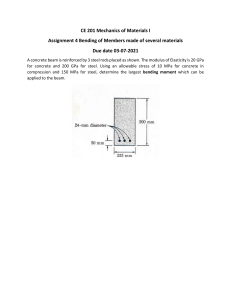
Sr. No. Name of Material Alternative I 1. Traditional Concrete Ashcrete 2. Rigid Metal Electrical Conduit Flexible Metal Conduit 3. Galvanized Steel Plumbing Piping 4. Standard Steel Rebar Reinforcement 6. Bitumen Stainless Steel Plumbing Piping Engineered Bamboo Reinforcement Lime Plastering Asphalt 7. Flat Mud Roofing Metal Roofing 8. Stainless Steel Kitchen Sink Fireclay 9. Doors Knobs 10. Conventional Incandescent Lighting 5. Gypsum Plastering Ball Door Knob Fluorescent Lighting Alternative II GGBS Concrete Electrical Metallic Tubing ABS Plumbing Piping GFRP Rebar Cement Plastering Lignin Alternative III Self-Healing Concrete Electrical Non-Metallic Tubing PVC Plumbing Piping Helix Micro Rebar Reinforcement Gypsum Board Blast Furnace Cool Roofing System Built-UpRoofing Composite Granite Square Door Knob Acrylic Solid Surface Keyed Door Knob Halogen Lighting LED Lighting Alternative IV Hempcrete PVC Conduit PEX Plumbing Piping Spray Polyurethane Foam Roofing Porcelain Enamel Half Dummy Door Knob Solar Lighting 1. Traditional Concrete Introduction: An artificial stone-like mass i.e. Concrete is the composite material that is created by mixing binding material (cement or lime) along with the aggregate (sand, gravel, stone, brick chips, etc.), water, admixtures, etc. in specific proportions. The strength and quality are dependent on the mixing proportions. Concrete = Binding Material + Fine & Coarse Aggregate + Water + Admixture (optional) Concrete is a very necessary and useful material for construction work. Once all the ingredients -cement, aggregate, and water unit of measurement mixed inside the required proportions, the cement and water begin a reaction with one another to bind themselves into a hardened mass. This hardens the rock-like mass in the concrete. Advantages: Ingredients of concrete are readily available in most places. Unlike natural stones, concrete is free from defects and flaws. Concrete can be manufactured to the desired strength with an economy. The durability of concrete is very high. It can be cast to any desired shape. The casting of concrete can be done on the working site which makes it economical. Its strength and sustainability increase over time. The maintenance cost of concrete is almost negligible. The deterioration of concrete is not appreciable with age. Concrete makes a building fire-safe due to its non-combustible nature. Concrete can withstand high temperatures. Concrete is resistant to wind and water. Therefore, it is very useful in storm shelters. Disadvantages: The tensile strength of concrete is relatively low. Concrete is less ductile. The weight of concrete is high compared to its strength. It can easily split and rupture under extreme cold weather conditions and low temperatures. Rate of Concrete: M20/M25 - 4300/cum M35 - 5000/cum Alternative-I of Concrete: Ashcrete Ashcrete: Fly ash is a sustainable building material consisting of ash, usually derived from industrial waste such as coal combustion or agricultural by-products. It replaces or partially replaces cement in concrete mixes, providing environmental benefits, comparable strength, durability and potential savings, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional concrete. Advantages: It stronger and more durable than conventional concrete. Fine particles of fly ash and their pozzolanic properties reduce the cracking and bleeding of fresh Ashcrete, resulting in low permeability. The resistance of Ashcrete to acid and fire is higher than traditional concrete. Ashcrete is a cost-effective material because it is mainly produced from fly ash. Hence, the overall cost of Ashcrete is less than conventional concrete. Ashcrete can trap CO2 from the air, reducing carbon emissions. Thus, it is more environmentally ecofriendly than traditional concrete. Disadvantages: Strength development in Ashcrete is slower than in normal concrete due to the presence of fly ash in the mixture. Ashcrete is susceptible to low temperatures during pouring, significantly increasing the setting time and strength gain. So, using fly ash in the winter is not desirable. Application: bridges pavements embankments roads buildings Alternative-II of Concrete: GGBS- Ground Granulated Blast Slag Concrete The iron-making process requires iron ore, limestone and coke to be blasted at 1500°C. As the ore reduces to iron, the remaining materials float on top and get removed in the form of molten slag. If you rapidly quench that molten iron slag in water or steam, you get glassy granules that are ground down to produce a fine powder – GGBS. This powder is not only extremely cementitious, but also contains high levels of calcium silicate hydrates (CSH) that enhance its strength and durability. GGBS will usually replace between 30% and 70% of cement in the concrete, although that figure can go up to as high as 85%. It usually replaces cement in exactly the same quantity – i.e. you would replace one ton of Portland cement in the mix with one ton of GGBS. It is usually added at the mixer stage. Advantages: GGBS in concrete increases the strength and durability of the concrete structure It reduces voids in concrete hence decreasing permeability GGBS gives a workable mix Penetration of Chloride can be decreased Gives a good surface finish and improves aesthetics Unlike cement, GGBS does not produce carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides. Disadvantages: Additional quality control costs Slow and small hydration heat, not suitable during winter concreting GGBS can sometimes result in delayed setting time compared to conventional concrete mixes. Although GGBS contributes to the long-term strength and durability of concrete, it may initially result in lower early-age strength compared to concrete mixes without GGBS. Application: There are many areas in which GGBS can be used, including: The major use of GGBS is in Ready Mixed Concrete In-Situ Stabilisation of Soil Alternative-III of Concrete: Self-Healing Concrete Crack formation is a typical phenomenon related to durability. Percolation of cracks may lead to leakage problems, causing deterioration of the concrete matrix or corrosion of embedded steel reinforcement. In recent years, a Bacteria Based SELF HEALING CONCRETE is being developed in order to extend the service life. There are two elements which are added to the concrete mixture as the Healing Agent. The Healing Agent consists of Bacteria and an organic Mineral precursor compound. It is a special type of concrete which is cement based material that repair themselves after the material or structure gets damaged due to some sort of deterioration mechanism. It is specially made to increase the lifespan or the durability of concrete structure by the SelfHealing Action of Concrete. There are two special things present in this Concrete: 1. The special bacteria that has to resist the alkalinity and the mechanical stress of concrete 2. The chemical precursor to activate the bacteria When the cracks are formed on the surface of concrete due to any reasons like shrinkage, inadequate water for hydration etc., the water is deliberately forced into the crack then the precursor is activated. The chemical precursor activates the bacteria to react with that precursor and form a base of calcium carbonate called as limestone. Limestone will heal the cracks that appear on the surface on the concrete structures. Advantages: It has a long lifespan, which reduces the number of repairs or replacements required. Self -healing concrete decreases concrete maintenance. In normal concrete, you have to fill and seal the cracks. But you do not have to do or worry about this with self-healing concrete. Improved in compressive strength of concrete. Disadvantages: It is more expensive than traditional concrete Not many contractors know how to use this product yet. Because it is a new product many people do not have an idea of using it. There is no code available to standardize the self-healing concrete. Skilled labor is required. Growth of any bacteria is not good in any atmosphere media. Application: Self-healing concrete can be used for sectors such as tunnel-lining structural basement walls, highways, bridges, concrete floors and marine structures. This is new technology can provide ways to durable roads. High strength buildings with more bearing capacity. Rate of Self-Healing Concrete: M20/M25 - 6000/cum to 7000/cum Alternative-IV of Concrete: Hempcrete: Hempcrete is a plant based sustainable building construction material that is made with a low environmental impact that removes waste production, decreases both energy use and the consumption of natural resources. Hempcrete is a building construction material made from Industrial hemp fibers, lime and water. For building purposes, the hemp crop’s inner woody core, hurds is mixed with a lime-based binder forming a bio-aggregate concrete, known as “Hempcrete”. The hemp-lime composite material is mainly used to make walls, although floor slabs, ceiling, and roof insulation can be made. Hemp has eco-friendliness, low carbon footprint, thermal regulation, and moisture-absorbing properties. Industrial hemp fiber is an ecologically and financially sensible solution, especially in a climatically diverse country like India. Advantages: Hempcrete meets condition of eco-friendly material and is made of renewable resources. Production is less energy intensive. It provides resistance and durability construction and healthy living condition. This material is recyclable. It is proposed to undertake a LCA (Life Cycle Assessment) of hempcrete in the future. The hemp plant absorbs up to 15 tonnes /hectare of carbon dioxide from the air, thus reducing the greenhouse gas effect on the planet Transporting hempcrete is more economical compared to concrete, as it is a lightweight and low-density material Hempcrete walls have a high degree of sound insulation by trapping sound waves, thus reducing noise pollution Hempcrete costs less than other synthetic insulation materials, which can compensate for the larger thickness of hempcrete walls Disadvantages: Use of hempcrete include its capacity to retain water, which can cause swelling and bio-decay of the material, as well as poor mechanical performance which currently prevents it from use as a load bearing material Hemp is not readily available everywhere, so procuring the material for construction can be difficult or expensive Hempcrete building construction is relatively new, not enough research and development Application: Hempcrete blocks serve as effective insulation for both internal and external walls. They are utilized to provide insulation in floors and roofs. Hempcrete is applied as a supportive material beneath flooring. It is employed as a plastering material, contributing to both structure and insulation. They are used to retrofit older buildings, enhancing their insulation properties. Rate: Rs 20000/cubic meter 2. Rigid Metal Electrical Conduit Introduction Rigid metal conduit (RMC) has a thick wall and is constructed of either coated steel, stainless steel, aluminium or galvanized steel. This variety is one of the most heavy-duty types of conduit used in many industrial applications. Rigid Metal Conduit affords maximum mechanical protection to conductors within the raceway. Rigid metal conduit can be installed indoors and outdoors, in dry locations or wet locations, exposed