 A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.07 m3
of nitrogen gas at 130 kPa and 1208C. The nitrogen is now
expanded polytropically to a state of 100 kPa and 1008C.
Determine the boundary work done during this process.
4–6 A piston–cylinder device with a set of stops initially
contains 0.6 kg of steam at 1.0 MPa and 4008C. The location of the stops corresponds to 40 percent of the initial
volume. Now the steam is cooled. Determine the compression work if the final state is (a) 1.0 MPa and 2508C and
(b) 500 kPa. (c) Also determine the temperature at the final
state in part (b).
4–10 A gas is compressed from an initial volume of 0.42 m3
to a final volume of 0.12 m3. During the quasi-equilibrium process, the pressure changes with volume according to the relation P 5 aV 1 b, where a 5 21200 kPa/m3 and b 5 600 kPa.
Calculate the work done during this process (a) by plotting the
process on a P-V diagram and finding the area under the process curve and (b) by performing the necessary integrations.
Gas
P = aV + b
FIGURE P4–10
* Problems designated by a “C” are concept questions, and
students are encouraged to answer them all. Problems designated
by an “E” are in English units, and the SI users can ignore them.
Problems with the
icon are solved using EES, and complete
solutions together with parametric studies are included on the text
website. Problems with the
icon are comprehensive in nature,
and are intended to be solved with an equation solver such as EES.
4–11 A mass of 1.5 kg of air at 120 kPa and 248C is contained in a gas-tight, frictionless piston–cylinder device. The
air is now compressed to a final pressure of 600 kPa. During
the process, heat is transferred from the air such that the temperature inside the cylinder remains constant. Calculate the
work input during this process. Answer: 206 kJ
197
CHAPTER 4
4–12
During some actual expansion and compression
processes in piston–cylinder devices, the gases
have been observed to satisfy the relationship PV n 5 C,
where n and C are constants. Calculate the work done when a
gas expands from 350 kPa and 0.03 m3 to a final volume of
0.2 m3 for the case of n 5 1.5.
N2
160 kPa
140°C
4–13
Reconsider Prob. 4–12. Using the EES (or other)
software, plot the process described in the problem on a P-V diagram, and investigate the effect of the polytropic exponent n on the boundary work. Let the polytropic
exponent vary from 1.1 to 1.6. Plot the boundary work versus
the polytropic exponent, and discuss the results.
4–14 A frictionless piston–cylinder device contains 5 kg of
nitrogen at 100 kPa and 250 K. Nitrogen is now compressed
slowly according to the relation PV1.4 5 constant until it
reaches a final temperature of 360 K. Calculate the work
input during this process. Answer: 408 kJ
N2
PV 1.4 = const.
FIGURE P4–14
FIGURE P4–18
4–19E Hydrogen is contained in a piston–cylinder device at
14.7 psia and 15 ft3. At this state, a linear spring (F ~ x) with a
spring constant of 15,000 lbf/ft is touching the piston but exerts
no force on it. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 3 ft2. Heat
is transferred to the hydrogen, causing it to expand until its volume doubles. Determine (a) the final pressure, (b) the total work
done by the hydrogen, and (c) the fraction of this work done
against the spring. Also, show the process on a P-V diagram.
4–20 A piston–cylinder device contains 0.15 kg of air initially
at 2 MPa and 3508C. The air is first expanded isothermally to
500 kPa, then compressed polytropically with a polytropic exponent of 1.2 to the initial pressure, and finally compressed at the
constant pressure to the initial state. Determine the boundary
work for each process and the net work of the cycle.
4–21 1-kg of water that is initially at 908C with a quality of 10
percent occupies a spring-loaded piston–cylinder device, such as
that in Fig. P4–21. This device is now heated until the pressure
rises to 800 kPa and the temperature is 2508C. Determine the
total work produced during this process, in kJ. Answer: 24.5 kJ
4–15
The equation of state of a gas is given as v (P 1
10/ v 2) 5 RuT, where the units of v and P are
m3/kmol and kPa, respectively. Now 0.2 kmol of this gas is
expanded in a quasi-equilibrium manner from 2 to 4 m3 at a
constant temperature of 350 K. Determine (a) the unit of the
quantity 10 in the equation and (b) the work done during this
isothermal expansion process.
4–16
Reconsider Prob. 4–15. Using the integration
feature of the EES software, calculate the work
done, and compare your result with the “hand-calculated”
result obtained in Prob. 4–15. Plot the process described in
the problem on a P-v diagram.
4–17E During an expansion process, the pressure of a gas
changes from 15 to 100 psia according to the relation P 5
aV 1 b, where a 5 5 psia/ft3 and b is a constant. If the initial
volume of the gas is 7 ft3, calculate the work done during the
process. Answer: 181 Btu
4–18 A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.4 kg
of nitrogen gas at 160 kPa and 1408C. The nitrogen is now
expanded isothermally to a pressure of 100 kPa. Determine
the boundary work done during this process. Answer: 23.0 kJ
Q
Water, 90°C
x = 0.10
FIGURE P4–21
4–22 0.75-kg water that is initially at 0.5 MPa and
30 percent quality occupies a spring-loaded piston–cylinder
device. This device is now cooled until the water is a saturated liquid at 1008C. Calculate the total work produced during this process, in kJ.
4–23 An ideal gas undergoes two processes in a pistoncylinder device as follows:
1-2 Polytropic compression from T1 and P1 with a polytropic
exponent n and a compression ratio of r 5 V1/V2.
198
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
2-3 Constant pressure expansion at P3 5 P2 until V35V1.
(a) Sketch the processes on a single P-V diagram.
(b) Obtain an expression for the ratio of the compressionto-expansion work as a function of n and r.
(c) Find the value of this ratio for values of n 5 1.4 and
r 5 6.
Answers: (b)
1 2 r1 2 n
1
a
b (c) 0.256
n21 r21
4–24 A piston–cylinder device contains 50 kg of water at
250 kPa and 258C. The cross-sectional area of the piston is
0.1 m2. Heat is now transferred to the water, causing part of
it to evaporate and expand. When the volume reaches 0.2 m3,
the piston reaches a linear spring whose spring constant is
100 kN/m. More heat is transferred to the water until the piston rises 20 cm more. Determine (a) the final pressure and
temperature and (b) the work done during this process. Also,
show the process on a P-V diagram. Answers: (a) 450 kPa,
147.9°C, (b) 44.5 kJ
4–27E A closed system undergoes a process in which there
is no internal energy change. During this process, the system
produces 1.13106 1bf·ft of work. Calculate the heat transfer
for this process, in Btu.
4–28 A rigid container equipped with a stirring device contains 2.5 kg of motor oil. Determine the rate of specific energy
increase when heat is transferred to the oil at a rate of 1 W, and
1.5 W of power is applied to the stirring device.
4–29 A 0.5-m3 rigid tank contains refrigerant-134a initially
at 160 kPa and 40 percent quality. Heat is now transferred to
the refrigerant until the pressure reaches 700 kPa. Determine
(a) the mass of the refrigerant in the tank and (b) the amount
of heat transferred. Also, show the process on a P-v diagram
with respect to saturation lines.
4–30E A 20-ft3 rigid tank initially contains saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 160 psia. As a result of heat transfer from
the refrigerant, the pressure drops to 50 psia. Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines, and
determine (a) the final temperature, (b) the amount of refrigerant that has condensed, and (c) the heat transfer.
4–31 A rigid 10-L vessel initially contains a mixture of
liquid water and vapor at 1008C with 12.3 percent quality. The
mixture is then heated until its temperature is 1508C. Calculate
the heat transfer required for this process. Answer: 46.9 kJ
Water
10 L
100°C
x = 0.123
A = 0.1 m2
H 2O
m = 50 kg
Q
Q
FIGURE P4–24
4–25
Reconsider Prob. 4–24. Using the EES software,
investigate the effect of the spring constant on
the final pressure in the cylinder and the boundary work
done. Let the spring constant vary from 50 kN/m to 500 kN/m.
Plot the final pressure and the boundary work against the
spring constant, and discuss the results.
Closed System Energy Analysis
4–26E Complete the table below on the basis of the conservation of energy principle for a closed system.
Qin
Btu
Wout
Btu
E1
Btu
E2
Btu
m
lbm
e2 – e1
Btu/lbm
350
350
—
2500
—
—
130
260
—
250
1020
550
600
1400
1000
860
—
—
900
—
3
5
2
7
3
—
—
150
—
2200
FIGURE P4–31
4–32 A fixed mass of saturated water vapor at 400 kPa is
isothermally cooled until it is a saturated liquid. Calculate the
amount of heat rejected during this process, in kJ/kg.
4–33 A piston–cylinder device contains steam initially at
1 MPa, 4508C, and 2.5 m3. Steam is allowed to cool at constant pressure until it first starts condensing. Show the process on a T-v diagram with respect to saturation lines and
determine (a) the mass of the steam, (b) the final temperature, and (c) the amount of heat transfer.
4–34 An insulated piston–cylinder device contains 5 L of
saturated liquid water at a constant pressure of 175 kPa. Water
is stirred by a paddle wheel while a current of 8 A flows for
45 min through a resistor placed in the water. If one-half of
the liquid is evaporated during this constant-pressure process
and the paddle-wheel work amounts to 400 kJ, determine the
voltage of the source. Also, show the process on a P-v diagram
with respect to saturation lines. Answer: 224 V
199
CHAPTER 4
radiator are initially at 108C. The radiator with a rating of
2.4 kW is now turned on. At the same time, heat is lost from
the room at an average rate of 0.35 kJ/s. After some time,
the average temperature is measured to be 208C for the air
in the room, and 508C for the oil in the radiator. Taking the
density and the specific heat of the oil to be 950 kg/m3 and
2.2 kJ/kg·8C, respectively, determine how long the heater is
kept on. Assume the room is well-sealed so that there are no
air leaks.
FIGURE P4–34
4–35
A piston–cylinder device initially contains steam
at 200 kPa, 2008C, and 0.4 m3. At this state, a
linear spring (F ~ x) is touching the piston but exerts no force
on it. Heat is now slowly transferred to the steam, causing the
pressure and the volume to rise to 250 kPa and 0.6 m3,
respectively. Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect
to saturation lines and determine (a) the final temperature,
(b) the work done by the steam, and (c) the total heat transferred. Answers: (a) 6068C, (b) 45 kJ, (c) 288 kJ
10°C
Room
Q
Radiator
FIGURE P4–38
4–39 Steam at 75 kPa and 8 percent quality is contained
in a spring-loaded piston–cylinder device, as shown in
Fig. P4–39, with an initial volume of 2 m3. Steam is now
heated until its volume is 5 m3 and its pressure is 225 kPa.
Determine the heat transferred to and the work produced by
the steam during this process.
FIGURE P4–35
4–36
Reconsider Prob. 4–35. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the initial temperature of steam on the final temperature, the work done,
and the total heat transfer. Let the initial temperature vary
from 150 to 2508C. Plot the final results against the initial
temperature, and discuss the results.
4–37 A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.8 m3 of
saturated water vapor at 250 kPa. At this state, the piston is
resting on a set of stops, and the mass of the piston is such
that a pressure of 300 kPa is required to move it. Heat is now
slowly transferred to the steam until the volume doubles.
Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines and determine (a) the final temperature, (b) the
work done during this process, and (c) the total heat transfer.
Answers: (a) 6628C, (b) 240 kJ, (c) 1213 kJ
4–38 A 40-L electrical radiator containing heating oil is
placed in a 50-m3 room. Both the room and the oil in the
FIGURE P4–39
4–40E Saturated R-134a vapor at 1008F is condensed at
constant pressure to a saturated liquid in a closed piston–
cylinder system. Calculate the heat transfer and work done
during this process, in Btu/lbm.
4–41 An insulated tank is divided into two parts by a partition. One part of the tank contains 2.5 kg of compressed
liquid water at 608C and 600 kPa while the other part is evacuated. The partition is now removed, and the water expands
to fill the entire tank. Determine the final temperature of
the water and the volume of the tank for a final pressure of
10 kPa.
200
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
Evacuated
Partition
H2O
FIGURE P4–41
4–42
Reconsider Prob. 4–41. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the initial
pressure of water on the final temperature in the tank. Let the
initial pressure vary from 100 to 600 kPa. Plot the final temperature against the initial pressure, and discuss the results.
Specific Heats, Du, and Dh of Ideal Gases
4–43C Is the relation Du 5 mcv,avgDT restricted to constantvolume processes only, or can it be used for any kind of process of an ideal gas?
4–44C Is the relation Dh 5 mcp,avg DT restricted to constant-pressure processes only, or can it be used for any kind
of process of an ideal gas?
4–45C Is the energy required to heat air from 295 to 305 K
the same as the energy required to heat it from 345 to 355 K?
Assume the pressure remains constant in both cases.
4–52 The temperature of 2 kg of neon is increased from 20
to 1808C. Calculate the change in the total internal energy of
the neon, in kJ. Would the internal energy change be any different if the neon were replaced with argon?
4–53 Calculate the change in the enthalpy of argon, in
kJ/kg, when it is cooled from 75 to 258C. If neon had undergone this same change of temperature, would its enthalpy
change have been any different?
4–54 Determine the internal energy change Du of hydrogen, in kJ/kg, as it is heated from 200 to 800 K, using
(a) the empirical specific heat equation as a function of temperature (Table A–2c), (b) the cv value at the average temperature (Table A–2b), and (c) the cv value at room temperature
(Table A–2a).
4–55 Determine the enthalpy change Dh of nitrogen, in kJ/kg,
as it is heated from 600 to 1000 K, using (a) the empirical specific heat equation as a function of temperature (Table A–2c),
(b) the cp value at the average temperature (Table A–2b), and
(c) the cp value at room temperature (Table A–2a).
Answers: (a) 447.8 kJ/kg, (b) 448.4 kJ/kg, (c) 415.6 kJ/kg
4–56E 1-ft3 of air is contained in the spring-loaded pistoncylinder device shown in Fig. P4–56E. The spring constant
is 5 lbf/in, and the piston diameter is 10 in. When no force
is exerted by the spring on the piston, the state of the air is
250 psia and 4608F. This device is now cooled until the volume is one-half its original size. Determine the change in the
specific internal energy and enthalpy of the air. Answers:
78.9 Btu/lbm, 111 Btu/lbm
4–46C A fixed mass of an ideal gas is heated from 50 to
808C at a constant pressure of (a) 1 atm and (b) 3 atm. For
which case do you think the energy required will be greater?
Why?
4–47C A fixed mass of an ideal gas is heated from 50 to
808C at a constant volume of (a) 1 m3 and (b) 3 m3. For
which case do you think the energy required will be greater?
Why?
4–48C A fixed mass of an ideal gas is heated from 50 to
808C (a) at constant volume and (b) at constant pressure. For
which case do you think the energy required will be greater?
Why?
_
_
4–49 Show that for an ideal gas c p 5 c v1 Ru.
FIGURE P4–56E
4–50 What is the change in the enthalpy, in kJ/kg, of oxygen as its temperature changes from 150 to 2508C? Is there
any difference if the temperature change were from 0 to
1008C? Does the pressure at the beginning and end of this
process have any effect on the enthalpy change?
Closed-System Energy Analysis: Ideal Gases
4–51E Air is compressed from 20 psia and 708F to 150 psia
in a compressor. The compressor is operated such that the air
temperature remains constant. Calculate the change in the specific volume of air as it passes through this compressor.
4–58 A 3-m3 rigid tank contains hydrogen at 250 kPa and
550 K. The gas is now cooled until its temperature drops
to 350 K. Determine (a) the final pressure in the tank and
(b) the amount of heat transfer.
4–57C Is it possible to compress an ideal gas isothermally
in an adiabatic piston–cylinder device? Explain.
201
CHAPTER 4
4–59E A 10-ft3 tank contains oxygen initially at 14.7 psia
and 808F. A paddle wheel within the tank is rotated until the
pressure inside rises to 20 psia. During the process 20 Btu
of heat is lost to the surroundings. Determine the paddlewheel work done. Neglect the energy stored in the paddle
wheel.
4–60E A rigid tank contains 10 lbm of air at 30 psia and
658F. The air is now heated until its pressure doubles. Determine (a) the volume of the tank and (b) the amount of heat
transfer. Answers: (a) 64.8 ft3, (b) 920 Btu
4–61E Nitrogen gas to 20 psia and 1008F initially occupies
a volume of 1 ft3 in a rigid container equipped with a stirring
paddle wheel. After 5000 lbf·ft of paddle wheel work is done
on nitrogen, what is its final temperature? Answer: 489°F
4–62 An insulated rigid tank is divided into two equal parts
by a partition. Initially, one part contains 4 kg of an ideal
gas at 800 kPa and 508C, and the other part is evacuated.
The partition is now removed, and the gas expands into the
entire tank. Determine the final temperature and pressure in
the tank.
Room
3m×4m×4m
Fan
FIGURE P4–64
4–65 A 4-m 3 5-m 3 7-m room is heated by the radiator
of a steam-heating system. The steam radiator transfers heat
at a rate of 10,000 kJ/h, and a 100-W fan is used to distribute
the warm air in the room. The rate of heat loss from the room
is estimated to be about 5000 kJ/h. If the initial temperature
of the room air is 108C, determine how long it will take for
the air temperature to rise to 208C. Assume constant specific
heats at room temperature.
5000 kJ/h
Ideal
gas
800 kPa
50°C
Evacuated
Room
4m×5m×7m
Steam
FIGURE P4–62
4–63 A 4-m 3 5-m 3 6-m room is to be heated by a
baseboard resistance heater. It is desired that the resistance
heater be able to raise the air temperature in the room from
5 to 258C within 11 min. Assuming no heat losses from
the room and an atmospheric pressure of 100 kPa, determine the required power of the resistance heater. Assume
constant specific heats at room temperature. Answer:
3.28 kW
4–64 A student living in a 3-m 3 4-m 3 4-m dormitory
room turns on her 100-W fan before she leaves the room
on a summer day, hoping that the room will be cooler when
she comes back in the evening. Assuming all the doors and
windows are tightly closed and disregarding any heat transfer through the walls and the windows, determine the temperature in the room when she comes back 8 h later. Use
specific heat values at room temperature, and assume the
room to be at 100 kPa and 208C in the morning when she
leaves. Answer: 90.3°C
10,000 kJ/h
·
Wpw
FIGURE P4–65
4–66 Argon is compressed in a polytropic process with n 5
1.2 from 120 kPa and 108C to 800 kPa in a piston–cylinder
device. Determine the work produced and heat transferred
during this compression process, in kJ/kg.
Argon
120 kPa
10°C
Pv n = constant
FIGURE P4–66
Q
202
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
4–67 An insulated piston–cylinder device contains 100 L of
air at 400 kPa and 258C. A paddle wheel within the cylinder
is rotated until 15 kJ of work is done on the air while the
pressure is held constant. Determine the final temperature of
the air. Neglect the energy stored in the paddle wheel.
4–68 A spring-loaded piston-cylinder device contains 1 kg
of carbon dioxide. This system is heated from 100 kPa and
258C to 1000 kPa and 3008C. Determine the total heat transfer to and work produced by this system.
FIGURE P4–71
Q
CO2
FIGURE P4–68
4–69E A piston–cylinder device contains 25 ft3 of nitrogen at 40 psia and 7008F. Nitrogen is now allowed to cool
at constant pressure until the temperature drops to 2008F.
Using specific heats at the average temperature, determine
the amount of heat loss.
4–70 Air is contained in a variable-load piston-cylinder
device equipped with a paddle wheel. Initially, air is at
400 kPa and 178C. The paddle wheel is now turned by an
external electric motor until 75 kJ/kg of work has been transferred to air. During this process, heat is transferred to maintain a constant air temperature while allowing the gas volume
to triple. Calculate the required amount of heat transfer, in
kJ/kg. Answer: 16.4 kJ/kg
4–72 A piston–cylinder device contains 2.2 kg of nitrogen
initially at 100 kPa and 258C. The nitrogen is now compressed slowly in a polytropic process during which PV 1.3 5
constant until the volume is reduced by one-half. Determine
the work done and the heat transfer for this process.
Reconsider Prob. 4–72. Using EES (or other)
4–73
software, plot the process described in the problem on a P-V diagram, and investigate the effect of the polytropic exponent n on the boundary work and heat transfer.
Let the polytropic exponent vary from 1.0 to 1.4. Plot the
boundary work and the heat transfer versus the polytropic
exponent, and discuss the results.
4–74E A piston–cylinder device contains 3 ft3 of air at
60 psia and 1508F. Heat is transferred to the air in the amount
of 40 Btu as the air expands isothermally. Determine the
amount of boundary work done during this process.
A piston–cylinder device, with a set of stops on
4–75
the top, initially contains 3 kg of air at 200 kPa
and 278C. Heat is now transferred to the air, and the piston
rises until it hits the stops, at which point the volume is twice
the initial volume. More heat is transferred until the pressure
inside the cylinder also doubles. Determine the work done
and the amount of heat transfer for this process. Also, show
the process on a P-v diagram.
4–76 Air is contained in a cylinder device fitted with a
piston-cylinder. The piston initially rests on a set of stops, and
a pressure of 200 kPa is required to move the piston. Initially,
the air is at 100 kPa and 238C and occupies a volume of
0.25 m3. Determine the amount of heat transferred to the air, in
kJ, while increasing the temperature to 700 K. Assume air has
constant specific heats evaluated at 300 K. Answer: 94.5 kJ
FIGURE P4–70
4–71 A mass of 15 kg of air in a piston–cylinder device is
heated from 25 to 778C by passing current through a resistance heater inside the cylinder. The pressure inside the cylinder is held constant at 300 kPa during the process, and a heat
loss of 60 kJ occurs. Determine the electric energy supplied,
in kWh. Answer: 0.235 kWh
FIGURE P4–76
203
CHAPTER 4
4–77 Air is contained in a piston-cylinder device at 600 kPa
and 9278C, and occupies a volume of 0.8 m3. The air undergoes and isothermal (constant temperature) process until the
pressure in reduced to 300 kPa. The piston is now fixed in
place and not allowed to move while a heat transfer process
takes place until the air reaches 278C.
(a) Sketch the system showing the energies crossing the
boundary and the P-V diagram for the combined processes.
(b) For the combined processes determine the net amount of
heat transfer, in kJ, and its direction.
Assume air has constant specific heats evaluated at 300 K.
4–78 A piston–cylinder device contains 4 kg of argon at
250 kPa and 358C. During a quasi-equilibrium, isothermal
expansion process, 15 kJ of boundary work is done by the
system, and 3 kJ of paddle-wheel work is done on the system. Determine the heat transfer for this process.
4–82 Stainless steel ball bearings (r 5 8085 kg/m3 and
cp 5 0.480 kJ/kg·8C) having a diameter of 1.2 cm are to be
quenched in water at a rate of 800 per minute. The balls leave
the oven at a uniform temperature of 9008C and are exposed
to air at 258C for a while before they are dropped into the
water. If the temperature of the balls drops to 8508C prior to
quenching, determine the rate of heat transfer from the balls
to the air.
4–83E ln a production facility, 1.6-in-thick 2-ft 3 2-ft square
brass plates (r 5 532.5 lbm/ft3 and cp 5 0.091 Btu/lbm·8F)
that are initially at a uniform temperature of 758F are heated
by passing them through an oven at 15008F at a rate of 300
per minute. If the plates remain in the oven until their average temperature rises to 9008F, determine the rate of heat
transfer to the plates in the furnace.
Furnace, 1500°F
Closed-System Energy Analysis: Solids and Liquids
4–79E The state of liquid water is changed from 50 psia
and 508F to 2000 psia and 1008F. Determine the change in
the internal energy and enthalpy of water on the basis of the
(a) compressed liquid tables, (b) incompressible substance
approximation and property tables, and (c) specific-heat model.
4–80E During a picnic on a hot summer day, all the cold
drinks disappeared quickly, and the only available drinks
were those at the ambient temperature of 858F. In an effort to
cool a 12-fluid-oz drink in a can, a person grabs the can and
starts shaking it in the iced water of the chest at 328F. Using
the properties of water for the drink, determine the mass of
ice that will melt by the time the canned drink cools to 378F.
4–81 Consider a 1000-W iron whose base plate is made of
0.5-cm-thick aluminum alloy 2024-T6 (r 5 2770 kg/m3 and
cp 5 875 J/kg·8C). The base plate has a surface area of 0.03 m2.
Initially, the iron is in thermal equilibrium with the ambient air
at 228C. Assuming 90 percent of the heat generated in the resistance wires is transferred to the plate, determine the minimum
time needed for the plate temperature to reach 2008C.
1.6 in
Brass plate, 75°F
FIGURE P4–83E
4–84 Long cylindrical steel rods (r 5 7833 kg/m3 and
cp 5 0.465 kJ/kg·8C) of 8-cm diameter are heat-treated by
drawing them at a velocity of 2 m/min through an oven maintained at 9008C. If the rods enter the oven at 308C and leave
at a mean temperature of 7008C, determine the rate of heat
transfer to the rods in the oven.
4–85 An electronic device dissipating 25 W has a mass of
20 g and a specific heat of 850 J/kg·8C. The device is lightly
used, and it is on for 5 min and then off for several hours,
during which it cools to the ambient temperature of 258C.
Determine the highest possible temperature of the device
at the end of the 5-min operating period. What would your
answer be if the device were attached to a 0.5-kg aluminum
heat sink? Assume the device and the heat sink to be nearly
isothermal.
4–86
Reconsider Prob. 4–85. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the mass of the
heat sink on the maximum device temperature. Let the mass of
heat sink vary from 0 to 1 kg. Plot the maximum temperature
against the mass of heat sink, and discuss the results.
FIGURE P4–81
4–87 If you ever slapped someone or got slapped yourself,
you probably remember the burning sensation. Imagine you
had the unfortunate occasion of being slapped by an angry
204
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
person, which caused the temperature of the affected area of
your face to rise by 2.48C (ouch!). Assuming the slapping
hand has a mass of 0.9 kg and about 0.150 kg of the tissue on
the face and the hand is affected by the incident, estimate the
velocity of the hand just before impact. Take the specific heat
of the tissue to be 3.8 kJ/kg·K.
4–88 In a manufacturing facility, 5-cm-diameter brass balls
(r 5 8522 kg/m3 and cp 5 0.385 kJ/kg · 8C) initially at 1208C
are quenched in a water bath at 508C for a period of 2 min
at a rate of 100 balls per minute. If the temperature of the
balls after quenching is 748C, determine the rate at which
heat needs to be removed from the water in order to keep its
temperature constant at 508C.
120°C
Brass balls
50°C
Water bath
FIGURE P4–88
4–89
Repeat Prob. 4–88 for aluminum balls.
Special Topic: Biological Systems
4–90C Is the metabolizable energy content of a food the
same as the energy released when it is burned in a bomb calorimeter? If not, how does it differ?
4–91C Is the number of prospective occupants an important
consideration in the design of heating and cooling systems of
classrooms? Explain.
4–92C What do you think of a diet program that allows for
generous amounts of bread and rice provided that no butter or
margarine is added?
4–93 The average specific heat of the human body is
3.6 kJ/kg · 8C. If the body temperature of an 80-kg man rises
from 378C to 398C during strenuous exercise, determine the
increase in the thermal energy of the body as a result of this
rise in body temperature.
4–94 Consider two identical 80-kg men who are eating
identical meals and doing identical things except that one of
them jogs for 30 min every day while the other watches TV.
Determine the weight difference between the two in a month.
Answer: 1.04 kg
4–95 A 68-kg woman is planning to bicycle for an hour.
If she is to meet her entire energy needs while bicycling by
eating 30-g chocolate candy bars, determine how many candy
bars she needs to take with her.
4–96 A 90-kg man gives in to temptation and eats an entire
1-L box of ice cream. How long does this man need to jog
to burn off the calories he consumed from the ice cream?
Answer: 1.54 h
4–97 A 60-kg man used to have an apple every day after
dinner without losing or gaining any weight. He now eats a
200-ml serving of ice cream instead of an apple and walks
20 min every day. On this new diet, how much weight will he
lose or gain per month? Answer: 0.087-kg gain
4–98 Consider a man who has 20 kg of body fat when he
goes on a hunger strike. Determine how long he can survive
on his body fat alone.
4–99 Consider two identical 50-kg women, Candy and
Wendy, who are doing identical things and eating identical
food except that Candy eats her baked potato with four teaspoons of butter while Wendy eats hers plain every evening.
Determine the difference in the weights of Candy and Wendy
after one year. Answer: 6.5 kg
4–100E A woman who used to drink about one liter of regular cola every day switches to diet cola (zero calorie) and
starts eating two slices of apple pie every day. Is she now
consuming fewer or more calories?
4–101E A 190-pound man and a 130-pound woman went to
Burger King for lunch. The man had a BK Big Fish sandwich
(720 Cal), medium french fries (400 Cal), and a large Coke
(225 Cal). The woman had a basic hamburger (330 Cal),
medium french fries (400 Cal), and a diet Coke (0 Cal).
After lunch, they start shoveling snow and burn calories at a
rate of 420 Cal/h for the woman and 610 Cal/h for the man.
Determine how long each one of them needs to shovel snow
to burn off the lunch calories.
4–102 A person eats a McDonald’s Big Mac sandwich
(530 Cal), a second person eats a Burger King Whopper
sandwich (640 Cal), and a third person eats 50 olives with
regular french fries (350 Cal) for lunch. Determine who consumes the most calories. An olive contains about 5 Calories.
4–103 A 75-kg man decides to lose 5 kg without cutting
down his intake of 4000 Calories a day. Instead, he starts fast
swimming, fast dancing, jogging, and biking each for an hour
every day. He sleeps or relaxes the rest of the day. Determine
how long it will take him to lose 5 kg.
4–104E The range of healthy weight for adults is usually
expressed in terms of the body mass index (BMI), defined, in
SI units, as
BMI 5
W (kg)
H 2 (m2)
where W is the weight (actually, the mass) of the person in
kg and H is the height in m, and the range of healthy weight
is 19 # BMI $ 25. Convert the previous formula to English units such that the weight is in pounds and the height in
inches. Also, calculate your own BMI, and if it is not in the
healthy range, determine how many pounds (or kg) you need
to gain or lose to be fit.
205
CHAPTER 4
4–105 The body mass index (BMI) of a 1.6-m tall woman who
normally has 3 large slices of cheese pizza and a 400-ml Coke
for lunch is 30. She now decides to change her lunch to 2 slices
of pizza and a 200-ml Coke. Assuming that the deficit in the calorie intake is made up by burning body fat, determine how long
it will take for the BMI of this person to drop to 20. Use the data
in the text for calories and take the metabolizable energy content
of 1 kg of body fat to be 33,100 kJ. Answer: 463 days
4–106E Alcohol provides 7 Calories per gram, but it provides no essential nutrients. A 1.5 ounce serving of 80-proof
liquor contains 100 Calories in alcohol alone. Sweet wines and
beer provide additional calories since they also contain carbohydrates. About 75 percent of American adults drink some sort
of alcoholic beverage, which adds an average of 210 Calories a
day to their diet. Determine how many pounds less an average
American adult will weigh per year if he or she quit drinking
alcoholic beverages and started drinking diet soda.
Review Problems
4–107 The temperature of air changes from 0 to 108C while
its velocity changes from zero to a final velocity, and its elevation changes from zero to a final elevation. At which values of final air velocity and final elevation will the internal,
kinetic, and potential energy changes be equal?
4–112 A well-insulated rigid vessel contains 3 kg of saturated liquid water at 408C. The vessel also contains an electrical resistor that draws 10 amperes when 50 volts are applied.
Determine the final temperature in the vessel after the resistor
has been operating for 30 minutes. Answer: 119°C
4–113 In order to cool 1 ton of water at 208C in an insulated tank, a person pours 80 kg of ice at 258C into the
water. Determine the final equilibrium temperature in the
tank. The melting temperature and the heat of fusion of ice
at atmospheric pressure are 08C and 333.7 kJ/kg, respectively. Answer: 12.4°C
4–114 A mass of 3 kg of saturated liquid–vapor mixture
of water is contained in a piston–cylinder device at 160 kPa.
Initially, 1 kg of the water is in the liquid phase and the rest
is in the vapor phase. Heat is now transferred to the water,
and the piston, which is resting on a set of stops, starts moving when the pressure inside reaches 500 kPa. Heat transfer continues until the total volume increases by 20 percent.
Determine (a) the initial and final temperatures, (b) the
mass of liquid water when the piston first starts moving, and
(c) the work done during this process. Also, show the process on a P-v diagram.
Answers: 120 m/s, 732 m
4–108 Consider a piston–cylinder device that contains
0.5 kg air. Now, heat is transferred to the air at constant pressure and the air temperature increases by 58C. Determine the
expansion work done during this process.
4–109E Air in the amount of 2 lbm is contained in a wellinsulated, rigid vessel equipped with a stirring paddle wheel.
The initial state of this air is 30 psia and 608F. How much
work, in Btu, must be transferred to the air with the paddle
wheel to raise the air pressure to 40 psia? Also, what is the
final temperature of air?
Air
2 lbm
30 psia
60°F
Wsh
FIGURE P4–114
4–115 A mass of 12 kg of saturated refrigerant-134a vapor
is contained in a piston–cylinder device at 240 kPa. Now
300 kJ of heat is transferred to the refrigerant at constant pressure while a 110-V source supplies current to a resistor within
the cylinder for 6 min. Determine the current supplied if the
final temperature is 708C. Also, show the process on a T-v
diagram with respect to the saturation lines. Answer: 12.8 A
FIGURE P4–109E
4–110 Air is expanded in a polytropic process with n 5
1.2 from 1 MPa and 4008C to 110 kPa in a piston-cylinder
device. Determine the final temperature of the air.
4–111 Nitrogen at 100 kPa and 258C in a rigid vessel is
heated until its pressure is 300 kPa. Calculate the work done
and the heat transferred during this process, in kJ/kg.
FIGURE P4–115
206
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
4–116 Saturated water vapor at 2008C is condensed to a
saturated liquid at 508C in a spring-loaded piston-cylinder
device. Determine the heat transfer for this process, in kJ/kg.
the amount of ice added. The melting temperature and the
heat of fusion of ice at atmospheric pressure are 08C and
333.7 kJ/kg, respectively.
4–117 A piston–cylinder device contains 0.8 kg of an ideal
gas. Now, the gas is cooled at constant pressure until its temperature decreases by 108C. If 16.6 kJ of compression work
is done during this process, determine the gas constant and
the molar mass of the gas. Also, determine the constantvolume and constant-pressure specific heats of the gas if its
specific heat ratio is 1.667.
4–120 Nitrogen gas is expanded in a polytropic process
with n 5 1.25 from 2 MPa and 1200 K to 200 kPa in a
piston–cylinder device. How much work is produced and heat
is transferred during this expansion process, in kJ/kg?
Q
4–121 A passive solar house that is losing heat to the outdoors at an average rate of 50,000 kJ/h is maintained at 228C
at all times during a winter night for 10 h. The house is to be
heated by 50 glass containers each containing 20 L of water that
is heated to 808C during the day by absorbing solar energy. A
thermostat-controlled 15-kW back-up electric resistance heater
turns on whenever necessary to keep the house at 228C. (a) How
long did the electric heating system run that night? (b) How
long would the electric heater run that night if the house incorporated no solar heating? Answers: (a) 4.77 h, (b) 9.26 h
Ideal gas
0.8 kg
ΔT = 10°C
FIGURE P4–117
22°C
4–118 A piston–cylinder device contains helium gas initially at 100 kPa, 108C, and 0.2 m3. The helium is now compressed in a polytropic process (PV n 5 constant) to 700 kPa
and 2908C. Determine the heat loss or gain during this process. Answer: 6.51 kJ loss
Water
80°C
Pump
FIGURE P4–121
He
PV n = constant
4–122 One ton (1000 kg) of liquid water at 508C is brought
into a well-insulated and well-sealed 4-m 3 5-m 3 6-m
room initially at 158C and 95 kPa. Assuming constant
specific heats for both air and water at room temperature,
determine the final equilibrium temperature in the room.
Answer: 49.2°C
FIGURE P4–118
4–119 An insulated piston–cylinder device initially
contains 0.01 m3 of saturated liquid–vapor mixture with
a quality of 0.2 at 1208C. Now some ice at 08C is added
to the cylinder. If the cylinder contains saturated liquid at
1208C when thermal equilibrium is established, determine
4–123 Water is boiled at sea level in a coffee maker
equipped with an immersion-type electric heating element.
The coffee maker contains 1 L of water when full. Once
boiling starts, it is observed that half of the water in the coffee maker evaporates in 25 min. Determine the power rating of the electric heating element immersed in water. Also,
determine how long it will take for this heater to raise the
temperature of 1 L of cold water from 188C to the boiling
temperature.
207
CHAPTER 4
1 atm
Coffee
maker
1L
down. Taking the average specific heat of the human body
to be 3.6 kJ/kg·8C, determine the drop in the average body
temperature of this person under the influence of this cold
water.
4–127 An insulated rigid tank initially contains 1.4-kg saturated liquid water at 2008C and air. At this state, 25 percent
of the volume is occupied by liquid water and the rest by air.
Now an electric resistor placed in the tank is turned on, and the
tank is observed to contain saturated water vapor after 20 min.
Determine (a) the volume of the tank, (b) the final temperature, and (c) the electric power rating of the resistor. Neglect
energy added to the air. Answers: (a) 0.00648 m3, (b) 3718C,
(c) 1.58 kW
FIGURE P4–123
4–124 A 3-m 3 4-m 3 5-m room is to be heated by one ton
(1000 kg) of liquid water contained in a tank that is placed in
the room. The room is losing heat to the outside at an average rate of 6000 kJ/h. The room is initially at 208C and 100
kPa and is maintained at an average temperature of 208C at
all times. If the hot water is to meet the heating requirements
of this room for a 24-h period, determine the minimum temperature of the water when it is first brought into the room.
Assume constant specific heats for both air and water at room
temperature.
4–125 The energy content of a certain food is to be determined in a bomb calorimeter that contains 3 kg of water
by burning a 2-g sample of it in the presence of 100 g of
air in the reaction chamber. If the water temperature rises
by 3.28C when equilibrium is established, determine the
energy content of the food, in kJ/kg, by neglecting the thermal energy stored in the reaction chamber and the energy
supplied by the mixer. What is a rough estimate of the error
involved in neglecting the thermal energy stored in the reaction chamber? Answer: 20,060 kJ/kg
Air
We
Water
1.4 kg, 200°C
FIGURE P4–127
4–128 A 0.3-L glass of water at 208C is to be cooled with
ice to 58C. Determine how much ice needs to be added to
the water, in grams, if the ice is at (a) 08C and (b) 2208C.
Also determine how much water would be needed if the
cooling is to be done with cold water at 08C. The melting
temperature and the heat of fusion of ice at atmospheric
pressure are 08C and 333.7 kJ/kg, respectively, and the density of water is 1 kg/L.
4–129
Reaction
chamber
Food
ΔT = 3.2°C
FIGURE P4–125
4–126 A 68-kg man whose average body temperature is
398C drinks 1 L of cold water at 38C in an effort to cool
Reconsider Prob. 4–128. Using EES (or
other) software, investigate the effect of the
initial temperature of the ice on the final mass required. Let
the ice temperature vary from 226 to 08C. Plot the mass of
ice against the initial temperature of ice, and discuss the
results.
4–130 A well-insulated 3-m 3 4-m 3 6-m room initially at
78C is heated by the radiator of a steam heating system. The
radiator has a volume of 15 L and is filled with superheated
vapor at 200 kPa and 2008C. At this moment both the inlet
and the exit valves to the radiator are closed. A 120-W fan
is used to distribute the air in the room. The pressure of the
steam is observed to drop to 100 kPa after 45 min as a result
of heat transfer to the room. Assuming constant specific heats
for air at room temperature, determine the average temperature of air in 45 min. Assume the air pressure in the room
remains constant at 100 kPa.
208
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
N2
1 m3
500 kPa
120°C
7°C
3m×4m×6m
He
1 m3
500 kPa
40°C
Fan
Steam
radiator
FIGURE P4–133
4–134 Repeat Prob. 4–133 by assuming the piston is made
of 8 kg of copper initially at the average temperature of the
two gases on both sides. Answer: 83.7°C
4–135
FIGURE P4–130
4–131 Two rigid tanks are connected by a valve. Tank A
contains 0.2 m3 of water at 400 kPa and 80 percent quality.
Tank B contains 0.5 m3 of water at 200 kPa and 2508C.
The valve is now opened, and the two tanks eventually
come to the same state. Determine the pressure and the
amount of heat transfer when the system reaches thermal
equilibrium with the surroundings at 258C. Answers: 3.17
kPa, 2170 kJ
Reconsider Prob. 4–134. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the mass of
the copper piston on the final equilibrium temperature. Let
the mass of piston vary from 1 to 10 kg. Plot the final temperature against the mass of piston, and discuss the results.
4–136 An insulated piston-cylinder device initially
contains 1.8-kg saturated liquid water at 1208C. Now an
electric resistor placed in the tank is turned on for 10 min
until the volume quadruples. Determine (a) the volume
of the tank, (b) the final temperature, and (c) the electrical power rating of the resistor. Answers: (a) 0.00763 m3,
(b) 1208C, (c) 0.0236 kW
H 2O
H2 O
400 kPa
200 kPa
Q
A
B
We
Water
1.8 kg
120°C
sat. liquid
FIGURE P4–131
FIGURE P4–136
4–132
Reconsider Prob. 4–131. Using EES (or
other) software, investigate the effect of the
environment temperature on the final pressure and the heat
transfer. Let the environment temperature vary from 0 to
508C. Plot the final results against the environment temperature, and discuss the results.
4–133 Consider a well-insulated horizontal rigid cylinder
that is divided into two compartments by a piston that is free
to move but does not allow either gas to leak into the other
side. Initially, one side of the piston contains 1 m3 of N2 gas
at 500 kPa and 1208C while the other side contains 1 m3 of
He gas at 500 kPa and 408C. Now thermal equilibrium is
established in the cylinder as a result of heat transfer through
the piston. Using constant specific heats at room temperature,
determine the final equilibrium temperature in the cylinder.
What would your answer be if the piston were not free to
move?
4–137 A vertical 12-cm diameter piston–cylinder device
contains an ideal gas at the ambient conditons of 1 bar and
248C. Initially, the inner face of the piston is 20 cm from the
base of the cylinder. Now an external shaft connected to the
piston exerts a force corresponding to a boundary work input
of 0.1 kJ. The temperature of the gas remains constant during the process. Determine (a) the amount of heat transfer,
(b) the final pressure in the cylinder, and (c) the distance that
the piston is displaced.
4–138 A vertical 12-cm diameter piston–cylinder device
contains an ideal gas at the ambient conditons of 1 bar and
248C. Initially, the inner face of the piston is 20 cm from the
base of the cylinder. Now an external shaft connected to the
piston exerts a force corresponding to a boundary work input
of 0.1 kJ. The temperature of the gas remains constant during the process. Determine (a) the amount of heat transfer,
209
CHAPTER 4
(b) the final pressure in the cylinder, and (c) the distance that
the piston is displaced.
arranged to execute a polytropic process with n 5 1.3. Use
the compressibility factor to determine the final temperature.
4–139 A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.35-kg
steam at 3.5 MPa, superheated by 7.48C. Now the steam loses
heat to the surroundings and the piston moves down, hitting
a set of stops at which point the cylinder contains saturated
liquid water. The cooling continues until the cylinder contains water at 2008C. Determine (a) the final pressure and the
quality (if mixture), (b) the boundary work, (c) the amount of
heat transfer when the piston first hits the stops, (d) and the
total heat transfer.
4–142 In solar-heated buildings, energy is often stored as
sensible heat in rocks, concrete, or water during the day for
use at night. To minimize the storage space, it is desirable
to use a material that can store a large amount of heat while
experiencing a small temperature change. A large amount of
heat can be stored essentially at constant temperature during
a phase change process, and thus materials that change phase
at about room temperature such as glaubers salt (sodium sulfate decahydrate), which has a melting point of 328C and a
heat of fusion of 329 kJ/L, are very suitable for this purpose.
Determine how much heat can be stored in a 5-m3 storage
space using (a) glaubers salt undergoing a phase change,
(b) granite rocks with a heat capacity of 2.32 kJ/kg · 8C and a
temperature change of 208C, and (c) water with a heat capacity of 4.00 kJ/k · 8C and a temperature change of 208C.
FIGURE P4–139
4–140 An insulated rigid tank is divided into two compartments of different volumes. Initially, each compartment contains the same ideal gas at identical pressure but at different
temperatures and masses. The wall separating the two compartments is removed and the two gases are allowed to mix.
Assuming constant specific heats, find the simplest expression for the mixture temperature written in the form
m1 m2
T3 5 f a , , T1, T2 b
m3 m3
4–143 The early steam engines were driven by the atmospheric pressure acting on the piston fitted into a cylinder
filled with saturated steam. A vacuum was created in the cylinder by cooling the cylinder externally with cold water, and
thus condensing the steam.
Consider a piston–cylinder device with a piston surface
area of 0.1 m2 initially filled with 0.05 m3 of saturated water
vapor at the atmospheric pressure of 100 kPa. Now cold water
is poured outside the cylinder, and the steam inside starts
condensing as a result of heat transfer to the cooling water outside. If the piston is stuck at its initial position, determine the
friction force acting on the piston and the amount of heat transfer when the temperature inside the cylinder drops to 308C.
Cold
water
where m3 and T3 are the mass and temperature of the final
mixture, respectively.
0.05 m 3
100 kPa
Steam
Side 1
Mass = m1
Temperature = T1
Side 2
Mass = m2
Temperature = T2
FIGURE P4–143
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Problems
FIGURE P4–140
4–141 One kilogram of carbon dioxide is compressed from
0.5 MPa and 2008C to 3 MPa in a piston-cylinder device
4–144 The specific heat of a material is given in a strange
unit to be c 5 3.60 kJ/kg·8F. The specific heat of this material
in the SI units of kJ/kg·8C is
(a) 2.00 kJ/kg·8C (b) 3.20 kJ/kg·8C (c) 3.60 kJ/kg·8C
(d) 4.80 kJ/kg·8C (e) 6.48 kJ/kg·8C
210
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
4–145 A 3-m3 rigid tank contains nitrogen gas at 500 kPa
and 300 K. Now heat is transferred to the nitrogen in the tank
and the pressure of nitrogen rises to 800 kPa. The work done
during this process is
(a) 500 kJ
(b) 1500 kJ
(c) 0 kJ
(d) 900 kJ
(e) 2400 kJ
4–152 A glass of water with a mass of 0.45 kg at 208C is to
be cooled to 08C by dropping ice cubes at 08C into it. The latent
heat of fusion of ice is 334 kJ/kg, and the specific heat of water
is 4.18 kJ/kg·8C. The amount of ice that needs to be added is
(a) 56 g
(b) 113 g
(c) 124 g
(d) 224 g
(e) 450 g
4–146 A 0.5-m3 rigid tank contains nitrogen gas at 600 kPa
and 300 K. Now the gas is compressed isothermally to a volume of 0.1 m3. The work done on the gas during this compression process is
(a) 720 kJ
(b) 483 kJ
(c) 240 kJ
(d) 175 kJ
(e) 143 kJ
4–153 A 2-kW electric resistance heater submerged in 5-kg
water is turned on and kept on for 10 min. During the process, 300 kJ of heat is lost from the water. The temperature
rise of water is
(a) 0.48C
(b) 43.18C
(c) 57.48C
(d) 71.88C
(e) 1808C
4–147 A well-sealed room contains 60 kg of air at 200 kPa
and 258C. Now solar energy enters the room at an average
rate of 0.8 kJ/s while a 120-W fan is turned on to circulate the air in the room. If heat transfer through the walls
is negligible, the air temperature in the room in 30 min
will be
(a) 25.68C
(b) 49.88C
(c) 53.48C
(d) 52.58C
(e) 63.48C
4–154 1.5 kg of liquid water initially at 128C is to be heated at
958C in a teapot equipped with a 800-W electric heating element
inside. The specific heat of water can be taken to be 4.18 kJ/kg·8C,
and the heat loss from the water during heating can be neglected.
