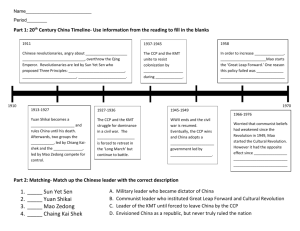
Role of USA in WWI ➢ USA not involved in the war till April 1917 ○ USA enters due to the German offensive ○ USA was hesitant on joining previously as the Russian government was an autocratic government and USSR was a part of the Allied bloc, hence USA was not very happy in joining forces with the USSR as the Czar’s rule was antidemocratic. ○ Another occurrence takes place in March 1917 where there is a revolution in USSR that overthrows the Czar ➢ Contribution of USA: ○ Supplying Britain and France with food, merchant ships and money (credit) ○ They are also providing military support gradually (towards the end of 1917) ○ By mid 1918, almost over half a million Americans were involved in WWI, because of which Britain and France were getting a boost, hampering the German side, in which the Germans started losing mental stability. ○ President was Woodrow Wilson, who was actively involved in the war with his full wit and mind ○ He wanted a moderate policy ○ A sober truce between the allied and axis powers ○ In favour of maintaining world peace so that a WWII doesn’t occur ○ From this perspective, the League of Nations was put forth, which was rejected by the US congress. ○ The republican governments in the USA (1921-1933) were in favour of isolation (no signing of major international treaties and no joining blocs). ○ Due to the economic needs of the country, the bare minimum interaction with other countries was needed ○ In the 1920s they have tried to increase their trade & investments abroad ○ Direct threat of Japanese invasion due to the rapid expansion of the Japanese empire ○ During the war, the loans given to the allied powers were worth $12 billion at 5% p.a. These powers felt that the USA would write off the loans but since USA provided military support as well, they demanded repayment in full, without any negotiations. ○ Britain and France were dependant on German payment to them for the repayment of loans to the USA ○ Eventually, the UK agreed to pay in full, and then France and the rest of the allied powers agreed as well. The USA said that interest rates would be reduced as per the amount of poverty in the countries. (Italy was made to pay only 0.4% interest whereas the UK had to pay the whole 5% interest). This made the allied powers unhappy and also offended the Germans as the Treaty of Versailles was anyway very harsh plus they felt that their money was being distributed. ○ Another big blunder made by the USA was that they helped the German people in monetary terms and this was initially denied by the USA and then they had to admit it. This is one of the reasons that caused the great depression in 1929 ○ Around the 1930s, the USA was going into complete isolation and when the Japanese aggression was increasing, the USA did not agree to impose any sanctions, hence even Britain and France could not impose sanctions. ○ The USA has tried to improve relations with the UK since they are still awaiting the repayment of loans from them. Wilsonian Peace ➢ Spoke for world peace and the League of Nations at the Paris Convention ➢ He was disappointed when his 14-point programme was ignored ➢ He wanted world peace but also accepted the idea that the British and French govts should repay the debts ➢ He agreed to the point of German disarmament per the Treaty of Versailles ➢ As far as the reparations were concerned, he wanted to limit it to the loss of people and loss of civilian property, whereas the Treaty of Versailles wanted Germany to bare the entire cost of the war ➢ He was in favour of countries to be free of foreign rule and for democratic governments to be set up (decolonisation) ➢ The 14-point programme was given from this perspective, which was completely ignored by everyone ➢ Wilson’s Fourteen Point Plan: ○ Given in Jan 1918 1. Abolition of secret diplomacy 2. Free navigation at sea for all nations at war and peace 3. Removal of economic barriers between states 4. All-round reduction in armaments 5. Decolonisation 6. Evacuation of Russian territory 7. Restoration of Belgium 8. Liberation of France (return of Alsace and Lorraine) 9. Readjustment of Italian frontiers 10. Self-government in Austria and Hungary 11. Romania, Serbia & Montenegro to be given access to sea 12. Self-government of non-Turkish people 13. Independent Poland with access to sea 14. General association to preserve peace (did not specifically quote LoN) Role of USA in WWII ➢ September 1940: ○ US is supplying active military forces to allied powers ○ Till Dec 1941- Indirect investment of US forces in WWII ○ 7 December - pearl harbour after which there is direct involvement by the US ○ Roosevelt was President of the US. He was effectively helping the UK with hard currency ○ The US was also ready to supply food, military support and raw materials to the UK. ○ All this was against the wishes of the UK people. ➢ Neutrality Act of 1939 ○ This act said that we should not help the countries by providing raw materials if they did not pay with interest the costs. ○ “Cash and carry” basis ○ Rethink about countries who have been redundant to pay the war loans. ➢ Johnson Act 1934 ○ This act supported the previous Neutrality act of 1939 ➢ Britain + France ○ The US people realised that the moment France falls, Britain will not be able to survive ○ Therefore, the US was telling Roosevelt not to help the UK after which Roosevelt explained to the US that the allies were better as compared to the Japanese and German forces who were more aggressive that is why the US would rather help the allies ○ Now Roosevelt had to balance■ General wish of the people ■ Legalities ➢ 1940- Destroyer for bases ○ 50 obsolete destroyers were given to the UK ○ Against that, the US took ‘newfoundland’ and the Caribbean on rent. This rent was supposed to be for 99 years. ➢ Dec 1940- lend and lease initiative ○ Acc to this, US will provide the allies with help but payment can be deferred ○ UK+ 30 countries (military, food, etc.) ______________________________________________________________________________ Theodore Roosevelt ➢ There is 2 Roosevelt, Theodore comes first and later on comes Franklin Roosevelt ➢ Prez from 1901-1909 (2 terms) ➢ He has 2 policies ○ Domestic (square deal policy) ■ Three C’s: ● Consumer protection ○ Meat packing plants: workers working here who had very bad working conditions which needed improvement. ○ The kind of meat and food that was being served was of poor quality. ○ Pharmaceuticals that were supplied were contaminated or mislabelled ○ For the improvement of all this, The Pure Food & Drug Act was passed, and The Meat Inspection Act (federal inspection of meat produced) ○ Interstate commerce commission was instituted to regulate the railroad rates ● Control of corporations ○ Controlling the businesses- this is radical as the businesses financially support the government ○ He gives importance to the labour unions ○ Concerned about the problems of the labour, the problems need to be voiced and heard, and he also appoints a commission to settle the labour issues ○ National Child Labour Commission, 1904 is constituted. There is a labour policy that he is devising. ● Conservation of natural resources ○ First act was passed in 1902- Newlands Reclamation Act to generate revenue for irrigation projects ○ 1904- Dept. of Agriculture to protect the forest resources. It will also make a new environment policy ○ 1905- Forest Services Act, created 5 national parks, 18 national monuments and 51 wildlife refuge ○ 1906- Antiquities Act to protect cultural and natural resources ■ All these three policies