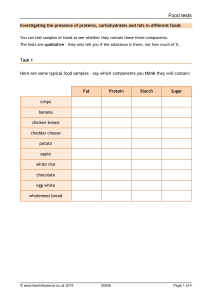
🧪 Biochemistry 1st section : identification of carbon Physical properties Color : colorless Oduor: odurless Taste: sweet Reaction : neutral State : liquid Solubility: soluble in cold water except starch soluble in Hot water 🧪 In molish test using H2SO4 acts as dehydrating agent which takes 3 molecules of H2O giving either a pentose ring ( furfural) or hexose ring ( 5 hyroxy furfural) Reducing sugar contains free carbinol group All monosaccharides are reducing sugars All disaccharides are reducing sugar except sucrose All polysaccharides are non reducing sugar In Fehling the cupric ion (+2) is turned into caprous ion (+1) and oxidized Suger Biochemistry Test Ratio Molish test Heat Observation Report 2 ml H2SO4 slowly in the Violet Ring between acid Carbohydrates wall of the test tube + 2 drops and solution by 1 of alcohol alpha naphthol + 2 ml of the solution shaking causes spread 2 ml Fehling Fehling test Benedict test reagent + 2 ml solution 1 ml solution + 5ml Benedict's Direct heat Colored ppt Reducing sugar Direct heat Colored ppt Reducing sugar Heat Observation Result reagent 2nd section Test Molish test Ratio 2 ml H2SO4 slowly in the Violet Ring wall of the test tube + 2 drops of alcohol alpha between acid and solution by shaking causes naphthol + 2 ml spread Carbohydrates of the solution 2 ml Fehling Fehling test reagent + 2 ml Direct heat Colored ppt Reducing sugar Direct heat Colored ppt Reducing sugar solution Benedict test 1 ml solution + 5ml Benedict's reagent Red color after Barfoued Test 3ml solution+ 3ml barfoued reagent short time Monsaccharide Red color after Disaccharide Water bath long time Needle shaped crystal Ozasone test Biochemistry Sun shaped crystal Mono.(Glucose, fructose) Di. ( Lactose) 2 3rd section : differentiate between keto Suger abd Aldo Suger Physical properties: Color : colorless Oduor: odurless State : liquid Reaction : neutral Solubility: soluble in cold water 🧪 If solution is swelanoiff or ketose it will give color according to presence of Fructose but it will take more heat Sucrose acts as keto Suger If we won't to differentiate between fructose and sucrose we use Fehling solution Test Molish test Ratio Heat Observation 2 ml H2SO4 slowly in the Violet Ring wall of the test between acid tube + 2 drops and solution by of alcohol alpha naphthol + 2 ml shaking causes spread Report Carbohydrates of the solution Fehling test 2 ml Fehling reagent + 2 ml Direct heat Colored ppt Reducing sugar Direct heat Colored ppt Reducing sugar solution 1 ml solution + Benedict test 5ml Benedict's reagent 3ml solution+ Barfoued Test 3ml barfoued reagent Ozasone test Biochemistry Water bath Red color with short time Needle shaped Monosaccharide Monosaccharide 3 1 ml solution + Swelanoiff test Ketose test 3 ml swelanoiff reagent 3 ml solution + 1.5 ml HCL Onion color Fructose No color Glucose Deep onion Fructose Direct heat Direct heat color No color Glucose Observation Report 4th section: lactose Physical properties Color : Colorless Oduor: odurless State: solution Aspect : clear Reaction: neutral Solubility: soluble in cold water Test Ratio Heat 2 ml H2SO4 Molish test slowly in the Violet Ring wall of the test tube + 2 drops between acid and solution by No heat of alcohol alpha shaking causes naphthol + 2 ml spread Carbohydrates of the solution 2 ml Fehling Fehling test reagent + 2 ml Direct heat Colored ppt Reducing sugar Direct heat Colored ppt Reducing sugar Red color after Reducing long time disaccharide solution 1 ml solution + Benedict test 5ml Benedict's reagent Barfoued Test 3ml solution+ 3ml barfoued reagent Ozasone test Biochemistry Water bath Sun shaped crystal Lactose 4 5th section: sucrose Glucose + Fructose Non reducing disaccharide Test Components Notes Observation Result 2 ml H2SO4 Molish slowly in the Violet Ring wall of the test between acid tube + 2 drops No heat and solution by of alcohol alpha shaking causes naphthol + 2 ml of the solution spread 2 ml Fehling Fehling reagent + 2 ml Direct heat No Colored ppt Direct heat No Colored ppt solution 1 ml solution + Benedict 5ml Benedict's reagent Carbohydrates Non reducing sugar Non reducing sugar Heat Then adding NaCo3 Hydrolysis