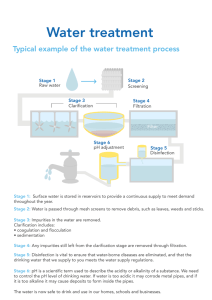
WATER LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Describe chemical tests for water using cobalt (II) chloride and copper (II) sulphate • Describe, in outline, the treatment of the water supply in terms of filtration and chlorination. 2 Uses Of Water USES OF WATER Water In Industry As A Coolant Too Water treatment process flow diagram WATER TREATMENT Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it more acceptable for a specific end use Describe, in outline, the treatment of *Sludge Coagulants Sludge the water supply in terms of filtration and chlorination Raw Water Screening Coagulation Flocculation Sedimentation Distribution Storage Disinfection Filtration Cl2 Sludge *sludge = Wet muddy solid/semisolid Screening WATER TREATMENT Remove large solids like logs, branches and twigs, fishes… Coagulation Destabilization of stable suspension by the addition of chemicals (coagulants) Colloidal suspensions are: Describe, in outline, the treatment of negatively charged due to dissolved organic matter the water supply in terms of filtration stable due to charge repulsion and chlorination - - - - - - - - -- -- - - - - -- -- - - - - - - - - -- -- -- Negatively charged colloids (size < 1μm) Addition of coagulants (Fe2+, Al3+ …) Neutralization Neutralized particle Flocculation and Sedimentation WATER TREATMENT Flocculation: The process of particle aggregation Sedimentation: Settling of large flocs Describe, in outline, the treatment of Collision the water supply in terms of filtration due to Brownian motion of the medium or agitation and chlorination Neutralized particle calm water Flocculation Coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation removes: dissolved organic materials or Natural Organic Matter suspended particles and inorganic precipitates such as iron between 27-84% of viruses and between 32 and 87% bacteria (most bacteria and viruses are attached with NOM) Sedimentation Filtration WATER TREATMENT The process of separating suspended particles/ particulate matter from a liquid by forcing the liquid through a filter media Two Major Types (based on filter media) Describe, in outline, the treatment of 1. Sand Filtration the water supply in terms of filtration and chlorination raw water Raw water Raw water Mechanical Adsorption Lodging of large particles Sticking to the filter media sand coarse sand gravel water out Filtration WATER TREATMENT 2. Membrane Filtration virus bacteria multivalent ions monovalent ions the water supply in terms of filtration and chlorination Raw water Describe, in outline, the treatment of Pure water suspended solid Ultra filtration Reverse osmosis < 1nm (0.1μm – 0.01μm) Micro filtration (10μm – 0.1μm) Nano filtration (10nm – 1nm) Sand Filtration Removes Suspended particulate matter Slow sand filtration also removes considerable amount bacteria, virus and protozoa Chlorination WATER TREATMENT Used for disinfecting the water- i.e. the removal, deactivation or killing of pathogenic microorganisms. Describe, in outline, the treatment of the water supply in terms of filtration and chlorination Chlorinating agents : Cl2(g), Ca(OCl)2 (calcium hypochlorite) and NaOCl (sodium hypochlorite) Chemistry of chlorination (Cl2) Chlorine gas + Water Hypochlorous acid + Hydrochloric acid Cl2(g) + H2O HOCl (hypochlorous acid) + HCl HOCl H+ + OCl- (at 250C and pH7.5) When a hypochlorite is used NaOCl + H2O OCl- (hypochlorite ion) + OH Together, HOCl and OCl- are referred as free chlorine HOCl and OCl- are both disinfection agents HOCl is 80-100 times more effective than OCl- Chlorination WATER TREATMENT Mechanism of Action Negatively charged hypochlorite ions damages the cell membrane Neutral HClO molecules penetrates the cell wall and disrupts the cell respiration Describe, in outline, the treatment of and DNA activity the water supply in terms of filtration and chlorination Cl H O Cl Cl O - Cl - O O Other uses of chlorination It oxidize Fe, Mn, taste and odour compounds, remove colour and destroy H2S Global water use USES OF WATER 8% Residential 22% Industrial 70% Agricultural Name some of the uses of water in industry and in the home Major residential uses of water Toilet 24-32.6% Faucet 20-27% Shower 20-27% Clothes washer 16-20% Leaks +other 21-28% Major industrial uses of water USES OF WATER Name some of the uses of water in Thermal Power Plants Wood and Paper Industry Steel Industry steam production and as coolant cooking, bleaching and washing cooling, concentrating the ore, dust suppression… Refineries Distilleries Textile Industry cooling malting, mashing and dilution washing, dyeing, bleaching, Fertilizer Industry Leather and Sugar Chemicals (e.g. H2SO4) industry and in the home World water crisis- Some facts EFFECTS OF WATER SCARCITY 844M 5000 40% People living without access to clean water Children World’s Food die everyday from water related diseases currently cultivated in artificially irrigated areas Discuss the implications of an inadequate supply of water, limited to safe water for drinking and water for irrigating crops 55% 70% Global Water Demand Agricultural Production increases by 2050 need to expand by 2050 World water crisis- Causes EFFECTS OF WATER SCARCITY Water Pollution Discuss the implications of an Misuse and overuse inadequate supply of water, limited to safe water for drinking and water for irrigating crops Most sources of water in rural area are polluted due to poor sanitation and lack of waste water treatment facility Flood irrigation, poor crop choice, leaky taps, overwatering of plants, long baths….. Ground water over drafting Occurs when water removal exceeds water recharge. This leads to drying up of wells, deterioration in quality, reduction in water level in streams and rivers Climate change Changes in rain and evaporation pattern Corruption, mismanagement, lack of infrastructure, unfair pricing…. Effect of inadequate water supply on plants EFFECTS OF WATER SCARCITY Discuss the implications of an Plants need water for Photosynthesis Germination Transpiration Nutrient transfer 6CO2+ 6H2O C6H12O6 +6O2 water activate the process and softens the seed continual flow of water keep the cell firm plants absorb and transfer only ions dissolved in water inadequate supply of water, limited to safe water for drinking and water for irrigating crops Implications of water stress Symptoms of mild water stress Symptoms of severe water stress Slow and stunted growth Yellowing of leaves Leaves turn from shiny to dull Wilting of leaves Burning and scorching the edges of the leaves Dropping some or all the leaves Inadequate supply of drinking water EFFECTS OF WATER SCARCITY Discuss the implications of an inadequate supply of water, limited to safe water for drinking and water for Drinking water requirement by age (in litres) 0.7 -0.8 1.3 -1.7 2.5 3.0 2.2 Babies and Infants Children Boys & Girls (age 9-13) Men Women Health effects due to lack of water irrigating crops Fatigue and lack of energy Due to decrease in enzymatic activity Overweight and obesity Water maintains healthy metabolism and releases more toxic and waste products from the body Premature aging Reduces antioxidant activity in the body Constipation Due to dehydration of intestine stool will not form easily Inadequate supply of drinking water EFFECTS OF WATER SCARCITY Discuss the implications of an inadequate supply of water, limited to Water quality refers to biological, chemical, physical and radiological characteristics of water No safe water for drinking and water for irrigating crops Pathogens Poisonous chemicals Colour Radioactive virus, bacteria, protozoa Heavy metals (Pb, Hg..) Pesticides… Heavy water (<600mg/L) odour, taste pH = 6.5-8.5 materials Essential electrolytes and minerals in drinking water Fe oxygen transport, metabolism of neurotransmitters , DNA synthesis…. I a critical component of thyroid hormones P a structural component of bones Cu Zn Mg responsible for catalytic properties of enzymes… Ca primary structural constituent of the skeleton , regulates many enzyme and hormonal responses….. Sodium, potassium, chloride….. Inadequate drinking water and health effects EFFECTS OF WATER SCARCITY Health effects due to biological contamination Typhoid Discuss the implications of an (Salmonella typhi) high fever, diarrhea, vomiting Cholera (Vibrio cholerae) watery diarrhea, vomiting, muscle cramps inadequate supply of water, limited to safe water for drinking and water for irrigating crops Amoebiasis (Entamoeba) Bloody diarrhea, abdomen pain Dysentery, Malaria, Jaundice… Hepatitis A and E (Virus) abdomen pain, dark urine, loss of appetite Inadequate drinking water and health effects EFFECTS OF WATER SCARCITY Health effects due to chemical contamination Arsenic Fluorides (Fluorosis) Discuss the implications of an Causes liver damage, skin cancer & vascular disease Yellowing of teeth and damages spinal cord inadequate supply of water, limited to NO3- safe water for drinking and water for irrigating crops Pb As Lead Accumulates in the body and damages central nervous system F- Pesticides, Herbicides & Insecticide Damages central nervous system, causes cancer, endocrinal damage … Nitrates Restrict the amount of oxygen in the brain THANK YOU Thank you for watching this presentation Your feedback and suggestions will be greatly appreciated Rate this on tes.com SIJI GEORGE (sijiparekattil@gmail.com)