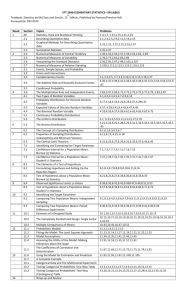
Steps of hypothesis testing • Step 1: The null hypothesis is states and a second statement called the alternative hypothesis is made. The alternative Hypothesis is accepted if the null hypothesis is rejected. • Step2: A level of significance is chosen. Usually 0.05 and 0.01 level is selected. It is refers to the probability of making a type I error. • Step 3: A test statistic is chosen. This value will be used in step 4 and step 5 to arrive at a decision regarding the null hypothesis. • Step 4: A decision rule is set up based on the level of significance chosen in step 2 and the sampling distribution of the test statistic from step 3. • Step 5: Finally, the decision rule in step 4 is used to make a decision- either to reject the null hypothesis or not to reject the null hypothesis. Analysis • Univariate (One variable at a time) • Bivariate (Two variable at a time) • Multivariate (More than two variable at a time) Variable • Categorical • Possible Bivariate Analysis: • Categorical Vs Categorical • Categorical Vs Numerical • Numerical Vs Numerical Numerical 1. Categorical vs Categorical X>2, Y>2 X=2, Y=2 Unrelated Related Unrelated - Pearson’s Chi square - Mc. Nemar -Pearson’s Chi square - Yates's Chi square - Binomial -Linear by Linear - Fishers Exact Chi square X :Group variable Y :Outcome variable -Likely-hood Ratio 2. Categorical vs Numerical Parametric X=2 & Y: Normal Unrelated Related Student’s t test <=30 `Paired ‘t’ Or test Z test N>30 X> 2 & Unrelated Y: Normal Related Non-Parametric X=2 & Y: Non Normal Unrelated Related Wilcoxson rank-sum Wilcoxson sign-rank Or Mann-Whitney U X>2 & Unrelated One way ANOVA Repeated measures ANOVA Kruskal Wallis H test Y: Non-Normal Related Freidmans test 3. Quantitative vs Quantitative Number Vs Number X: Normal and Y: Normal (Both should be normal) - Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) X: Non-Normal and Y: Non-Normal or any one non –Normal or Rank data - Spearman’s rank correlation (ρ) Rho