are radical policies ○ Foreign (Big stick policy) ■ Termed big stick policy because he had given a speech where he had said “speak softly and carry a big stick, you will go far” ■ You will never see USA speaking harshly against any other country or openly criticising the policies of any other country, nor would they impose economic sanctions until very recently ■ He wanted to focus on Latin America and the Pacific Ocean ■ He was willing to build a strong army and navy, so much so that the mere existence of the forces should be a fear for any aggressor ■ Creation of the Panama canals. In Panama the water levels were managed for docking of ships and cruising. There was a proposal given for building the canal across central America to dominate the seas in those areas. A proposal was given to Columbia and was rejected. The central government sent the navy to intervene and support the rebels in Columbia to oppose the government and create the nation of Panama. ■ Latin America: ● Any kind of financial help needed by South America was provided by the USA. they did not want European countries to interfere, this policy was called Corollary policy. This policy was validated by Monroe Doctrine of 1823. ● The Monroe Doctrine spoke about the consequences of interference of European countries. ● USA was also trying to dominate Dominican Republic and this was all being done to protect the western hemisphere ● This was the foreign policy of Roosevelt ● Latin America was first under Portugal and Spain ■ Philippines: ● The largest overseas colony of the USA ● Being given sovereignty under the treaty of Paris, 1898 ● The island country got sovereignty in 1898 for $20m William Taft ➢ 1909-1913 ➢ Contributions in Philippines (self-governance, social reforms, etc) ➢ 27th Prez of the USA (in power for one term) ➢ Lawyer by profession and a distinguished jurist, very well acquainted with the law ➢ He became the Chief Justice of US after presidency ➢ Highly educated, but not a good administrator ➢ He always preferred the law over politics and spent uncomfortable years serving as the prez of US ➢ Policy called Dollar Diplomacy. ○ Active participation of USA in the supply of arms and ammunition, dollars would be substituted for bullets (financial assistance instead of military assistance) ○ Done with the help of the foreign policy of T. Roosevelt to secure markets and opportunities for American businesses ○ Economic might over the foreign affairs ○ Central American countries were taking money from the European countries and were unable to repay it to them so the US gave money to the central American countries so that they can repay the European countries. ○ Mexico opposed the payment of money by the US ○ This policy was implemented in a majority of countries. In Mexico and China, it failed, the rest of the countries it was a success ○ The Caribbean was happy ○ This policy was led by Taft but was helped by his secretary, Philander Knox Woodrow Wilson ➢ 28th Prez of the USA ➢ 1913-1921 ➢ He supported the entry of the USA in WWI in the name of protecting democracy ➢ He was very active into promoting individualism and wanted states’ rights ➢ He lowered the tariffs on imports but at the same time also increased income tax for government revenue ➢ Passed a federal reserve act for elastic money ➢ Federal trade commission was established and it controlled the unethical business practices ➢ Prohibition of child labour (1916) ➢ He regulated shifts of workers (8-hour shifts) ➢ Write the 14 points here ➢ In his second term, he passed the women's rights to vote ➢ However, it is also said that he had made racial remarks in his speeches ➢ His decision to be personally present in the Paris Peace Treaty was a controversial decision because people didn't want that to happen ➢ Very idealistic thinker and in 1919 he was given the Nobel Peace Prize ______________________________________________________________________________ Warren Harding ➢ 29th US Prez, 1921-1923 ➢ Died mid-term, lot of controversies related to his death ➢ His VP was Coolidge, who takes over the presidency after his untimely death ➢ After WW I Harding wins elections and becomes president. ➢ His presidency is a landslide victory- 60% victory (votes) ➢ Tagline “less government in businesses as well as more businesses in government” ➢ Government should work more towards the functionality of businesses and social welfare. ➢ Harding was the one who wanted businesses to flourish without any interference. ➢ When he was campaigning for his presidency (electoral candidature) he always spoke about “returning to normalcy” ➢ “Returning to normalcy”- the US population did not want to be in WWI. However, the government moulded the opinion. people were at the threshold and there was a lot of unrest in the atmosphere. Us people were unhappy due to ww I ➢ After WWI, economic impacts, life threatening things and therefore he wanted things to go back to normal. ➢ 1) 1914-1918: world war I ➢ 2) 1915-1919: influenza epidemic ➢ 3) Red scare- due to communist revolution. People were happy and ready to promote and accept communist ideology. Due to this, the US started arresting leaders of communism. There was unrest among people. ➢ 4) racial tensions- migration of African-American to northern states due to which there was racial tensions. ➢ Due to all these reasons people in the US were not happy. Therefore, the slogan “return to normalcy” and for this he promoted the policy – “America First Policy” ➢ America First Policy: ○ Non participation in LoN ○ Priority to American business ➢ Harding introduced the budget system in government. ➢ His biggest achievement was hosting the Washington Naval Disarmament Conference in 1921-1922. ➢ In this conference, the world’s major powers agreed to halt the arms race. ➢ Production of large naval vessels had to be zeroed down. ➢ This was the most important contribution. ➢ In order to promote businesses, he lowered the tax on business. ➢ There was a sharp decline in the immigrants due to strong policies. ➢ His cabinet was a mixture (not everyone supported him) which is why he thought it was the right way for administration. ➢ His mistake was to trust his cabinet blindly. He did not check what his cabinet was doing. He was not personally involved in any of the scandals. ➢ Due to this trauma of having a corrupt government, he died an untimely death and his Vice President Coolidge took over. ______________________________________________________________________________ Coolidge ➢ 30th president (1923-1929) ➢ supported business. To this effect, he established the Federal Trade Commission. ➢ Reduced income tax and estate tax. ➢ Economic prosperity increased. ➢ The era of prosperity- the roaring 20s (1920s) ○ This is because the real wages of workers have increased. ○ Majority residencies in town ○ Fast/cosmopolitan ways of living ○ Emergence of modern medicine ○ Subsidised medical clinics. ➢ 1921-1929: doubling industrial production and this is with the numbers of workers being constant. ➢ Sales profits wages increased ➢ Technological advancements- radio sets, refrigerators, washing machines, vacuum cleaners, motorcars etc. ➢ Industrial expansion – 19th century ○ USA > UK, Germany ○ Entry of American goods in European markets. ○ Economic policies of the government – import duties increased. ○ This tariff is known as Fordney-McCumber. ○ Lowering of income tax ○ Focusing on productionality-use of machinery ○ Advertising – radio, cinema, newspaper ○ Allied industries increased. ○ Increase in transportation- canals, railroads etc ○ Giant corporations coming up ______________________________________________________________________________ Herbert Hoover ➢ 31st prez ➢ His tenure was dominated by the 1929 great depression ➢ Humanitarian crisis- help rendered ○ Stranded people in WW1 ○ Germany occupied areas- given food assistance ○ Labour sensitive president ○ Against laying off workforce during the great depression ______________________________________________________________________________ The Great Depression 1929 ➢ Begins in 1929 ➢ Till 1928 (Calvin Collinge), he was very optimistic about the economy of USA, and did not anticipate anything like the great depression could occur ➢ Herbert Hoover too could not see the great depression and till then America was being called “America the Golden” ➢ In September 1929, Wall St. was slowing down and it was being said that the boom of the 1920s was over ➢ Before the stock prices fell too much, there was a massive sell off and rumours were floating that there would be shortage of liquidity ➢ By 24th October, there was a rush with people panic selling as the share prices were hitting lower lows every moment ➢ This is known as the Wall St. crash, The Great Depression ➢ Causes of the GD: ○ Domestic overproduction: ■ People were profit oriented; thus, many goods were manufactured. ■ There was too much production but people suddenly stopped buying goods so there was stockpiling and this leads to excessive overproduction ○ Wrong income distribution: ■ Avg income of workers were increased by 8%, whereas the industrial profit was 72%, leading to uneven distribution of wealth ■ The workers who were receiving the 8% income increase did not have the purchasing power ■ Poverty remained the same on the ground ○ Reduction in exports: ■ Import tariffs in 1922 increased import duty and hence foreign trade was reduced. ■ Products had become costly hence people stopped buying those goods ■ Local buyers stopped buying the goods too due to the rumours of economic slowdown ○ Speculation: ■ Everyone was focusing on savings and not on investments ➢ Impacts: ○ Millions of investors who bought shares at high rates were negatively impacted and there was little to no chance of making profits ○ People started withdrawing savings, leading to money shortage with banks ○ Goods were not being sold, leading to mass layoffs amongst the working class ○ Germany was the worst hit during the depression for obvious reasons (unable to repay American loans at high rates) ______________________________________________________________________________ Roosevelt’s Policy ➢ President Franklin D. Roosevelt ➢ New deal ➢ Era where the roaring 20s are in place ➢ The new deal is at the backdrop of the depression that has come about (set of economic reforms) ➢ 3 parameters to the new deal ○ Relief ■ From poverty due to the suffering caused due to the depression ○ Recovery ■ From the unemployment ○ Reform ■ To ensure there would be no great depression again (economic reforms) ➢ The new deal puts in place 8/9 measures ○ Banking and financial systems ■ The government was trying to take over the financial systems and temporarily boost the confidence of the depositors as the banking system collapsed during the depression ■ This was trying to boost the system and is still prevalent in democracies, where the government interventions put confidence into the people ■ Securities exchange commission (SEC) was formed for the reformation and restructuring of Wall St. (NASDAQ) ○ Farmers relief Act, 1933 ■ To keep the average income of the farmers the same, thus telling the farmers to produce more of agricultural product in order to keep the prices low ○ Civilian Conversion Corps, 1940s ■ Similar to MGNREGA ■ This was being done for the young men and the salary that was to be paid would be minimum but they would provide shelter, food and clothing ○ National Industrial Recovery Act, 1933 ■ Public works administration was being set up (like PWD) ■ National Recovery administration to monitor the child labour and 8-hour shifts ○ Federal Emergency Relief Administration, 1935 ■ A committee was constituted under this, called Works progress Administration to monitor the progress of the work undertaken ○ Social Security Act, 1935 ■ For old age pension, dearness allowance and unemployment insurance ○ Working Conditions ■ Wagner Act ● Senator of NYC passed the act, giving a legal foundation to the trade unions and were no more considered illegal ■ Fair Labour Standards Act ● It was decided that a minimum 45 hours of working was needed ○ Tennessee Valley Authority ■ To control the forest cover, protection of biodiversity and from soil erosion ○ Increasing taxes for the wealthy people ➢ Criticisms of the New Deal ○ Industrialists ○ State government ○ Supreme court criticising the Prez that he was trying to overpower the people ○ Socialists opposed it as they felt it was not a very drastic change ➢ Achievements of the New Deal ○ Relief to the jobless and destitute people ○ Restoration of the confidence in the minds of the people about the government ○ Public works schemes were being implemented ○ Welfare benefits were in place (due to social security act) ○ Other innovations were in place ______________________________________________________________________________ Harry Truman ➢ 1945-1953 ➢ He came up with the ‘Fair Deal’ policy ○ Included a national health scheme ○ Higher minimum wage (increasing wage floor) ○ Slum clearance ○ Full employment ➢ During his tenure, he was also unable to pass all the measures that he wished to as it was not possible for him to do so since the congress was not in his favour ➢ He was in favour of the working-class support and wanted more of social security benefits to reach the working class ➢ He was also in favour of the rights of the Black people ______________________________________________________________________________ Dwight Eisenhower ➢ 1953-1961 ➢ Did not promote any new policies, but maintain the existing policies and improve on them ○ He said that the insurance benefit should not be a long-term insurance benefit ○ Financial help was the be given only for medical bills and only of people who were 65+ ○ He was willing to give the federal cash for housing. ○ There should have been more spending on education, specifically on maths and science since Russia has launched the Sputnik mission so for America to match the competition this step was taken ➢ 1950s, there was a lot of trouble to the farmers as they were unable to make a profit margin due to the failure of the implementation of the new deal ➢ There policies were more inclined towards socialist ideologies ______________________________________________________________________________ John F. Kennedy ➢ 1961-1963 ➢ He was the one who had won elections on the basis of the blame game ○ Rather than talking about his own achievements, he would talk about what was not done by the opposition during their tenure ➢ He is often compared to Rajiv Gandhi since people expected a ‘new era’ and a ‘new regime’ ➢ Detailed programme for: ○ the medical payments of the poor and aged people ○ Federal cash was to be given for education and housing ○ Increased benefits ■ Unemployment benefit ■ Social security ➢ All these principles were inclined towards socialism and hence it was opposed by the republicans and the democrats as it was during the peak of the cold war hence no support to socialism was given ➢ Successes of his tenure: ○ Social security ■ brought an extension to the Social Security Act ■ Social security was to be given to children whose fathers were unemployed ○ Helped the poor ■ Raised the minimum wage ■ 