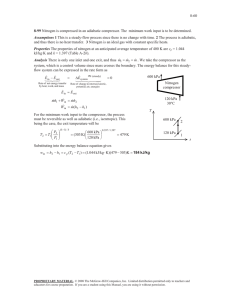
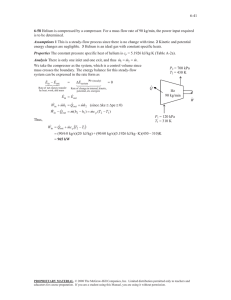
HOT SEAT Thermodynamics A 214 5th May 2020 Adam Venter PhD Candidate Solar Thermal Energy Research Group (STERG) | Stellenbosch University QUESTION 7 (7-127) Problem: Air enters a compressor steadily at the ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20 °C and leaves at 800 kPa. Heat is lost from the compressor in the amount of 120 kJ/kg and the air experiences an entropy decrease of 0.40 kJ/kg.k. Using constant specific heats. Determine (a) the exit temperature of the air, (b) the work input to the compressor, and (c) the entropy generation during this process. Key notes: Air, Compressor, Steadily, kJ/kg Ideal gas Control volume analysis Steady flow process Per unit mass basis QUESTION 7 (7-127) 1 Problem: 2 Air enters a compressor steadily at the ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20 °C and leaves at 800 kPa. Heat is lost from the compressor in the amount of 120 kJ/kg and the air experiences an entropy decrease of 0.40 kJ/kg.k. Using constant specific heats. Determine (a) the exit temperature of the air, (b) the work input to the compressor, and (c) the entropy generation during this process. 0 𝑒𝑒𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 − 𝑒𝑒𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 = Δ𝑒𝑒𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 800 kPa 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 Compressor Air 100 kPa 20 °C QUESTION 7 (7-127) Problem: Air enters a compressor steadily at the ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20 °C and leaves at 800 kPa. Heat is lost from the compressor in the amount of 120 kJ/kg and the air experiences an entropy decrease of 0.40 kJ/kg.k. Using constant specific heats. Determine (a) the exit temperature of the air, (b) the work input to the compressor, and (c) the entropy generation during this process. 𝑒𝑒𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑒𝑒𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 800 kPa 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 0 Compressor Air 100 kPa 20 °C 𝑞𝑞𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 + 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 + 𝜃𝜃𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 + 𝑤𝑤𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 + 𝜃𝜃𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 0 0 0 0 0 𝑞𝑞𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 + 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 + ℎ𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 + 𝑘𝑘𝑒𝑒𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 + 𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 + 𝑤𝑤𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 + ℎ𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 + 𝑘𝑘𝑒𝑒𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 + 𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 ASSUMPTIONS - Steady operating conditions exist - 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 = 𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝 = 0 - Ideal gas with constant specific heats @ 300 K - 𝑤𝑤𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 = 𝑞𝑞𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 0 QUESTION 7 (7-127) Problem: Air enters a compressor steadily at the ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20 °C and leaves at 800 kPa. Heat is lost from the compressor in the amount of 120 kJ/kg and the air experiences an entropy decrease of 0.40 kJ/kg.k. Using constant specific heats. Determine (a) the exit temperature of the air, (b) the work input to the compressor, and (c) the entropy generation during this process. 𝑒𝑒𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑒𝑒𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 800 kPa 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 Compressor Air 100 kPa 20 °C 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 + ℎ𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 + ℎ𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = ℎ𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 − ℎ𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 + 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 Δℎ = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝,𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 Δ𝑇𝑇 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝 𝑇𝑇2 − 𝑇𝑇1 + 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 QUESTION 7 (7-127) Problem: Air enters a compressor steadily at the ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20 °C and leaves at 800 kPa. Heat is lost from the compressor in the amount of 120 kJ/kg and the air experiences an entropy decrease of 0.40 kJ/kg.k. Using constant specific heats. Determine (a) the exit temperature of the air, (b) the work input to the compressor, and (c) the entropy generation during this process. 