The time it takes to heat water to the desired temperature is
(a) 5.9 min
(b) 7.3 min
(c) 10.8 min
(d) 14.0 min
(e) 17.0 min
4–148 A 2-kW baseboard electric resistance heater in a
vacant room is turned on and kept on for 15 min. The mass
of the air in the room is 75 kg, and the room is tightly sealed
so that no air can leak in or out. The temperature rise of air at
the end of 15 min is
(a) 8.58C
(b) 12.48C
(c) 24.08C
(d) 33.48C
(e) 54.88C
4–149 A room contains 75 kg of air at 100 kPa and 158C.
The room has a 250-W refrigerator (the refrigerator consumes 250 W of electricity when running), a 120-W TV, a
1.8-kW electric resistance heater, and a 50-W fan. During a
cold winter day, it is observed that the refrigerator, the TV,
the fan, and the electric resistance heater are running continuously but the air temperature in the room remains constant.
The rate of heat loss from the room that day is
(a) 5832 kJ/h
(b) 6192 kJ/h
(c) 7560 kJ/h
(d) 7632 kJ/h
(e) 7992 kJ/h
4–150 A piston–cylinder device contains 5 kg of air at
400 kPa and 308C. During a quasi-equilibium isothermal
expansion process, 15 kJ of boundary work is done by the
system, and 3 kJ of paddle-wheel work is done on the system.
The heat transfer during this process is
(a) 12 kJ
(b) 18 kJ
(c) 2.4 kJ
(d) 3.5 kJ
(e) 60 kJ
4–151 A 6-pack canned drink is to be cooled from 188C to
38C. The mass of each canned drink is 0.355 kg. The drinks
can be treated as water, and the energy stored in the aluminum can itself is negligible. The amount of heat transfer from
the 6 canned drinks is
(a) 22 kJ
(b) 32 kJ
(c) 134 kJ
(d) 187 kJ
(e) 223 kJ
4–155 An ordinary egg with a mass of 0.1 kg and a specific
heat of 3.32 kJ/kg·8C is dropped into boiling water at 958C.
If the initial temperature of the egg is 58C, the maximum
amount of heat transfer to the egg is
(a) 12 kJ
(b) 30 kJ
(c) 24 kJ
(d) 18 kJ
(e) infinity
4–156 An apple with an average mass of 0.18 kg and average specific heat of 3.65 kJ/kg·8C is cooled from 228C to
58C. The amount of heat transferred from the apple is
(a) 0.85 kJ
(b) 62.1 kJ
(c) 17.7 kJ
(d) 11.2 kJ
(e) 7.1 kJ
4–157 The specific heat at constant volume for an ideal gas
is given by cv 5 0.7 1 (2.7 3 1024)T (kJ/kg·K) where T is
in kelvin. The change in the internal energy for this ideal gas
undergoing a process in which the temperature changes from
27 to 1278C is most nearly
(a) 70 kJ/kg
(b) 72.1 kJ/kg
(c) 79.5 kJ/kg
(d) 82.1 kJ/kg
(e) 84.0 kJ/kg
4–158 An ideal gas has a gas constant R 5 0.3 kJ/kg·K
and a constant-volume specific heat cv 5 0.7 kJ/kg·K. If the
gas has a temperature change of 1008C, choose the correct
answer for each of the following:
1. The change in enthalpy is, in kJ/kg
(a) 30
(b) 70
(c) 100
(d) insufficient information to determine
2. The change in internal energy is, in kJ/kg
(a) 30
(b) 70
(c) 100
(d) insufficient information to determine
3. The work done is, in kJ/kg
(a) 30
(b) 70
(c) 100
(d) insufficient information to determine
211
CHAPTER 4
F
4. The heat transfer is, in kJ/kg
(a) 30
(b) 70
(c) 100
(d) insufficient information to determine
5. The change in the pressure-volume product is, in kJ/kg
(a) 30
(b) 70
(c) 100
(d) insufficient information to determine
4–159 An ideal gas undergoes a constant temperature (isothermal) process in a closed system. The heat transfer and
work are, respectively
(b) cv DT, 0
(a) 0, –cv DT
(d) R ln(T2/T1), R ln(T2/T1)
(c) cp DT, RDT
4–160 An ideal gas undergoes a constant volume (isochoric) process in a closed system. The heat transfer and
work are, respectively
(b) cv DT, 0
(a) 0, –cv DT
(d) R ln(T2/T1), R ln(T2/T1)
(c) cp DT, RDT
4–161 An ideal gas undergoes a constant pressure (isobaric) process in a closed system. The heat transfer and work
are, respectively
(b) cv DT, 0
(a) 0, –cv DT
(d) R ln(T2/T1), R ln(T2/T1)
(c) cp DT, RDT
Design and Essay Problems
4–162 Find out how the specific heats of gases, liquids, and
solids are determined in national laboratories. Describe the
experimental apparatus and the procedures used.
4–163 Someone has suggested that the device shown
in Fig. P4–163 be used to move the maximum force F
against the spring, which has a spring constant of k.
This is accomplished by changing the temperature of the
liquid–vapor mixture in the container. You are to design
such a device to close sun-blocking window shutters that
require a maximum force of 0.5 lbf. The piston must
move 6 inches to close these shutters completely. You
elect to use R-134a as the working fluid and arrange the
liquid–vapor mixture container such that the temperature
changes from 708F when shaded from the sun to 1008F
when exposed to the full sun. Select the sizes of the various components in this system to do this task. Also select
the necessary spring constant and the amount of R-134a
to be used.
Vapor
D
Liquid
FIGURE P4–163
4–164 You are asked to design a heating system for a
swimming pool that is 2 m deep, 25 m long, and 25 m wide.
Your client desires that the heating system be large enough to
raise the water temperature from 20 to 308C in 3 h. The rate
of heat loss from the water to the air at the outdoor design
conditions is determined to be 960 W/m2, and the heater must
also be able to maintain the pool at 308C at those conditions.
Heat losses to the ground are expected to be small and can
be disregarded. The heater considered is a natural gas furnace whose efficiency is 80 percent. What heater size (in kW
input) would you recommend to your client?
4–165 It is claimed that fruits and vegetables are cooled by
68C for each percentage point of weight loss as moisture during vacuum cooling. Using calculations, demonstrate if this
claim is reasonable.
4–166 Using a thermometer, measure the boiling temperature of water and calculate the corresponding saturation pressure. From this information, estimate the altitude of your
town and compare it with the actual altitude value.
4–167 Design an experiment complete with instrumentation to determine the specific heats of a gas using a resistance
heater. Discuss how the experiment will be conducted, what
measurements need to be taken, and how the specific heats
will be determined. What are the sources of error in your
system? How can you minimize the experimental error?
This page intentionally left blank
CHAPTER
5
MASS AND ENERGY
A N A LY S I S O F C O N T R O L
VOLUMES
I
n Chap. 4, we applied the general energy balance relation expressed as
Ein 2 Eout 5 DEsystem to closed systems. In this chapter, we extend the
energy analysis to systems that involve mass flow across their boundaries
i.e., control volumes, with particular emphasis to steady-flow systems.
We start this chapter with the development of the general conservation
of mass relation for control volumes, and we continue with a discussion of
flow work and the energy of fluid streams. We then apply the energy balance to systems that involve steady-flow processes and analyze the common
steady-flow devices such as nozzles, diffusers, compressors, turbines, throttling devices, mixing chambers, and heat exchangers. Finally, we apply the
energy balance to general unsteady-flow processes such as the charging and
discharging of vessels.
OBJECTIVES
The objectives of Chapter 5 are to:
■
Develop the conservation of
mass principle.
■
Apply the conservation of mass
principle to various systems
including steady- and unsteadyflow control volumes.
■
■
■
■
Apply the first law of thermodynamics as the statement of the
conservation of energy principle
to control volumes.
Identify the energy carried by a
fluid stream crossing a control
surface as the sum of internal
energy, flow work, kinetic energy,
and potential energy of the fluid
and to relate the combination of
the internal energy and the flow
work to the property enthalpy.
Solve energy balance problems
for common steady-flow devices
such as nozzles, compressors,
turbines, throttling valves,
mixers, heaters, and heat
exchangers.
Apply the energy balance to
general unsteady-flow processes
with particular emphasis on
the uniform-flow process as the
model for commonly encountered charging and discharging
processes.
213
214
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
5–1
2 kg
H2
16 kg
O2
18 kg
H2O
FIGURE 5–1
Mass is conserved even during
chemical reactions.
■
CONSERVATION OF MASS
The conservation of mass principle is one of the most fundamental principles in nature. We are all familiar with this principle, and it is not difficult
to understand. A person does not have to be a rocket scientist to figure
out how much vinegar-and-oil dressing will be obtained by mixing 100 g
of oil with 25 g of vinegar. Even chemical equations are balanced on the
basis of the conservation of mass principle. When 16 kg of oxygen reacts
with 2 kg of hydrogen, 18 kg of water is formed (Fig. 5–1). In an electrolysis process, the water separates back to 2 kg of hydrogen and 16 kg
of oxygen.
Technically, mass is not exactly conserved. It turns out that mass m and
energy E can be converted to each other according to the well-known formula proposed by Albert Einstein (1879–1955):
E 5 mc2
(5–1)
where c is the speed of light in a vacuum, which is c 5 2.9979 3 108 m/s.
This equation suggests that there is equivalence between mass and energy.
All physical and chemical systems exhibit energy interactions with their surroundings, but the amount of energy involved is equivalent to an extremely
small mass compared to the system’s total mass. For example, when 1 kg
of liquid water is formed from oxygen and hydrogen at normal atmospheric
conditions, the amount of energy released is 15.8 MJ, which corresponds
to a mass of only 1.76 3 10210 kg. However, in nuclear reactions, the mass
equivalence of the amount of energy interacted is a significant fraction of
the total mass involved. Therefore, in most engineering analyses, we consider both mass and energy as conserved quantities.
For closed systems, the conservation of mass principle is implicitly used
by requiring that the mass of the system remain constant during a process.
For control volumes, however, mass can cross the boundaries, and so we
must keep track of the amount of mass entering and leaving the control
volume.
Mass and Volume Flow Rates
V
Vn
dAc
n
Control surface
FIGURE 5–2
The normal velocity Vn for a
surface is the component of velocity
perpendicular to the surface.
The amount of mass flowing through a cross section per unit time is called
the mass flow rate and is denoted by m# . The dot over a symbol is used to
indicate time rate of change.
A fluid flows into or out of a control volume, usually through pipes or
ducts. The differential mass flow rate of fluid flowing across a small area
element dAc in a cross section of a pipe is proportional to dAc itself, the fluid
density r, and the component of the flow velocity normal to dAc, which we
denote as Vn, and is expressed as (Fig. 5–2)
#
dm 5 rVn dAc
(5–2)
Note that both d and d are used to indicate differential quantities, but d is
typically used for quantities (such as heat, work, and mass transfer) that are
path functions and have inexact differentials, while d is used for quantities
(such as properties) that are point functions and have exact differentials. For
flow through an annulus of inner radius r1 and outer radius r2, for example,
215
CHAPTER 5
#
2
2
dAc 5 Ac2 2 Ac1 5 p(r 22 2 r 21) but
1
# dm# 5 m# (total mass flow rate through
total
1
the annulus), not m# 2 2 m# 1. For specified values of r1 and r2, the value of
the integral of dAc is fixed (thus the names point function and exact differ#
ential), but this is not the case for the integral of dm (thus the names path
function and inexact differential).
The mass flow rate through the entire cross-sectional area of a pipe or
duct is obtained by integration:
#
m5
# dm# 5 # rV dA
n
Ac
(kg/s)
c
(5–3)
Ac
While Eq. 5–3 is always valid (in fact it is exact), it is not always practical
for engineering analyses because of the integral. We would like instead to
express mass flow rate in terms of average values over a cross section of the
pipe. In a general compressible flow, both r and Vn vary across the pipe. In
many practical applications, however, the density is essentially uniform over
the pipe cross section, and we can take r outside the integral of Eq. 5–3.
Velocity, however, is never uniform over a cross section of a pipe because
of the no-slip condition at the walls. Rather, the velocity varies from zero at
the walls to some maximum value at or near the centerline of the pipe. We
define the average velocity Vavg as the average value of Vn across the entire
cross section of the pipe (Fig. 5–3),
Average velocity:
Vavg 5
1
V dA
A c Ac n c
#
(5–4)
where Ac is the area of the cross section normal to the flow direction. Note
that if the speed were Vavg all through the cross section, the mass flow rate
would be identical to that obtained by integrating the actual velocity profile. Thus for incompressible flow or even for compressible flow where r is
approximated as uniform across Ac, Eq. 5–3 becomes
#
m 5 rVavg Ac
(kg/s)
(5–5)
For compressible flow, we can think of r as the bulk average density over
the cross section, and then Eq. 5–5 can be used as a reasonable approximation. For simplicity, we drop the subscript on the average velocity. Unless
otherwise stated, V denotes the average velocity in the flow direction. Also,
Ac denotes the cross-sectional area normal to the flow direction.
The volume of the fluid flowing
through a cross section per unit time is
.
called the volume flow rate V (Fig. 5–4) and is given by
#
V5
# V dA 5 V A 5 VA
n
c
avg
c
c
(m3/s)
(5–6)
Ac
An early form of Eq. 5–6 was published in 1628 by the Italian monk
Benedetto Castelli (circa. 1577–1644). Note that many fluid
. mechanics textbooks use Q instead of V for volume flow rate. We use V to avoid confusion
with heat transfer.
Vavg
FIGURE 5–3
The average velocity Vavg is defined
as the average speed through a
cross section.
Ac
Vavg
V = VavgAc
Cross section
FIGURE 5–4
The volume flow rate is the volume of
fluid flowing through a cross section
per unit time.
216
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
The mass and volume flow rates are related by
#
#
V
#
m 5 rV 5
v
(5–7)
where v is the specific volume. This relation is analogous to m 5 rV 5
V/v, which is the relation between the mass and the volume of a fluid in a
container.
Conservation of Mass Principle
The conservation of mass principle for a control volume can be expressed
as: The net mass transfer to or from a control volume during a time interval
Dt is equal to the net change (increase or decrease) of the total mass within
the control volume during Dt. That is,
a
Total mass entering
Total mass leaving
Net change of mass
b 2 a
b 5 a
b
the CV during Dt
the CV during Dt
within the CV during Dt
or
min = 50 kg
g
k
ter = 20
Wa – m out
min 2 mout 5 DmCV
= m in
tub
Δm bath
#
#
min 2 mout 5 dmCV/dt
FIGURE 5–5
Conservation of mass principle for an
ordinary bathtub.
dV
n
dA
Control
volume (CV)
(5–8)
where DmCV 5 mfinal – minitial is the change in the mass of the control volume during the process (Fig. 5–5). It can also be expressed in rate form as
mout = 30 kg
dm
(kg)
u
V
(5–9)
.
.
where min and mout are the total rates of mass flow into and out of the control volume, and dmCV/dt is the rate of change of mass within the control
volume boundaries. Equations 5–8 and 5–9 are often referred to as the mass
balance and are applicable to any control volume undergoing any kind of
process.
Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig. 5–6. The
mass of a differential volume dV within the control volume is dm 5 r dV.
The total mass within the control volume at any instant in time t is determined by integration to be
Total mass within the CV:
mCV 5
# r dV
(5–10)
CV
Control surface (CS)
FIGURE 5–6
The differential control volume dV and
the differential control surface dA used
in the derivation of the conservation of
mass relation.
(kg/s)
Then the time rate of change of the amount of mass within the control volume
is expressed as
Rate of change of mass within the CV:
dmCV
dt
5
d
r dV
dt CV
#
(5–11)
For the special case of no mass crossing the control surface (i.e., the control volume is a closed system), the conservation of mass principle reduces
to dmCV/dt 5 0. This relation is valid whether the control volume is fixed,
moving, or deforming.
217
CHAPTER 5
Now consider mass flow into or out of the control volume through a dif!
ferential area dA on the control surface of a fixed control
volume. Let n be
!
the outward unit vector of dA normal to dA and V be the flow velocity at
dA relative to a fixed coordinate system, as shown in Fig. 5–6. In general,
the velocity may cross dA at an angle u off the normal of dA, and
! the! mass
flow rate is proportional to the normal component
of velocity V n 5 V cos u
!
ranging from a maximum outflow of V for u 5 0 (flow is normal to dA)
to a minimum
! of zero for u 5 908 (flow is tangent to dA) to a maximum
inflow of V for u 5 1808 (flow is normal to dA but in the opposite direction). Making use of the concept of dot product of two vectors, the magnitude of the normal component of velocity is
! !
Vn 5 V cos u 5 V ·n
Normal component of velocity:
(5–12)
The mass flow rate through dA is proportional to the fluid density r, normal
velocity Vn, and the flow area dA, and is expressed as
Differential mass flow rate:
! !
#
dm 5 rVn dA 5 r(V cos u) dA 5 r(V ·n ) dA
(5–13)
The net flow rate into or out of the control volume through the entire con.
trol surface is obtained by integrating dm over the entire control surface,
Net mass flow rate:
#
mnet 5
! !
# dm# 5 # rV dA 5 # r(V ·n ) dA
n
CS
CS
(5–14)
CS
! !
Note that Vn 5 V · n 5 V cos u is positive for u , 908 (outflow) and negative for u . 908 (inflow). Therefore, the direction of flow is automatically
accounted for, and the surface integral in Eq. 5–14 directly gives the net
.
mass flow rate. A positive value for mnet indicates a net outflow of mass and
a negative value indicates a net inflow of mass.
.
.
Rearranging Eq. 5–9 as dmCV/dt 1 mout 2 min 5 0, the conservation of
mass relation for a fixed control volume is then expressed as
d
dt
General conservation of mass:
! !
# r dV 1 # r(V ·n ) dA 5 0
CV
(5–15)
CS
It states that the time rate of change of mass within the control volume plus
the net mass flow rate through the control surface is equal to zero.
Splitting the surface integral in Eq. 5–15 into two parts—one for the
outgoing flow streams (positive) and one for the incoming flow streams
(negative)—the general conservation of mass relation can also be
expressed as
d
dt
# r dV 1 a r k V k A 2 a r k V k A 5 0
n
CV
out
n
in
(5–16)
218
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
A
A/cos u
V
u
n
where A represents the area for an inlet or outlet, and the summation
signs are used to emphasize that all the inlets and outlets are to be considered. Using the definition of mass flow rate, Eq. 5–16 can also be
expressed as
Vn = V cos u
m = r(V cos u)(A/cos u) = rVA
d
dt
(a) Control surface at an angle to the flow
# r dV 5 a m# 2 a m#
CV
in
or
out
dmCV
dt
#
#
5 am 2 am
in
(5–17)
out
A
n
V
m = rVA
(b) Control surface normal to the flow
FIGURE 5–7
A control surface should always be
selected normal to the flow at all
locations where it crosses the fluid
flow to avoid complications, even
though the result is the same.
There is considerable flexibility in the selection of a control volume when
solving a problem. Many control volume choices are available, but some are
more convenient to work with. A control volume should not introduce any
unnecessary complications. A wise choice of a control volume can make the
solution of a seemingly complicated problem rather easy. A simple rule in
selecting a control volume is to make the control surface normal to the flow
at all locations where
! ! it crosses the fluid flow, whenever possible. This way
the dot product V · n simply becomes the magnitude of the velocity, and the
! !
integral r(V ·n ) dA becomes simply rVA (Fig. 5–7).
#
A
Equations 5–15 and 5–16 are also valid for moving
! or deforming control volumes provided
that the absolute velocity V is replaced by the
!
relative velocity Vr, which is the fluid velocity relative to the control
surface.
Mass Balance for Steady-Flow Processes
m 1 = 2 kg/s
m 2 = 3 kg/s
CV
m3 = m1 + m2 = 5 kg/s
FIGURE 5–8
Conservation of mass principle for
a two-inlet–one-outlet steady-flow
system.
During a steady-flow process, the total amount of mass contained within
a control volume does not change with time (mCV 5 constant). Then the
conservation of mass principle requires that the total amount of mass
entering a control volume equal the total amount of mass leaving it. For a
garden hose nozzle in steady operation, for example, the amount of water
entering the nozzle per unit time is equal to the amount of water leaving
it per unit time.
When dealing with steady-flow processes, we are not interested in the
amount of mass that flows in or out of a device over time; instead, we
are interested in the amount of mass flowing per unit time, that is, the
.
mass flow rate m . The conservation of mass principle for a general steadyflow system with multiple inlets and outlets is expressed in rate form as
(Fig. 5–8)
Steady flow:
#
#
am 5 am
in
(kg/s)
(5–18)
out
It states that the total rate of mass entering a control volume is equal to the
total rate of mass leaving it.
Many engineering devices such as nozzles, diffusers, turbines, compressors, and pumps involve a single stream (only one inlet and one outlet). For
these cases, we typically denote the inlet state by the subscript 1 and the
219
CHAPTER 5
outlet state by the subscript 2, and drop the summation signs. Then Eq. 5–18
reduces, for single-stream steady-flow systems, to
Steady flow (single stream):
#
#
m1 5 m2
S
r1V1 A1 5 r2V2 A2
(5–19)
Special Case: Incompressible Flow
The conservation of mass relations can be simplified even further when the
fluid is incompressible, which is usually the case for liquids. Canceling the
density from both sides of the general steady-flow relation gives
Steady, incompressible flow:
#
#
aV 5 aV
in
(m3/s)
˙ 2 = 2 kg/s
m
V˙ = 0.8 m3/s
(5–20)
2
out
For single-stream steady-flow systems Eq. 5–20 becomes
Steady, incompressible flow (single stream):
#
#
V 1 5 V 2 S V1 A1 5 V2 A2
(5–21)
It should always be kept in mind that there is no such thing as a “conservation of volume” principle. Therefore, the volume flow rates into and
out of a steady-flow device may be different. The volume flow rate at
the outlet of an air compressor is much less than that at the inlet even
though the mass flow rate of air through the compressor is constant
(Fig. 5–9). This is due to the higher density of air at the compressor exit.
For steady flow of liquids, however, the volume flow rates remain nearly
constant since liquids are essentially incompressible (constant-density)
substances. Water flow through the nozzle of a garden hose is an example of the latter case.
The conservation of mass principle requires every bit of mass to be
accounted for during a process. If you can balance your checkbook
(by keeping track of deposits and withdrawals, or by simply observing the
“conservation of money” principle), you should have no difficulty applying
the conservation of mass principle to engineering systems.
EXAMPLE 5–1
Air
compressor
˙ 1 = 2 kg/s
m
V˙ = 1.4 m3/s
1
FIGURE 5–9
During a steady-flow process,
volume flow rates are not necessarily
conserved although mass flow
rates are.
Water Flow through a Garden Hose Nozzle
A garden hose attached with a nozzle is used to fill a 10-gal bucket. The
inner diameter of the hose is 2 cm, and it reduces to 0.8 cm at the nozzle
exit (Fig. 5–10). If it takes 50 s to fill the bucket with water, determine
(a) the volume and mass flow rates of water through the hose, and (b) the
average velocity of water at the nozzle exit.
SOLUTION A garden hose is used to fill a water bucket. The volume and
mass flow rates of water and the exit velocity are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Water is a nearly incompressible substance. 2 Flow through
the hose is steady. 3 There is no waste of water by splashing.
Properties We take the density of water to be 1000 kg/m3 5 1 kg/L.
FIGURE 5–10
Schematic for Example 5–1.
Photo by John M. Cimbala
220
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
Analysis (a) Noting that 10 gal of water are discharged in 50 s, the volume
and mass flow rates of water are
#
10 gal 3.7854 L
V
5
a
b 5 0.757 L/s
V5
Dt
50 s
1 gal
#
#
m 5 rV 5 (1 kg/L)(0.757 L/s) 5 0.757 kg/s
(b) The cross-sectional area of the nozzle exit is
Ae 5 pr 2e 5 p(0.4 cm)2 5 0.5027 cm2 5 0.5027 3 10 24 m2
The volume flow rate through the hose and the nozzle is constant. Then the
average velocity of water at the nozzle exit becomes
#
V
0.757 L/s
1 m3
b 5 15.1 m/s
Ve 5
5
a
24
2
Ae
0.5027 3 10 m 1000 L
Discussion It can be shown that the average velocity in the hose is 2.4 m/s.
Therefore, the nozzle increases the water velocity by over six times.
Air
h0
Water
Djet
h2
h
EXAMPLE 5–2
0
Dtank
FIGURE 5–11
Schematic for Example 5–2.
Discharge of Water from a Tank
A 4-ft-high, 3-ft-diameter cylindrical water tank whose top is open to the atmosphere is initially filled with water. Now the discharge plug near the bottom of
the tank is pulled out, and a water jet whose diameter is 0.5 in streams out
(Fig. 5–11). The average velocity of the jet is approximated as V 5 !2gh,
where h is the height of water in the tank measured from the center of the
hole (a variable) and g is the gravitational acceleration. Determine how long it
takes for the water level in the tank to drop to 2 ft from the bottom.
SOLUTION The plug near the bottom of a water tank is pulled out. The
time it takes for half of the water in the tank to empty is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Water is a nearly incompressible substance. 2 The distance between the bottom of the tank and the center of the hole is negligible compared to the total water height. 3 The gravitational acceleration
is 32.2 ft/s2.
Analysis We take the volume occupied by water as the control volume. The
size of the control volume decreases in this case as the water level drops,
and thus this is a variable control volume. (We could also treat this as a
fixed control volume that consists of the interior volume of the tank by disregarding the air that replaces the space vacated by the water.) This is obviously an unsteady-flow problem since the properties (such as the amount of
mass) within the control volume change with time.
The conservation of mass relation for a control volume undergoing any process is given in rate form as
dmCV
#
#
min 2 mout 5
dt
(1)
221
CHAPTER 5
.
During this process no mass enters the control volume (m in 5 0), and the
mass flow rate of discharged water is
#
mout 5 (rVA)out 5 r"2gh Ajet
(2)
2
where Ajet 5 pD jet
/4 is the cross-sectional area of the jet, which is constant.
Noting that the density of water is constant, the mass of water in the tank
at any time is
mCV 5 rV 5 rAtankh
(3)
2
where Atank 5 Dtank
/4 is the base area of the cylindrical tank. Substituting
Eqs. 2 and 3 into the mass balance relation (Eq. 1) gives
2 r"2gh Ajet 5
d(rAtankh)
dt
S 2r"2gh(pD 2jet /4) 5
r(pD 2tank/4)dh
dt
Canceling the densities and other common terms and separating the variables give
dt 5 2
D2tank
dh
D 2jet "2gh
Integrating from t 5 0 at which h 5 h0 to t 5 t at which h 5 h2 gives
#
t
dt 5 2
0
D2tank
h2
2
jet
h0
dh
# "h S t 5
D "2g
"h0 2 "h2 Dtank 2
a
b
Djet
"g/2
Substituting, the time of discharge is determined to be
t5
"4 ft 2 "2 ft 3 3 12 in 2
a
b 5 757 s 5 12.6 min
0.5 in
"32.2/2 ft/s2
Therefore, it takes 12.6 min after the discharge hole is unplugged for half of
the tank to be emptied.
Discussion Using the same relation with h2 5 0 gives t 5 43.1 min for the
discharge of the entire amount of water in the tank. Therefore, emptying the
bottom half of the tank takes much longer than emptying the top half. This is
due to the decrease in the average discharge velocity of water with decreasing h.
5–2
■
FLOW WORK AND THE ENERGY OF
A FLOWING FLUID
Unlike closed systems, control volumes involve mass flow across their
boundaries, and some work is required to push the mass into or out of the
control volume. This work is known as the flow work, or flow energy, and
is necessary for maintaining a continuous flow through a control volume.
To obtain a relation for flow work, consider a fluid element of volume V
as shown in Fig. 5–12. The fluid immediately upstream forces this fluid element to enter the control volume; thus, it can be regarded as an imaginary
piston. The fluid element can be chosen to be sufficiently small so that it
has uniform properties throughout.
A
F
V
P
m
CV
L
Imaginary
piston
FIGURE 5–12
Schematic for flow work.
222
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
A
F
If the fluid pressure is P and the cross-sectional area of the fluid element is A
(Fig. 5–13), the force applied on the fluid element by the imaginary piston is
F 5 PA
P
FIGURE 5–13
In the absence of acceleration, the
force applied on a fluid by a piston is
equal to the force applied on the piston
by the fluid.
To push the entire fluid element into the control volume, this force must
act through a distance L. Thus, the work done in pushing the fluid element
across the boundary (i.e., the flow work) is
Wflow 5 FL 5 PAL 5 PV
P
v
CV
(a) Before entering
wflow
P
v
CV
(b) After entering
FIGURE 5–14
Flow work is the energy needed to
push a fluid into or out of a control
volume, and it is equal to Pv.
(kJ)
(5–23)
The flow work per unit mass is obtained by dividing both sides of this equation by the mass of the fluid element:
wflow 5 Pv
wflow
(5–22)
(kJ/kg)
(5–24)
The flow work relation is the same whether the fluid is pushed into or out
of the control volume (Fig. 5–14).
It is interesting that unlike other work quantities, flow work is expressed
in terms of properties. In fact, it is the product of two properties of the fluid.
For that reason, some people view it as a combination property (like enthalpy)
and refer to it as flow energy, convected energy, or transport energy instead of
flow work. Others, however, argue rightfully that the product PV represents
energy for flowing fluids only and does not represent any form of energy for
nonflow (closed) systems. Therefore, it should be treated as work. This controversy is not likely to end, but it is comforting to know that both arguments
yield the same result for the energy balance equation. In the discussions that
follow, we consider the flow energy to be part of the energy of a flowing
fluid, since this greatly simplifies the energy analysis of control volumes.
Total Energy of a Flowing Fluid
As we discussed in Chap. 2, the total energy of a simple compressible
system consists of three parts: internal, kinetic, and potential energies
(Fig. 5–15). On a unit-mass basis, it is expressed as
e 5 u 1 ke 1 pe 5 u 1
V2
1 gz
2
(kJ/kg)
(5–25)
where V is the velocity and z is the elevation of the system relative to some
external reference point.
Flow
energy
Kinetic
energy
Nonflowing
fluid
FIGURE 5–15
The total energy consists of three parts
for a nonflowing fluid and four parts
for a flowing fluid.
e= u+
Internal
energy
V2
+ gz
2
Potential
energy
Flowing
fluid
Kinetic
energy
2
= Pv + u + V + gz
2
Internal
energy
Potential
energy
223
CHAPTER 5
The fluid entering or leaving a control volume possesses an additional
form of energy—the flow energy Pv, as already discussed. Then the total
energy of a flowing fluid on a unit-mass basis (denoted by u) becomes
u 5 Pv 1 e 5 Pv 1 (u 1 ke 1 pe)
(5–26)
But the combination Pv 1 u has been previously defined as the enthalpy h.
So the relation in Eq. 5–26 reduces to
u 5 h 1 ke 1 pe 5 h 1
V2
1 gz
2
(kJ/kg)
(5–27)
By using the enthalpy instead of the internal energy to represent the
energy of a flowing fluid, one does not need to be concerned about the
flow work. The energy associated with pushing the fluid into or out of
the control volume is automatically taken care of by enthalpy. In fact, this
is the main reason for defining the property enthalpy. From now on, the
energy of a fluid stream flowing into or out of a control volume is represented by Eq. 5–27, and no reference will be made to flow work or flow
energy.
˙ i, kg/s
m
ui, kJ/kg
Energy Transport by Mass
Noting that u is total energy per unit mass, the total energy of a flowing
fluid of mass m is simply mu, provided that the properties of the mass m
are uniform. Also, when a fluid stream with uniform properties is flowing
at a mass flow rate of m· , the rate of energy flow with that stream is m· u
(Fig. 5–16). That is,
Amount of energy transport:
Emass 5 mu 5 m ah 1
V2
1 gz b
2
(kJ)
(5–28)
Rate of energy transport:
#
V2
#
#
Emass 5 m u 5 m ah 1
1 gzb
2
(kW)
(5–29)
When the kinetic and potential energies of a fluid stream are# negligible, as
#
is often the case, these relations simplify to Emass 5 mh and E mass 5 mh.
In general, the total energy transported by mass into or out of the control volume is not easy to determine since the properties of the mass at
each inlet or exit may be changing with time as well as over the cross
section. Thus, the only way to determine the energy transport through an
opening as a result of mass flow is to consider sufficiently small differential masses dm that have uniform properties and to add their total energies
during flow.
Again noting that u is total energy per unit mass, the total energy of a
flowing fluid of mass dm is u dm. Then the total energy transported by mass
through an inlet or exit (miui and meue) is obtained by integration. At an
inlet, for example, it becomes
Ein,mass 5
#
mi
ui dmi 5
#
mi
ahi 1
V i2
2
1 gzi b dmi
(5–30)
CV
˙ iui
m
(kW)
FIGURE 5–16
#
The product miui is the energy
transported into control volume by
mass per unit time.
224
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
Most flows encountered in practice can be approximated as being steady
and one-dimensional, and thus the simple relations in Eqs. 5–28 and 5–29
can be used to represent the energy transported by a fluid stream.
EXAMPLE 5–3
Energy Transport by Mass
Steam is leaving a 4-L pressure cooker whose operating pressure is 150 kPa
(Fig. 5–17). It is observed that the amount of liquid in the cooker has
decreased by 0.6 L in 40 min after the steady operating conditions are
established, and the cross-sectional area of the exit opening is 8 mm2.
Determine (a) the mass flow rate of the steam and the exit velocity, (b) the
total and flow energies of the steam per unit mass, and (c) the rate at which
energy leaves the cooker by steam.
FIGURE 5–17
Schematic for Example 5–3.
SOLUTION Steam leaves a pressure cooker at a specified pressure. The
velocity, flow rate, the total and flow energies, and the rate of energy transfer
by mass are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 The flow is steady, and the initial start-up period is disregarded. 2 The kinetic and potential energies are negligible, and thus they are
not considered. 3 Saturation conditions exist within the cooker at all times
so that steam leaves the cooker as a saturated vapor at the cooker pressure.
Properties The properties of saturated liquid water and water vapor at
150 kPa are vf 5 0.001053 m3/kg, vg 5 1.1594 m3/kg, ug 5 2519.2 kJ/kg,
and hg 5 2693.1 kJ/kg (Table A–5).
Analysis (a) Saturation conditions exist in a pressure cooker at all times
after the steady operating conditions are established. Therefore, the liquid
has the properties of saturated liquid and the exiting steam has the properties
of saturated vapor at the operating pressure. The amount of liquid that has
evaporated, the mass flow rate of the exiting steam, and the exit velocity are
m5
DV liquid
vf
5
0.6 L
1 m3
a
b 5 0.570 kg
3
0.001053 m /kg 1000 L
0.570 kg
m
#
m5
5
5 0.0142 kg/min 5 2.37 3 1024 kg/s
Dt
40 min
#
#
mvg
(2.37 3 1024 kg/s)(1.1594 m3/kg)
m
V5
5
5
5 34.3 m/s
rg Ac
Ac
8 3 1026 m2
(b) Noting that h 5 u 1 Pv and that the kinetic and potential energies are
disregarded, the flow and total energies of the exiting steam are
eflow 5 Pv 5 h 2 u 5 2693.1 2 2519.2 5 173.9 kJ/kg
u 5 h 1 ke 1 pe > h 5 2693.1 kJ/kg
Note that the kinetic energy in this case is ke 5 V 2y2 5 (34.3 m/s)2y2 5
588 m2/s2 5 0.588 kJ/kg, which is small compared to enthalpy.
(c) The rate at which energy is leaving the cooker by mass is simply the
product of the mass flow rate and the total energy of the exiting steam per
unit mass,
#
#
Emass 5 m u 5 (2.37 3 1024 kg/s)(2693.1 kJ/kg) 5 0.638 kJ/s 5 0.638 kW
225
CHAPTER 5
Discussion The numerical value of the energy leaving the cooker with steam
alone does not mean much since this value depends on the reference point
selected for enthalpy (it could even be negative). The significant quantity
is the difference between the enthalpies of the exiting vapor and the liquid
inside (which is hfg) since it relates directly to the amount of energy supplied
to the cooker.
5–3
■
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF STEADY-FLOW
SYSTEMS
A large number of engineering devices such as turbines, compressors, and
nozzles operate for long periods of time under the same conditions once the
transient start-up period is completed and steady operation is established,
and they are classified as steady-flow devices (Fig. 5–18). Processes involving such devices can be represented reasonably well by a somewhat idealized process, called the steady-flow process, which was defined in Chap. 1
as a process during which a fluid flows through a control volume steadily.
That is, the fluid properties can change from point to point within the control volume, but at any point, they remain constant during the entire process.
(Remember, steady means no change with time.)
During a steady-flow process, no intensive or extensive properties within
the control volume change with time. Thus, the volume V, the mass m, and
the total energy content E of the control volume remain constant (Fig. 5–19).
As a result, the boundary work is zero for steady-flow systems (since VCV 5
constant), and the total mass or energy entering the control volume must
be equal to the total mass or energy leaving it (since mCV 5 constant and
ECV 5 constant). These observations greatly simplify the analysis.
The fluid properties at an inlet or exit remain constant during a steadyflow process. The properties may, however, be different at different inlets
and exits. They may even vary over the cross section of an inlet or an exit.
However, all properties, including the velocity and elevation, must remain
constant with time at a fixed point at an inlet or exit. It follows that the mass
flow rate of the fluid at an opening must remain constant during a steadyflow process (Fig. 5–20). As an added simplification, the fluid properties at
an opening are usually considered to be uniform (at some average value)
over the cross section. Thus, the fluid properties at an inlet or exit may be
specified by the average single values. Also, the heat and work interactions
between a steady-flow system and its surroundings do not change with time.
Thus, the power delivered by a system and the rate of heat transfer to or
from a system remain constant during a steady-flow process.
The mass balance for a general steady-flow system was given in Sec. 5–1 as
#
#
am 5 am
in
(kg/s)
©Malcolm Fife /Getty Images RF
Mass
in
Control
volume
mCV = constant
ECV = constant
Mass
out
FIGURE 5–19
Under steady-flow conditions, the
mass and energy contents of a control
volume remain constant.
.
m2
h2
.
m1
h1
Control
volume
.
m3
h3
(5–31)
out
The mass balance for a single-stream (one-inlet and one-outlet) steady-flow
system was given as
#
#
m1 5 m2
FIGURE 5–18
Many engineering systems such as
power plants operate under steady
conditions.
h
r1V1A1 5 r2V2 A2
(5–32)
FIGURE 5–20
Under steady-flow conditions, the
fluid properties at an inlet or exit
remain constant (do not change
with time).
226
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
where the subscripts 1 and 2 denote the inlet and the exit states, respectively, r is density, V is the average flow velocity in the flow direction, and
A is the cross-sectional area normal to flow direction.
During a steady-flow process, the total energy content of a control volume
remains constant (ECV 5 constant), and thus the change in the total energy
of the control volume is zero (DECV 5 0). Therefore, the amount of energy
entering a control volume in all forms (by heat, work, and mass) must be
equal to the amount of energy leaving it. Then the rate form of the general
energy balance reduces for a steady-flow process to
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
5
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
0 (steady)
Q
dEsystem/dt
50
('''')''''*
(5–33)
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
or
Energy balance:
#
Ein
()*
5
Rate of net energy transfer in
by heat, work, and mass
#
Eout
()*
(kW)
(5–34)
Rate of net energy transfer out
by heat, work, and mass
Noting that energy can be transferred by heat, work, and mass only, the
energy balance in Eq. 5–34 for a general steady-flow system can also be
written more explicitly as
#
#
#
#
#
#
Qin 1 Win 1 a mu 5 Qout 1 Wout 1 a mu
in
(5–35)
out
or
#
#
#
#
V2
V2
#
#
Qin 1 Win 1 a m ah 1
1 gzb 5 Qout 1 Wout 1 a m ah 1
1 gzb (5–36)
2
2
in
out
(''')'''*
(''')'''*
for each inlet
Q˙ out
Electric
heating
element
.
Win
˙2 = m
˙1
m
Hot
water
out
CV
(Hot-water tank)
˙1
m
Cold
water
in
FIGURE 5–21
A water heater in steady operation.
for each exit
since the energy of a flowing fluid per unit mass is u 5 h 1 ke 1 pe 5
h 1 V 2/2 1 gz. The energy balance relation for steady-flow systems first
appeared in 1859 in a German thermodynamics book written by Gustav
Zeuner.
Consider, for example, an ordinary electric hot-water heater under steady
operation, as shown in Fig. 5–21. A cold-water stream with a mass flow rate
.
m is continuously flowing into the water heater, and a hot-water stream of
the same mass flow rate is continuously flowing out of it. The water heater
·
(the control volume) is losing heat to the surrounding air at a rate of Q out,
and the electric heating
element is supplying electrical work (heating) to the
#
water at a rate of Win. On the basis of the conservation of energy principle,
we can say that the water stream experiences an increase in its total energy
as it flows through the water heater that is equal to the electric energy supplied to the water minus the heat losses.
The energy balance relation just given is intuitive in nature and is easy
to use when the magnitudes and directions of heat and work transfers are
known. When performing a general analytical study or solving a problem
that involves an unknown heat or work interaction, however, we need to
assume a direction for the heat or work interactions. In such cases, it is
227
CHAPTER 5
common practice to assume heat to be transferred into the system (heat
·
input) at# a rate of Q, and work produced by the system (work output) at a
rate of W, and then solve the problem. The first-law or energy balance relation in that case for a general steady-flow system becomes
#
#
V2
V2
#
#
Q 2 W 5 a m ah 1
1 gzb 2 2 a m ah 1
1 gzb
2
2
out (''')'''*
in (''')'''*
for each exit
(5–37)
for each inlet
·
·
Obtaining a negative quantity for Q or W simply means that the assumed
direction is wrong and should be reversed. For single-stream devices, the
steady-flow energy balance equation becomes
V 22 2 V 21
#
#
#
Q 2 W 5 m c h2 2 h1 1
1 g(z2 2 z1)d
2
(5–38)
.
Dividing Eq. 5–38 by m gives the energy balance on a unit-mass basis as
q 2 w 5 h2 2 h1 1
V 22 2 V 21
2
1 g(z2 2 z1)
(5–39)
· .
· .
where q 5 Q / m and w 5 W / m are the heat transfer and work done per unit
mass of the working fluid, respectively. When the fluid experiences negligible changes in its kinetic and potential energies (that is, Dke > 0, Dpe > 0),
the energy balance equation is reduced further to
q 2 w 5 h2 2 h1
˙
W
e
CV
˙
W
sh
(5–40)
The various terms appearing in the above equations are as follows:
·
Q 5 rate of heat transfer between the control volume and its
surroundings. When the control volume is losing heat (as in the case
·
of the water heater), Q is negative. If the control volume is well insu·
lated (i.e., adiabatic), then Q 5 0.
·
W 5 power. For steady-flow devices, the control volume is constant;
thus, there is no boundary work involved. The work required to push
mass into and out of the control volume is also taken care of by using
enthalpies
# for the energy of fluid streams instead of internal energies.
Then W represents the remaining forms of work done per unit time
(Fig. 5–22). Many steady-flow devices, such as turbines, compressors,
·
and pumps, transmit power through a shaft, and W simply becomes the
shaft power for those devices. If the control surface is crossed by elec·
tric wires (as in the case of an electric water heater), W represents the
·
electrical work done per unit time. If neither is present, then W 5 0.
Dh 5 h2 2 h1. The enthalpy change of a fluid can easily be determined by
reading the enthalpy values at the exit and inlet states from the tables.
For ideal gases, it can be approximated by Dh 5 cp,avg(T2 2 T1). Note
that (kg/s)(kJ/kg) ; kW.
Dke 5 (V 22 2 V 21)/2. The unit of kinetic energy is m2/s2, which is equivalent to J/kg (Fig. 5–23). The enthalpy is usually given in kJ/kg. To add
these two quantities, the kinetic energy should be expressed in kJ/kg.
This is easily accomplished by dividing it by 1000. A velocity of
FIGURE 5–22
Under steady operation, shaft work
and electrical work are the only forms
of work a simple compressible system
may involve.
J
N.m
m
≡
≡ kg 2
kg
kg
s
Also,
m m2
≡
kg s2
Btu
ft2
≡ 25,037 2
lbm
s
FIGURE 5–23
The units m2/s2 and J/kg are
equivalent.
228
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
V1
m/s
V2
m/s
Δke
kJ/kg
0
50
100
200
500
45
67
110
205
502
1
1
1
1
1
45 m/s corresponds to a kinetic energy of only 1 kJ/kg, which is a very
small value compared with the enthalpy values encountered in practice.
Thus, the kinetic energy term at low velocities can be neglected. When
a fluid stream enters and leaves a steady-flow device at about the same
velocity (V1 > V2), the change in the kinetic energy is close to zero
regardless of the velocity. Caution should be exercised at high velocities, however, since small changes in velocities may cause significant
changes in kinetic energy (Fig. 5–24).
Dpe 5 g(z2 2 z1). A similar argument can be given for the potential
energy term. A potential energy change of 1 kJ/kg corresponds to an
elevation difference of 102 m. The elevation difference between the
inlet and exit of most industrial devices such as turbines and compressors is well below this value, and the potential energy term is always
neglected for these devices. The only time the potential energy term is
significant is when a process involves pumping a fluid to high elevations and we are interested in the required pumping power.
FIGURE 5–24
At very high velocities, even small
changes in velocities can cause
significant changes in the kinetic
energy of the fluid.
5–4
■
SOME STEADY-FLOW ENGINEERING DEVICES
Many engineering devices operate essentially under the same conditions
for long periods of time. The components of a steam power plant (turbines,
compressors, heat exchangers, and pumps), for example, operate nonstop for
months before the system is shut down for maintenance (Fig. 5–25). Therefore, these devices can be conveniently analyzed as steady-flow devices.
LPC bleed
air collector
5-Stage
low pressure
compressor (LPC)
14-Stage
high pressure
compressor
2-Stage
Combustor high pressure
turbine
Fuel system
manifolds
5-Stage
low pressure
turbine
Hot end
drive flange
Cold end
drive flange
FIGURE 5–25
A modern land-based gas turbine used for electric power production. This is a General
Electric LM5000 turbine. It has a length of 6.2 m, it weighs 12.5 tons, and produces
55.2 MW at 3600 rpm with steam injection.
Courtesy of GE Power Systems.
229
CHAPTER 5
In this section, some common steady-flow devices are described, and the
thermodynamic aspects of the flow through them are analyzed. The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for these devices
are illustrated with examples.
1
Nozzles and Diffusers
Nozzles and diffusers are commonly utilized in jet engines, rockets, spacecraft, and even garden hoses. A nozzle is a device that increases the velocity
of a fluid at the expense of pressure. A diffuser is a device that increases
the pressure of a fluid by slowing it down. That is, nozzles and diffusers
perform opposite tasks. The cross-sectional area of a nozzle decreases in the
flow direction for subsonic flows and increases for supersonic flows. The
reverse is true for diffusers.
