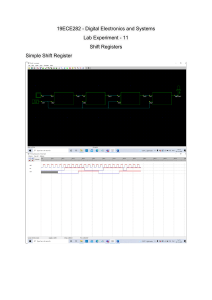
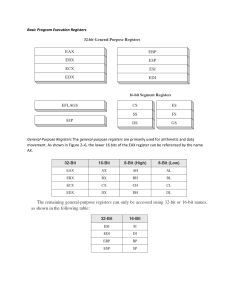
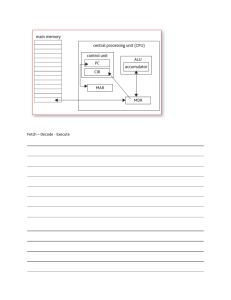
30. Register Summary Address Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (0xFF) Reserved (0xFE) Reserved (0xFD) Reserved (0xFC) Reserved (0xFB) Reserved (0xFA) Reserved (0xF9) Reserved (0xF8) Reserved (0xF7) Reserved (0xF6) Reserved (0xF5) Reserved (0xF4) Reserved (0xF3) Reserved (0xF2) Reserved (0xF1) Reserved (0xF0) Reserved (0xEF) Reserved (0xEE) Reserved (0xED) Reserved (0xEC) Reserved (0xEB) Reserved (0xEA) Reserved (0xE9) Reserved (0xE8) Reserved (0xE7) Reserved (0xE6) Reserved (0xE5) Reserved (0xE4) Reserved (0xE3) Reserved (0xE2) Reserved (0xE1) Reserved (0xE0) Reserved (0xDF) Reserved (0xDE) Reserved (0xDD) Reserved (0xDC) Reserved (0xDB) Reserved (0xDA) Reserved Notes: Page 1. For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed. Reserved I/O memory addresses should never be written. 2. I/O registers within the address range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI and CBI instructions. In these registers, the value of single bits can be checked by using the SBIS and SBIC instructions. 3. Some of the status flags are cleared by writing a logical one to them. Note that, unlike most other AVR®, the CBI and SBI instructions will only operate on the specified bit, and can therefore be used on registers containing such status flags. The CBI and SBI instructions work with registers 0x00 to 0x1F only. 4. When using the I/O specific commands IN and OUT, the I/O addresses 0x00 - 0x3F must be used. When addressing I/O registers as data space using LD and ST instructions, 0x20 must be added to these addresses. The ATmega328P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can be supported within the 64 location reserved in opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For the extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM, only the ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instructions can be used. ATmega328P [DATASHEET] 7810DAVR01/15 275 30. Register Summary (Continued) Address Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (0xD9) Reserved (0xD8) Reserved (0xD7) Reserved (0xD6) Reserved (0xD5) Reserved (0xD4) Reserved (0xD3) Reserved (0xD2) Reserved (0xD1) Reserved (0xD0) Reserved (0xCF) Reserved (0xCE) Reserved (0xCD) Reserved (0xCC) Reserved (0xCB) Reserved (0xCA) Reserved (0xC9) Reserved (0xC8) Reserved (0xC7) Reserved (0xC6) UDR0 (0xC5) UBRR0H USART I/O data register (0xC4) UBRR0L (0xC3) Reserved (0xC2) UCSR0C (0xC1) UCSR0B RXCIE0 (0xC0) UCSR0A (0xBF) Reserved 159 USART baud rate register high 162 USART baud rate register low Page 162 UPM01 UPM00 USBS0 UCSZ01 /UDORD0 UCSZ00 / UCPHA0 UCPOL0 161/172 TXCIE0 UDRIE0 RXEN0 TXEN0 UCSZ02 RXB80 TXB80 160 RXC0 TXC0 UDRE0 FE0 DOR0 UPE0 U2X0 MPCM0 159 UMSEL01 UMSEL00 (0xBE) Reserved (0xBD) TWAMR TWAM6 TWAM5 TWAM4 TWAM3 TWAM2 TWAM1 TWAM0 201 (0xBC) TWCR TWINT TWEA TWSTA TWSTO TWWC TWEN TWIE 199 (0xBB) TWDR (0xBA) TWAR TWA6 TWA5 TWA4 TWA3 TWA2 TWA1 TWA0 TWGCE 201 (0xB9) TWSR TWS7 TWS6 TWS5 TWS4 TWS3 TWPS1 TWPS0 200 (0xB8) TWBR (0xB7) Reserved (0xB6) ASSR EXCLK AS2 TCN2UB (0xB5) Reserved Notes: 276 2-wire serial interface data register 200 2-wire serial interface bit rate register 198 OCR2AUB OCR2BUB TCR2AUB TCR2BUB 133 1. For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed. Reserved I/O memory addresses should never be written. 2. I/O registers within the address range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI and CBI instructions. In these registers, the value of single bits can be checked by using the SBIS and SBIC instructions. 