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝 𝑇𝑇2 − 𝑇𝑇1 + 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 800 kPa 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 Δ𝑆𝑆𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝 ln Compressor Air 100 kPa 20 °C 𝑑𝑑𝑑 𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 𝑑𝑑𝑑𝑑 = − 𝑇𝑇 𝑇𝑇 2 2 𝑑𝑑𝑑 𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 Δ𝑠𝑠 = � −� 𝑇𝑇 𝑇𝑇 1 1 𝑇𝑇2 𝑃𝑃2 − 𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 𝑇𝑇1 𝑃𝑃1 𝑇𝑇𝑇𝑇𝑇𝑇 = 𝑑𝑑𝑑 − 𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣𝑣 𝑑𝑑𝑑 = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝 𝑑𝑑𝑑𝑑 𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 𝑣𝑣 = 𝑃𝑃 2 𝑐𝑐 𝑑𝑑𝑑𝑑 𝑝𝑝 Δ𝑠𝑠 = � 1 𝑇𝑇 2 2 𝑅𝑅𝑑𝑑𝑑𝑑 𝑃𝑃 1 −� 2 𝑑𝑑𝑑𝑑 𝑑𝑑𝑑𝑑 Δ𝑠𝑠 = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝 � − 𝑅𝑅 � 𝑇𝑇 1 1 𝑃𝑃 QUESTION 7 (7-127) Problem: Air enters a compressor steadily at the ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20 °C and leaves at 800 kPa. Heat is lost from the compressor in the amount of 120 kJ/kg and the air experiences an entropy decrease of 0.40 kJ/kg.k. Using constant specific heats. Determine (a) the exit temperature of the air, (b) the work input to the compressor, and (c) the entropy generation during this process. 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝 𝑇𝑇2 − 𝑇𝑇1 + 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 800 kPa 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 Compressor Air 100 kPa 20 °C Δ𝑆𝑆𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝 ln 𝑇𝑇2 𝑃𝑃2 − 𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 𝑇𝑇1 𝑃𝑃1 Table A-2 −0.40 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘. 𝐾𝐾 = (1.005 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘. 𝐾𝐾) ln 𝑇𝑇2 800 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 − (0.287 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘. 𝐾𝐾)𝑙𝑙𝑙𝑙 22 + 273𝐾𝐾 100 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑇𝑇2 = 358.8𝐾𝐾 QUESTION 7 (7-127) Problem: Air enters a compressor steadily at the ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20 °C and leaves at 800 kPa. Heat is lost from the compressor in the amount of 120 kJ/kg and the air experiences an entropy decrease of 0.40 kJ/kg.k. Using constant specific heats. Determine (a) the exit temperature of the air, (b) the work input to the compressor, and (c) the entropy generation during this process. 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑐𝑐𝑝𝑝 𝑇𝑇2 − 𝑇𝑇1 + 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 800 kPa 85.8 °C 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 Compressor Air 100 kPa 20 °C 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 1.005 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 °𝐶𝐶 85.8 − 20 °𝐶𝐶 + 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 184.1 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 QUESTION 7 (7-127) Problem: Air enters a compressor steadily at the ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 20 °C and leaves at 800 kPa. Heat is lost from the compressor in the amount of 120 kJ/kg and the air experiences an entropy decrease of 0.40 kJ/kg.k. Using constant specific heats. Determine (a) the exit temperature of the air, (b) the work input to the compressor, and (c) the entropy generation during this process. 𝑠𝑠𝑔𝑔𝑔𝑔𝑔𝑔 = Δ𝑠𝑠𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡al = Δ𝑠𝑠𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎𝑎 + Δ𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 800 kPa 85.8 °C 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝑤𝑤𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 184.1 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 Compressor Air 100 kPa 20 °C 𝑞𝑞𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 120 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 Δ𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 = = = 0.4068 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘. 𝐾𝐾 𝑇𝑇𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 22 + 273 𝐾𝐾 𝑠𝑠𝑔𝑔𝑔𝑔𝑔𝑔 = −0.40 + 0.4068 = 0.0068 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘. 