The rate of heat transfer between the fluid flowing through a nozzle or a
·
diffuser and the surroundings is usually very small (Q < 0) since the fluid
has high velocities, and thus it does not spend enough time in the device
for any significant heat transfer to take place. Nozzles and diffusers typi·
cally involve no work (W 5 0) and any change in potential energy is
negligible (Dpe > 0). But nozzles and diffusers usually involve very high
velocities, and as a fluid passes through a nozzle or diffuser, it experiences
large changes in its velocity (Fig. 5–26). Therefore, the kinetic energy
changes must be accounted for in analyzing the flow through these devices
(Dke Þ 0).
EXAMPLE 5–4
V1
Nozzle
V2 .. V1
V1
Diffuser
V2 ,, V1
FIGURE 5–26
Nozzles and diffusers are shaped so
that they cause large changes in fluid
velocities and thus kinetic energies.
Deceleration of Air in a Diffuser
Air at 108C and 80 kPa enters the diffuser of a jet engine steadily with a
velocity of 200 m/s. The inlet area of the diffuser is 0.4 m2. The air leaves
the diffuser with a velocity that is very small compared with the inlet velocity. Determine (a) the mass flow rate of the air and (b) the temperature of
the air leaving the diffuser.
SOLUTION Air enters the diffuser of a jet engine steadily at a specified
velocity. The mass flow rate of air and the temperature at the diffuser exit
are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with
time at any point and thus DmCV 5 0 and DECV 5 0. 2 Air is an ideal gas
since it is at a high temperature and low pressure relative to its critical-point
values. 3 The potential energy change is zero, Dpe 5 0. 4 Heat transfer is
negligible. 5 Kinetic energy at the diffuser exit is negligible. 6 There are no
work interactions.
Analysis We take the diffuser as the system (Fig. 5–27). This is a control volume since mass crosses the system boundary during the process. We
.
.
.
observe that there is only one inlet and one exit and thus m1 5 m2 5 m.
(a) To determine the mass flow rate, we need to find the specific volume of the
air first. This is determined from the ideal-gas relation at the inlet conditions:
(0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K)(283 K)
v1 5
5
5 1.015 m3/kg
P1
80 kPa
RT1
FIGURE 5–27
The diffuser of a jet engine discussed
in Example 5–4.
Photo by Yunus Çengel
230
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
Then,
1
1
#
m 5 V1A1 5
(200 m/s)(0.4 m2) 5 78.8 kg/s
v1
1.015 m3/kg
Since the flow is steady, the mass flow rate through the entire diffuser
remains constant at this value.
(b) Under stated assumptions and observations, the energy balance for this
steady-flow system can be expressed in the rate form as
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
0 (steady)
dEsystem
50
('''')''''*
Q
/dt
5
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
#
#
Ein 5 Eout
2
2
V1
V2
#
#
m ah1 1
b 5 m ah2 1
b
2
2
h2 5 h1 2
#
#
(since Q > 0, W 5 0, and Dpe > 0)
V 22 2 V 21
2
The exit velocity of a diffuser is usually small compared with the inlet
velocity (V2 ,, V1); thus, the kinetic energy at the exit can be neglected.
The enthalpy of air at the diffuser inlet is determined from the air table
(Table A–17) to be
h1 5 h @ 283 K 5 283.14 kJ/kg
Substituting, we get
h2 5 283.14 kJ/kg 2
1 kJ/kg
0 2 (200 m/s)2
b
a
2
1000 m2/s2
5 303.14 kJ/kg
From Table A–17, the temperature corresponding to this enthalpy value is
T2 5 303 K
Discussion This result shows that the temperature of the air increases by
about 208C as it is slowed down in the diffuser. The temperature rise of the
air is mainly due to the conversion of kinetic energy to internal energy.
EXAMPLE 5–5
Acceleration of Steam in a Nozzle
Steam at 250 psia and 7008F steadily enters a nozzle whose inlet area
is 0.2 ft2. The mass flow rate of steam through the nozzle is 10 lbmys.
Steam leaves the nozzle at 200 psia with a velocity of 900 ft/s. Heat
losses from the nozzle per unit mass of the steam are estimated to be
1.2 Btu/lbm. Determine (a) the inlet velocity and (b) the exit temperature
of the steam.
231
CHAPTER 5
qout = 1.2 Btu/lbm
SOLUTION Steam enters a nozzle steadily at a specified flow rate and velocity. The inlet velocity of steam and the exit temperature are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with
time at any point and thus DmCV 5 0 and DECV 5 0. 2 There are no work
interactions. 3 The potential energy change is zero, Dpe 5 0.
Analysis We take the nozzle as the system (Fig. 5–28). This is a control volume since mass crosses the system boundary during the process. We observe
that there is only one inlet and one exit and thus m·1 5 m·2 5 m·.
(a) The specific volume and enthalpy of steam at the nozzle inlet are
P1 5 250 psia
v 5 2.6883 ft3/lbm
f 1
T1 5 7008F
h1 5 1371.4 Btu/lbm
(Table A–6E)
Then,
1
#
m 5 V1A1
v1
10 lbm/s 5
1
(V )(0.2 ft2)
2.6883 ft3/lbm 1
V1 5 134.4 ft/s
(b) Under stated assumptions and observations, the energy balance for this
steady-flow system can be expressed in the rate form as
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
0 (steady)
dEsystem
50
('''')''''*
Q
/dt
5
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
#
#
Ein 5 Eout
V 21
V 22
#
#
#
m ah1 1
b 5 Qout 1 m ah2 1
b
2
2
#
(since W 5 0, and Dpe > 0)
Dividing by the mass flow rate m· and substituting, h2 is determined to be
h2 5 h1 2 qout 2
V 22 2 V 21
2
5 (1371.4 2 1.2) Btu/lbm 2
(900 ft/s)2 2 (134.4 ft/s)2 1 Btu/lbm
b
a
2
25,037 ft2/s2
5 1354.4 Btu/lbm
Then,
P2 5 200 psia
f T2 5 662.08F
h2 5 1354.4 Btu/lbm
(Table A–6E)
Discussion Note that the temperature of steam drops by 38.08F as it flows
through the nozzle. This drop in temperature is mainly due to the conversion
of internal energy to kinetic energy. (The heat loss is too small to cause any
significant effect in this case.)
Steam
.
m = 10 lbm/s
P1 = 250 psia
T1 = 700°F
A1 = 0.2 ft2
P2 = 200 psia
V2 = 900 ft/s
FIGURE 5–28
Schematic for Example 5–5.
232
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
2 Turbines and Compressors
FIGURE 5–29
Turbine blades attached to the
turbine shaft.
©Royalty-Free/Corbis
In steam, gas, or hydroelectric power plants, the device that drives the electric generator is the turbine. As the fluid passes through the turbine, work
is done against the blades, which are attached to the shaft. As a result, the
shaft rotates, and the turbine produces work (Fig. 5–29).
Compressors, as well as pumps and fans, are devices used to increase
the pressure of a fluid. Work is supplied to these devices from an external source through a rotating shaft. Therefore, compressors involve work
inputs. Even though these three devices function similarly, they do differ in
the tasks they perform. A fan increases the pressure of a gas slightly and is
mainly used to mobilize a gas. A compressor is capable of compressing the
gas to very high pressures. Pumps work very much like compressors except
that they handle liquids instead of gases.
Note that turbines produce power output whereas compressors, pumps,
and fans
# require power input. Heat transfer from turbines is usually negligible (Q < 0) since they are typically well insulated. Heat transfer is also negligible for compressors unless there is intentional cooling. Potential energy
changes are negligible for all of these devices (Dpe > 0). The velocities
involved in these devices, with the exception of turbines and fans, are usually too low to cause any significant change in the kinetic energy (Dke > 0).
The fluid velocities encountered in most turbines are very high, and the
fluid experiences a significant change in its kinetic energy. However, this
change is usually very small relative to the change in enthalpy, and thus it is
often disregarded.
EXAMPLE 5–6
Compressing Air by a Compressor
Air at 100 kPa and 280 K is compressed steadily to 600 kPa and 400 K.
The mass flow rate of the air is 0.02 kg/s, and a heat loss of 16 kJ/kg occurs
during the process. Assuming the changes in kinetic and potential energies
are negligible, determine the necessary power input to the compressor.
SOLUTION
qout = 16 kJ/kg
P2 = 600 kPa
T2 = 400 K
Air
˙ = 0.02 kg/s
m
˙ =?
W
in
P1 = 100 kPa
T1 = 280 K
FIGURE 5–30
Schematic for Example 5–6.
Air is compressed steadily by a compressor to a specified temperature and pressure. The power input to the compressor is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with
time at any point and thus DmCV 5 0 and DECV 5 0. 2 Air is an ideal gas
since it is at a high temperature and low pressure relative to its critical-point
values. 3 The kinetic and potential energy changes are zero, Dke 5 Dpe 5 0.
Analysis We take the compressor as the system (Fig. 5–30). This is a control volume since mass crosses the system boundary during the process. We
#
#
#
observe that there is only one inlet and one exit and thus m1 5 m2 5 m.
Also, heat is lost from the system and work is supplied to the system.
Under stated assumptions and observations, the energy balance for this
steady-flow system can be expressed in the rate form as
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
0 (steady)
Q
dEsystem/dt
50
('''')''''*
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
233
CHAPTER 5
#
#
Ein 5 Eout
#
#
#
#
Win 1 mh1 5 Qout 1 mh2 (since Dke 5 Dpe > 0)
#
#
#
Win 5 mqout 1 m(h2 2 h1)
The enthalpy of an ideal gas depends on temperature only, and the enthalpies of the air at the specified temperatures are determined from the air
table (Table A–17) to be
h1 5 h @ 280 K 5 280.13 kJ/kg
h2 5 h@ 400 K 5 400.98 kJ/kg
Substituting, the power input to the compressor is determined to be
#
Win 5 (0.02 kg/s)(16 kJ/kg) 1 (0.02 kg/s)(400.98 2 280.13) kJ/kg
5 2.74 kW
Discussion Note that the mechanical energy input to the compressor manifests itself as a rise in enthalpy of air and heat loss from the compressor.
EXAMPLE 5–7
Power Generation by a Steam Turbine
The power output of an adiabatic steam turbine is 5 MW, and the inlet and
the exit conditions of the steam are as indicated in Fig. 5–31.
(a) Compare the magnitudes of Dh, Dke, and Dpe.
(b) Determine the work done per unit mass of the steam flowing through the
turbine.
(c) Calculate the mass flow rate of the steam.
SOLUTION The inlet and exit conditions of a steam turbine and its power
output are given. The changes in kinetic energy, potential energy, and
enthalpy of steam, as well as the work done per unit mass and the mass flow
rate of steam are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with
time at any point and thus DmCV 5 0 and DECV 5 0. 2 The system is adiabatic and thus there is no heat transfer.
Analysis We take the turbine as the system. This is a control volume since
mass crosses the system boundary during the process. We observe that there
#
#
#
is only one inlet and one exit and thus m1 5 m2 5 m. Also, work is done by
the system. The inlet and exit velocities and elevations are given, and thus
the kinetic and potential energies are to be considered.
(a) At the inlet, steam is in a superheated vapor state, and its enthalpy is
P1 5 2 MPa
f h1 5 3248.4 kJ/kg
T1 5 4008C
(Table A–6)
At the turbine exit, we obviously have a saturated liquid–vapor mixture at
15-kPa pressure. The enthalpy at this state is
h2 5 hf 1 x 2hfg 5 [225.94 1 (0.9)(2372.3)] kJ/kg 5 2361.01 kJ/kg
P1 = 2 MPa
T1 = 400°C
V1 = 50 m/s
z1 = 10 m
Steam
turbine
˙
W
out = 5 MW
P2 = 15 kPa
x2 = 0.90
V2 = 180 m/s
z2 = 6 m
FIGURE 5–31
Schematic for Example 5–7.
234
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
Then
Dh 5 h2 2 h1 5 (2361.01 2 3248.4) kJ/kg 5 2887.39 kJ/kg
Dke 5
V 22 2 V 21
2
5
1 kJ/kg
(180 m/s)2 2 (50 m/s)2
a
b 5 14.95 kJ/kg
2
1000 m2/s2
Dpe 5 g(z2 2 z1) 5 (9.81 m/s2)[(6 2 10) m] a
1 kJ/kg
b 5 20.04 kJ/kg
1000 m2/s2
(b) The energy balance for this steady-flow system can be expressed in the
rate form as
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
0 (steady)
dEsystem
50
('''')''''*
Q
/dt
5
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
#
#
Ein 5 Eout
#
V 21
V 22
#
#
m ah1 1
1 gz1 b 5 Wout 1 m ah2 1
1 gz 2 b
2
2
#
(since Q 5 0)
.
Dividing by the mass flow rate m and substituting, the work done by the turbine per unit mass of the steam is determined to be
wout 5 2 c (h2 2 h1) 1
V 22 2 V 21
2
1 g(z 2 2 z 1)d 5 2(Dh 1 Dke 1 Dpe)
5 2[2887.39 1 14.95 2 0.04] kJ/kg 5 872.48 kJ/kg
(c) The required mass flow rate for a 5-MW power output is
#
Wout
5000 kJ/s
#
m5
5
5 5.73 kg/s
wout
872.48 kJ/kg
Discussion Two observations can be made from these results. First, the
change in potential energy is insignificant in comparison to the changes in
enthalpy and kinetic energy. This is typical for most engineering devices.
Second, as a result of low pressure and thus high specific volume, the steam
velocity at the turbine exit can be very high. Yet the change in kinetic energy
is a small fraction of the change in enthalpy (less than 2 percent in our
case) and is therefore often neglected.
(a) An adjustable valve
3 Throttling Valves
(b) A porous plug
(c) A capillary tube
FIGURE 5–32
Throttling valves are devices that
cause large pressure drops in the fluid.
Throttling valves are any kind of flow-restricting devices that cause a
significant pressure drop in the fluid. Some familiar examples are ordinary adjustable valves, capillary tubes, and porous plugs (Fig. 5–32).
Unlike turbines, they produce a pressure drop without involving any
work. The pressure drop in the fluid is often accompanied by a large
drop in temperature, and for that reason throttling devices are commonly used in refrigeration and air-conditioning applications. The
235
CHAPTER 5
magnitude of the temperature drop (or, sometimes, the temperature rise)
during a throttling process is governed by a property called the JouleThomson coefficient, discussed in Chap. 12.
Throttling valves are usually small devices, and the flow through them
may be assumed to be adiabatic (q > 0) since there is neither sufficient time
nor large enough area for any effective heat transfer to take place. Also,
there is no work done (w 5 0), and the change in potential energy, if any,
is very small (Dpe > 0). Even though the exit velocity is often considerably
higher than the inlet velocity, in many cases, the increase in kinetic energy
is insignificant (Dke > 0). Then the conservation of energy equation for this
single-stream steady-flow device reduces to
h2 > h1
(kJ/kg)
(5–41)
That is, enthalpy values at the inlet and exit of a throttling valve are the
same. For this reason, a throttling valve is sometimes called an isenthalpic
device. Note, however, that for throttling devices with large exposed surface
areas such as capillary tubes, heat transfer may be significant.
To gain some insight into how throttling affects fluid properties, let us
express Eq. 5–41 as follows:
u1 1 P1v 1 5 u2 1 P2v 2
or
Throttling
valve
Internal energy 1 Flow energy 5 Constant
Thus the final outcome of a throttling process depends on which of the two
quantities increases during the process. If the flow energy increases during
the process (P2v2 . P1v1), it can do so at the expense of the internal energy.
As a result, internal energy decreases, which is usually accompanied by a
drop in temperature. If the product Pv decreases, the internal energy and the
temperature of a fluid will increase during a throttling process. In the case
of an ideal gas, h 5 h(T), and thus the temperature has to remain constant
during a throttling process (Fig. 5–33).
EXAMPLE 5–8
Expansion of Refrigerant-134a in a Refrigerator
Refrigerant-134a enters the capillary tube of a refrigerator as saturated liquid at 0.8 MPa and is throttled to a pressure of 0.12 MPa. Determine the
quality of the refrigerant at the final state and the temperature drop during
this process.
SOLUTION Refrigerant-134a that enters a capillary tube as saturated liquid
is throttled to a specified pressure. The exit quality of the refrigerant and the
temperature drop are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Heat transfer from the tube is negligible. 2 Kinetic energy
change of the refrigerant is negligible.
Analysis A capillary tube is a simple flow-restricting device that is commonly used in refrigeration applications to cause a large pressure drop in the
Ideal
gas
T1
T2 = T1
h1
h2 = h1
FIGURE 5–33
The temperature of an ideal gas
does not change during a throttling
(h 5 constant) process since h 5 h(T).
236
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
Throttling
valve
u1 = 94.80 kJ/kg
P1v1 = 0.68 kJ/kg
(h1 = 95.48 kJ/kg)
refrigerant. Flow through a capillary tube is a throttling process; thus, the
enthalpy of the refrigerant remains constant (Fig. 5–34).
u2 = 88.80 kJ/kg
P2v2 = 6.68 kJ/kg
(h2 = 95.48 kJ/kg)
FIGURE 5–34
During a throttling process, the
enthalpy (flow energy 1 internal
energy) of a fluid remains constant.
But internal and flow energies may be
converted to each other.
At inlet:
T 5 Tsat @ 0.8 MPa 5 31.318C
P1 5 0.8 MPa
f 1
sat. liquid
h1 5 hf @ 0.8 MPa 5 95.48 kJ/kg
At exit:
P2 5 0.12 MPa
(h2 5 h1)
h
(Table A–12)
hf 5 22.47 kJ/kg Tsat 5 222.328C
hg 5 236.99 kJ/kg
Obviously hf , h2 , hg ; thus, the refrigerant exists as a saturated mixture at
the exit state. The quality at this state is
x2 5
h2 2 hf
hfg
5
95.48 2 22.47
5 0.340
236.99 2 22.47
Since the exit state is a saturated mixture at 0.12 MPa, the exit temperature
must be the saturation temperature at this pressure, which is 222.328C.
Then the temperature change for this process becomes
DT 5 T2 2 T1 5 (222.32 2 31.31)8C 5 2 53.638C
Discussion Note that the temperature of the refrigerant drops by 53.638C
during this throttling process. Also note that 34.0 percent of the refrigerant
vaporizes during this throttling process, and the energy needed to vaporize
this refrigerant is absorbed from the refrigerant itself.
Cold
water
Hot
water
T-elbow
FIGURE 5–35
The T-elbow of an ordinary shower
serves as the mixing chamber for the
hot- and the cold-water streams.
4a
Mixing Chambers
In engineering applications, mixing two streams of fluids is not a rare occurrence. The section where the mixing process takes place is commonly referred
to as a mixing chamber. The mixing chamber does not have to be a distinct “chamber.” An ordinary T-elbow or a Y-elbow in a shower, for example,
serves as the mixing chamber for the cold- and hot-water streams (Fig. 5–35).
The conservation of mass principle for a mixing chamber requires that the
sum of the incoming mass flow rates equal the mass flow rate of the outgoing mixture.
Mixing chambers are usually well insulated (q > 0) and usually do not
involve any kind of work (w 5 0). Also, the kinetic and potential energies
of the fluid streams are usually negligible (ke > 0, pe > 0). Then all there
is left in the energy equation is the total energies of the incoming streams
and the outgoing mixture. The conservation of energy principle requires that
these two equal each other. Therefore, the conservation of energy equation
becomes analogous to the conservation of mass equation for this case.
EXAMPLE 5–9
Mixing of Hot and Cold Waters in a Shower
Consider an ordinary shower where hot water at 1408F is mixed with cold
water at 508F. If it is desired that a steady stream of warm water at 1108F
be supplied, determine the ratio of the mass flow rates of the hot to cold
water. Assume the heat losses from the mixing chamber to be negligible and
the mixing to take place at a pressure of 20 psia.
237
CHAPTER 5
SOLUTION In a shower, cold water is mixed with hot water at a specified
temperature. For a specified mixture temperature, the ratio of the mass flow
rates of the hot to cold water is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with
time at any point and thus DmCV 5 0 and DECV 5 0. 2 The kinetic and
potential energies are negligible, ke > pe > 0. 3 Heat losses from the sys·
tem are negligible and thus Q > 0. 4 There is no work interaction involved.
Analysis We take the mixing chamber as the system (Fig. 5–36). This is a
control volume since mass crosses the system boundary during the process.
We observe that there are two inlets and one exit.
Under the stated assumptions and observations, the mass and energy balances for this steady-flow system can be expressed in the rate form as follows:
Mass balance:
#
#
min 2 mout 5 dmsystem/dt Q
T1 = 140°F
m·
1
Mixing
chamber
P = 20 psia
T3 = 110°F
m·
T2 = 50°F
m·
2
3
FIGURE 5–36
Schematic for Example 5–9.
0 (steady)
50
#
#
#
#
#
min 5 mout S m1 1 m2 5 m3
Energy balance:
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
0 (steady)
dEsystem
50
('''')''''*
Q
/dt
5
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
#
#
Ein 5 Eout
T
co
ns
t.
#
#
#
#
#
m1h1 1 m2h2 5 m3h3 (since Q > 0, W 5 0, ke > pe > 0)
#
#
#
#
m1h1 1 m2h2 5 (m1 1 m2)h3
P
=
Combining the mass and energy balances,
Tsat
Dividing this equation by m· 2 yields
yh1 1 h2 5 (y 1 1)h3
where y 5 m·1/m·2 is the desired mass flow rate ratio.
The saturation temperature of water at 20 psia is 227.928F. Since the
temperatures of all three streams are below this value (T , Tsat), the water
in all three streams exists as a compressed liquid (Fig. 5–37). A compressed
liquid can be approximated as a saturated liquid at the given temperature.
Thus,
h1 > hf @ 1408F 5 107.99 Btu/lbm
h2 > hf @ 508F 5 18.07 Btu/lbm
h3 > hf @ 1108F 5 78.02 Btu/lbm
Solving for y and substituting yields
y5
h3 2 h2
h1 2 h3
5
78.02 2 18.07
5 2.0
107.99 2 78.02
Discussion Note that the mass flow rate of the hot water must be twice the
mass flow rate of the cold water for the mixture to leave at 1108F.
Compressed
liquid states
v
FIGURE 5–37
A substance exists as a compressed
liquid at temperatures below the
saturation temperatures at the
given pressure.
238
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
4b
FIGURE 5–38
A heat exchanger can be as simple as
two concentric pipes.
Heat Exchangers
As the name implies, heat exchangers are devices where two moving fluid
streams exchange heat without mixing. Heat exchangers are widely used in
various industries, and they come in various designs.
The simplest form of a heat exchanger is a double-tube (also called
tube-and-shell) heat exchanger, shown in Fig. 5–38. It is composed of
two concentric pipes of different diameters. One fluid flows in the inner
pipe, and the other in the annular space between the two pipes. Heat is
transferred from the hot fluid to the cold one through the wall separating
them. Sometimes the inner tube makes a couple of turns inside the shell to
increase the heat transfer area, and thus the rate of heat transfer. The mixing chambers discussed earlier are sometimes classified as direct-contact
heat exchangers.
The conservation of mass principle for a heat exchanger in steady operation requires that the sum of the inbound mass flow rates equal the sum of
the outbound mass flow rates. This principle can also be expressed as follows: Under steady operation, the mass flow rate of each fluid stream flowing through a heat exchanger remains constant.
Heat exchangers typically involve no work interactions (w 5 0) and
negligible kinetic and potential energy changes (Dke > 0, Dpe > 0) for
each fluid stream. The heat transfer rate associated with heat exchangers depends on how the control volume is selected. Heat exchangers are
intended for heat transfer between two fluids within the device, and the
outer shell is usually well insulated to prevent any heat loss to the surrounding medium.
#
When the entire heat exchanger is selected as the control volume, Q
becomes zero, since the boundary for this case lies just beneath the insulation and little or no heat crosses the boundary (Fig. 5–39). If, however,
only one of the fluids is selected as the control volume, then # heat will
cross this boundary
# as it flows from one fluid to the other and Q will not
be zero. In fact, Q in this case will be the rate of heat transfer between the
two fluids.
Fluid B
Fluid B
CV boundary
CV boundary
Fluid A
FIGURE 5–39
The heat transfer associated with
a heat exchanger may be zero or
nonzero depending on how the control
volume is selected.
Fluid A
Heat
Heat
(a) System: Entire heat
exchanger (QCV = 0)
(b) System: Fluid A (QCV ≠ 0)
239
CHAPTER 5
EXAMPLE 5–10
Cooling of Refrigerant-134a by Water
Refrigerant-134a is to be cooled by water in a condenser. The refrigerant enters
the condenser with a mass flow rate of 6 kg/min at 1 MPa and 708C and leaves
at 358C. The cooling water enters at 300 kPa and 158C and leaves at 258C.
Neglecting any pressure drops, determine (a) the mass flow rate of the cooling
water required and (b) the heat transfer rate from the refrigerant to water.
SOLUTION Refrigerant-134a is cooled by water in a condenser. The mass
flow rate of the cooling water and the rate of heat transfer from the refrigerant to the water are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with
time at any point and thus DmCV 5 0 and DECV 5 0. 2 The kinetic and
potential energies are negligible, ke > pe > 0. 3 Heat losses from the sys·
tem are negligible and thus Q > 0. 4 There is no work interaction.
Analysis We take the entire heat exchanger as the system (Fig. 5–40). This
is a control volume since mass crosses the system boundary during the process. In general, there are several possibilities for selecting the control volume for multiple-stream steady-flow devices, and the proper choice depends
on the situation at hand. We observe that there are two fluid streams (and
thus two inlets and two exits) but no mixing.
(a) Under the stated assumptions and observations, the mass and energy balances for this steady-flow system can be expressed in the rate form as follows:
#
#
min 5 mout
Mass balance:
for each fluid stream since there is no mixing. Thus,
#
#
#
m1 5 m2 5 mw
#
#
#
m3 5 m4 5 mR
Energy balance:
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
5
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
0 (steady)
dEsystem/dt Q
50
('''')''''*
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
#
#
Ein 5 Eout
#
#
#
#
m1h1 1 m3h3 5 m2h2 1 m4h4
#
#
(since Q > 0, W 5 0, ke > pe > 0)
Combining the mass and energy balances and rearranging give
#
#
mw(h1 2 h2) 5 mR(h4 2 h3)
Now we need to determine the enthalpies at all four states. Water exists as
a compressed liquid at both the inlet and the exit since the temperatures
at both locations are below the saturation temperature of water at 300 kPa
(133.528C). Approximating the compressed liquid as a saturated liquid at
the given temperatures, we have
h1 > hf @ 158 C 5 62.982 kJ/kg
(Table A–4)
h2 > hf @ 258 C 5 104.83 kJ/kg
Water
15°C
300 kPa
1
R-134a
3
70°C
1 MPa
4
35°C
2
25°C
FIGURE 5–40
Schematic for Example 5–10.
240
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
The refrigerant enters the condenser as a superheated vapor and leaves as a
compressed liquid at 358C. From refrigerant-134a tables,
P3 5 1 MPa
f h3 5 303.87 kJ/kg
T3 5 708C
(Table A–13)
P4 5 1 MPa
f h4 > hf @ 358C 5 100.88 kJ/kg
T4 5 358C
(Table A–11)
Substituting, we find
#
mw(62.982 2 104.83) kJ/kg 5 (6 kg/min)[(100.88 2 303.87) kJ/kg]
#
mw 5 29.1 kg/min
(b) To determine the heat transfer from the refrigerant to the water, we have
to choose a control volume whose boundary lies on the path of heat transfer.
We can choose the volume occupied by either fluid as our control volume.
For no particular reason, we choose the volume occupied by the water. All
the assumptions stated earlier apply, except that the heat transfer is no longer zero. Then assuming heat to be transferred to water, the energy balance
for this single-stream steady-flow system reduces to
.
.
Qw,in = QR,out
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
5
0 (steady)
Q
dEsystem/dt
50
('''')''''*
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
#
#
Ein 5 Eout
R-134a
#
#
#
Qw, in 1 mwh1 5 mwh2
Rearranging and substituting,
Control volume
boundary
FIGURE 5–41
In a heat exchanger, the heat transfer
depends on the choice of the control
volume.
.
Qout
Surroundings 20°C
Hot fluid
70°C
FIGURE 5–42
Heat losses from a hot fluid flowing
through an uninsulated pipe or duct to
the cooler environment may be very
significant.
#
#
Qw, in 5 m w(h2 2 h1) 5 (29.1 kg/min)[(104.83 2 62.982) kJ/kg]
5 1218 kJ/min
Discussion Had we chosen the volume occupied by the refrigerant as the
control volume (Fig. 5–41), we would have obtained the same result for
·
QR,out since the heat gained by the water is equal to the heat lost by the
refrigerant.
5 Pipe and Duct Flow
The transport of liquids or gases in pipes and ducts is of great importance
in many engineering applications. Flow through a pipe or a duct usually
satisfies the steady-flow conditions and thus can be analyzed as a steadyflow process. This, of course, excludes the transient start-up and shut-down
periods. The control volume can be selected to coincide with the interior
surfaces of the portion of the pipe or the duct that we are interested in
analyzing.
Under normal operating conditions, the amount of heat gained or lost by
the fluid may be very significant, particularly if the pipe or duct is long
(Fig. 5–42). Sometimes heat transfer is desirable and is the sole purpose of
241
CHAPTER 5
the flow. Water flow through the pipes in the furnace of a power plant, the
flow of refrigerant in a freezer, and the flow in heat exchangers are some
examples of this case. At other times, heat transfer is undesirable, and the
pipes or ducts are insulated to prevent any heat loss or gain, particularly
when the temperature difference between the flowing fluid and the surroundings is large. Heat transfer in this case is negligible.
If the control volume involves a heating section (electric wires), a fan, or
a pump (shaft), the work interactions should be considered (Fig. 5–43). Of
these, fan work is usually small and often neglected in energy analysis.
The velocities involved in pipe and duct flow are relatively low, and the
kinetic energy changes are usually insignificant. This is particularly true
when the pipe or duct diameter is constant and the heating effects are negligible. Kinetic energy changes may be significant, however, for gas flow in
ducts with variable cross-sectional areas especially when the compressibility
effects are significant. The potential energy term may also be significant
when the fluid undergoes a considerable elevation change as it flows in a
pipe or duct.
EXAMPLE 5–11
Ẇe
Control volume
˙
W
sh
FIGURE 5–43
Pipe or duct flow may involve
more than one form of work at the
same time.
Electric Heating of Air in a House
The electric heating systems used in many houses consist of a simple duct
with resistance heaters. Air is heated as it flows over resistance wires. Consider a 15-kW electric heating system. Air enters the heating section at
100 kPa and 178C with a volume flow rate of 150 m3/min. If heat is lost
from the air in the duct to the surroundings at a rate of 200 W, determine
the exit temperature of air.
SOLUTION The electric heating system of a house is considered. For specified electric power consumption and air flow rate, the air exit temperature is
to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with
time at any point and thus DmCV 5 0 and DECV 5 0. 2 Air is an ideal gas
since it is at a high temperature and low pressure relative to its criticalpoint values. 3 The kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible,
Dke > Dpe > 0. 4 Constant specific heats at room temperature can be used
for air.
Analysis We take the heating section portion of the duct as the system
(Fig. 5–44). This is a control volume since mass crosses the system boundary during the process. We observe that there is only one inlet and one exit
and thus m· 1 5 m· 2 5 m·. Also, heat is lost from the system and electrical
work is supplied to the system.
At temperatures encountered in heating and air-conditioning applications,
Dh can be replaced by cp DT where cp 5 1.005 kJ/kg·8C—the value at room
temperature—with negligible error (Fig. 5–45). Then the energy balance for
this steady-flow system can be expressed in the rate form as
#
#
Ein 2 Eout
(')'*
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
0 (steady)
Q
dEsystem/dt
50
('''')''''*
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
·
Qout = 200 W
T2 = ?
T1 = 17°C
·
We,in = 15 kW
P1 = 100 kPa
·
V1 = 150 m3/min
FIGURE 5–44
Schematic for Example 5–11.
Air
–20 to 70°C
Δh = 1.005 ΔT (kJ/kg)
FIGURE 5–45
The error involved in D h 5 cp DT,
where cp 5 1.005 kJ/kg·8C, is less than
0.5 percent for air in the temperature
range 220 to 708C.
242
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
#
#
Ein 5 Eout
#
#
#
#
We,in 1 mh1 5 Qout 1 mh2 (since Dke > Dpe > 0)
#
#
#
We,in 2 Qout 5 mcp(T2 2 T1)
From the ideal-gas relation, the specific volume of air at the inlet of the duct
is
v1 5
RT1
P1
5
(0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K)(290 K)
5 0.832 m3/kg
100 kPa
The mass flow rate of the air through the duct is determined from
#
V1
150 m3/min 1 min
#
m5
5
a
b 5 3.0 kg/s
v1
0.832 m3/kg 60 s
Substituting the known quantities, the exit temperature of the air is determined to be
(15 kJ/s) 2 (0.2 kJ/s) 5 (3 kg/s)(1.005 kJ/kg·8C)(T2 2 17)8C
T2 5 21.98C
Discussion
of air.
5–5
Supply line
Control
volume
CV boundary
FIGURE 5–46
Charging of a rigid tank from a supply
line is an unsteady-flow process since
it involves changes within the control
volume.
■
Note that heat loss from the duct reduces the exit temperature
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF UNSTEADY-FLOW
PROCESSES
During a steady-flow process, no changes occur within the control volume;
thus, one does not need to be concerned about what is going on within the
boundaries. Not having to worry about any changes within the control volume with time greatly simplifies the analysis.
Many processes of interest, however, involve changes within the control
volume with time. Such processes are called unsteady-flow, or transientflow, processes. The steady-flow relations developed earlier are obviously
not applicable to these processes. When an unsteady-flow process is analyzed, it is important to keep track of the mass and energy contents of the
control volume as well as the energy interactions across the boundary.
Some familiar unsteady-flow processes are the charging of rigid vessels
from supply lines (Fig. 5–46), discharging a fluid from a pressurized vessel,
driving a gas turbine with pressurized air stored in a large container, inflating tires or balloons, and even cooking with an ordinary pressure cooker.
Unlike steady-flow processes, unsteady-flow processes start and end over
some finite time period instead of continuing indefinitely. Therefore in this
section, we deal with changes that occur over some time interval Dt instead
of with the rate of changes (changes per unit time). An unsteady-flow system, in some respects, is similar to a closed system, except that the mass
within the system boundaries does not remain constant during a process.
Another difference between steady- and unsteady-flow systems is that
steady-flow systems are fixed in space, size, and shape. Unsteady-flow systems,
243
CHAPTER 5
however, are not (Fig. 5–47). They are usually stationary; that is, they are fixed
in space, but they may involve moving boundaries and thus boundary work.
The mass balance for any system undergoing any process can be
expressed as (see Sec. 5–1)
min 2 mout 5 Dmsystem
(kg)
(5–42)
where Dmsystem 5 mfinal 2 minitial is the change in the mass of the system. For
control volumes, it can also be expressed more explicitly as
mi 2 me 5 (m2 2 m1)CV
Ein 2 Eout
DEsystem
5
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
(kJ)
(5–44)
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
The general unsteady-flow process, in general, is difficult to analyze
because the properties of the mass at the inlets and exits may change during
a process. Most unsteady-flow processes, however, can be represented
reasonably well by the uniform-flow process, which involves the following
idealization: The fluid flow at any inlet or exit is uniform and steady, and
thus the fluid properties do not change with time or position over the cross
section of an inlet or exit. If they do, they are averaged and treated as constants for the entire process.
Note that unlike the steady-flow systems, the state of an unsteady-flow
system may change with time, and that the state of the mass leaving the
control volume at any instant is the same as the state of the mass in the
control volume at that instant. The initial and final properties of the control
volume can be determined from the knowledge of the initial and final states,
which are completely specified by two independent intensive properties for
simple compressible systems.
Then the energy balance for a uniform-flow system can be expressed
explicitly as
aQin 1 Win 1 a mub 2 aQout 1 Wout 1 a mub 5 (m2e2 2 m1e1)system
in
Control
volume
(5–43)
where i 5 inlet, e 5 exit, 1 5 initial state, and 2 5 final state of the control
volume. Often one or more terms in the equation above are zero. For example,
mi 5 0 if no mass enters the control volume during the process, me 5 0 if no
mass leaves, and m1 5 0 if the control volume is initially evacuated.
The energy content of a control volume changes with time during an
unsteady-flow process. The magnitude of change depends on the amount
of energy transfer across the system boundaries as heat and work as well
as on the amount of energy transported into and out of the control volume
by mass during the process. When analyzing an unsteady-flow process, we
must keep track of the energy content of the control volume as well as the
energies of the incoming and outgoing flow streams.
The general energy balance was given earlier as
Energy balance:
CV boundary
(5–45)
out
where u 5 h 1 ke 1 pe is the energy of a fluid stream at any inlet or exit
per unit mass, and e 5 u 1 ke 1 pe is the energy of the nonflowing fluid
within the control volume per unit mass. When the kinetic and potential
FIGURE 5–47
The shape and size of a control
volume may change during an
unsteady-flow process.
244
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
Q
energy changes associated with the control volume and fluid streams are
negligible, as is usually the case, the energy balance above simplifies to
W
Q 2 W 5 a mh 2 a mh 1 (m2u2 2 m1u1)system
out
Closed
system
Closed
Q – W = ΔU
Closed
FIGURE 5–48
The energy equation of a uniformflow system reduces to that of a closed
system when all the inlets and exits
are closed.
where Q 5 Qnet,in 5 Qin 2 Qout is the net heat input and W 5 Wnet,out 5
Wout 2 Win is the net work output. Note that if no mass enters or leaves
the control volume during a process (mi 5 me 5 0, and m1 5 m2 5 m),
this equation reduces to the energy balance relation for closed systems (Fig.
5–48). Also note that an unsteady-flow system may involve boundary work
as well as electrical and shaft work (Fig. 5–49).
Although both the steady-flow and uniform-flow processes are somewhat
idealized, many actual processes can be approximated reasonably well by
one of these with satisfactory results. The degree of satisfaction depends on
the desired accuracy and the degree of validity of the assumptions made.
EXAMPLE 5–12
Wb
Moving
boundary
We
(5–46)
in
Charging of a Rigid Tank by Steam
A rigid, insulated tank that is initially evacuated is connected through a
valve to a supply line that carries steam at 1 MPa and 3008C. Now the valve
is opened, and steam is allowed to flow slowly into the tank until the pressure reaches 1 MPa, at which point the valve is closed. Determine the final
temperature of the steam in the tank.
SOLUTION
Wsh
FIGURE 5–49
A uniform-flow system may involve
electrical, shaft, and boundary work
all at once.
A valve connecting an initially evacuated tank to a steam line is
opened, and steam flows in until the pressure inside rises to the line level.
The final temperature in the tank is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This process can be analyzed as a uniform-flow process
since the properties of the steam entering the control volume remain constant
during the entire process. 2 The kinetic and potential energies of the streams
are negligible, ke > pe > 0. 3 The tank is stationary and thus its kinetic and potential energy changes are zero; that is, DKE 5 DPE 5 0 and DEsystem 5 DUsystem.
4 There are no boundary, electrical, or shaft work interactions involved. 5 The tank
is well insulated and thus there is no heat transfer.
Analysis We take the tank as the system (Fig. 5–50). This is a control
volume since mass crosses the system boundary during the process. We
observe that this is an unsteady-flow process since changes occur within the
control volume. The control volume is initially evacuated and thus m1 5 0
and m1u1 5 0. Also, there is one inlet and no exits for mass flow.
Noting that microscopic energies of flowing and nonflowing fluids are represented by enthalpy h and internal energy u, respectively, the mass and
energy balances for this uniform-flow system can be expressed as
0
min 2 mout 5 Dmsystem
Mass balance:
Q
S m 5m 2m 5m
i
2
1
2
Energy balance:
Ein 2 Eout
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
DEsystem
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
mihi 5 m2u2
(since W 5 Q 5 0, ke > pe > 0, m1 5 0)
245
CHAPTER 5
Imaginary
piston
Pi = 1 MPa
Ti = 300°C
Pi = 1 MPa (constant)
mi = m2
Steam
m1 = 0
P2 = 1 MPa
T2 = ?
(a) Flow of steam into
an evacuated tank
(b) The closed-system
equivalence
FIGURE 5–50
Schematic for Example 5–12.
Combining the mass and energy balances gives
u2 5 hi
That is, the final internal energy of the steam in the tank is equal to the
enthalpy of the steam entering the tank. The enthalpy of the steam at the
inlet state is
Pi 5 1 MPa
f hi 5 3051.6 kJ/kg
Ti 5 3008C
(Table A–6)
which is equal to u2. Since we now know two properties at the final state, it is
fixed and the temperature at this state is determined from the same table to be
P2 5 1 MPa
f T2 5 456.18C
u2 5 3051.6 kJ/kg
Discussion Note that the temperature of the steam in the tank has increased
by 156.18C. This result may be surprising at first, and you may be wondering where the energy to raise the temperature of the steam came from. The
answer lies in the enthalpy term h 5 u 1 Pv. Part of the energy represented
by enthalpy is the flow energy Pv, and this flow energy is converted to sensible internal energy once the flow ceases to exist in the control volume, and
it shows up as an increase in temperature (Fig. 5–51).
Alternative solution This problem can also be solved by considering the
region within the tank and the mass that is destined to enter the tank
as a closed system, as shown in Fig. 5–50b. Since no mass crosses the
boundaries, viewing this as a closed system is appropriate.
During the process, the steam upstream (the imaginary piston) will push
the enclosed steam in the supply line into the tank at a constant pressure of
1 MPa. Then the boundary work done during this process is
2
Wb,in 5 2
# P dV 5 2P (V 2 V ) 5 2P [V
i
1
i
2
1
i
tank 2 (V tank 1 V i)] 5 PiV i
Steam
Ti = 300°C
T2 = 456.1°C
FIGURE 5–51
The temperature of steam rises from
300 to 456.18C as it enters a tank as a
result of flow energy being converted
to internal energy.
246
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
where Vi is the volume occupied by the steam before it enters the tank and
Pi is the pressure at the moving boundary (the imaginary piston face). The
energy balance for the closed system gives
Ein 2 Eout
DEsystem
5
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
Wb,in 5 DU
miPiv i 5 m2u2 2 miui
u2 5 ui 1 Piv i 5 hi
since the initial state of the system is simply the line conditions of the
steam. This result is identical to the one obtained with the uniform-flow
analysis. Once again, the temperature rise is caused by the so-called flow
energy or flow work, which is the energy required to move the fluid during
flow.
EXAMPLE 5–13
Discharge of Heated Air at Constant
Temperature
An insulated 8-m3 rigid tank contains air at 600 kPa and 400 K. A valve
connected to the tank is now opened, and air is allowed to escape until the
pressure inside drops to 200 kPa. The air temperature during the process
is maintained constant by an electric resistance heater placed in the tank.
Determine the electrical energy supplied to air during this process.
SOLUTION
Air
V = 8 m3
P = 600 kPa
We,in
T = 400 K
FIGURE 5–52
Schematic for Example 5–13.
Pressurized air in an insulated rigid tank equipped with an electric heater is allowed to escape at constant temperature until the pressure
inside drops to a specified value. The amount of electrical energy supplied
to air is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 This is an unsteady process since the conditions within the
device are changing during the process, but it can be analyzed as a uniformflow process since the exit conditions remain constant. 2 Kinetic and potential energies are negligible. 3 The tank is insulated and thus heat transfer is
negligible. 4 Air is an ideal gas with variable specific heats.
Analysis We take the contents of the tank as the system, which is a control
volume since mass crosses the boundary (Fig. 5–52). Noting that the microscopic energies of flowing and nonflowing fluids are represented by enthalpy
h and internal energy u, respectively, the mass and energy balances for this
uniform-flow system can be expressed as
Mass balance:
min 2 mout 5 Dmsystem S me 5 m1 2 m2
Energy balance: Ein 2 Eout
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
DEsystem
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
We, in 2 mehe 5 m2u2 2 m1u1 (since Q > ke > pe > 0)
247
CHAPTER 5
The gas constant of air is R 5 0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K (Table A-1). The initial
and final masses of air in the tank and the discharged amount are determined from the ideal gas relation to be
P1V 1
m1 5
RT1
P2V 2
m2 5
RT2
5
(600 kPa)(8 m3)
5 41.81 kg
(0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K)(400 K)
5
(200 kPa)(8 m3)
5 13.94 kg
(0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K)(400 K)
me 5 m1 2 m2 5 41.81 2 13.94 5 27.87 kg
The enthalpy and internal energy of air at 400 K are he 5 400.98 kJ/kg and
u1 5 u2 5 286.16 kJ/kg (Table A-17). The the electrical energy supplied to
air is determined from the energy balance to be
We,in 5 mehe 1 m2u2 2 m1u1
5 (27.87 kg)(400.98 kJ/kg) 1 (13.94 kg)(286.16 kJ/kg)
2 (41.81 kg)(286.16 kJ/kg)
5 3200 kJ 5 0.889 kWh
since 1 kWh 5 3600 kJ.
Discussion If the temperature of discharged air changes during the process,
the problem can be solved with reasonable accuracy by evaluating he at the
average discharge temperature Te 5 (T2 1 T1)/2, and treating it as constant.
TOPIC OF SPECIAL INTEREST*
General Energy Equation
One of the most fundamental laws in nature is the first law of thermodynamics, also known as the conservation of energy principle, which provides a sound basis for studying the relationships among the various forms of
energy and energy interactions. It states that energy can be neither created nor
destroyed during a process; it can only change forms.
The energy content of a fixed quantity of mass (a closed system) can be
changed by two mechanisms: heat transfer Q and work transfer W. Then the
conservation of energy for a fixed quantity of mass can be expressed in rate
form as
dEsys
#
#
#
#
d
Q2W5
or Q 2 W 5
re dV
dt
dt sys
#
(5–47)
#
#
#
#
where Q 5 Q net,in 5 Q in 2 Q out # is the # net rate of# heat transfer
to the system
#
(negative, if from the system), W 5 Wnet,out 5 Wout 2 Win is the net power
output from the system in all forms (negative, if power input) and dEsys/dt
*This section can be skipped without a loss in continuity.
248
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
is the rate of change of the total energy content of the system. The overdot
stands for time rate. For simple compressible systems, total energy consists
of internal, kinetic, and potential energies, and it is expressed on a unit-mass
basis as
e 5 u 1 ke 1 pe 5 u 1
V2
1 gz
2
(5–48)
Note that total energy is a property, and its value does not change unless the
state of the system changes.
An energy interaction is heat if its driving force is a temperature difference, and it is work if it is associated with a force acting through a distance,
as explained in Chap. 2. A system may involve numerous forms of work, and
the total work can be expressed as
Wtotal 5 Wshaft 1 Wpressure 1 Wviscous 1 Wother
where Wshaft is the work transmitted by a rotating shaft, Wpressure is the work
done by the pressure forces on the control surface, Wviscous is the work done
by the normal and shear components of viscous forces on the control surface, and Wother is the work done by other forces such as electric, magnetic,
and surface tension, which are insignificant for simple compressible systems
and are not considered in this text. We do not consider Wviscous either since
it is usually small relative to other terms in control volume analysis. But
it should be kept in mind that the work done by shear forces as the blades
shear through the fluid may need to be considered in a refined analysis of
turbomachinery.