3. Some of the status flags are cleared by writing a logical one to them. Note that, unlike most other AVR®, the CBI and SBI instructions will only operate on the specified bit, and can therefore be used on registers containing such status flags. The CBI and SBI instructions work with registers 0x00 to 0x1F only. 4. When using the I/O specific commands IN and OUT, the I/O addresses 0x00 - 0x3F must be used. When addressing I/O registers as data space using LD and ST instructions, 0x20 must be added to these addresses. The ATmega328P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can be supported within the 64 location reserved in opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For the extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM, only the ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instructions can be used. ATmega328P [DATASHEET] 7810DAVR01/15 30. Register Summary (Continued) Address Name (0xB4) OCR2B Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Timer/Counter2 output compare register B Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 131 (0xB3) OCR2A Timer/Counter2 output compare register A 131 (0xB2) TCNT2 Timer/Counter2 (8-bit) (0xB1) TCCR2B FOC2A FOC2B WGM22 CS22 CS21 CS20 130 (0xB0) TCCR2A COM2A1 COM2A0 COM2B1 COM2B0 WGM21 WGM20 127 131 (0xAF) Reserved (0xAE) Reserved (0xAD) Reserved (0xAC) Reserved (0xAB) Reserved (0xAA) Reserved (0xA9) Reserved (0xA8) Reserved (0xA7) Reserved (0xA6) Reserved (0xA5) Reserved (0xA4) Reserved (0xA3) Reserved (0xA2) Reserved (0xA1) Reserved (0xA0) Reserved (0x9F) Reserved (0x9E) Reserved (0x9D) Reserved (0x9C) Reserved (0x9B) Reserved (0x9A) Reserved (0x99) Reserved (0x98) Reserved (0x97) Reserved (0x96) Reserved (0x95) Reserved (0x94) Reserved (0x93) Reserved (0x92) Reserved (0x91) Reserved (0x90) Reserved (0x8F) Reserved Notes: Page 1. For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed. Reserved I/O memory addresses should never be written. 2. I/O registers within the address range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI and CBI instructions. In these registers, the value of single bits can be checked by using the SBIS and SBIC instructions. 3. Some of the status flags are cleared by writing a logical one to them. Note that, unlike most other AVR®, the CBI and SBI instructions will only operate on the specified bit, and can therefore be used on registers containing such status flags. The CBI and SBI instructions work with registers 0x00 to 0x1F only. 4. When using the I/O specific commands IN and OUT, the I/O addresses 0x00 - 0x3F must be used. When addressing I/O registers as data space using LD and ST instructions, 0x20 must be added to these addresses. The ATmega328P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can be supported within the 64 location reserved in opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For the extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM, only the ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instructions can be used. ATmega328P [DATASHEET] 7810DAVR01/15 277 30. Register Summary (Continued) Address Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (0x8E) Reserved (0x8D) Reserved (0x8C) Reserved (0x8B) OCR1BH Timer/Counter1 - Output compare register B high byte 111 (0x8A) OCR1BL Timer/Counter1 - Output compare register B low byte 111 (0x89) OCR1AH Timer/Counter1 - Output compare register A high byte 111 (0x88) OCR1AL Timer/Counter1 - Output compare register A low byte 111 (0x87) ICR1H Timer/Counter1 - Input capture register high byte 112 (0x86) ICR1L Timer/Counter1 - Input capture register low byte 112 (0x85) TCNT1H Timer/Counter1 - Counter register high byte 111 Timer/Counter1 - Counter register low byte Page (0x84) TCNT1L (0x83) Reserved (0x82) TCCR1C FOC1A FOC1B 111 (0x81) TCCR1B ICNC1 ICES1 WGM13 WGM12 CS12 CS11 CS10 110 111 (0x80) TCCR1A COM1A1 COM1A0 COM1B1 COM1B0 WGM11 WGM10 108 (0x7F) DIDR1 AIN1D AIN0D 204 (0x7E) DIDR0 ADC5D ADC4D ADC3D ADC2D ADC1D ADC0D 