1 hour= $1.25 (raised from $1) ○ Federal cash for housing: ■ Loans to people for purchase of houses ○ Unemployment: ■ States were given federal grants to extend unemployment benefits All these steps were taken as when his tenure began, almost 4.5m people were unemployed ➢ He was assassinated in 1963 ______________________________________________________________________________ Johnson ➢ 1963-1969 ➢ He was the VP under Kennedy ➢ The election was conducted in 1964 where he was elected till 1969, winning a landslide victory due to the social service he did during the one year completing the term of Kennedy ➢ The first thing he brought in was an economic legislature: ○ People who were having an annual income of $3000 for a family were considered at par with the poverty line. This included almost 20% of the population of USA, where the people were on or below the poverty line and this included Mexicans, Latin Americans and Blacks ➢ He wanted the American society to be a great society: ○ The motto of this was “abundance and liberty for all” ○ Majority of his supporters were a part of the same congress due to the landslide victory, making is easier to pass legislations ○ Passed the following acts: ■ Economic Opportunity Act, 1964 ● Young people from poor families would receive job training and higher education ● Federal Money was given only for specific education schemes ● Financial aid for clearing slums and rebuilding cities ● Creation of new jobs in the poorest regions ● Social Security Amendment Act, 1965 for Medicare for the people above 65 years of age ○ All the schemes were underfinanced and the money was being diverted to wars like the Vietnam War ○ People started becoming unemployed for benefits in these schemes ➢ There were racial problems ➢ students were against the government for participating in the Vietnam war so they were protesting in universities ➢ Multiple assassinations were taking place, thus he had to deal with law and order ○ 1963- JFK ○ 1968- Martin L. King + Senator ➢ There was a general discontent and he did not have an answer for it as he was fighting a war on poverty ➢ Due to all these issues, he did not stand for the 1968 elections and the Republicans won in the pretext of restoring law and order _____________________________________________________________________________ Richard Nixon ➢ 1969-1974 ➢ In 1971 4m Americans became unemployed and hence Johnson’s social services (poverty alleviation programmes) were cut down ➢ Social security benefits were increased, Medicare was extended (for disabled people under 65) and there was a council for urban affairs that was set up to deal with the slums and ghetto rehabilitation ➢ Foreign policy: ○ During Nixon’s tenure there were a lot of overseas problems, starting with Vietnam. He understood that a lot of money was spent in the war and thus in 1973 a peace treaty was signed between Vietnam and the USA. this treaty was celebrated as peace with honour ○ During his tenure, there were radical changes in the American foreign policy, where he tried to improve relations with USSR and China ○ In Feb 1972, he met with Chairman Mao in Beijing as well as people in Moscow in May that year. ○ The Arms Limitation Treaty was signed in 1972 with USSR ➢ Achievements during his first term, till 1972: ○ Bringing Peace ○ Law & Order ○ Sensible Defence policies with USSR & China ○ Sent first men to the moon- Neil Armstrong & Buzz Aldrin ______________________________________________________________________________ Jimmy Carter (1977-1981) ➢ He was not an administrative specialist; hence he was not very successful as he was unable to handle matters in the right manner ➢ Achievements: ○ Keeping communism out ■ Gave a strong right-wing government to USA ○ Supported Britain for bringing black majority rule in Zimbabwe ■ Asians and non-Americans were ruling Zimbabwe ○ SALT (Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty) with USSR ○ Peace between Egypt & Israel (after the 7-day war) ■ Attempted to restore the peace between Egypt & Israel ➢ During the 1980s there was recession again: ○ More unemployment, more oil shortage ➢ The SALT was not well perceived amongst the military leaders of USA as they didn’t want this to happen ➢ Around 1979, when Russians were taking over the Afghan region and USA was not taking any strong action against it, which made the people unhappy ➢ In November 1979, some Americans were hostages in Tehran by Iranian students, against which there was no serious action taken ➢ With all this in the backdrop, Jimmy Carter lost the next election but his efforts to release the students from Tehran were noted as they were released as soon as Ronald Regan won the next election ______________________________________________________________________________ Ronald Regan (1981-1989) ➢ His popularity was rising after WWII ➢ He was the one who used to communicate directly with the people transparently, which earned him the people’s trust ➢ He wanted to establish peace with USSR but wanted USA to be in a more commanding position ➢ He also wanted friendly relations with China ○ He visited Beijing in 1984 ➢ For the Americans, he was working for the economy to recover, and he was the one who was trying to take ahead the economic recovery that America witnessed from 1945 onwards. ○ His economics is called ‘Reaganomics’ ➢ Second Term: ○ Starts in 1984 November ○ He had a landslide victory ○ There were a lot of controversies: ■ Economic problems● The federal budget was facing a deficit. In 1987, he proposed to increase expenditure in defence and it was rejected by the Senate as the deficit needed to be reduced ● Depression in the agricultural field as the govt is unable to give subsidies & prices of agricultural goods was falling, all this led to unemployment in the agricultural sector ■ Disasters in the space program● There was a space shuttle called ‘challenger’ that exploded, leading to the death of 7 crew members ● The ‘delta’ rocket failed as it exploded ● The ‘titan’ rocket failed as it exploded ➢ Foreign policy: ○ Bombings in Libya that occurred in 1986 which provoked a mixed reaction, some supported it while others didn’t. Regan himself was convinced that the bombings were justified and the act by the USA was right. It led to almost 100 deaths. The citizens were happy about the bombings but the world criticised it ○ American policy in South Africa: ■ Regan wanted limited sanctions in S. Africa whereas the congress wanted rigorous sanctions to be imposed. American interest in SA was due to the apartheid going on there ○ Meeting with Mikhail Gorbachev: ■ In 1986 he met with Gorbachev, which turned out to be a success as there was a treaty (INF Treaty, 1987- for mutual cooperation, etc) signed between the two countries. ○ Iran gate scandal: ■ This was a major blow to the politics that Regan was trying to play in terms of the distribution of arms to Iran that was taking place in exchange for the release of the 7 American students. Regan was criticising terrorism publicly but then his government was supporting the supply of arms and ammunition to Iran. ■ An investigation took place against the advisors of Regan as he could not be directly sued being the president of the USA. Due to this, his image was destroyed and his political career suffered dearly. ➢ Stock market crash of 1987: ○ Major budget deficit as the income and expenditure could not be balanced. Defence spendings had increased after 1981 and he had also cut down takes, leading to an unstable source of government income. ○ This was a time when the US economy was facing the largest