or concealed, in all atmospheric conditions and in hazardous locations. Steel RMC has the thickest-wall of the steel raceways. It is available with either a straight-tapped or integral coupling. The thicker walls of RMC protects the cables inside from electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can be harmful to sensitive equipment. Galvanized Rigid Steel Conduit is the heaviest weight and and thickest wall of electrical conduits, for the applications that need superior protection, strength, safety and ductility. GRC can be used indoors, outdoors, underground, concealed and exposed. It is manufactured from high-quality flat-rolled steel utilizing an Electric Resistance Welding process followed by hotdipped galvanizing. The finished product has strong and smooth welds and a tightly-adhering, uniform zinc coating. Galvanized Steel RMC may have a primary coating of zinc on the exterior and interior of the conduit; a combination of zinc and non-metallic coating are also permitted. Supplementary coatings can be applied for additional corrosion protection. Advantages Rigid Metal Conduit Long life; durable, strong, and suitable for the harshest environmental conditions. The steel is seam welded to ensure quality standards are met strictly. The inside surface of our conduit is seamless and extra smooth, making wire pulling and pushing easy and reducing friction between wall and wire. Electro-line Rigid Steel Conduit (RSC) has excellent ductility that resists flaking, cracking, peeling, impact, and damage from severe bending. Its physical and mechanical properties ensure that the conduit has an extended life cycle. Galvanized Rigid Metal Conduit Rust Protection: By providing an extra layer the rust must go through if it becomes contaminated. Rust can be easily caused by the iron in steel reacting with oxygen and water which will lead to the object deteriorating. With zinc coating, it is harder for these elements to cause such a reaction. Lower Price: The galvanization process usually costs less than other popular methods of protecting pipe. This is because the other methods are often labor intensive and Galvanization requires less manual labor. At the same time, galvanized steel pipe has a long life. can last more than 50 years in many rural areas, and more than 25 years in severely exposed urban and coastal environments. Therefore, less maintenance costs is needed. Easy Inspection: The inspection process for galvanized pipe is simple and straightforward. Galvanized coatings can be examined by eye, and their thickness can be tested with simple, non-destructive methods. Disadvantages Rigid Metal Conduit Since all connections are threaded, there is much more labor required when installing the system-this makes RMC much more expensive. The thick walls of the tubing make the conduit much heavier, which also makes installation more labor intensive and expensive. when it is cut, all cut ends must be reamed to remove any rough edges, if any rough edges are left, they are likely to tear the insulation when insulated conductors are pulled through. Galvanized Rigid Metal Conduit Internal Corrosion: Although the zinc barrier in galvanized pipes does prevent rusting for a certain amount of time, it eventually after a long time. When this happens, pipes begin to corrode from the inside out, which can eventually lead to a leak or a broken pipe Water Contamination: When galvanized pipes begin to corrode, the corrosion materials and lead from exposed metal can seep into your water supply. When this happens, those minerals begin to form a plaque that coats the inside of your pipes. Over time, that plaque begins to restrict your home’s water flow. Then water can even change its colour. Application Rigid Steel Conduit Rigid Metal Conduit is a type of steel conduit that is commonly used for electrical wiring in commercial and industrial buildings. It is the thickest and heaviest of the steel conduit options, providing the greatest protection against physical damage, moisture, and other environmental factors. Rigid Metal Conduit is designed to protect electrical cables and wires from damage and is particularly well-suited for applications where the conduit will be exposed to heavy physical abuse or where high levels of protection are required. It is often used in outdoor or industrial settings where the conduit needs to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Rigid Metal Conduit is commonly used in a variety of electrical applications, including Commercial and Industrial Buildings, Bridges and Tunnels, Outdoor Lighting and Electrical Systems, Oil and Gas Facilities, Chemical Processing Plants, Pharmaceutical Facilities, Food Processing Plants, Waste Water Treatment Plants. Galvanized Rigid Steel Conduit Both types steel pipe is designed for indoor, outdoor and underground application. Galvanized steel pipe can be widely used for pipeline, such as heating pipeline and conveying gas etc. Galvanized rigid steel conduit are special designed for electrical application, it provides good protection for electrical wire. Specifications Rigid Metal Conduit Trade Metric Threads/ Size Designator Inch 16 21 27 35 41 53 63 78 91 103 129 155 ½ ¾ 1 1¼ 1½ 2 2½ 3 3½ 4 5 6 14 14 11 ½ 11 ½ 11 ½ 11 ½ 8 8 8 8 8 8 Weight Per 100 ft. Ibs. 82 109 161 218 263 350 559 727 880 1030 1400 1840 Kg 37.2 49.4 73.0 98.9 119.3 158.8 253.6 329.8 399.2 467.2 635.0 834.6 Nominal Outside Diameter Inch mm 0.840 21.34 1.050 26.67 1.315 33.40 1.660 42.16 1.900 48.26 2.375 60.33 2.875 73.03 3.500 88.90 4.000 101.60 4.500 114.30 5.563 141.30 6.625 168.28 Nominal Inside Diameter Inch mm 0.632 16.05 0.836 21.23 1.063 27.00 1.394 35.41 1.624 41.25 2.083 52.91 2.489 63.22 3.090 78.49 3.570 90.68 4.050 102.87 5.073 128.85 6.093 154.76 Nominal Wall Thickness Inch mm 0.104 2.64 0.107 2.72 0.126 3.20 0.133 3.38 0.138 3.51 0.146 3.71 0.193 4.90 0.205 5.21 0.215 5.46 0.225 5.72 0.245 6.22 0.266 6.76 Galvanized Rigid Metal Conduit Trade Size Metric Designator ½ ¾ 1 1¼ 1½ 2 2½ 3 3½ 4 5 6 16 21 27 35 41 53 63 78 91 103 129 155 Outside Diameter Inch 0.840 1.050 1.315 1.660 1.900 2.375 2.875 3.500 4.000 4.500 5.563 6.625 mm 21.34 26.67 33.40 42.16 48.26 60.33 73.03 88.90 101.60 114.30 141.30 168.28 Rate Galvanized Rigid Metal Conduit 3 - 6 Metre 3000/ Pack 25 mm 17.25 / meter Nominal Wall Thickness Inch 0.104 0.107 0.126 0.133 0.138 0.146 0.193 0.205 0.215 0.225 0.245 0.266 mm 2.64 2.72 3.20 3.38 3.51 3.71 4.90 5.21 5.46 5.72 6.22 6.76 Approximate Weight Per 100 ft. (30.5m) Ib Kg 82 37.5 109 49.4 161 73.0 218 98.9 263 119.3 350 158.8 559 253.6 727 329.8 880 399.2 1030 467.2 1520 689.5 1785 809.7 Quantity in Master Bundle ft 2500 2000 1250 900 800 600 370 300 250 200 150 100 m 762.5 610.0 381.3 274.5 244.0 183.0 112.9 91.5 76.3 61.0 45.8 30.5 Rigid Metal Conduit 20mm /25mm/32mm/40mm/50mm 46/ meter 20 mm to 50 mm 100 / meter Alternative-I: Flexible Metal Conduit Introduction Flexible metal conduit (FMC, informally called greenfield or flex) is made by the helical coiling of a self-interlocked ribbed strip of aluminium or steel, forming a hollow tube through which wires can be pulled. Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC) is typically available in diameters between 3/8’’ and 3’’, but larger sizes can sometimes be found. It is made by coiling selfinterlocked aluminium or steel strips, which forms a hollow tube that wires can be pulled through. FMC comes in a standard wall sometimes called full wall thickness or a reduced wall thickness. Most manufacturers also produce an extra-flexible FMC for tighter bend radiuses, but this is generally not usually approved. FMC is used primarily in dry areas where it would be impractical to install EMT or other non-flexible conduit, yet where metallic strength to protect conductors is still required. The flexible tubing does not maintain any permanent bend, and can flex freely. Advantages One of the key advantages of Flexible Metal Conduit is its unparalleled flexibility, allowing it to navigate through intricate pathways with ease. Durability is a cornerstone in any electrical infrastructure, and Flexible Metal Conduit delivers on this front. Constructed from high-quality materials, it provides robust protection against physical damage, corrosion, and environmental factors. longevity ensures that your electrical system remains resilient over the long term, minimizing maintenance requirements. Electromagnetic interference can be a significant concern in modern electrical systems. FMC, with its metal construction, acts as a shield against such interference, safeguarding the integrity of signals and preventing disruptions. Efficiency in installation is a critical factor in any project, and Flexible Conduit excels in this regard. Its flexibility not only simplifies routing through complex spaces but also reduces the need for labour-intensive processes. This leads to substantial time savings during installation, making it a preferred choice for projects with tight timelines. While the initial cost of Waterproof Flexible Metal Conduit may be marginally higher than some alternatives, its long-term value becomes apparent. The durability, adaptability, and ease of installation contribute to lower maintenance costs and fewer replacements over time. Disadvantages A flexible metal conduit is designed for use where flexibility is required due to movement or vibration, or where bends and offsets make the installation process tricky. It’s not intended for use in wet locations unless conductors are specially approved for the conditions. Besides short runs, for wiring outdoor air conditioning equipment and wiring under kitchen sinks, the use of FMC in residence is pretty limited. In extremely hot conditions, the conduit material may become more pliable, potentially affecting its structural integrity. Similarly, in extremely cold temperatures, LFNC could become less flexible, making installation and routing more challenging. FNC offers some mechanical protection to enclosed cables, it may not be as robust as rigid metal conduits or other reinforced conduit types. While FNC is designed to be flexible and easy to install, its flexibility can also present challenges. In some cases, particularly complex installations or layouts with numerous bends and turns, the conduit may be harder to install effectively without kinks or bends that could affect cable integrity. FNC's flexibility can lead to limitations in terms of the size and number of cables it can effectively protect. In applications requiring larger cable bundles, the conduit's interior space may be limited, potentially leading to difficulties in installation and cable management. Application Use of flexible galvanized steel conduit is in the construction industry, where it is used to route electrical wiring and cables through walls, floors, and ceilings. Flexible galvanized steel conduit is also commonly used in outdoor environments, as it is able to withstand exposure to the elements and provide protection against moisture and dirt. Flexible galvanized steel conduit is also widely used in the automotive and transportation sectors. It is often used to route electrical wiring and cables in cars, trucks, buses, and other vehicles, as well as in aircraft and boats. It is particularly useful in these settings due to its ability to be easily routed through walls and other tight spaces, as well as its ability to withstand the wear and