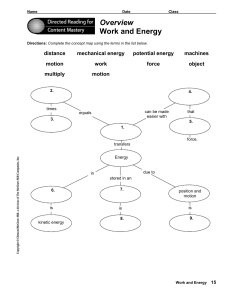
Forms and Uses of Energy 16.1 What is Energy? • Energy is the ability to do work. • Living things need energy for the processes that keep them alive. • Non-living systems also need energy to function. o For example, cars and aeroplanes need fuel to provide them with energy to move. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Potential Energy o Potential energy is stored energy due to a body’s position or condition. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Examples of potential energy: o Chemical potential energy • Energy stored in fuels such as petrol and food that can be released through chemical reactions. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Examples of potential energy: o Gravitational potential energy • Energy that an object has because of its position or location. • When the object is in a higher position with respect to the ground, it has more gravitational potential energy than in a lower position. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Examples of potential energy: o Elastic potential energy • Energy that an object has when it is stretched or compressed. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Kinetic Energy o Kinetic energy is the energy that a body has due to its motion. • All moving objects have kinetic energy. • Examples: a bird flying in the sky, a girl walking down the street and a car speeding down the road. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Heat o Heat is the energy that flows from a region of higher temperature to one of lower temperature. • Heat flows from things that are hot. • The Sun is an important source of heat energy during the day. • Heat is used in homes for cooking, heating water, ironing clothes. • In factories, heat is needed for processes like melting metals, creating steam to turn turbines and making chemicals react. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Light o Light is the energy that enables us to see. • Things that are luminous can give out light energy. • The Sun is an important source of light energy during the day. • Without light, the world would be completely dark, and we would not be able to see things around us. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Sound o Sound is the energy produced when objects vibrate. • Sound allows us to communicate and enjoy music. • Sound is also used as a warning. – For example, when a fire breaks out, the fire alarm goes off and alerts everyone to get to safety. 16.2 Forms of Energy • Electricity o Electricity or electrical energy is the energy that results from the flow of charged particles. • Electricity is a useful form of energy that can be transformed into many other forms of energy. • Almost all electrical appliances or equipment in homes and offices need electricity to work. 16.3 Energy Transformations • Photosynthesis in plants o Light energy → Chemical potential energy 16.3 Energy Transformations • An archer releasing his bow o Elastic potential energy → Kinetic energy 16.3 Energy Transformations • A moving car o Chemical potential energy → Kinetic energy + Sound energy + Light energy + Heat energy 16.3 Energy Transformations • Generation of electricity o Electricity is a useful form of energy. o Electrical generators are used to convert kinetic energy to electricity. o Power stations produce large amounts of electricity needed in homes, schools and offices. o In a power station, a series of energy changes occur before electricity is produced. 16.3 Energy Transformations • In a power station 1. A fuel such as coal, oil or natural gas is burnt and heat is produced to boil the water in the boiler. Chemical potential energy of fuel → Heat energy of water 3.2.The are connected a Theturbines heat energy turns watertointo generator, which convertswhich the kinetic steam at high pressure, goes energy theboiler turbine blades throughofthe and turns into the electricity. turbines. Kinetic energy of turbines → Electricity Potential and kinetic energy of steam → Kinetic energy of turbines steam line turbine generator coal supply switchyard boiler condenser cooling water 16.3 Energy Transformations • Generation of electricity o In a nuclear power station, nuclear reactions occur by bombarding radioactive elements with neutrons. o This creates large amounts of heat to boil the water into steam to turn turbines. o Nuclear energy in radioactive elements → Heat → Kinetic energy of steam → Kinetic energy of turbines → Electricity 16.4 Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy transformations in a swing When the swing is at its highest point, A, it only has gravitational potential energy. When the swing is midway between A and B, some of the gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. When the swing is at its lowest point, B, all the gravitational potential energy has been converted to kinetic energy. A C B 16.4 Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy transformations in a swing o In theory, the child would be able to swing to and fro for an unlimited period of time. o However, the swing will eventually stop moving if no one gives it a push every now and then. What happened to the energy? o The law of conservation of energy states that energy can change from one form to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed. o When energy is not lost, we say it is conserved. The swing stops moving as the energy was converted to other forms of energy such as heat and sound energy due to friction between the swing and surrounding air. 16.4 Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy transformations in a ball falling on the floor o Let the total energy possessed by the ball be E. o According to the conservation of energy, the total amount of energy, E, does not change. At position B, the ball is falling. It gains kinetic At position A, the ball energy, KEB, while has potential energy losing some potential PEA. This is equal to E. energy. The potential PEAat=position E energy left B is PEB . At the ballC, hits the AtD,position just KE B + PEB = PEA = E floor andthe becomes before ball hits the compressed. A sound is floor, only kinetic heard andKE heat energy left. C is is produced due to friction. KEC = PEC + KEC = PEA Elastic = E potential energy of ball + heat + sound = E A B C D 16.4 Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy transformations in a ball falling on the floor o Then ball is unable to reach its original height of position A when it bounces back up. o This is because some of the energy, E, is lost as sound and heat when it hits the floor. o With less energy, the ball cannot regain its original height. A B C D 16.5 Conserving Energy • It is important to conserve energy because most of the energy we use comes from non-renewable resources. • Non-renewable resources include crude oil and coal. These sources of energy are limited and will run Coal Extracting, power plants processing produce and more burning pollution crude than oil cause oil power large plants. amounts Butofcoal out one day. is more pollution, commonly which destroy used in developing the countries environment. as it is cheaper than oil. Renewable sources of energy • Renewable sources of energy are sources of energy that can be sustained or renewed indefinitely, due to unlimited supplies or because of new growth. Renewable sources of energy • Solar energy o Solar energy is used in solar furnaces for smelting iron. o Solar energy is also used to generate steam in power station. This steam is used to turn turbines of a generator to produce electricity. Renewable sources of energy • Wind energy o A wind farm is a collection of wind turbines used to generate electricity. o The wind turbines use the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electrical energy. Renewable sources of energy • Wave energy o Wave farms use the kinetic energy of waves to generate electricity. o The up-and-down movement of the wave will shift gears to turn turbines to generate electricity. Renewable sources of energy • Biomass o Biomass refers to plant and animal material from which we can: • extract oil (oil palm, jatropha, jojoba) • ferment into gas (water hyacinth, manure) • burn (dried plant material, wood, charcoal) Renewable sources of energy • Conserving energy in Singapore o Singapore uses natural gas for its power stations but has started using solar energy, wind energy and biomass. o Since Singapore does not have many natural resources, we are dependent on other countries for our fuel needs. o Hence, it is important for us to be aware of conserving energy. Renewable sources of energy • Conserving energy in Singapore o We should use energy more efficiently and avoid wasting electricity. o For example, you should turn off electrical appliances that are not in use. Miscellaneous • http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/science/f ormsofenergy.html • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy_transformatio n • http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/phys/mmedi a/energy/ce.html • http://fi.edu/guide/hughes/energyconservation.ht ml • http://www.reupower.com/energysvc/53ways.html • http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/sources/r enewable/renewable.html