Oxidative Phosphorylation: Steps & Chemiosmosis
advertisement

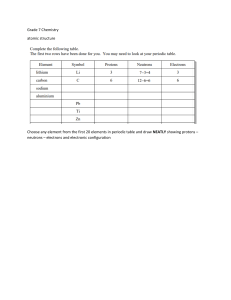
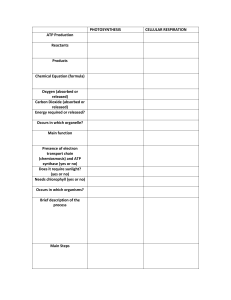
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION Steps: 1) Reduced NAD and Reduced FAD release hydrogen 2) Hydrogen splits into H* (proton) and electron 3) Electrons are transported through electron carriers in an electron transport chain. As electrons moves, some of its energy is released 4) Energy released is used to move H*(protons) from matrix to intramembrane spaces. This creates a potential ditterence across membrane 5) Protons are moved back to matrix through ATPase from higher concentration to lower concentration 6) Energy of protons is used to synthesise ATP from ADP 7) Low energy state e fall back into matrix. They are accepted by oxygen. Oxygen, electrons and protons combine to form water O2 + 4e + 4H+ 2H2O *IF oxygen is not available, none of the reactions inside mitochondrion will occur Link reaction, Krebs Cycle, Oxidative phosphorylation do not occur only glycolysis occurs which releases only a small amount of energy Anaerobic respiration occurs Chemiosmosis: the synthesis of ATP using energy released by the movement of hydrogen ions down their concentration gradient, across a membrane in mitochondria or chloroplast