220 (0x7D) Reserved (0x7C) ADMUX REFS1 REFS0 ADLAR MUX3 MUX2 MUX1 MUX0 217 (0x7B) ADCSRB ACME ADTS2 ADTS1 ADTS0 220 (0x7A) ADCSRA ADEN ADSC ADATE ADIF ADIE ADPS2 ADPS1 ADPS0 218 (0x79) ADCH ADC data register high byte 219 (0x78) ADCL ADC data register low byte 219 (0x77) Reserved (0x76) Reserved (0x75) Reserved (0x74) Reserved (0x73) Reserved (0x72) Reserved (0x71) Reserved (0x70) TIMSK2 OCIE2B OCIE2A TOIE2 132 (0x6F) TIMSK1 ICIE1 OCIE1B OCIE1A TOIE1 112 (0x6E) TIMSK0 OCIE0B OCIE0A TOIE0 88 (0x6D) PCMSK2 PCINT23 PCINT22 PCINT21 PCINT20 PCINT19 PCINT18 PCINT17 PCINT16 57 (0x6C) PCMSK1 PCINT14 PCINT13 PCINT12 PCINT11 PCINT10 PCINT9 PCINT8 57 (0x6B) PCMSK0 PCINT7 PCINT6 PCINT5 PCINT4 PCINT3 PCINT2 PCINT1 PCINT0 57 (0x6A) Reserved (0x69) EICRA ISC11 ISC10 ISC01 ISC00 Notes: 278 54 1. For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed. Reserved I/O memory addresses should never be written. 2. I/O registers within the address range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI and CBI instructions. In these registers, the value of single bits can be checked by using the SBIS and SBIC instructions. 3. Some of the status flags are cleared by writing a logical one to them. Note that, unlike most other AVR®, the CBI and SBI instructions will only operate on the specified bit, and can therefore be used on registers containing such status flags. The CBI and SBI instructions work with registers 0x00 to 0x1F only. 4. When using the I/O specific commands IN and OUT, the I/O addresses 0x00 - 0x3F must be used. When addressing I/O registers as data space using LD and ST instructions, 0x20 must be added to these addresses. The ATmega328P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can be supported within the 64 location reserved in opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For the extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM, only the ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instructions can be used. ATmega328P [DATASHEET] 7810DAVR01/15 30. Register Summary (Continued) Address Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (0x68) PCICR PCIE2 PCIE1 PCIE0 Page (0x67) Reserved (0x66) OSCCAL (0x65) Reserved (0x64) PRR PRTWI PRTIM2 PRTIM0 PRTIM1 PRSPI PRUSAR0 PRADC (0x63) Reserved (0x62) Reserved (0x61) CLKPR CLKPCE CLKPS3 CLKPS2 CLKPS1 CLKPS0 33 (0x60) WDTCSR WDIF WDIE WDP3 WDCE WDE WDP2 WDP1 WDP0 47 0x3F (0x5F) SREG I T H S V N Z C 10 Oscillator calibration register 32 36 0x3E (0x5E) SPH (SP10) SP9 SP8 13 0x3D (0x5D) SPL SP7 SP6 SP5 SP4 SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0 13 0x3C (0x5C) Reserved 0x3B (0x5B) Reserved 0x3A (0x5A) Reserved 0x39 (0x59) Reserved 0x38 (0x58) Reserved 0x37 (0x57) SPMCSR SPMIE (RWWSB) (RWWSRE) BLBSET PGWRT PGERS SELFPRGN 0x36 (0x56) Reserved 0x35 (0x55) MCUCR BODS BODSE PUD IVSEL IVCE 38/52/72 0x34 (0x54) MCUSR WDRF BORF EXTRF PORF 46 0x33 (0x53) SMCR SM2 SM1 SM0 SE 35 0x32 (0x52) Reserved 0x31 (0x51) Reserved 0x30 (0x50) ACSR ACD ACBG ACO ACI ACIE ACIC ACIS1 ACIS0 0x2F (0x4F) Reserved 0x2E (0x4E) SPDR 239 203 SPI data register 142 0x2D (0x4D) SPSR SPIF WCOL SPI2X 141 0x2C (0x4C) SPCR SPIE SPE DORD MSTR CPOL CPHA SPR1 SPR0 140 0x2B (0x4B) GPIOR2 General purpose I/O register 2 0x2A (0x4A) GPIOR1 General purpose I/O register 1 0x29 (0x49) Reserved 0x28 (0x48) OCR0B Timer/Counter0 output compare register B 0x27 (0x47) OCR0A Timer/Counter0 output compare register A 0x26 (0x46) TCNT0 0x25 (0x45) TCCR0B FOC0A FOC0B WGM02 CS02 0x24 (0x44) TCCR0A COM0A1 COM0A0 COM0B1 COM0B0 WGM01 WGM00 0x23 (0x43) GTCCR TSM PSRASY PSRSYNC Notes: 23 23 CS01 CS00 Timer/Counter0 (8-bit) 115/134 1. For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed. Reserved I/O memory addresses should never be written. 