Uploaded by
isudananjaya97
Electrical Engineering Assignment: Renewable Energy & Circuits
advertisement

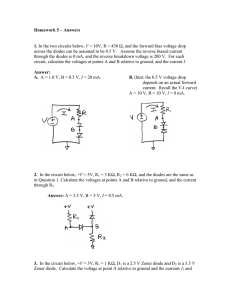
The Open University of Sri Lanka Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEX3410 Introduction to Electrical Engineering - TMA 3 - 2022/2023 Answer all questions. Solutions will be evaluated, through a viva, during the Lab 3 session. Question 01 a) The renewable sources are freely available for use and the cost for purchasing fuel for electricity generation is almost zero and the non-renewable energy requires costly fuel procurement. The shift towards renewable energy gained momentum in the mid2000s and earlier there was not such enthusiasm for renewable sources. Briefly explain why there was a lack of eagerness to transition towards renewable energy sources prior to the mid-2000s. b) Describe the two methods that are used to convert solar irradiation into electricity. c) What are the transmission voltages in Sri Lanka? The maximum permissible transmission voltage in the world is typically less than 1200 kV. Is it convenient to increase the transmission voltages even more than these maximum values? Justify your answer giving reasons. d) Ring distribution systems are often preferred over radial distribution systems due to several advantages. Briefly explain two of them. e) A 2-wire ring DC distributor (AB) is shown in figure 1. The total length of the ring distributer is 300 m and it is fed at the point A at 240 V and loads of 120 A and 80A are tapped off from the positions B (which are at a distance of 150 m from A into the clockwise direction) and C (which is at a distance of 100 m from A into the anticlockwise direction) respectively, as shown in the picture below. If the resistance of single conductor per meter is 0.0003 Ω, calculate the currents in each section of the distributer (IAB, IBC and ICA) and the voltages at point B and C. IAB IBC ICA Figure 1 Hint According to Kirchhoff’s voltage law, the voltage drop in a closed loop is zero! Question 02 A Zener diode voltage-stabiliser is designed with a regulating resistance of 1 kΩ to feed a load resistance of 1 kΩ. The Zener diode has the following specifications: • Working (Zenner) voltage VZ = 4.1 V • Minimum Zener diode current IZ(min) = 1 mA • Maximum power dissipation PZ(max) = 900 mW • Zener diode resistance RZ can be neglected a) Find the range of supply (input) voltage which can safely operate the regulating circuit. b) Out of 1/4 W, 1/2 W, 1 W, 2 W and 5 W, what would be the suitable power rating for the regulating resistor? Justify your answer. Question 03 a) What is meant by the Operating point (Q-point) of a transistor amplifier? Explain briefly. b) Briefly explain how the input affects the output of a transistor in common emitter configuration when it operates in the following 3 regions: i. Active region ii. Cut-off region iii. Saturation region c) The common emitter transistor amplifier shown in figure2 is designed to amplify small signals. Assume VBE = 0.7 V and current gain β = 275 Figure 2 a) b) c) d) Describe the purpose of the capacitors C1 & C2. Calculate the base current (IB). Calculate the collector current IC, Emitter current IE and VCE at Q-point. Draw the DC load line and mark the operating point (Q-point) on the load line.