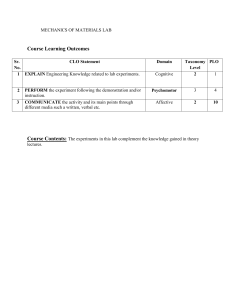
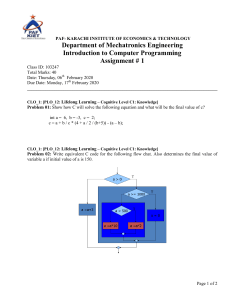
MEHRAN UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, JAMSHORO INSTITUTE OF ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING & MANAGEMENT TENTATIVE TEACHING PLAN Name of Teacher: Subject: Engr. Barkatullah Kandhro Environmental Physics (EE110) Term Starting Date: 19-12-2022 Batch 22 Year: 2022-2023 Term Suspension Date: 24-03-2023 COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES (CLOs): After completing the “Environment Physics” course, each student will be able to Mapping of CLOs and PLOs CLO No. CLO_1 CLO_2 Course Learning Outcomes Define the physical processes in environment Discuss basic principles of physics in the context of environmental engineering Sr.# Topic 1. Introduction to environmental physics: Process and issues Physics in environments: Human environment, built environment, urban environment, global, and biological environment Laws of thermodynamics and human body: First law of thermodynamics an second law of thermodynamics Modes of heat transfer: Conduction, radiation, convection, and evaporation Joseph Fourier equation, Stefan Boltzmann law, and newton’s law of cooling Transport of pollutants in environment: Advection, dispersion and diffusion, hydrodynamic dispersion Fick’s law of dispersion Introduction to energy resources: Renewable and non-renewable energy resources i.e. Solar, wind, geothermal and hydel energy Application: Power generation from solar, wind and hydel energy resources Class test Ozone Depletion Cosmic Rays and origins Radioactivity and types of radiations and impacts on biosphere Electromagnetic spectrum Case study of review of environmental impacts of Fukushima Nuclear disaster Noise pollution and sources of noise pollution Applications of measuring noise pollution Composition of earth’s water resources 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Blooms Taxonomy C-1 PLO_1 C-2 PLO_1 PLOs 1 No: of Lectures Required 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 CLO Related 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Interactions between biosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere in terms of global evaporation, transpiration and rainfall mechanisms Application of quantifying global energy requirements of evaporation, transpiration and precipitation Structure and composition of earth atmosphere Physical science related to greenhouse effect, surface effect, albedo effect and global warming Climate change and effects Terrestrial radiations and earth energy budget Atmospheric motions: air masses and weather fronts; principal forces acting on parcels of air in the atmosphere Global weather and climate patterns: Global pressure fields, global wind patterns, temperature fields, and cloud patterns. Presentations Total Lecture Hours 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 48 Signature of Teacher Dated: Remarks of DMRC: Dated: Signature of Chairman/Director: Dated: