The Course of Second World War (p.70-75)
Major theatres (where the war takes place)
1. The Pacific Theatre: Germany and Italy’s attacks on
France, Britain, Poland and Soviet Union.
2. The European- African- Middle East Theatre: Japan’s
attacks.
Timeline:
1937: Japan’s invasion of China
1939- 1941: Axis Power’s successful period
1939 September 1: invasion of Poland: Blitzkrieg strategy was
adopted -> successfully occupied Poland within a month
1940 May: Germany occupied Denmark and Norway <obtained air and naval bases for attacks on Britain
1940 May: Germany invaded Belgium and the Netherlands ->
invade France via Belgium
1940 June: fall of France:
- 370,000 allied soldiers retreated to Britain
1940 June 13: Fall of Paris
1940 June 22: France surrendered to Germany
1940 July: Battle of Britain: battle between Britain and German
air forces
1940 August: Italy attack North Africa (Britain’s oil supplies)
-> Britain counter- attack -> Hitler sent troops to Africa to help
Italy
1941 June: Germany attacks Soviet Union (capture Soviet lands
-> kill Jews), however, failed to defeat Soviet Union
1941 December 8:
Pearl Harbour Incident: Japanese troops suddenly attack
American naval base at Pearl Harbor (in Hawaii) -> US declare
war on the Axis Powers
1941: the outbreak of the Pacific War
1942- 1945: Allied counter- offensives - the end of WW2
1942: US defeated Japan in the battles in the pacific
1942 May: German troops forced to retreat from North Africa
1943: Soviet Union defeated German troops
1944 June 6: D- Day: 156000 Allied soldiers landed on the
beaches of Normandy in Northern France (then occupied by
Germany)
1944 August 24: freed france from Nazi control
1945 April 30: Soviet troops took Berlin (Germany capital city)
+ Hiter’s sucicide
1945 August 15: Japan surrendered after atomic bombs are
dropped in Hiroshima (6 August) and Nagasaki (9 August)
1945 August 30: End of war
The Lessons Learned from the Second World War (p.76-85)
Results:
1. Wartime conferences and Agreements
- dominated by U.S., U.S.S.R., Britain <- The big three
- Events: Yalta Conferences, Potsdam Conferences (to
discuss wartime strategies and post- war arrangements)
2. War crime trials
- important for development of International Law
- guidelines for prosecutions
- advocate establishing International Criminal Court
- Events: International Military Tribunal 1945 (Germany)
International Military Tribunal for the Far East 1946
(Japan)
Post-war Arrangements
Germany
- divided into four zones (occupied by Britain, France, U.S.,
U.SS.R. -> to denazify Germany
- Germans from other European countries were sent back to
Germany
Austria
- divided into four zones (occupied by Britain, France, U.S.,
U.S.S.R.)
- seperated from Germany
- denazification
- cannot unite with Germany
Japan
- occupied by U.S. (originally occupied by U.S., Britain
(who had too many colonies to handle), China (internal
war), U.S.S.R (Cold War with U.S.)
- General MacArthur was the first SCAP (Supreme
Commander of the Allied Powers) in Japan
- signed the Treaty of San Francisco 1951 -> return
conquered land to China (Manchukuo/ Manchuria) and
gave up control of Korea.