trading deficit. ○ Economic slowdown, and at the same time investors started panic selling their shares, amounting to the stock market crash. ○ This occurred during the end of his tenure and when the next elections came around George Bush won the election. ______________________________________________________________________________ George Bush (1989-1993) ➢ He was the VP during the tenure of Regan and his tenure was famous for the decisions he took against Saddam Hussain (Iraq). ➢ Invasion of Kuwait took place in 1990, August and Saddam became the main target for the USA. ➢ The Gulf War started, leading to direct conflict between Iraq & USA ➢ He was criticised that though after the victory of the Gulf war, there was no strict action taken against Saddam, making the people unhappy ➢ Around the 1990s the US economy was facing a recession and the budget deficit continued. There was unemployment increasing as a result of collateral damage of the war. This was a time when Bush was forced to impose indirect taxes which went against his election manifesto (he promised that no kind of taxes would be imposed). This made the people happy. The middle class in particular was very unhappy. Due to the rising unemployment rates, there was a rise in crimes., illegal activities, drug trafficking and consumption, and with all this in the background, bush had to face the next election in November, 1992 ______________________________________________________________________________ Bill Clinton (1993-2001) ➢ He was the one who was into the political scenario from the time of Regan. He published a lot of articles against the concept of reaganomics. ➢ Achievements: ○ Introduction of minimum wages: ■ $4.75 per hour to be increased to $5.15 at a later stage ○ Foreign policy: ■ Positive contribution towards Middle East, Bosnia and N. Ireland ➢ However, his tenure was clouded by the ‘Whitewater scandal’: ○ It was alleged that along with his wife, Hillary Clinton they made some shaky business deals for their personal interest. ➢ There was peace and prosperity during his tenure but he could not win the support of the Senate and House of Representatives Second Term: ➢ Introduced policies that were more towards the side of Republican ideologies ______________________________________________________________________________ Civil Rights Movement ➢ Abolition of slavery in 1863 due to which people were expecting that there would be equal rights, but that didn’t happen. ○ Right to property was not prevalent for blacks ○ Black people could not receive good education and could not vote ○ These black people were supposed to attend a separate school and did not enjoy the same kind of quality education as the whites. Since there was no good education, the jobs they got were very unpleasant ○ There were separate seatings for the blacks at restaurants ○ The first organised attempt to bring in parity began in 1910 and an organisation was formulated called “National Association for The Advancement of Coloured People” ○ After the formulation of this org, there was a change in the attitude of the government. ➢ In 1946, Harry Truman appointed a committee to investigate civil rights which recommended the formation of laws that would stop racial discrimination in jobs and voting rights. The committee was asked to justify why they wanted such a drastic change after so many years. Their reasons are as follows: ○ They said it was not right to treat the fellow humans in such an unfair way ○ If, from the top jobs, these people were excluded then it would be a waste of talent and expertise ○ The blacks were becoming outspoken (something needed to be done to calm them down) ○ Almost 10% of the total population of the USA were black people, and if suppressing them it would give USSR good reason to say that USA was not a good enough democracy ○ Asia and African countries were gaining independence during these years and since most of these populations were dark skinned, if their rights were not protected then they would side with communism which would be a huge blow for the USA The SC had to pass a few laws to bring in parity and it did. ➢ Separate schools for whites and blacks were made illegal ➢ All juries were to consist of black people ➢ The Civil Rights Act was set up and a commission to investigate the violation of the rights of the blacks was incorporated ○ Under this act itself, the blacks were supposed to register as voters ➢ Some southern white states were not accepting these laws ○ When Eisenhower became Prez, he had to send federal troops to escort the black children to school as the opposition was so strong ➢ In the 1950s a stringent civil rights movement began ➢ Campaign for equal rights: ○ By 1955 a lot of blacks started living in the northern states as there is discrimination in the southern states ○ In 1900, 90% of the black population was living in the southern states, working in those plantations. By 1955, 50% of the black people started living in the northern states and working in the industries. The more they worked in the industrial areas, the more aware they became of their rights ○ By working in the industries, they gained more economic freedom ○ With the Asian and African states gaining independence, the black Americans were resenting the unfair treatment even more ○ When the laws were in the picture, people were raising concerns that those laws were being implemented at a very slow pace. ○ There was hostility between whites and blacks, especially in the southern states. ○ It was evident that there had to be a nationwide movement that would bring in civil rights for the blacks. This nationwide campaign began in 1955 when Dr. Martin Luther King, a Baptist minister, was the leader of the blacks. This was supposed to be a non-violent black movement. ○ Rosa Parks (black lady)- she sat on a bus seat that was reserved only for white people; this is what triggered the movement (immediate cause). This happened in Alabama. All the buses in the region were to be boycotted by the blacks ○ After the boycott of the buses, the campaign became successful and in the region of Montgomery the segregation of seats stopped. ○ In 1963, there was a massive rally in Washington where MLK was talking about his dream of a future of America and it all took place peacefully. ○ In 1967, the king awarded MLK with a Nobel peace prize but in 1968, he was assassinated in Tennessee ○ After this, the progress was slow in the civil rights movement which irritated the people. This makes the movement violent. ○ In 1964 there were riots in NYC, in 1965 there were racial riots in LA. Some of the black people converted themselves to Islam as they thought Christianity was a racist religion. ○ Boxing legend (Muhammad Ali) was a convert. His original name was Cassius Clay. ○ The democrat presidents (JFK & Johnson) ■ JFK was sympathetic to the problem of the blacks and so was Johnson ■ JFK appointed the first black ambassador of the USA and was the one who presented the civil rights bill in congress. This bill was passed after a discussion of 736 hours (passed in 1964) ■ This bill was meant to make racial discrimination illegal and all civil rights were to be given to the blacks. ■ The southern states did not accept this act. ■ Johnson introduced the voting rights act, 1965 for the voting rights of the blacks, and the civil rights act, 1968, giving blacks the right to property. The whites were against the passing of both these acts ■ By 1975 there was huge progress that took place. The congress had 18 black members, 278 black members in the state government, 120 black mayors were appointed ■ The blacks got education, civil rights, etc which led to minor improvements in the situation. ■ This discrimination still prevails as of 2023 and this is the sad reality. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ THE END OF AMERICAN HISTORY ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ HISTORY OF CHINA ______________________________________________________________________________ China has a history of National unity, tracing back to the mid 1600s. The dynasties that ruled China were: 1. Manchus Dynasty 2. Ch’ing Dynasty During the 1840s there was a foreign influence in China & this was where the troubled period of Chinese history began. This is due to: 1. Foreign interference 2. Civil war 3. Disintegration ➢ This continues till 1949 till the Communist party of China came into power, bringing stability ➢ In 1911, the last emperor of Chinese history was overthrown, after which the Republic of China arose. The period from 1916-1928 was called the ‘warlord era’, which was an era of great chaos as different generals seized power in different regions of the country. ➢ This was when a party called Kuomintang (KMT) came into power- it was a nationalist party. The party was very active in capturing provinces. There were two leaders of the party, but there was no harmony between the two. The two leaders are: 1. Dr. Sun Yat-sen who was alive till 1925 2. General Chiang Kai-shek ➢ In 1921, the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) was founded and it was cooperating with the Kuomintang very well for the regulation of Chinese affairs. ➢ Till the time The Kuomintang was struggling to take over China, they were taking help from the CCP, but as soon as Kuomintang managed to take over the country, they tried to sideline the CCP workers. ➢ The CCP tolerated the side-lining for a long time, but eventually they reacted and took control under the worthy leadership of Mao Zedong ○ A civil war is in place and Japanese interference also came about in 1937. Japan conducted a full-scale invasion and took over the country. ➢ After Hiroshima-Nagasaki (1945), Japanese control ended, after which KMT & CCP were fighting for control once again ➢ Chiang Kai-shek would seek help from the USA, but in 1949 Mao Zedong was winning so Chiang Kai-shek fled to Taiwan. Mao continued to be the supreme leader of China till 1976. Chiang establishes his own government in Taiwan, giving rise to the long-standing conflict between China and Taiwan. Date 1. 1640s (Manchus)- Early 19th Century Events - No involvement in international politics Country is peaceful and quiet 2. Mid 19th century - Crises arise - Europeans interfere in the country (British came into the country for trade purposes) - Opium wars (1839-1842). Hong Kong is handed over so British can gain control over certain ports - Other European countries follow after the Brits 3. Taiping Rebellion (1850-1864) - It is a religious movement as well as a political reform movement Aim: to set up a Heavenly Kingdom of great peace This was followed by the warlord era (1916-1928) This rebellion gave the Chinese a sense of independence 4. 1984 - Defeated by Japan 5. 1898-1900 - Boxer Rebellion. It was against the foreign rule. 6. 1904-05 - China is a sorry state, it is in shatters 7. 1911 - - - - Revolution took place The government was trying to introduce a few radical reformspromising democracy, setting up of elected provincial assemblies. All these reforms encouraged the provinces to secede from the government as the government did not take the consent of the provinces before making these reforms. A rebellion started taking place in the ‘Wuchang’ area by the soldiers. The people were seceding themselves from Beijing. The emperor who was in place was a 5-year-old child- Pu Yi. There was a commander in the army, whose help Pu Yi took, named Yuan Shikai. Yuan Shikai’s plans backfired as he had his own personal interests and no intention of helping Pu Yi. 1912-1915 - Military Dictatorship of Yuan Shikai He dies in 1916 1916 - Warlord era begins The death of Yuan Shikai brought about some sort of unity in China Each province was controlled by an individual warlord Each lord was supposed to maintain their own arms and maintain the provinces The students carried forward demonstrations with the Kuomintang against the warlords. - ➢ Kuomintang (KMT) ○ Formed in 1912 by Dr. Sun Yat-sen who was the first leader of the party ○ Aim- creation of modern, united, democratic China ○ Canton in South China (1917)- setting up government for the first time ■ Their popularity was limited to South China only ■ He needs to expand the party to become the president of China ○ Cooperated with the communists and formed a party as well as a constitution on communist lines as they had cooperated with the CCP ○ 3 principles: ■ Nationalism ● Getting rid of the foreign influence in China ● They wanted influence only of the indigenous culture ■ Democracy ● Government by the people, of the people and for the people ● Wanted to get rid of the warlords ● Self-governance and educated leaders were needed ■ Land reforms ● As it is an agricultural economy, tillers must get profits. ● Devising a long-term policy for an economy to be based around agriculture ○ Sun Yat-sen dies in 1925 & KMT cannot expand beyond South China ○ Chiang Kai-shek comes into power ■ He becomes the second leader of the KMT ■ Contact with Russia, guidance from Russia. In 1923, he spent time in Moscow studying about the red army & communist party ■ Continued his alliance with the communists but removed them from important positions in the party as he is a hardcore right-wing thinker (democratic thinker) ■ In 1926 the KMT conducted a Northern march to destroy warlords from central and northern China as he needed to gain control over the rest of China and expand the influence of the KMT ■ Captured Shanghai, Nanking in 1927 and Beijing (Peking) in 1928. ■ In Beijing he was helped by Zhou Enlai for conducting the takeover ■ He gained the support of the peasants and industrial workers which helped him in capturing Beijing ■ The communists were becoming powerful in KMT hence he conducted the “purification movement”, expelling them from the party ■ Achieved nationalism only (from 3 of the principles established by Sun Yat-sen he could only achieve one, failing the achieve Land reforms and democracy) ➢ Mao Zedong & communist victory in 1949: ○ Chinese Communist Party (CCP) was founded in 1921, comprising mostly intellectuals and did not possess any military strength ○ After KMT breach, Mao changed the party strategy to focus on winning the support of the peasants and industrial workers (mass support) rather than winning over the industrial towns ○ In 1931, he became the chairman of the Central Executive Committee ○ 1930-1934- Chiang Kai-shek carried out an extermination campaign. Mao promoted guerrilla warfare in order to build the Red Army ○ Faced initial defeats but they breakthrough in 1934 and carried an October-long march ■ 1 lakh communists joined the march and they covered 6000 miles in 368 days ○ Shensi & Kansu were the provisions that were taken over by the CCP ○ Chiang & KMT gradually lost popularity ■ CCP started emerging victorious ■ When Japan attacked China during WWII, Mao was the one who stood up against the Japanese aggression and thus the people gave him their support ○ In 1945, Japan was defeated and this is when USA enters the picture ○ The USA started supporting Chiang Kai-shek to promote democracy. ■ Since Mao had the support of the masses, he then opened direct offensive against