𝐾𝐾 QUESTION 8 (6-100) 𝑇𝑇𝐿𝐿 Problem: 𝑇𝑇𝐻𝐻 A Carnot heat pump is to be used to heat a house and maintain an average temperature of 25°C in winter. On a day when the average outdoor temperature remains at about 2°C, the house is estimated to lose heat at a rate of 55,000 kJ/h. if the heat pump consumes 4.8 kW of power while operating, determine 𝑊𝑊̇ 𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 to compensate the heat lost a. How long it will take the heat pump b. The total heating costs, assuming an average price of 11 c/kWh for electricity; c. The heating cost for the same day if resistance heating is used instead of a heat pump. Key notes: Heat pump Coefficient of performance QUESTION 8 (6-100) Problem: a. b. c. 𝑇𝑇𝐿𝐿 = 2 °𝐶𝐶 𝑇𝑇𝐻𝐻 = 25°𝐶𝐶 𝑊𝑊̇ 𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 4.8 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 How long it will take the heat pump to compensate the heat lost The total heating costs, assuming an average price of 11 c/kWh for electricity; The heating cost for the same day if resistance heating is used instead of a heat pump. 𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷𝐷 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑄𝑄𝐻𝐻 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝑃𝑃𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 = = 𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 𝑊𝑊𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛,𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝑃𝑃𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 = 𝑄𝑄𝐻𝐻 𝑄𝑄𝐻𝐻 − 𝑄𝑄𝐿𝐿 1 1 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝑃𝑃𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻,𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 = = = 14.1 𝑇𝑇𝐿𝐿 2 + 273 1 − �𝑇𝑇 1− 25 + 273 𝐻𝐻 𝑄𝑄̇ 𝐻𝐻 𝑄𝑄̇ 𝐿𝐿 HP 𝑊𝑊̇ 𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 QUESTION 8 (6-100) Problem: a. b. c. 𝑇𝑇𝐿𝐿 = 2 °𝐶𝐶 𝑇𝑇𝐻𝐻 = 25°𝐶𝐶 𝑊𝑊̇ 𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 4.8 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 How long it will take the heat pump to compensate the heat lost The total heating costs, assuming an average price of 11 c/kWh for electricity; The heating cost for the same day if resistance heating is used instead of a heat pump. 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝑃𝑃𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻,𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 = 14.1 𝑄𝑄𝐻𝐻 = 𝑄𝑄̇ H 1day = (55,000 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘⁄ℎ) 24ℎ𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 = 1,320 𝑀𝑀𝑀𝑀 𝑄𝑄𝐻𝐻 1,320 𝑊𝑊𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛,𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = = = 93,617 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝑃𝑃𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 14.1 𝑊𝑊𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛,𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 93,617 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 Δ𝑡𝑡 = = = 5.42 ℎ𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 4.8 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘/𝑠𝑠 𝑊𝑊̇ 𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛,𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 𝑄𝑄̇ 𝐻𝐻 𝑄𝑄̇ 𝐿𝐿 HP 𝑊𝑊̇ 𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 QUESTION 8 (6-100) Problem: a. b. c. 𝑇𝑇𝐿𝐿 = 2 °𝐶𝐶 𝑇𝑇𝐻𝐻 = 25°𝐶𝐶 𝑊𝑊̇ 𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 4.8 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 How long it will take the heat pump to compensate the heat lost The total heating costs, assuming an average price of 11 c/kWh for electricity; The heating cost for the same day if resistance heating is used instead of a heat pump. Δ𝑡𝑡 = 5.42 ℎ𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶 = 𝑊𝑊𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛𝑛,𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 × 𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶 = (4.8 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘)(5.42 ℎ)(0.11 $⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘) = $ 2.86 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶𝑡𝑡𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 = 𝑄𝑄𝐻𝐻 × 𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝𝑝 = 1,320 𝑀𝑀𝑀𝑀 1 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 3600 𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 0.11 $⁄𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 = $ 40.33 𝑄𝑄̇ 𝐻𝐻 𝑄𝑄̇ 𝐿𝐿 HP 𝑊𝑊̇ 𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 Moving boundary work 𝛿𝛿𝑊𝑊𝑏𝑏 = 𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹𝐹 = 𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃 = 𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃 𝐹𝐹 = 𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃 2 𝑑𝑑𝑑𝑑 = 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 𝑊𝑊𝑏𝑏 = ∫1 𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃 = Area under P-V diagram