IMPACTS
Aspects:
1. Political:
- Formation of the United Nations (sign of United
Nations Charter on 26/6 1945) -> to maintain world
peace and promote the economic, social and cultural
developments of nations
- Decolonization (driven by nationalism, weakened
European powers, self determination)
- Rise of U.S. and U.S.S.R. as superpowers (traditional
European powered weakened and less colonies -> US
& USSR rose -> competed for world leadership -> led
to Cold War)
2. Technological:
- technological advancement <- new weapons eg atomic
bombs (for bombing) and tools created -> higher
casualties
- penicillin (medicine), radio, airplanes (adopted to
military use originally) -> now used within the
civilians
3. Military:
- strategic bombing: It is believed that war could be
won by demoralizing the enemy (to make surrender a
more preferable choice than struggling) -> direct
attacks upon enemy cities -> rapid collapse of civilian
morale -> increase political pressure to maintain peace
- Hiroshima and Nagasaki: to weaken Japanese’s will of
resistance and reduce the casualties sustained by the
allied forces
- The power of atomic weapons triggered the nuclear
arms race (Cold War era)
4. Social:
- Concept of war changed -. the determination of
declaring a war is weakened due to the serious
post-war problems caused (the war cost is too high)
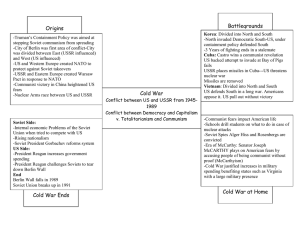
The Features and Development of the Cold War
(p.93-123)
Timeline: 1945-1991 Cold War (1946-1991)
1945 Apr 25 United Nations Conference of International
organisations
1945 May 7: surrender of Germany
1945 June 26: the signing of United Nations Charter
=> the birth of the United Nations
=> maintain world peace
=> promote economic, social, and cultural
developments of nations
1945 August 15: Atomic bombs dropped on Japan (Hiroshima
& Nagasaki) by US
End of WWII
Surrender of Japan
1945 Oct 24: establishment of United Nations
1945 Nov: International Military Tribunal in Nuremberg
1946 Apr: International Military Tribunal for the Far East
1946-1949: Chinese Civil War
1946 Feb: Long Telegram
1946 March: Iron Curtain Speech {also called The Sinews of
Peace}
- speech delivered by British Prime Minister Winston
Churchill
- announced that the former wartime allies would no longer
cooperate
- a grand alliance involving all countries should be formed to
maintain peace
- Effect => marked the beginning of the Cold War (allied
powers no longer cooperate)
1947 March: Truman Doctrine
- Challenge: Greece and Turkey broke out communist
activities <- U.S. feared they’re pro- communist
- Response -> Harry Truman (suggested by George Kennan)
announced that the U.S. would help countries that are
threatened by communism (by providing financial aid)
- Effect: Greece and Turkey government successfully
stopped the expansion of communism
W
1947 June: Introduction of Marshall Plan (in response to
Truman Doctrine -> really form a plan to help countries
financially)
*Formulated by George Marshall, the Secretary of State*
- Intention of US was not to dominate Europe
- BUT USSR thought that US wanted to instil its ideology to
destroy communism => highlighted the feature of Cold War
: Ideology differences / mutual distrust
- helped Western European countries rebuild their economies
-> stop communism from spreading [ U.S. had an idea that
communism spread because of bad economy] )
Effect:
- 16 nations responded to the offer
- stopped the spread of communism
- strengthen their ties with US
- Caused the Molotov plan (as a response to the Marshall
plan)
1947 July: Introduction of Molotov Plan (response to the
Marshall Plan)
- Challenge: USSR did not trust the Marshall Plan
- Response: provided economic aid to Eastern European
countries + tightened control
- Effect: The two plans divided Europe into two economic
blocs: East-West relationships further worsened
1948-1949: Berlin Blockade
Background: According to the Potsdam Conference:
- Germany and Berlin were each divided into four
occupation zones (Berlin: USSR, Western Germany: US,
Britain, France)
1948 June: Blockade of routes to West Berlin by USSR
- Challenge: US, France, Britain conducted a currency
reform to facilitate economic recovery in western Germany
USSR: suspicious and did not trust them (features of the Cold
War: mutual distrust)*
- Response: close all land routes into Western Berlin to cut
off the food and water supply to Berlin in order to make the
three abandon the reform of German economy
- Solution & effect: -Western countries sent supplies to
Western Berlin by air
- Formation of NATO to protect each other from Soviet
attack
1949 April: North Atlantic Treaty (Atlantic Pact) Organisation
(NATO)
Purpose: a united military strength to protect each other in case
of any foreign attack from U.S.S.R
- Effect: USSR ended the Berlin blockade as it was under
pressure of the united military strength
1949 May: End of blockade of West Berlin by USSR
1949 May: establishment of the federal Republic of Germany
(West Germany)
- West Berlin (US, Britain, France <- merged economically
(currency reform) and politically)
1949 October: Establishment of the German Democratic
Republic (East Germany)
1955 May: Warsaw Pact
- Challenge: NATO formed by US and western European
countries -> enabling US to station troops and deploy
missiles in NATO members -> threatening the safety of
U.S.S.R.