P
ds
A
Vpiston
System
(gas in cylinder)
Work Done by Pressure Forces
Consider a gas being compressed in the piston-cylinder device shown in
Fig. 5–53a. When the piston moves down a differential distance ds under the
influence of the pressure force PA, where A is the cross-sectional area of the
piston, the boundary work done on the system is dWboundary 5 PA ds. Dividing both sides of this relation by the differential time interval dt gives the
time rate of boundary work (i.e., power),
(a)
dV
P
dm
dA
System
(5–49)
n
#
#
dWpressure 5 dWboundary 5 PAVpiston
u
V
System boundary, A
(b)
FIGURE 5–53
The pressure force acting on (a) the
moving boundary of a system in a
piston–cylinder device, and (b) the
differential surface area of a system of
arbitrary shape.
where Vpiston 5 ds/dt is the piston velocity, which is the velocity of the moving boundary at the piston face.
Now consider a material chunk of fluid (a system) of arbitrary shape,
which moves with the flow and is free to deform under the influence of pressure, as shown in Fig. 5–53b. Pressure always acts inward and normal to the
surface, and the pressure force acting on a differential area dA is P dA. Again
noting that work is force times distance and distance traveled per unit time is
velocity, the time rate at which work is done by pressure forces on this differential part of the system is
! !
#
dWpressure 5 P dA Vn 5 P dA(V ·n )
(5–50)
249
CHAPTER 5
since the normal component
of velocity through the differential area dA is
! !
!
Vn 5 V cos
u
5
V
·
n
.
Note
that
n is the outer normal of dA, and thus the
! !
quantity V · n is positive for expansion and negative for compression.
# The
total rate of work done by pressure forces is obtained by integrating dWpressure
over the entire surface A,
#
Wpressure,net out 5
! !
! !
P
# P (V ·n ) dA 5 # r r (V ·n ) dA
A
(5–51)
A
In light of these discussions, the net power transfer can be expressed as
#
#
#
#
Wnet,out 5 Wshaft,net out 1 Wpressure,net out 5 Wshaft,net out 1
! !
# (V ·n ) dA (5–52)
A
Then the rate form of the conservation of energy relation for a closed system
becomes
dEsys
#
#
#
Qnet,in 2 Wshaft,net out 2 Wpressure,net out 5
dt
(5–53)
To obtain a relation for the conservation of energy for a control volume, we
apply the Reynolds transport theorem by replacing the extensive property B
with total energy E, and its associated intensive property b with total energy
per unit mass e, which is e 5 u 1 ke 1 pe 5 u 1 V 2/2 1 gz (Fig. 5–54).
This yields
dEsys
dt
5
! !
d
er dV 1
er (V · n ) A
dt CV
CS
#
#
(5–54)
Substituting the left-hand side of Eq. 5–53 into Eq. 5–54, the general form
of the energy equation that applies to fixed, moving, or deforming control
volumes becomes
! !
#
#
#
d
Qnet,in 2 Wshaft,net out 2 Wpressure,net out 5
er dV 1
er(Vr · n ) dA
dt CV
CS
#
#
(5–55)
which can be stated as
The net rate of energy
The time rate of
The net flow rate of
° transfer into a CV by ¢ 5 °change of the energy¢ 1 °energy out of the control¢
heat and work transfer
content of the CV
surface by mass flow
!
!
!
Here V r 5 V 2! V CS is the fluid velocity relative to the control surface, and
!
the product r 1V r · n 2 dA represents the mass flow rate through area element
!
dA into or out of the control
! ! volume. Again noting that n is the outer normal of dA, the quantity V r · n and thus mass flow is positive for outflow and
negative for inflow.
FIGURE 5–54
The conservation of energy equation
is obtained by replacing an extensive
property B in the Reynolds transport
theorem by energy E and its associated
intensive property b by e (Ref. 3).
250
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
Qnet in
min ,
energyin
In
min ,
energyin
In
Out
mout ,
energyout
Fixed
control
volume
Out
Wshaft, net in
Out
mout ,
mout ,
energyout
energyout
FIGURE 5–55
In a typical engineering problem, the
control volume may contain many
inlets and outlets; energy flows in
at each inlet, and energy flows out
at each outlet. Energy also enters
the control volume through net heat
transfer and net shaft work.
Substituting the surface integral for the rate of pressure work from Eq. 5–51
into Eq. 5–55 and combining it with the surface integral on the right give
! !
#
#
d
P
Qnet,in 2 Wshaft,net out 5
er dV 1
a 1 ebr(Vr · n ) dA
r
dt CV
CS
#
#
(5–56)
This is a very convenient form for the energy equation since pressure work is
now combined with the energy of the fluid crossing the control surface and
we no longer have to deal with pressure work.
The term P/r 5 Pv 5 wflow is the flow work, which is the work associated with pushing a fluid into or out of a control volume per unit mass. Note
that the fluid velocity at a solid surface is equal to the velocity of the solid
surface because of the no-slip condition and is zero for nonmoving surfaces.
As a result, the pressure work along the portions of the control surface that
coincide with nonmoving solid surfaces is zero. Therefore, pressure work for
fixed control volumes can exist only along the imaginary part of the control
surface where the fluid enters and leaves the control volume (i.e., inlets and
outlets).
This equation is not in a convenient form for solving practical engineering problems because of the integrals, and thus it is desirable to rewrite it in
terms of average velocities and mass flow rates through inlets and outlets.
If P/r 1 e is nearly uniform across an inlet or outlet, we can simply take it
#
outside the integral. Noting that m 5
! !
# r(V · n ) dA is the mass flow rate
r
c
Ac
across an inlet or outlet, the rate of inflow or outflow of energy through the
#
inlet or outlet can be approximated as m(P/r 1 e). Then the energy equation
becomes (Fig. 5–55)
#
#
d
# P
# P
Qnet,in 2 Wshaft,net out 5
er dV 1 a m a 1 eb 2 a m a 1 eb
r
r
dt CV
out
in
#
(5–57)
where e 5 u 1 V 2/2 1 gz is the total energy per unit mass for both the control volume and flow streams. Then,
#
#
d
V2
V2
# P
# P
Qnet,in 2 Wshaft,net out 5
er dV 1 a m a 1 u 1
1 gzb 2 a m a 1 u 1
1 gzb
r
r
dt CV
2
2
out
in
#
(5–58)
or
#
#
d
V2
V2
#
#
Qnet,in 2 Wshaft,net out 5
er dV 1 a m ah 1
1 gzb 2 a m ah 1
1 gzb
dt CV
2
2
out
in
#
(5–59)
where we used the definition of enthalpy h 5 u 1 Pv 5 u 1 P/r. The last
two equations are fairly general expressions of conservation of energy, but
their use is still limited to uniform flow at inlets and outlets and negligible
work due to viscous forces and other effects. Also, the subscript “net,in”
stands for “net input,” and thus any heat or work transfer is positive if to the
system and negative if from the system.
251
CHAPTER 5
SUMMARY
The conservation of mass principle states that the net mass
transfer to or from a system during a process is equal to the
net change (increase or decrease) in the total mass of the
system during that process, and is expressed as
#
#
min 2 mout 5 Dmsystem and min 2 mout 5 dmsystem/dt
where Dmsystem 5 mfinal 2 minitial is the change in the mass of
#
#
the system during the process, m in and m out are the total rates
of mass flow into and out of the system, and dmsystemydt is
the rate of change of mass within the system boundaries. The
relations above are also referred to as the mass balance and
are applicable to any system undergoing any kind of process.
The amount of mass flowing through a cross section per
unit time is called the mass flow rate, and is expressed as
#
m 5 rVA
Thermodynamic processes involving control volumes can
be considered in two groups: steady-flow processes and
unsteady-flow processes. During a steady-flow process, the
fluid flows through the control volume steadily, experiencing no change with time at a fixed position. The mass and
energy content of the control volume remain constant during a steady-flow process. Taking heat transfer to the system
and work done by the system to be positive quantities, the
conservation of mass and energy equations for steady-flow
processes are expressed as
#
#
am 5 am
in
out
#
#
V2
V2
#
#
Q 2 W 5 a m ah 1
1 gzb 2 a m ah 1
1 gzb
2
2
out
in
for each exit
where r 5 density of fluid, V 5 average fluid velocity normal
to A, and A 5 cross-sectional area normal to flow direction.
The volume of the fluid flowing through a cross section per
unit time is called the volume flow rate and is expressed as
#
#
V 5 VA 5 m/r
The work required to push a unit mass of fluid into or out
of a control volume is called flow work or flow energy, and
is expressed as wflow 5 Pv. In the analysis of control volumes, it is convenient to combine the flow energy and internal energy into enthalpy. Then the total energy of a flowing
fluid is expressed as
u 5 h 1 ke 1 pe 5 h 1
V2
1 gz
2
The total energy transported by a flowing fluid of mass m
with uniform properties is mu. The rate of energy transport
#
#
by a fluid with a mass flow rate of m is mu. When the kinetic
and potential energies of a fluid stream are negligible, the
amount
and rate of energy transport become Emass5 mh and
#
#
Emass 5 m h, respectively.
The first law of thermodynamics is essentially an expression of the conservation of energy principle, also called the
energy balance. The general mass and energy balances for
any system undergoing any process can be expressed as
Ein 2 Eout
5
Net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
DEsystem
Change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
It can also be expressed in the rate form as
Ein 2 Eout
Rate of net energy transfer
by heat, work, and mass
5
dEsystem /dt
Rate of change in internal, kinetic,
potential, etc., energies
for each inlet
These are the most general forms of the equations for
steady-flow processes. For single-stream (one-inlet–one-exit)
systems such as nozzles, diffusers, turbines, compressors,
and pumps, they simplify to
1
1
#
#
V1 A1 5
V A
m1 5 m 2 h
v1
v2 2 2
V 22 2 V 21
#
#
#
Q 2 W 5 m c h2 2 h1 1
1 g(z2 2 z1)d
2
In these relations, subscripts 1 and 2 denote the inlet and
exit states, respectively.
Most unsteady-flow processes can be modeled as a
uniform-flow process, which requires that the fluid flow at
any inlet or exit is uniform and steady, and thus the fluid
properties do not change with time or position over the cross
section of an inlet or exit. If they do, they are averaged and
treated as constants for the entire process. When kinetic and
potential energy changes associated with the control volume
and the fluid streams are negligible, the mass and energy
balance relations for a uniform-flow system are expressed as
min 2 mout 5 Dmsystem
Q 2 W 5 a mh 2 a mh 1 (m2u2 2 m1u1)system
out
in
where Q 5 Qnet,in 5 Qin 2 Qout is the net heat input and
W 5 Wnet,out 5 Wout 2 Win is the net work output.
When solving thermodynamic problems, it is recommended
that the general form of the energy balance Ein 2 Eout 5
DEsystem be used for all problems, and simplify it for the particular problem instead of using the specific relations given
here for different processes.
252
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
REFERENCES AND SUGGESTED READINGS
1. ASHRAE Handbook of Fundamentals. SI version. Atlanta,
GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and AirConditioning Engineers, Inc., 1993.
3. Y. A. Çengel and J. M. Cimbala, Fluid Mechanics:
Fundamentals and Applications, 3rd ed. New York:
McGraw-Hill, 2014.
2. ASHRAE Handbook of Refrigeration. SI version. Atlanta,
GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and AirConditioning Engineers, Inc., 1994.
PROBLEMS*
Conservation of Mass
5–1C When is the flow through a control volume steady?
5–2C Define mass and volume flow rates. How are they
related to each other?
5–3C Does the amount of mass entering a control volume
have to be equal to the amount of mass leaving during an
unsteady-flow process?
5–4C Consider a device with one inlet and one outlet. If the
volume flow rates at the inlet and at the outlet are the same,
is the flow through this device necessarily steady? Why?
5–5 The ventilating fan of the bathroom of a building has
a volume flow rate of 30 L/s and runs continuously. If the
density of air inside is 1.20 kg/m3, determine the mass of air
vented out in one day.
5–6E Air whose density is 0.078 lbm/ft3 enters the duct of an
air-conditioning system at a volume flow rate of 450 ft3/min.
If the diameter of the duct is 10 in, determine the velocity of
the air at the duct inlet and the mass flow rate of air.
5–8E A steady-flow compressor is used to compress helium
from 15 psia and 708F at the inlet to 200 psia and 6008F at the
outlet. The outlet area and velocity are 0.01 ft2 and 100 ft/s,
respectively, and the inlet velocity is 50 ft/s. Determine the mass
flow rate and the inlet area. Answers: 0.0704 lbm/s, 0.133 ft2
5–9 A 2-m3 rigid tank initially contains air whose density is
1.18 kg/m3. The tank is connected to a high-pressure supply line
through a valve. The valve is opened, and air is allowed to enter
the tank until the density in the tank rises to 5.30 kg/m3. Determine the mass of air that has entered the tank. Answer: 8.24 kg
5–10 A cyclone separator like that in Fig. P5–10 is used
to remove fine solid particles, such as fly ash, that are suspended in a gas stream. In the flue-gas system of an electrical power plant, the weight fraction of fly ash in the exhaust
gases is approximately 0.001. Determine the mass flow rates
at the two outlets (flue gas and fly ash) when 10 kg/s of
flue gas and ash mixture enters this unit. Also determine the
amount of fly ash collected per year.
5–7 Air enters a 28-cm diameter pipe steadily at 200 kPa
and 208C with a velocity of 5 m/s. Air is heated as it flows,
and leaves the pipe at 180 kPa and 408C. Determine (a) the
volume flow rate of air at the inlet, (b) the mass flow rate of
air, and (c) the velocity and volume flow rate at the exit.
Air
200 kPa
20°C
5 m/s
Flue gas
Q
180 kPa
40°C
Flue gas and ash
FIGURE P5–7
* Problems designated by a “C” are concept questions, and
students are encouraged to answer them all. Problems designated
by an “E” are in English units, and the SI users can ignore them.
Problems with the
icon are solved using EES, and complete
solutions together with parametric studies are included on the text
website. Problems with the
icon are comprehensive in nature,
and are intended to be solved with an equation solver such as EES.
Ash
FIGURE P5–10
253
CHAPTER 5
5–11 A spherical hot-air balloon is initially filled with air at
120 kPa and 208C with an initial diameter of 5 m. Air enters
this balloon at 120 kPa and 208C with a velocity of 3 m/s
through a 1-m diameter opening. How many minutes will
it take to inflate this balloon to a 15-m diameter when the
pressure and temperature of the air in the balloon remain the
same as the air entering the balloon? Answer: 12.0 min
5–13 A pump increases the water pressure from 100 kPa at
the inlet to 900 kPa at the outlet. Water enters this pump at
158C through a 1-cm-diameter opening and exits through a
1.5-cm-diameter opening. Determine the velocity of the water
at the inlet and outlet when the mass flow rate through the
pump is 0.5 kg/s. Will these velocities change significantly if
the inlet temperature is raised to 408C?
900 kPa
Water
100 kPa
15°C
FIGURE P5–13
5–14 Refrigerant-134a enters a 28-cm-diameter pipe
steadily at 200 kPa and 208C with a velocity of 5 m/s. The
refrigerant gains heat as it flows and leaves the pipe at
180 kPa and 408C. Determine (a) the volume flow rate of the
refrigerant at the inlet, (b) the mass flow rate of the refrigerant, and (c) the velocity and volume flow rate at the exit.
FIGURE P5–11
©Photo Link/Getty Images RF
5–12 A desktop computer is to be cooled by a fan whose
flow rate is 0.34 m3/min. Determine the mass flow rate of
air through the fan at an elevation of 3400 m where the air
density is 0.7 kg/m3. Also, if the average velocity of air is not
to exceed 110 m/min, determine the diameter of the casing of
the fan. Answers: 0.238 kg/min, 0.063 m
5–15 A smoking lounge is to accommodate 15 heavy
smokers. The minimum fresh air requirement for smoking
lounges is specified to be 30 L/s per person (ASHRAE, Standard 62, 1989). Determine the minimum required flow rate
of fresh air that needs to be supplied to the lounge, and the
diameter of the duct if the air velocity is not to exceed 8 m/s.
Smoking
lounge
15 smokers
Fan
Air
outlet
Air
inlet
Exhaust
fan
FIGURE P5–12
FIGURE P5–15
5–16 Consider a 300-L storage tank of a solar water heating
system initially filled with warm water at 458C. Warm water
is withdrawn from the tank through a 2-cm diameter hose at
an average velocity of 0.5 m/s while cold water enters the
tank at 208C at a rate of 15 L/min. Determine the amount of
water in the tank after a 20-minute period. Assume the pressure in the tank remains constant at 1 atm. Answer: 189 kg
254
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
from the nozzle is estimated to be 6.5 Btu/lbm of air flowing. The inlet area of the nozzle is 0.1 ft2. Determine
(a) the exit temperature of air and (b) the exit area of the
nozzle. Answers: (a) 507 R, (b) 0.048 ft2
Cold water
20°C
15 L/min
300 L
45°C
Warm water
45°C
0.5 m/s
FIGURE P5–16
Flow Work and Energy Transfer by Mass
5–17C What is flow energy? Do fluids at rest possess any
flow energy?
5–27E The stators in a gas turbine are designed to increase
the kinetic energy of the gas passing through them adiabatically. Air enters a set of these nozzles at 300 psia and 7008F
with a velocity of 80 ft/s and exits at 250 psia and 6458F.
Calculate the velocity at the exit of the nozzles.
5–28 The diffuser in a jet engine is designed to decrease the
kinetic energy of the air entering the engine compressor without any work or heat interactions. Calculate the velocity at the
exit of a diffuser when air at 100 kPa and 308C enters it with
a velocity of 350 m/s and the exit state is 200 kPa and 908C.
5–18C How do the energies of a flowing fluid and a fluid
at rest compare? Name the specific forms of energy associated with each case.
5–19 A house is maintained at 1 atm and 248C, and warm air
inside a house is forced to leave the house at a rate of 150 m3/h
as a result of outdoor air at 58C infiltrating into the house
through the cracks. Determine the rate of net energy loss of the
house due to mass transfer. Answer: 0.945 kW
5–20E A water pump increases the water pressure from
15 psia to 80 psia. Determine the flow work, in Btu/lbm,
required by the pump.
5–21 Refrigerant-134a enters the compressor of a refrigeration system as saturated vapor at 0.14 MPa, and leaves as
superheated vapor at 0.8 MPa and 608C at a rate of 0.06 kg/s.
Determine the rates of energy transfers by mass into and out
of the compressor. Assume the kinetic and potential energies
to be negligible.
5–22E Steam is leaving a pressure cooker whose operating pressure is 20 psia. It is observed that the amount of
liquid in the cooker has decreased by 0.6 gal in 45 minutes
after the steady operating conditions are established, and the
cross-sectional area of the exit opening is 0.15 in2. Determine (a) the mass flow rate of the steam and the exit velocity,
(b) the total and flow energies of the steam per unit mass, and
(c) the rate at which energy is leaving the cooker by steam.
FIGURE P5–28
©Stockbyte/Punchstock RF
5–29 Air at 600 kPa and 500 K enters an adiabatic nozzle
that has an inlet-to-exit area ratio of 2:1 with a velocity of
120 m/s and leaves with a velocity of 380 m/s. Determine
(a) the exit temperature and (b) the exit pressure of the
air. Answers: (a) 437 K, (b) 331 kPa
5–30 Steam enters a nozzle at 4008C and 800 kPa with a
velocity of 10 m/s, and leaves at 3008C and 200 kPa while
losing heat at a rate of 25 kW. For an inlet area of 800 cm2,
determine the velocity and the volume flow rate of the steam
at the nozzle exit. Answers: 606 m/s, 2.74 m3/s
Steady-Flow Energy Balance: Nozzles and Diffusers
400°C
800 kPa
10 m/s
5–23C A diffuser is an adiabatic device that decreases the
kinetic energy of the fluid by slowing it down. What happens
to this lost kinetic energy?
•
Q
5–24C The kinetic energy of a fluid increases as it is accelerated in an adiabatic nozzle. Where does this energy come from?
5–25C Is heat transfer to or from the fluid desirable as it
flows through a nozzle? How will heat transfer affect the
fluid velocity at the nozzle exit?
5–26E Air enters a nozzle steadily at 50 psia, 1408F, and
150 ft/s and leaves at 14.7 psia and 900 ft/s. The heat loss
300°C
200 kPa
Steam
FIGURE P5–30
5–31
Steam at 3 MPa and 4008C enters an adiabatic
nozzle steadily with a velocity of 40 m/s and
leaves at 2.5 MPa and 300 m/s. Determine (a) the exit temperature and (b) the ratio of the inlet to exit area A1/A2.
255
CHAPTER 5
5–32E Air at 13 psia and 658F enters an adiabatic diffuser
steadily with a velocity of 750 ft/s and leaves with a low
velocity at a pressure of 14.5 psia. The exit area of the diffuser is 3 times the inlet area. Determine (a) the exit temperature and (b) the exit velocity of the air.
Turbines and Compressors
5–40C Consider an air compressor operating steadily. How
would you compare the volume flow rates of the air at the
compressor inlet and exit?
5–41C Will the temperature of air rise as it is compressed
by an adiabatic compressor? Why?
P1 = 13 psia
T1 = 65°F
V1 = 750 ft/s
Air
P2 = 14.5 psia
V2 << V1
A2 = 3A1
FIGURE P5–32E
5–33 Carbon dioxide enters an adiabatic nozzle steadily at
1 MPa and 5008C with a mass flow rate of 6000 kg/h and
leaves at 100 kPa and 450 m/s. The inlet area of the nozzle
is 40 cm2. Determine (a) the inlet velocity and (b) the exit
temperature. Answers: (a) 60.8 m/s, (b) 686 K
5–34 Refrigerant-134a at 700 kPa and 1208C enters an adiabatic nozzle steadily with a velocity of 20 m/s and leaves at
400 kPa and 308C. Determine (a) the exit velocity and (b) the
ratio of the inlet to exit area A1/A2.
5–35 Nitrogen gas at 60 kPa and 78C enters an adiabatic
diffuser steadily with a velocity of 275 m/s and leaves at 85
kPa and 278C. Determine (a) the exit velocity of the nitrogen
and (b) the ratio of the inlet to exit area A1/A2.
5–36
Reconsider Prob. 5–35. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the inlet velocity on the exit velocity and the ratio of the inlet-to-exit area.
Let the inlet velocity vary from 210 to 350 m/s. Plot the final
results against the inlet velocity, and discuss the results.
5–37 Refrigerant-134a enters a diffuser steadily as saturated
vapor at 600 kPa with a velocity of 160 m/s, and it leaves at
700 kPa and 408C. The refrigerant is gaining heat at a rate
of 2 kJ/s as it passes through the diffuser. If the exit area
is 80 percent greater than the inlet area, determine (a) the
exit velocity and (b) the mass flow rate of the refrigerant.
5–42C Somebody proposes the following system to cool a
house in the summer: Compress the regular outdoor air, let it
cool back to the outdoor temperature, pass it through a turbine, and discharge the cold air leaving the turbine into the
house. From a thermodynamic point of view, is the proposed
system sound?
5–43E Air flows steadily through an adiabatic turbine,
entering at 150 psia, 9008F, and 350 ft/s and leaving at
20 psia, 3008F, and 700 ft/s. The inlet area of the turbine is
0.1 ft2. Determine (a) the mass flow rate of the air and (b) the
power output of the turbine.
5–44 Refrigerant-134a enters an adiabatic compressor as
saturated vapor at 2248C and leaves at 0.8 MPa and 608C.
The mass flow rate of the refrigerant is 1.2 kg/s. Determine
(a) the power input to the compressor and (b) the volume
flow rate of the refrigerant at the compressor inlet.
5–45 Refrigerant-134a enters a compressor at 180 kPa as
a saturated vapor with a flow rate of 0.35 m3/min and leaves
at 700 kPa. The power supplied to the refrigerant during
compression process is 2.35 kW. What is the temperature of
R-134a at the exit of the compressor? Answer: 48.98C
5–46 Steam flows steadily through an adiabatic turbine. The
inlet conditions of the steam are 4 MPa, 5008C, and 80 m/s, and
the exit conditions are 30 kPa, 92 percent quality, and 50 m/s.
The mass flow rate of the steam is 12 kg/s. Determine (a) the
change in kinetic energy, (b) the power output, and (c) the turbine
inlet area. Answers: (a) 21.95 k J/kg, (b) 12.1 MW, (c) 0.0130 m2
P1 = 4 MPa
T1 = 500°C
V1 = 80 m/s
Answers: (a) 82.1 m/s, (b) 0.298 kg/s
5–38 Steam at 4 MPa and 4008C enters a nozzle steadily
with a velocity of 60 m/s, and it leaves at 2 MPa and 3008C.
The inlet area of the nozzle is 50 cm2, and heat is being lost
at a rate of 75 kJ/s. Determine (a) the mass flow rate of the
steam, (b) the exit velocity of the steam, and (c) the exit area
of the nozzle.
5–39 Air at 80 kPa, 278C, and 220 m/s enters a diffuser at
a rate of 2.5 kg/s and leaves at 428C. The exit area of the diffuser is 400 cm2. The air is estimated to lose heat at a rate of
18 kJ/s during this process. Determine (a) the exit velocity
and (b) the exit pressure of the air. Answers: (a) 62.0 m/s,
(b) 91.1 kPa
Steam
m
˙ = 12 kg/s
·
Wout
P2 = 30 kPa
x2 = 0.92
V2 = 50 m/s
FIGURE P5–46
256
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
5–47
Reconsider Prob. 5–46. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the turbine
exit pressure on the power output of the turbine. Let the exit
pressure vary from 10 to 200 kPa. Plot the power output
against the exit pressure, and discuss the results.
5–48 Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 10 MPa and
5008C and leaves at 10 kPa with a quality of 90 percent.
Neglecting the changes in kinetic and potential energies,
determine the mass flow rate required for a power output of
5 MW. Answer: 4.852 kg/s
5–49E Steam flows steadily through a turbine at a rate of
45,000 lbm/h, entering at 1000 psia and 9008F and leaving at
5 psia as saturated vapor. If the power generated by the turbine is 4 MW, determine the rate of heat loss from the steam.
5–50 Helium is to be compressed from 105 kPa and 295 K
to 700 kPa and 460 K. A heat loss of 15 kJ/kg occurs during
the compression process. Neglecting kinetic energy changes,
determine the power input required for a mass flow rate of
60 kg/min.
15 kJ/kg
P2 = 700 kPa
T2 = 460 K
He
m· = 60 kg/min
Let the cooling rate vary from 0 to 100 Btu/lbm. Plot the air
exit temperature against the rate of cooling, and discuss the
results.
5–54 An adiabatic gas turbine expands air at 1300 kPa and
5008C to 100 kPa and 1278C. Air enters the turbine through
a 0.2-m2 opening with an average velocity of 40 m/s, and
exhausts through a 1-m2 opening. Determine (a) the mass
flow rate of air through the turbine and (b) the power produced by the turbine. Answers: (a) 46.9 kg/s, (b) 18.3 MW
5–55 Steam enters a steady-flow turbine with a mass flow
rate of 13 kg/s at 6008C, 8 MPa, and a negligible velocity.
The steam expands in the turbine to a saturated vapor at
300 kPa where 10 percent of the steam is removed for some
other use. The remainder of the steam continues to expand to
the turbine exit where the pressure is 10 kPa and quality is 85
percent. If the turbine is adiabatic, determine the rate of work
done by the steam during this process. Answer: 17.8 MW
8 MPa
600°C
13 kg/s
Steam
13 kg/s
·
Win
P1 = 105 kPa
T1 = 295 K
FIGURE P5–50
5–51 Carbon dioxide enters an adiabatic compressor at
100 kPa and 300 K at a rate of 0.5 kg/s and leaves at 600 kPa
and 450 K. Neglecting kinetic energy changes, determine
(a) the volume flow rate of the carbon dioxide at the compressor inlet and (b) the power input to the compressor.
Answers: (a) 0.28 m3/s, (b) 68.8 kW
5–52E Air is compressed from 14.7 psia and 608F to a pressure of 150 psia while being cooled at a rate of 10 Btu/lbm
by circulating water through the compressor casing. The volume flow rate of the air at the inlet conditions is 5000 ft3/min,
and the power input to the compressor is 700 hp. Determine
(a) the mass flow rate of the air and (b) the temperature at the
compressor exit. Answers: (a) 6.36 lbm/s, (b) 801 R
5–53E
Reconsider Prob. 5–52E. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the rate of
cooling of the compressor on the exit temperature of air.
0.3 MPa
1.3 kg/s
sat. vap.
10 kPa
x = 0.85
FIGURE P5–55
5–56 Steam flows steadily into a turbine with a mass
flow rate of 26 kg/s and a negligible velocity at 6 MPa and
6008C. The steam leaves the turbine at 0.5 MPa and 2008C
with a velocity of 180 m/s. The rate of work done by the
steam in the turbine is measured to be 20 MW. If the elevation change between the turbine inlet and exit is negligible,
determine the rate of heat transfer associated with this process. Answer: 455 kW
5–57 Air enters the compressor of a gas-turbine plant at
ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 258C with a low velocity
and exits at 1 MPa and 3478C with a velocity of 90 m/s. The
compressor is cooled at a rate of 1500 kJ/min, and the power
input to the compressor is 250 kW. Determine the mass flow
rate of air through the compressor.
257
CHAPTER 5
Throttling Valves
5–58C Why are throttling devices commonly used in refrigeration and air-conditioning applications?
5–59C Would you expect the temperature of air to drop as
it undergoes a steady-flow throttling process? Explain.
5–60C Would you expect the temperature of a liquid to
change as it is throttled? Explain.
5–61C During a throttling process, the temperature of a
fluid drops from 30 to 2208C. Can this process occur adiabatically?
5–62 Refrigerant-134a is throttled from the saturated liquid
state at 700 kPa to a pressure of 160 kPa. Determine the temperature drop during this process and the final specific volume of the refrigerant. Answers: 42.38C, 0.0345 m3/kg
P1 = 700 kPa
sat. liquid
pressure of steam on the exit temperature after throttling. Let
the exit pressure vary from 6 to 1 MPa. Plot the exit temperature of steam against the exit pressure, and discuss the results.
5–67E Refrigerant-134a enters the expansion valve of
a refrigeration system at 120 psia as a saturated liquid and
leaves at 20 psia. Determine the temperature and internal
energy changes across the valve.
Mixing Chambers and Heat Exchangers
5–68C Consider a steady-flow mixing process. Under what
conditions will the energy transported into the control volume
by the incoming streams be equal to the energy transported
out of it by the outgoing stream?
5–69C Consider a steady-flow heat exchanger involving
two different fluid streams. Under what conditions will the
amount of heat lost by one fluid be equal to the amount of
heat gained by the other?
5–70C When two fluid streams are mixed in a mixing
chamber, can the mixture temperature be lower than the temperature of both streams? Explain.
5–71 Liquid water at 300 kPa and 208C is heated in a
chamber by mixing it with superheated steam at 300 kPa
and 3008C. Cold water enters the chamber at a rate of
1.8 kg/s. If the mixture leaves the mixing chamber at 608C,
determine the mass flow rate of the superheated steam
required. Answer: 0.107 kg/s
R-134a
P2 = 160 kPa
FIGURE P5–62
5–63 Saturated liquid-vapor mixture of water, called wet
steam, in a steam line at 1500 kPa is throttled to 50 kPa and
1008C. What is the quality in the steam line? Answer: 0.944
Throttling valve
Steam
1.5 MPa
50 kPa
100°C
5–72 In steam power plants, open feedwater heaters are
frequently utilized to heat the feedwater by mixing it with
steam bled off the turbine at some intermediate stage. Consider an open feedwater heater that operates at a pressure of
1000 kPa. Feedwater at 508C and 1000 kPa is to be heated
with superheated steam at 2008C and 1000 kPa. In an ideal
feedwater heater, the mixture leaves the heater as saturated
liquid at the feedwater pressure. Determine the ratio of the
mass flow rates of the feedwater and the superheated vapor
for this case. Answer: 3.73
. T1 = 5
m
0°C
1
H2O
FIGURE P5–63
5–64
Refrigerant-134a at 800 kPa and 258C is throttled to a temperature of 2208C. Determine the
pressure and the internal energy of the refrigerant at the final
state. Answers: 133 kPa, 80.7 kJ/kg
5–65 A well-insulated valve is used to throttle steam from
8 MPa and 3508C to 2 MPa. Determine the final temperature
of the steam. Answer: 2858C
5–66
Reconsider Prob. 5–65. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the exit
C
00°
=2
.2
T2
(P = 1000 kPa)
sat.
liquid
m
FIGURE P5–72
5–73E Water at 658F and 20 psia is heated in a chamber
by mixing it with saturated water vapor at 20 psia. If both
streams enter the mixing chamber at the same mass flow
258
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
rate, determine the temperature and the quality of the exiting
stream. Answers: 2288F, 0.415
Air
95 kPa
20°C
0.6 m3/s
5–74 A stream of refrigerant-134a at 1 MPa and 208C is
mixed with another stream at 1 MPa and 808C. If the mass
flow rate of the cold stream is twice that of the hot one,
determine the temperature and the quality of the exit stream.
5–75
Reconsider Prob. 5–74. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the mass flow
rate of the cold stream of R-134a on the temperature and the
quality of the exit stream. Let the ratio of the mass flow rate
of the cold stream to that of the hot stream vary from 1 to 4.
Plot the mixture temperature and quality against the cold-tohot mass flow rate ratio, and discuss the results.
5–76 A heat exchanger is to heat water (cp 5 4.18 kJ/kg·8C)
from 25 to 608C at a rate of 0.2 kg/s. The heating is to be
accomplished by geothermal water (cp 5 4.31 kJ/kg·8C)
available at 1408C at a mass flow rate of 0.3 kg/s. Determine
the rate of heat transfer in the heat exchanger and the exit
temperature of geothermal water.
5–77E Steam is to be condensed on the shell side of a heat
exchanger at 758F. Cooling water enters the tubes at 508F
at a rate of 45 lbm/s and leaves at 658F. Assuming the heat
exchanger to be well-insulated, determine the rate of heat
transfer in the heat exchanger and the rate of condensation
of the steam.
5–78 A thin-walled double-pipe counter-flow heat exchanger is used to cool oil (cp 5 2.20 kJ/kg·8C) from 150 to 408C
at a rate of 2 kg/s by water (cp 5 4.18 kJ/kg·8C) that enters at
228C at a rate of 1.5 kg/s. Determine the rate of heat transfer
in the heat exchanger and the exit temperature of water.
Exhaust gases
0.95 kg/s
95°C
FIGURE P5–79
5–80E
In a steam heating system, air is heated by
being passed over some tubes through which
steam flows steadily. Steam enters the heat exchanger at
30 psia and 4008F at a rate of 15 lbm/min and leaves at
25 psia and 2128F. Air enters at 14.7 psia and 808F and leaves
at 1308F. Determine the volume flow rate of air at the inlet.
5–81 Refrigerant-134a at 1 MPa and 908C is to be cooled
to 1 MPa and 308C in a condenser by air. The air enters at
100 kPa and 278C with a volume flow rate of 600 m3/min
and leaves at 95 kPa and 608C. Determine the mass flow rate
of the refrigerant. Answer: 100 kg/min
R-134a
Air
∙
V3 = 600 m3/min
P3 = 100 kPa
T3 = 27°C
P1 = 1 MPa
T1 = 90°C
P4 = 95 kPa
T4 = 60°C
P2 = 1 MPa
T2 = 30°C
FIGURE P5–81
FIGURE P5–78
5–79 Air (cp 5 1.005 kJ/kg·8C) is to be preheated by
hot exhaust gases in a cross-flow heat exchanger before it
enters the furnace. Air enters the heat exchanger at 95 kPa
and 208C at a rate of 0.6 m3/s. The combustion gases (cp 5
1.10 kJ/kg·8C) enter at 1608C at a rate of 0.95 kg/s and leave
at 958C. Determine the rate of heat transfer to the air and its
outlet temperature.
5–82E Air enters the evaporator section of a window air
conditioner at 14.7 psia and 908F with a volume flow rate
of 200 ft3/min. Refrigerant-134a at 20 psia with a quality of
30 percent enters the evaporator at a rate of 4 lbm/min and
leaves as saturated vapor at the same pressure. Determine
(a) the exit temperature of the air and (b) the rate of heat
transfer from the air.
5–83 An air-conditioning system involves the mixing of
cold air and warm outdoor air before the mixture is routed
to the conditioned room in steady operation. Cold air enters
the mixing chamber at 78C and 105 kPa at a rate of 0.55 m3/s
while warm air enters at 348C and 105 kPa. The air leaves the
259
CHAPTER 5
room at 248C. The ratio of the mass flow rates of the hot to
cold air streams is 1.6. Using variable specific heats, determine (a) the mixture temperature at the inlet of the room and
(b) the rate of heat gain of the room.
water from a nearby lake, which enters the tubes of the
condenser at 188C at a rate of 101 kg/s and leaves at 278C.
Determine the rate of condensation of the steam in the condenser. Answer: 1.60 kg/s
Steam
50°C
Cold air
7°C
Room
Cooling
water
24°C
18°C
Warm air
34°C
FIGURE P5–83
27°C
5–84 Hot exhaust gases of an internal combustion engine
are to be used to produce saturated water vapor at 2 MPa
pressure. The exhaust gases enter the heat exchanger at
4008C at a rate of 32 kg/min while water enters at 158C. The
heat exchanger is not well insulated, and it is estimated that
10 percent of heat given up by the exhaust gases is lost to the
surroundings. If the mass flow rate of the exhaust gases is 15
times that of the water, determine (a) the temperature of the
exhaust gases at the heat exchanger exit and (b) the rate of
heat transfer to the water. Use the constant specific heat properties of air for the exhaust gases.
.
Q
Exhaust
gases
400°C
Heat
exchanger
2 MPa
sat. vap.
Water
15°C
FIGURE P5–84
5–85 The evaporator of a refrigeration cycle is basically
a heat exchanger in which a refrigerant is evaporated by
absorbing heat from a fluid. Refrigerant-22 enters an evaporator at 200 kPa with a quality of 22 percent and a flow rate
of 2.65 L/h. R-22 leaves the evaporator at the same pressure
superheated by 58C. The refrigerant is evaporated by absorbing heat from air whose flow rate is 0.75 kg/s. Determine
(a) the rate of heat absorbed from the air and (b) the temperature change of air. The properties of R-22 at the inlet and exit
of the condenser are h1 5 220.2 kJ/kg, v1 5 0.0253 m3/kg,
and h2 5 398.0 kJ/kg.
5–86 Steam is to be condensed in the condenser of a
steam power plant at a temperature of 508C with cooling
50°C
FIGURE P5–86
5–87
Reconsider Prob. 5–86. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the inlet temperature of cooling water on the rate of condensation of
steam. Let the inlet temperature vary from 10 to 208C, and
assume the exit temperature to remain constant. Plot the rate
of condensation of steam against the inlet temperature of the
cooling water, and discuss the results.
5–88 Two mass streams of the same ideal gas are mixed in
a steady-flow chamber while receiving energy by heat transfer from the surroundings. The mixing process takes place
at constant pressure with no work and negligible changes in
kinetic and potential energies. Assume the gas has constant
specific heats.
(a) Determine the expression for the final temperature of the
mixture in terms of the rate of heat transfer to the mixing
chamber and the inlet and exit mass flow rates.
(b) Obtain an expression for the volume flow rate at the exit
of the mixing chamber in terms of the volume flow rates
of the two inlet streams and the rate of heat transfer to the
mixing chamber.
(c) For the special case of adiabetic mixing, show that the
exit volume flow rate is the sum of the two inlet volume
flow rates.
Pipe and Duct Flow
5–89E Water enters a boiler at 500 psia as a saturated liquid and leaves at 6008F at the same pressure. Calculate the
heat transfer per unit mass of water.
260
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
5–90 A 110-volt electrical heater is used to warm 0.3 m3/s
of air at 100 kPa and 158C to 100 kPa and 308C. How much
current in amperes must be supplied to this heater?
5–91E The fan on a personal computer draws 0.3 ft3/s of
air at 14.7 psia and 708F through the box containing the
CPU and other components. Air leaves at 14.7 psia and 838F.
Calculate the electrical power, in kW, dissipated by the PC
components. Answer: 0.0740 kW
5–96 Repeat Prob. 5–95 for a circular horizontal duct of
diameter 20 cm.
5–97 Consider a hollow-core printed circuit board 9 cm
high and 18 cm long, dissipating a total of 15 W. The width
of the air gap in the middle of the PCB is 0.25 cm. If the
cooling air enters the 12-cm-wide core at 258C and 1 atm at
a rate of 0.8 L/s, determine the average temperature at which
the air leaves the hollow core. Answer: 46.08C
5–98 A computer cooled by a fan contains eight PCBs,
each dissipating 10 W power. The height of the PCBs is
12 cm and the length is 18 cm. The cooling air is supplied by
a 25-W fan mounted at the inlet. If the temperature rise of air
as it flows through the case of the computer is not to exceed
108C, determine (a) the flow rate of the air that the fan needs
to deliver and (b) the fraction of the temperature rise of air
that is due to the heat generated by the fan and its motor.
Answers: (a) 0.0104 kg/s, (b) 24 percent
FIGURE P5–91E
Air
outlet
©PhotoDisc/Getty Images RF
5–92E Water enters the tubes of a cold plate at 708F with an
average velocity of 40 ft/min and leaves at 1058F. The diameter
of the tubes is 0.25 in. Assuming 15 percent of the heat generated
is dissipated from the components to the surroundings by convection and radiation, and the remaining 85 percent is removed by
the cooling water, determine the amount of heat generated by the
electronic devices mounted on the cold plate. Answer: 614 W
5–93 A sealed electronic box is to be cooled by tap water
flowing through the channels on two of its sides. It is specified that the temperature rise of the water not exceed 48C.
The power dissipation of the box is 2 kW, which is removed
entirely by water. If the box operates 24 hours a day, 365 days
a year, determine the mass flow rate of water flowing through
the box and the amount of cooling water used per year.
5–94
Repeat Prob. 5–93 for a power dissipation of 4 kW.
5–95
The components of an electronic system dissipating 180 W are located in a 1.4-m-long horizontal duct whose cross section is 20 cm 3 20 cm. The components in the duct are cooled by forced air that enters the
duct at 308C and 1 atm at a rate of 0.6 m3/min and leaves at
408C. Determine the rate of heat transfer from the outer surfaces of the duct to the ambient. Answer: 63 W
Natural
convection
40°C
180 W
30°C
0.6 m3/min
FIGURE P5–95
1.4 m
Air
inlet
PCB, 10 W
FIGURE P5–98
5–99 A 4-m 3 5-m 3 6-m room is to be heated by an electric resistance heater placed in a short duct in the room. Initially, the room is at 158C, and the local atmospheric pressure is
98 kPa. The room is losing heat steadily to the outside at a rate
of 150 kJ/min. A 200-W fan circulates the air steadily through
the duct and the electric heater at an average mass flow rate of
40 kg/min. The duct can be assumed to be adiabatic, and there is
no air leaking in or out of the room. If it takes 20 min for the
room air to reach an average temperature of 258C, find (a) the
power rating of the electric heater and (b) the temperature rise
that the air experiences each time it passes through the heater.
5–100 A long roll of 2-m-wide and 0.5-cm-thick
1-Mn manganese steel plate (r 5 7854 kg/m3 and cp 5
0.434 kJ/kg·8C) coming off a furnace at 8208C is to be
quenched in an oil bath at 458C to a temperature of 51.18C.
If the metal sheet is moving at a steady velocity of 10 m/min,
determine the required rate of heat removal from the oil to
keep its temperature constant at 458C. Answer: 4368 kW
261
CHAPTER 5
Furnace
Steel
plate
10 m/min
5–107 Water is heated in an insulated, constant-diameter
tube by a 7-kW electric resistance heater. If the water enters
the heater steadily at 208C and leaves at 758C, determine the
mass flow rate of water.
Oil bath, 45°C
FIGURE P5–100
5–101
Reconsider Prob. 5–100. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the moving
velocity of the steel plate on the rate of heat transfer from
the oil bath. Let the velocity vary from 5 to 50 m/min. Plot
the rate of heat transfer against the plate velocity, and discuss
the results.
5–102E The hot-water needs of a household are to be met
by heating water at 558F to 1808F by a parabolic solar collector at a rate of 4 lbm/s. Water flows through a 1.25-indiameter thin aluminum tube whose outer surface is blackanodized in order to maximize its solar absorption ability.
The centerline of the tube coincides with the focal line of the
collector, and a glass sleeve is placed outside the tube to minimize the heat losses. If solar energy is transferred to water
at a net rate of 400 Btu/h per ft length of the tube, determine
the required length of the parabolic collector to meet the hotwater requirements of this house.
5–103 A house has an electric heating system that consists
of a 300-W fan and an electric resistance heating element
placed in a duct. Air flows steadily through the duct at a rate
of 0.6 kg/s and experiences a temperature rise of 78C. The
rate of heat loss from the air in the duct is estimated to be
300 W. Determine the power rating of the electric resistance
heating element. Answer: 4.22 kW
5–104 Steam enters a long, horizontal pipe with an inlet
diameter of D1 5 16 cm at 2 MPa and 3008C with a velocity
of 2.5 m/s. Farther downstream, the conditions are 1.8 MPa
and 2508C, and the diameter is D2 5 14 cm. Determine
(a) the mass flow rate of the steam and (b) the rate of heat
transfer. Answers: (a) 0.401 kg/s, (b) 45.1 kJ/s
5–105 Refrigerant-134a enters the condenser of a refrigerator at 900 kPa and 608C, and leaves as a saturated liquid
at the same pressure. Determine the heat transfer from the
refrigerant per unit mass.
qout
900 kPa
60°C
FIGURE P5–105
R-134a
5–106 Saturated liquid water is heated at constant pressure
in a steady-flow device until it is a saturated vapor. Calculate
the heat transfer, in kJ/kg, when the vaporization is done at a
pressure of 500 kPa.
900 kPa
sat. liq.
5–108 Air at 300 K and 100 kPa steadily flows into a hair
dryer having electrical work input of 1500 W. Because of the
size of the air intake, the inlet velocity of the air is negligible.
The air temperature and velocity at the hair dryer exit are
808C and 21 m/s, respectively. The flow process is both constant pressure and adiabatic. Assume air has constant specific
heats evaluated at 300 K. (a) Determine the air mass flow
rate into the hair dryer, in kg/s. (b) Determine the air volume
flow rate at the hair dryer exit, in m3/s.
Answers: (a) 0.0280 kg/s, (b) 0.0284 m3/s
T2 = 80°C
P1 = 100 kPa
T1 = 300 K
V2 = 21 m/s
·
We = 1500 W
FIGURE P5–108
5–109
Reconsider Prob. 5–108. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the exit
velocity on the mass flow rate and the exit volume flow rate.
Let the exit velocity vary from 5 to 25 m/s. Plot the mass
flow rate and exit volume flow rate against the exit velocity,
and discuss the results.
5–110E Air enters the duct of an air-conditioning system
at 15 psia and 508F at a volume flow rate of 450 ft3/min. The
diameter of the duct is 10 in, and heat is transferred to the air
in the duct from the surroundings at a rate of 2 Btu/s. Determine (a) the velocity of the air at the duct inlet and (b) the
temperature of the air at the exit.
Charging and Discharging Processes
5–111 A rigid, insulated tank that is initially evacuated is
connected through a valve to a supply line that carries steam
at 4 MPa. Now the valve is opened, and steam is allowed to
flow into the tank until the pressure reaches 4 MPa, at which
point the valve is closed. If the final temperature of the steam
in the tank is 5508C, determine the temperature of the steam
in the supply line and the flow work per unit mass of the
steam.
