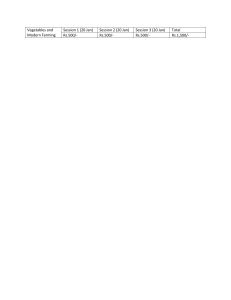
AGRICULTURAL PRACTICES Meaning of Agricultural practices Agricultural practices can be broadly divided into two: farming practices and cropping practices. FARMING PRACTICES The common types of farming systems used by most West African farmers include the following: 1. Shifting cultivation: This is a system of farming in which a farmer 4.2. abandons a plot of land after planting on it for two or more years. The farmer may come back to this and piece of land after some years. Advantages of Shifting Cultivation i) The soil regains lost nutrients without any effort by the farmer. ii) Shifting cultivation helps to check the build-up of insect pests and diseases. Disadvantages of Shifting Cultivation i. It can only be practiced in areas where land is abundant and population is low. ii. Time, energy and money are wasted in clearing new farmland. iii. The soil is exposed to the danger of erosion and valuable soil nutrients and organic matte are lost during burning. 2. Mixed Farming: In this type of farming, the farmer raises both crops and animals on the same farm. In this system, the farmer may keep different animals for different purposes. For example, he can keep cows for milk production., poultry for eggs, goats and sheep for meat and horses as work animals. He can also plant different types of crops e.g. Maize, cowpea, sorghum rice yam etc. The remain of the crops may be used by the farmer to feed his animals while their dung and droppings are in turn used to enrich the soil for the crop. Advantages of Mixed Farming i. Animal dung and droppings can be added to soil as manure to improve soil fertility. ii. Remains of crops such as maize, rice or sorghum may be used to feed animals. iii. It encourages efficient use of farm labour. iv. The risk of total loss is considerably reduced as both crops and farm animals will not fail. v. The sale of farm animals and crops provides additional source of income and prevents financial hardship for the farmer. Disadvantages of Mixed Farming i. It is capital intensive, that is, the capital needed to set up this type of farming system is high. ii. If the animals are not properly managed, they can break loose and destroy the crops. iii. Animals can be expensive to maintain. 3. Pastoral farming: This is a farming practice in which a farmer keeps only livestock, such as cattle, sheep and goats. Pastoral farmers may be unsettled (nomadic herding) or settled (ranching). a. Nomadic herding This is a system of pastoral farming which involves the movement of the herdsman with his animals from place to place in search of pasture and water during the dry season. This system is commonly practiced by the Fulani of Nigeria and the Massai of East Africa. Advantages of nomadic herding The main advantage of this system is that the movement of the herds prevent starvation and death in areas where food and water are relatively scarce. Disadvantages of nomadic herding i. There could be irregular supply of feed and water to the animals. ii. Animals are exposed to insect pests and diseases. iii. Poor-quality animals result from poor and unplanned breeding of animals. iv. The herdsmen and their animals are exposed to the risk of being killed by wild animals. b. Ranching : This is the settled form of livestock production. In this system, the pasture is managed properly to provide feed for the animals all year round. Hence. the farmer does not need to move his animals from place to place in search of feed and water. Advantages of ranching i. Pasture and water are available all the year round. ii. Low incidence of pests and diseases result from good management of farm animals. iii. Low death rate and production of high quality animals due to proper breeding practices. Disadvantages of ranching i. Ranching can be very expensive to practice. ii. Overstocking will reduce the pasture available to each animal and consequently brings about the death of the weaker animals. 4. Ley farming: This is a system of cropping which involves the planting of forage crops and food crops in alternation. The forage crops may include grasses, legumes and other plants acceptable to farm animals while the food crops may be maize, rice, cowpea, etc. The main advantage of this system is that the farmer can feed his animals with the forage crops and at the same time harvest food crops from the farm. However, the system requires a lot of management skills by farmer. Plantation farming: In plantation farming, a large expanse of land is set aside for cultivation of perennial crops such as cocoa, oil palm, citrus, guava, rubber, etc. The area of land set aside for this purpose is called a plantation. Advantages of plantation farming i. There is high economic returns in producing such crops under plantation agriculture than arable crop farming. ii. The canopy of tree crops prevent the high impacts of wind and water on the soil, thereby preventing erosion. Disadvantages of plantation farming i. High capital investment is required. ii. It takes a long time for the crops to start yielding fruits. For example, cocoa will take about 3-5 years to mature after planting. This makes it a long-term investment. Taungya farming or agro forestry: This involves the planting of both food crops and forest trees together in government forests. It involves the integration of agriculture and forestry. In this system, the farmer is allowed to plant only annual and biennial crops in government forests with the understanding that the farmer will tend some tree seedling alongside his crops. i. ii. iii. i. ii. iii. iv. Advantages of taungya farming The farmer can make adequate use of available fertile land for growing his crops. The farmer's knowledge on other areas of agriculture e.g. forestry is enhanced. The standard of living of the farmer can be improved. Disadvantages of taungya farming Only annual and biennial crops are cultivated in the forest reserve. Competition may exist between the food crops and forest trees. Crops may be destroyed by annual bush burning. Harvesting of tuber crops may be difficult when present under the roots of trees.