- Response: U.S.S.R formed the Warsaw Treaty Organisation
with Eastern European states
1960: U2 incident (spying activities against each other)
Effects of the Berlin Blockade
1. Division of Germany
- US, Britain, France => West Germany (believing that
a strong West Germany could resist Soviet expansion
into West Europe)
- USSR => East Germany (response to the formation of
West Germany)
2. Two rival military blocs
- NATO
- Warsaw Pact
=> divided Europe into two military blocs
1950-1953: Korean War (indirect conflict between the
superpowers*)
Background:
- Soviet army overran Japanese army in Manchukuo and
northern Korea (during WW2)
- Tension between north and South Korea over the issue of
unification
SK: Rhee Syngman (support from U.S)
NK: Kim Il- sung (support from U.S.S.R)
1950 June 25: North Korea’s invasion of South Korea
(supported by the USSR)
- the United Nations security council condemned the
invasion -> NATO members (mostly American troops since
they are in Japan) => pushed the NK forces back over the
38th Parallel
- The People’s republic of China, fearing the invasion of
Manchukuo (national security), sent ‘voluntary troops’ to
North Korea
1953 July 27: armistices were signed -> established the Korean
Demilitarised zone.
Impact of Korean War
- United Nations became a stage of American-Soviet
confrontation (both the U.S. & the U.S.S.R tried to
influence the decisions of the UN security council
concerning Korea)
- US was determined to build up an Asian defence line,
fearing the expansion of U.S.S.R
1962: Cuban Missile Crisis (**IMPORTANT -> TURNING
POINT OF COLD WAR**)
- Nikita Khrushchev (USSR)-> the idea of ‘peaceful
coexistence’ <- relationship between US and USSR
repaired
1959 Feb: Pro- American (support U.S.) government in Cuba
overthrown by Fidel Castro <- ‘Maoism’ (communism)
1961 Apr: US supported the Cuban exiles to overthrow the
Castro’s government (proposed by John Kennedy) => failed
Effect:
1. worsened relationships between Cuba and US
2. Castro turned to USSR and USSR responded positively
(John Kennedy’s decision indirectly contributed to the
alliance of Cuba and USSR)
1961 Oct : USSR detonated the Tzar Bomba (most powerful
bomb in history) to seek for balance of nuclear power against
US {wanted to put the bomb in Cuba}
1962 Sep:
- US discovered the plan of missiles (espionage) and
imposed a naval blockade to prevent Soviet ships from
reaching Cuba
- demanded USSR to withdraw the missiles from Cuba
(Khrushchev refused => came close to a nuclear war)
1962 Oct:
- Agreement between the Kennedy and Khrushchev, both
concerned about the consequences of a nuclear war (from
Khrushchev’s personal messages)
- John Kennedy believed in Khrushchev as he thought he
was responsible for all people’s safety, and lifted the
blockade (diffusing the mutual distrust between the
superpowers)
- Khrushchev agreed to withdraw the missiles to defuse the
tension
- John Kennedy promised not to invade Cuba in the future
Importance of the Cuban Missile Crisis
- closest moment to a nuclear war
- change of attitude between Khrushchev and Kennedy: from
having mutual distrust to having mutual trust
- a direct communication channel 1963“the hotline” was set
up between US and USSR to allow direct communication
in case of crises
=> embodying the two’s mutual trust
=> Before: mutual distrust and political conflicts due to
ideological differences (communism vs capitalism)
=> After: mutual trust {reducing importance of ideological
differences -> feature of Cold War: unavoidable co-existence of
communist and capitalist bloc}
=> realize the importance of mutual trust and direct
communication
=> development of nuclear weapons must be limited to avoid a
nuclear war
1963: (signing of Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty)
1970-1979: Detente
Cause: Cuban Missile Crisis
- tension between the two superpowers now eased
- fear of nuclear war further deterred any ideas of direct
military conflicts (needed to be limited)
Impact: => U.S. and U.S.S.R. had frequent negotiations
Nikita Khrushchev and his successor Leonid Brezhnev: promote
