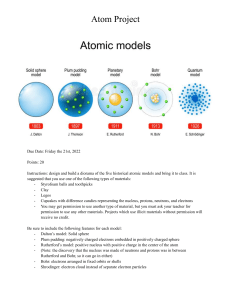
The P-N Junction Diode, Diode Applications, Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT), DC Biasing of the BJT Amplifier, Transistor Modelling, Cascade Amplifier, Small-Signal BJT Amplifier, Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor FET (MOSFET), MOSFET Amplifier, Frequency Response of BJT and FET Amplifiers. Assessment Distribution Quiz 10% Assignment 5% Mid Term 20% Lab Test 10% Lab (Activity) 15% Final Exam 40% Total 100% An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the characteristics of that element. Bohr model, atoms have a planetary type of structure that consists of a central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons, as illustrated in Figure. The nucleus consists of positively charged particles called protons and uncharged particles called neutrons. The basic particles of negative charge are called electrons. The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus, which is the same as the number of electrons in an electrically balanced (neutral) atom. Atomic weight is the number of protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus. For example: H-Atomic no. is 1. Atomic weight is 1. He-Atomic no. is 2. Atomic weight is 4. Energy Levels: Electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom at certain distances from the nucleus. Electrons near the nucleus have less energy than those in more distant orbits. Only discrete (separate and distinct) values of electron energies exist within atomic structures. Therefore, electrons must orbit only at discrete distances from the nucleus. Each discrete distance (orbit) from the nucleus corresponds to a certain energy level. In an atom, the orbits are grouped into energy levels known as shells. A given atom has a fixed number of shells. Each shell has a fixed maximum number of electrons. The shells (energy levels) are designated 1, 2, 3, and so on, with 1 being closest to the nucleus. The Bohr model of the silicon atom is shown in Figure. Notice that there are 14 electrons and 14 each of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. . Atomic structure: (a) germanium (b) silicon. Electrons moving around the nucleus in orbits. Nucleus contains protons and neutrons. Two semiconductor materials used to fabricate most diodes and transistors are germanium (Ge) and silicon (Si). • Similarity - each Ge and Si has 4 electrons in its outermost shell. • Difference – Si has 14 protons but Ge has 32. • Si is more popular as the devices that are made of Si have better performance at higher temperature. Valence electrons of Ge are in the 4 shell. Valence electrons of Si are in the 3 shell. Hence, Ge valence electrons are of higher energy and require smaller amount of additional energy to escape from the atom. This property makes Ge more unstable at high temperatures.