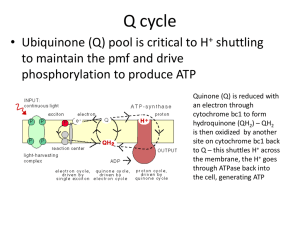
Aim : To investigate the effect of plant derived extracts against biofilm activity of Bacteria in food industry. Introduction: A biofilm is a sessile form of bacterial existence on solid surface or air liquid interfaces in which bacteria multiply covered by a cell produce biofilm matrix composed of bacterial intercellular polysaccharides proteins and extracellularly released nucleic acids. 1. Biofilm in food industry: In produce, microorganisms attach to the surfaces and biofilms develop internally. During the washing process biofilm resist sanitization and allows bacteria to spread across the produce, especially via kitchen utensils. This problem is also found in ready to eat foods, because the food goes through limited cleaning procedures before consumption. Due to the perishability of dairy products and a limitation in cleaning, procedures resulting in the buildup of bacteria, dairy is susceptible to biofilm formation and contamination. The bacteria can spoil the product more readily, and contaminated products pose a health risk to the consumers. Consequently, there is a pressing need to explore alternative antimicrobial agents to combat biofilm formation and associated infection. Plant derived extracts have garnered attention for their potential antimicrobial properties, including activity against biofilm. This proposal outlines a research study aimed at investigating the effectiveness of plant derived extract against bacterial biofilm activity. 2. Research objectives: • To evaluate the antibiofilm activity on these extracts on biofilm forming bacteria in food industry. • To provide insights into practical applications of plant derived extracts in mitigating biofilm related issues in food industry. 3. Review of literature: Previous studies have demonstrated that plant secondary metabolites including polyphenols such as flavonoids, phenolic acids and tannins show antibacterial and/or antibiofilm activities ( Slobodnikova et al.,2016). These compounds have exhibited inhibitory effects against a wide range of bacterial species which creates a problem in food industry such as Salmonella sp. which is associated with raw meat, poultry, eggs, milk and dairy products and it is the major cause of foodborne diseases. (Olawuwo et al.,2022), Listeria monocytogenes which survived for the prolonged period on the stainless steel and creates hindrance in cleaning process (Upadhyay, A,et al.,2013). Lactobacillus curvatus which could lead to the defect caused by the formation of calcium lactate crystal in cheddar cheese (Porcellato D et al. 2015). Plant derived extracts such as polyphenols are important in plant defense against microbial pathogens. Tannins possesses antibacterial activity both against gram positive and gram negative bacteria. For example, catechins are able to penetrate and interact with lipid bilayers. Alternatively, they may cause membrane fusion, a process that result in leakage of intramembrane materials and aggregation (Slobodnikova et al. ,2016) 4. Methodology: 1.Selection of plant source for extracts • A diverse range of plants will be selected for the sake of their extracts based on their known antimicrobial properties and safety profiles. 2.Extraction of plant derived extracts Plants were extracted in various organic as well as aqueous solvents. • Conventional extraction methods include. Soxhlet extraction, hydro distillation Maceration, agitated solvent extraction etc • Novel extraction methods which are comparatively environmentally friendly, faster and more efficient. Includes ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) microwave assisted extraction (MAE) Supercritical fluid extraction, enzyme assisted extraction, etc. 3.Bacterial strains forming biofilm • Clinically relevant bacterial strains commonly associated with food borne illness will be selected. • Biofilm formation will be induced under controlled conditions using standard protocols. 4.Assessment of Antibiofilm Activity • The effect of land derived extracts on preformed biofilms will be assessed using crystal violet staining and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). 5.Data analysis • Will be performed using appropriate statistical methods. 6.Expected outcomes • We can expect a negative effect of plant derived extracts on biofilm forming bacteria in the food industry. • Recommendations for practical application of plant derived extracts as biofilm control agents in the food industry. 7.Significance of study This research holds significant implications for the food industry by offering novel strategies for controlling bacterial biofilms and reducing the risk of food borne contamination. The finding of this study may contribute to the development of natural, ecofriendly alternatives to conventional antimicrobial agents, thereby promoting food safety and public health. This research can be boom as it will lead to a safer and more productive food industry. 8.Conclusion • Plant-derived extracts have the potential of reducing food infectious bacteria by their anti-biofilm activity hence can be used as an anti-biofilm agent against microorganisms in the food industry. 9.References • Azwanida NN. A review on the extraction method used in medicinal plants Principal strength and limitation. Med Aromat plants 2015;4(3):196 • Stalikas extraction ,sepration and detection methods for phenolic acids and flavanoids. J Sep Sci 2007; 30(18):3268-95 • A . Scalbert,phytochemistry,1991,30,3875 • N.J .Baxter,T.H Lilley,E. Haslam and M.P. williamson , Biochemistry,1997,36,5566 • WHO( World Health Organisation): Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveillance.2014. • Hoiby N.; Bjarnsholt,t.; givskov,M; Molin,S.;Cifou,O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms . Int.j. Antimicrob. Agents 2010,35,322-332 [Gross Rej] [Pub Med] • Daglia ,M. Polyphenols as antimicrobial agents.Curr.Opin.biotechnol.2012,23,174-181[Gross Ref].