262
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
5–112 A 2-m3 rigid insulated tank initially containing saturated water vapor at 1 MPa is connected through a valve to
a supply line that carries steam at 4008C. Now the valve is
opened, and steam is allowed to flow slowly into the tank
until the pressure in the tank rises to 2 MPa. At this instant
the tank temperature is measured to be 3008C. Determine the
mass of the steam that has entered and the pressure of the
steam in the supply line.
Air
100 kPa
22°C
35 L
evacuated
400°C
Steam
FIGURE P5–114
5–115 A 0.2-m3 rigid tank equipped with a pressure regulator contains steam at 2 MPa and 3008C. The steam in the
tank is now heated. The regulator keeps the steam pressure
constant by letting out some steam, but the temperature
inside rises. Determine the amount of heat transferred when
the steam temperature reaches 5008C.
Sat. vapor
2 m3
1 MPa
FIGURE P5–112
5–113 A rigid, insulated tank that is initially evacuated is connected through a valve to a supply line that
carries helium at 200 kPa and 1208C. Now the valve is
opened, and helium is allowed to flow into the tank until
the pressure reaches 200 kPa, at which point the valve is
closed. Determine the flow work of the helium in the supply line and the final temperature of the helium in the
tank. Answers: 816 kJ/kg, 655 K
5–116E A 3-ft3 rigid tank initially contains saturated water
vapor at 3008F. The tank is connected by a valve to a supply line that carries steam at 200 psia and 4008F. Now the
valve is opened, and steam is allowed to enter the tank.
Heat transfer takes place with the surroundings such that
the temperature in the tank remains constant at 3008F at all
times. The valve is closed when it is observed that one-half
of the volume of the tank is occupied by liquid water. Find
(a) the final pressure in the tank, (b) the amount of steam
that has entered the tank, and (c) the amount of heat transfer.
Answers: (a) 67.03 psia, (b) 85.74 lbm, (c ) 80,900 Btu
Helium
200 kPa, 120°C
5–117 A 4-L pressure cooker has an operating pressure of
175 kPa. Initially, one-half of the volume is filled with liquid
and the other half with vapor. If it is desired that the pressure cooker not run out of liquid water for 1 h, determine the
highest rate of heat transfer allowed.
Initially
evacuated
FIGURE P5–113
5–114 Consider a 35-L evacuated rigid bottle that is surrounded by the atmosphere at 100 kPa and 228C. A valve
at the neck of the bottle is now opened and the atmospheric
air is allowed to flow into the bottle. The air trapped in
the bottle eventually reaches thermal equilibrium with the
atmosphere as a result of heat transfer through the wall
of the bottle. The valve remains open during the process
so that the trapped air also reaches mechanical equilibrium with the atmosphere. Determine the net heat transfer
through the wall of the bottle during this filling process.
Answer: 3.50 kJ
V=4L
(P = 175 kPa)
·
Qin
FIGURE P5–117
263
CHAPTER 5
5–118 An insulated, vertical piston–cylinder device
initially contains 10 kg of water, 6 kg of which is in the
vapor phase. The mass of the piston is such that it maintains a constant pressure of 200 kPa inside the cylinder.
Now steam at 0.5 MPa and 3508C is allowed to enter the
cylinder from a supply line until all the liquid in the cylinder has vaporized. Determine (a) the final temperature in
the cylinder and (b) the mass of the steam that has entered.
Answers: (a) 120.28C, (b) 19.07 kg
P = 200 kPa
m1 = 10 kg
H2O
Pi = 0.5 MPa
Determine the mass of oxygen used and the total heat transfer to the tanks.
5–122 A 0.06-m3 rigid tank initially contains refrigerant-134a
at 0.8 MPa and 100 percent quality. The tank is connected by
a valve to a supply line that carries refrigerant-134a at 1.2 MPa
and 368C. Now the valve is opened, and the refrigerant is
allowed to enter the tank. The valve is closed when it is observed
that the tank contains saturated liquid at 1.2 MPa. Determine
(a) the mass of the refrigerant that has entered the tank and
(b) the amount of heat transfer. Answers: (a) 64.8 kg, (b) 627 kJ
5–123 A 0.3-m3 rigid tank is filled with saturated liquid
water at 2008C. A valve at the bottom of the tank is opened,
and liquid is withdrawn from the tank. Heat is transferred to
the water such that the temperature in the tank remains constant. Determine the amount of heat that must be transferred
by the time one-half of the total mass has been withdrawn.
Ti = 350°C
FIGURE P5–118
5–119E A scuba diver’s 2-ft3 air tank is to be filled with air
from a compressed air line at 120 psia and 858F. Initially, the
air in this tank is at 20 psia and 608F. Presuming that the tank
is well insulated, determine the temperature and mass in the
tank when it is filled to 120 psia.
5–120 An air-conditioning system is to be filled from a
rigid container that initially contains 5 kg of liquid R-134a
at 248C. The valve connecting this container to the air-conditioning system is now opened until the mass in the container
is 0.25 kg, at which time the valve is closed. During this
time, only liquid R-134a flows from the container. Presuming
that the process is isothermal while the valve is open, determine the final quality of the R-134a in the container and the
total heat transfer. Answers: 0.506, 22.6 kJ
A-C line
Qin
H2O
V = 0.3 m3
T = 200°C
sat. liquid
1
me = – m1
2
FIGURE P5–123
5–124E A 2-ft3 rigid tank contains saturated refrigerant134a at 160 psia. Initially, 5 percent of the volume is occupied by liquid and the rest by vapor. A valve at the top of the
tank is now opened, and vapor is allowed to escape slowly
from the tank. Heat is transferred to the refrigerant such that
the pressure inside the tank remains constant. The valve is
closed when the last drop of liquid in the tank is vaporized.
Determine the total heat transfer for this process.
Liquid R-134a
5 kg
24°C
R-134a
FIGURE P5–120
5–121E Oxygen is supplied to a medical facility from ten
1.5-ft3 compressed oxygen tanks. Initially, these tanks are at
1500 psia and 808F. The oxygen is removed from these tanks
slowly enough that the temperature in the tanks remains at
808F. After two weeks, the pressure in the tanks is 300 psia.
Sat. mixture
P = 160 psia
V = 2 ft3
FIGURE P5–124E
Qin
264
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
5–125 A 0.3-m3 rigid tank initially contains refrigerant134a at 148C. At this state, 55 percent of the mass is in the
vapor phase, and the rest is in the liquid phase. The tank is
connected by a valve to a supply line where refrigerant at
1.4 MPa and 1008C flows steadily. Now the valve is opened
slightly, and the refrigerant is allowed to enter the tank.
When the pressure in the tank reaches 1 MPa, the entire
refrigerant in the tank exists in the vapor phase only. At this
point the valve is closed. Determine (a) the final temperature in the tank, (b) the mass of refrigerant that has entered
the tank, and (c) the heat transfer between the system and the
surroundings.
the final volume of the balloon and work produced by the air
inside the balloon as it expands the balloon skin.
5–126 A balloon that initially contains 50 m3 of steam at
100 kPa and 1508C is connected by a valve to a large reservoir that supplies steam at 150 kPa and 2008C. Now the
valve is opened, and steam is allowed to enter the balloon
until the pressure equilibrium with the steam at the supply
line is reached. The material of the balloon is such that its
volume increases linearly with pressure. Heat transfer also
takes place between the balloon and the surroundings, and
the mass of the steam in the balloon doubles at the end of the
process. Determine the final temperature and the boundary
work during this process.
Steam
150 kPa
200°C
Steam
50 m3
100 kPa
150°C
FIGURE P5–126
5–127 The air-release flap on a hot-air balloon is used to
release hot air from the balloon when appropriate. On one
hot-air balloon, the air release opening has an area of 0.5 m2,
and the filling opening has an area of 1 m2. During a two
minute adiabatic flight maneuver, hot air enters the balloon at
100 kPa and 358C with a velocity of 2 m/s; the air in the balloon remains at 100 kPa and 358C; and air leaves the balloon
through the air-release flap at velocity 1 m/s. At the start of
this maneuver, the volume of the balloon is 75 m3. Determine
FIGURE P5–127
©Photo Link/Getty Images RF
5–128 An insulated 0.15-m3 tank contains helium at 3 MPa
and 1308C. A valve is now opened, allowing some helium to
escape. The valve is closed when one-half of the initial mass
has escaped. Determine the final temperature and pressure in
the tank. Answers: 257 K, 956 kPa
5–129E An insulated 40-ft3 rigid tank contains air at 50 psia
and 1208F. A valve connected to the tank is now opened, and
air is allowed to escape until the pressure inside drops to
25 psia. The air temperature during this process is maintained
constant by an electric resistance heater placed in the tank.
Determine the electrical work done during this process.
Air
V = 40 ft3
P = 50 psia
We,in
T = 120°F
FIGURE P5–129E
5–130 A vertical piston–cylinder device initially contains
0.2 m3 of air at 208C. The mass of the piston is such that
265
CHAPTER 5
it maintains a constant pressure of 300 kPa inside. Now a
valve connected to the cylinder is opened, and air is allowed
to escape until the volume inside the cylinder is decreased by
one-half. Heat transfer takes place during the process so that
the temperature of the air in the cylinder remains constant.
Determine (a) the amount of air that has left the cylinder and
(b) the amount of heat transfer. Answers: (a) 0.357 kg, (b) 0
5–131 A vertical piston–cylinder device initially contains
0.25 m3 of air at 600 kPa and 3008C. A valve connected to
the cylinder is now opened, and air is allowed to escape until
three-quarters of the mass leave the cylinder at which point
the volume is 0.05 m3. Determine the final temperature in the
cylinder and the boundary work during this process.
Air
0.25 m3
600 kPa
300°C
5–134 An insulated vertical piston–cylinder device initially
contains 0.8 m3 of refrigerant-134a at 1.4 MPa and 1208C.
A linear spring at this point applies full force to the piston. A
valve connected to the cylinder is now opened, and refrigerant is allowed to escape. The spring unwinds as the piston
moves down, and the pressure and volume drop to 0.7 MPa
and 0.5 m3 at the end of the process. Determine (a) the
amount of refrigerant that has escaped and (b) the final temperature of the refrigerant.
Air
FIGURE P5–134
FIGURE P5–131
5–132 A vertical piston–cylinder device initially contains
0.01 m3 of steam at 2008C. The mass of the frictionless piston is such that it maintains a constant pressure of 500 kPa
inside. Now steam at 1 MPa and 3508C is allowed to enter
the cylinder from a supply line until the volume inside doubles. Neglecting any heat transfer that may have taken place
during the process, determine (a) the final temperature of the
steam in the cylinder and (b) the amount of mass that has
entered. Answers: (a) 261.78C, (b) 0.0176 kg
5–133 The air in an insulated, rigid compressed-air tank
whose volume is 0.5 m3 is initially at 4000 kPa and 208C.
Enough air is now released from the tank to reduce the pressure to 2000 kPa. Following this release, what is the temperature of the remaining air in the tank?
Review Problems
5–135 The air in a 6-m 3 5-m 3 4-m hospital room is to
be completely replaced by conditioned air every 15 min. If
the average air velocity in the circular air duct leading to the
room is not to exceed 5 m/s, determine the minimum diameter of the duct.
5–136 A long roll of 1-m-wide and 0.5-cm-thick 1-Mn
manganese steel plate (r 5 7854 kg/m3) coming off a furnace
is to be quenched in an oil bath to a specified temperature. If
the metal sheet is moving at a steady velocity of 10 m/min,
determine the mass flow rate of the steel plate through the
oil bath.
Furnace
Steel
plate
10 m/min
Oil bath
FIGURE P5–136
5–137 Air at 4.18 kg/m3 enters a nozzle that has an inletto-exit area ratio of 2:1 with a velocity of 120 m/s and leaves
with a velocity of 380 m/s. Determine the density of air at the
exit. Answer: 2.64 kg/m3
FIGURE P5–133
©C Squared Studios/Getty Images RF
5–138 An air compressor compresses 15 L/s of air at 120 kPa
and 208C to 800 kPa and 3008C while consuming 6.2 kW of
266
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
power. How much of this power is being used to increase the
pressure of the air versus the power needed to move the fluid
through the compressor? Answers: 4.48 kW, 1.72 kW
amount of 26 kJ for every kilogram of steam flowing through
the nozzle. Determine (a) the exit velocity of the steam and
(b) the mass flow rate of the steam at the nozzle entrance if
the nozzle exit area is 0.001 m2.
5–139 Saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 348C is to be
condensed as it flows in a 1-cm-diameter tube at a rate of
0.1 kg/min. Determine the rate of heat transfer from the
refrigerant. What would your answer be if the condensed
refrigerant is cooled to 208C?
5–146 In a gas-fired boiler, water is boiled at 1808C by hot
gases flowing through a stainless steel pipe submerged in
water. If the rate of heat transfer from the hot gases to water
is 48 kJ/s, determine the rate of evaporation of water.
5–140 A steam turbine operates with 1.6 MPa and 3508C
steam at its inlet and saturated vapor at 308C at its exit. The
mass flow rate of the steam is 22 kg/s, and the turbine produces 12,350 kW of power. Determine the rate at which heat
is lost through the casing of this turbine.
5–147 Saturated steam at 1 atm condenses on a vertical
plate that is maintained at 908C by circulating cooling water
through the other side. If the rate of heat transfer by condensation to the plate is 180 kJ/s, determine the rate at which the
condensate drips off the plate at the bottom.
1.6 MPa
350°C
22 kg/s
90°C
1 atm
Steam
Heat
Turbine
m·
30°C
sat. vapor
FIGURE P5–140
5–141E Nitrogen gas flows through a long, constant-diameter adiabatic pipe. It enters at 100 psia and 1208F and leaves
at 50 psia and 708F. Calculate the velocity of the nitrogen at
the pipe’s inlet and outlet.
5–142 A 110-V electric hot-water heater warms 0.1 L/s of
water from 18 to 308C. Calculate the current in amperes that
must be supplied to this heater. Answer: 45.6 A
5–143 Steam enters a long, insulated pipe at 1200 kPa,
2508C, and 4 m/s, and exits at 1000 kPa. The diameter of the
pipe is 0.15 m at the inlet, and 0.1 m at the exit. Calculate the
mass flow rate of the steam and its speed at the pipe outlet.
5–144 Air enters a pipe at 658C and 200 kPa and leaves at
608C and 175 kPa. It is estimated that heat is lost from the
pipe in the amount of 3.3 kJ per kg of air flowing in the pipe.
The diameter ratio for the pipe is D1/D2 5 1.4. Using constant specific heats for air, determine the inlet and exit velocities of the air. Answers: 29.9 m/s, 66.1 m/s
5–145 Steam enters a nozzle with a low velocity at 1508C
and 200 kPa, and leaves as a saturated vapor at 75 kPa. There
is a heat transfer from the nozzle to the surroundings in the
FIGURE P5–147
5–148E The condenser of a steam power plant operates at a
pressure of 0.95 psia. The condenser consists of 144 horizontal tubes arranged in a 12 3 12 square array. Steam condenses
on the outer surfaces of the tubes whose inner and outer diameters are 1 in and 1.2 in, respectively. If steam is to be condensed at a rate of 6800 lbm/h and the temperature rise of the
cooling water is limited to 88F, determine (a) the rate of heat
transfer from the steam to the cooling water and (b) the average velocity of the cooling water through the tubes.
5–149 In large steam power plants, the feedwater is frequently heated in a closed feedwater heater by using steam
extracted from the turbine at some stage. Steam enters the
feedwater heater at 1 MPa and 2008C and leaves as saturated
liquid at the same pressure. Feedwater enters the heater at
2.5 MPa and 508C and leaves at 108C below the exit temperature of the steam. Determine the ratio of the mass flow rates
of the extracted steam and the feedwater.
5–150 Cold water enters a steam generator at 208C and
leaves as saturated vapor at 2008C. Determine the fraction of
heat used in the steam generator to preheat the liquid water
from 208C to the saturation temperature of 2008C.
5–151 Cold water enters a steam generator at 208C and
leaves as saturated vapor at the boiler pressure. At what
267
CHAPTER 5
pressure will the amount of heat needed to preheat the water
to saturation temperature be equal to the heat needed to
vaporize the liquid at the boiler pressure?
5–152 An ideal gas expands in an adiabatic turbine from
1200 K and 900 kPa to 800 K. Determine the turbine inlet
volume flow rate of the gas, in m3/s, required to produce
turbine work output at the rate of 650 kW. The average
values of the specific heats for this gas over the temperature range and the gas constant are cp 5 1.13 kJ/kg·K, cv 5
0.83 kJ/kg·K, and R 5 0.30 kJ/kg·K.
5–153 Chickens with an average mass of 2.2 kg and
average specific heat of 3.54 kJ/kg·8C are to be cooled by
chilled water that enters a continuous-flow-type immersion
chiller at 0.58C. Chickens are dropped into the chiller at a
uniform temperature of 158C at a rate of 500 chickens per
hour and are cooled to an average temperature of 38C before
they are taken out. The chiller gains heat from the surroundings at a rate of 200 kJ/h. Determine (a) the rate of heat
removal from the chickens, in kW, and (b) the mass flow
rate of water, in kg/s, if the temperature rise of water is not
to exceed 28C.
Qout
Flour
Water
15°C
Cooling
section
Dough
5–156 A glass bottle washing facility uses a well-agitated
hot-water bath at 508C that is placed on the ground. The bottles enter at a rate of 450 per minute at an ambient temperature of 208C and leave at the water temperature. Each bottle
has a mass of 150 g and removes 0.2 g of water as it leaves
the bath wet. Make-up water is supplied at 158C. Disregarding any heat losses from the outer surfaces of the bath, determine the rate at which (a) water and (b) heat must be supplied to maintain steady operation.
5–157 The heat of hydration of dough, which is 15 kJ/kg,
will raise its temperature to undesirable levels unless some
cooling mechanism is utilized. A practical way of absorbing the heat of hydration is to use refrigerated water when
kneading the dough. If a recipe calls for mixing 2 kg of
flour with 1 kg of water, and the temperature of the city
water is 158C, determine the temperature to which the city
water must be cooled before mixing in order for the water
to absorb the entire heat of hydration when the water temperature rises to 158C. Take the specific heats of the flour
and the water to be 1.76 and 4.18 kJ/kg·8C, respectively.
Answer: 4.28C
Dough
FIGURE P5–157
5–158 Long aluminum wires of diameter 5 mm (r 5 2702
kg/m3 and cp 5 0.896 kJ/kg·8C) are extruded at a temperature
of 3508C and are cooled to 508C in atmospheric air at 258C.
If the wire is extruded at a velocity of 8 m/min, determine the
rate of heat transfer from the wire to the extrusion room.
350°C
Tair = 25°C
8 m/min
5–154 Repeat Prob. 5–153 assuming heat gain of the chiller
is negligible.
5–155E A refrigeration system is being designed to cool
eggs ( r 5 67.4 lbm/ft3 and cp 5 0.80 Btu/lbm·8F) with an
average mass of 0.14 lbm from an initial temperature of 908F
to a final average temperature of 508F by air at 348F at a
rate of 10,000 eggs per hour. Determine (a) the rate of heat
removal from the eggs, in Btu/h and (b) the required volume
flow rate of air, in ft3/h, if the temperature rise of air is not to
exceed 108F.
15 kJ/kg
Aluminum
wire
FIGURE P5–158
5–159 Repeat Prob. 5–158 for a copper wire (r 5 8950 kg/m3
and cp 5 0.383 kJ/kg·8C).
5–160E Steam at 80 psia and 4008F is mixed with water at
608F and 80 psia steadily in an adiabatic device. Steam enters
the device at a rate of 0.05 lbm/s, while the water enters at
1 lbm/s. Determine the temperature of the mixture leaving
this device when the outlet pressure is 80 psia. Answer: 1178F
5–161 A constant-pressure R-134a vapor separation unit
separates the liquid and vapor portions of a saturated mixture
into two separate outlet streams. Determine the flow power
needed to pass 6 L/s of R-134a at 320 kPa and 55 percent
quality through this unit. What is the mass flow rate, in kg/s,
of the two outlet streams?
Liquid-vapor
mixture
Saturated
vapor
1
2
Vapor separation unit
3
Saturated
liquid
FIGURE P5–161
268
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
5–163E It is well established that indoor air quality (IAQ) has a
significant effect on general health and productivity of employees
at a workplace. A study showed that enhancing IAQ by increasing the building ventilation from 5 cfm (cubic feet per minute)
to 20 cfm increased the productivity by 0.25 percent, valued at
$90 per person per year, and decreased the respiratory illnesses
by 10 percent for an average annual savings of $39 per person
while increasing the annual energy consumption by $6 and the
equipment cost by about $4 per person per year (ASHRAE Journal, December 1998). For a workplace with 120 employees,
determine the net monetary benefit of installing an enhanced IAQ
system to the employer per year. Answer: $14,280/yr
5–164 The ventilating fan of the bathroom of a building
has a volume flow rate of 30 L/s and runs continuously. The
building is located in San Francisco, California, where the
average winter temperature is 12.28C, and is maintained at
228C at all times. The building is heated by electricity whose
unit cost is $0.12/kWh. Determine the amount and cost of the
heat “vented out” per month in winter.
30 L/s
12.2°C
Fan
Bathroom
22°C
5–165E During the inflation and deflation of a safety airbag
in an automobile, the gas enters the airbag with a specific
volume of 15 ft3/lbm and at a mass flow rate that varies with
time as illustrated in Fig. P5–165E. The gas leaves this airbag
with a specific volume of 13 ft3/lbm, with a mass flow rate
that varies with time, as shown in Fig. P5–165E. Plot the volume of this bag (i.e., airbag size) as a function of time, in ft3.
Mass flow rate, lbm/s
5–162 Consider two identical buildings: one in Los Angeles,
California, where the atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa and
the other in Denver, Colorado, where the atmospheric pressure is 83 kPa. Both buildings are maintained at 218C, and
the infiltration rate for both buildings is 1.2 air changes per
hour (ACH). That is, the entire air in the building is replaced
completely by the outdoor air 1.2 times per hour on a day
when the outdoor temperature at both locations is 108C. Disregarding latent heat, determine the ratio of the heat losses by
infiltration at the two cities.
20
In
16
0
Out
10 12
25
30
Time, milliseconds
FIGURE P5–165E
5–166 Determine the rate of sensible heat loss from a building due to infiltration if the outdoor air at 258C and 95 kPa
enters the building at a rate of 60 L/s when the indoors is
maintained at 258C.
5–167 An air-conditioning system requires airflow at the
main supply duct at a rate of 130 m3/min. The average velocity of air in the circular duct is not to exceed 8 m/s to avoid
excessive vibration and pressure drops. Assuming the fan
converts 80 percent of the electrical energy it consumes into
kinetic energy of air, determine the size of the electric motor
needed to drive the fan and the diameter of the main duct.
Take the density of air to be 1.20 kg/m3.
130 m3/min
8 m/s
FIGURE P5–164
50
FIGURE P5–167
269
CHAPTER 5
5–168 The maximum flow rate of standard shower heads
is about 3.5 gpm (13.3 L/min) and can be reduced to
2.75 gpm (10.5 L/min) by switching to low-flow shower
heads that are equipped with flow controllers. Consider a
family of four, with each person taking a 5-min shower
every morning. City water at 158C is heated to 558C in
an electric water heater and tempered to 428C by cold
water at the T-elbow of the shower before being routed
to the shower heads. Assuming a constant specific heat of
4.18 kJ/kg·8C for water, determine (a) the ratio of the flow
rates of the hot and cold water as they enter the T-elbow
and (b) the amount of electricity that will be saved per
year, in kWh, by replacing the standard shower heads by
the low-flow ones.
enters the compressor as a saturated vapor at 108C and leaves
the compressor at 1400 kPa with an enthalpy of 281.39 kJ/kg
and a velocity of 50 m/s. The rate of work done on the refrigerant is measured to be 132.4 kW. If the elevation change
between the compressor inlet and exit is negligible, determine
the rate of heat transfer associated with this process, in kW.
1400 kPa
50 m/s
R-134a
5–169
Reconsider Prob. 5–168. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the inlet temperature of cold water on the energy saved by using the lowflow shower head. Let the inlet temperature vary from 108C
to 208C. Plot the electric energy savings against the water
inlet temperature, and discuss the results.
5–170 An adiabatic air compressor is to be powered
by a direct-coupled adiabatic steam turbine that is also
driving a generator. Steam enters the turbine at 12.5 MPa
and 5008C at a rate of 25 kg/s and exits at 10 kPa and a
quality of 0.92. Air enters the compressor at 98 kPa and
295 K at a rate of 10 kg/s and exits at 1 MPa and 620 K.
Determine the net power delivered to the generator by
the turbine.
1 MPa
620 K
Air
compressor
98 kPa
295 K
12.5 MPa
500°C
5 kg/s
10°C
sat. vap.
FIGURE P5–172
5–173 Submarines change their depth by adding or removing air from rigid ballast tanks, thereby displacing seawater in the tanks. Consider a submarine that has a 700 m3
air-ballast tank originally partially filled with 100 m3 of air
at 1500 kPa and 158C. For the submarine to surface, air at
1500 kPa and 208C is pumped into the ballast tank, until it
is entirely filled with air. The tank is filled so quickly that
the process is adiabatic and the seawater leaves the tank
at 158C. Determine the final temperature and mass of the air
in the ballast tank.
5–174 In Prob. 5-173, presume that air is added to the tank
in such a way that the temperature and pressure of the air
in the tank remain constant. Determine the final mass of the
air in the ballast tank under this condition. Also determine
the total heat transfer while the tank is being filled in this
manner.
Steam
turbine
10 kPa
FIGURE P5–170
5–171 Determine the power input for a compressor that
compresses helium from 110 kPa and 208C to 400 kPa and
2008C. Helium enters this compressor through a 0.1-m2 pipe
at a velocity of 9 m/s.
5–172 Refrigerant 134a enters a compressor with a mass
flow rate of 5 kg/s and a negligible velocity. The refrigerant
5–175 Water flows through a shower head steadily at a rate
of 10 L/min. An electric resistance heater placed in the water
pipe heats the water from 16 to 438C. Taking the density of
water to be 1 kg/L, determine the electric power input to the
heater, in kW.
In an effort to conserve energy, it is proposed to pass the
drained warm water at a temperature of 398C through a heat
exchanger to preheat the incoming cold water. If the heat
exchanger has an effectiveness of 0.50 (that is, it recovers
only half of the energy that can possibly be transferred from
the drained water to incoming cold water), determine the
electric power input required in this case. If the price of the
electric energy is 11.5 ¢/kWh, determine how much money
is saved during a 10-min shower as a result of installing this
heat exchanger.
270
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
Resistance
heater
5–178 A liquid R-134a bottle has an internal volume of
0.0015 m3. Initially it contains 0.55 kg of R-134a (saturated
mixture) at 268C. A valve is opened and R-134a vapor only
(no liquid) is allowed to escape slowly such that temperature remains constant until the mass of R-134a remaining is
0.15 kg. Find the heat transfer necessary with the surroundings to maintain the temperature and pressure of the R-134a
constant.
5–179
Steam enters a turbine steadily at 7 MPa and
6008C with a velocity of 60 m/s and leaves at
25 kPa with a quality of 95 percent. A heat loss of 20 kJ/kg
occurs during the process. The inlet area of the turbine is
150 cm2, and the exit area is 1400 cm2. Determine (a) the
mass flow rate of the steam, (b) the exit velocity, and (c) the
power output.
5–180
FIGURE P5–175
5–176
Reconsider Prob. 5–175. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the heat
exchanger effectiveness on the money saved. Let effectiveness range from 20 to 90 percent. Plot the money saved
against the effectiveness, and discuss the results.
5–177 A tank with an internal volume of 1 m3 contains air at
800 kPa and 258C. A valve on the tank is opened allowing air
to escape and the pressure inside quickly drops to 150 kPa, at
which point the valve is closed. Assume there is negligible heat
transfer from the tank to the air left in the tank.
(a) Using the approximation he < constant 5 he,avg 5
0.5(h1 1 h2), calculate the mass withdrawn during the process.
(b) Consider the same process but broken into two parts. That
is, consider an intermediate state at P2 5 400 kPa, calculate
the mass removed during the process from P1 5 800 kPa to
P2 and then the mass removed during the process from P2 to
P3 5 150 kPa, using the type of approximation used in part
(a), and add the two to get the total mass removed.
(c) Calculate the mass removed if the variation of he is
accounted for.
Reconsider Prob. 5–179. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effects of turbine exit
area and turbine exit pressure on the exit velocity and power
output of the turbine. Let the exit pressure vary from 10 to
50 kPa (with the same quality), and the exit area to vary from
1000 to 3000 cm2. Plot the exit velocity and the power outlet
against the exit pressure for the exit areas of 1000, 2000, and
3000 cm2, and discuss the results.
5–181 In large gas-turbine power plants, air is preheated by
the exhaust gases in a heat exchanger called the regenerator
before it enters the combustion chamber. Air enters
the regenerator at 1 MPa and 550 K at a mass flow rate
of 800 kg/min. Heat is transferred to the air at a rate of
3200 kJ/s. Exhaust gases enter the regenerator at 140 kPa
and 800 K and leave at 130 kPa and 600 K. Treating the
exhaust gases as air, determine (a) the exit temperature of
the air and (b) the mass flow rate of exhaust gases.
Answers: (a) 775 K, (b) 14.9 kg/s
5–182 It is proposed to have a water heater that consists
of an insulated pipe of 7.5-cm diameter and an electric
resistor inside. Cold water at 208C enters the heating section steadily at a rate of 24 L/min. If water is to be heated
to 488C, determine (a) the power rating of the resistance
heater and (b) the average velocity of the water in the
pipe.
5–183
Air
800 kPa
25°C, 1 m3
FIGURE P5–177
An insulated vertical piston–cylinder device
initially contains 0.11 m3 of air at 150 kPa
and 228C. At this state, a linear spring touches the piston
but exerts no force on it. The cylinder is connected by a
valve to a line that supplies air at 700 kPa and 228C. The
valve is opened, and air from the high-pressure line is
allowed to enter the cylinder. The valve is turned off when
the pressure inside the cylinder reaches 600 kPa. If the
enclosed volume inside the cylinder doubles during this
process, determine (a) the mass of air that entered the cylinder, and (b) the final temperature of the air inside the
cylinder.
271
CHAPTER 5
5–186 In a single-flash geothermal power plant, geothermal
water enters the flash chamber (a throttling valve) at 2308C
as a saturated liquid at a rate of 50 kg/s. The steam resulting from the flashing process enters a turbine and leaves at
20 kPa with a moisture content of 5 percent. Determine the
temperature of the steam after the flashing process and the
power output from the turbine if the pressure of the steam
at the exit of the flash chamber is (a) 1 MPa, (b) 500 kPa,
(c) 100 kPa, (d) 50 kPa.
Air
V1 = 0.11 m3
P1 = 150 kPa
T1 = 22°C
Pi = 700 kPa
Ti = 22°C
FIGURE P5–183
(b) 60.7 kJ
5–185 A piston–cylinder device initially contains 1.2 kg
of air at 700 kPa and 2008C. At this state, the piston is
touching on a pair of stops. The mass of the piston is such
that 600-kPa pressure is required to move it. A valve at the
bottom of the tank is opened, and air is withdrawn from the
cylinder. The valve is closed when the volume of the cylinder decreases to 80 percent of the initial volume. If it is
estimated that 40 kJ of heat is lost from the cylinder, determine (a) the final temperature of the air in the cylinder,
(b) the amount of mass that has escaped from the cylinder,
and (c) the work done. Use constant specific heats at the
average temperature.
Q
Air
1.2 kg
700 kPa
200°C
FIGURE P5–185
1
230°C
sat. liq.
5–184 A piston–cylinder device initially contains 2 kg
of refrigerant-134a at 800 kPa and 808C. At this state, the
piston is touching on a pair of stops at the top. The mass
of the piston is such that a 500-kPa pressure is required to
move it. A valve at the bottom of the tank is opened, and
R-134a is withdrawn from the cylinder. After a while, the
piston is observed to move and the valve is closed when
half of the refrigerant is withdrawn from the tank and the
temperature in the tank drops to 208C. Determine (a) the
work done and (b) the heat transfer. Answers: (a) 11.6 kJ,
Separator
Flash
chamber
2
3
Steam
turbine
4
20 kPa
x = 0.95
Liquid
FIGURE P5–186
5–187 The turbocharger of an internal combustion engine
consists of a turbine and a compressor. Hot exhaust gases
flow through the turbine to produce work and the work output from the turbine is used as the work input to the compressor. The pressure of ambient air is increased as it flows
through the compressor before it enters the engine cylinders. Thus, the purpose of a turbocharger is to increase the
pressure of air so that more air gets into the cylinder. Consequently, more fuel can be burned and more power can be
produced by the engine.
In a turbocharger, exhaust gases enter the turbine at 4008C
and 120 kPa at a rate of 0.02 kg/s and leave at 3508C. Air
enters the compressor at 508C and 100 kPa and leaves at
130 kPa at a rate of 0.018 kg/s. The compressor increases
the air pressure with a side effect: It also increases the air
temperature, which increases the possibility of a gasoline
engine to experience an engine knock. To avoid this, an aftercooler is placed after the compressor to cool the warm air by
cold ambient air before it enters the engine cylinders. It is
estimated that the aftercooler must decrease the air temperature below 808C if knock is to be avoided. The cold ambient
air enters the aftercooler at 308C and leaves at 408C. Disregarding any frictional losses in the turbine and the compressor and treating the exhaust gases as air, determine (a) the
temperature of the air at the compressor outlet and (b) the
minimum volume flow rate of ambient air required to avoid
knock.
272
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
5–189 A D0 5 10-m-diameter tank is initially filled with
water 2 m above the center of a D 5 10-cm-diameter valve
near the bottom. The tank surface is open to the atmosphere,
and the tank drains through a L 5 100-m-long pipe connected to the valve. The friction factor of the pipe is given
to be f 5 0.015, and the discharge velocity is expressed as
2gz
where z is the water height above the
V5
Å 1.5 1 fL/D
Air
100 kPa
50°C
350°C
Compressor
Turbine
center of the valve. Determine (a) the initial discharge velocity from the tank and (b) the time required to empty the tank.
The tank can be considered to be empty when the water level
drops to the center of the valve.
130 kPa
Exhaust
gases
120 kPa
400°C
Aftercooler
Cold air
30°C
40°C
FIGURE P5–187
5–188 A building with an internal volume of 400 m3 is to
be heated by a 30-kW electric resistance heater placed in the
duct inside the building. Initially, the air in the building is
at 148C, and the local atmospheric pressure is 95 kPa. The
building is losing heat to the surroundings at a steady rate
of 450 kJ/min. Air is forced to flow through the duct and the
heater steadily by a 250-W fan, and it experiences a temperature rise of 58C each time it passes through the duct, which
may be assumed to be adiabatic.
(a) How long will it take for the air inside the building to
reach an average temperature of 248C?
(b) Determine the average mass flow rate of air through the duct.
Answers: (a) 146 s, (b) 6.02 kg/s
450 kJ/min
T2 = T 1+ 5°C
·
We,in = 30 kW
T1
FIGURE P5–188
·
m
250 W
5–191 Two streams of the same ideal gas having different
mass flow rates and temperatures are mixed in a steady-flow,
adiabatic mixing device. Assuming constant specific heats,
find the simplest expression for the mixture temperature written in the form
#
#
m1 m2
T3 5 f a # , # , T1, T2 b
m3 m3
m· 1, T1
m· 2, T2
Mixing device
m· 3, T3
FIGURE P5–191
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Problems
V = 400 m3
P = 95 kPa
14°C → 24°C
5–190 The velocity of a liquid flowing in a circular pipe
of radius R varies from zero at the wall to a maximum at
the pipe center. The velocity distribution in the pipe can be
represented as V(r), where r is the radial distance from the
pipe center. Based on the definition of mass flow rate m· ,
obtain a relation for the average velocity in terms of V(r),
R, and r.
5–192 Steam is compressed by an adiabatic compressor
from 0.2 MPa and 1508C to 2.5 MPa and 2508C at a rate of
1.30 kg/s. The power input to the compressor is
(a) 144 kW
(b) 234 kW
(c) 438 kW
(d) 717 kW
(e) 901 kW
5–193 Steam enters a diffuser steadily at 0.5 MPa, 3008C,
and 122 m/s at a rate of 3.5 kg/s. The inlet area of the diffuser is
(b) 50 cm2
(c) 105 cm2
(a) 15 cm2
2
2
(d) 150 cm
(e) 190 cm
273
CHAPTER 5
5–194 An adiabatic heat exchanger is used to heat cold
water at 158C entering at a rate of 5 kg/s by hot air at 908C
entering also at a rate of 5 kg/s. If the exit temperature of hot
air is 208C, the exit temperature of cold water is
(a) 278C
(b) 328C
(c) 528C
(d) 858C
(e) 908C
5–195 A heat exchanger is used to heat cold water at 158C
entering at a rate of 2 kg/s by hot air at 858C entering at a
rate of 3 kg/s. The heat exchanger is not insulated and is losing heat at a rate of 25 kJ/s. If the exit temperature of hot air
is 208C, the exit temperature of cold water is
(a) 288C
(b) 358C
(c) 388C
(d) 418C
(e) 808C
5–196 An adiabatic heat exchanger is used to heat cold
water at 158C entering at a rate of 5 kg/s by hot water at 908C
entering at a rate of 4 kg/s. If the exit temperature of hot
water is 508C, the exit temperature of cold water is
(a) 428C
(b) 478C
(c) 558C
(d) 788C
(e) 908C
5–197 In a shower, cold water at 108C flowing at a rate of
5 kg/min is mixed with hot water at 608C flowing at a rate of
2 kg/min. The exit temperature of the mixture is
(a) 24.38C
(b) 35.08C
(c) 40.08C
(d) 44.38C
(e) 55.28C
5–198 In a heating system, cold outdoor air at 78C flowing
at a rate of 4 kg/min is mixed adiabatically with heated air at
708C flowing at a rate of 3 kg/min. The exit temperature of
the mixture is
(a) 348C
(b) 398C
(c) 458C
(d) 638C
(e) 778C
5–199 Hot combustion gases (assumed to have the
properties of air at room temperature) enter a gas turbine
at 1 MPa and 1500 K at a rate of 0.1 kg/s, and exit at
0.2 MPa and 900 K. If heat is lost from the turbine to the
surroundings at a rate of 15 kJ/s, the power output of the
gas turbine is
(a) 15 kW
(b) 30 kW
(c) 45 kW
(d) 60 kW
(e) 75 kW
5–200 Steam expands in a turbine from 4 MPa and 5008C
to 0.5 MPa and 2508C at a rate of 1350 kg/h. Heat is lost
from the turbine at a rate of 25 kJ/s during the process. The
power output of the turbine is
(a) 157 kW
(b) 207 kW
(c) 182 kW
(d) 287 kW
(e) 246 kW
5–201 Steam is compressed by an adiabatic compressor
from 0.2 MPa and 1508C to 0.8 MPa and 3508C at a rate of
1.30 kg/s. The power input to the compressor is
(a) 511 kW
(b) 393 kW
(c) 302 kW
(d) 717 kW
(e) 901 kW
5–202 Refrigerant-134a is compressed by a compressor
from the saturated vapor state at 0.14 MPa to 0.9 MPa and
608C at a rate of 0.108 kg/s. The refrigerant is cooled at a
rate of 1.10 kJ/s during compression. The power input to the
compressor is
(a) 4.94 kW
(b) 6.04 kW
(c) 7.14 kW
(d) 7.50 kW
(e) 8.13 kW
5–203 Refrigerant-134a expands in an adiabatic turbine
from 1.2 MPa and 1008C to 0.18 MPa and 508C at a rate of
1.25 kg/s. The power output of the turbine is
(a) 44.7 kW
(b) 66.4 kW
(c) 72.7 kW
(d) 89.2 kW
(e) 112.0 kW
5–204 Refrigerant-134a at 1.4 MPa and 908C is throttled
to a pressure of 0.6 MPa. The temperature of the refrigerant
after throttling is
(b) 568C
(c) 828C
(a) 228C
(d) 808C
(e) 908C
5–205 Air at 278C and 5 atm is throttled by a valve to
1 atm. If the valve is adiabatic and the change in kinetic
energy is negligible, the exit temperature of air will be
(a) 108C
(b) 158C
(c) 208C
(d) 238C
(e) 278C
5–206 Steam at 1 MPa and 3008C is throttled adiabatically
to a pressure of 0.4 MPa. If the change in kinetic energy is
negligible, the specific volume of the steam after throttling is
(b) 0.233 m3/kg
(c) 0.375 m3/kg
(a) 0.358 m3/kg
3
3
(e) 0.655 m /kg
(d) 0.646 m /kg
5–207 Air is to be heated steadily by an 8-kW electric
resistance heater as it flows through an insulated duct. If the
air enters at 508C at a rate of 2 kg/s, the exit temperature of
air is
(b) 50.08C
(c) 54.08C
(a) 46.08C
(d) 55.48C
(e) 58.08C
Design and Essay Problems
5–208 You have been given the responsibility of picking a steam turbine for an electrical-generation station that
is to produce 300 MW of electrical power that will sell for
$0.05 per kilowatt-hour. The boiler will produce steam at
700 psia and 7008F, and the condenser is planned to operate
at 808F. The cost of generating and condensing the steam is
$0.01 per kilowatt-hour of electricity produced. You have narrowed your selection to the three turbines in the table below.
Your criterion for selection is to pay for the equipment as
quickly as possible. Which turbine should you choose?
Turbine
Capacity
(MW)
A
B
C
50
100
100
h
Cost
($Million)
Operating
Cost
($/kWh)
0.9
0.92
0.93
5
11
10.5
0.01
0.01
0.015
274
MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS
5–209E You are to design a small, directional control
rocket to operate in space by providing as many as 100 bursts
of 5 seconds each with a mass flow rate of 0.5 lbm/s at a
velocity of 400 ft/s. Storage tanks that will contain up to
3000 psia are available, and the tanks will be located in an
environment whose temperature is 408F. Your design criterion
is to minimize the volume of the storage tank. Should you
use a compressed-air or an R-134a system?
5–210 An air cannon uses compressed air to propel a projectile from rest to a final velocity. Consider an air cannon
that is to accelerate a 10-gram projectile to a speed of 300 m/s
using compressed air, whose temperature cannot exceed 208C.
The volume of the storage tank is not to exceed 0.1 m3. Select
the storage volume size and maximum storage pressure that
requires the minimum amount of energy to fill the tank.
5–211 Design a 1200-W electric hair dryer such that the air
temperature and velocity in the dryer will not exceed 508C
and 3 m/s, respectively.
5–212 Design a scalding unit for slaughtered chickens to
loosen their feathers before they are routed to feather-picking
machines with a capacity of 1200 chickens per hour under
the following conditions:
The unit will be of an immersion type filled with hot
water at an average temperature of 538C at all times.
Chicken with an average mass of 2.2 kg and an average
temperature of 368C will be dipped into the tank, held in
the water for 1.5 min, and taken out by a slow-moving conveyor. The chicken is expected to leave the tank 15 percent
heavier as a result of the water that sticks to its surface. The
center-to-center distance between chickens in any direction
will be at least 30 cm. The tank can be as wide as 3 m and
as high as 60 cm. The water is to be circulated through and
heated by a natural gas furnace, but the temperature rise of
water will not exceed 58C as it passes through the furnace.
The water loss is to be made up by the city water at an average temperature of 168C. The walls and the floor of the tank
are well-insulated. The unit operates 24 h a day and 6 days
a week. Assuming reasonable values for the average properties, recommend reasonable values for (a) the mass flow
rate of the makeup water that must be supplied to the tank,
(b) the rate of heat transfer from the water to the chicken,
in kW, (c) the size of the heating system in kJ/h, and (d) the
operating cost of the scalding unit per month for a unit cost
of $1.12/therm of natural gas.
CHAPTER
6
T H E S E C O N D L AW O F
THERMODYNAMICS
T
o this point, we have focused our attention on the first law of thermodynamics, which requires that energy be conserved during a process. In this chapter, we introduce the second law of thermodynamics,
which asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that energy has
quality as well as quantity. A process cannot take place unless it satisfies
both the first and second laws of thermodynamics. In this chapter, the thermal energy reservoirs, reversible and irreversible processes, heat engines,
refrigerators, and heat pumps are introduced first. Various statements of the
second law are followed by a discussion of perpetual-motion machines and
the thermodynamic temperature scale. The Carnot cycle is introduced next,
and the Carnot principles are discussed. Finally, the idealized Carnot heat
engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps are examined.
OBJECTIVES
The objectives of Chapter 6 are to:
■
Introduce the second law of
thermodynamics.
■
Identify valid processes as those
that satisfy both the first and
second laws of thermodynamics.
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
Discuss thermal energy
reservoirs, reversible and
irreversible processes, heat
engines, refrigerators, and heat
pumps.
Describe the Kelvin–Planck
and Clausius statements of the
second law of thermodynamics.
Discuss the concepts of
perpetual-motion machines.
Apply the second law of
thermodynamics to cycles and
cyclic devices.
Apply the second law to develop
the absolute thermodynamic
temperature scale.
Describe the Carnot cycle.
Examine the Carnot principles,
idealized Carnot heat engines,
refrigerators, and heat pumps.
Determine the expressions for
the thermal efficiencies and
coefficients of performance for
reversible heat engines, heat
pumps, and refrigerators.
275
276
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
6–1
Hot
coffee
Heat
FIGURE 6–1
A cup of hot coffee does not get
hotter in a cooler room.
Heat
I=0
FIGURE 6–2
Transferring heat to a wire will not
generate electricity.
Heat
FIGURE 6–3
Transferring heat to a paddle wheel
will not cause it to rotate.
ONE WAY
FIGURE 6–4
Processes occur in a certain direction,
and not in the reverse direction.
Process
1st law
2nd law
FIGURE 6–5
A process must satisfy both the first
and second laws of thermodynamics to
proceed.
■
INTRODUCTION TO THE SECOND LAW
In Chaps. 4 and 5, we applied the first law of thermodynamics, or the conservation of energy principle, to processes involving closed and open systems.
As pointed out repeatedly in those chapters, energy is a conserved property,
and no process is known to have taken place in violation of the first law of
thermodynamics. Therefore, it is reasonable to conclude that a process must
satisfy the first law to occur. However, as explained here, satisfying the first
law alone does not ensure that the process will actually take place.
It is common experience that a cup of hot coffee left in a cooler room
eventually cools off (Fig. 6–1). This process satisfies the first law of thermodynamics since the amount of energy lost by the coffee is equal to the
amount gained by the surrounding air. Now let us consider the reverse
process—the hot coffee getting even hotter in a cooler room as a result of
heat transfer from the room air. We all know that this process never takes
place. Yet, doing so would not violate the first law as long as the amount of
energy lost by the air is equal to the amount gained by the coffee.
As another familiar example, consider the heating of a room by the passage of electric current through a resistor (Fig. 6–2). Again, the first law
dictates that the amount of electric energy supplied to the resistance wires
be equal to the amount of energy transferred to the room air as heat. Now
let us attempt to reverse this process. It will come as no surprise that transferring some heat to the wires does not cause an equivalent amount of electric energy to be generated in the wires.
Finally, consider a paddle-wheel mechanism that is operated by the fall
of a mass (Fig. 6–3). The paddle wheel rotates as the mass falls and stirs a
fluid within an insulated container. As a result, the potential energy of the
mass decreases, and the internal energy of the fluid increases in accordance
with the conservation of energy principle. However, the reverse process,
raising the mass by transferring heat from the fluid to the paddle wheel,
does not occur in nature, although doing so would not violate the first law
of thermodynamics.