tear of everyday use. Specification Item Code Conduit Size FMCUL050 FMCUL075 FMCUL100 FMCUL125 FMCUL150 FMCUL200 ½ ¾ 1 1¼ 1½ 2 Acceptable External Metric designator Diameters mm Min Max 23.37 16 21.84 28.07 21 26.54 33.02 35.05 27 39.37 41.4 35 46.99 49.53 41 59.68 62.32 53 Acceptable Internal Diameters mm Min Max 15.88 16.38 20.62 21.21 25.4 26.42 31.75 33.02 38.1 40.01 50.8 52.83 Min. Bending Radius mm 76.2 101.6 127 158.75 190.5 254 Length of Conduit m/Roll 30 30 15 15 7.5 7.5 Rate Alternative-I: Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) Introduction Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) is a light-weight tubular steel raceway without threads on the ends. It is a type of wiring installation which is designed to lessen or eliminate fire hazard and electrical accident. Steel and aluminum are the two main choices used to make the pipe, and in many cases, it is also galvanized with a zinc coating so that it will remain corrosionresistant. EMT is connected together using clamp-type fittings that slide onto the tubing and then are secured with a set-screw. Some electricians are sceptical of using EMT in critical areas because the set-screws in the clamps can loosen over time. In order to prevent this, a torque wrench or driver can be used to be sure the screws are set to the correct tension as required by the manufacturer. Advantages EMT conduit is lightweight, flexible, and easy to bend EMT fittings are available everywhere and are relatively easy. Set-screw or compression-type fittings are an option. A safe solution for fire-rated enclosures because it is non-flammable EMT conduits are aesthetically more attractive than others, such as PVC, making them excellent for exposed environments where appearance matters. Disadvantages As a thin-wall conduit, EMT cannot be used where physical damage is a strong possibility. Raintight electrical metallic tubing (EMT) fittings are not currently available on the market. While possessing excellent moisture resistance, the EMT conduit is not watertight, so it cannot be submerged in water. EMT is not suitable for wet areas or where corrosive fumes and vapors exist-special corrosive -resistant tubing and gasketed clamps are required in these areas. While EMT provides a good amount of protection for the cables inside, it should not be used in hazardous areas where it is exposed to sever damage like power plants or around vehicular traffic. Application It is suitable for exposed and concealed applications Rated for indoors and outdoors Permitted to be embedded in concrete Perfect for commercial, industrial, and residential applications where not much physical damage is expected. It can be used in overhead lighting circuits It is used in retrofitting and remodelling projects for rerouting of cabling because of flexibility Specification Rate Alternative-III: Electrical Non-Metallic Tubing Introduction Electrical non-metallic tubing is a flexible corrugated plastic-type of tubing that is moistureresistant and flame-retardant. It’s so flexible it can be bent without using tools. It is usually installed with glued plastic fittings or snap-lock. Additionally, when installing metal-frame walls or standard woods, ENT can be connected within concrete block structures and covered with concrete. ENT is nicknamed the “smurfing tube” because it is blue. It is easier to install than other conduits because it can be routed around obstructions without cutting and welding the pipe. Special ENT connectors are used-these are generally snap-in connections and are not watertight. Advantages Lightweight, non-conductive and flame retardant Speedy Installation time There is use of colour Codification It is easily hand bendable and no sharp edges Available in long length coils and reels to reduce scrap Easy to work with-no special equipment needed Disadvantages It is not suitable for outdoor use, Not suitable for direct burial, It is not suitable in hazardous locations, where subject to physical damage, where ambient temperature exceeds 122°F (50°C) or where the operating voltages of the conductors is greater than 600 volts. Because it's nonconductive, it may not be used as an equipment grounding conductor. Where equipment grounding is required, a separate equipment grounding conductor must be installed within the conduit. Application Electrical Non-Metallic Tubing is a pliable raceway that is used in concealed or exposed work in dry/ damp/ wet locations; concrete slabs; in walls and ceilings; raised floors for information technology equipment; and in buildings exceeding three floors from grade. Specification Rate Alternative-IV: PVC Conduit Introduction PVC conduit has long been considered the lightest in weight compared to steel conduit materials, and usually lower in cost than other forms of conduit. Rigid PVC conduit and flexible PVC conduit are two popular options. Rigid PVC conduit, also known as PVC pipe, is a sturdy and durable option for electrical applications. It is composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a rigid plastic material known for its strength and resistance to impact and corrosion. Rigid PVC conduit provides excellent protection for electrical wires, making it ideal for installations that require added durability. Flexible PVC conduit, also known as liquid-tight conduit, is a flexible option designed for ease of installation and adaptability. It is constructed with a PVC material that contains plasticisers, allowing it to bend and conform to different shapes without compromising its structural integrity. Advantages Rigid PVC Conduit It excels in providing superior physical protection and resistance to impact, making it ideal for installations where wires may be exposed to potential damage. It exhibits excellent resistance to UV rays, moisture, and most chemicals, making it suitable for outdoor and corrosive environments. The material cost of rigid PVC conduit is lower compared to flexible PVC conduit. Additionally, the maintenance requirements for Rigid PVC Conduit type is minimal. Flexible PVC Conduit While not as rigid as its counterpart, it offers good protection against moisture, sunlight, and some level of physical impact. Its flexible nature allows for easy bending and routing, minimizing the need for additional fittings and simplifying the installation process, particularly in tight or complex spaces. the ease of installation and flexibility can potentially reduce labour costs. Additionally, the maintenance requirements for Flexible PVC Conduit type is minimal. Disadvantages Rigid PVC Conduit It requires precise measurements, cutting, and fitting of rigid sections. Bending is not typically possible without additional fittings or heat bending techniques. However, the installation process may require additional fittings and tools, which can add to the overall cost. Flexible PVC Conduit While it offers good resistance to UV rays and some chemicals, it may not provide the same level of protection against moisture or harsh environmental conditions as rigid PVC conduit. While the material cost may be slightly higher Application Rigid PVC Conduit Our Rigid PVC Conduit Pipe & Fittings can be used in exposed, concrete encased and underground environments. They are well suited for many applications, including: utilities and communication lines, industrial and residential buildings, transportation systems, water and wastewater treatment plants, marinas, mines and more. Flexible PVC Conduit Flexible conduit systems are generally used to encase wires, helping to reduce the risks of electrical hazards, such as electrocution. Liquid-tight conduits, for instance, are covered in a watertight plastic coating that in combination with the rated liquid-tight fittings, protects cables against water damage. This type of flexible conduit is best used for outdoor applications. Flexible conduits are also an excellent choice if you’re worried pets may chew through cables, providing a protective barrier. Specification Rate Galvanized Steel Plumbing Piping Introduction Galvanized steel pipes are steel pipes that have undergone a specialized coating process to prevent corrosion and increase their longevity. These pipes are typically made from carbon steel and are coated with a layer of zinc, forming a protective barrier between the steel and the surrounding environment. The zinc coating not only provides exceptional resistance against rust and corrosion but also enhances the overall strength of the pipe. They are also known as galvanizing pipes or pipes galvanized. Galvanized steel pipes have an average life expectancy of 40 to 50 years. If your supply lines are made of galvanized steel, there is constant water pressure pushing the water towards the faucets, placing pressure on the corroded pipes. If your waste lines are made of galvanized steel, there is less pressure on them, as the waste liquid is just flowing out of the home, and the lifespan may be a bit longer. Advantages Rust protection: By providing an extra layer the rust must go through if it becomes contaminated. Rust can be easily caused by the iron in steel reacting with oxygen and water which will lead to the object deteriorating. With zinc coating, it is harder for these elements to cause such a reaction. Lower price: The galvanization process usually costs less than other popular methods of protecting pipe. This is because the other methods are often labour intensive and Galvanization requires less manual labour. At the same time, galvanized steel pipe has a long life. can last more than 50 years in many rural areas, and more than 25 years in severely exposed urban and coastal environments. Therefore, less maintenance cost is needed. Easy Inspection: The inspection process for galvanized pipe is simple and straightforward. Galvanized coatings can be examined by eye, and their thickness can be tested with simple, nondestructive methods. Disadvantages Restricted Flow: Over time, galvanized iron pipes can develop build-up, restricting water flow and making it harder to use them for large hot water systems, showerheads, or other fixtures requiring high water pressure. Prone to Corrosion: Despite their zinc coating, galvanized iron pipes can still corrode over time, especially in hot water systems. This can lead to leaks, damages, and contaminated or unpleasanttasting water. Difficult to Work With: Galvanized iron pipes require a specialized tool kit to cut and fit. They are heavier and harder to work with compared to other plumbing materials, which can increase the installation time and cost. Application Galvanized steel pipes are often used in construction projects, homes, traffic projects, fire protection water systems on high-rise buildings, domestic plumbing systems, oil and lubricant pipes, and chemicals, making fence systems, gates or assembling prefabricated steel house frames, making ultrasonic pile systems in foundation structures, load-bearing scaffolding. The strength and resilience of galvanized iron pipes make them suitable for both residential and commercial plumbing installations. They are fit to withstand the rigors of heavy flow and fluctuating temperatures, ensuring reliability under diverse circumstances. These pipes are also used for fire sprinkler systems because this system demands pipe material that can handle sudden and high-pressure water flow. Galvanized steel pipes are also used as water, oil, and chemical pipes and are