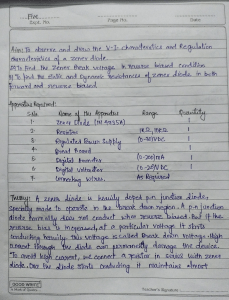
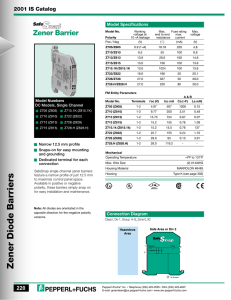
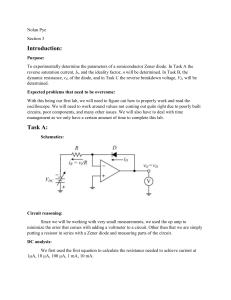
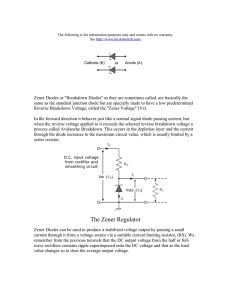
ELE 124 - Electronics (1) Lecture 10 : Special Purpose Diodes Dr. Said Emam Outline • Networks with a dc and ac source • Special Purpose Diodes • Zener Diodes • Light Emitting Diodes (LED) • Photodiode • Laser Diode • Varactor Diodes • Schottky Barrier diode (SBD) • PIN diode • Tunnel Diode • Photovoltaic Cell Networks with a dc and ac source • Using Superposition Theorem. The response of any network with both an ac and a dc source can be found by finding the response to each source independently and then combining the results. (1) Using Superposition Theorem DC Source only (AC = S.C.): • In the absence of the ac source (i.e. replaced by a short-circuit): AC Source only (DC= S.C.): • In the absence of the dc source (i.e. replaced by a short-circuit): The diode will be replaced by the ac resistance given by 𝑽𝑻 𝒓𝒅 = 𝑰𝑫 Combining the results of the dc and ac analysis will result in the waveforms of for ZENER DIODES • A Zener diode is a silicon diode that is designed for operation in the breakdown region. • The Zener diode is the backbone of voltage regulators, • The location of the Zener region can be controlled by varying the doping levels. Doping 𝑉𝑍 𝑉𝑍 = 1.8𝑉 𝑡𝑜 200𝑉 Zener Effect • When a diode is heavily doped, the depletion layer becomes very narrow. Because of this, the electric field across the depletion layer (voltage divided by distance) is very intense. • When the field strength reaches approximately 300,000 V/cm, the field is intense enough to pull electrons out of their valence orbits (breaks the covalent bonds). • The creation of free electrons in this way is called the Zener effect (also known as high-field emission). • This is distinctly different from the avalanche effect, which depends on high-speed minority carriers dislodging valence electrons. • When the breakdown voltage is less than 5 V, only the Zener effect occurs. • When the breakdown voltage is greater than approximately 7 V, the avalanche effect occurs. • When the breakdown voltage is between 5 and 7 V, both effects are present The specification sheet for a 10-V, 500-mW Zener diode The Zener potential of a Zener diode is very sensitive to the temperature of operation. Example1: Find the zener potential if the temperature is increased to 100°C Analysis of Zener diode circuits 1) Determine the state of the diode 2) Substitute the appropriate model 3) Determine the unknown quantities of the circuit. The Zener diode as a regulator Vi and R Fixed Solution: a. First we compute the Thevenin voltage across the zener diode as : • Since 𝑉 = 8.73𝑉 < 𝑉𝑍 = 10𝑉 , the zener diode is in the “OFF” state. • Substituting the open-circuit equivalent results in: b. For 𝑹𝑳 = 𝟑𝒌𝜴 Since 𝑉 = 12𝑉 > 𝑉𝑍 = 10𝑉 , the zener diode is in the “ON” state. The Network in the “ON” state. The power dissipated is which is less than the specified Solution • To determine 𝑅𝐿(𝑚𝑖𝑛) that will turn the Zener diode ON, we calculate the value of 𝑅𝐿 that will result in a load voltage 𝑉𝐿 = 𝑉𝑍 . That is, 𝑉𝐿 10𝑉 • 𝐼𝐿(𝑚𝑎𝑥) = = = 40𝑚𝐴. 𝑅𝐿(𝑚𝑖𝑛) 250Ω • 𝐼𝐿(𝑚𝑖𝑛) 𝑖𝑠 𝑜𝑏𝑡𝑎𝑖𝑛𝑒𝑑 𝑎𝑡 𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 𝑧𝑒𝑛𝑒𝑟 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐼𝑍𝑀 = 32𝑚𝐴 𝐼𝐿 𝑚𝑖𝑛 = 𝐼𝑅 − 𝐼𝑍𝑀 = 40 − 32 = 8mA • 𝑅𝐿(𝑚𝑎𝑥) 𝑖𝑠 𝑏𝑡𝑎𝑖𝑛𝑒𝑑 𝑎𝑡 𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 𝑙𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡, Therefore 𝑉𝐿 10𝑉 𝑅𝐿(𝑚𝑎𝑥) = = = 1.25𝑘Ω 𝐼𝐿(𝑚𝑖𝑛) 8𝑚𝐴 Zener Limiter Determine the output voltage for each zener limiting circuit in Figure. HOMEWORK 10 1. At what temperature will the 10-V Zener diode of table. 1 have a nominal voltage of 10.75 V? Table. 1 2. Determine the temperature coefficient of a 5-V Zener diode (rated 25°C value) if the nominal voltage drops to 4.8 V at a temperature of 100°C. 3) 4) i. Determine and draw the output voltage and current for the zener limiting circuit shown in Figure. ii. Draw the transfer characteristics