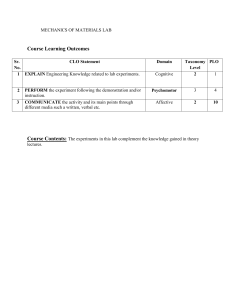
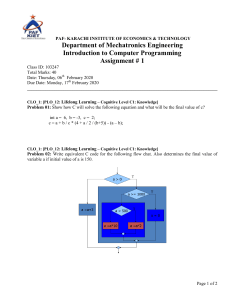
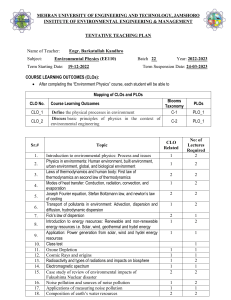
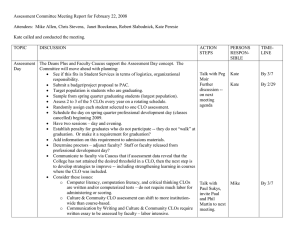
ECO 4108 Research Methodology (Lab) a. Course Code: 0311 ECO 4107 Course Title: Research Methodology Credits: 4.0 This course is intended to educate students about the research process and methodologies involved. It facilitates the development of a research concept, identification of difficulties, review of existing literature, establishment of objectives, design of sample methods, data collection and analysis, discussion of outcomes, and writing a comprehensive report on a specific topic. Rationale b. Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs): Upon completion of this course the students will be able toComprehend meaning and objectives of a research and explore the criteria of a good research. Identify the research problem and sampling design and also learn measurement and scaling techniques. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Apply data and analyze to fulfill the research gap. CLO 4 Evaluate the significance of research and its report writing. c. Mapping Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) with the PLOs: PLO 1 PLO 2 PLO 3 CLO 1 3 CLO 2 3 2 1 CLO 3 3 3 1 CLO 4 1 PLO 4 PLO 5 3 1 Sl. d. Summary of course contents No. PLO 6 PLO 7 Hrs. Alignment to CLOs 6 CLO 1 Section A 1 Introduction to Research Methodology Meaning and objectives of research, Types of research, Significance of research, Research methods vs. PLO 8 methodology, Research and scientific method, Research process, Criteria of a good research. Research Problem Meaning, Selection of research problem, Techniques involved in selecting the problem. 6 CLO 2 3 Research Design Features of a good design, Important concept relating to research design, Types of research design, Basic principles of experimental design. 6 CLO 2 4 Sampling Design Steps in sampling design, Characteristics of a good sample design, Types of sample design, Selection of sample, Complex random sampling design. 10 CLO 2 6 CLO 2 6 CLO 3 12 CLO 3 4 CLO 4 2 Section B 5 6 7 Measurement and Scaling Measurement scales, Sources of errors in measurement, tests of sound measurement, Meaning of scale, Bases of scale classification, Scaling techniques, Scale construction techniques. Methods of Data Collection Collection of primary data, Observation and survey method, Some other methods of data collection, Collection of secondary data, Case study method Processing and Analysis of Data Processing operations, Problems in processing, Statistics in research, Measures of central tendency, dispersion, skewness and relationship; Simple and multiple regression analysis, Other measures. Interpretation and Report Writing 8 Meaning and importance of interpretation, Techniques of interpretation, Significance of report writing, Steps in report writing, types of reports, Oral presentation. e. Mapping Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) with the Teaching-Learning and Assessment strategy: CLOs Teaching-Learning Strategy Assessment Strategy CLO 1 Lecture Quiz, Class Test and Final Exam CLO 2 Lecture and Group discussion Viva voce and Final Exam CLO 3 Lecture and Presentation Continuous Assessment and Final Exam CLO 4 Problem based learning and Presentation Assignment and Final Exam f. Textbooks: 1. Kothari, C.R. (2004). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques, 2nd Edition, New Age International Publishers, Ltd. New Delhi. 2. Sekaran, U. (2003). Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach, 4th Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York. 3. Zikmund, W.G. and B.J. Babin (2010). Essentials of Marketing Research, 4th Edition, Nelson Education, Ltd. Canada. 4. Walliman, N. (2011). Research Methods: The Basics, 1st Edition, Routledge, New York. 5. Shukla, P. (2008). Marketing Research, 1st Edition. 6. Greener, S. and J. Martelli (2015). An Introduction to Business Research Methods, 2nd Edition. Course Title: Software a. Course Code: 0311 ECO 4109 Applications for Economic Credits:4.0 Analysis This course attempts to provide students with a foundational understanding of how to utilize computer software for database management and analysis. The Rationale approach focuses on economic concerns by utilizing statistical software packages for data entry, processing, cleansing, categorizing, coding, and analysing. b. Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs): Upon completion of this course the students will be able toCLO 1 Comprehend the fundamentals of computer application software, including Excel, SPSS, Stata, R, and Python. CLO 2 Utilize application software to manage databases, including data entry, data cleansing, organization, processing, recoding and coding, and editing in preparation for analysis. CLO 3 Generate descriptive analyses utilizing basic statistical measures, tables, and graphs. CLO 4 Analyze the outcomes that are produced by the data analysis. c. Mapping Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) with the PLOs: PLO 1 CLO 1 2 CLO 2 2 PLO 2 PLO 3 Sl. No. PLO 5 PLO 6 PLO 7 PLO 8 3 2 1 3 3 CLO 3 CLO 4 PLO 4 3 2 2 3 d. Summary of course contents Hrs. Alignment to CLOs 3 CLO 2, CLO 3 Section A DATA MANAGEMENT AND PREPARATION 1 Types of Data, Data Collection Methods, Importing Data from different sources, World Bank Data set, Preparing data for analysis, Working with variables, Data analysis, Importing result to word or excel. REGRESSION ANALYSIS 2 PRF, SRF, Creating a simple Econometrics Model, Different types of regression, Assumptions of CLRM, BLUE estimator, OLS, Types of regression techniques (linear, logistic, polynomial, stepwise, Ridge, Lasso, etc), How to select regression model, Double log, lin-log, log-lin, and exponential Model, Why take log form of the variables. 3 CLO 2, CLO 4 6 CLO 1, CLO 3,CLO 4 6 CLO 1, CLO 3,CLO 4 12 CLO 1, CLO 3,CLO 4 9 CLO 1, CLO 3,CLO 4 INTRODUCE TO SOFTWARE: EXCEL 3 Introduction to Excel, Data Storage, Analysis and Program Writing in Excel, Regression and Other Analysis in Excel, Laboratory Work with Excel Section B INTRODUCE TO SOFTWARE: SPSS 4 Introduction to SPSS, Data Storage, Analysis and Program Writing in SPSS, Regression and Other Analysis in SPSS, Graphical Analysis, Laboratory Work with SPSS INTRODUCE TO SOFTWARE: STATA 5 Introduction to STATA, Data Storage, Analysis and Program Writing in STATA, STATA commands, Regression and Other Analysis in STATA, Graphical Analysis, Laboratory Work with STATA INTRODUCE TO SOFTWARE: EVIEWS 6 Introduction to EViews, Data Storage, Analysis and Program Writing in EViews, Regression and Other Analysis in EViews, Graphical Analysis, Laboratory Work with EViews. INTRODUCE TO SOFTWARE: R 7 Introduction to R, Data Storage, Analysis and Program Writing in R, Regression and Other Analysis in R, Graphical Analysis, Laboratory Work with R. 9 CLO 1, CLO 3,CLO 4 8 CLO 1, CLO 3,CLO 4 PYTHON FOR ECONOMETRIC ANALYSIS 8 Introduction to Python, Coding in Python, Data analysis with Python, Regression with Python, Graphical Analysis, Laboratory work with Python. e. Mapping Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) with the Teaching-Learning and Assessment strategy: CLOs Teaching-Learning Strategy Assessment Strategy CLO 1 Lecture, Group Work, Lab Work CLO 2 Lecture, Group Work, Lab Work CLO 3 Lecture, Presentation, Group Work Quiz, Class Tests and Final Exam Class Tests, Viva Voce, and Final Exam Class Tests, Assignment, and Final Exam CLO 4 Case Studies, Group Work, Presentation Assignment and Viva Voce f. Textbooks: 1. Bittmann, F. (2019). STATA, A Really Short Introduction, De Gruyter Oldenbourg. 2. Cameron, A. C. and Trivedi, K. P. (2022). Microeconometrics Using Stata, 2nd edition. 3. StataCorp (2021). Stata User’s Guide: Release 17, Statistical Software, College Station, Texas: StataCorp LLC. 4. Handouts in SPSS, STATA, EVIEWS, R, and PYTHON. 5. YouTube Channel: StataCorp LLC Course Title: Research Methodology a. Course Code: ECO 4108 Credits: 1.0 This course focuses on advanced econometric issues such as multicollinearity, heteroscedasticity, and autocorrelation. Students will further develop their skills using econometric software to address complex econometric problems. Rationale b. Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs): Upon completion of this course the students will be able toCLO 1 Identify and diagnose multicollinearity, autocorrelation in econometric models. heteroscedasticity, and CLO 2 Apply remedial techniques to correct issues in econometric models using STATA, E-Views, and SPSS. CLO 3 Conduct comprehensive econometric analysis with a focus on advanced econometric problems. CLO 4 Interpret and report findings from advanced econometric analyses in the context of economic theory. c. Mapping Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) with the PLOs: PLO 1 PLO 2 PLO 3 PLO 4 CLO 1 3 3 CLO 2 3 3 CLO 3 3 3 3 3 CLO 4 3 3 3 3 PLO 5 PLO 6 PLO 7 PLO 8 Sl. No. d. Summary of course contents Hrs. Alignment to CLOs 21 CLO 1, CLO 2, CLO 3 ,CLO 4 Section A All problems & exercises with STATA, EViews, SPSS and other related software. 1 e. Mapping Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) with the Teaching-Learning and Assessment strategy: CLOs Teaching-Learning Strategy Assessment Strategy CLO 1 Lecture, Presentation Quiz, Class Tests and Final Exam CLO 2 Lecture, Presentation, Group Discussion Viva voce and Final Exam CLO 3 Lecture, Presentation, and Case Studies Class Test, Assignment, and Final Exam CLO 4 Lecture, Journal Article and Case Studies Assignment and Final Exam f. Textbooks: 1. Wooldridge, J. M. (2005). Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach, 3rd Edition, SouthWestern College Pub. 2. Judge, G. G., et. al. (1980). Theory and Practice of Econometrics, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 3. Kmenta, J. (1986). Elements of Econometrics, 2nd Edition, Macmillan, New York. 4. Gujarati, D. N., & Porter, D. C. (2009). Basic econometrics.5th edition, McGraw-hill.