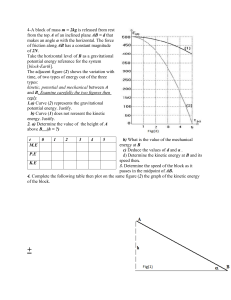
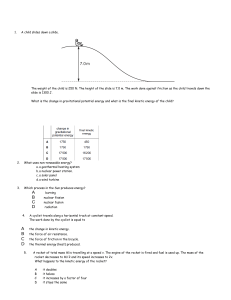
Name Date Class Overview Work and Energy Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. distance mechanical energy potential energy machines motion work force object multiply motion 2. 4. times can be made easier with equals 3. that 5. 1. force. transfers Energy due to in stored in an 6. is 7. is 8. position and motion is 9. kinetic energy Work and Energy 15 Name Date Class Section 1 ■ Work and Machines Section 2 ■ Describing Energy Directions: Determine whether the italicized term makes each statement true or false. If the statement is true, write true in the blank. If the statement is false, write the term that makes the statement true. 1. When a force is applied through a distance, work is done. 2. A device that makes energy easier is a machine. 3. The work done to a machine is input work. 4. A device that does work with only one movement is a simple machine. 5. The efficiency is the number of times a machine multiplies the input force. Directions: Use these words to fill in the blanks below. Words may be used more than once. energy more kinetic less joule gravitational potential chemical 6. Two baseballs have the same mass. The ball that is closer to the ground has gravitational potential energy than the other ball does. 7. Two trucks have the same velocity but different mass. The truck with the greater mass has kinetic energy than the other truck does. 8. 9. A is the ability to cause change. is a unit of measure of all forms of energy. 10. When an object falls, some of its energy. 11. The energy of an object depends on its mass and height. 12. The energy of food and other fuels is 16 Work and Energy energy changes to potential energy. Name Date Class Section 3 ■ Conservation of Energy Directions: Write the term that matches each description below on the spaces provided. The boxed letters should spell the answer to question 9. 1. Type of energy due to both the position and motion of an object 2. The rate at which energy is converted 3. Type of energy transformed into thermal energy in a toaster 4. Force that acts between two sticks when they are rubbed together 5. Unit used to measure the amount of energy that people get from food 6. Type of energy transformed into chemical energy by plants 7. Type of energy that is greatest at the top of a swing’s path 8. Type of energy that is greatest at the bottom of a swing’s path 9. What law of energy has never been broken? Work and Energy 17 Name Date Class Key Terms Work and Energy Directions: Unscramble the terms in italics to complete the sentences below. Write the terms on the lines provided. 1. A nimcsh amleiep is a machine that does work with only one movement of the machine. 2. The ratio of output work to input work is the ynieficcef of a machine. 3. Rokw is the measure of the force that is applied over a distance. 4. The ratio of output force to input force of a machine is its haevangcla nacmeidta. 5. A humpcnid enocaom is made of two or more simple machines. 6. The stored energy an object has as a result of its height above the ground is aaagiilnrottv potential energy. 7. The law of aceinnoorstv of energy states that the total amount of energy in the universe remains the same. 8. Energy is measured in SI units called ejlosu. 9. The energy stored in the bonds between atoms is accehilm potential energy. .10. The stored energy an object has as a result of its position is aeilnoptt energy. .11. Energy in the form of motion is ceiiknt energy. .12. An object’s aaccehilmn energy is its total amount of potential and kinetic energy. .13. The energy stored in stretched or compressed objects is aceilst potential energy. 18 Work and Energy