“Peaceful Coexistence” => (due to) unavoidable coexistence of
both capitalist and communist
Richard Nixon (U.S.): more conversations between U.S. and
communist countries
1968: Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons
1972: First Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT I)
1975: Helsinki Agreement
- improving Sino-American relationships (NATO & Warsaw
Pact)
=> Ping Pong diplomacy
=> US supported China in recovering its legal position in United
Nations
1985-1991: End of Cold War
1970- 1985: Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan (deterioration of US
& USSR relationship)
1985: Mikhail Gorbachev became the leader of USSR
- introduced reforms to save U.S.S.R.’s collapsing economy
AIM:
- reconstruct Soviet economy
- reduce Soviet military expenditure and aid
- reform the government
- improve relations with US
Policies:
=> adopted a “new political thinking” to remove the ideological
considerations in foreign policy
=> led to great changes in Eastern Europe
Sinatra Doctrine (loosening policy of Soviet control over
Eastern Europe)
- End of communist rule
- people in Eastern Europe were allowed to choose their own
political and economic systems
1989 Dec 3: Gorbachev and George HW Bush agreed on
reductions in troops and weapons
=> End of cold war
The collapse of the Soviet Union:
- the mishandling of reforms
1. communist regimes in Eastern Europe failed to solve
structural problems and economic problems => collapse
2. Gorbachev’s reforms failed to improve the living standards
of people
3. discontent of hardliners brought a military coup against
Gorbachev
1990: Unification of Germany (east and west)
1991 July: End of the Warsaw Treaty Organisation
1991: August Coup :discontent of hardliners brought a coup
against Gorbachev
1991 Dec 25: Gorbachev resigned -> End of Soviet Union
What is the Cold War?
- US, USSR => superpowers
- Western bloc (US), Communist bloc (USSR) were
formed to protect national interests
- confronted each other in different areas
- mutual distrust and fear affected the two governments’
decision
- NO military conflicts -> deterrence only (the use of
nuclear weapons to scare each other)
- coexistence of conflicts and cooperations (such as the
Marshall & Molotov plan)
Causes of Cold War
1. Ideological differences
- Ideology => a set of ideas, beliefs, values that
explain how the society should work to achieve
ultimate goals
- Difference between Communism (USSR) and
Capitalism (US) => different political, economic,
social systems
- USSR and US believed their nations embodied
the superior way of life => affected their
construction and views on the world
E.g. Their perceptions on threats and opportunities
2. Mutual mistrust
- To the Western European countries:
=> seen expansion of Soviet influence in Eastern
Europe as a threat
=> excluded USSR from Paris Peace Conference,
League of Nations, Munich Conference
- To USSR:
=> the international intention to intervene the Russian
Civil War revealed the capitalist’s intention to
suppress the people’s October Revolution
=> Western European countries refused to form an
alliance with USSR when Nazi Germany expanded to
Eastern Europe
=> Joseph Stalin signed the Nazi-Soviet
Non-Aggression Pact
3. American-Soviet confrontation in Europe
- Western powers and USSR had conflicts over
war-time strategies and post-war arrangements
- Soviet armies liberated Eastern Europe from Nazi
control + supported local communists to establish
pro-Soviet government
=> SO, US was worried about Soviet expansion in
Eastern Europe and was determined to resist Soviet
expansion
Features of the Cold War
1. Co-existence of conflicts and cooperation
2. Use of nuclear weapons as a mean of deterrence
(not really use to attack others)
3. Use of propaganda as a tool to denonce
opponents
- justify government’s policy (e.g. US used
propaganda to justify their nuclear weapons,
US and USSR attacked each other’s
political, economic and social systems)
- intentionally praise the country
4. Spying / Espionage
- Due to mutual distrust between countries
- steal technology and intelligence secrets