the KMT forces ○ In Jan, 1949 the communist army took over Beijing ■ Mao gains command over mainland China and Chiang flees to Taiwan Date 1. Constitution of 1950s Events - 2. Hundred flowers campaign 1957 - - - - 3. Great Leap forward - The people’s congress became the final authority in the legislation (this takes place in 1954) The National People’s congress was elected for a period of 4 years and comprised of people who were above the age of 18 Once the constitution was drafted, a state council and chairman of republic were meant to ensure smooth administration The state council was supposed to elect a political bureau known as ‘Polit Bureau’ to take all the important decisions This entire system was dominated by the CCP This government was providing a strong centre to China This was a product of industrialization as there was a new class of technicians and engineers that had come up There were party cadres that were created. These were about the groups that organised the masses politically and economically They demanded collectivisation of farms. This saw an emergence of a slightly capitalist system and for converting it into a socialist system this was needed. Equal production, equal distribution of farming products, etc were taken up. Mao was the leader at that time and it was decided that there would be an open discussion of problems which were supposed to be with the intellectuals so that the peasants could tell them what their problems were. At that time Mao made a statement “let a hundred flowers bloom, and a hundred schools of thought contend'”. By this he meant that he wanted constructive criticism In this it was said that the cadres were overenthusiastic and incompetent. Over-centralisation of the govt was criticised, criticism of the CCP for being nondemocratic, they wanted opposition parties to be in place. Due to all this, Mao hurriedly called this campaign off and this is where he thought that a revolution was needed to spread the idea of socialism and communism. This led to the Great Leap forward To bring in communist and socialist changes in agriculture and industries - Introduction of communes: - It was the larger version of cadres - They were supposed to run their own collective farms and factories - They were almost running the local government there and also undertook special local projects - The families were going to receive a share out of the profits, as well as small private plots of land - Complete change of emphasis in the industry. They wanted smaller factories to be set up in the countryside to build roads, canals, dams, reservoirs and irrigation channels. - There were 2 blocs. One supported it and one opposed it The bloc opposed as: - From 1959-1961, there were bad harvests. - During the rule of Chiang Kai-shek, they were very dependent on the support of USSR and they soviets withdrew their support from China in the 1950s Positives of great leap forward: - Agricultural and industrial production increased substantially - Due to the increase in agricultural production, they were able to feed the massive population of China. - Avoided over-centralisation of the government - The industry grew in the countryside - The rate of unemployment reduced - In the beginning it is seen that this was the age of new technicians due to the spread of education, the increase in welfare schemes and the position of women saw great improvement. - 4. Cultural revolution 1966-1969 - Around 1960s there was a great success for the policy of the great leap forward There were some right-wing ideologies which were opposing the success of the great leap forward - They were proposing to give the communes some incentive - this was a right-wing idea - The existence of the expert managerial class was supposed to push forward the concept for industrialisation. This consisted of capitalistsanother right leaning idea. - These ideas were struck down by Mao. - He propagated communist ideologies to emphasise how the communist ideology was right The red army was now called ‘Red guard’ His position as chairman was being used to dictate public opinion. - This led to a situation that was almost a civil war in the country. - When all this was being done, in 1967, the red guard leaders were out of control, so much so that they stopped listening to Chairman Mao as well. Mao called the commanders of the red guard to control the fellow commanders (extremist red guards) who had gone out of control. ‘Committing the excesses’- the clause used to capture and execute the commanders who went out of control. In 1969, the cultural revolution came to an end and Mao declared it in the party meeting. - - ______________________________________________________________________________ DENG XIAO PING (DXP) ➢ Mid 1978, Deng Xiao Ping took over ➢ The reforms he brought in were 4 modernisations: ○ In agriculture ○ In industry ○ In science ○ In defence ➢ There were policy changes that he brought about; many changes that happened during the cultural revolution were reversed. ○ There were revolutionary committees set up to run the local government and they were abolished. ■ These were replaced by democratically elected groups to run the local government ■ Property was confiscated from former capitalists and it was returned to the survivors ■ Greater freedom was given to the intellectuals ■ Religious freedom was given to people ■ People were also given freedom to express themselves in literature and arts ○ He brought new economic policies by seeking help from the west for modernising the industry. If the industry is modified then agriculture, science and defence would develop. To fund this development, he seeked funding from the west. They accepted loans from foreign governments and banks. MOUs were being signed with foreign companies. In the 1980s, the IMF and The World Bank were joined by China. At the home front, state farms were given more control over planning, financing and profit. Bonuses & profit-sharing schemes were encouraged. The state was giving higher prices to the communes for the produce. There was a reduced rate of taxes. Due to all this, the output was increased and so was the liquidity and efficiency. ➢ After these, the people demanded more reforms (radical reforms). ➢ There were demonstrations with the support of DXP, ban marches against the government, poster campaigns for the criticism of the government policies were introduced. A range of basic human rights was given to the people. ○ Right to criticise the government openly ○ Representation of the non-communist parties in the national people’s congress. ○ Right to travel abroad ○ Right to change/ switch jobs ○ Abolition of communes for the rights of peasants (they could keep the profits to themselves→ increase in agriculture production & standard of living. State did not buy the produce compulsorily, nor would it set prices. Prices of surplus grain, pork, cotton and veggies were allowed to fluctuate. Due to this, in 1984, Chinese exports increased by 10% and imports increased by 38%. DXP believed that to get rich was not a crime, hence made these changes) ➢ China’s role in the international politics: ○ Led to a peace alliance of the rest of the world against two ambitious blocs, i.e., USA & USSR ➢ A war on democracy wall in place. ○ DXP was initially in support on this and then after he was being criticised on the wall, he abolished it ______________________________________________________________________________ Vietnam War ➢ Former Indo-China. ➢ Vietnam consisted of Laos, Cambodia and Vietnam. ➢ French colony earlier and there are 2 phases of independence