and neutralization test. Fehling solution after 0.5 ml HCL + 5 ml solution Benedict cooling until the buffering stops Colored ppt Sucrose Onion color Sucrose which mean that the acidity is neutralized complete 1 ml solution + Swelanoiff 3 ml swelanoiff Direct heat reagent Ketose 3 ml solution + 1.5 ml HCL Direct heat Deep onion color Sucrose Report Test Molish Biochemistry Observation Violet Ring between acid and solution by shaking causes spread Result Carbohydrates 5 Fehling No Colored ppt Benedict No Colored ppt Non reducing sugar Non reducing sugar Hydrolysis and neutralization test. Fehling Colored ppt Sucrose Swelanoiff Onion color Sucrose Ketose Deep onion color Sucrose Benedict 6th section: polysaccharides Homopolysacchride : starch Physical properties: 1. Color : whitish or Colorless 2. Taste : tasteless 3. Oduor: odurless 4. Solubility: soluble in Hot water 5. Aspect : turbid Test Components Significant notes Observation Result Violet Ring Carbohydrates 2ml of solution Molish test 2drops of alcoholic alpha naphthol No heat 2ml of H2SO4 If turned blue : Iodine test Biochemistry 3 ml solution 2 drop iodine If nothing starch changed then is mono or di saccharide If turned redish violet : dextrine Polysaccharide ( Starch or dextrine) 6 No heat Taking a drop from the beaker and adding iodine .. if : 1) turned blue : no hydrolysis and it's still starch Hydrolysis of starch and dextrine 2) turned red : no hydrolysis and it's still 1 ml HCL 5 ml solution Starch or Dextrine hydrolyzed to dextrine 3) no change : Glucose It's hydrolyzed and it gave glucose and maltose * Start adding Na2Co3 after cooling until the whole medium Is neutralized Full saturation: 5ml solution Ammonium sulfate(powder) Full saturation: Suspended ppt It's either starch or dextrine Preceptation of starch and dextrine Half saturation: 5ml solution 5 ml ammonium sulfate Starch or dextrine Half saturation: Suspended ppt: Starch No suspended ppt: dextrine Report Test Biochemistry Observation Result 7 Molish test Violet Ring Carbohydrates If turned blue : starch Iodine test If turned red : Polysaccharide ( Starch or dextrine) dextrine Hydrolysis of starch and dextrine Starch or Dextrine hydrolyzed to Glucose Preceptation of starch and dextrine Starch or dextrine Heteropolysaccharide: Gum arabic Physical properties Colour: whitish or colorless Taste: tasteless Odour : odourless Solubility: in hot water Aspect : Turbid Chemical properties: report Test Observation Result Molish Violet ring Carbohydrate Iodine No blue or reddish Neither starch or dextrine Fehiling Benedict No coloured ppt Non reducing suger Seliwanoff No onion colour Gum arabic Ketos No deep onion colour Gum arabic Proteins Physical properties Biochemistry 8 1. Colour : colorless 2. Odour: odourless 3. Aspect : Turbid 4. Reaction: neutral except casine it's reaction is alkaline 5. Solubility: a. Albumin : soluble in cold water b. Casine: soluble in alkaline medium c. Gelatin : soluble in hot water General test of proteins : Beirut's test No heating Test tube 🧪 Traces of copper sulphate 2 ml solution 1 ml of NaOH 10% If the color : Violet: proteins Blue : carbohydrate The protein is either. Albumin Casein Gelatin HCT : Heat coagulation test Test tube 🧪 2/3 the test tube is filled with solution Heat the upper 1/3 If the observation : White colour: albumin Biochemistry 9 No White colour: gelatin, casein Saturation (precipitation) test Full saturation Albumin : suspended ppt Casein : suspended ppt Gelatin : suspended ppt Half saturation Gelatin, casine : suspended ppt Albumin : no suspended ppt Colour reaction test 1. Xantho proetic test a. 2 ml of sol. + 1 ml nitric acid conc. Then heating b. Then cooling c. Results i. Deep orange colour with albumin, casine 2. Rosenhims test a. Like molish b. Purple ring with albumin, casine 3. Millions test a. 2ml sol +2 ml millions reagent b. Brick red ppt with albumin, casine 4. Silver test a. With proteins containing sulphur containing amino acid b. Gives off with albumin c. 2ml sol. + 2ml of lead acetate d. Grey to black color 5. Gel formation test Biochemistry 10 a. -ve with albumin, casine b. +ve with gelatin 1. The arranged steps a. Molish b. Bireuts c. Rosenhims Biochemistry 11