2. I/O registers within the address range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI and CBI instructions. In these registers, the value of single bits can be checked by using the SBIS and SBIC instructions. 3. Some of the status flags are cleared by writing a logical one to them. Note that, unlike most other AVR®, the CBI and SBI instructions will only operate on the specified bit, and can therefore be used on registers containing such status flags. The CBI and SBI instructions work with registers 0x00 to 0x1F only. 4. When using the I/O specific commands IN and OUT, the I/O addresses 0x00 - 0x3F must be used. When addressing I/O registers as data space using LD and ST instructions, 0x20 must be added to these addresses. The ATmega328P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can be supported within the 64 location reserved in opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For the extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM, only the ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instructions can be used. ATmega328P [DATASHEET] 7810DAVR01/15 279 30. Register Summary (Continued) Address Name 0x22 (0x42) EEARH Bit 7 (EEPROM address register high byte) 20 0x21 (0x41) EEARL EEPROM address register low byte 20 0x20 (0x40) EEDR EEPROM data register 0x1F (0x3F) EECR 0x1E (0x3E) GPIOR0 0x1D (0x3D) EIMSK INT1 INT0 55 0x1C (0x3C) EIFR INTF1 INTF0 55 0x1B (0x3B) PCIFR PCIF2 PCIF1 PCIF0 0x1A (0x3A) Reserved 0x19 (0x39) Reserved 0x18 (0x38) Reserved 0x17 (0x37) TIFR2 OCF2B OCF2A TOV2 132 0x16 (0x36) TIFR1 ICF1 OCF1B OCF1A TOV1 113 0x15 (0x35) TIFR0 OCF0B OCF0A TOV0 0x14 (0x34) Reserved 0x13 (0x33) Reserved 0x12 (0x32) Reserved 0x11 (0x31) Reserved 0x10 (0x30) Reserved Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 EEPM1 EEPM0 Bit 3 EERIE Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Page 20 EEMPE EEPE EERE General purpose I/O register 0 20 23 0x0F (0x2F) Reserved 0x0E (0x2E) Reserved 0x0D (0x2D) Reserved 0x0C (0x2C) Reserved 0x0B (0x2B) PORTD PORTD7 PORTD6 PORTD5 PORTD4 PORTD3 PORTD2 PORTD1 PORTD0 73 0x0A (0x2A) DDRD DDD7 DDD6 DDD5 DDD4 DDD3 DDD2 DDD1 DDD0 73 0x09 (0x29) PIND PIND7 PIND6 PIND5 PIND4 PIND3 PIND2 PIND1 PIND0 73 0x08 (0x28) PORTC PORTC6 PORTC5 PORTC4 PORTC3 PORTC2 PORTC1 PORTC0 73 0x07 (0x27) DDRC DDC6 DDC5 DDC4 DDC3 DDC2 DDC1 DDC0 73 0x06 (0x26) PINC PINC6 PINC5 PINC4 PINC3 PINC2 PINC1 PINC0 73 0x05 (0x25) PORTB PORTB7 PORTB6 PORTB5 PORTB4 PORTB3 PORTB2 PORTB1 PORTB0 72 0x04 (0x24) DDRB DDB7 DDB6 DDB5 DDB4 DDB3 DDB2 DDB1 DDB0 72 0x03 (0x23) PINB PINB7 PINB6 PINB5 PINB4 PINB3 PINB2 PINB1 PINB0 72 0x02 (0x22) Reserved 0x01 (0x21) Reserved 0x0 (0x20) Reserved Notes: 280 1. For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed. Reserved I/O memory addresses should never be written. 2. I/O registers within the address range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI and CBI instructions. In these registers, the value of single bits can be checked by using the SBIS and SBIC instructions. 3. Some of the status flags are cleared by writing a logical one to them. Note that, unlike most other AVR®, the CBI and SBI instructions will only operate on the specified bit, and can therefore be used on registers containing such status flags. The CBI and SBI instructions work with registers 0x00 to 0x1F only. 4. When using the I/O specific commands IN and OUT, the I/O addresses 0x00 - 0x3F must be used. When addressing I/O registers as data space using LD and ST instructions, 0x20 must be added to these addresses. The ATmega328P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can be supported within the 64 location reserved in opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For the extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM, only the ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instructions can be used. ATmega328P [DATASHEET] 7810DAVR01/15