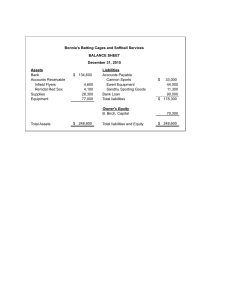
Accounting Principles Definition: Accounting refers to the process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information to permit informed judgments and decisions by users of the information”. Functions: To prepare financial statements, income statements, balance sheets, owner’s equity statements, and cash flow statements. 5 Managerial functions control of financial policy & formation of planning preparation of budget cost control evaluation of employees’ performance prevention of errors and frauds 5 Principles of Accounting (1) Revenue recognition principle → revenue being recognized in the income statement Ex: On 30 April, a customer buys a shirt, but pays on 1 May → Revenue is recorded for 30 April cash flow (2) Historical cost principle Ex: A bought a building for $100,000. But 6 months later the value of this building increased to $200.000 The building is kept being recorded at $100.000 as the initial accounting record. ⇒ (3) Matching principle → expenses match with the revenues in the same accounting period. Ex: October: buy a shirt to resell it → Nov: resell the shirt revenue and the cost of this shirt for the Nov. Accounting Principles ⇒ Record both the 1 (4) Full disclosure principle → Financial statements must disclose all the relevant and reliable information which they purport to represent so that the information may be useful for the users. (5) Objectivity principle → Accounting data should be definite, verifiable, and free from the personal bias of the accountant. The Recording Process Journal: Is the first stage of the accounting process Journal is a book wherein the transactions are recorded in chronological order of dates after determining the debit account and credit account of transactions with an explanation Ledger: an account to record, categorize and sort transactions, for maintaining the balance of the company’s each asset, liabilities, owners’ equity, revenue, and expenses accounts so that the balance sheet and income statement can be properly prepared. transactions are first recorded in the journal → transferred to the ledger under respective heads of accounts Trial balance: The statement which is prepared at a particular date with the ledger account balances to test the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger accounts and also to facilitate the preparation of financial statements Accounting Principles 2 Balance Sheet [Bảng cân đối kế toán]: Is a summary of the financial balances of a sole proprietorship [quyền sở hữu], a business partnership, a corporation, or another business organization. Assets, liabilities, and ownership equity [vốn chủ sở hữu] are listed as of a specific date, such as the end of its financial year. 📌 Assets = Current assets + Non-current assets (fixed assets) Current assets= Cash and cash equivalents [include foreign currency] + Accounts receivable [tài sản, nợ phải thu] + Prepaid expenses for future service using [khoản trả trước cho người bán] + Deposits Paid [Các khoản đem đi đặt cọc] + Allowance for Doubtful Accounts [Dự phòng nợ khó đòi] + Short-term Investment [Đầu tư ngắn hạn] + Inventory [hàng tồn kho]. Non-current assets = Property, plant and equipment [đất đai, nhà xưởng, thiết bị máy móc] + Investment property, such as real estate held for investment purposes [các tài sản đầu tư] + Intangible assets [tài sản vô hình] + Financial assets [tài sản tài chính: không bao gồm tiền, các khoản đầu tư ngắn hạn, nợ phải thu] + Investments accounted for using the equity method [các khoản đầu tư vào công ty con] + Biological assets [các tài sản sinh học: gia cầm, gia súc, cây cối, …]+ Accumulated Depreciation [Khấu hao lũy kế; mang giá trị âm]. 📌 Liabilities [nợ] = Current liabilities [=<1 year] + Long-term Debts/Liabilities [> 1 year] Current liabilities = Accounts payable [khoản phải trả người bán] + Salaries Payable [Lương phải trả] + Interest payable [Lãi vay phải thanh toán] + Tax payable [thuế phải nộp] + Security Deposit [Khoản kí quỹ = khoản do cty khác đặt cọc] + Unearned revenue for services paid for by customers but not yet provided [tiền đã nhận của người mua nhưng chưa cung cấp dịch vụ=thanh toán trước] Accounting Principles 3 Long term debts = Note payable [các khoản nợ tài chính: trái phiếu, giấy ghi nợ>1 year] Equities [Vốn] = Owner capital/Common stock [cổ phiếu phổ thông] + retained earnings [Lợi nhuận giữ lại] 📌 Total Liabilities + Equities = Total Assets. Common financial ratios: Debt Ratio = Total Liabilities / Total Assets [tỉ lệ nợ/tài sản] Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities [tỉ lệ tài sản lưu động/nợ ngắn hạn] Working Capital = Current Assets - Current Liabilities)[vốn lưu động] is a financial metric that represents operating liquidity available to a business. [đo mức độ thanh khoản] Assets-to-Equity Ratio = Total Assets / Owner's Equity [tỉ lệ tài sản/vốn chủ sở hữu] Accounting Principles 4 Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Liabilities / Owner's Equity[tỉ lệ nợ/vốn chủ sở hữu] Accounting Principles 5