It is clear from these arguments that processes proceed in a certain direction and not in the reverse direction (Fig. 6–4). The first law places no
restriction on the direction of a process, but satisfying the first law does
not ensure that the process can actually occur. This inadequacy of the first
law to identify whether a process can take place is remedied by introducing
another general principle, the second law of thermodynamics. We show later
in this chapter that the reverse processes discussed above violate the second
law of thermodynamics. This violation is easily detected with the help of a
property, called entropy, defined in Chap. 7. A process cannot occur unless
it satisfies both the first and the second laws of thermodynamics (Fig. 6–5).
There are numerous valid statements of the second law of thermodynamics. Two such statements are presented and discussed later in this chapter in
relation to some engineering devices that operate on cycles.
The use of the second law of thermodynamics is not limited to identifying the direction of processes. The second law also asserts that energy has
quality as well as quantity. The first law is concerned with the quantity of
energy and the transformations of energy from one form to another with no
regard to its quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern to
277
CHAPTER 6
engineers, and the second law provides the necessary means to determine
the quality as well as the degree of degradation of energy during a process.
As discussed later in this chapter, more of high-temperature energy can be
converted to work, and thus it has a higher quality than the same amount of
energy at a lower temperature.
The second law of thermodynamics is also used in determining the theoretical limits for the performance of commonly used engineering systems,
such as heat engines and refrigerators, as well as predicting the degree of
completion of chemical reactions. The second law is also closely associated
with the concept of perfection. In fact, the second law defines perfection for
thermodynamic processes. It can be used to quantify the level of perfection
of a process, and point the direction to eliminate imperfections effectively.
6–2
■
THERMAL ENERGY RESERVOIRS
In the development of the second law of thermodynamics, it is very convenient to have a hypothetical body with a relatively large thermal energy
capacity (mass 3 specific heat) that can supply or absorb finite amounts of
heat without undergoing any change in temperature. Such a body is called
a thermal energy reservoir, or just a reservoir. In practice, large bodies of
water such as oceans, lakes, and rivers as well as the atmospheric air can
be modeled accurately as thermal energy reservoirs because of their large
thermal energy storage capabilities or thermal masses (Fig. 6–6). The atmosphere, for example, does not warm up as a result of heat losses from residential buildings in winter. Likewise, megajoules of waste energy dumped
in large rivers by power plants do not cause any significant change in water
temperature.
A two-phase system can also be modeled as a reservoir since it can absorb
and release large quantities of heat while remaining at constant temperature.
Another familiar example of a thermal energy reservoir is the industrial furnace. The temperatures of most furnaces are carefully controlled, and they
are capable of supplying large quantities of thermal energy as heat in an
essentially isothermal manner. Therefore, they can be modeled as reservoirs.
A body does not actually have to be very large to be considered a reservoir. Any physical body whose thermal energy capacity is large relative to
the amount of energy it supplies or absorbs can be modeled as one. The air
in a room, for example, can be treated as a reservoir in the analysis of the
heat dissipation from a TV set in the room, since the amount of heat transfer
from the TV set to the room air is not large enough to have a noticeable
effect on the room air temperature.
A reservoir that supplies energy in the form of heat is called a source,
and one that absorbs energy in the form of heat is called a sink (Fig. 6–7).
Thermal energy reservoirs are often referred to as heat reservoirs since
they supply or absorb energy in the form of heat.
Heat transfer from industrial sources to the environment is of major concern to environmentalists as well as to engineers. Irresponsible management
of waste energy can significantly increase the temperature of portions of
the environment, causing what is called thermal pollution. If it is not carefully controlled, thermal pollution can seriously disrupt marine life in lakes
Atmosphere
River
Lake
Ocean
FIGURE 6–6
Bodies with relatively large thermal
masses can be modeled as thermal
energy reservoirs.
Thermal energy
Source
Heat
Heat
Thermal energy
Sink
FIGURE 6–7
A source supplies energy in the form
of heat, and a sink absorbs it.
278
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Work
No work
Heat
6–3
Heat
Water
Water
FIGURE 6–8
Work can always be converted to
heat directly and completely, but the
reverse is not true.
■
HEAT ENGINES
As pointed out earlier, work can easily be converted to other forms of energy,
but converting other forms of energy to work is not that easy. The mechanical work done by the shaft shown in Fig. 6–8, for example, is first converted
to the internal energy of the water. This energy may then leave the water as
heat. We know from experience that any attempt to reverse this process will
fail. That is, transferring heat to the water does not cause the shaft to rotate.
From this and other observations, we conclude that work can be converted
to heat directly and completely, but converting heat to work requires the use
of some special devices. These devices are called heat engines.
Heat engines differ considerably from one another, but all can be characterized by the following (Fig. 6–9):
1. They receive heat from a high-temperature source (solar energy, oil
furnace, nuclear reactor, etc.).
2. They convert part of this heat to work (usually in the form of a rotating
shaft).
3. They reject the remaining waste heat to a low-temperature sink (the
atmosphere, rivers, etc.).
4. They operate on a cycle.
High-temperature
Source
Qin
Heat
engine
and rivers. However, by careful design and management, the waste energy
dumped into large bodies of water can be used to improve the quality of
marine life by keeping the local temperature increases within safe and desirable levels.
Wnet,out
Qout
Low-temperature
Sink
FIGURE 6–9
Part of the heat received by a heat
engine is converted to work, while the
rest is rejected to a sink.
Heat engines and other cyclic devices usually involve a fluid to and from
which heat is transferred while undergoing a cycle. This fluid is called the
working fluid.
The term heat engine is often used in a broader sense to include workproducing devices that do not operate in a thermodynamic cycle. Engines
that involve internal combustion such as gas turbines and car engines fall
into this category. These devices operate in a mechanical cycle but not in a
thermodynamic cycle since the working fluid (the combustion gases) does
not undergo a complete cycle. Instead of being cooled to the initial temperature, the exhaust gases are purged and replaced by fresh air-and-fuel
mixture at the end of the cycle.
The work-producing device that best fits into the definition of a heat
engine is the steam power plant, which is an external-combustion engine.
That is, combustion takes place outside the engine, and the thermal energy
released during this process is transferred to the steam as heat. The schematic of a basic steam power plant is shown in Fig. 6–10. This is a rather
simplified diagram, and the discussion of actual steam power plants is given
in later chapters. The various quantities shown on this figure are as follows:
Qin 5 amount of heat supplied to steam in boiler from a high-temperature source (furnace)
Qout 5 amount of heat rejected from steam in condenser to a lowtemperature sink (the atmosphere, a river, etc.)
Wout 5 amount of work delivered by steam as it expands in turbine
Win 5 amount of work required to compress water to boiler pressure
279
CHAPTER 6
Energy source
(such as a furnace)
System boundary
Qin
Boiler
Win
Wout
Pump
Turbine
Condenser
Qout
Energy sink
(such as the atmosphere)
FIGURE 6–10
Schematic of a steam power plant.
Notice that the directions of the heat and work interactions are indicated
by the subscripts in and out. Therefore, all four of the described quantities
are always positive.
The net work output of this power plant is simply the difference between
the total work output of the plant and the total work input (Fig. 6–11):
Wnet,out 5 Wout 2 Win (kJ)
Wnet,out
Heat
engine
(6–1)
Win
The net work can also be determined from the heat transfer data alone.
The four components of the steam power plant involve mass flow in and
out, and therefore should be treated as open systems. These components,
together with the connecting pipes, however, always contain the same fluid
(not counting the steam that may leak out, of course). No mass enters or
leaves this combination system, which is indicated by the shaded area on
Fig. 6–10; thus, it can be analyzed as a closed system. Recall that for a
closed system undergoing a cycle, the change in internal energy DU is zero,
and therefore the net work output of the system is also equal to the net heat
transfer to the system:
Wnet,out 5 Qin 2 Qout (kJ)
Wout
(6–2)
Thermal Efficiency
In Eq. 6–2, Qout represents the magnitude of the energy wasted in order to
complete the cycle. But Qout is never zero; thus, the net work output of a heat
engine is always less than the amount of heat input. That is, only part of the
FIGURE 6–11
A portion of the work output of a heat
engine is consumed internally to maintain continuous operation.
280
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
heat transferred to the heat engine is converted to work. The fraction of the
heat input that is converted to net work output is a measure of the performance of a heat engine and is called the thermal efficiency hth (Fig. 6–12).
For heat engines, the desired output is the net work output, and the
required input is the amount of heat supplied to the working fluid. Then the
thermal efficiency of a heat engine can be expressed as
Source
Heat input
100 kJ 100 kJ
Net work output
Total heat input
Thermal efficiency 5
1
2
Net
work
output
20 kJ
Waste heat
80 kJ
Sink
Net
work
output
30 kJ
Waste heat
70 kJ
or
hth 5
FIGURE 6–12
Some heat engines perform better than
others (convert more of the heat they
receive to work).
Wnet,out
(6–4)
Qin
It can also be expressed as
hth 5 1 2
hth,2 = 30%
hth,1 = 20%
(6–3)
Qout
(6–5)
Qin
since Wnet,out 5 Qin 2 Qout.
Cyclic devices of practical interest such as heat engines, refrigerators, and
heat pumps operate between a high-temperature medium (or reservoir) at
temperature TH and a low-temperature medium (or reservoir) at temperature
TL. To bring uniformity to the treatment of heat engines, refrigerators, and
heat pumps, we define these two quantities:
QH 5 magnitude of heat transfer between the cyclic device and the hightemperature medium at temperature TH
QL 5 magnitude of heat transfer between the cyclic device and the lowtemperature medium at temperature TL
High-temperature reservoir
at TH
Notice that both QL and QH are defined as magnitudes and therefore are
positive quantities. The direction of QH and QL is easily determined by
inspection. Then, the net work output and thermal efficiency relations for
any heat engine (shown in Fig. 6–13) can also be expressed as
Wnet,out 5 QH 2 QL
QH
and
Wnet,out
HE
QL
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL
FIGURE 6–13
Schematic of a heat engine.
hth 5
Wnet,out
QH
or
hth 5 1 2
QL
QH
(6–6)
The thermal efficiency of a heat engine is always less than unity since both
QL and QH are defined as positive quantities.
Thermal efficiency is a measure of how efficiently a heat engine converts
the heat that it receives to work. Heat engines are built for the purpose of
converting heat to work, and engineers are constantly trying to improve the
efficiencies of these devices since increased efficiency means less fuel consumption and thus lower fuel bills and less pollution.
The thermal efficiencies of work-producing devices are relatively low.
Ordinary spark-ignition automobile engines have a thermal efficiency of
about 25 percent. That is, an automobile engine converts about 25 percent
281
CHAPTER 6
of the chemical energy of the gasoline to mechanical work. This number is
as high as 40 percent for diesel engines and large gas-turbine plants and as
high as 60 percent for large combined gas-steam power plants. Thus, even
with the most efficient heat engines available today, almost one-half of the
energy supplied ends up in the rivers, lakes, or the atmosphere as waste or
useless energy (Fig. 6–14).
Furnace
QH = 100 MJ
Wnet,out = 55 MJ
Can We Save Qout?
HE
In a steam power plant, the condenser is the device where large quantities
of waste heat is rejected to rivers, lakes, or the atmosphere. Then one may
ask, can we not just take the condenser out of the plant and save all that
waste energy? The answer to this question is, unfortunately, a firm no for
the simple reason that without a heat rejection process in a condenser, the
cycle cannot be completed. (Cyclic devices such as steam power plants cannot run continuously unless the cycle is completed.) This is demonstrated
next with the help of a simple heat engine.
Consider the simple heat engine shown in Fig. 6–15 that is used to lift
weights. It consists of a piston–cylinder device with two sets of stops. The
working fluid is the gas contained within the cylinder. Initially, the gas temperature is 308C. The piston, which is loaded with the weights, is resting on
top of the lower stops. Now 100 kJ of heat is transferred to the gas in the
cylinder from a source at 1008C, causing it to expand and to raise the loaded
piston until the piston reaches the upper stops, as shown in the figure. At this
point, the load is removed, and the gas temperature is observed to be 908C.
The work done on the load during this expansion process is equal to
the increase in its potential energy, say 15 kJ. Even under ideal conditions
(weightless piston, no friction, no heat losses, and quasi-equilibrium expansion), the amount of heat supplied to the gas is greater than the work done
since part of the heat supplied is used to raise the temperature of the gas.
Now let us try to answer this question: Is it possible to transfer the 85 kJ
of excess heat at 908C back to the reservoir at 1008C for later use? If it
is, then we will have a heat engine that can have a thermal efficiency of
100 percent under ideal conditions. The answer to this question is again
QL = 45 MJ
The atmosphere
FIGURE 6–14
Even the most efficient heat engines
reject almost one-half of the energy
they receive as waste heat.
(15 kJ)
Load
Load
Gas
90°C
Gas
30°C
Heat in
(100 kJ)
Reservoir at
100°C
Gas
30°C
Heat out
(85 kJ)
Reservoir at
20°C
FIGURE 6–15
A heat-engine cycle cannot be
completed without rejecting some
heat to a low-temperature sink.
282
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
no, for the very simple reason that heat is always transferred from a hightemperature medium to a low-temperature one, and never the other way
around. Therefore, we cannot cool this gas from 90 to 308C by transferring
heat to a reservoir at 1008C. Instead, we have to bring the system into contact with a low-temperature reservoir, say at 208C, so that the gas can return
to its initial state by rejecting its 85 kJ of excess energy as heat to this reservoir. This energy cannot be recycled, and it is properly called waste energy.
We conclude from this discussion that every heat engine must waste some
energy by transferring it to a low-temperature reservoir in order to complete the cycle, even under idealized conditions. The requirement that a heat
engine exchange heat with at least two reservoirs for continuous operation
forms the basis for the Kelvin–Planck expression of the second law of thermodynamics discussed later in this section.
EXAMPLE 6–1
Net Power Production of a Heat Engine
Heat is transferred to a heat engine from a furnace at a rate of 80 MW.
If the rate of waste heat rejection to a nearby river is 50 MW, determine the
net power output and the thermal efficiency for this heat engine.
Furnace
·
QH = 80 MW
·
Wnet,out
HE
SOLUTION The rates of heat transfer to and from a heat engine are given.
The net power output and the thermal efficiency are to be determined.
Assumptions Heat losses through the pipes and other components are
negligible.
Analysis A schematic of the heat engine is given in Fig. 6–16. The furnace
serves as the high-temperature reservoir for this heat engine and the river as
the low-temperature reservoir. The given quantities can be expressed as
#
#
QH 5 80 MW and QL 5 50 MW
·
QL = 50 MW
The net power output of this heat engine is
River
#
#
#
Wnet,out 5 QH 2 QL 5 (80 2 50) MW 5 30 MW
Then the thermal efficiency is easily determined to be
#
Wnet,out
30 MW
hth 5
5
5 0.375 (or 37.5%)
#
80 MW
QH
FIGURE 6–16
Schematic for Example 6–1.
Discussion Note that the heat engine converts 37.5 percent of the heat it
receives to work.
EXAMPLE 6–2
Fuel Consumption Rate of a Car
A car engine with a power output of 65 hp has a thermal efficiency of
24 percent. Determine the fuel consumption rate of this car if the fuel has a
heating value of 19,000 Btu/lbm (that is, 19,000 Btu of energy is released
for each lbm of fuel burned).
SOLUTION The power output and the efficiency of a car engine are given.
The rate of fuel consumption of the car is to be determined.
Assumptions The power output of the car is constant.
283
CHAPTER 6
Analysis A schematic of the car engine is given in Fig. 6–17. The car
engine is powered by converting 24 percent of the chemical energy released
during the combustion process to work. The amount of energy input required
to produce a power output of 65 hp is determined from the definition of
thermal efficiency to be
m· fuel
Combustion chamber
#
Wnet,out
#
65 hp 2545 Btu/h
QH 5
5
a
b 5 689,270 Btu/h
hth
0.24
1 hp
·
QH
·
Wnet,out = 65 hp
Car
engine
(idealized)
To supply energy at this rate, the engine must burn fuel at a rate of
689,270 Btu/h
#
5 36.3 lbm/h
mfuel 5
19,000 Btu/lbm
·
QL
since 19,000 Btu of thermal energy is released for each lbm of fuel burned.
Discussion Note that if the thermal efficiency of the car could be doubled,
the rate of fuel consumption would be reduced by half.
Atmosphere
The Second Law of Thermodynamics:
Kelvin–Planck Statement
FIGURE 6–17
Schematic for Example 6–2.
We have demonstrated earlier with reference to the heat engine shown in
Fig. 6–15 that, even under ideal conditions, a heat engine must reject some
heat to a low-temperature reservoir in order to complete the cycle. That
is, no heat engine can convert all the heat it receives to useful work. This
limitation on the thermal efficiency of heat engines forms the basis for the
Kelvin–Planck statement of the second law of thermodynamics, which is
expressed as follows:
It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a
single reservoir and produce a net amount of work.
That is, a heat engine must exchange heat with a low-temperature sink as well
as a high-temperature source to keep operating. The Kelvin–Planck statement
can also be expressed as no heat engine can have a thermal efficiency of 100
percent (Fig. 6–18), or as for a power plant to operate, the working fluid must
exchange heat with the environment as well as the furnace.
Note that the impossibility of having a 100 percent efficient heat engine is
not due to friction or other dissipative effects. It is a limitation that applies
to both the idealized and the actual heat engines. Later in this chapter, we
develop a relation for the maximum thermal efficiency of a heat engine. We
also demonstrate that this maximum value depends on the reservoir temperatures only.
6–4
■
REFRIGERATORS AND HEAT PUMPS
We all know from experience that heat is transferred in the direction of
decreasing temperature, that is, from high-temperature mediums to lowtemperature ones. This heat transfer process occurs in nature without requiring any devices. The reverse process, however, cannot occur by itself.
Thermal energy reservoir
·
QH = 100 kW
Heat
engine
·
Wnet,out = 100 kW
·
QL = 0
FIGURE 6–18
A heat engine that violates
the Kelvin–Planck statement
of the second law.
284
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Surrounding medium
such as the kitchen air
QH
800 kPa
30°C
800 kPa
60°C
Condenser
Expansion
valve
120 kPa
–25°C
FIGURE 6–19
Basic components of a refrigeration
system and typical operating
conditions.
Warm environment
at TH > TL
QH
Required
input
Wnet,in
R
QL
Desired
output
Cold refrigerated
space at TL
FIGURE 6–20
The objective of a refrigerator is to
remove QL from the cooled space.
Compressor
Evaporator
Wnet,in
120 kPa
–25°C
QL
Refrigerated space
The transfer of heat from a low-temperature medium to a high-temperature
one requires special devices called refrigerators.
Refrigerators, like heat engines, are cyclic devices. The working fluid
used in the refrigeration cycle is called a refrigerant. The most frequently
used refrigeration cycle is the vapor-compression refrigeration cycle, which
involves four main components: a compressor, a condenser, an expansion
valve, and an evaporator, as shown in Fig. 6–19.
The refrigerant enters the compressor as a vapor and is compressed to the
condenser pressure. It leaves the compressor at a relatively high temperature
and cools down and condenses as it flows through the coils of the condenser
by rejecting heat to the surrounding medium. It then enters a capillary tube
where its pressure and temperature drop drastically due to the throttling
effect. The low-temperature refrigerant then enters the evaporator, where it
evaporates by absorbing heat from the refrigerated space. The cycle is completed as the refrigerant leaves the evaporator and reenters the compressor.
In a household refrigerator, the freezer compartment where heat is absorbed
by the refrigerant serves as the evaporator, and the coils, usually behind the
refrigerator where heat is dissipated to the kitchen air, serve as the condenser.
A refrigerator is shown schematically in Fig. 6–20. Here QL is the magnitude of the heat removed from the refrigerated space at temperature TL,
QH is the magnitude of the heat rejected to the warm environment at temperature TH, and Wnet,in is the net work input to the refrigerator. As discussed
before, QL and QH represent magnitudes and thus are positive quantities.
Coefficient of Performance
The efficiency of a refrigerator is expressed in terms of the coefficient of
performance (COP), denoted by COPR. The objective of a refrigerator is
285
CHAPTER 6
to remove heat (QL) from the refrigerated space. To accomplish this objective, it requires a work input of Wnet,in. Then the COP of a refrigerator can
be expressed as
COPR 5
QL
Desired output
5
Required input
Wnet,in
Warm heated space
at TH > TL
(6–7)
Desired
output
QH
#
This relation can also be expressed in rate form by replacing QL by QL and
#
Wnet,in by Wnet,in.
Wnet,in
HP
The conservation of energy principle for a cyclic device requires that
Wnet,in 5 QH 2 QL
(kJ)
(6–8)
1
QH/QL 2 1
(6–9)
Required
input
QL
Then the COP relation becomes
COPR 5
QL
QH 2 QL
5
Notice that the value of COPR can be greater than unity. That is, the
amount of heat removed from the refrigerated space can be greater than the
amount of work input. This is in contrast to the thermal efficiency, which
can never be greater than 1. In fact, one reason for expressing the efficiency
of a refrigerator by another term—the coefficient of performance—is the
desire to avoid the oddity of having efficiencies greater than unity.
Cold environment
at TL
FIGURE 6–21
The objective of a heat pump is to supply heat QH into the warmer space.
Heat Pumps
Another device that transfers heat from a low-temperature medium to a hightemperature one is the heat pump, shown schematically in Fig. 6–21. Refrigerators and heat pumps operate on the same cycle but differ in their objectives.
The objective of a refrigerator is to maintain the refrigerated space at a
low emperature by removing heat from it. Discharging this heat to a highertemperature medium is merely a necessary part of the operation, not the purpose. The objective of a heat pump, however, is to maintain a heated space
at a high temperature. This is accomplished by absorbing heat from a lowtemperature source, such as well water or cold outside air in winter, and supplying this heat to the high-temperature medium such as a house (Fig. 6–22).
An ordinary refrigerator that is placed in the window of a house with its
door open to the cold outside air in winter will function as a heat pump
since it will try to cool the outside by absorbing heat from it and rejecting
this heat into the house through the coils behind it (Fig. 6–23).
The measure of performance of a heat pump is also expressed in terms of
the coefficient of performance COPHP, defined as
COPHP 5
QH
Desired output
5
Required input
Wnet,in
(6–10)
Warm
indoors
at 20°C
QH = 7 kJ
Wnet,in = 2 kJ
COP = 3.5
HP
QL = 5 kJ
Cold outdoors
at 4°C
which can also be expressed as
COPHP 5
QH
QH 2 QL
5
1
1 2 QL /QH
(6–11)
A comparison of Eqs. 6–7 and 6–10 reveals that
COPHP 5 COPR 1 1
(6–12)
FIGURE 6–22
The work supplied to a heat pump
is used to extract energy from the
cold outdoors and carry it into
the warm indoors.
286
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
for fixed values of QL and QH. This relation implies that the coefficient of
performance of a heat pump is always greater than unity since COPR is a
positive quantity. That is, a heat pump will function, at worst, as a resistance
heater, supplying as much energy to the house as it consumes. In reality,
however, part of QH is lost to the outside air through piping and other
devices, and COPHP may drop below unity when the outside air temperature
is too low. When this happens, the system usually switches to a resistance
heating mode. Most heat pumps in operation today have a seasonally averaged COP of 2 to 3.
Most existing heat pumps use the cold outside air as the heat source in
winter, and they are referred to as air-source heat pumps. The COP of such
heat pumps is about 3.0 at design conditions. Air-source heat pumps are not
appropriate for cold climates since their efficiency drops considerably when
temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (also
called ground-source) heat pumps that use the ground as the heat source can
be used. Geothermal heat pumps require the burial of pipes in the ground
1 to 2 m deep. Such heat pumps are more expensive to install, but they
are also more efficient (up to 45 percent more efficient than air-source heat
pumps). The COP of ground-source heat pumps can be as high as 6 in the
cooling mode.
Air conditioners are basically refrigerators whose refrigerated space is a
room or a building instead of the food compartment. A window air-conditioning
unit cools a room by absorbing heat from the room air and discharging it to
the outside. The same air-conditioning unit can be used as a heat pump in
winter by installing it backwards. In this mode, the unit absorbs heat from
the cold outside and delivers it to the room. Air-conditioning systems that
are equipped with proper controls and a reversing valve operate as air conditioners in summer and as heat pumps in winter.
Performance of Refrigerators, Air-Conditioners, and
Heat Pumps
The performance of air conditioners and heat pumps is often expressed in
terms of the energy efficiency ratio (EER) or seasonal energy efficiency
ratio (SEER) determined by following certain testing standards. SEER is
the ratio the total amount of heat removed by an air conditioner or heat
pump during a normal cooling season (in Btu) to the total amount of electricity consumed (in watt-hours, Wh), and it is a measure of seasonal performance of cooling equipment. EER, on the other hand, is a measure of the
instantaneous energy efficiency, and is defined as the ratio of the rate of
heat removal from the cooled space by the cooling equipment to the rate of
electricity consumption in steady operation. Therefore, both EER and SEER
have the unit Btu/Wh. Considering that 1 kWh 5 3412 Btu and thus 1 Wh 5
3.412 Btu, a device that removes 1 kWh of heat from the cooled space for
each kWh of electricity it consumes (COP 5 1) will have an EER of 3.412.
Therefore, the relation between EER (or SEER) and COP is
EER ; 3.412 COPR
To promote the efficient use of energy, governments worldwide have
mandated minimum standards for the performance of energy consuming
287
CHAPTER 6
equipment. Most air conditioners or heat pumps in the market have SEER
values from 13 to 21, which correspond to COP values of 3.8 to 6.2. Best
performance is achieved using units equipped with variable-speed drives
(also called inverters). Variable-speed compressors and fans allow the unit
to operate at maximum efficiency for varying heating/cooling needs and
weather conditions as determined by a microprocessor. In the air-conditioning mode, for example, they operate at higher speeds on hot days and at
lower speeds on cooler days, enhancing both efficiency and comfort.
The EER or COP of a refrigerator decreases with decreasing refrigeration temperature. Therefore, it is not economical to refrigerate to a lower
temperature than needed. The COPs of refrigerators are in the range of
2.6–3.0 for cutting and preparation rooms; 2.3–2.6 for meat, deli, dairy,
and produce; 1.2–1.5 for frozen foods; and 1.0–1.2 for ice cream units.
Note that the COP of freezers is about half of the COP of meat refrigerators, and thus it costs twice as much to cool the meat products with
refrigerated air that is cold enough to cool frozen foods. It is good energy
conservation practice to use separate refrigeration systems to meet different refrigeration needs.
EXAMPLE 6–3
Heat Rejection by a Refrigerator
Kitchen
The food compartment of a refrigerator, shown in Fig. 6–23, is maintained at
48C by removing heat from it at a rate of 360 kJ/min. If the required power
input to the refrigerator is 2 kW, determine (a) the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator and (b) the rate of heat rejection to the room that
houses the refrigerator.
·
QH
·
Wnet,in = 2 kW
HP
SOLUTION The power consumption of a refrigerator is given. The COP and
the rate of heat rejection are to be determined.
Assumptions Steady operating conditions exist.
Analysis (a) The coefficient of performance of the refrigerator is
·
QL = 360 kJ/min
#
QL
360 kJ/min
1 kW
COPR 5 #
5
a
b 53
2 kW
60 kJ/min
Wnet,in
That is, 3 kJ of heat is removed from the refrigerated space for each kJ of
work supplied.
(b) The rate at which heat is rejected to the room that houses the refrigerator is determined from the conservation of energy relation for cyclic devices,
#
#
#
60 kJ/min
QH 5 QL 1 Wnet,in 5 360 kJ/min 1 (2 kW)a
b 5 480 kJ/min
1 kW
Discussion Notice that both the energy removed from the refrigerated
space as heat and the energy supplied to the refrigerator as electrical work
eventually show up in the room air and become part of the internal energy
of the air. This demonstrates that energy can change from one form to
another, can move from one place to another, but is never destroyed during
a process.
Food compartment
4°C
FIGURE 6–23
Schematic for Example 6–3.
288
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
EXAMPLE 6–4
House
20°C
Heat loss
80,000 kJ/h
·
QH
·
Wnet,in = ?
COP = 2.5
HP
·
QL = ?
Outdoor air at –2°C
FIGURE 6–24
Schematic for Example 6–4.
Heating a House by a Heat Pump
A heat pump is used to meet the heating requirements of a house and maintain it at 208C. On a day when the outdoor air temperature drops to 228C,
the house is estimated to lose heat at a rate of 80,000 kJ/h. If the heat
pump under these conditions has a COP of 2.5, determine (a) the power
consumed by the heat pump and (b) the rate at which heat is absorbed from
the cold outdoor air.
SOLUTION The COP of a heat pump is given. The power consumption and
the rate of heat absorption are to be determined.
Assumptions Steady operating conditions exist.
Analysis (a) The power consumed by this heat pump, shown in Fig. 6–24,
is determined from the definition of the coefficient of performance to be
#
Wnet,in 5
#
QH
COPHP
5
80,000 kJ/h
5 32,000 kJ/h (or 8.9 kW)
2.5
(b) The house is losing heat at a rate of 80,000 kJ/h. If the house is to be
maintained at a constant temperature of 208C, the heat pump must deliver
heat to the house at the same rate, that is, at a rate of 80,000 kJ/h. Then
the rate of heat transfer from the outdoor becomes
#
#
#
QL 5 QH 2 Wnet,in 5 (80,000 2 32,000) kJ/h 5 48,000 kJ/h
Discussion Note that 48,000 of the 80,000 kJ/h heat delivered to the
house is actually extracted from the cold outdoor air. Therefore, we are paying only for the 32,000-kJ/h energy that is supplied as electrical work to
the heat pump. If we were to use an electric resistance heater instead, we
would have to supply the entire 80,000 kJ/h to the resistance heater as
electric energy. This would mean a heating bill that is 2.5 times higher.
This explains the popularity of heat pumps as heating systems and why they
are preferred to simple electric resistance heaters despite their considerably
higher initial cost.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics:
Clausius Statement
There are two classical statements of the second law—the Kelvin–Planck
statement, which is related to heat engines and discussed in the preceding
section, and the Clausius statement, which is related to refrigerators or heat
pumps. The Clausius statement is expressed as follows:
It is impossible to construct a device that operates in a cycle and produces
no effect other than the transfer of heat from a lower-temperature body to a
higher-temperature body.
It is common knowledge that heat does not, of its own volition, transfer from a cold medium to a warmer one. The Clausius statement does
not imply that a cyclic device that transfers heat from a cold medium to a
warmer one is impossible to construct. In fact, this is precisely what a common household refrigerator does. It simply states that a refrigerator cannot
289
CHAPTER 6
operate unless its compressor is driven by an external power source, such as
an electric motor (Fig. 6–25). This way, the net effect on the surroundings
involves the consumption of some energy in the form of work, in addition to
the transfer of heat from a colder body to a warmer one. That is, it leaves a
trace in the surroundings. Therefore, a household refrigerator is in complete
compliance with the Clausius statement of the second law.
Both the Kelvin–Planck and the Clausius statements of the second law are
negative statements, and a negative statement cannot be proved. Like any
other physical law, the second law of thermodynamics is based on experimental observations. To date, no experiment has been conducted that contradicts the second law, and this should be taken as sufficient proof of its
validity.
Warm environment
QH = 5 kJ
Wnet,in = 0
R
QL = 5 kJ
Equivalence of the Two Statements
The Kelvin–Planck and the Clausius statements are equivalent in their consequences, and either statement can be used as the expression of the second
law of thermodynamics. Any device that violates the Kelvin–Planck statement also violates the Clausius statement, and vice versa. This can be demonstrated as follows.
Consider the heat-engine-refrigerator combination shown in Fig. 6–26a,
operating between the same two reservoirs. The heat engine is assumed to
have, in violation of the Kelvin–Planck statement, a thermal efficiency of
100 percent, and therefore it converts all the heat QH it receives to work W.
This work is now supplied to a refrigerator that removes heat in the amount
of QL from the low-temperature reservoir and rejects heat in the amount
of QL 1 QH to the high-temperature reservoir. During this process, the
high-temperature reservoir receives a net amount of heat QL (the difference
between QL 1 QH and QH). Thus, the combination of these two devices can
be viewed as a refrigerator, as shown in Fig. 6–26b, that transfers heat in
Wnet
Heat
engine
hth = 100% = QH
FIGURE 6–25
A refrigerator that violates the
Clausius statement of the second law.
High-temperature reservoir
at TH
High-temperature reservoir
at TH
QH
Cold refrigerated space
QH + QL
QL
Refrigerator
Refrigerator
QL
QL
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL
(a) A refrigerator that is powered by
a 100 percent efficient heat engine
(b) The equivalent refrigerator
FIGURE 6–26
Proof that the violation of the Kelvin–
Planck statement leads to the violation
of the Clausius statement.
290
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
an amount of QL from a cooler body to a warmer one without requiring
any input from outside. This is clearly a violation of the Clausius statement.
Therefore, a violation of the Kelvin–Planck statement results in the violation of the Clausius statement.
It can also be shown in a similar manner that a violation of the Clausius
statement leads to the violation of the Kelvin–Planck statement. Therefore,
the Clausius and the Kelvin–Planck statements are two equivalent expressions of the second law of thermodynamics.
6–5
■
PERPETUAL-MOTION MACHINES
We have repeatedly stated that a process cannot take place unless it satisfies both
the first and second laws of thermodynamics. Any device that violates either
law is called a perpetual-motion machine, and despite numerous attempts, no
perpetual-motion machine is known to have worked. But this has not stopped
inventors from trying to create new ones.
A device that violates the first law of thermodynamics (by creating
energy) is called a perpetual-motion machine of the first kind (PMM1),
and a device that violates the second law of thermodynamics is called a
perpetual-motion machine of the second kind (PMM2).
Consider the steam power plant shown in Fig. 6–27. It is proposed to heat
the steam by resistance heaters placed inside the boiler, instead of by the
energy supplied from fossil or nuclear fuels. Part of the electricity generated
by the plant is to be used to power the resistors as well as the pump. The
rest of the electric energy is to be supplied to the electric network as the net
work output. The inventor claims that once the system is started, this power
plant will produce electricity indefinitely without requiring any energy input
from the outside.
System boundary
Boiler
Wnet,out
Resistance heater
Pump
Turbine
Condenser
Qout
FIGURE 6–27
A perpetual-motion machine that violates the first law of
thermodynamics (PMM1).
Generator
291
CHAPTER 6
Well, here is an invention that could solve the world’s energy problem—if
it works, of course. A careful examination of this invention reveals that the
system enclosed by the
# area is continuously supplying energy to the
# shaded
any energy. That is, this
outside at a rate of Qout 1 Wnet,out without
#
# receiving
system is creating energy at a rate of Qout 1 Wnet,out, which is clearly a violation of the first law. Therefore, this wonderful device is nothing more than
a PMM1 and does not warrant any further consideration.
Now let us consider another novel idea by the same inventor. Convinced
that energy cannot be created, the inventor suggests the following modification that will greatly improve the thermal efficiency of that power plant
without violating the first law. Aware that more than one-half of the heat
transferred to the steam in the furnace is discarded in the condenser to the
environment, the inventor suggests getting rid of this wasteful component
and sending the steam to the pump as soon as it leaves the turbine, as shown
in Fig. 6–28. This way, all the heat transferred to the steam in the boiler
will be converted to work, and thus the power plant will have a theoretical efficiency of 100 percent. The inventor realizes that some heat losses
and friction between the moving components are unavoidable and that these
effects will hurt the efficiency somewhat, but still expects the efficiency to
be no less than 80 percent (as opposed to 40 percent in most actual power
plants) for a carefully designed system.
Well, the possibility of doubling the efficiency would certainly be very
tempting to plant managers and, if not properly trained, they would probably give this idea a chance, since intuitively they see nothing wrong with it.
A student of thermodynamics, however, will immediately label this device
as a PMM2, since it works on a cycle and does a net amount of work while
exchanging heat with a single reservoir (the furnace) only. It satisfies the
first law but violates the second law, and therefore it will not work.
Countless perpetual-motion machines have been proposed throughout history, with many more still being proposed. Some proposers have even gone
so far as to patent their inventions, only to find out that what they actually
have in their hands is a worthless piece of paper.
Some perpetual-motion machine inventors were very successful in
fund-raising. For example, a Philadelphia carpenter named J. W. Kelly
collected millions of dollars between 1874 and 1898 from investors in his
hydropneumatic-pulsating-vacu-engine, which supposedly could push a railroad train 3000 miles on 1 L of water. Of course, it never did. After his
death in 1898, the investigators discovered that the demonstration machine
was powered by a hidden motor. Recently, a group of investors was set to
invest $2.5 million into a mysterious energy augmentor, which multiplied
whatever power it took in, but their lawyer wanted an expert opinion first.
Confronted by the scientists, the “inventor” fled the scene without even
attempting to run his demo machine.
Tired of applications for perpetual-motion machines, the U.S. Patent
Office decreed in 1918 that it would no longer consider any perpetualmotion machine applications. However, several such patent applications
were still filed, and some made it through the patent office undetected. Some
applicants whose patent applications were denied sought legal action. For
example, in 1982 the U.S. Patent Office dismissed as just another perpetualmotion machine a huge device that involves several hundred kilograms of
System boundary
·
Qin
Boiler
·
Wnet,out
Pump
Turbine
FIGURE 6–28
A perpetual-motion machine
that violates the second law of
thermodynamics (PMM2).
292
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
rotating magnets and kilometers of copper wire that is supposed to be generating more electricity than it is consuming from a battery pack. However,
the inventor challenged the decision, and in 1985 the National Bureau of
Standards finally tested the machine just to certify that it is battery-operated.
However, it did not convince the inventor that his machine will not work.
The proposers of perpetual-motion machines generally have innovative
minds, but they usually lack formal engineering training, which is very
unfortunate. No one is immune from being deceived by an innovative
perpetual-motion machine. As the saying goes, however, if something
sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
6–6
(a) Frictionless pendulum
(b) Quasi-equilibrium expansion
and compression of a gas
FIGURE 6–29
Two familiar reversible processes.
■
REVERSIBLE AND IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES
The second law of thermodynamics states that no heat engine can have an efficiency of 100 percent. Then one may ask, what is the highest efficiency that a
heat engine can possibly have? Before we can answer this question, we need to
define an idealized process first, which is called the reversible process.
The processes that were discussed at the beginning of this chapter
occurred in a certain direction. Once having taken place, these processes
cannot reverse themselves spontaneously and restore the system to its initial state. For this reason, they are classified as irreversible processes. Once
a cup of hot coffee cools, it will not heat up by retrieving the heat it lost
from the surroundings. If it could, the surroundings, as well as the system
(coffee), would be restored to their original condition, and this would be a
reversible process.
A reversible process is defined as a process that can be reversed without
leaving any trace on the surroundings (Fig. 6–29). That is, both the system
and the surroundings are returned to their initial states at the end of the reverse
process. This is possible only if the net heat and net work exchange between
the system and the surroundings is zero for the combined (original and reverse)
process. Processes that are not reversible are called irreversible processes.
It should be pointed out that a system can be restored to its initial state
following a process, regardless of whether the process is reversible or irreversible. But for reversible processes, this restoration is made without leaving any net change on the surroundings, whereas for irreversible processes,
the surroundings usually do some work on the system and therefore does
not return to their original state.
Reversible processes actually do not occur in nature. They are merely
idealizations of actual processes. Reversible processes can be approximated
by actual devices, but they can never be achieved. That is, all the processes
occurring in nature are irreversible. You may be wondering, then, why we
are bothering with such fictitious processes. There are two reasons. First,
they are easy to analyze, since a system passes through a series of equilibrium states during a reversible process. Second, they serve as idealized
models to which actual processes can be compared.
In daily life, the concepts of Mr. Right and Ms. Right are also idealizations, just like the concept of a reversible (perfect) process. People who
insist on finding Mr. or Ms. Right to settle down are bound to remain
Mr. or Ms. Single for the rest of their lives. The possibility of finding the
perfect prospective mate is no higher than the possibility of finding a perfect
293
CHAPTER 6
(reversible) process. Likewise, a person who insists on perfection in friends
is bound to have no friends.
Engineers are interested in reversible processes because work-producing
devices such as car engines and gas or steam turbines deliver the most
work, and work-consuming devices such as compressors, fans, and pumps
consume the least work when reversible processes are used instead of
irreversible ones (Fig. 6–30).
Reversible processes can be viewed as theoretical limits for the corresponding
irreversible ones. Some processes are more irreversible than others. We may
never be able to have a reversible process, but we can certainly approach it.
The more closely we approximate a reversible process, the more work delivered
by a work-producing device or the less work required by a work-consuming
device.
The concept of reversible processes leads to the definition of the secondlaw efficiency for actual processes, which is the degree of approximation
to the corresponding reversible processes. This enables us to compare the
performance of different devices that are designed to do the same task on
the basis of their efficiencies. The better the design, the lower the irreversibilities and the higher the second-law efficiency.
Irreversibilities
The factors that cause a process to be irreversible are called irreversibilities. They include friction, unrestrained expansion, mixing of two fluids, heat transfer across a finite temperature difference, electric resistance,
inelastic deformation of solids, and chemical reactions. The presence of any
of these effects renders a process irreversible. A reversible process involves
none of these. Some of the frequently encountered irreversibilities are discussed briefly below.
Friction is a familiar form of irreversibility associated with bodies in motion.
When two bodies in contact are forced to move relative to each other (a piston
in a cylinder, for example, as shown in Fig. 6–31), a friction force that opposes
the motion develops at the interface of these two bodies, and some work is
needed to overcome this friction force. The energy supplied as work is eventually converted to heat during the process and is transferred to the bodies in
contact, as evidenced by a temperature rise at the interface. When the direction
of the motion is reversed, the bodies are restored to their original position, but
the interface does not cool, and heat is not converted back to work. Instead,
more of the work is converted to heat while overcoming the friction forces that
also oppose the reverse motion. Since the system (the moving bodies) and the
surroundings cannot be returned to their original states, this process is irreversible. Therefore, any process that involves friction is irreversible. The larger the
friction forces involved, the more irreversible the process is.
Friction does not always involve two solid bodies in contact. It is also
encountered between a fluid and solid and even between the layers of a
fluid moving at different velocities. A considerable fraction of the power
produced by a car engine is used to overcome the friction (the drag force)
between the air and the external surfaces of the car, and it eventually
becomes part of the internal energy of the air. It is not possible to reverse
this process and recover that lost power, even though doing so would not
violate the conservation of energy principle.
Expansion
Compression
Pressure
distribution
Water
Water
(a) Slow (reversible) process
Expansion
Water
Compression
Water
(b) Fast (irreversible) process
FIGURE 6–30
Reversible processes deliver the most
and consume the least work.
Friction
Gas
FIGURE 6–31
Friction renders a process
irreversible.
294
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
(a) Fast compression
(b) Fast expansion
50 kPa
700 kPa
(c) Unrestrained expansion
FIGURE 6–32
Irreversible compression and
expansion processes.
20°C
Heat
20°C
5°C
(a) An irreversible heat transfer process
20°C
Heat
5°C
Another example of irreversibility is the unrestrained expansion of
a gas separated from a vacuum by a membrane, as shown in Fig. 6–32.
When the membrane is ruptured, the gas fills the entire tank. The only
way to restore the system to its original state is to compress it to its
initial volume, while transferring heat from the gas until it reaches its
initial temperature. From the conservation of energy considerations, it can
easily be shown that the amount of heat transferred from the gas equals
the amount of work done on the gas by the surroundings. The restoration
of the surroundings involves conversion of this heat completely to work,
which would violate the second law. Therefore, unrestrained expansion of
a gas is an irreversible process.
A third form of irreversibility familiar to us all is heat transfer through
a finite temperature difference. Consider a can of cold soda left in a warm
room (Fig. 6–33). Heat is transferred from the warmer room air to the cooler
soda. The only way this process can be reversed and the soda restored to its
original temperature is to provide refrigeration, which requires some work
input. At the end of the reverse process, the soda will be restored to its initial state, but the surroundings will not be. The internal energy of the surroundings will increase by an amount equal in magnitude to the work supplied to the refrigerator. The restoration of the surroundings to the initial
state can be done only by converting this excess internal energy completely
to work, which is impossible to do without violating the second law. Since
only the system, not both the system and the surroundings, can be restored
to its initial condition, heat transfer through a finite temperature difference
is an irreversible process.
Heat transfer can occur only when there is a temperature difference between
a system and its surroundings. Therefore, it is physically impossible to have a
reversible heat transfer process. But a heat transfer process becomes less
and less irreversible as the temperature difference between the two bodies
approaches zero. Then, heat transfer through a differential temperature
difference dT can be considered to be reversible. As dT approaches zero, the
process can be reversed in direction (at least theoretically) without requiring
any refrigeration. Notice that reversible heat transfer is a conceptual process
and cannot be duplicated in the real world.
The smaller the temperature difference between two bodies, the smaller
the heat transfer rate will be. Any significant heat transfer through a small
temperature difference requires a very large surface area and a very long
time. Therefore, even though approaching reversible heat transfer is desirable from a thermodynamic point of view, it is impractical and not economically feasible.
2°C
Internally and Externally Reversible Processes
(b) An impossible heat transfer process
FIGURE 6–33
(a) Heat transfer through a
temperature difference is irreversible,
and (b) the reverse process is
impossible.
A typical process involves interactions between a system and its surroundings, and a reversible process involves no irreversibilities associated with
either of them.
A process is called internally reversible if no irreversibilities occur
within the boundaries of the system during the process. During an internally reversible process, a system proceeds through a series of equilibrium
states, and when the process is reversed, the system passes through exactly
295
CHAPTER 6
the same equilibrium states while returning to its initial state. That is, the
paths of the forward and reverse processes coincide for an internally reversible process. The quasi-equilibrium process is an example of an internally
reversible process.
A process is called externally reversible if no irreversibilities occur outside the system boundaries during the process. Heat transfer between a reservoir and a system is an externally reversible process if the outer surface of
the system is at the temperature of the reservoir.
A process is called totally reversible, or simply reversible, if it involves
no irreversibilities within the system or its surroundings (Fig. 6–34). A
totally reversible process involves no heat transfer through a finite temperature difference, no nonquasi-equilibrium changes, and no friction or other
dissipative effects.
As an example, consider the transfer of heat to two identical systems
that are undergoing a constant-pressure (thus constant-temperature)
phase-change process, as shown in Fig. 6–35. Both processes are internally reversible, since both take place isothermally and both pass through
exactly the same equilibrium states. The first process shown is externally
reversible also, since heat transfer for this process takes place through an
infinitesimal temperature difference dT. The second process, however, is
externally irreversible, since it involves heat transfer through a finite temperature difference DT.
No
irreversibilities
outside
the system
No
irreversibilities
inside
the system
FIGURE 6–34
A reversible process involves no
internal and external irreversibilities.
20°C
Heat
Thermal energy
reservoir at 20.000…1°C
(a) Totally reversible
6–7
■
THE CARNOT CYCLE
We mentioned earlier that heat engines are cyclic devices and that the working fluid of a heat engine returns to its initial state at the end of each cycle.
Work is done by the working fluid during one part of the cycle and on the
working fluid during another part. The difference between these two is
the net work delivered by the heat engine. The efficiency of a heat-engine
cycle greatly depends on how the individual processes that make up the
cycle are executed. The net work, thus the cycle efficiency, can be maximized by using processes that require the least amount of work and deliver
the most, that is, by using reversible processes. Therefore, it is no surprise
that the most efficient cycles are reversible cycles, that is, cycles that consist
entirely of reversible processes.