- collect important information for their
country’s security
5. Intentional avoidance of direct military conflicts
between the superpowers
=> Competition through forming rival blocs and
arms race
– Military blocs
- NATO 1949 formed by US, Canada and ten
Western countries to resist Soviet expansion
- Warsaw Pact 1955 established by USSR
with Eastern European countries
– Economic blocs
- Marshall Plan 1947 is introduced by US to
help Western European countries to rebuild
their economy=> become more tied to US
- In response to the Marshall Plan, Molotov
Plan 1947 is introduced by USSR to provide
aid to Eastern European
countries=>enabling USSR to tighten
control over Eastern European countries
– Nuclear race
- US and USSR competed for the
development of atomic bombs
- spent huge sum of money developing more
destructive nuclear weapons
=> world living under the threat of nuclear war
–Space race
- 1957 USSR launched the first satellite
=> US accelerate developing its space technology
=> begin of space race
6. Competition for influence in less developed
countries
- made use of military and economic aid to
less developed countries in Asia and Africa
- intervened in local conflicts
7. Reducing importance of ideological differences
- realised that it was not possible to let one
ideology dominate the world
- started to view the world with different lens
- unavoidable coexistence of the communist
bloc and the capitalist bloc
8. Indirect conflicts between superpowers
- Korean War
Overview Timeline:
1937: Japan’s invasion of China
1939- 1941: Axis Power’s successful period
1939 September 1: invasion of Poland: Blitzkrieg strategy was
adopted -> successfully occupied Poland within a month
1940 May: Germany occupied Denmark and Norway <obtained air and naval bases for attacks on Britain
1940 May: Germany invaded Belgium and the Netherlands ->
invade France via Belgium
1940 June: fall of France:
370,000 allied soldiers retreated to Britain
1940 June 13: Fall of Paris
1940 June 22: France surrendered to Germany
-France was divided into two parts
1. German occupied zone
2. Pro-German Vichy France
1940 July: Battle of Britain: battle between Britain and German
air forces
1940 August: Italy attack North Africa (Britain’s oil supplies)
-> Britain counter- attack -> Hitler sent troops to Africa to help
Italy
1940 September: Japan signed the Tripartite Pact with
Germany and Italy (Berlin- Rome- Tokyo- Axis)
1941 April: Japan signed the Soviet- Japanese Treaty of
Neutrality- (even though Japan is one of the axis powers, it did
not attack the Soviet Union from Manchuria (its puppet state) ->
signed a pact of neutrality)
1941 June: Germany attacks Soviet Union (capture Soviet lands
-> kill Jews), however, failed to defeat Soviet Union
1941 December 8:
Pearl Harbour Incident: Japanese troops suddenly attack
American naval base at Pearl Harbour (in Hawaii) -> US declare
war on the Axis Powers
-> Roosevelt consecutively declared war on Japan (Germany
and Italy also declared war on the US)
1941: the outbreak of the Pacific War (8/12)
1942- 1945: Allied counter- offensives - the end of WW2
1942 June: Battle of Midway -> Japanese troops tried to destroy
the American fleet -> suffered from heavy losses (turning point
in the pacific war)
1942: US defeated Japan in the battles in the pacific
1942 Aug: Battle of Stalingrad =>SU defeated Germany(turning
point of WW2)
1943 Feb: Soviet Union defeated German troops
1943 May: German troops forced to retreat from North Africa
1943 July: Battle of Kursk =>End of the German offensive
capability on the Eastern Front (turning point of WW2)
1943: Liberation of Italy
1944 June 6: D- Day: 156000 Allied soldiers landed on the
beaches of Normandy in Northern France (then occupied by
Germany)
1944 August 24: freed France from Nazi control
1944 October: Battle of the Philippines ((Battle of Leyte
oct-dec) <- Japan lost to the US (General MacArthur), cutting
off the its oil supply lines with Southeast Asia)
1945 February: Battle of Iwo Jima (the most violent battle in
the pacific war) -> heavy casualties -> US decided to drop the
atomic bombs on Japan.