widely used on ships, trains, and other floating vehicles. Galvanized steel pipes are also used in gas distribution, industrial boiler systems, refineries, oilfields and offshore drilling rigs. Rate Alternative-I: Stainless Steel Plumbing Piping Introduction Stainless steel pipe can be generally defined as a heavy wall thickness tubing, with dimensions as specified by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). A stainless steel pipe system is the product of choice for carrying corrosive or sanitary fluids, slurries and gases, particularly where high pressures, high temperatures or corrosive environments are involved. Due to stainless steel’s aesthetic properties, stainless steel pipe is also used in architectural applications. Stainless steel pipe and fittings are supplied in the annealed condition to facilitate fabrication and ensure best corrosion resistance. Advantages Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel plumbing fittings and fixtures are known for corrosion resistance like any other stainless-steel product. Generally, these items are produced with chromium oxide, making them resistant to corrosion and similar issues. Heat Resistance: Aside from corrosion resistance, stainless products are also known for their resistance to heat and fire. Because of this, stainless steel pipes and fixtures are also appropriate hot water conduits. Even high temperatures won't dent or melt the fittings as the chromium content protects the stainless steel from being damaged. Ease Of Cleaning: Because stainless steel products are durable and non-porous, they're easier to clean than galvanized iron and traditional steel. Disadvantages Initially Expensive: Stainless steel products are generally expensive because they've undergone melting, casting, and hardening processes. In addition, they typically require special elements that make them easy to maintain, durable, and corrosion-resistant. Because of this, stainless steel plumbing fittings and fixtures are more expensive than traditional choices. May Require Professional Installation: While many fittings and fixtures can be installed instantly, some stainless-steel products may require a professional. Applications Sanitary Pipes: Sanitary pipes are made of stainless steel and are used in high sanitation applications such as sensitive applications. This pipe type is given the greatest priority in the industry for efficient fluid flow. The pipe has the best corrosion resistance and does not rust due to its simplicity of maintenance. Various tolerance limits are determined based on the application. Mechanical Pipes: Hallow components, bearing parts, and cylinder parts are commonly utilized in mechanical pipe applications. The mechanics may be readily regulated to a broad range of sectional shapes such as rectangular, square, and other shapes that add up to conventional or traditional shapes. They have excellent machinability and are used in applications like automotive or agricultural machinery. Polished Pipes: The polished stainless-steel pipes are utilized in the home facility depending on the specifications. The polished pipes aid in the reduction of wear and tear on working components. It also aids in the reduction of adhesion and contamination of various equipment surfaces. The electropolished surface has a wide range of uses. Stainless steel polished pipes do not require any extra coating. Polished pipes have an essential and critical role in aesthetic and architectural applications. Rate Alternative-II: ABS Plumbing Piping Introduction ABS is an abbreviation for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, a plastic used in the manufacture of some pipes and fittings by extrusion and injection moulding respectively. ABS has different properties to PVC, most specifically in that it is very ductile and so does not split or shatter easily and retains these properties at temperatures well below freezing. ABS plastic pipe is the standard material for many types of DWV systems. Its properties make it ideal for residential homes, manufactured housing, commercial and industrial buildings, and recreational vehicles. Advantages Abrasion Resistance: ABS offer outstanding resistance to abrasion and erosion from aggressive slurries which can rapidly damage steel or other traditional pipe materials. Weather Resistance: ABS is one of the most weather resistant polymers available today. Successful field tests have been completed on piping systems having been exposed to weathering for over 30 years. Light Weight: ABS is one-sixth the weight of steel systems, making easy to handle and install. This reduces the cost of installation, handling and transport. Chemical Resistance: ABS is unaffected by both internal and external attack by a wide range of acids, alkalis, ground water salts and other environmental factors. Non-Toxic: The ABS formulation contains no harmful metallic stabilizers and it has been widely used for many years in piping systems for drinking water, medical preparations, food products and potable water. Exceptionally Smooth Bore: ABS do not suffer from internal corrosion and provides a smooth bore for the life of the piping systems. The smooth bore does not support formation of scale and slime as do cement based lined products. Cold Solvent Weld Joining: The ABS size range also utilizes the proven traditional method of joining ABS pipes, cold solvent cement welding, which provides a homogenous bond between pipes and fittings. Temperature Range: A great advantage of ABS over other plastic systems is its ability to perform over a wide temperature range from -30°C to +60°C. This makes ABS very versatile and capable of handling a wide variety of fluids from refrigerants to moderately hot corrosive liquids. Disadvantages The material itself has a low melting point which renders it useless for high-temperature applications. It’s also flammable, which means it’s not suitable for indoor use. An ABS waste pipe doesn’t stand up so well to UV exposure and can warp with exposure to direct sunlight. Applications Pipes & Fittings are widely used in a variety of applications such as: HVAC, chilled water and condenser Water reticulation Domestic plumbing Water treatment plants Waste water treatment and recycling plants Power generation plants Industrial plants such as electronics, food processing, chemical, paper mills, palm oils and rubber mills. Rate Alternative-III: PVC Plumbing Piping Introduction PVC stands for polyvinyl chloride, and it’s become a common replacement for metal piping. PVC’s strength, durability, easy installation, and low cost have made it one of the most widely used plastics in the world. PVC is a thermoplastic material that is molded into different shapes to create pipes, fittings, valves and other liquid handling supplies. It's the white plastic pipe commonly used for plumbing and drainage. Advantages Resistant to Corrosion: Most older homes use galvanized steel, clay, or cast-iron pipes for plumbing. These materials are highly prone to corrosion. Corroded pipes can easily crack or break, leading to major leaks in your home’s plumbing and drain system. None of these issues are associated with PVC pipes. Easy to Install: Plumbers everywhere enjoy working with PVC pipes thanks to their ease of installation. Unlike steel pipes, PVC pipes are easier to cut to install. PVC pipe installation takes less time than steel pipes, giving you less time without working plumbing pipes. Smooth Surface: If you ever touch a PVC pipe, you will notice its smoothness. PVC plastic pipe’s smooth surface provides less friction, producing efficient water flow for your home. Less friction in PVC pipes is also why they are used indoors because it allows for silent water flow. Lightweight: Steel pipes are heavy and require more workforce and machinery to carry. PVC plastic pipes are lightweight, which makes them easier to transport and move from one job site to another. Heavier equipment requires more labour, and more labour usually equals higher costs. Durable and Strong: PVC pipes are versatile because they can be used for indoor and underground plumbing. According to our technicians, indoor PVC pipes can last around 55 to 80 years, and underground PVC pipes can last 100 years before being replaced. Resistant to Low Impact: Underground pipes must be sturdy for water transportation support. PVC plastic pipes for plumbing can handle water pressure without weakening. If it weren’t impact resistant, these pipes would have had a high chance of cracking or breaking. Thanks to PVC’s density, these pipes can withstand high impact. These plastic pipes are resilient enough to withstand small impacts without sustaining any damage. Affordable: Homeowners and professional plumbing companies select PVC pipes because of their low cost. PVC pipes are an inexpensive material. Pipe replacement jobs for sewage line repair should cost significantly less PVC than steel pipes, given you don’t run into any major issues along the way. Pipe material is just one of the many things involved with pipe replacement cost, which you can read more about here. Easy to Mould: Manufacturers can mould PVC plastic into any shape to fit every home. Because of its easy moulding capabilities, PVC plastic is used to make pipes and pipe connections like valves, bends, elbows, and clips. Eco-Friendly: Everyone does their part to be more earth-conscious. PVC plastic production produces fewer carbon emissions than galvanized steel and iron pipes. With PVC plastic, you will feel more eco-friendly thanks to fewer carbon emissions being released into the atmosphere. Disadvantages Weak to High Heat: While it may not stand up to heat as well as steel, PVC pipes can still withstand temperatures up to 140 degrees Fahrenheit. PVC pipes are vulnerable to fire since it causes the plastic to warp or melt. Could Freeze: PVC pipes may freeze during freezing temperatures. A frozen PVC pipe doesn’t always break, but any wet material inside can freeze and cause a buildup. Cost: In general, PVC is more expensive to manufacture. The cost difference is not huge, so, for smaller buildings, the higher price can be negligible. For larger buildings, though, costs can add up. While the front-end costs for PVC can be higher, PVC potentially can save money over time once maintenance and energy efficiency are factored in. Application Water applications: VC piping systems are used in several areas for the transport of water - from delivery of drinking water over the removal of sewage or waste products to drainage of water from the ground or roof. Drinking water: Pipes and fittings for the distribution of water under pressure. The main application is the distribution of drinking water. The diameters are of medium size (generally between 75 mm and 250 mm). Soil and waste: Pipes and fittings for the evacuation of waste water without pressure inside the buildings (generally vertical). These are usually of medium diameters (< 160 mm). They can be made of compact PVC or have structured walls (foam core). Sewage and underground drainage: Pipes and fittings for the collection and evacuation of waste water without pressure and intended to be buried in the ground (horizontally). These are usually of large diameter (160 mm and up to 630 mm). They can be made of compact PVC or have structured walls (foam core or twin wall with a corrugated layer). Rate Alternative-IV: PEX Plumbing Piping