Thermodynamics Review Notes: Laws, Devices, Efficiency
advertisement

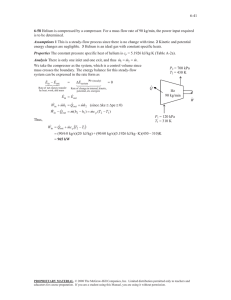
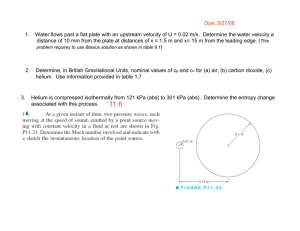
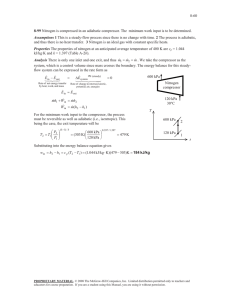
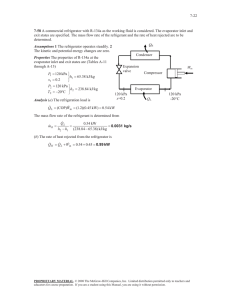
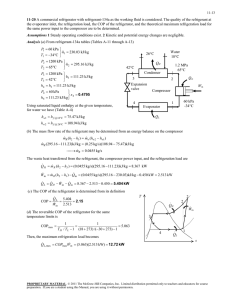
REVIEW Final Exam Sample Problems 6-173 A refrigerator is removing heat from a cold medium at 3°C at a rate of 7200 kJ/h and rejecting the waste heat to a medium at 30°C. If the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator is 2, the power consumed by the refrigerator is (a) 0.1 kW (b) 0.5 kW (c) 1.0 kW (d) 2.0 kW (e) 5.0 kW 7-256 Air at 15°C is compressed steadily and isothermally from 100 kPa to 700 kPa at a rate of 0.12 kg/s. The minimum power input to the compressor is (a) 1.0 kW (b) 11.2 kW (c) 25.8 kW (d) 19.3 kW (e) 161 kW 7-264 Helium gas is compressed steadily from 90 kPa and 25°C to 600 kPa at a rate of 2 kg/min by an adiabatic compressor. If the compressor consumes 70 kW of power while operating, the isentropic efficiency of this compressor is (a) 56.7% (b) 83.7% (c) 75.4% (d) 92.1% (e) 100.0% 9-203 Helium gas in an ideal Otto cycle is compressed from 20°C and 2.5 L to 0.25 L, and its temperature increases by an additional 700°C during the heat addition process. The temperature of helium before the expansion process is (a) 1790°C (b) 2060°C (c) 1240°C (d) 620°C (e) 820°C 9-206 Consider an ideal Brayton cycle executed between the pressure limits of 1200 kPa and 100 kPa and temperature limits of 20°C and 1000°C with argon as the working fluid. The net work output of the cycle is (a) 68 kJ/kg (b) 93 kJ/kg (c) 158 kJ/kg (d) 186 kJ/kg (e) 310 kJ/kg 10-126 A steam power plant operates on the simple ideal Rankine cycle between the pressure limits of 10 kPa and 10 MPa, with a turbine inlet temperature of 600°C. The rate of heat transfer in the boiler is 800 kJ/s. Disregarding the pump work, the power output of this plant is (a) 243 kW (b) 284 kW (c) 508 kW (d) 335 kW (e) 800 kW