1945 April 30: Soviet troops took Berlin (Germany capital city)
+ Hiter’s suicide
1945 June 26: signing of the United Nations Charter
1945 August 15: Japan surrendered after atomic bombs are
dropped in Hiroshima (6 August) and Nagasaki (9 August),
decision made by President Truman
1945 August 30: End of war
1945 October 24: the official operation of the United Nations
1945 November: International Military Tribunal <- Germany’s
war crime trial
1946-1949: Chinese Civil War
1946- 1991: Cold War
1946 March: Iron Curtain Speech (speech delivered by British
Prime Minister Winston Churchill -> marked the beginning of
the Cold War <- allied powers no longer cooperate)
1947 March: Truman Doctrine (Greece and Turkey broke out
communist activities <- U.S. feared they’re pro- communist ->
Harry Truman annoyed that the U.S. would help countries that
are threatened by communism)
1947 June: Introduction of Marshall Plan (helped Western
European countries rebuild their economies -> stop communism
from spreading [ U.S. had an idea that communism spread
because of bad economy] )
1947 July: Introduction of Molotov Plan (soviet’s response to
the Marshall Plan -> provided economic aid to Eastern European
countries + tightened control)
1948-1949: Berlin Blockade
1948 June: Blockade of routes to West Berlin by USSR
1949 April: North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO is
formed) -> united military strength to ‘defend’ each other in
case of any foreign attack from U.S.S.R
1949 May: End of blockade of West Berlin by USSR
- West Berlin (US, Britain, France <- merged economically
(currency reform) and politically)
1949 May: establishment of the federal Republic of Germany
(West Germany)
1949 October: Establishment of the German Democratic
Republic (East Germany)
1950-1953: Korean War
1950 June 25: North Korea’s invasion of South Korea
(supported by the USSR)
1951: japan signed the treaty of San Francisco (to give China
Manchuria & give up Korea)
1953 July 27: armistices (Korean war) were signed ->
established the Korean Demilitarized zone.
1955 May: Warsaw Pact <- (West Germany joined NATO) <U.S.S.R formed the Warsaw Treaty Organization with Eastern
European states -> divide Europe into two rival military blocks.
1959 Feb: Pro- American (support U.S.) government in Cuba
overthrown by Fidel Castro <- ‘Maoism’ (communism)
1961 Apr: US supported the Cuban exiles to overthrow the
Castro’s government (proposed by John Kennedy) => failed
1961 Oct : USSR detonated the Tzar Bomba (most powerful
bomb in history) to seek for balance of nuclear power against
US {wanted to put the bomb in Cuba}
1962: Cuban Missile Crisis
1962 Sep:
- US discovered the plan of missiles (espionage) and
imposed a naval blockade to prevent Soviet ships from
reaching Cuba
- demanded USSR to withdraw the missiles from Cuba
(Khrushchev refused => came close to a nuclear war)
1962 Oct:
- Agreement between the Kennedy and Khrushchev, both
concerned about the consequences of a nuclear war (from
Khrushchev’s personal messages)
1970-1979: Detente
1963: (signing of Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty)
1968: Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons
1969: First Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT I)
1975: Helsinki Agreement
- improving Sino-American relationships (NATO & Warsaw
Pact)
=> Ping Pong diplomacy
=> US supported China in recovering its legal position in United
Nations
1970- 1985: Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan (deterioration of US
& USSR relationship)
1985: Mikhail Gorbachev became the leader of USSR
- introduced reforms to save U.S.S.R.’s collapsing economy
1989 Dec 3: end of Cold War Gorbachev and George HW
Bush agreed on reductions in troops and weapons
1990: Unification of Germany (east and west)
1991: August Coup :discontent of hardliners brought a coup
against Gorbachev
1991 Dec 25: Gorbachev resigned -> End of Soviet Union