Introduction PVC stands for polyvinyl chloride, and it’s become a common replacement for metal piping. PVC’s strength, durability, easy installation, and low cost have made it one of the most widely used plastics in the world. PVC is a thermoplastic material that is molded into different shapes to create pipes, fittings, valves and other liquid handling supplies. It's the white plastic pipe commonly used for plumbing and drainage. Two main types of PVC pipe exist: schedule 40 and schedule 80. The difference lies in the thickness of the pipe wall. Schedule 40 PVC pipes have thinner walls than their schedule 80 counterparts. If you come across a different schedule number than the typical 40 or 80, know that the higher the number, the thicker the pipe wall. Thicker walls come in handy for different pressure and temperature applications Advantages PEX Piping is Cost-Effective: This plastic pipe is easier to install and is one of the lightest options when compared to copper pipes. Its low installation cost means you will pay less for PEX and have high-quality piping in your home. Plastic pipes are also cheaper than copper pipes to produce, so those savings are passed down to the homeowner. Ease of Installation: Thanks to its physical and usage flexibility, plumbers can use one single-length pipe to connect water lines in hard-to-reach places. PEX connections are easier to install since the fittings require less specialized tools to connect. PEX pipes are easy to install because of their unique color-coding system not available on other pipes. Blue pipes are for cold water, red for hot, and white/gray colored pipes are for both. PEX Pipes Reduce Noise: You may hear water flowing through pipes because of loose pipes or high water pressure, but that's not the case with PEX plastic. These pipes provide silent water flow, so you don't hear running water while trying to enjoy music or watch a movie in your living room. PEX Plastic is Durable: PEX pipes will not corrode over time like metal pipes. These pipes have a lifespan of 30 years with proper water treatment and a yearly check-up from a professional plumber. PEX piping is also resistant to freeze-cracking, so it can handle temperatures of -40 degrees Fahrenheit without breaking, thanks to its ability to expand and contract. PEX Pipes Are Energy Efficient: PEX plastic is an excellent thermal insulator for hot water. With PEX piping, water heater systems use less energy. This ensures that hot water from your home's water heater arrives at your faucets without losing a lot of heat. With thick PEX piping, hot water will lose only one or two degrees of heat which aren’t enough to call it cold water. Disadvantages PEX Plastic Is Weak to Fire: The chances of a fire inside your home are very low, but it still remains a nightmare scenario for any homeowner because you can lose everything in your home. But if there were a fire, PEX plastic pipes would melt, requiring new replacement pipes. Ultra Violet UV Light Sensitivity: PEX pipes don't do well for outside plumbing, even if underground, because UV light can penetrate through the dirt and affect PEX pipes. If left outside, PEX pipes will deteriorate and become useless. These plastic pipes should not be stored exposed to the sun. PEX Pipes Are Not Recyclable: If you are trying to implement an eco-conscious lifestyle, you will not want PEX pipes in your home. PEX plastic can't be broken down like other plastics, like PVC plastic, for reuse. Discarded PEX can end up in landfills instead of being processed for reuse. This plastic can last 30 years, so it isn’t like it’s disposed of every couple of years. Susceptible to Rodents: If your home has a rodent problem, it can affect your PEX pipes. On rare occasions, rodents have been shown to chew through PEX plastic. PEX pipes are very thick, but they are still susceptible to rodent damage that can cause pipes to crack or break. Possible Leaching: Although uncommon, some homeowners and plumbing companies have reported a few PEX pipes leaching harmful contaminants like BPA (Bisphenol A) into the water supply. BPA chemicals can cause neurological, reproductive, and immunity issues, according to scientific study. Application Radiant Heating and Cooling Systems: Warm water or “hydronic” radiant heating systems utilize PEX pipes embedded within floors, walls or ceilings. Warm water is circulated through the pipe, which conducts heat to the panel, usually the floor. The warm floor then radiates heat to the space above it, warming the objects and people in the room, while also allowing warm air to gently rise from the floor. The resulting comfort is unmatched with other forms of heat delivery. The warm water may be produced by a variety of heat sources such as high efficiency boilers, geothermal heat pumps and thermal solar collection systems. Benefits of radiant heating include increased efficiency, more uniform heat distribution in the lower portion of rooms, and easier zoning. Radiant heating systems are commonly found in all types of construction and applications, from houses to schools to hotels. Municipal Water Service Pipe: In addition to supplying water within a home or building, PEX pipe is also used to distribute water to buildings and entire communities through municipal water service pipes in sizes up to 3 in. Unlike buried metal pipes, PEX water service pipes will not corrode or suffer mineral build-up. Because PEX pipe has higher resistance to slow crack growth than other piping materials, it ensures high-impact resistance with normal backfill. PEX pipe is more flexible and resistant to freeze damage, lessening the chance of splitting or cracking. It provides excellent resistance to chlorine and chloramines, reducing risk of damage due to disinfectants. It connects to standard compression joint valves, and fittings, so it’s easy and convenient to install. Finally, PEX water service pipes can save up to half the cost of copper—a significant savings for budget-constrained waterworks professionals. Snow and Ice Melting Systems: PEX pipes are often used in hydronic systems designed to augment the removal of snow and ice by circulating a heat transfer fluid through pipes installed within outdoor surfaces. The durability and flexibility of PEX pipes designed for these applications allows these systems to provide years of reliable service, with no worries about pipe corrosion or failing electrical connections. Common applications of hydronic SIM systems include driveways, steps, sidewalks, hospital entrances, parking garage ramps, wheelchair ramps, car washes, hot tub/ pool surrounds, and even helicopter landing pads. Benefits include safety, access, reduced maintenance costs, no snow removal costs, reduced liability, and obvious convenience. Fire Suppression: UL-approved PEX piping and fitting systems listed to UL Standards can be used to supply water to fire suppression sprinklers for residential applications. While many sprinkler systems are largely independent from the water distribution system, for some building types they can be combined with a building’s cold-water plumbing system. This has the potential to reduce installation costs and the total amount of installed pipe and fittings. Sprinklers, PEX piping, and fittings must comply with National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) requirements for residential fire sprinkler systems. Already, several PEX systems meet the requirements of NFPA 13D for domestic applications. Local codes must be consulted when implementing any fire suppression system to ensure that PEX and/or combined systems are permitted for each building type. Rate Standard Steel Rebar Reinforcement Introduction Steel bars and wires that are used to strengthen and support concrete in buildings are called steel reinforcement. Steel bars and wires are put inside concrete structures to add to the load bearing capacity of the structure. To understand steel reinforcement, you need to also learn about concrete reinforcement. This term explains the concrete structures erected with the help of steel reinforcement. Simply put, a concrete structure with steel reinforcement (steel bars and wires) is called reinforced concrete and the process is called concrete reinforcement. Rebars Rebars or reinforcing bars are steel bars specifically built for the construction industry for concrete support. The surface of a rebar is often deformed to increase the bonding with concrete. There are different types of rebar: Carbon steel bars: Carbon steel is used for purposes where ultimate tensile strength is taken into consideration. However, ductility and corrosion resistance are very low. Mild steel bars: Mild steel bars have round sections whose diameter varies from 6 mm to 50 mm. They are characterised by the plain surface of the bar. These rebars are easy to cut and bend. The grade of this rebar is determined by the yield stress, which is denoted on the bar, i.e.; “FE250” where FE stands for iron and 250 means yield stress. High Yield Strength Deformed (HYSD) bars: Deformed bars are distinguished by a ribbed rough surface on the bar. This is done to increase the bar bonding between reinforcement and concrete and to maintain friction between them. HYSD bars are divided into: TMT bar: Known to be the best among steel bars, TMT bars showcase features including qualities like excellent ductility, high corrosion resistance, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, better elongation and better weldability. Cold Twisted Bars – CTD: Cold Twisted Bars are also called TOR steel in India. Once hot steel is obtained from the furnace it is cooled at ambient temperature and then stretched and twisted to increase yield strength. Epoxy coated rebar: Epoxy powder is applied on hot steel at a pre-set temperature using an electrostatic spray to obtain epoxy coated rebar. These are extremely corrosion resistant and are largely used in infrastructures, buildings, bridges, roadways, etc. Galvanised rebar: When a rebar is coated with Zinc it is then known as galvanised rebars. Featuring excellent corrosion resistance, they perform better than epoxy coated rebars. Stainless steel rebar: Designed similar to carbon steel, stainless steel rebars have a long lifespan. These are highly corrosion resistant, and less maintenance is required compared to other kinds of steel. Grades of steel reinforcement According to IS 1786:2008 the grades of high strength deformed bars and wires for concrete reinforcement used in construction is as follows: Fe 415, Fe 415D, Fe 415S Fe 500, Fe 500D, Fe 500S Fe 550, Fe 550D Fe 600 Advantages Modulus of Elasticity: Steel has high modulus of Elasticity i.e. 200GPa (200 x 10⁹ N/m²). This helps the steel to stretch in tension(upto 200GPa) without breaking and regain its shape on removal of load. Ductility of Steel: Ductility of steel is high. i.e. Steel rebar will behave ductile under higher loads. Ductility is the ability of material to allow plastic deformations (i.e. permanent change in its dimensions) under application of load before breaking. Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: Steel and concrete has almost same coefficient of thermal expansion (change in dimension due to temperatures). Due to this both (concrete and steel) will experience same length changes in high temperatures. Resistance: Steel is resistant to rough conditions during transport, storage, bundling and placing on construction site. If minor damage happens, it does not significantly affect its performance. Strength: It is strong enough to withstand high impact load. Readily Available: Structural Steel industry has enough production capacity to meet the demands of construction industry and is available at ease for any house construction. Ready Build: These days ready build steel is also available. Ready build steel eliminate the time of cutting and bending. This saves lots of construction time as well as minimizes the wastage of steel in bending and cutting. Steel can be recycled easily. Disadvantages High Cost: Steel is expensive and considerably increases the cost of structure. High Temperatures: Steel show tendency to melt in extremely high temperatures. This is also one of the reasons; steel is tied and not welded. Reaction: Too little concrete cover allows the water to penetrate and react with steel rebars causing concrete to crack. Occasionally concrete aggregates react with steel causing concrete to spall. Rust: Steel exposed to weather rusts and reduces the strength of reinforced concrete. When rusts start building up around the steel rebars, it causes severe internal pressure on the surrounding concrete, leading to cracks in concrete. Weight: It is not a light weight material. Application It is used in bridges, buildings, skyscrapers, homes, warehouses, and foundations to increase the strength of a concrete structure. It is used in bridges, buildings, skyscrapers, homes, warehouses, and foundations to increase the strength of a concrete structure. Rebar is used in concrete to provide additional strength, as concrete is weak in tension, while steel is strong in both tension and compression. Steel and concrete have similar coefficients of thermal expansion, so a concrete structural member reinforced with steel will experience minimal stress as the temperature changes. Rate Alternative-I: Engineered Bamboo Reinforcement Introduction Bamboo is a naturally sustainable material that has been used in construction for a very long time. However, the lack of construction codes and design procedures for bamboo-reinforced concrete (BRC) structures is preventing structural engineers and construction firms from using bamboo in construction. Bamboo is frequently referred as a highly renewable and high-strength alternative material to timber and, occasionally as a ‘strong-as-steel’ reinforcement for concrete. The high rate of biomass production and renewability of sustainably managed bamboo plantations are undeniably key benefits of bamboo. Bamboo is one of the potential materials as a substitute for steel reinforcement. Bamboo is very cheap, easily available, and available in ample quantity. Bamboo is cultivated in farm by farmers. Bamboo is having very good mechanical properties to use it as reinforcing material in concrete. From bamboo small thin strips were prepared. These strips were tied together in two directions to form a bamboostrip-mat. All these strips while making bamboo-strip-mat was tied together with small thin Mild Steel wire to ensure their position in mat formation. Testing is done using bamboo-stripmat as reinforcement in cement concrete prismatic section at bottom side. Concrete beams thus produced using bamboo as a reinforcement. Bamboo strips were prepared from old age bamboo. Advantages Sustainability: Bamboo is a rapidly renewable resource that grows much faster than trees used for wood or steel production. It can be harvested in a sustainable manner without causing significant environmental damage. Using bamboo as reinforcement reduces the reliance on finite resources like steel and contributes to environmental conservation. Lightweight: Bamboo is significantly lighter than steel, making it easier to transport, handle, and install on construction sites. This can lead to lower transportation costs and reduced labor requirements during construction. High Tensile Strength: Engineered bamboo has a high tensile strength, comparable to or even higher than that of steel. This makes it an effective reinforcement material for concrete structures, providing adequate strength and durability. Corrosion Resistance: Unlike steel, bamboo does not corrode or rust when exposed to moisture or harsh environmental conditions. This increases the longevity of reinforced concrete structures and reduces the need for maintenance and repair. Thermal Insulation: Bamboo has natural thermal insulation properties, which can help improve the energy efficiency of buildings. Reinforced concrete structures incorporating bamboo may exhibit better thermal performance compared to those reinforced with steel. Flexibility and Ductility: Bamboo is inherently flexible and ductile, allowing it to absorb energy and deform under stress without catastrophic failure. This property is beneficial in earthquake-prone areas, as bamboo-reinforced structures can exhibit enhanced resilience to seismic forces. Aesthetics: Bamboo has a natural and aesthetic appeal that can enhance the architectural character of buildings. Bamboo-reinforced elements such as beams, columns, and panels can add warmth and visual interest to construction projects. Disadvantages Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality and performance of engineered bamboo products can be difficult due to variations in bamboo species, growth conditions, and manufacturing processes. Quality control measures are essential to maintain the integrity and reliability of bamboo reinforcements. Durability Concerns: While bamboo is naturally resistant to pests and decay, its long-term durability in outdoor or high-moisture environments may be a concern. Proper treatment and protection against environmental factors are necessary to prevent degradation over time. Fire Resistance: Bamboo is inherently less fire-resistant than steel. In fire-prone areas, special precautions and fire-resistant coatings may be required to mitigate the risk of structural failure in bamboo-reinforced buildings. Cost: The initial cost of engineered bamboo reinforcements may be higher than that of steel reinforcements, particularly in regions where bamboo materials are not readily available. However, long-term savings in terms of reduced maintenance and environmental benefits may offset this initial investment. Code Compliance: Building codes and standards may not always explicitly address the use of bamboo reinforcements, leading to uncertainty or reluctance among designers and builders. Advocacy for the inclusion of bamboo in building codes and standards is necessary to promote its widespread adoption in construction. Application Engineered bamboo can be used as an alternative to traditional steel reinforcements in concrete structures. Bamboo-reinforced concrete offers comparable strength and durability while being significantly lighter and more sustainable. It can be employed in various structural elements such as beams, columns, and slabs. Small cane or bamboo splints may be an alternative for crack control reinforcement for slabs on grade (slabs cast on the ground) provided at least 3% bamboo is used. Such slabs are designed to remain uncracked and/or are provided with control joints to facilitate controlled cracking. Slabs on grade are known to absorb moisture from the ground; thus, this must be mitigated in order to avoid the potential for rot of the embedded bamboo. Light cement bamboo frame (LCBF) panels, known colloquially as bahareque construction, are well established. LCBF construction is a modern technique utilising composite shear panels constituted of a wall matrix of bamboo or metal lath nailed onto a bamboo framing system, plastered with cement or lime mortar render. This method works well because the stresses in the wall matrix are very low. Provided the bamboo is treated against insect attack and kept dry through good design, the lifespan of the system is expected to exceed 30 years. Rate Alternative-II: GFRP Rebar Introduction The traditional strengthened concrete members such as beams are composed of concrete included Portland cement and steel rebars reinforcement. The function of concrete in these beams is the resistance to compressive loads. The tensile and shear loads will be resisted by steel rebars embedded in the concrete. Such structure is efficient where the concrete inseparable resistance to compressive loads, while the steel enhances tensile and partially shear strengths. However, the problem of corrosion associated with the steel rebars reduced its live time and the solutions such as the coating of the steel rebars are costly. Recent technologies have resulted in alternative reinforcing materials such as GFRP materials commercially available in the form of bars or sheets that can be bonded in concrete members to fulfil several desired properties. The most important is that the corrosion resistance feature of the polymer and the elongated strain to failure that give enough time to alert before failure takes place. The considerably new FRP rebar technology is based on pultruded composite products, which are made from longitudinally bundled fibres — along the bar axis — embedded in a resin matrix. The fibres are the main load carrying component and the resin binds the fibres together, and therefore, transfers the load between individual fibres while protecting them from chemical and physical attacks. the most widely used fibre type for FRP rods in the United States is glass based for the production of Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) rebars. E- and E-CR (Electrical/Chemical Resistant) glass fibres are the most commonly used ones because they possess high tensile strength, offer high chemical resistance, and feature low production cost. Advantages Lightweight: GRP is a lightweight material. It can be up to 75% lighter than steel and up to 30% lighter than aluminium. High strength-to-weight ratio: Despite its low weight, GRP has a high strength-to-weight ratio, which means it can support heavy loads while remaining lightweight. Corrosion-resistant: GRP is highly resistant to corrosion, making it a durable and long-lasting material that can withstand exposure to harsh environments like saltwater, chemicals, and UV radiation. Design flexibility: GRP can be moulded into complex shapes and can be customized to fit specific design requirements. This makes it a versatile material that can be used for a wide range of applications. Low maintenance: GRP requires very little maintenance and is easy to clean. It does not rust, rot, or corrode, and it is resistant to fading, chalking, and cracking. Fire-resistant: GRP is a fire-resistant material that can withstand high temperatures without melting or emitting toxic fumes. This makes it a safe material for use in applications where fire is a concern. Cost-effective: While the initial cost of GRP may be higher than traditional materials, its low maintenance requirements and long lifespan make it a cost-effective material in the long run. Versatile: GRP can be moulded into complex shapes, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and structures. It can also be customized to meet specific design requirements. Disadvantages Brittleness: GRP can be brittle and prone to cracking or breaking under sudden impact. This can be a concern in applications where the material is exposed to high stress or impact loads. Difficult to repair: GRP can be difficult to repair, especially