struggle for Vietnam which is 1946-1961 and 1961-1975. ➢ 1946-1961: they fight with the French colony and win. No financial strength to maintain ➢ Next phase: 2nd phase, civil war in south Vietnam because of US interference who wanted to limit the communism spreading in these region ➢ 1st PHASE ➢ 1954 landmark year GENEVA AGREEMENT ➢ Fighting with the French to gain independence. ➢ It was triggered due to WW2 when the Japanese were capturing Vietnam as it was a French colony. ➢ Vietnam had to fight Japanese aggression and fight the French also. ➢ An organisation called Viet Minh was a league for Vietnamese independence and they are organising a resistance to gain independence. Leader was Ho Chi Minh. ➢ Toughest standoff for Vietnam was in Hanoi and this is where they attacked the French. The struggle lasted for 8 years ➢ In 1954 the French were defeated. ➢ Reasons for victory ➢ Use of guerrilla tactic ➢ Support of common masses. ➢ The French government and army were hampered due to WW2 so they were already weak which gave Vietnam an upper edge. ➢ Vietnam is being supported by China. ➢ The US supports the French naturally. ➢ In 1954 after Vietnam emerged victorious and signed the Geneva agreement. Laos and Cambodia will be independent and Vietnam will be divided in the 17th parallel as north and south Vietnam. In the North there is the government of Ho Chi Minh and people are happy with it. ➢ 2Nd PHASE ➢ In the south there has been a provisional democratic government for 2 years led by Ngo Dinh Diem (USA supported). After 2 years an election is supposed to be held and north and south Vietnam will be united. ➢ But this never took place and there is general discontent among the people. People are also not happy as they preferred communism but the leader came from a wealthy family who had no sympathy towards the wishes of general people whatsoever. ➢ Apart from that he is Roman Catholic and people of Vietnam are Buddhists. There were demands from people to introduce land reforms and people wanted redistribution of land from wealthy peasants to small peasants. Corruption is also there. But these people are politically aware and they will not keep quiet. ➢ There's the National Liberation Front. The foundation was of communist leader and a coalition govt is supposed to be formed which will respect both communist and capitalist ideologies ➢ Guerrilla Warfare is being used and South Vietnam is supported by the USA. So, weapons ➢ Since the country is Buddhist so they will not use violent measures. The Buddhist monks were lighting themselves on fire demanding their own govt. The leader of South Vietnam is imposing strict measures to curb this and this is not taken nicely by people. This is the time where he’s overthrown and murdered in 1963 and the army general took over. Eisen hover Johnson and Kennedy ➢ Viet Kong is coming up- secret police from north Vietnam is helping south to reduce us interference ➢ Kennedy introduced ➢ Nixon Vietnamization policy- equip trained Vietnam people so they can protect themselves and started gradual withdrawal of US troops. But parallelly he’s bombing ho chi minh train connecting north and south Vietnam NATO, SEATO, CENTO ➢ This is in the times of the cold war era. Power blocs/ different ideas. To protect each country’s interest, regional co-operations have been established. To talk about the countries, in and around India (example BRICS). Once, any ideology enters any territory, it will go on hijacking the other countries also. Colonies ka kuch faayda nahi hota, they just get exploited by the colonists ● NATO North Atlantic Treaty Organization OBJECTIVES ➢ To guarantee freedom and security of member nations through political and military means so freedom and security is their concern. That too is only to the member nations. ➢ Promotion of democratic values, liberal values. ➢ Consultation and cooperation on defence and security related issues. Consultation if internal issues and cooperation when external aggression. This is limited to security and defence ➢ Building trust and avoiding conflict ➢ Commitment to peaceful dispute resolution ➢ According to NATO, if the diplomatic mission fails, then only there should be a military mission (never initiate with a military mission) ➢ All the decisions will be taken by a consensus ➢ Washington Treaty 1949(04th April) marks the birth of NATO and there were only 12 nations at the beginning of the organisation. They swore in to stand together against aggression. ➢ 1989- second landmark year- fall of the Berlin War. ➢ 1991- disintegration of USSR. After the disintegration, USSR k satellite states k saath partnership kiya ➢ 1995- first major crisis management- Bosnia and Herzegovina. ➢ The Washington Treaty was invoked in 2001 (the first and only time) ➢ Self-defence in Europe and North America ● CENTO Central Treaty Organization ➢ Formerly Treaty Organization/Baghdad Pact Organization Middle eastern countries to work on themselves ➢ Functional from 1955-1979 ➢ Mutual security organisation- started in 1955 ➢ Headquarters- Baghdad ➢ To counter the soviet expansion in the middle east oil producing regions organisation. ➢ Iraq withdrew from it in 1959 ➢ America became a member ➢ Ankara is a part of CENTO. After iraq left, Ankara became the HQ ➢ Dissolved in 1979 ➢ Oil was the most crucial this time ● SEATO ➢ South East Asia Treaty Organization ➢ Founded in 1954 ➢ Prevention of communism ➢ Among South Asian nations only Thailand and Philippines ➢ Headquarters in Bangkok ➢ Works on strong economic foundations and increase in standard of living ➢ Fellowship for scholars and exhibitions ➢ Individual country crisis is no help ➢ Disbanded in 1977 due to cultural differences. ______________________________________________________________________________ JIM CROW LAWS ➢ Formal & codified system of racial apartheid from 1890, till late 19th century. ➢ Total segregation of blacks. Everywhere. Schools, Parks, marriages etc. voting was not permitted ➢ "Whites only" or "coloured" signs. ➢ Local government supported 1896, SC established a doctrine of separate but equal ➢ The North didn't officially adopt but segregation was practised. ______________________________________________________________________________ Malcolm X ➢ 1955 to 1965. Expressed bitterness of African Americans. ➢ critique of the mainstream Civil Rights Movement. Specifically, non-violence and integration. "By any means necessary" encouraged armed resistance ______________________________________________________________________________ Second Wave Feminism ➢ 1963 end - beginning ➢ Extended into 1980 ➢ First wave- employment, marriage laws, education and voting rights. ➢ Second wave- equality of sexes at workplace, right to choose, feminine sexuality and political action. ➢ Report from the committee on status of women discriminatory policies highlight the Equal Pay Act passed in 1963. ➢ Betty Friedman wrote feminine mystique about gender specific roles. ➢ Civil rights act 1964 title VII- gender/ workplace discrimination illegal. Equal employment opportunity, commission to check complaints. ➢ Gloria Steinem- travelling around raising awareness- messenger of the ➢ Equal rights amendment 1971. Steimen presented this issue. ➢ School discrimination- Roe v. Wade 1973- first trimester of pregnancy legal abortion. ______________________________________________________________________________ Roe v. Wade ➢ Right to privacy = Right to abortion ➢ why opposed ○ To protect medical hazardousness ○ pre-natal life ➢ past cases seen. 7-2 judgement abortion legal. No inherent right to privacy.