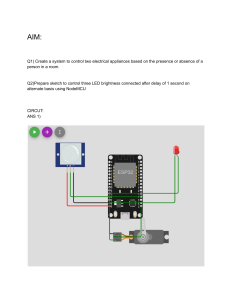
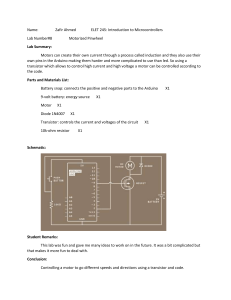
REVIEWER FOR ROBOTICS 9
Basic Parts of a Circuit
1.
LED Bulb - Light-Emitting Diode that lights up when electricity passes through in the correct
direction.
1.1 Cathode – the negative wire of an LED Bulb where negative wires are connected.
1.2 Anode – the positive wire of an LED Bulb where positive wires are connected.
2. Resistor – restricts the flow of electricity in a circuit, reducing the voltage and current as a
result.
Ohms (Ω) is the symbol for resistance.
3. Pushbutton – a switch that closes a circuit when pressed.
4. Breadboard small – 30 rows, 10 columns, and two pairs of power rails.
5. Arduino Uno R3 – programmable board with 13 pins (PIN 0 – PIN 13) that output power
based on the code written.
Power Sources
•
•
•
•
9V Battery (9 Volts)
Coin Cell 3V Battery (3 Volts)
1.5V Battery (1.5 Volts)
Power Supply
Control Loops (Pre-test and Post-test)
The Control Loops has 3 Main Parts: Initialization, condition, and increment
Initialization; tells the board where to start outputting power. For example, if your first LED bulb
is connected to PIN 2, then the code for it is x = 2;. In this situation, we used the letter x to
function as the variable. However, you can use any letter or symbol, as long as it is also the
symbol you used for int x; (int; is written before the void setup() line)
(condition) instructs the board to have a limit of outputting power on the PINs. For example, if
you used PINs 2 to 6 to power five LED Bulbs, then the Arduino board will only output power for
pins 2 to 6 and not exceeding it. In this situation, the code for this will be: (x < 7) because PINs
2 to 6 is less than 7.
Increment; commands the board to keep outputting power on assigned PINs by utilizing the
(condition). It will not only power PIN 2 but also PINs 3, 4, 5, and 6. The code for this situation
is: (x++), same letter you used for the condition and initialization.
1. WHILE Loop
// this is a code format for WHILE Loop
void setup()
{
}
void loop()
{
initialization;
while (condition)
{
statements; //codes to execute
increment;
}
}
// WHILE Loop
int x;
void setup()
{
pinMode(2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
pinMode(6, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{ // WHILE Loop
x = 2; // initialization
while (x < 7) // condition
{
digitalWrite(x, 1);
delay(250);
digitalWrite(x, 0);
delay(250);
x++; // increment
}
}
2. FOR Loop
// this is a code format for FOR Loop
void setup()
{
}
void loop()
{
for (initialization; condition; increment;)
{
statements; //codes to execute
}
}
// C++ code
// FOR Loop
int x;
void setup()
{
pinMode(2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
pinMode(6, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{ // FOR Loop
for (x = 2; x < 7; x++)
{
digitalWrite(x, 1);
delay(250);
digitalWrite(x, 0);
delay(250);
}
}
3. DO-WHILE Loop
// this is a code format for DO-WHILE Loop
void setup()
{
}
void loop()
{
initialization;
do {
statements; //codes to execute
increment;
} while(condition);
}
// C++ code
// DO-WHILE Loop
int x;
void setup()
{
pinMode(2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
pinMode(6, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{ // DO-WHILE Loop
x = 2;
do {
digitalWrite(x, 1);
delay(250);
digitalWrite(x, 0);
delay(250);
x++;
} while (x < 7);
}