if damage is in a critical area or if the damage is extensive. Repairs may require specialized knowledge and equipment, which can be costly. Limited temperature range: GRP has a limited temperature range in which it can be used, typically between -40°C and 100°C. This can be a concern in applications where the material is exposed to extreme temperatures. Environmental impact: The manufacturing process of GRP involves the use of chemicals, some of which can be harmful to the environment. Additionally, GRP products may not be recyclable, which can lead to waste management issues. Design limitations: Although GRP can be moulded into complex shapes, there may be limitations in terms of size and design. The manufacturing process may also be limited by the size of the mould and the ability to remove the finished product from the mould. Application The use of GFRP in civil engineering enables engineers to achieve better functionality, safety, and economy of construction. Following are some of the new construction applications of GFRP bars: Highway applications (bridges, overpasses, etc.) Marine applications (seawalls, retaining walls, etc.) Mining and tunnelling Transport infrastructure (bus stops, runways, etc.) Rate Alternative-IV: Helix Micro Rebar Reinforcement Introduction Helix Micro-Rebar is an alternative steel product for reinforcing concrete. Helix Micro-Rebar consists of short, twisted, steel wires of polygonal cross-section that are added to concrete during mixing stage. The shape and the twist maximise both the frictional and mechanical bonds between the rebar and a cement-based matrix. The twist drives the failure mechanism from frictional pull-out to a torsional (or untwisting) mode. Helix Micro-Rebar is made from a minimum 50% recycled steel. Concrete construction with this reinforcement product consumes less steel than with traditional steel bar and mesh. Helix Micro-Rebar is applied to better meet seismic conditions and heavy loads. Cracks in the concrete tend to be minimal and small and should not develop into large deep cracks. And because Helix is spread as a fine matrix throughout the concrete mix, cracks in concrete do not expose major steel reinforcements. Helix Micro-Rebar is electroplated with zinc and has been tested to resist corrosion three times longer than standard bar and mesh reinforcement that has no coating. Advantages Helix Micro-Rebar offers four times the tensile strength of rebar as well as increased durability, ductility, and shear strength. Replacing conventional concrete reinforcements with Helix Micro-Rebar results in substantial savings in project time. Helix is mixed into concrete at the job site or ready-mix plant in a matter of minutes, whereas rebar and mesh reinforcements take hours to assemble. Helix eliminates most of the labour and equipment related to measuring, cutting, placing, and tying rebar, making it a more cost-effective option. Concrete can be poured directly pumping and finished using conventional finishing techniques. It eliminates the complexity and difficulty of bending bar and mesh to suit curved concrete constructions. Almost eliminates site waste - Helix is incorporated through your concrete mix so there is no oversupply of bar or mesh. Improved worker safety - reduces tripping hazards and cuts from exposed reinforcing steel. Improved crack resistance - cracks are reduced and, when they do appear, they are fine and short. Cost savings – approx. 20%. Disadvantages Cost: Helix Micro Rebar can be more expensive upfront compared to traditional reinforcement materials like steel rebar. However, the overall cost-effectiveness may vary depending on factors such as project size, labour costs, and the specific application. Compatibility: Helix Micro Rebar may not be compatible with all types of concrete mixes or construction methods. Ensuring compatibility with other construction materials and techniques is crucial to avoid potential issues during the construction process. Knowledge and Training: Working with Helix Micro Rebar may require specialized knowledge and training for construction workers. Proper installation techniques are essential to maximize its effectiveness and ensure structural integrity. Application Helix Micro Rebar reinforcement finds applications across various construction sectors due to its versatility and superior performance. It's commonly used in concrete structures such as foundations, slabs, walls, and columns to enhance durability, crack resistance, and structural integrity. In infrastructure projects like bridges, tunnels, and roads, Helix Micro Rebar provides added strength and resilience to withstand heavy loads and environmental stresses. Moreover, it's employed in industrial facilities, parking structures, and residential buildings to mitigate issues like shrinkage cracking and improve overall durability. With its ease of installation and ability to reduce labour costs, Helix Micro Rebar offers a compelling solution for enhancing the longevity and reliability of concrete structures in diverse construction applications. Rate Gypsum Plastering Introduction Gypsum plaster is a white cementing substance that is created by partially or completely drying the mineral gypsum, frequently with the addition of specialised retarders or hardeners. When gypsum and water are combined chemically after being applied in a flexible condition, the gypsum settles and contracts. Gypsum plaster is made from gypsum and is also known as the plaster of Paris (POP). Dry gypsum granules, water, and occasionally a tiny quantity of accelerator are the main ingredients of gypsum plaster, which can be made anhydrous. Gypsum plaster uses retarders, such as organic acids, dissolved substances, basic phosphates, and peptides, to speed up the setting process. It comes in powder form and, when combined with water, creates a ready-to-use paste that can be spread to the surfaces of the wall and roof right away. Gypsum plaster typically has a thickness of 11 millimetres for walls and 8 millimetres for ceilings. The ceiling-sloped roofs and mouldings are also made out of gypsum plaster. To create a consistent slurry, pure water is combined with gypsum plaster at the job site at the recommended ratio. Gypsum plastering is the practice of applying gypsum plaster mud to walls and roofs at the correct thickness using professional applicators. Based on the amount of thermal energy they get during the production process; gypsum cement can be classified. The two varieties of gypsum plaster are as follows: 1. Gypsum anhydrite plaster that has been heated to 170°C. 2. Gypsum is heated to a temperature above 170°C to create hemihydrate, which is then combined with particular additives like perlite and vermiculite to improve working and setting qualities to create plaster. Advantages Low Thermal Conductivity: Gypsum plaster offers low thermal conductivity, making it great for saving heating and cooling costs in a building. Readily Available: Gypsum is the principal component of gypsum plaster. It is a readily available raw material, whereas natural sand, the vital ingredient for cement plaster, is hard to find and even banned in several countries. No Curing Time: Gypsum plaster is ready-made and doesn’t require additional curing time. It also helps save resources such as the water needed for the process. Flexible: You can directly apply gypsum over the brick/wood base without it needing separate finishing. Also, gypsum plaster is easy to use and level, making it more flexible than the traditional plaster variants. Easy To Apply: A traditional cement plaster takes around 21 days to dry and settle. A gypsum plaster takes only three days for drying and setting. It is beneficial, especially when you are looking for multi-story constructions. Efficient Setting Time: Plaster requires drying time before you can initiate the painting job on it. Gypsum plaster takes only around 30 minutes to set, much faster than the traditional cement finishing. It means that the painting job can start as soon as three to four days of gypsum application. Durable: Gypsum plasters are very lightweight, meaning that their application barely adds weight to the overall construction. It ensures that the frames are better equipped to handle natural calamities and are more likely to hold their shape in the long run. Fire resistant: Gypsum plaster is highly fire-resistant and can hold fire for up to three hours. No shrinkage: Cement is known to react when it comes in contact with water. So its plaster ends up getting cracks once it dries. Gypsum plaster is more effective and suffers from few to no shrinkage cracks, making it a better alternative to mortar plaster. Great finish: Gypsum plaster walls are perfectly lined and levelled, unlike mortar plaster which requires a lot of labour to achieve smoothness. It helps create visually appealing living rooms with ease. Disadvantages It doesn’t perform well against water: We cannot use gypsum plaster for outer walls. These retain dampness and are not the most suitable for areas with walls that come in regular contact with water, such as bathrooms and toilets. Even though there are modified water-resistant, they do not perform as well as cement plaster. Costly: If you compare cement plaster to gypsum plaster, the latter is costlier for the same thickness level in most conditions. But mortar plaster requires natural sand. So, if it is difficult to procure, gypsum plaster may be an economical option for such areas. Low shelf life: Gypsum, as a material, comes with a limited shelf life. You can keep gypsum plaster for up to 4 months, but if you take extra care, its life goes up to around ten months. Application Rate Alternative-I: Lime Plastering Introduction Lime plaster is an integral part of the chemical substances used in modern applications. It is also called hot lime, fat lime, lime putty, etc. It is made up of lime, water, and sand. When talking about lime plaster, it is for the non-hydraulic version. It is different from the traditional cement plaster. It is an innovative form of plaster that is made up of calcium hydroxide, sand, and water. It is one of the best plasters available and offers multiple benefits like condensation, breathability, flexibility, and ease of working. The popularity of lime plaster is high because it protects the building and offers support to the structural integrity of the building. Lime plastering is prepared by heating the limestone or calcium carbonate at a temperature above 850 degrees Celsius. The quick lime or calcium oxide thus produced is converted to the slaked lime or calcium hydroxide by adding water. Hence, lime plaster is sold as a white powder or wet putty. Water is added to this powder before using it. Further, when it reacts with atmospheric carbon dioxide, calcium hydroxide turns back to calcium carbonate. Advantages It has a high pH value and is perfect for eliminating the growth of fungi and bacteria. Hence, there is no possibility of mould growth in the lime plaster. It is least affected by water. Hence, it is beneficial over gypsum plaster, earthen plaster, or drywall plaster. It is absorbent plaster that allows quick diffusion and moisture evaporation. It is one of the most durable forms of plaster compared to other counterparts like clay plaster, gypsum, etc. Hence, lime plaster is widely used as the lime render on the exterior of buildings. There is no