Reversible cycles cannot be achieved in practice because the irreversibilities associated with each process cannot be eliminated. However, reversible
cycles provide upper limits on the performance of real cycles. Heat engines
and refrigerators that work on reversible cycles serve as models to which
actual heat engines and refrigerators can be compared. Reversible cycles
also serve as starting points in the development of actual cycles and are
modified as needed to meet certain requirements.
Probably the best known reversible cycle is the Carnot cycle, first proposed in 1824 by French engineer Sadi Carnot. The theoretical heat engine
that operates on the Carnot cycle is called the Carnot heat engine. The
Carnot cycle is composed of four reversible processes—two isothermal
and two adiabatic—and it can be executed either in a closed or a steadyflow system.
20°C
Boundary
at 20°C
Heat
Thermal energy
reservoir at 30°C
(b) Internally reversible
FIGURE 6–35
Totally and internally reversible
heat transfer processes.
296
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Consider a closed system that consists of a gas contained in an adiabatic
piston–cylinder device, as shown in Fig. 6–36. The insulation of the cylinder head is such that it may be removed to bring the cylinder into contact
with reservoirs to provide heat transfer. The four reversible processes that
make up the Carnot cycle are as follows:
(2)
TH = const.
(1)
Energy
source
at TH
QH
(a) Process 1-2
Insulation
(2)
Reversible Isothermal Expansion (process 1-2, TH 5 constant). Initially
(state 1), the temperature of the gas is TH and the cylinder head is in close
contact with a source at temperature TH. The gas is allowed to expand
slowly, doing work on the surroundings. As the gas expands, the temperature of the gas tends to decrease. But as soon as the temperature drops by
an infinitesimal amount dT, some heat is transferred from the reservoir
into the gas, raising the gas temperature to TH. Thus, the gas temperature
is kept constant at TH. Since the temperature difference between the gas
and the reservoir never exceeds a differential amount dT, this is a reversible heat transfer process. It continues until the piston reaches position 2.
The amount of total heat transferred to the gas during this process is QH.
Reversible Adiabatic Expansion (process 2-3, temperature drops
from TH to TL). At state 2, the reservoir that was in contact with the
cylinder head is removed and replaced by insulation so that the system
becomes adiabatic. The gas continues to expand slowly, doing work
on the surroundings until its temperature drops from TH to TL (state 3).
The piston is assumed to be frictionless and the process to be quasiequilibrium, so the process is reversible as well as adiabatic.
Reversible Isothermal Compression (process 3-4, TL 5 constant). At
state 3, the insulation at the cylinder head is removed, and the cylinder
is brought into contact with a sink at temperature TL. Now the piston is
pushed inward by an external force, doing work on the gas. As the gas
is compressed, its temperature tends to rise. But as soon as it rises by
an infinitesimal amount dT, heat is transferred from the gas to the sink,
causing the gas temperature to drop to TL. Thus, the gas temperature
remains constant at TL. Since the temperature difference between the gas
and the sink never exceeds a differential amount dT, this is a reversible
heat transfer process. It continues until the piston reaches state 4. The
amount of heat rejected from the gas during this process is QL.
Reversible Adiabatic Compression (process 4-1, temperature rises
from TL to TH). State 4 is such that when the low-temperature reservoir
is removed, the insulation is put back on the cylinder head, and the gas
is compressed in a reversible manner, the gas returns to its initial state
(state 1). The temperature rises from TL to TH during this reversible
adiabatic compression process, which completes the cycle.
(3)
TH
TL
(b) Process 2-3
(3)
TL = const.
(4)
Energy
sink
at TL
QL
(c) Process 3-4
Insulation
(1)
(4)
TH
TL
(d) Process 4-1
FIGURE 6–36
Execution of the Carnot cycle
in a closed system.
P
1
QH
2 TH = const.
Wnet,out
TL = con
4
st.
QL
3
V
FIGURE 6–37
P-V diagram of the Carnot cycle.
The P-V diagram of this cycle is shown in Fig. 6–37. Remembering that
on a P-V diagram the area under the process curve represents the boundary
work for quasi-equilibrium (internally reversible) processes, we see that the
area under curve 1-2-3 is the work done by the gas during the expansion
part of the cycle, and the area under curve 3-4-1 is the work done on the gas
during the compression part of the cycle. The area enclosed by the path of
the cycle (area 1-2-3-4-1) is the difference between these two and represents
the net work done during the cycle.
297
CHAPTER 6
Notice that if we acted stingily and compressed the gas at state 3 adiabatically instead of isothermally in an effort to save QL , we would end up back
at state 2, retracing the process path 3-2. By doing so we would save QL ,
but we would not be able to obtain any net work output from this engine.
This illustrates once more the necessity of a heat engine exchanging heat
with at least two reservoirs at different temperatures to operate in a cycle
and produce a net amount of work.
The Carnot cycle can also be executed in a steady-flow system. It is discussed in later chapters in conjunction with other power cycles.
Being a reversible cycle, the Carnot cycle is the most efficient cycle operating between two specified temperature limits. Even though the Carnot
cycle cannot be achieved in reality, the efficiency of actual cycles can be
improved by attempting to approximate the Carnot cycle more closely.
P
The Reversed Carnot Cycle
1
The Carnot heat-engine cycle just described is a totally reversible cycle.
Therefore, all the processes that comprise it can be reversed, in which case
it becomes the Carnot refrigeration cycle. This time, the cycle remains
exactly the same, except that the directions of any heat and work interactions
are reversed: Heat in the amount of QL is absorbed from the low-temperature
reservoir, heat in the amount of QH is rejected to a high-temperature reservoir,
and a work input of Wnet,in is required to accomplish all this.
The P-V diagram of the reversed Carnot cycle is the same as the one given
for the Carnot cycle, except that the directions of the processes are reversed,
as shown in Fig. 6–38.
6–8
■
4 TH = const.
Wnet,in
QL
st.
3
V
FIGURE 6–38
P-V diagram of the reversed
Carnot cycle.
The second law of thermodynamics puts limits on the operation of cyclic
devices as expressed by the Kelvin–Planck and Clausius statements. A heat
engine cannot operate by exchanging heat with a single reservoir, and a refrigerator cannot operate without a net energy input from an external source.
We can draw valuable conclusions from these statements. Two conclusions
pertain to the thermal efficiency of reversible and irreversible (i.e., actual)
heat engines, and they are known as the Carnot principles (Fig. 6–39),
expressed as follows:
These two statements can be proved by demonstrating that the violation
of either statement results in the violation of the second law of thermodynamics.
To prove the first statement, consider two heat engines operating between
the same reservoirs, as shown in Fig. 6–40. One engine is reversible and the
other is irreversible. Now each engine is supplied with the same amount of
heat QH. The amount of work produced by the reversible heat engine is Wrev,
and the amount produced by the irreversible one is Wirrev.
TL = con
2
THE CARNOT PRINCIPLES
1. The efficiency of an irreversible heat engine is always less than the
efficiency of a reversible one operating between the same two reservoirs.
2. The efficiencies of all reversible heat engines operating between the
same two reservoirs are the same.
QH
High-temperature reservoir
at TH
1
Irrev.
HE
2
Rev.
HE
hth,1 < hth,2
3
Rev.
HE
hth,2 = hth,3
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL
FIGURE 6– 39
The Carnot principles.
298
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
High-temperature reservoir
at TH
QH
Irreversible
HE
QH
Wirrev
Reversible
HE
(or R)
QL,irrev < QL,rev
(assumed)
FIGURE 6– 40
Proof of the first Carnot principle.
Wrev
QL,rev
Combined
HE + R
Wirrev – Wrev
QL,rev – QL,irrev
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL
(a) A reversible and an irreversible heat
engine operating between the same two
reservoirs (the reversible heat engine is
then reversed to run as a refrigerator)
(b) The equivalent combined system
In violation of the first Carnot principle, we assume that the irreversible
heat engine is more efficient than the reversible one (that is, hth,irrev . hth,rev)
and thus delivers more work than the reversible one. Now let the reversible
heat engine be reversed and operate as a refrigerator. This refrigerator will
receive a work input of Wrev and reject heat to the high-temperature reservoir. Since the refrigerator is rejecting heat in the amount of QH to the hightemperature reservoir and the irreversible heat engine is receiving the same
amount of heat from this reservoir, the net heat exchange for this reservoir
is zero. Thus, it could be eliminated by having the refrigerator discharge QH
directly into the irreversible heat engine.
Now considering the refrigerator and the irreversible engine together, we
have an engine that produces a net work in the amount of Wirrev 2 Wrev
while exchanging heat with a single reservoir—a violation of the Kelvin–
Planck statement of the second law. Therefore, our initial assumption that
hth,irrev . hth,rev is incorrect. Then we conclude that no heat engine can be
more efficient than a reversible heat engine operating between the same
reservoirs.
The second Carnot principle can also be proved in a similar manner. This
time, let us replace the irreversible engine by another reversible engine that
is more efficient and thus delivers more work than the first reversible engine.
By following through the same reasoning, we end up having an engine that
produces a net amount of work while exchanging heat with a single reservoir, which is a violation of the second law. Therefore, we conclude that no
reversible heat engine can be more efficient than a reversible one operating
between the same two reservoirs, regardless of how the cycle is completed
or the kind of working fluid used.
299
CHAPTER 6
6–9
■
THE THERMODYNAMIC TEMPERATURE SCALE
A temperature scale that is independent of the properties of the substances
that are used to measure temperature is called a thermodynamic temperature scale. Such a temperature scale offers great conveniences in thermodynamic calculations, and its derivation is given below using some reversible
heat engines.
The second Carnot principle discussed in Section 6–8 states that all reversible heat engines have the same thermal efficiency when operating between the
same two reservoirs (Fig. 6–41). That is, the efficiency of a reversible engine
is independent of the working fluid employed and its properties, the way the
cycle is executed, or the type of reversible engine used. Since energy reservoirs
are characterized by their temperatures, the thermal efficiency of reversible
heat engines is a function of the reservoir temperatures only. That is,
High-temperature reservoir
at TH = 1000 K
hth,A = hth,B = 70%
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL = 300 K
hth,rev 5 g(TH, TL)
or
QH
QL
5 f (TH, TL)
(6–13)
since hth 5 1 2 QL/QH. In these relations TH and TL are the temperatures of
the high- and low-temperature reservoirs, respectively.
The functional form of f(TH , TL) can be developed with the help of the
three reversible heat engines shown in Fig. 6–42. Engines A and C are supplied with the same amount of heat Q1 from the high-temperature reservoir
at T1. Engine C rejects Q3 to the low-temperature reservoir at T3. Engine B
receives the heat Q2 rejected by engine A at temperature T2 and rejects heat
in the amount of Q3 to a reservoir at T3.
The amounts of heat rejected by engines B and C must be the same since
engines A and B can be combined into one reversible engine operating
between the same reservoirs as engine C and thus the combined engine will
have the same efficiency as engine C. Since the heat input to engine C is the
same as the heat input to the combined engines A and B, both systems must
reject the same amount of heat.
Applying Eq. 6–13 to all three engines separately, we obtain
Q1
Q2
5 f (T1, T2),
Q2
Q3
5 f (T2, T3), and
Q1
Q3
5 f (T1, T3)
Now consider the identity
Another
reversible
HE
hth,B
A reversible
HE
hth,A
FIGURE 6–41
All reversible heat engines operating
between the same two reservoirs have
the same efficiency (the second Carnot
principle).
Thermal energy reservoir
at T1
Q1
Q1
Rev. HE
A
WA
Q2
Q2
Rev. HE
B
Rev. HE
C
T2
WB
WC
Q3
Q3
Q1
Q3
5
Q1 Q2
Q2 Q3
Thermal energy reservoir
at T3
which corresponds to
f (T1, T3) 5 f (T1, T2)· f (T2, T3)
A careful examination of this equation reveals that the left-hand side is a function of T1 and T3, and therefore the right-hand side must also be a function of
FIGURE 6–42
The arrangement of heat engines
used to develop the thermodynamic
temperature scale.
300
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
High-temperature reservoir
at TH
f (T1, T2) 5
QH
Reversible
heat engine or
refrigerator
T1 and T3 only, and not T2. That is, the value of the product on the right-hand
side of this equation is independent of the value of T2. This condition will be
satisfied only if the function f has the following form:
Q1
QL
QL
f(T2)
=
TH
TL
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL
Q3
5 f (T1, T3) 5
f(T2)
f(T3)
FIGURE 6– 43
For reversible cycles, the heat transfer
ratio QH/QL can be replaced by the
absolute temperature ratio TH/TL.
QH
QH
W
QL
273.16 K (assigned)
Water at triple point
QH
T = 273.16 –––
Q
f(T3)
(6–14)
5
f(TH)
f(TL)
(6–15)
This is the only requirement that the second law places on the ratio of heat
transfers to and from the reversible heat engines. Several functions f(T) satisfy this equation, and the choice is completely arbitrary. Lord Kelvin first
proposed taking f(T) 5 T to define a thermodynamic temperature scale as
(Fig. 6–43)
a
Heat reservoir
T
f(T1)
This relation is much more specific than Eq. 6–13 for the functional form of
Q1/Q3 in terms of T1 and T3.
For a reversible heat engine operating between two reservoirs at temperatures TH and TL, Eq. 6–14 can be written as
QL
Carnot
HE
and f (T2, T3) 5
so that f(T2) will cancel from the product of f (T1, T2) and f (T2, T3), yielding
Wnet
QH
f(T1)
QH
QL
5
b
rev
TH
TL
(6–16)
This temperature scale is called the Kelvin scale, and the temperatures on
this scale are called absolute temperatures. On the Kelvin scale, the temperature ratios depend on the ratios of heat transfer between a reversible
heat engine and the reservoirs and are independent of the physical properties of any substance. On this scale, temperatures vary between zero and
infinity.
The thermodynamic temperature scale is not completely defined by
Eq. 6–16 since it gives us only a ratio of absolute temperatures. We also
need to know the magnitude of a kelvin. At the International Conference on
Weights and Measures held in 1954, the triple point of water (the state at
which all three phases of water exist in equilibrium) was assigned the value
273.16 K (Fig. 6–44). The magnitude of a kelvin is defined as 1/273.16 of
the temperature interval between absolute zero and the triple-point temperature
of water. The magnitudes of temperature units on the Kelvin and Celsius
scales are identical (1 K ; 18C). The temperatures on these two scales
differ by a constant 273.15:
L
T(8C) 5 T(K) 2 273.15
FIGURE 6– 44
A conceptual experimental
setup to determine thermodynamic
temperatures on the Kelvin scale by
measuring heat transfers QH and QL.
Even though the thermodynamic temperature scale is defined with the
help of the reversible heat engines, it is not possible, nor is it practical,
to actually operate such an engine to determine numerical values on the
absolute temperature scale. Absolute temperatures can be measured accurately by other means, such as the constant-volume ideal-gas thermometer
(6–17)
301
CHAPTER 6
together with extrapolation techniques as discussed in Chap. 1. The validity
of Eq. 6–16 can be demonstrated from physical considerations for a reversible cycle using an ideal gas as the working fluid.
6–10
■
High-temperature reservoir
at TH = 1000 K
THE CARNOT HEAT ENGINE
QH
The hypothetical heat engine that operates on the reversible Carnot cycle is
called the Carnot heat engine. The thermal efficiency of any heat engine,
reversible or irreversible, is given by Eq. 6–6 as
hth 5 1 2
QL
QL
QH
where QH is heat transferred to the heat engine from a high-temperature reservoir at TH , and QL is heat rejected to a low-temperature reservoir at TL.
For reversible heat engines, the heat transfer ratio in the above relation can
be replaced by the ratio of the absolute temperatures of the two reservoirs,
as given by Eq. 6–16. Then the efficiency of a Carnot engine, or any reversible heat engine, becomes
hth,rev 5 1 2
TL
TH
(6–18)
This relation is often referred to as the Carnot efficiency, since the Carnot
heat engine is the best known reversible engine. This is the highest efficiency
a heat engine operating between the two thermal energy reservoirs at temperatures TL and TH can have (Fig. 6–45). All irreversible (i.e., actual) heat
engines operating between these temperature limits (TL and TH) have lower
efficiencies. An actual heat engine cannot reach this maximum theoretical
efficiency value because it is impossible to completely eliminate all the irreversibilities associated with the actual cycle.
Note that TL and TH in Eq. 6–18 are absolute temperatures. Using 8C or
8F for temperatures in this relation gives results grossly in error.
The thermal efficiencies of actual and reversible heat engines operating
between the same temperature limits compare as follows (Fig. 6–46):
,
hth • 5
.
hth,rev irreversible heat engine
hth,rev reversible heat engine
hth,rev impossible heat engine
Wnet,out
Carnot
HE
hth = 70%
(6–19)
Most work-producing devices (heat engines) in operation today have
efficiencies under 40 percent, which appear low relative to 100 percent.
However, when the performance of actual heat engines is assessed, the
efficiencies should not be compared to 100 percent; instead, they should
be compared to the efficiency of a reversible heat engine operating between
the same temperature limits—because this is the true theoretical upper limit
for the efficiency, not 100 percent.
The maximum efficiency of a steam power plant operating between TH 5
1000 K and TL 5 300 K is 70 percent, as determined from Eq. 6–18. Compared with this value, an actual efficiency of 40 percent does not seem so
bad, even though there is still plenty of room for improvement.
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL = 300 K
FIGURE 6–45
The Carnot heat engine is the most
efficient of all heat engines operating
between the same high- and
low-temperature reservoirs.
High-temperature reservoir
at TH = 1000 K
Rev. HE
hth = 70%
Irrev. HE
hth = 45%
Impossible
HE
hth = 80%
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL = 300 K
FIGURE 6–46
No heat engine can have a higher
efficiency than a reversible heat engine
operating between the same high- and
low-temperature reservoirs.
302
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
It is obvious from Eq. 6–18 that the efficiency of a Carnot heat engine
increases as TH is increased, or as TL is decreased. This is to be expected
since as TL decreases, so does the amount of heat rejected, and as TL
approaches zero, the Carnot efficiency approaches unity. This is also true
for actual heat engines. The thermal efficiency of actual heat engines can
be maximized by supplying heat to the engine at the highest possible temperature (limited by material strength) and rejecting heat from the engine at
the lowest possible temperature (limited by the temperature of the cooling
medium such as rivers, lakes, or the atmosphere).
High-temperature reservoir
at TH = 652°C
QH = 500 kJ
Wnet,out
Carnot
HE
EXAMPLE 6–5
QL
Analysis of a Carnot Heat Engine
A Carnot heat engine, shown in Fig. 6–47, receives 500 kJ of heat per cycle
from a high-temperature source at 6528C and rejects heat to a low-temperature
sink at 308C. Determine (a) the thermal efficiency of this Carnot engine and
(b) the amount of heat rejected to the sink per cycle.
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL = 30°C
SOLUTION The heat supplied to a Carnot heat engine is given. The thermal
efficiency and the heat rejected are to be determined.
Analysis (a) The Carnot heat engine is a reversible heat engine, and so its
efficiency can be determined from Eq. 6–18 to be
FIGURE 6– 47
Schematic for Example 6–5.
hth,rev 5 1 2
TL
TH
512
(30 1 273) K
5 0.672
(652 1 273) K
That is, this Carnot heat engine converts 67.2 percent of the heat it receives
to work.
(b) The amount of heat rejected QL by this reversible heat engine is easily
determined from Eq. 6–16 to be
QL,rev 5
High-temperature reservoir
at TH
Rev. HE
hth
TL
TH
QH,rev 5
(30 1 273) K
(500 kJ) 5 164 kJ
(652 1 273) K
Discussion Note that this Carnot heat engine rejects to a low-temperature
sink 164 kJ of the 500 kJ of heat it receives during each cycle.
TH, K
hth, %
925
800
700
500
350
67.2
62.1
56.7
39.4
13.4
Low-temperature reservoir
at TL = 303 K
FIGURE 6–48
The fraction of heat that can be
converted to work as a function of
source temperature (for TL 5 303 K).
The Quality of Energy
The Carnot heat engine in Example 6–5 receives heat from a source at 925 K
and converts 67.2 percent of it to work while rejecting the rest (32.8 percent)
to a sink at 303 K. Now let us examine how the thermal efficiency varies
with the source temperature when the sink temperature is held constant.
The thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine that rejects heat to a sink at
303 K is evaluated at various source temperatures using Eq. 6–18 and is listed
in Fig. 6–49. Clearly, the thermal efficiency decreases as the source temperature
is lowered. When heat is supplied to the heat engine at 500 instead of 925 K,
for example, the thermal efficiency drops from 67.2 to 39.4 percent. That is,
the fraction of heat that can be converted to work drops to 39.4 percent when
the temperature of the source drops to 500 K. When the source temperature is
350 K, this fraction becomes a mere 13.4 percent.
These efficiency values show that energy has quality as well as quantity.
It is clear from the thermal efficiency values in Fig. 6–48 that more of the
303
CHAPTER 6
high-temperature thermal energy can be converted to work. Therefore, the
higher the temperature, the higher the quality of the energy (Fig. 6–49).
Large quantities of solar energy, for example, can be stored in large
bodies of water called solar ponds at about 350 K. This stored energy can
then be supplied to a heat engine to produce work (electricity). However,
the efficiency of solar pond power plants is very low (under 5 percent)
because of the low quality of the energy stored in the source, and the construction and maintenance costs are relatively high. Therefore, they are not
competitive even though the energy supply of such plants is free. The temperature (and thus the quality) of the solar energy stored could be raised
by utilizing concentrating collectors, but the equipment cost in that case
becomes very high.
Work is a more valuable form of energy than heat since 100 percent of
work can be converted to heat, but only a fraction of heat can be converted
to work. When heat is transferred from a high-temperature body to a lowertemperature one, it is degraded since less of it now can be converted to
work. For example, if 100 kJ of heat is transferred from a body at 1000 K to
a body at 300 K, at the end we will have 100 kJ of thermal energy stored at
300 K, which has no practical value. But if this conversion is made through
a heat engine, up to 1 2 300/1000 5 70 percent of it could be converted to
work, which is a more valuable form of energy. Thus 70 kJ of work potential is wasted as a result of this heat transfer, and energy is degraded.
Quantity versus Quality in Daily Life
At times of energy crisis, we are bombarded with speeches and articles
on how to “conserve” energy. Yet we all know that the quantity of energy
is already conserved. What is not conserved is the quality of energy, or
the work potential of energy. Wasting energy is synonymous to converting it to a less useful form. One unit of high-quality energy can be
more valuable than three units of lower-quality energy. For example, a
finite amount of thermal energy at high temperature is more attractive
to power plant engineers than a vast amount of thermal energy at low
temperature, such as the energy stored in the upper layers of the oceans
at tropical climates.
As part of our culture, we seem to be fascinated by quantity, and little
attention is given to quality. However, quantity alone cannot give the whole
picture, and we need to consider quality as well. That is, we need to look at
something from both the first- and second-law points of view when evaluating something, even in nontechnical areas. Below we present some ordinary
events and show their relevance to the second law of thermodynamics.
Consider two students Andy and Wendy. Andy has 10 friends who never
miss his parties and are always around during fun times. However, they
seem to be busy when Andy needs their help. Wendy, on the other hand,
has five friends. They are never too busy for her, and she can count on them
at times of need. Let us now try to answer the question, Who has more
friends? From the first-law point of view, which considers quantity only, it
is obvious that Andy has more friends. However, from the second-law point
of view, which considers quality as well, there is no doubt that Wendy is the
one with more friends.
T, K
Quality
2000
1500
Thermal
energy
1000
500
FIGURE 6–49
The higher the temperature of the
thermal energy, the higher its quality.
304
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Another example with which most people will identify is the multibilliondollar diet industry, which is primarily based on the first law of thermodynamics. However, considering that 90 percent of the people who lose weight
gain it back quickly, with interest, suggests that the first law alone does
not give the whole picture. People who seem to be eating whatever they
want, whenever they want, without gaining weight are living proof that the
calorie-counting technique (the first law) leaves many questions on dieting
unanswered. Obviously, more research focused on the second-law effects
of dieting is needed before we can fully understand the weight-gain and
weight-loss process.
It is tempting to judge things on the basis of their quantity instead of their
quality since assessing quality is much more difficult than assessing quantity. However, assessments made on the basis of quantity only (the first law)
may be grossly inadequate and misleading.
6–11
■
THE CARNOT REFRIGERATOR
AND HEAT PUMP
A refrigerator or a heat pump that operates on the reversed Carnot cycle is
called a Carnot refrigerator, or a Carnot heat pump. The coefficient of
performance of any refrigerator or heat pump, reversible or irreversible, is
given by Eqs. 6–9 and 6–11 as
COPR 5
1
1
and COPHP 5
QH /QL 2 1
1 2 QL /QH
where QL is the amount of heat absorbed from the low-temperature medium and
QH is the amount of heat rejected to the high-temperature medium. The COPs
of all reversible refrigerators or heat pumps can be determined by replacing the
heat transfer ratios in the above relations by the ratios of the absolute temperatures of the high- and low-temperature reservoirs, as expressed by Eq. 6–16.
Then the COP relations for reversible refrigerators and heat pumps become
COPR,rev 5
1
TH /TL 2 1
(6–20)
COPHP,rev 5
1
1 2 TL /TH
(6–21)
and
These are the highest coefficients of performance that a refrigerator or a
heat pump operating between the temperature limits of TL and TH can have.
All actual refrigerators or heat pumps operating between these temperature
limits (TL and TH) have lower coefficients of performance (Fig. 6–50).
The coefficients of performance of actual and reversible refrigerators
operating between the same temperature limits can be compared as follows:
, COPR,rev
COPR • 5 COPR,rev
. COPR,rev
irreversible refrigerator
reversible refrigerator
impossible refrigerator
(6–22)
305
CHAPTER 6
Warm environment
at TH = 300 K
Reversible
refrigerator
COPR = 11
Irreversible
refrigerator
COPR = 7
Impossible
refrigerator
COPR = 13
Cool refrigerated space
at TL = 275 K
FIGURE 6–50
No refrigerator can have a higher COP
than a reversible refrigerator operating
between the same temperature limits.
A similar relation can be obtained for heat pumps by replacing all COPR’s
in Eq. 6–22 by COPHP.
The COP of a reversible refrigerator or heat pump is the maximum theoretical value for the specified temperature limits. Actual refrigerators or heat
pumps may approach these values as their designs are improved, but they
can never reach them.
As a final note, the COPs of both the refrigerators and the heat pumps
decrease as TL decreases. That is, it requires more work to absorb heat
from lower-temperature media. As the temperature of the refrigerated space
approaches zero, the amount of work required to produce a finite amount of
refrigeration approaches infinity and COPR approaches zero.
EXAMPLE 6–6
A Carnot Refrigeration Cycle Operating in the
Saturation Dome
A Carnot refrigeration cycle is executed in a closed system in the saturated
liquid–vapor mixture region using 0.8 kg of refrigerant-134a as the working
fluid (Fig. 6–51). The maximum and the minimum temperatures in the cycle
are 20 and 288C, respectively. It is known that the refrigerant is saturated
liquid at the end of the heat rejection process, and the net work input to
the cycle is 15 kJ. Determine the fraction of the mass of the refrigerant that
vaporizes during the heat addition process, and the pressure at the end of
the heat rejection process.
T
QH
20°C
−8°C
4
3
1
2
QL
V
SOLUTION A Carnot refrigeration cycle is executed in a closed system.
The mass fraction of the refrigerant that vaporizes during the heat addition
process and the pressure at the end of the heat rejection process are to be
determined.
Assumptions The refrigerator operates on the ideal Carnot cycle.
Analysis Knowing the high and low temperatures, the coefficient of performance of the cycle is
COPR 5
1
1
5
5 9.464
TH /TL 2 1
(20 1 273 K)/(28 1 273 K) 2 1
FIGURE 6–51
Schematic for Example 6–6.
306
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
The amount of cooling is determined from the definition of the coefficient of
performance to be
QL 5 COPR 3 Win 5 (9.464)(15 kJ) 5 142 kJ
The enthalpy of vaporization R-134a at 288C is hfg 5 204.59 kJ/kg
(Table A-11). Then the amount of refrigerant that vaporizes during heat
absorption becomes
QL 5 mevaphfg@288C S mevap 5
142 kJ
5 0.694 kg
204.59 kJ/kg
Therefore, the fraction of mass that vaporized during heat addition process
to the refrigerant is
Mass fraction 5
mevap
mtotal
5
0.694 kg
5 0.868 or 86.8%
0.8 kg
The pressure at the end of heat rejection process is simply the saturation
pressure at heat rejection temperature,
P4 5 Psat@208C 5 572.1 kPa
Discussion Carnot cycle is an idealized refrigeration cycle, thus it cannot be
achieved in practice. Practical refrigeration cycles are analyzed in Chap. 11.
EXAMPLE 6–7
135,000 kJ/h
Heat loss
House
TH = 21°C
·
QH
·
Wnet,in = ?
HP
·
QL
Heating a House by a Carnot Heat Pump
A heat pump is to be used to heat a house during the winter, as shown in
Fig. 6–52. The house is to be maintained at 218C at all times. The house
is estimated to be losing heat at a rate of 135,000 kJ/h when the outside
temperature drops to 258C. Determine the minimum power required to drive
this heat pump.
SOLUTION A heat pump maintains a house at a constant temperature. The
required minimum power input to the heat pump is to be determined.
Assumptions Steady operating conditions exist.
·
Analysis The heat pump must supply heat to the house at a rate of QH 5
135,000 kJ/h 5 37.5 kW. The power requirements are minimum when a
reversible heat pump is used to do the job. The COP of a reversible heat
pump operating between the house and the outside air is
COPHP,rev 5
1
1
5 11.3
5
1 2 TL /TH
1 2 (25 1 273 K)/(21 1 273 K)
Then, the required power input to this reversible heat pump becomes
Cold outside air
TL = −5°C
FIGURE 6–52
Schematic for Example 6–7.
#
Wnet,in 5
.
QH
COPHP
5
37.5 kW
5 3.32 kW
11.3
Discussion This reversible heat pump can meet the heating requirements
of this house by consuming electric power at a rate of 3.32 kW only. If this
307
CHAPTER 6
house were to be heated by electric resistance heaters instead, the power
consumption would jump up 11.3 times to 37.5 kW. This is because in
resistance heaters the electric energy is converted to heat at a one-to-one
ratio. With a heat pump, however, energy is absorbed from the outside and
carried to the inside using a refrigeration cycle that consumes only 3.32 kW.
Notice that the heat pump does not create energy. It merely transports it
from one medium (the cold outdoors) to another (the warm indoors).
TOPIC OF SPECIAL INTEREST*
Household Refrigerators
Refrigerators to preserve perishable foods have long been one of the essential appliances in a household. They have proven to be highly durable and
reliable, providing satisfactory service for over 15 years. A typical household refrigerator is actually a combination refrigerator-freezer since it has a
freezer compartment to make ice and to store frozen food.
Today’s refrigerators use much less energy as a result of using smaller and
higher-efficiency motors and compressors, better insulation materials, larger
coil surface areas, and better door seals (Fig. 6–53). At an average electricity rate of 8.3 cents per kWh, an average refrigerator costs about $72 a
year to run, which is half the annual operating cost of a refrigerator 25 years
ago. Replacing a 25-year-old, 18-ft3 refrigerator with a new energy-efficient
model will save over 1000 kWh of electricity per year. For the environment,
this means a reduction of over 1 ton of CO2, which causes global climate
change, and over 10 kg of SO2, which causes acid rain.
Despite the improvements made in several areas during the past 100 years
in household refrigerators, the basic vapor-compression refrigeration cycle has
remained unchanged. The alternative absorption refrigeration and thermoelectric
refrigeration systems are currently more expensive and less efficient, and they
have found limited use in some specialized applications (Table 6–1).
A household refrigerator is designed to maintain the freezer section at 2188C
(08F) and the refrigerator section at 38C (378F). Lower freezer temperatures
increase energy consumption without improving the storage life of frozen
foods significantly. Different temperatures for the storage of specific foods
can be maintained in the refrigerator section by using special-purpose compartments.
Practically all full-size refrigerators have a large air-tight drawer for leafy
vegetables and fresh fruits to seal in moisture and to protect them from the
drying effect of cool air circulating in the refrigerator. A covered egg compartment in the lid extends the life of eggs by slowing down the moisture
loss from the eggs. It is common for refrigerators to have a special warmer
compartment for butter in the door to maintain butter at spreading temperature. The compartment also isolates butter and prevents it from absorbing odors and tastes from other food items. Some upscale models have a
temperature-controlled meat compartment maintained at 20.58C (318F),
which keeps meat at the lowest safe temperature without freezing it, and
*This section can be skipped without a loss in continuity.
Better door
seals
Better insulation
materials
Refrigerator
More efficient motors
and compressors
FIGURE 6–53
Today’s refrigerators are much more
efficient because of the improvements
in technology and manufacturing.
TABLE 6–1
Typical operating efficiencies of
some refrigeration systems for a
freezer temperature of 2188C and
ambient temperature of 328C
Type of
refrigeration
system
Coefficient
of
performance
Vapor-compression
Absorption
refrigeration
Thermoelectric
refrigeration
1.3
0.4
0.1
308
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
thus extending its storage life. The more expensive models come with an
automatic icemaker located in the freezer section that is connected to the
water line, as well as automatic ice and chilled-water dispensers. A typical
icemaker can produce 2 to 3 kg of ice per day and store 3 to 5 kg of ice in a
removable ice storage container.
Household refrigerators consume from about 90 to 600 W of electrical
energy when running and are designed to perform satisfactorily in environments at up to 438C (1108F). Refrigerators run intermittently, as you may
have noticed, running about 30 percent of the time under normal use in a
house at 258C (778F).
For specified external dimensions, a refrigerator is desired to have maximum
food storage volume, minimum energy consumption, and the lowest possible
cost to the consumer. The total food storage volume has been increased over
the years without an increase in the external dimensions by using thinner but
more effective insulation and minimizing the space occupied by the compressor and the condenser. Switching from the fiber-glass insulation (thermal
conductivity k 5 0.032–0.040 W/m·8C) to expanded-in-place urethane foam
insulation (k 5 0.019 W/m·8C) made it possible to reduce the wall thickness
of the refrigerator by almost half, from about 90 to 48 mm for the freezer
section and from about 70 to 40 mm for the refrigerator section. The rigidity
and bonding action of the foam also provide additional structural support.
However, the entire shell of the refrigerator must be carefully sealed to prevent any water leakage or moisture migration into the insulation since moisture degrades the effectiveness of insulation.
The size of the compressor and the other components of a refrigeration
system are determined on the basis of the anticipated heat load (or refrigeration load), which is the rate of heat flow into the refrigerator. The heat load
consists of the predictable part, such as heat transfer through the walls and
door gaskets of the refrigerator, fan motors, and defrost heaters (Fig. 6–54),
and the unpredictable part, which depends on the user habits such as opening the door, making ice, and loading the refrigerator. The amount of energy
Thermal insulation
6%
Defrost
heater
6%
Fan
motor
6%
External
heater
FIGURE 6–54
The cross section of a refrigerator
showing the relative magnitudes of
various effects that constitute the
predictable heat load.
52%
Wall
insulation
30%
Door
gasket
region
Plastic breaker strips
Plastic door liner
309
CHAPTER 6
consumed by the refrigerator can be minimized by practicing good conservation measures as discussed below.
1. Open the refrigerator door the fewest times possible for the shortest
duration possible. Each time the refrigerator door is opened, the cool air
inside is replaced by the warmer air outside, which needs to be cooled.
Keeping the refrigerator or freezer full will save energy by reducing the
amount of cold air that can escape each time the door is opened.
2. Cool the hot foods to room temperature first before putting them into
the refrigerator. Moving a hot pan from the oven directly into the refrigerator not only wastes energy by making the refrigerator work longer,
but it also causes the nearby perishable foods to spoil by creating a
warm environment in its immediate surroundings (Fig. 6–55).
3. Clean the condenser coils located behind or beneath the refrigerator.
The dust and grime that collect on the coils act as insulation that
slows down heat dissipation through them. Cleaning the coils a couple
of times a year with a damp cloth or a vacuum cleaner will improve
cooling ability of the refrigerator while cutting down the power
consumption by a few percent. Sometimes a fan is used to force-cool
the condensers of large or built-in refrigerators, and the strong air
motion keeps the coils clean.
4. Check the door gasket for air leaks. This can be done by placing a flashlight into the refrigerator, turning off the kitchen lights, and looking for
light leaks. Heat transfer through the door gasket region accounts for
almost one-third of the regular heat load of the refrigerators, and thus
any defective door gaskets must be repaired immediately.
5. Avoid unnecessarily low temperature settings. The recommended
temperatures for freezers and refrigerators are 2188C (08F) and 38C
(378F), respectively. Setting the freezer temperature below 2188C adds
significantly to the energy consumption but does not add much to the
storage life of frozen foods. Keeping temperatures 68C (or 108F) below
recommended levels can increase the energy use by as much as 25 percent.
6. Avoid excessive ice build-up on the interior surfaces of the evaporator.
The ice layer on the surface acts as insulation and slows down heat
transfer from the freezer section to the refrigerant. The refrigerator
should be defrosted by manually turning off the temperature control
switch when the ice thickness exceeds a few millimeters.
Defrosting is done automatically in no-frost refrigerators by supplying heat to the evaporator by a 300-W to 1000-W resistance heater or
by hot refrigerant gas, periodically for short periods. The water is then
drained to a pan outside where it is evaporated using the heat dissipated
by the condenser. The no-frost evaporators are basically finned tubes
subjected to air flow circulated by a fan. Practically all the frost collects
on fins, which are the coldest surfaces, leaving the exposed surfaces of
the freezer section and the frozen food frost-free.
7. Use the power-saver switch that controls the heating coils and prevents
condensation on the outside surfaces in humid environments. The lowwattage heaters are used to raise the temperature of the outer surfaces
Warm air
30°C
Hot food
80°C
5°C
FIGURE 6–55
Putting hot foods into the refrigerator
without cooling them first not
only wastes energy but also could
spoil the foods nearby.
310
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Cabinet
Warm
air
Refrigerator
Coils
of the refrigerator at critical locations above the dew point in order to
avoid water droplets forming on the surfaces and sliding down. Condensation is most likely to occur in summer in hot and humid climates in
homes without air-conditioning. The moisture formation on the surfaces
is undesirable since it may cause the painted finish of the outer surface
to deteriorate and it may wet the kitchen floor. About 10 percent of the
total energy consumed by the refrigerator can be saved by turning this
heater off and keeping it off unless there is visible condensation on the
outer surfaces.
8. Do not block the air flow passages to and from the condenser coils
of the refrigerator. The heat dissipated by the condenser to the air is
carried away by air that enters through the bottom and sides of the
refrigerator and leaves through the top. Any blockage of this natural
convection air circulation path by large objects such as several cereal
boxes on top of the refrigerator will degrade the performance of the
condenser and thus the refrigerator (Fig. 6–56).
Cool
air
FIGURE 6–56
The condenser coils of a refrigerator
must be cleaned periodically, and the
airflow passages must not be blocked
to maintain high performance.
Light bulb
40 W
These and other commonsense conservation measures will result in a reduction in the energy and maintenance costs of a refrigerator as well as an extended
trouble-free life of the device.
EXAMPLE 6–8
Malfunction of a Refrigerator Light Switch
The interior lighting of refrigerators is provided by incandescent lamps whose
switches are actuated by the opening of the refrigerator door. Consider a
refrigerator whose 40-W lightbulb remains on continuously as a result of a
malfunction of the switch (Fig. 6–57). If the refrigerator has a coefficient of
performance of 1.3 and the cost of electricity is 12 cents per kWh, determine the increase in the energy consumption of the refrigerator and its cost
per year if the switch is not fixed.
SOLUTION The lightbulb of a refrigerator malfunctions and remains on. The
increases in the electricity consumption and cost are to be determined.
Assumptions The life of the lightbulb is more than 1 year.
Analysis The lightbulb consumes 40 W of power when it is on, and thus
adds 40 W to the heat load of the refrigerator. Noting that the COP of the
refrigerator is 1.3, the power consumed by the refrigerator to remove the
heat generated by the lightbulb is
#
Qrefrig
#
40 W
Wrefrig 5
5
5 30.8 W
COPR
1.3
FIGURE 6–57
Schematic for Example 6–8.
Therefore, the total additional power consumed by the refrigerator is
#
#
#
Wtotal,additional 5 Wlight 1 Wrefrig 5 40 1 30.8 5 70.8 W
The total number of hours in a year is
Annual hours 5 (365 days/yr)(24 h/day) 5 8760 h/yr
311
CHAPTER 6
Assuming the refrigerator is opened 20 times a day for an average of 30 s,
the light would normally be on for
Normal operating hours 5 (20 times/day)(30 s/time)(1 h/3600 s)(365 days/yr)
5 61 h/yr
Then the additional hours the light remains on as a result of the malfunction
becomes
Additional operating hours 5 Annual hours 2 Normal operating hours
5 8760 2 61 5 8699 h/yr
Therefore, the additional electric power consumption and its cost per year are
#
Additional power consumption 5 Wtotal,additional 3 (Additional operating hours)
5 (0.0708 kW)(8699 h/yr) 5 616 kWh/yr
and
Additional power cost 5 (Additional power consumption)(Unit cost)
5 (616 kWh/yr)($0.12/kWh) 5 $73.9/yr
Discussion Note that not repairing the switch will cost the homeowner about
$75 a year. This is alarming when we consider that at $0.12/kWh, a typical
refrigerator consumes about $100 worth of electricity a year.
SUMMARY
The second law of thermodynamics states that processes
occur in a certain direction, not in any direction. A process does not occur unless it satisfies both the first and the
second laws of thermodynamics. Bodies that can absorb or
reject finite amounts of heat isothermally are called thermal
energy reservoirs or heat reservoirs.
Work can be converted to heat directly, but heat can be
converted to work only by some devices called heat engines.
The thermal efficiency of a heat engine is defined as
hth 5
Wnet,out
QH
512
QL
QH
where Wnet,out is the net work output of the heat engine, QH
is the amount of heat supplied to the engine, and QL is the
amount of heat rejected by the engine.
Refrigerators and heat pumps are devices that absorb heat
from low-temperature media and reject it to higher-temperature ones. The performance of a refrigerator or a heat pump
is expressed in terms of the coefficient of performance,
which is defined as
COPR 5
COPHP 5
QL
Wnet,in
QH
Wnet,in
5
1
QH /QL 2 1
5
1
1 2 QL /QH
The Kelvin–Planck statement of the second law of thermodynamics states that no heat engine can produce a net
amount of work while exchanging heat with a single reservoir only. The Clausius statement of the second law states
that no device can transfer heat from a cooler body to a
warmer one without leaving an effect on the surroundings.
Any device that violates the first or the second law of
thermodynamics is called a perpetual-motion machine.
A process is said to be reversible if both the system
and the surroundings can be restored to their original conditions. Any other process is irreversible. The
effects such as friction, non-quasi-equilibrium expansion
or compression, and heat transfer through a finite temperature difference render a process irreversible and are
called irreversibilities.
312
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
The Carnot cycle is a reversible cycle that is composed of
four reversible processes, two isothermal and two adiabatic.
The Carnot principles state that the thermal efficiencies of
all reversible heat engines operating between the same two
reservoirs are the same, and that no heat engine is more
efficient than a reversible one operating between the same
two reservoirs. These statements form the basis for establishing a thermodynamic temperature scale related to the heat
transfers between a reversible device and the high- and lowtemperature reservoirs by
a
QH
QL
5
b
rev
engines, is given by
hth,rev 5 1 2
This is the maximum efficiency a heat engine operating
between two reservoirs at temperatures TH and TL can have.
The COPs of reversible refrigerators and heat pumps are
given in a similar manner as
TH
TL
Therefore, the QH/QL ratio can be replaced by TH/TL for
reversible devices, where TH and TL are the absolute temperatures of the high- and low-temperature reservoirs,
respectively.
A heat engine that operates on the reversible Carnot cycle
is called a Carnot heat engine. The thermal efficiency of
a Carnot heat engine, as well as all other reversible heat
TL
TH
COPR,rev 5
1
TH /TL 2 1
COPHP,rev 5
1
1 2 TL /TH
and
Again, these are the highest COPs a refrigerator or a heat
pump operating between the temperature limits of TH and TL
can have.
REFERENCES AND SUGGESTED READINGS
1. ASHRAE Handbook of Refrigeration, SI version. Atlanta,
GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and AirConditioning Engineers, Inc. 1994.
3. J. T. Amann, A. Wilson, and K. Ackerly, Consumer Guide
to Home Energy Saving, 9th ed., American Council for an
Energy-Efficient Economy, Washington, D. C., 2007.
2. D. Stewart. “Wheels Go Round and Round, but Always
Run Down.” November 1986, Smithsonian, pp. 193–208.
PROBLEMS*
Second Law of Thermodynamics and Thermal Energy
Reservoirs
6–1C Describe an imaginary process that violates both the
first and the second laws of thermodynamics.
6–2C Describe an imaginary process that satisfies the first
law but violates the second law of thermodynamics.
6–3C Describe an imaginary process that satisfies the second law but violates the first law of thermodynamics.
6–4C An experimentalist claims to have raised the temperature
of a small amount of water to 1508C by transferring heat from
high-pressure steam at 1208C. Is this a reasonable claim? Why?
Assume no refrigerator or heat pump is used in the process.
6–5C
What is a thermal energy reservoir? Give some examples.
6–6C Consider the process of baking potatoes in a conventional oven. Can the hot air in the oven be treated as a thermal energy reservoir? Explain.
Heat Engines and Thermal Efficiency
* Problems designated by a “C” are concept questions, and
students are encouraged to answer them all. Problems designated
by an “E” are in English units, and the SI users can ignore them.
icon are solved using EES, and complete
Problems with the
solutions together with parametric studies are included on the text
website. Problems with the
icon are comprehensive in nature,
and are intended to be solved with an equation solver such as EES.
6–7C
What are the characteristics of all heat engines?
6–8C What is the Kelvin–Planck expression of the second
law of thermodynamics?
6–9C Is it possible for a heat engine to operate without
rejecting any waste heat to a low-temperature reservoir?
Explain.
313
CHAPTER 6
6–10C Baseboard heaters are basically electric resistance
heaters and are frequently used in space heating. A home
owner claims that her 5-year-old baseboard heaters have a
conversion efficiency of 100 percent. Is this claim in violation of any thermodynamic laws? Explain.
6–11C Does a heat engine that has a thermal efficiency of
100 percent necessarily violate (a) the first law and (b) the
second law of thermodynamics? Explain.
6–12C In the absence of any friction and other irreversibilities,
can a heat engine have an efficiency of 100 percent? Explain.
6–13C Are the efficiencies of all the work-producing
devices, including the hydroelectric power plants, limited by
the Kelvin–Planck statement of the second law? Explain.
6–14C Consider a pan of water being heated (a) by placing
it on an electric range and (b) by placing a heating element in
the water. Which method is a more efficient way of heating
water? Explain.
6–15 A steam power plant receives heat from a furnace at a
rate of 280 GJ/h. Heat losses to the surrounding air from the
steam as it passes through the pipes and other components
are estimated to be about 8 GJ/h. If the waste heat is transferred to the cooling water at a rate of 145 GJ/h, determine
(a) net power output and (b) the thermal efficiency of this
power plant. Answers: (a) 35.3 MW, (b) 45.4 percent
6–16E A car engine with a power output of 110 hp has a
thermal efficiency of 28 percent. Determine the rate of fuel
consumption if the heating value of the fuel is 19,000 Btu/lbm.
