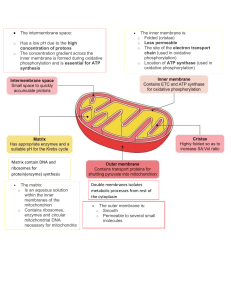
NAME_______________________________ 14. Identify and label in Figure 14.1 the portion of ATP that, when reacted with the Benedict test, will produce a positive result. Fig.14.1 [1] 15. Figure 15.1 shows part of the process of respiration in a specialized mammal cell. A) Determine which stage of breathing is shown in Fig. 15.1? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [1] B) Using Figure 15.1, explain which two processes would occur more often if this mammal were cold. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [1] C) Identify structure A _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [1] 16. Figure 16.1 is an electron micrograph showing the main structural features of a mitochondrion in section. Fig. 16.1 A) Indicate clearly on the diagram where: electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation occur. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [1] B) Describe ONE way in which the structure of the mitochondrion is adapted for oxidative phosphorylation. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] 17. Explain the transformations of carbon atoms during one turn of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and counting the reduced electron carriers NADH end FADH2- and ATP produced. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [3] 18. Cells generate ATP by adding a phosphate group (Pi) to ADP. During the complete oxidation of glucose, cells have two ways of doing this: substrate level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation. Fig.19.1 and 19.2 are diagrams that show the main details of these two processes (not drawn to the same scale). Fig. 19.1 Fig. 19.2 A) State precisely where these two processes occur in a cell. Substrate level phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] B) Compare the relative amounts of ATP produced by the processes when a molecule of glucose is completely oxidized. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] 19. Only substrate level phosphorylation is possible in the absence of oxygen. Explain why oxidative phosphorylation is not possible in the absence of oxygen. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] 20. Aerobic respiration consists of three main processes. Match the table data with the proposed options for the main products of each process. I. ATP; reduced NAD/reduced FAD; CO2 II. ATP; Pyruvate; reduced NAD; III. ATP; water; NAD; FAD [3] 21. The Bowman’s capsule (Fig.21.1) is a cup-shaped structure that is part of the nephron. What is the source of glucose in the fluid in the Bowman’s capsule. Fig. 21.1 A) Blood in the glomerulus B) Urine in the renal pelvis C) Filtrate in the distal convoluted tubule D) Interstitial fluid in the medulla [1] 22. Explain the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in water monitoring. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] 23. Explain whether a dialyzer in a sick person with kidney failure can do what the kidneys of a healthy person once did. Fig. 23.1 [1] 24. Explain the advantages (at least one) and disadvantages (at least one) of kidney transplantation. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ [2] 14 1 С 15 А) 1 Oxidative phosphorylation В) 1 Process 1 and 3 C) 1 A: ATP synthase B: cristae/inner mitochondrial membrane (both correct for 1 mark) 16 1 correctly indicated on inner mitochondrial membrane; cristae Only one 2 folded inner membrane / cristae; increases surface area available; intermembrane space; allows accumulation of H+ ; impermeability of inner membrane to H+ ; maintains H+ gradient / H+ only go through channels; stalked particles / ATPase; channel for H+ / ATP synthesis; linear arrangement of ETC on inner membrane; greater efficiency; Only two ideas 17 3 • two carbons enter from acetyl CoA and two molecules of carbon dioxide are released; • three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH2 are generated; • one molecule of ATP or GTP is produced 18 А) 2 Substrate level phosphorylation – cytoplasm (in glycolysis), matrix of mitochondria (in Krebs cycle); Oxidative phosphorylation – inner membrane of mitochondria/cristae В) 2 Oxidative phosphorylation more than substrate level phosphorylation; Ref.to quantity, e.g. 32/34 vs.4/6 per glucose; 19 2 Requires proton gradient produced by ETC; With no oxygen ETC does not occur/no electron flow; NAD cannot be reformed/NADH cannot be oxidized; Oxygen combines with electron /proton/oxygen final acceptor in ETC. Accept any 2 variants 20 3 II I III 21 1 A 22 2 Play role in osmoregulation; transport of salts into the medulla of kidney; changes salt concentration so water is reabsorbed; ADH released into blood when water is required; ADH causes concentrated urine / no/low ADH causes dilute urine; this causes more reabsorption of water from the collecting duct; excess water is released as urine; urine concentration depends on the body’s need for water; drinking a lot gives dilute urine. Accept any 2 variants 23 1 No. Hemodialysis can replace part, but not all, of your kidney function. Dialysis will help improve your energy level, and changes you make to your diet can help you feel better. 24 2 Pros: Kidney works like a normal kidney. Less restriction in the diet. There is no need for dialysis. Cons: Required major surgery. Will have to wait for a donor. The body may reject the new kidney. Will have to take meds the rest of your life. Accept any 1 variants for pros and any 1 for cons.