requirement for the expansion joints in lime plaster. It is less brittle than cement plaster and is used widely in modern buildings. Disadvantages The non-hydraulic form of lime plaster sets slowly. It is highly acidic white when in wet form and hence needs utmost care for the elimination of patches. The lime plaster may cause chemical burns as it can have a pH as high as 12. Hence, the plasterers use mild acids or vinegar or lemon juice to neutralise chemical burns. It requires sufficient moisture to set and needs to be protected from drying for a couple of days. There is an increasing shortage of plasterers capable of doing lime plaster activities. Application This plaster is used for the plain side of a brick wall, 13 mm thick plaster is provided and for the rough side of a brick wall, 16 mm thick plaster is suggested. Also, for the stone masonry wall, 19 mm thick plaster is provided due to surface unevenness. Lime plaster can be applied in one, two, or even three coats on the surface of the finished wall between the screeds. For a coat plaster, mortar is applied on a uniform surface that is slightly higher than the required one. This surface is then crushed within the thin strips of bamboo so that the joints can be filled and conveyed to the required surface. Applying a solution of lime putty to the surface eliminates plastering work, making it smooth with a metal float. Rate Alternative-II: Cement Plastering Introduction The materials in the plastering cement mortar are cement and sand in a specified proportion. The sand is of good quality and must be free from dust and other organic materials. In the plastering cement mortar, the cement shall be fresh Portland cement according to the I.S. code. During the preparation of mortar, the potable type of water shall be used. During the preparation of mortar, the cement and sand are thoroughly mixed without water till uniform colour is obtained. After the uniform colour is obtained a required amount of potable water is added into the dray mixed mortar and mixed the mortar thoroughly until a uniform consistency is obtained. The prepared mortar shall be used within the initial setting time of cement and this initial setting time for Ordinary Portland Cement is a minimum of 30 minutes. The brickwork surface which is going for the plastering work must be cleaned, brushed, and keep the surface wet for two days before the plastering. In the case of cement concrete surface, the face is lightly roughened, cleaned, and the surface is wet for two days before the plastering. In the process of plastering, first ceiling plastering must be completed before the starting of wall plastering. The thickness of plastering is usually 12mm applied in two or three coats. The plater thickness must be uniform throughout the whole surface and it is ensured by using a 1-meter strip which is applied on the laid mortar. The smooth and uniform surface is obtained by applying the float, trowel on the laid mortar. The plaster surface must be protected against rain, storm, or other atmospheric agents which affect the plaster surface. The water is poured on the plaster surface to keep the surface wet after 12 hours of plastering work at least for 7 days continuously. Advantages Durable: Cement plaster is highly durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions. Water-Resistant: Cement plaster is water resistant, making it an excellent choice for exterior walls. Versatile: Cement plaster can be used for both interior and exterior walls and can be painted or textured. Affordable: Cement plaster is relatively cheaper compared to other alternatives of plastering. Disadvantages Time-Consuming: Cement Plaster takes longer to apply and dry than gypsum plaster, which can increase the time and cost of construction projects. Minimum twenty-four-hour interval between coats of interior Portland cement plaster. After 48 hours period finished coat plaster may be applied to interior cement base coats. Compressive Strength: Compressive Strength of Cement Plastering is lesser compared to Gypsum Plastering. It is around 3.5 to 7.5 MPA and for Gypsum Plastering it is around 5 to 7 MPA. Tension Strength: Cement mortar is basically weak in tension and flexural strength ad hence prone to cracking. Density: Density of Cement Plastering is higher than gypsum plaster; hence the load on the building is increased as compared to gypsum plaster and needs water to attain strength. Prone to cracking: Cement Plaster is prone to cracking if not applied correctly Rough Finish: Cement Plaster can create a rough finish, which may not be suitable for interior walls and ceilings. Wastage: Percentage of wastage is higher during application. Application Cement Plastering is mostly recommended for External Plaster, all wet internal areas like Kitchen, Toilet, Terrace and Balcony. Rate 2000/- Alternative-III: Gypsum Board Introduction Gypsum board (also known as plasterboard, wallboard, gypsum panel, sheet rock, or Drywall) is a panel made of calcium sulphate dihydrate (gypsum) with or without additives and normally pressed between a facer and a backer (typically thick sheets of paper). It is used to make interior walls and ceilings. The plaster is mixed with fibre (typically paper and/or fibre glass), plasticizer, foaming agent, and various additives that can decrease mildew, increase fire resistance, and lower water absorption. Gypsum building materials are used in all construction types (residential, non-residential, new or refurbished), ranging from complex high-tech systems to easy to install products adapted for use by the general public. The different type of gypsum board generally available in the market are drywall white board, fireresistant board, water-resistant board and exterior board. Drywall white boards, like CoreX boards, are probably the most economical plasterboard type. This is used for walls and ceiling. This is the most used plasterboard and it is quick and easy to install, so it saves time and reduces construction costs. Fire-resistant board stops the chances of spreading of fire which ensures life safety. The core of the fireresistant plasterboard is enhanced by special fibres and additives. Both sides of this board are covered with special paper that gives flexibility and high strength to the plasterboard. Moisture-resistant plasterboard is manufactured with advanced technology. The core of this plasterboard is strengthened with water repellent agents. The sides of this board are covered with special paper that gives flexibility and high strength to the plasterboard. Green moisture-resistant board is suitable for areas where there is moisture in the area for example bathrooms. Exterior boards, like BoardeX orange boards, are used instead of cement boards nowadays, since they are lighter to handle and cut, and they can take all the weather elements. They are generally used in wet areas, in shafts, under wall cladding and areas where there is direct contact with water. There are other special boards available in the market like sound absorption boards, extra strong boards, and many more. It is important when buying gypsum boards that one explains what will be the ultimate need for the installation so that the supplier can offer you the best product available. Advantages Gypsum board provides a smooth finished surface: Gypsum is also used in plaster which provides a crack-free smooth surface. The Gypsum boards provide a continuous smooth finish surface on which you can directly apply paint. Gypsum enhances the beauty of the structure: Gypsum is the most widely used material in the interior design of the building because of its attractive and stunning design. The Gypsum products can be used for various decorative purposes in the interiors which enhances the aesthetical features of the building. Ease of Installation: Gypsum board building system are easy to install for several reasons. Gypsum board panels are relatively large compared to other materials. They come in 48 and 54 inch wide sheets and in lengths of 8, 10, 0r 12 feet, so they quickly cover large wall and ceiling areas. Gypsum board can be cut with either a utility knife or a variety of saws, and it can be attached with a variety of fasteners, including screws, nails, and staples. It can also be adhesively attached to many substances. Gypsum board is a lightweight material. Two workers can easily handle most panels and cover large areas in very short time periods. Gypsum board is easily finished using either a few hand tools or relatively modest machines. Gypsum board installers can quickly learn most application techniques in a few hours. Fire Resistance: Gypsum board is an excellent fire resistive building material Sound Isolation: Preventing the transfer of unwanted sound to adjoining areas is a key consideration when designing a building, specifically when considering the intended activities of the occupants in the various parts of the building. Gypsum board wall and ceilings system effectively help control sound transmission. Durability: Gypsum board is used to construct strong, high quality walls and ceilings that offer excellent dimensional stability and durability. Surfaces created using gypsum board are easily decorated and refinished. Economy: Gypsum board is readily available and easy to apply. It is an inexpensive wall surfacing material that provides a fire-resistant interior finish. Gypsum board building systems can generally be installed at significantly lower costs than most alternate systems Versatility: Gypsum board satisfies a wide range of architectural requirements for design. Ease of application, performance, ease of repair, availability, and its adaptability to all forms of decoration combine to make gypsum board unmatched by any other surfacing product. Disadvantages Temperature Limitation: For installation of gypsum board and finishes, maintain room temperature at not less than 40 °F for the mechanical application of gypsum board and not less than 50°F for the adhesive application of gypsum board and for joint treatment, texturing and decoration, unless recommended otherwise by the manufacturer. Gypsum is not water-resistant material: Gypsum has very less resistance to moisture due to which it cannot be used in the exterior of the buildings. The gypsum products may get disintegrate when it is exposed to moisture. Ventilation Requirement: Always maintain adequate ventilation during installation and curing period in the working area. Moisture: Where exposure to moisture is extreme or continuous, never use gypsum board on that area. Gypsum plaster is expensive as compared to cement plaster: The cost of plastering for the same thickness with the gypsum mortar is more than the cement mortar. So, it is not suitable to use gypsum mortar for low-budget construction projects. It is difficult to construct the Curved Shape with the help of Gypsum: The Gypsum is not flexible due to which it is difficult to construct the curved shape components with the help of gypsum. Application Gypsum board is widely used for internal walls and ceilings by the construction industry, and is a material of growing importance in the do it yourself sector. Gypsum board is also a common fire barrier used in house and general building construction. Commonly gypsum boards used in walls and ceilings, in moist areas, in exterior applications, for fire resistance and area separation and special systems. Rate