6–17E A heat engine has a heat input of 3 3 104 Btu/h and
a thermal efficiency of 40 percent. Calculate the power it will
produce, in hp.
Source
3 × 104 Btu/h
hth = 40%
HE
.
Wnet
Sink
FIGURE P6–17E
6–18 The thermal efficiency of a general heat engine is
35 percent, and it produces 60 hp. At what rate is heat transferred to this engine, in kJ/s?
6–19 A 600-MW steam power plant, which is cooled by a
nearby river, has a thermal efficiency of 40 percent. Determine
the rate of heat transfer to the river water. Will the actual heat
transfer rate be higher or lower than this value? Why?
6–20 A heat engine that pumps water out of an underground mine accepts 700 kJ of heat and produces 250 kJ of
work. How much heat does it reject, in kJ?
6–21 A heat engine with a thermal efficiency of 45 percent
rejects 500 kJ/kg of heat. How much heat does it
receive? Answer: 909 kJ/kg
6–22 A steam power plant with a power output of 150 MW
consumes coal at a rate of 60 tons/h. If the heating value of
the coal is 30,000 kJ/kg, determine the overall efficiency of
this plant. Answer: 30.0 percent
6–23 An automobile engine consumes fuel at a rate of
22 L/h and delivers 55 kW of power to the wheels. If the fuel
has a heating value of 44,000 kJ/kg and a density of 0.8 g/cm3,
determine the efficiency of this engine. Answer: 25.6 percent
6–24 In 2001, the United States produced 51 percent of its
electricity in the amount of 1.878 3 1012 kWh from coalfired power plants. Taking the average thermal efficiency to be
34 percent, determine the amount of thermal energy rejected
by the coal-fired power plants in the United States that year.
6–25E Solar energy stored in large bodies of water, called
solar pounds, is being used to generate electricity. If such a
solar power plant has an efficiency of 3 percent and a net
power output of 180 kW, determine the average value of the
required solar energy collection rate, in Btu/h.
6–26 A coal-burning steam power plant produces a net power
of 300 MW with an overall thermal efficiency of 32 percent.
The actual gravimetric air–fuel ratio in the furnace is calculated to be 12 kg air/kg fuel. The heating value of the coal is
28,000 kJ/kg. Determine (a) the amount of coal consumed during a 24-hour period and (b) the rate of air flowing through the
furnace. Answers: (a) 2.89 3 106 kg, (b) 402 kg/s
6–27E An Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC)
power plant built in Hawaii in 1987 was designed to operate
between the temperature limits of 868F at the ocean surface
and 418F at a depth of 2100 ft. About 13,300 gpm of cold
seawater was to be pumped from deep ocean through a 40-indiameter pipe to serve as the cooling medium or heat sink. If
the cooling water experiences a temperature rise of 68F and
the thermal efficiency is 2.5 percent, determine the amount of
power generated. Take the density of seawater to be 64 lbm/ft3.
Refrigerators and Heat Pumps
6–28C What is the difference between a refrigerator and a
heat pump?
6–29C What is the difference between a refrigerator and an
air conditioner?
314
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
6–30C In a refrigerator, heat is transferred from a lowertemperature medium (the refrigerated space) to a highertemperature one (the kitchen air). Is this a violation of the
second law of thermodynamics? Explain.
6–31C A heat pump is a device that absorbs energy from the
cold outdoor air and transfers it to the warmer indoors. Is this a
violation of the second law of thermodynamics? Explain.
6–32C Define the coefficient of performance of a refrigerator in words. Can it be greater than unity?
6–33C Define the coefficient of performance of a heat
pump in words. Can it be greater than unity?
6–34C A heat pump that is used to heat a house has a COP
of 2.5. That is, the heat pump delivers 2.5 kWh of energy to
the house for each 1 kWh of electricity it consumes. Is this a
violation of the first law of thermodynamics? Explain.
6–35C A refrigerator has a COP of 1.5. That is, the refrigerator removes 1.5 kWh of energy from the refrigerated space
for each 1 kWh of electricity it consumes. Is this a violation
of the first law of thermodynamics? Explain.
6–36C What is the Clausius expression of the second law
of thermodynamics?
6–37C Show that the Kelvin–Planck and the Clausius
expressions of the second law are equivalent.
6–38 Determine the COP of a refrigerator that removes heat
from the food compartment at a rate of 5040 kJ/h for each
kW of power it consumes. Also, determine the rate of heat
rejection to the outside air.
6–39 Determine the COP of a heat pump that supplies
energy to a house at a rate of 8000 kJ/h for each kW of
electric power it draws. Also, determine the rate of energy
absorption from the outdoor air. Answers: 2.22, 4400 kJ/h
6–40E A residential heat pump has a coefficient of performance of 2.4. How much heating effect, in Btu/h, will result
when 5 hp is supplied to this heat pump?
Reservoir
.
QH
HP
6–41 A refrigerator used to cool a computer requires 1.2 kW
of electrical power and has a COP of 1.8. Calculate the cooling effect of this refrigerator, in kW.
6–42 An air conditioner removes heat steadily from a house at a
rate of 750 kJ/min while drawing electric power at a rate of 6 kW.
Determine (a) the COP of this air conditioner and (b) the rate of
heat transfer to the outside air. Answers: (a) 2.08, (b) 1110 kJ/min
6–43 A food department is kept at 2128C by a refrigerator
in an environment at 308C. The total heat gain to the food
department is estimated to be 3300 kJ/h and the heat rejection in the condenser is 4800 kJ/h. Determine the power input
to the compressor, in kW and the COP of the refrigerator.
30°C
4800 kJ/h
3300 kJ/h
–12°C
FIGURE P6–43
6–44 A household refrigerator that has a power input of 450
W and a COP of 1.5 is to cool 5 large watermelons, 10 kg each,
to 88C. If the watermelons are initially at 288C, determine how
long it will take for the refrigerator to cool them. The watermelons can be treated as water whose specific heat is 4.2 kJ/kg·8C.
Is your answer realistic or optimistic? Explain. Answer: 104 min
6–45
When a man returns to his well-sealed house on a
summer day, he finds that the house is at 358C.
He turns on the air conditioner, which cools the entire house to
208C in 30 min. If the COP of the air-conditioning system is
2.8, determine the power drawn by the air conditioner. Assume
the entire mass within the house is equivalent to 800 kg of air
for which cv 5 0.72 kJ/kg·8C and cp 5 1.0 kJ/kg·8C.
5 hp
COP = 2.4
.
Win
R
·
Win
35°C
20°C
Reservoir
FIGURE P6–40E
A/C
FIGURE P6–45
315
CHAPTER 6
6–46
Reconsider Prob. 6–45. Using EES (or other)
software, determine the power input required by
the air conditioner to cool the house as a function for airconditioner EER ratings in the range 5 to 15. Discuss your
results and include representative costs of air-conditioning
units in the EER rating range.
·
Win
800
kJ/h
COP = 2.2
Refrigerator
6–47E A heat pump with a COP of 2.5 supplies energy
to a house at a rate of 60,000 Btu/h. Determine (a) the
electric power drawn by the heat pump and (b) the rate of
heat absorption from the outside air. Answers: (a) 9.43 hp,
(b) 36,000 Btu/h
6–48 Bananas are to be cooled from 24 to 138C at a rate of
215 kg/h by a refrigeration system. The power input to the
refrigerator is 1.4 kW. Determine the rate of cooling, in kJ/
min, and the COP of the refrigerator. The specific heat of
banana above freezing is 3.35 kJ/kg·8C.
6–49 A heat pump is used to maintain a house at a constant temperature of 238C. The house is losing heat to the
outside air through the walls and the windows at a rate of
85,000 kJ/h while the energy generated within the house
from people, lights, and appliances amounts to 4000 kJ/h. For
a COP of 3.2, determine the required power input to the heat
pump. Answer: 7.03 kW
85,000 kJ/h
·
Win
23°C
4000 kJ/h
HP
FIGURE P6–51
6–52 A heat pump used to heat a house runs about onethird of the time. The house is losing heat at an average rate
of 22,000 kJ/h. If the COP of the heat pump is 2.8, determine
the power the heat pump draws when running.
6–53E Consider an office room that is being cooled adequately by a 12,000 Btu/h window air conditioner. Now it is
decided to convert this room into a computer room by installing several computers, terminals, and printers with a total
rated power of 8.4 kW. The facility has several 7000 Btu/h
air conditioners in storage that can be installed to meet the
additional cooling requirements. Assuming a usage factor of
0.4 (i.e., only 40 percent of the rated power will be consumed
at any given time) and additional occupancy of seven people,
each generating heat at a rate of 100 W, determine how many
of these air conditioners need to be installed to the room.
6–54 Consider a building whose annual air-conditioning
load is estimated to be 40,000 kWh in an area where the
unit cost of electricity is $0.10/kWh. Two air conditioners
are considered for the building. Air conditioner A has a seasonal average COP of 2.3 and costs $5500 to purchase and
install. Air conditioner B has a seasonal average COP of 3.6
and costs $7000 to purchase and install. All else being equal,
determine which air conditioner is a better buy.
40,000 kWh
FIGURE P6–49
6–50E Water enters an ice machine at 558F and leaves
as ice at 258F. If the COP of the ice machine is 2.4 during
this operation, determine the required power input for an ice
production rate of 28 lbm/h. (169 Btu of energy needs to be
removed from each lbm of water at 558F to turn it into ice
at 258F.)
6–51 A household refrigerator runs one-fourth of the
time and removes heat from the food compartment at an
average rate of 800 kJ/h. If the COP of the refrigerator
is 2.2, determine the power the refrigerator draws when
running.
A
Air cond.
COP = 2.3
·
Win
FIGURE P6–54
House
40,000 kWh
B
Air cond.
COP = 3.6
·
Win
316
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
6–55 Refrigerant-134a enters the condenser of a residential heat pump at 800 kPa and 358C at a rate of 0.018 kg/s
and leaves at 800 kPa as a saturated liquid. If the compressor consumes 1.2 kW of power, determine (a) the COP of
the heat pump and (b) the rate of heat absorption from the
outside air.
.
QH
800 kPa
x=0
6–61C Show that processes that use work for mixing are
irreversible by considering an adiabatic system whose contents are stirred by turning a paddle wheel inside the system
(e.g., stirring a cake mix with an electric mixer).
6–62C Why does a nonquasi-equilibrium compression process require a larger work input than the corresponding quasiequilibrium one?
800 kPa
35°C
6–63C Why does a nonquasi-equilibrium expansion process
deliver less work than the corresponding quasi-equilibrium
one?
Condenser
Expansion
valve
6–60C Show that processes involving rapid chemical reactions are irreversible by considering the combustion of a
natural gas (e.g., methane) and air mixture in a rigid container.
Compressor
.
Win
Evaporator
.
QL
FIGURE P6–55
6–64C How do you distinguish between internal and external irreversibilities?
6–65C Is a reversible expansion or compression process necessarily quasi-equilibrium? Is a quasi-equilibrium
expansion or compression process necessarily reversible?
Explain.
6–66C Why are engineers interested in reversible processes
even though they can never be achieved?
The Carnot Cycle and Carnot Principles
6–67C
cycle?
Perpetual-Motion Machines
6–56C An inventor claims to have developed a resistance
heater that supplies 1.2 kWh of energy to a room for each
kWh of electricity it consumes. Is this a reasonable claim,
or has the inventor developed a perpetual-motion machine?
Explain.
6–57C It is common knowledge that the temperature of air
rises as it is compressed. An inventor thought about using
this high-temperature air to heat buildings. He used a compressor driven by an electric motor. The inventor claims that
the compressed hot-air system is 25 percent more efficient
than a resistance heating system that provides an equivalent
amount of heating. Is this claim valid, or is this just another
perpetual-motion machine? Explain.
What are the four processes that make up the Carnot
6–68C What are the two statements known as the Carnot
principles?
6–69C Is it possible to develop (a) an actual and (b) a
reversible heat-engine cycle that is more efficient than a
Carnot cycle operating between the same temperature limits?
Explain.
6–70C Somebody claims to have developed a new reversible heat-engine cycle that has a higher theoretical efficiency
than the Carnot cycle operating between the same temperature limits. How do you evaluate this claim?
6–71C Somebody claims to have developed a new reversible heat-engine cycle that has the same theoretical efficiency
as the Carnot cycle operating between the same temperature
limits. Is this a reasonable claim?
Reversible and Irreversible Processes
Carnot Heat Engines
6–58C A cold canned drink is left in a warmer room where
its temperature rises as a result of heat transfer. Is this a
reversible process? Explain.
6–72C Is there any way to increase the efficiency of a
Carnot heat engine other than by increasing TH or decreasing TL?
6–59C A block slides down an inclined plane with friction
and no restraining force. Is this process reversible or irreversible? Justify your answer.
6–73C Consider two actual power plants operating with
solar energy. Energy is supplied to one plant from a solar
pond at 808C and to the other from concentrating collectors
317
CHAPTER 6
that raise the water temperature to 6008C. Which of these
power plants will have a higher efficiency? Explain.
6–74 From a work-production perspective, which is more
valuable: (a) thermal energy reservoirs at 675 K and 325 K
or (b) thermal energy reservoirs at 625 K and 275 K?
6–75E A heat engine is operating on a Carnot cycle and
has a thermal efficiency of 55 percent. The waste heat from
this engine is rejected to a nearby lake at 608F at a rate of
800 Btu/min. Determine (a) the power output of the engine
and (b) the temperature of the source. Answers: (a) 23.1 hp,
(b) 1156 R
Source TH
temperature vary from 300 to 10008C, and the sink temperature to vary from 0 to 508C. Plot the power produced
and the cycle efficiency against the source temperature
for sink temperatures of 08C, 258C, and 508C, and discuss the results.
6–80E An inventor claims to have devised a cyclical
engine for use in space vehicles that operates with a
nuclear-fuel-generated energy source whose temperature
is 920 R and a sink at 490 R that radiates waste heat
to deep space. He also claims that this engine produces
4.5 hp while rejecting heat at a rate of 15,000 Btu/h. Is
this claim valid?
920 R
.
QH
·
Wnet, out
Carnot
HE
800 Btu/min
Sink 60° F
FIGURE P6–75E
6–76 A Carnot heat engine receives 650 kJ of heat from a
source of unknown temperature and rejects 250 kJ of it to a
sink at 248C. Determine (a) the temperature of the source and
(b) the thermal efficiency of the heat engine.
6–77 A Carnot heat engine operates between a source
at 1000 K and a sink at 300 K. If the heat engine is supplied with heat at a rate of 800 kJ/min, determine (a) the
thermal efficiency and (b) the power output of this heat
engine. Answers: (a) 70 percent, (b) 9.33 kW
6–78
A heat engine operates between a source at
4778C and a sink at 258C. If heat is supplied to
the heat engine at a steady rate of 65,000 kJ/min, determine
the maximum power output of this heat engine.
6–79
Reconsider Prob. 6–78. Using EES (or other)
software, study the effects of the temperatures of the heat source and the heat sink on the power
produced and the cycle thermal efficiency. Let the source
HE
4.5 hp
15,000 Btu/h
490 R
FIGURE P6–80E
6–81 A heat engine receives heat from a heat source at
12008C and has a thermal efficiency of 40 percent. The
heat engine does maximum work equal to 500 kJ. Determine the heat supplied to the heat engine by the heat
source, the heat rejected to the heat sink, and the temperature of the heat sink.
6–82 In tropical climates, the water near the surface of
the ocean remains warm throughout the year as a result of
solar energy absorption. In the deeper parts of the ocean,
however, the water remains at a relatively low temperature since the sun’s rays cannot penetrate very far. It is
proposed to take advantage of this temperature difference
and construct a power plant that will absorb heat from
the warm water near the surface and reject the waste heat
to the cold water a few hundred meters below. Determine
the maximum thermal efficiency of such a plant if the
water temperatures at the two respective locations are 24
and 38C.
318
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
24°C
Ocean
energy source to a higher-temperature medium by a heat
pump before energy is supplied to the power plant. What do
you think of this suggestion? Explain.
Boiler
Pump
Turbine
Condenser
6–90 During an experiment conducted in a room at
258C, a laboratory assistant measures that a refrigerator that draws 2 kW of power has removed 30,000 kJ of
heat from the refrigerated space, which is maintained at
2308C. The running time of the refrigerator during the
experiment was 20 min. Determine if these measurements
are reasonable.
25°C
3°C
FIGURE P6–82
2 kW
Refrig.
6–83 A well-established way of power generation involves
the utilization of geothermal energy—the energy of hot water
that exists naturally underground—as the heat source. If
a supply of hot water at 1408C is discovered at a location
where the environmental temperature is 208C, determine the
maximum thermal efficiency a geothermal power plant built
at that location can have. Answer: 29.1 percent
30,000 kJ
–30°C
FIGURE P6–90
Carnot Refrigerators and Heat Pumps
6–84C A homeowner buys a new refrigerator and a new air
conditioner. Which one of these devices would you expect to
have a higher COP? Why?
6–85C A homeowner buys a new refrigerator with no freezer
compartment and a deep freezer for the new kitchen. Which of
these devices would you expect to have a lower COP? Why?
6–86C
How can we increase the COP of a Carnot refrigerator?
6–87C In an effort to conserve energy in a heat-engine cycle,
somebody suggests incorporating a refrigerator that will absorb
some of the waste energy QL and transfer it to the energy
source of the heat engine. Is this a smart idea? Explain.
6–88C It is well established that the thermal efficiency of
a heat engine increases as the temperature TL at which heat
is rejected from the heat engine decreases. In an effort to
increase the efficiency of a power plant, somebody suggests
refrigerating the cooling water before it enters the condenser, where heat rejection takes place. Would you be in
favor of this idea? Why?
6–89C It is well known that the thermal efficiency of heat
engines increases as the temperature of the energy source
increases. In an attempt to improve the efficiency of a power
plant, somebody suggests transferring heat from the available
6–91 A Carnot refrigerator operates in a room in which
the temperature is 228C and consumes 2 kW of power when
operating. If the food compartment of the refrigerator is to be
maintained at 38C, determine the rate of heat removal from
the food compartment.
6–92 An air-conditioning system operating on the
reversed Carnot cycle is required to transfer heat from a
house at a rate of 750 kJ/min to maintain its temperature
at 248C. If the outdoor air temperature is 358C, determine
the power required to operate this air-conditioning system.
Answer: 0.46 kW
6–93 An inventor claims to have developed a heat pump
that produces a 200-kW heating effect for a 293 K heated
zone while only using 75 kW of power and a heat source at
273 K. Justify the validity of this claim.
6–94 A heat pump operates on a Carnot heat pump cycle
with a COP of 8.7. It keeps a space at 248C by consuming 2.15 kW of power. Determine the temperature of the
reservoir from which the heat is absorbed and the heating load provided by the heat pump. Answers: 263 K,
18.7 kW
319
CHAPTER 6
6–95 A refrigerator is to remove heat from the cooled
space at a rate of 300 kJ/min to maintain its temperature
at 288C. If the air surrounding the refrigerator is at 258C,
determine the minimum power input required for this
refrigerator. Answer: 0.623 kW
·
Win,min
300
kJ/min
Refrigerator
–8°C
25°C
6–98E A completely reversible refrigerator operates
between thermal energy reservoirs at 450 R and 540 R. How
many kilowatts of power are required for this device to produce a 15,000-Btu/h cooling effect?
6–99E An air-conditioning system is used to maintain a
house at 728F when the temperature outside is 908F. If this
air-conditioning system draws 5 hp of power when operating,
determine the maximum rate of heat removal from the house
that it can accomplish.
6–100 A refrigerator operating on the reversed Carnot cycle has a measured work input of 200 kW and
heat rejection of 2000 kW to a heat reservoir at 278C.
Determine the cooling load supplied to the refrigerator, in kW, and the temperature of the heat source, in 8C.
Answers: 1800 kW, 23°C
FIGURE P6–95
6–96 An inventor claims to have developed a refrigeration system that removes heat from the closed region
at 2128C and transfers it to the surrounding air at 258C
while maintaining a COP of 6.5. Is this claim reasonable?
Why?
6–97 A heat pump is used to maintain a house at 258C by
extracting heat from the outside air on a day when the outside air temperature is 48C. The house is estimated to lose
heat at a rate of 110,000 kJ/h, and the heat pump consumes
4.75 kW of electric power when running. Is this heat pump
powerful enough to do the job?
6–101 A commercial refrigerator with refrigerant-134a
as the working fluid is used to keep the refrigerated
space at 2358C by rejecting waste heat to cooling water
that enters the condenser at 188C at a rate of 0.25 kg/s
and leaves at 268C. The refrigerant enters the condenser
at 1.2 MPa and 508C and leaves at the same pressure subcooled by 58C. If the compressor consumes 3.3 kW of
power, determine (a) the mass flow rate of the refrigerant, (b) the refrigeration load, (c) the COP, and (d) the
minimum power input to the compressor for the same
refrigeration load.
Water
18°C
26°C
1.2 MPa
5°C subcooled
Condenser
110,000 kJ/h
Expansion
valve
25°C
1.2 MPa
50°C
Compressor
·
Win
Evaporator
4.75 kW
HP
·
QL
FIGURE P6–101
Outdoors
4°C
FIGURE P6–97
6–102 The performance of a heat pump degrades (i.e.,
its COP decreases) as the temperature of the heat source
decreases. This makes using heat pumps at locations with
320
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
severe weather conditions unattractive. Consider a house that
is heated and maintained at 208C by a heat pump during the
winter. What is the maximum COP for this heat pump if heat
is extracted from the outdoor air at (a) 108C, (b) 258C, and
(c) 2308C?
6–103E A heat pump is to be used for heating a house in
winter. The house is to be maintained at 788F at all times.
When the temperature outdoors drops to 258F, the heat losses
from the house are estimated to be 70,000 Btu/h. Determine
the minimum power required to run this heat pump if heat is
extracted from (a) the outdoor air at 258F and (b) the well
water at 508F.
6–104 A Carnot heat pump is to be used to heat a house
and maintain it at 258C in winter. On a day when the average
outdoor temperature remains at about 28C, the house is estimated to lose heat at a rate of 55,000 kJ/h. If the heat pump
consumes 4.8 kW of power while operating, determine (a)
how long the heat pump ran on that day; (b) the total heating
costs, assuming an average price of 11¢/kWh for electricity;
and (c) the heating cost for the same day if resistance heating is used instead of a heat pump. Answers: (a) 5.90 h,
(b) $3.11, (c) $40.3
55,000 kJ/h
6–106E A Carnot heat engine receives heat from a reservoir at 17008F at a rate of 700 Btu/min and rejects the waste
heat to the ambient air at 808F. The entire work output of
the heat engine is used to drive a refrigerator that removes
heat from the refrigerated space at 208F and transfers it to the
same ambient air at 808F. Determine (a) the maximum rate of
heat removal from the refrigerated space and (b) the total rate
of heat rejection to the ambient air. Answers: (a) 4200 Btu/
min, (b) 4900 Btu/min
6–107 The structure of a house is such that it loses heat at
a rate of 3800 kJ/h per 8C difference between the indoors and
outdoors. A heat pump that requires a power input of 4 kW
is used to maintain this house at 248C. Determine the lowest
outdoor temperature for which the heat pump can meet the
heating requirements of this house. Answer: 29.58C
6–108 An air-conditioner with refrigerant-134a as the
working fluid is used to keep a room at 238C by rejecting the waste heat to the outdoor air at 348C. The room
gains heat through the walls and the windows at a rate of
250 kJ/min while the heat generated by the computer, TV,
and lights amounts to 900 W. The refrigerant enters the compressor at 400 kPa as a saturated vapor at a rate of 80 L/min
and leaves at 1200 kPa and 708C. Determine (a) the actual
COP, (b) the maximum COP, and (c) the minimum volume
flow rate of the refrigerant at the compressor inlet for the
same compressor inlet and exit conditions. Answers: (a) 4.33,
(b) 26.9, (c) 12.9 L/min
25°C
.
QH
1.2 MPa
70°C
4.8 kW
HP
Condenser
Expansion
valve
.
Win
Compressor
2°C
Evaporator
FIGURE P6–104
6–105 A Carnot heat engine receives heat from a reservoir
at 9008C at a rate of 800 kJ/min and rejects the waste heat to
the ambient air at 278C. The entire work output of the heat
engine is used to drive a refrigerator that removes heat from
the refrigerated space at 258C and transfers it to the same
ambient air at 278C. Determine (a) the maximum rate of heat
removal from the refrigerated space and (b) the total rate of
heat rejection to the ambient air. Answers: (a) 4982 kJ/min,
(b) 5782 kJ/min
400 kPa
sat. vapor
.
QL
FIGURE P6–108
6–109 Derive an expression for the COP of a completely
reversible refrigerator in terms of the thermal energy reservoir temperatures, TL and TH.
321
CHAPTER 6
Special Topic: Household Refrigerators
6–110C Why are today’s refrigerators much more efficient
than those built in the past?
for the food to cool to room temperature before putting it into
the refrigerator.
6–111C Explain how you can reduce the energy consumption of your household refrigerator.
23°C
6–112C Why is it important to clean the condenser coils of
a household refrigerator a few times a year? Also, why is it
important not to block airflow through the condenser coils?
Hot food
95°C
6–113C Someone proposes that the refrigeration system of
a supermarket be overdesigned so that the entire air-conditioning needs of the store can be met by refrigerated air without installing any air-conditioning system. What do you think
of this proposal?
6–114C Someone proposes that the entire refrigerator/freezer
requirements of a store be met using a large freezer that
supplies sufficient cold air at 2208C instead of installing
separate refrigerators and freezers. What do you think of this
proposal?
6–115 The “Energy Guide” label of a refrigerator states
that the refrigerator will consume $170 worth of electricity per year under normal use if the cost of electricity is
$0.125/kWh. If the electricity consumed by the lightbulb
is negligible and the refrigerator consumes 400 W when
running, determine the fraction of the time the refrigerator
will run.
6–116 The interior lighting of refrigerators is usually provided by incandescent lamps whose switches are actuated
by the opening of the refrigerator door. Consider a refrigerator whose 40-W lightbulb remains on about 60 h per year.
It is proposed to replace the lightbulb by an energy-efficient
bulb that consumes only 18 W but costs $25 to purchase
and install. If the refrigerator has a coefficient of performance of 1.3 and the cost of electricity is 8 cents per kWh,
determine if the energy savings of the proposed lightbulb
justify its cost.
6–117 It is commonly recommended that hot foods be
cooled first to room temperature by simply waiting a while
before they are put into the refrigerator to save energy.
Despite this commonsense recommendation, a person keeps
cooking a large pan of stew three times a week and putting
the pan into the refrigerator while it is still hot, thinking that
the money saved is probably too little. But he says he can be
convinced if you can show that the money saved is significant. The average mass of the pan and its contents is 5 kg.
The average temperature of the kitchen is 238C, and the average temperature of the food is 958C when it is taken off the
stove. The refrigerated space is maintained at 38C, and the
average specific heat of the food and the pan can be taken to
be 3.9 kJ/kg·8C. If the refrigerator has a coefficient of performance of 1.5 and the cost of electricity is 10 cents per kWh,
determine how much this person will save a year by waiting
3°C
FIGURE P6–117
6–118 It is often stated that the refrigerator door should be
opened as few times as possible for the shortest duration of
time to save energy. Consider a household refrigerator whose
interior volume is 0.9 m3 and average internal temperature is
48C. At any given time, one-third of the refrigerated space is
occupied by food items, and the remaining 0.6 m3 is filled
with air. The average temperature and pressure in the kitchen
are 208C and 95 kPa, respectively. Also, the moisture contents of the air in the kitchen and the refrigerator are 0.010
and 0.004 kg per kg of air, respectively, and thus 0.006 kg of
water vapor is condensed and removed for each kg of air that
enters. The refrigerator door is opened an average of 20 times
a day, and each time half of the air volume in the refrigerator
is replaced by the warmer kitchen air. If the refrigerator has
a coefficient of performance of 1.4 and the cost of electricity is 11.5 cents per kWh, determine the cost of the energy
wasted per year as a result of opening the refrigerator door.
What would your answer be if the kitchen air were very dry
and thus a negligible amount of water vapor condensed in the
refrigerator?
Review Problems
6–119 An air-conditioning system is used to maintain a
house at a constant temperature of 208C. The house is gaining heat from outdoors at a rate of 20,000 kJ/h, and the heat
generated in the house from the people, lights, and appliances amounts to 8000 kJ/h. For a COP of 2.5, determine
the required power input to this air-conditioning system.
Answer: 3.11 kW
322
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
6–120E A Carnot heat pump is used to heat and maintain a residential building at 758F. An energy analysis of the
house reveals that it loses heat at a rate of 2500 Btu/h per 8F
temperature difference between the indoors and the outdoors.
For an outdoor temperature of 358F, determine (a) the coefficient of performance and (b) the required power input to the
heat pump. Answers: (a) 13.4, (b) 2.93 hp
Solar pond
35°C
Condenser
6–121 A heat engine receives heat from a heat source
at 12008C and rejects heat to a heat sink at 508C. The heat
engine does maximum work equal to 500 kJ. Determine the
heat supplied to the heat engine by the heat source and the
heat rejected to the heat sink.
Pump
Turbine
6–122E A heat pump creates a heating effect of 32,000 Btu/h
for a space maintained at 530 R while using 1.8 kW of
electrical power. What is the minimum temperature of the
source that satisfies the second law of thermodynamics?
Boiler
80°C
Answer: 428 R
6–123E A refrigeration system uses water-cooled condenser for rejecting the waste heat. The system absorbs heat
from a space at 258F at a rate of 24,000 Btu/h. Water enters
the condenser at 658F at a rate of 1.45 lbm/s. The COP of
the system is estimated to be 1.9. Determine (a) the power
input to the system, in kW, (b) the temperature of the water
at the exit of the condenser, in 8F and (c) the maximum
possible COP of the system. The specific heat of water is
1.0 Btu/bm∙8F.
6–124 A heat pump with a COP of 2.8 is used to heat an
air-tight house. When running, the heat pump consumes
5 kW of power. If the temperature in the house is 78C when
the heat pump is turned on, how long will it take for the heat
pump to raise the temperature of the house to 228C? Is this
answer realistic or optimistic? Explain. Assume the entire
mass within the house (air, furniture, etc.) is equivalent to
1500 kg of air. Answer: 19.2 min
6–125 A promising method of power generation involves
collecting and storing solar energy in large artificial lakes
a few meters deep, called solar ponds. Solar energy is
absorbed by all parts of the pond, and the water temperature rises everywhere. The top part of the pond, however,
loses to the atmosphere much of the heat it absorbs, and
as a result, its temperature drops. This cool water serves
as insulation for the bottom part of the pond and helps
trap the energy there. Usually, salt is planted at the bottom of the pond to prevent the rise of this hot water to
the top. A power plant that uses an organic fluid, such
as alcohol, as the working fluid can be operated between
the top and the bottom portions of the pond. If the water
temperature is 358C near the surface and 808C near the
bottom of the pond, determine the maximum thermal efficiency that this power plant can have. Is it realistic to use
35 and 808C for temperatures in the calculations? Explain.
Answer: 12.7 percent
FIGURE P6–125
6–126 Consider a Carnot refrigeration cycle executed in a
closed system in the saturated liquid–vapor mixture region
using 0.96 kg of refrigerant-134a as the working fluid. It is
known that the maximum absolute temperature in the cycle
is 1.2 times the minimum absolute temperature, and the net
work input to the cycle is 22 kJ. If the refrigerant changes
from saturated vapor to saturated liquid during the heat rejection process, determine the minimum pressure in the cycle.
6–127
Reconsider Prob. 6–126. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the net work
input on the minimum pressure. Let the work input vary from
10 to 30 kJ. Plot the minimum pressure in the refrigeration
cycle as a function of net work input, and discuss the results.
6–128 Consider two Carnot heat engines operating in series.
The first engine receives heat from the reservoir at 1400 K
and rejects the waste heat to another reservoir at temperature T.
The second engine receives this energy rejected by the first
one, converts some of it to work, and rejects the rest to a reservoir at 300 K. If the thermal efficiencies of both engines
are the same, determine the temperature T. Answer: 648 K
6–129 A Carnot heat engine receives heat at 900 K and
rejects the waste heat to the environment at 300 K. The entire
work output of the heat engine is used to drive a Carnot refrigerator that removes heat from the cooled space at 2158C at a
rate of 250 kJ/min and rejects it to the same environment at 300
K. Determine (a) the rate of heat supplied to the heat engine
and (b) the total rate of heat rejection to the environment.
6–130
Reconsider Prob. 6–129. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effects of the heat
323
CHAPTER 6
engine source temperature, the environment temperature, and
the cooled space temperature on the required heat supply to
the heat engine and the total rate of heat rejection to the environment. Let the source temperature vary from 500 to 1000 K,
the environment temperature vary from 275 to 325 K, and the
cooled space temperature vary from 220 to 08C. Plot the
required heat supply against the source temperature for the
cooled space temperature of 2158C and environment temperatures of 275, 300, and 325 K, and discuss the results.
6–131 A heat engine operates between two reservoirs at
800 and 208C. One-half of the work output of the heat engine
is used to drive a Carnot heat pump that removes heat from
the cold surroundings at 28C and transfers it to a house maintained at 228C. If the house is losing heat at a rate of 62,000 kJ/h,
determine the minimum rate of heat supply to the heat engine
required to keep the house at 228C.
6–132E An inventor claims to have developed a refrigerator
that maintains the refrigerated space at 408F while operating
in a room where the temperature is 858F and that has a COP
of 13.5. Is this claim reasonable?
6–133 An old gas turbine has an efficiency of 21 percent
and develops a power output of 6000 kW. Determine the
fuel consumption rate of this gas turbine, in L/min, if the
fuel has a heating value of 42,000 kJ/kg and a density of
0.8 g/cm3.
6–134 The COP of a refrigerator decreases as the temperature of the refrigerated space is decreased. That is, removing
heat from a medium at a very low temperature will require
a large work input. Determine the minimum work input
required to remove 1 kJ of heat from liquid helium at 3 K
when the outside temperature is 300 K. Answer: 99 kJ
6–135 Consider a Carnot heat-pump cycle executed in a
steady-flow system in the saturated liquid–vapor mixture
region using refrigerant-134a flowing at a rate of 0.22 kg/s
as the working fluid. It is known that the maximum absolute temperature in the cycle is 1.2 times the minimum
absolute temperature, and the net power input to the cycle
is 5 kW. If the refrigerant changes from saturated vapor to
saturated liquid during the heat rejection process, determine the ratio of the maximum to minimum pressures in
the cycle.
6–136 Replacing incandescent lights with energy-efficient
fluorescent lights can reduce the lighting energy consumption to one-fourth of what it was before. The energy consumed by the lamps is eventually converted to heat, and
thus switching to energy-efficient lighting also reduces
the cooling load in summer but increases the heating load
in winter. Consider a building that is heated by a natural
gas furnace with an efficiency of 80 percent and cooled by
an air conditioner with a COP of 3.5. If electricity costs
$0.12/kWh and natural gas costs $1.40/therm (1 therm 5
105,500 kJ), determine if efficient lighting will increase or
decrease the total energy cost of the building (a) in summer
and (b) in winter.
6–137 A heat pump supplies heat energy to a house at
the rate of 140,000 kJ/h when the house is maintained at
258C. Over a period of one month, the heat pump operates
for 100 hours to transfer energy from a heat source outside
the house to inside the house. Consider a heat pump receiving heat from two different outside energy sources. In one
application the heat pump receives heat from the outside air
at 08C. In a second application the heat pump receives heat
from a lake having a water temperature of 108C. If electricity costs $0.105/kWh, determine the maximum money
saved by using the lake water rather than the outside air as
the outside energy source.
6–138 The cargo space of a refrigerated truck whose inner
dimensions are 12 m 3 2.3 m 3 3.5 m is to be precooled
from 258C to an average temperature of 58C. The construction of the truck is such that a transmission heat gain occurs
at a rate of 120 W/8C. If the ambient temperature is 258C,
determine how long it will take for a system with a refrigeration capacity of 11 kW to precool this truck.
120 W/°C
25°C
Refrigerated
truck
12 m × 2.3 m × 3.5 m
25 to 5°C
FIGURE P6 –138
6–139 The maximum flow rate of a standard shower head is
about 3.5 gpm (13.3 L/min) and can be reduced to 2.75 gpm
(10.5 L/min) by switching to a low-flow shower head that is
equipped with flow controllers. Consider a family of four,
with each person taking a 6-minute shower every morning.
City water at 158C is heated to 558C in an oil water heater
whose efficiency is 65 percent and then tempered to 428C by
cold water at the T-elbow of the shower before being routed
to the shower head. The price of heating oil is $2.80/gal and
its heating value is 146,300 kJ/gal. Assuming a constant specific heat of 4.18 kJ/kg ∙ 8C for water, determine the amount
of oil and money saved per year by replacing the standard
shower heads by the low-flow ones.
324
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
6–140
Using EES (or other) software, determine the
maximum work that can be extracted from a
pond containing 105 kg of water at 350 K when the temperature
of the surroundings is 300 K. Notice that the temperature of
water in the pond will be gradually decreasing as energy is
extracted from it; therefore, the efficiency of the engine will
be decreasing. Use temperature intervals of (a) 5 K, (b) 2 K,
and (c) 1 K until the pond temperature drops to 300 K. Also
solve this problem exactly by integration and compare the
results.
at a unit cost of electricity of $0.11/kWh. A typical heat
pump–powered water heater has a COP of 3.3 but costs about
$800 more to install. Determine how many years it will take
for the heat pump water heater to pay for its cost differential
from the energy it saves.
6–141 A refrigeration system is to cool bread loaves with
an average mass of 350 g from 30 to 2108C at a rate of
1200 loaves per hour by refrigerated air at 2308C. Taking the
average specific and latent heats of bread to be 2.93 kJ/kg·8C
and 109.3 kJ/kg, respectively, determine (a) the rate of heat
removal from the breads, in kJ/h; (b) the required volume
flow rate of air, in m3/h, if the temperature rise of air is not to
exceed 88C; and (c) the size of the compressor of the refrigeration system, in kW, for a COP of 1.2 for the refrigeration
system.
6–142 The drinking water needs of a production facility
with 20 employees is to be met by a bubbler type water fountain. The refrigerated water fountain is to cool water from 22
to 88C and supply cold water at a rate of 0.4 L per hour per
person. Heat is transferred to the reservoir from the surroundings at 258C at a rate of 45 W. If the COP of the refrigeration system is 2.9, determine the size of the compressor, in
W, that will be suitable for the refrigeration system of this
water cooler.
Water
heater
FIGURE P6–143
©McGraw-Hill Education//Christopher
Kerrigan
Cold water
8°C
6–144
Water inlet
22°C
0.4 L/h·person
Water
reservoir
25°C
Water
fountain
Refrigeration
system
FIGURE P6–142
6–143
A typical electric water heater has an efficiency
of 95 percent and costs $350 a year to operate
Reconsider Prob. 6–143. Using EES (or other)
software, investigate the effect of the heat pump
COP on the yearly operation costs and the number of years
required to break even. Let the COP vary from 2 to 5. Plot the
payback period against the COP and discuss the results.
6–145 A homeowner is trying to decide between a highefficiency natural gas furnace with an efficiency of 97 percent and a ground-source heat pump with a COP of 3.5. The
unit costs of electricity and natural gas are $0.115/kWh and
$1.42/therm (1 therm 5 105,500 kJ). Determine which system will have a lower energy cost.
6–146 The “Energy Guide” label on a washing machine
indicates that the washer will use $85 worth of hot water per
year if the water is heated by an electric water heater at an
electricity rate of $0.113/kWh. If the water is heated from 12
to 558C, determine how many liters of hot water an average
family uses per week. Disregard the electricity consumed by
the washer, and take the efficiency of the electric water heater
to be 91 percent.
325
CHAPTER 6
6–147 The kitchen, bath, and other ventilation fans in a
house should be used sparingly since these fans can discharge a houseful of warmed or cooled air in just one
hour. Consider a 200-m2 house whose ceiling height is
2.8 m. The house is heated by a 96 percent efficient gas
heater and is maintained at 228C and 92 kPa. If the unit
cost of natural gas is $1.20/therm (1 therm 5 105,500 kJ),
determine the cost of energy “vented out” by the fans in
1 h. Assume the average outdoor temperature during the
heating season to be 58C.
6–148 Repeat Prob. 6–147 for the air-conditioning cost in a
dry climate for an outdoor temperature of 338C. Assume the
COP of the air-conditioning system to be 2.1, and the unit
cost of electricity to be $0.12/kWh.
6–149 A heat pump with refrigerant-134a as the working fluid is used to keep a space at 258C by absorbing heat
from geothermal water that enters the evaporator at 608C at a
rate of 0.065 kg/s and leaves at 408C. Refrigerant enters the
evaporator at 128C with a quality of 15 percent and leaves at
the same pressure as saturated vapor. If the compressor consumes 1.6 kW of power, determine (a) the mass flow rate of
the refrigerant, (b) the rate of heat supply, (c) the COP, and
(d) the minimum power input to the compressor for the same
rate of heat supply. Answers: (a) 0.0338 kg/s, (b) 7.04 kW,
(c) 4.40, (d ) 0.740 kW
Condenser
Expansion
valve
·
Win
Compressor
(a) Assuming the water to be an incompressible liquid that
does not change phase during heat addition, determine
the rate of heat supplied to the water, in kJ/s.
(b) Assuming the water heater acts as a heat sink having an
average temperature of 308C, determine the minimum
power supplied to the heat pump, in kW.
Water
inlet
Water
exit
Water
heater
HP
·
QH
Surroundings
0°C
·
Win
FIGURE P6–150
6–151 A heat pump receives heat from a lake that has an
average winter time temperature of 68C and supplies heat into
a house having an average temperature of 238C.
(a) If the house loses heat to the atmosphere at the rate of
52,000 kJ/h, determine the minimum power supplied to
the heat pump, in kW.
(b) A heat exchanger is used to transfer the energy from the
lake water to the heat pump. If the lake water temperature
decreases by 58C as it flows through the lake water-to-heat
pump heat exchanger, determine the minimum mass flow
rate of lake water, in kg/s. Neglect the effect of the lake
water pump.
Evaporator
·
Qlost
Sat. vapor
12°C
x = 0.15
·
QH
Geo. water
60°C
·
QL
Lake water
inlet
Lake water
to HP heat
exchanger
HP
Lake water
pump
·
QL
Lake, 6°C
40°C
House
·
Win
FIGURE P6–149
Lake
water
exit
FIGURE P6–151
6–150 Cold water at 108C enters a water heater at the rate
of 0.02 m3/min and leaves the water heater at 508C. The water
heater receives heat from a heat pump that receives heat from
a heat source at 08C.
6–152 Prove that the COP of all completely reversible
refrigerators must be the same when the reservoir temperatures are the same.
326
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
6–153 A Carnot heat engine is operating between a
source at TH and a sink at TL. If it is desired to double
the thermal efficiency of this engine, what should the new
source temperature be? Assume the sink temperature is
held constant.
6–155 Show that COPHP 5 COPR 1 1 when both the heat
pump and the refrigerator have the same QL and QH values.
6–154 When discussing Carnot engines, it is assumed that
the engine is in thermal equilibrium with the source and the
sink during the heat addition and heat rejection processes,
respectively. That is, it is assumed that T *H 5 TH and T *L 5 TL
so that there is no external irreversibility. In that case, the
thermal efficiency of the Carnot engine is hC 5 1 2 TL/TH.
In reality, however, we must maintain a reasonable
temperature difference between the two heat transfer media
in order to have an acceptable heat transfer rate through a
finite heat exchanger surface area. The heat transfer rates in
that case can be expressed as
6–156 A 2.4-m high 200-m2 house is maintained at 228C by
an air-conditioning system whose COP is 3.2. It is estimated
that the kitchen, bath, and other ventilating fans of the house
discharge a houseful of conditioned air once every hour. If
the average outdoor temperature is 328C, the density of air
is 1.20 kg/m3, and the unit cost of electricity is $0.10/kWh,
the amount of money “vented out” by the fans in 10 hours is
(a) $0.50
(b) $1.60
(c) $5.00
(d) $11.00
(e) $16.00
#
QH 5 (hA)H(TH 2 T *H)
#
QL 5 (hA)L(T *L 2 TL)
where h and A are the heat transfer coefficient and heat transfer surface area, respectively. When the values of h, A, TH,
and TL are fixed, show that the power output will be a maximum when
TL*
TL
TH
TH
5 a
*
1/2
b
Also, show that the maximum net power output in this case is
#
WC,max 5
(hA)HTH
1 1 (hA)H/(hA)L
c1 2 a
Heat source
TH
.
QH
T *H
Heat engine
T *L
.
QL
TL
Heat sink
FIGURE P6–154
TL
TH
1/2 2
b
d
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Problems
6–157 The drinking water needs of an office are met by
cooling tab water in a refrigerated water fountain from 23 to
68C at an average rate of 10 kg/h. If the COP of this refrigerator is 3.1, the required power input to this refrigerator is
(a) 197 W
(b) 612 W
(c) 64 W
(d) 109 W
(e) 403 W
6–158 The label on a washing machine indicates that the
washer will use $85 worth of hot water if the water is heated
by a 90 percent efficient electric heater at an electricity rate
of $0.09/kWh. If the water is heated from 18 to 458C, the
amount of hot water an average family uses per year is
(a) 11.6 tons
(b) 15.8 tons
(c) 27.1 tons
(d) 30.1 tons
(e) 33.5 tons
6–159 A heat pump is absorbing heat from the cold outdoors at 58C and supplying heat to a house at 258C at a rate
of 18,000 kJ/h. If the power consumed by the heat pump is
1.9 kW, the coefficient of performance of the heat pump is
(a) 1.3
(b) 2.6
(c) 3.0
(d) 3.8
(e) 13.9
6–160 A heat engine cycle is executed with steam in the
saturation dome. The pressure of steam is 1 MPa during heat
addition, and 0.4 MPa during heat rejection. The highest possible efficiency of this heat engine is
(a) 8.0%
(b) 15.6%
(c) 20.2%
(d) 79.8%
(e) 100%
6–161 A heat engine receives heat from a source at 10008C
and rejects the waste heat to a sink at 508C. If heat is supplied to this engine at a rate of 100 kJ/s, the maximum power
this heat engine can produce is
(b) 55.4 kW
(c) 74.6 kW
(a) 25.4 kW
(d) 95.0 kW
(e) 100 kW
6–162 A heat pump cycle is executed with R–134a under the
saturation dome between the pressure limits of 1.4 and 0.16 MPa.
The maximum coefficient of performance of this heat pump is
(b) 3.8
(c) 4.8
(a) 1.1
(d) 5.3
(e) 2.9
6–163 A refrigeration cycle is executed with R-134a under
the saturation dome between the pressure limits of 1.6 and
327
CHAPTER 6
0.2 MPa. If the power consumption of the refrigerator is
3 kW, the maximum rate of heat removal from the cooled
space of this refrigerator is
(a) 0.45 kJ/s
(b) 0.78 kJ/s
(c) 3.0 kJ/s
(d) 11.6 kJ/s
(e) 14.6 kJ/s
6–164 A heat pump with a COP of 3.2 is used to heat a
perfectly sealed house (no air leaks). The entire mass within
the house (air, furniture, etc.) is equivalent to 1200 kg of air.
When running, the heat pump consumes electric power at a
rate of 5 kW. Th